-
21世纪以来西藏地区社会经济得到快速发展,生活污水量随之增加[1],为保护脆弱的高原生态环境,高原生活污水的有效处理成为必然。目前西藏地区主要采用A2O、多级AO、氧化沟等工艺,设计和建设中通常参照内地经验,但污水处理厂出水水质却难以稳定达标[2],此外也面临运行操作困难、运行能耗高、污泥膨胀等问题[3]。究其原因,主要有以下3个方面。1)其独特饮食习惯使西藏地区生活污水碳氮比(3~10)偏低[4],而聚磷菌和反硝化菌对有限碳源的竞争[5],导致系统氮磷去除效果不佳。2)高海拔地理条件下,西藏地区主要城市大气压力为52.93~59.87 kPa,含氧量50.36%~67.24%[6],低压条件下不仅水中氧气溶解度降低,曝气时气泡数量和气体滞留律的降低也会间接影响氧气的传质[7];低氧条件与鼓风曝气机的曝气效率直接相关,需要加大曝气量来提高水中的DO。在高原低压低氧环境条件协同作用下,相同工艺的曝气能耗显著增加。3)在高海拔地理条件下,西藏地区城镇污水水温最低可至8 ℃[8],而低温条件下微生物酶活性、基质降解效率、微生物代谢活性、微生物比增长速率都会出现不同程度降低[9],污泥活性的降低使得工艺出水难以达标;此外,低温条件下系统易发生污泥膨胀,包括非丝状菌膨胀和丝状菌膨胀[10-12]。
针对以上高原城镇污水处理困境,近年来有学者进行了高原环境下适用处理工艺的探究。王利等[13]搭建了SBR系统,在低温低压低氧条件下实现系统的快速启动稳定,但出水NH4+-N未能达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级B标准。吴永刚[14]改造了氧化沟工艺,将所有预处理设施置于室内,并通过锅炉余热利用和蒸汽加热等措施克服低温问题,冬季出水可稳定达到GB 18918-2002一级B标准,但建设及维护成本显著增加。吕学斌等[15]搭建了深井中试装置实现高压曝气,可以克服低温低压低氧问题,但施工难度大。目前改良或新开发的工艺存在出水水质不稳定、成本高、施工难等不足,难以在高原推广应用。因此,针对高原气候环境三低特点和进水水质,提出适应高原环境且出水水质稳定达标的城镇污水低碳处理工艺十分必要。
本研究构建了多阶折流A2O一体化中试装置,分析了装置的启动运行特征,考察了常温下气水比、污泥内外回流比、进水量等工艺参数对运行效能的影响,解析了污染物的去除效能、磷在系统中的分布。以期为高原生活污水的高效低碳处理提供参考。
-
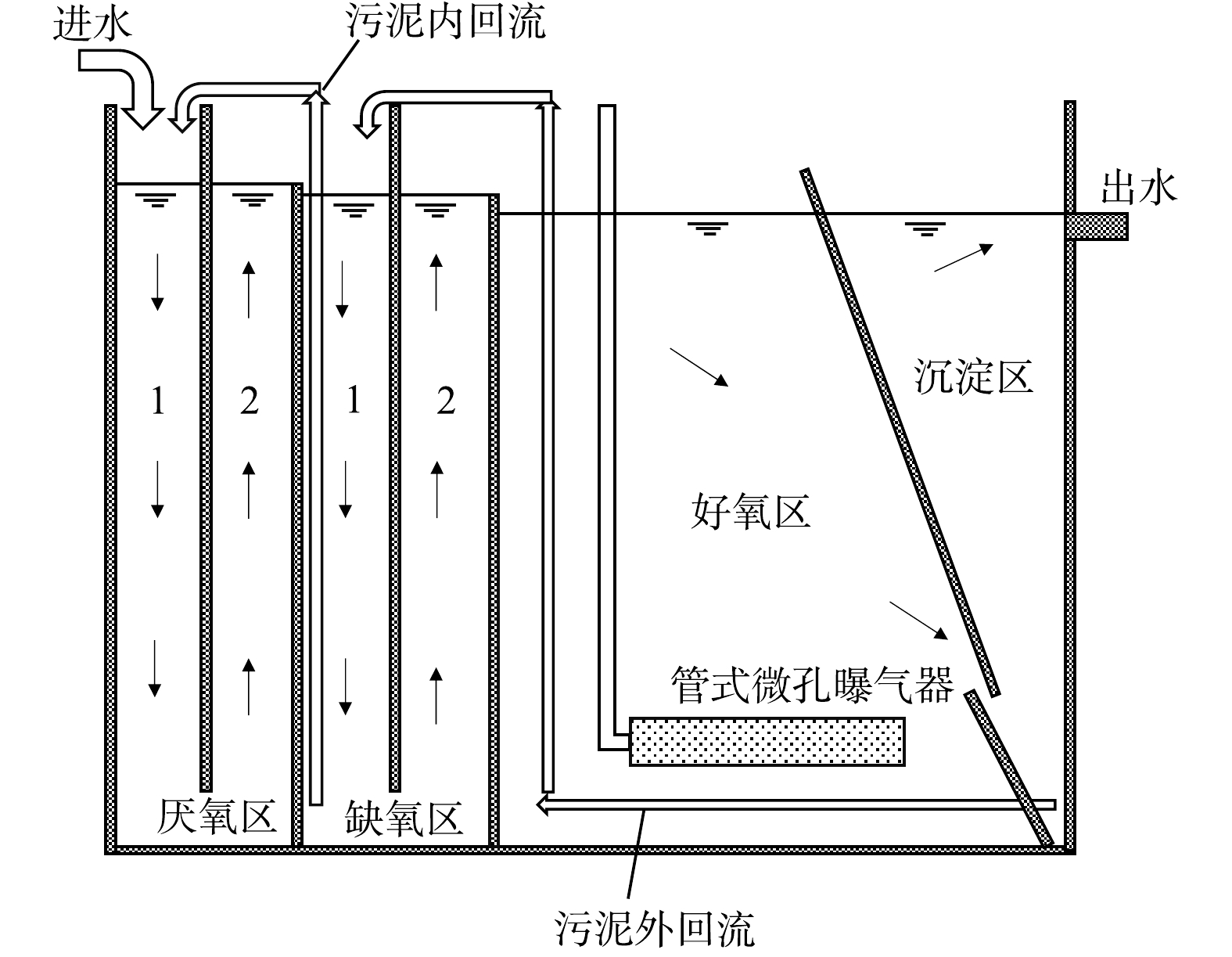
如图1所示,实验装置由厌氧区、缺氧区、好氧区和沉淀区顺序连接组成。污水由进水泵提升进入一体化中试装置,厌缺氧区内设置竖向导流板,将厌氧区和缺氧区均分别隔成1区和2区2个竖向流串联的反应室,污水通过重力流从第1格到最后一格上下折流至好氧区。好氧区池底配有膜式曝气器,混合液从隔板缝隙进入沉淀区泥斗中下部,上清液由排水槽收集后排放。沉淀区底部设置污泥外回流管,沉淀污泥气提外回流至缺氧1区;缺氧1区底部设置内回流管,污泥气提内回流至厌氧1区。含有硝酸盐的沉淀区外回流污泥与含有磷的厌氧区出水在缺氧区混合,具有发生反硝化除磷的条件[16]。
多阶折流A2O一体化中试装置有效容积为5.7 m³,厌氧区和缺氧区中的2个分区容积均为0.6 m³,好氧区和沉淀区的容积分别为2.35 m³和0.95 m³,进水流量为2~3 m³·d−1。如图2所示,装置循环运行,运行单周期为20 min,分为2个阶段。阶段1好氧区曝气且污泥气提回流;阶段2停止曝气,各区污泥沉降。其中阶段1的时间可根据实验需求进行调整(不超过10 min)。单周期的前10 min不进水,后10 min进水,进水控制在污泥沉降阶段,以使污泥保持悬浮状态。
-
一体化中试装置在拉萨市某污水处理厂内运行,实验实验用水取自污水厂粗格栅井。污水水质如表1所示。可见,进水COD/N比值为5.5~6.5,属于典型的低C/N污水。其中6月中旬至8月末为拉萨雨季,污染物的质量浓度较低。接种污泥取自污水处理厂改良型氧化沟工艺,接种后好氧区初始污泥质量浓度为2 100 mg·L−1左右,初始运行参数设置为进水量2 m³·d−1、气水比30、污泥内外回流比均为14。启动运行稳定后,以出水水质稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级B标准为目标,依次优化进水量、气水比、污泥内外回流比等参数。实验历时110 d,期间未排泥,进水水温为18~20 ℃。
-
水样经过0.45 μm滤膜(上海新亚)过滤后,COD、NH4+-N、NO3−-N、TN、TP分别采用快速消解分光光度法、纳氏试剂分光光度法、紫外分光光度法、碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法、钼酸铵分光光度法测定[17],药剂为连华科技预制试剂。采用称量法测定污泥质量浓度MLSS,通过SV30测定污泥体积指数SVI。采用多参数水质检测仪(哈希HQ30d)测定DO及ORP值。
-
多阶折流A2O工艺可在不排泥情况下,通过单位质量污泥TP含量和装置污泥总量的增加,实现系统可储磷总量不断提高从而达到工艺除磷目标,本研究考察分析了一体化中试装置稳定运行阶段单位质量污泥TP含量及不同形态磷分布。
单位质量污泥不同形态磷含量采用欧洲标准测量组织提出的SMT(Standards,Measure-ments and Testing Programme)法[18]测定,该方法将磷分为5种形态,包括总磷(TP)、有机磷(OP)、无机磷(IP)、非磷石灰态无机磷(NAIP,Fe、Mn、Al结合的磷)、磷灰石态无机磷(AP,与Ca结合的磷),采用钼酸铵分光光度法[19]测定各级提取液中磷。
-
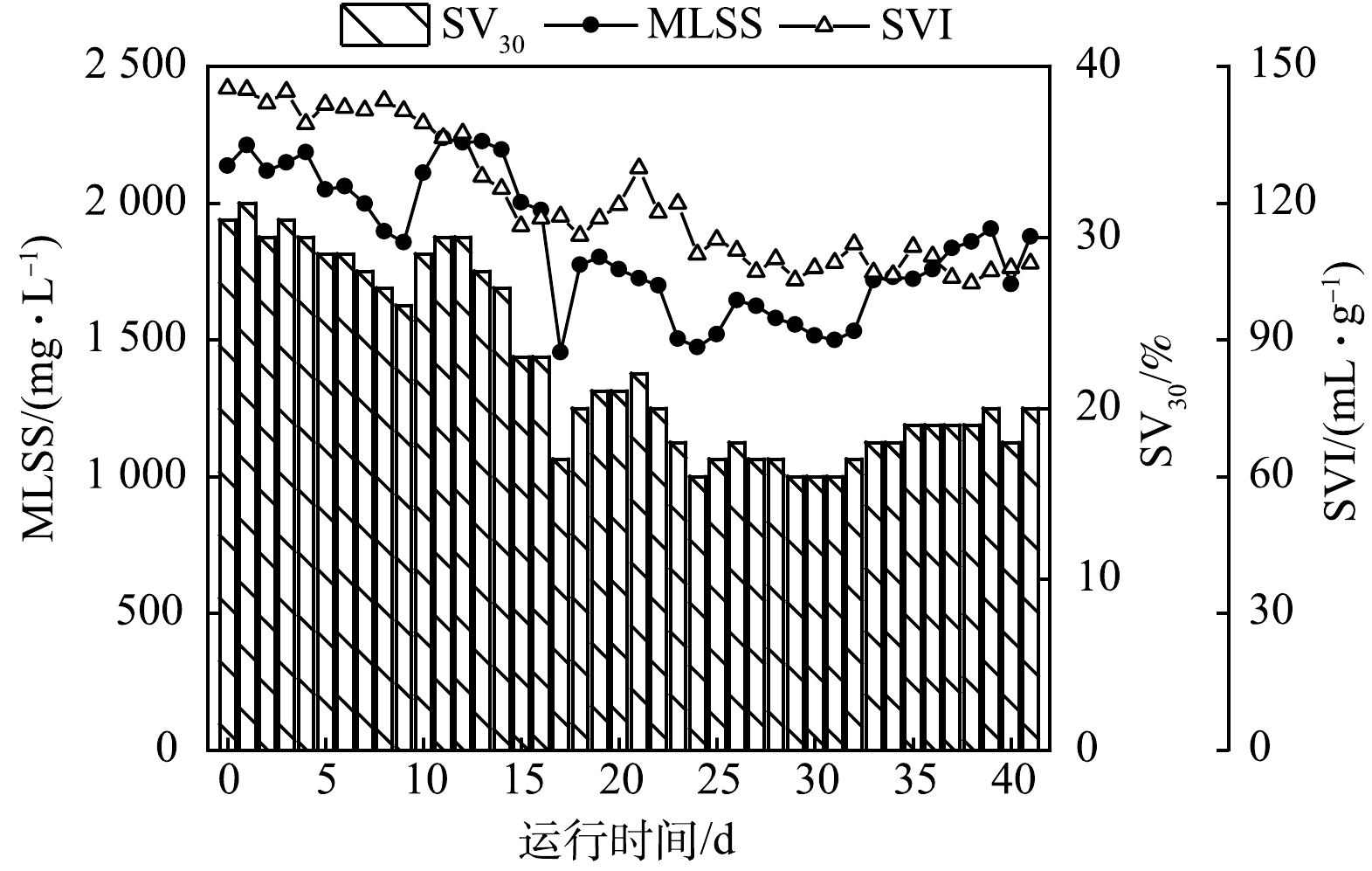
启动培养期间好氧区的污泥参数变化如图3所示。因厌氧缺氧折流区域污泥沉降均匀不一,取好氧区曝气混合状态下的污泥样品可反映工艺全池污泥参数变化。接种污泥后好氧区MLSS为2 136 mg·L−1,因沉淀区表面频繁出现漂浮老化污泥并清理,故系统污泥量缓慢降低,启动第23天好氧区MLSS已降至1 500 mg·L−1左右。随着活性污泥对池内环境逐步适应,系统污泥量逐渐上升,启动培养42 d后好氧区MLSS恢复至1 876 mg·L−1。实验中取自污水厂氧化沟的接种污泥SVI高达145 mL·g−1,处于膨胀状态,沉降性能差,启动培养41 d后好氧区SVI降至107 mL·g−1,沉降性能显著改善。这表明工艺间歇运行模式可有效抑制污泥膨胀[11]。
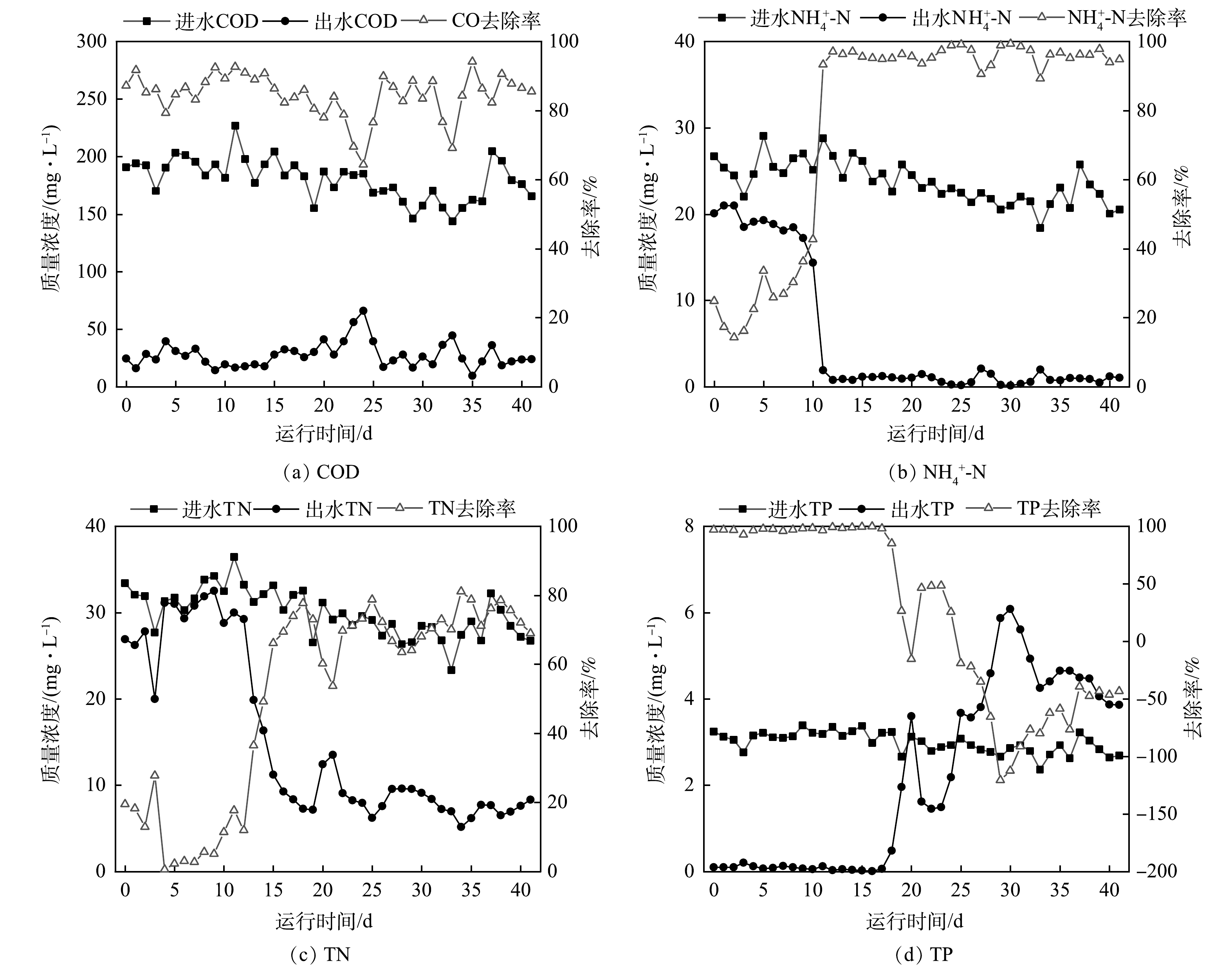
启动期间工艺处理效果如图4所示。出水COD为(40.3±25.8) mg·L−1,大部分时间可达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。启动前10 d,出水NH4+-N为(17.7±3.3) mg·L−1;第11天出水NH4+-N快速下降至1.9 mg·L−1。硝化效率的快速增长得益于有机物在前端厌氧、缺氧区得到了充分去除,并且在好氧区中28.2 h的水力停留时间为硝化菌的生长提供良好环境[20-21]。在硝化效率得到提升时,出水TN随反硝化脱氮作用的增强而持续降低,启动17d后出水TN为(8.8±3.6) mg·L−1。TP变化不同于其他指标,启动前17 d出水TP低于0.5 mg·L−1,但伴随着出水TN的降低,出水TP却于第18天快速波动上升,最高值达到6.1 mg·L−1,远高于进水TP(3.1 mg·L−1),富集于污泥中的磷得到释放。
厌氧区未实现厌氧环境是出水TP超标的主要原因。曝气结束时好氧区DO为3.6 mg·L−1,而在污泥内外回流共同作用下,部分富氧污泥从沉淀区经缺氧区回流至厌氧区,由于DO与ORP值呈正相关[22],导致污泥回流后厌氧1区ORP值提升至-75.8 mV,破坏了厌氧环境,进而影响有机物的转化和厌氧释磷[23]。另一方面,启动10 d后硝化效率显著提升,大量NO3−-N 在高内外污泥回流比时,从好氧区依次回流至缺氧区、厌氧区,并于厌氧区发生反硝化,与厌氧释磷过程竞争碳源,从而导致内碳源PHA生成量减少[24],好氧区聚磷过程所需能量不足,因此,在出水TN浓度降低的同时,TP浓度大幅上升。
-
为使出水TP达标,保持进水量为2 m³·d−1,调整气水比与污泥内回流比,以提供厌氧区厌氧释磷所需的环境条件。气水比在参数未优化的起始时刻和参数优化第3天由30分别降至25、20,气水比调整后好氧区DO降至(2.6±0.1) mg·L−1,厌氧区ORP值稳定低于−150 mV,满足厌氧释磷所需的厌氧区ORP低于-100 mV的条件[25-26]。
污泥内回流比在参数优化后的第7、24和41天由14分别降至12、9和7,内回流污泥NO3−-N 质量浓度保持在(5.5±0.5) mg·L−1,未发生显著变化,但回流总量降至初始的50%,携带至厌氧区NO3−-N量显著减少,因此,反硝化对厌氧释磷的碳源竞争减弱。装置运行中需通过一定的回流量维持厌氧区、缺氧区污泥悬浮所需的水力条件,避免污泥沉淀导致污泥厌氧发酵,因此,未进一步调低污泥内回流比。
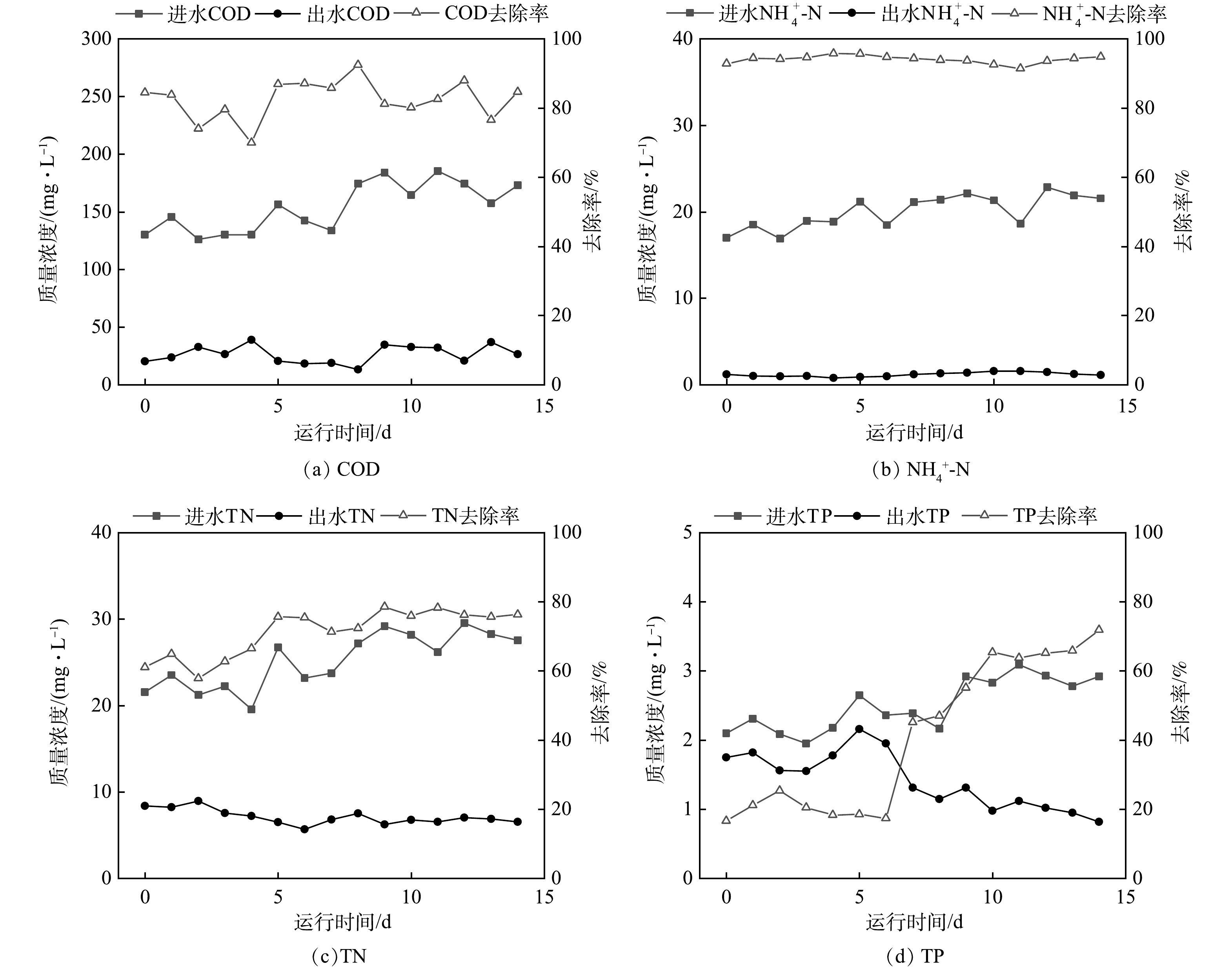
参数优化期间工艺处理效果如图5所示。出水COD、TN、NH4+-N分别为(25.2±15.1)、(7.8±3.1)和(1.1±0.8) mg·L−1,稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。参数优化43 d后出水TP降至(2.1±0.3) mg·L−1,相较于进水平均降低0.5 mg·L−1,系统除磷性能有所恢复。
-
参数未优化的起始时刻将进水量提高至3 m³·d−1,污泥内外回流量不变,但污泥内外回流比分别降至4.5、9.5,减少了反硝化对厌氧释磷过程碳源竞争的影响,同时兼顾了厌氧区和缺氧区混合液水力搅拌需求。
参数优化期间工艺处理效果如图6所示,出水COD、TN、NH4+-N分别为(26.1±12.9)、(7.3±1.6)和(1.2±0.6) mg·L−1,与2 m3·d−1优化运行期间出水水质相当,稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。参数优化后的第14天出水TP降至0.8 mg·L−1,去除率提升至71%,明显优于2 m3·d−1处理量时的TP去除率。
参数优化后的第14天分析了反应装置污染物浓度的沿程变化。在20 min运行周期内,分别考察曝气回流阶段(4 min)、污泥沉降中期(12 min)和污泥沉降末期(20 min,即单周期结束时)厌氧1区和2区、缺氧1区和2区上下层、好氧区进水和出水的水质变化,同时考察了曝气回流阶段(4 min)装置沿程水质。其中厌氧、缺氧折流区上下层水样采样点为每一单格水面以下0.1 m和池底以上0.1 m。由于多阶折流A2O工艺污泥内外回流比相较于常规活性污泥工艺更高[27],因此,对进水污染物稀释作用明显,各池污染物质量浓度变化较小。
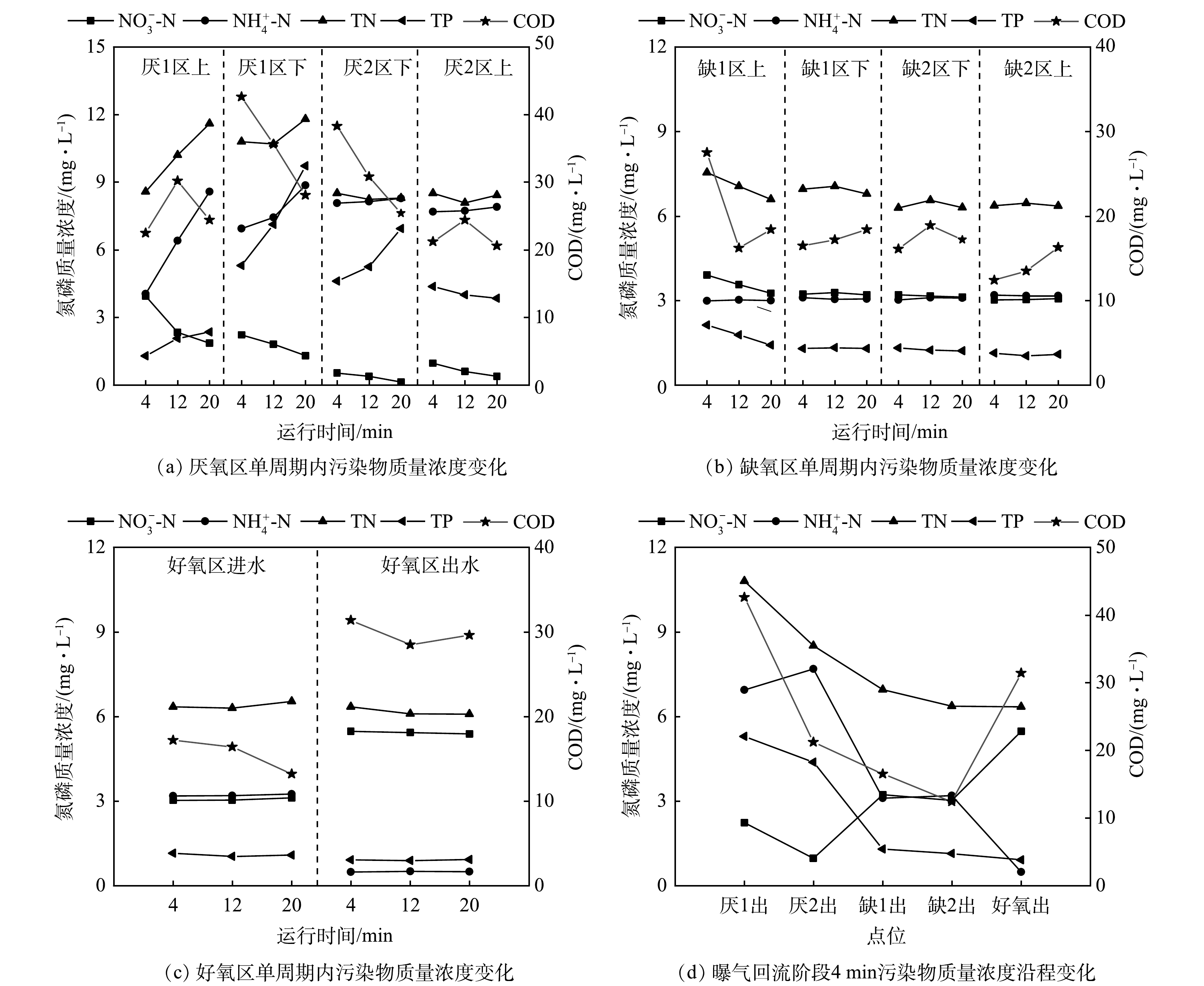
厌氧区水质变化如图7(a)所示。曝气回流阶段上一周期的进水在内回流推流作用下,分布于厌氧区,厌氧1区下层和2区下层的COD分别为42.6 mg·L−1和38.3 mg·L−1。沉降阶段伴随着厌氧释磷和反硝化反应的进行,厌氧1区下层和2区下层COD分别降至28.1 mg·L−1和25.4 mg·L−1 。曝气回流阶段厌氧1区上层和2区上层NO3−-N 分别为3.9 mg·L−1和0.7 mg·L−1,降低了3.2 mg·L−1。沉降阶段厌氧1区上层和1区下层NO3−-N 分别降低2.1 mg·L−1和0.9 mg·L−1,表明厌氧1区是厌氧区脱氮反应主要区域。曝气回流阶段厌氧2区上层TP为4.4 mg·L−1,释磷比达到157.7%,满足后端超量吸磷需求[28]。沉降阶段由于厌氧区碳源供给充分,因此是主要厌氧释磷区域,释磷后厌2区下TP最高达到9.7 mg·L−1。
缺氧区水质变化如图7(b)所示。曝气回流阶段缺氧1区上层和2区上层TP和NO3−-N分别为 2.1、1.1 mg·L−1和3.9、3.0 mg·L−1,对应质量浓度分别下降1.0 mg·L−1和0.9 mg·L−1,反硝化除磷过程去除的磷与氮理论比
ΔPO43−/ΔNO3−−N= 1.27 [29],本装置缺氧区相应比例为1.11,表明缺氧区的磷主要通过反硝化除磷过程去除,同时存在异养反硝化过程。沉降阶段缺氧1区上层TP和NO3−-N分别降低0.7 mg·L−1和0.6 mg·L−1,表明缺氧1区是主要的反硝化除磷场所。好氧区水质变化如图7(c)所示。曝气阶段NH4+-N由3.2 mg·L−1降至0.5 mg·L−1,NO3−-N由3.0 mg·L−1升至5.5 mg·L−1,硝化效果良好。COD由17.2 mg·L−1升至31.4 mg·L−1,其主要原因是好氧区水力停留时间达到18.8 h,部分衰亡期污泥在曝气过程中氧化分解释放有机物[30],回流至缺氧区后也为缺氧区的反硝化提供了碳源。由于聚磷菌内碳源在缺氧区的反硝化除磷过程被消耗,好氧聚磷的能量不足,TP仅由1.1 mg·L−1降至0.9 mg·L−1。
曝气回流末期沿程水质变化如图7(d)所示。水中有机物在厌氧区和缺氧区消耗后降至12.4 mg·L−1,而因部分老化污泥曝气氧化分解,好氧区出水增至31.4 mg·L−1。厌氧释磷后厌氧区出水TP为4.4 mg·L−1,外回流污泥中TP为1.1 mg·L−1,外回流污泥与厌氧区出水按9.5:4.5比混合汇入缺氧区前端,因此缺氧区进水TP为2.1 mg·L−1,经反硝化除磷作用缺氧区出水降至1.1 mg·L−1,缺氧区对磷去除的贡献率为83.3%。厌氧区出水NH4+-N为7.7 mg·L−1,在外回流污泥稀释作用及少量同化作用下,缺氧区出水NH4+-N降至3.2 mg·L−1,经硝化作用好氧区出水NH4+-N进一步降至0.5 mg·L−1。好氧区出水NO3−-N为5.5 mg·L−1,而通过外回流污泥(回流比为9.5)和内回流污泥(回流比为4.5),NO3−-N被带回厌氧区和缺氧区进行脱氮反应,厌氧区内和缺氧区内去除的NO3−-N分别为3.2 mg·L−1和0.9 mg·L−1,厌氧区、缺氧区对氮去除的贡献率分别为62.7%、37.3%。
综上所述,厌氧区实现有机物转化和厌氧释磷的同时,承担了系统主要脱氮功能;缺氧区发生反硝化除磷,其除磷脱氮比与理论值接近,是系统主要除磷单元;好氧区通过硝化反应有效去除NH4+-N,基本实现了多阶折流A2O工艺设计的各分区污染物去除功能。
-
自启动以来,仅清除厌氧区少量漂浮老化污泥,没有排出剩余污泥,进水TP为(2.7±0.7) mg·L−1,后期出水稳定低于1.0 mg·L−1。不同阶段单位质量污泥磷含量如表2所示,A、B、C分别为进水量2 m³·d−1参数优化开始、结束(53 d)和进水量3 m³·d−1参数优化结束(14 d)的装置沉淀区污泥样品,3份污泥样品TP含量为23.45~27.99 mg·g−1,较西藏地区污泥中TP含量平均值(15.9~16.2 mg·g−1)高60% [31],表明高原环境下多阶折流A2O工艺相较于其他工艺表现出更强的污泥储磷能力。随着时间的推移,单位质量污泥TP含量也在不断增高,进水量2 m³·d−1参数优化结束(B)较2 m³·d−1参数优化开始(A)增加1.87 mg·g−1,进水量3 m³·d−1参数优化结束(C)较2 m³·d−1参数优化结束(B)增加2.67 mg·g−1,好氧区MLSS由1 876 mg·L−1(A)提升至2 450 mg·L−1(C),单位质量污泥TP含量和污泥量的增加代表系统可储磷总量不断提高。在运行3~4个月后,可排出一部分污泥以维持系统稳定运行,并将磷移出系统外,长时段内集中排泥有利于污泥的处置管理,符合西藏地区污水厂运维技术薄弱现状。
IP是污泥中总磷主要存在形态,IP在TP中的占比为74.5%~79.9%;而NAIP则是主要无机磷形态,NAIP的占比为65.4%~74.6%。本研究中,这2种磷形态占比与国内市政污水厂单位质量污泥磷形态占比统计结果一致[31]。生物有效磷也是与SMT磷分类法密切相关的指标,其为能够以溶解态磷酸盐释放,并被植物、藻类等生物生长利用的磷[32]。根据RUBAN等[18]提出的方法,生物有效磷可通过NAIP+OP粗略计算得出。本系统中单位质量污泥生物有效磷占TP比例为68.6%~77.8%,表明系统中大部分的磷可以被生物利用,可为阶段性排放的污泥通过堆肥实现资源化利用提供参考。
-
1)多阶折流A2O工艺启动运行稳定后,出水TN、NH4+-N和COD稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。通过优化气水比、污泥回流比等参数,可为系统提供厌氧释磷和反硝化除磷环境。当进水量为3 m³·d−1、气水比为20、污泥内回流比为4.5、污泥外回流比为9.5时,在系统不排泥的情况下,出水TN、NH4+-N和COD稳定达到一级A标准,TP稳定达到一级B标准。
2)多阶折流A2O工艺中单位质量污泥TP含量较西藏污水厂平均水平高60%,其表现出更强的储磷能力,随着单位质量污泥TP含量和污泥量的增加,系统储磷总量不断提高,表明该工艺可用于高原城镇生活污水的处理。
高原生活污水多阶折流A2O处理工艺优化运行与磷去除特性
Optimization operation and phosphorus removal characteristics of multi-stage baffled A2O treatment process for plateau domestic sewage
-
摘要: 为探究适应高原环境且出水稳定达标的城镇污水低碳处理工艺,在拉萨某污水处理厂内搭建多阶折流A2O一体化中试装置,针对实际生活污水,考察了装置启动及参数优化过程中的脱氮除磷性能,并结合污泥磷含量对工艺磷去除特性进行了分析。结果表明:通过调整工艺参数可优化厌氧释磷和反硝化除磷的反应状态,当进水量为3 m³·d−1,气水比、污泥内回流比和污泥外回流比分别为20、4.5和9.5时,在连续运行 95 d不排剩余污泥状态下,出水COD、TN、NH4+-N和TP分别为(26.1±12.9)、(7.3±1.6)、(1.2±0.6)和(0.9±0.1) mg·L−1,反硝化除磷是磷的主要去除途径。多阶折流A2O工艺单位质量污泥TP含量相较西藏污水厂平均水平高60%,具有更强的储磷能力,随着单位质量污泥TP含量和污泥量的增加,系统可储磷总量不断提高。Abstract: In order to explore the low-carbon treatment process of urban sewage adapting to the plateau environment and discharging the stable effluent that can meet the standard, a multi-stage baffled A2O integrated pilot test device was built in a sewage treatment plant in Lhasa. For the actual sewage, the nitrogen and phosphorus removal performance was studied during the start-up and parameter optimization stages, and the phosphorus removal characteristics of the process were analyzed in combination with the phosphorus content in sludge. The results showed that adjusting the process parameters could optimize the reaction states of anaerobic phosphorus release and denitrifying phosphorus removal. when the water intake was 3m³·d−1, the gas-water ratio, sludge internal reflux ratio and sludge external reflux ratio were 20, 4.5 and 9.5, respectively, the process ran continuously for 95 days without excess activated sludge discharge, and the COD, TN, NH4+-N and TP of effluent were (26.1±12.9), (7.3±1.6) and (1.2±0.6), (0.9±0.1) mg·L−1, respectively. The main pathway of phosphorus removal was denitrifying phosphorus. TP content in per unit mass of sludge in multi-stage baffled A2O process was 60% higher than the average level in Xizang sewage treatment plant, and it had stronger phosphorus storage capacity. With the increase in the TP content in per unit mass of sludge and sludge amount, the total amount of phosphorus that can be stored in the system continued to increase.
-
21世纪以来西藏地区社会经济得到快速发展,生活污水量随之增加[1],为保护脆弱的高原生态环境,高原生活污水的有效处理成为必然。目前西藏地区主要采用A2O、多级AO、氧化沟等工艺,设计和建设中通常参照内地经验,但污水处理厂出水水质却难以稳定达标[2],此外也面临运行操作困难、运行能耗高、污泥膨胀等问题[3]。究其原因,主要有以下3个方面。1)其独特饮食习惯使西藏地区生活污水碳氮比(3~10)偏低[4],而聚磷菌和反硝化菌对有限碳源的竞争[5],导致系统氮磷去除效果不佳。2)高海拔地理条件下,西藏地区主要城市大气压力为52.93~59.87 kPa,含氧量50.36%~67.24%[6],低压条件下不仅水中氧气溶解度降低,曝气时气泡数量和气体滞留律的降低也会间接影响氧气的传质[7];低氧条件与鼓风曝气机的曝气效率直接相关,需要加大曝气量来提高水中的DO。在高原低压低氧环境条件协同作用下,相同工艺的曝气能耗显著增加。3)在高海拔地理条件下,西藏地区城镇污水水温最低可至8 ℃[8],而低温条件下微生物酶活性、基质降解效率、微生物代谢活性、微生物比增长速率都会出现不同程度降低[9],污泥活性的降低使得工艺出水难以达标;此外,低温条件下系统易发生污泥膨胀,包括非丝状菌膨胀和丝状菌膨胀[10-12]。
针对以上高原城镇污水处理困境,近年来有学者进行了高原环境下适用处理工艺的探究。王利等[13]搭建了SBR系统,在低温低压低氧条件下实现系统的快速启动稳定,但出水NH4+-N未能达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级B标准。吴永刚[14]改造了氧化沟工艺,将所有预处理设施置于室内,并通过锅炉余热利用和蒸汽加热等措施克服低温问题,冬季出水可稳定达到GB 18918-2002一级B标准,但建设及维护成本显著增加。吕学斌等[15]搭建了深井中试装置实现高压曝气,可以克服低温低压低氧问题,但施工难度大。目前改良或新开发的工艺存在出水水质不稳定、成本高、施工难等不足,难以在高原推广应用。因此,针对高原气候环境三低特点和进水水质,提出适应高原环境且出水水质稳定达标的城镇污水低碳处理工艺十分必要。
本研究构建了多阶折流A2O一体化中试装置,分析了装置的启动运行特征,考察了常温下气水比、污泥内外回流比、进水量等工艺参数对运行效能的影响,解析了污染物的去除效能、磷在系统中的分布。以期为高原生活污水的高效低碳处理提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验装置
如图1所示,实验装置由厌氧区、缺氧区、好氧区和沉淀区顺序连接组成。污水由进水泵提升进入一体化中试装置,厌缺氧区内设置竖向导流板,将厌氧区和缺氧区均分别隔成1区和2区2个竖向流串联的反应室,污水通过重力流从第1格到最后一格上下折流至好氧区。好氧区池底配有膜式曝气器,混合液从隔板缝隙进入沉淀区泥斗中下部,上清液由排水槽收集后排放。沉淀区底部设置污泥外回流管,沉淀污泥气提外回流至缺氧1区;缺氧1区底部设置内回流管,污泥气提内回流至厌氧1区。含有硝酸盐的沉淀区外回流污泥与含有磷的厌氧区出水在缺氧区混合,具有发生反硝化除磷的条件[16]。
多阶折流A2O一体化中试装置有效容积为5.7 m³,厌氧区和缺氧区中的2个分区容积均为0.6 m³,好氧区和沉淀区的容积分别为2.35 m³和0.95 m³,进水流量为2~3 m³·d−1。如图2所示,装置循环运行,运行单周期为20 min,分为2个阶段。阶段1好氧区曝气且污泥气提回流;阶段2停止曝气,各区污泥沉降。其中阶段1的时间可根据实验需求进行调整(不超过10 min)。单周期的前10 min不进水,后10 min进水,进水控制在污泥沉降阶段,以使污泥保持悬浮状态。
1.2 实验废水水质与实验方法
一体化中试装置在拉萨市某污水处理厂内运行,实验实验用水取自污水厂粗格栅井。污水水质如表1所示。可见,进水COD/N比值为5.5~6.5,属于典型的低C/N污水。其中6月中旬至8月末为拉萨雨季,污染物的质量浓度较低。接种污泥取自污水处理厂改良型氧化沟工艺,接种后好氧区初始污泥质量浓度为2 100 mg·L−1左右,初始运行参数设置为进水量2 m³·d−1、气水比30、污泥内外回流比均为14。启动运行稳定后,以出水水质稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级B标准为目标,依次优化进水量、气水比、污泥内外回流比等参数。实验历时110 d,期间未排泥,进水水温为18~20 ℃。
表 1 实验进水水质Table 1. Water quality of experimental influentmg·L−1 统计值 COD NH4+-N TN TP 范围 126.2~227.0 15.9~29.1 20.3~36.4 1.9~3.4 平均值 167.1 21.9 27.8 2.8 1.3 常规项目检测
水样经过0.45 μm滤膜(上海新亚)过滤后,COD、NH4+-N、NO3−-N、TN、TP分别采用快速消解分光光度法、纳氏试剂分光光度法、紫外分光光度法、碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法、钼酸铵分光光度法测定[17],药剂为连华科技预制试剂。采用称量法测定污泥质量浓度MLSS,通过SV30测定污泥体积指数SVI。采用多参数水质检测仪(哈希HQ30d)测定DO及ORP值。
1.4 污泥磷含量分析
多阶折流A2O工艺可在不排泥情况下,通过单位质量污泥TP含量和装置污泥总量的增加,实现系统可储磷总量不断提高从而达到工艺除磷目标,本研究考察分析了一体化中试装置稳定运行阶段单位质量污泥TP含量及不同形态磷分布。
单位质量污泥不同形态磷含量采用欧洲标准测量组织提出的SMT(Standards,Measure-ments and Testing Programme)法[18]测定,该方法将磷分为5种形态,包括总磷(TP)、有机磷(OP)、无机磷(IP)、非磷石灰态无机磷(NAIP,Fe、Mn、Al结合的磷)、磷灰石态无机磷(AP,与Ca结合的磷),采用钼酸铵分光光度法[19]测定各级提取液中磷。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 装置启动
启动培养期间好氧区的污泥参数变化如图3所示。因厌氧缺氧折流区域污泥沉降均匀不一,取好氧区曝气混合状态下的污泥样品可反映工艺全池污泥参数变化。接种污泥后好氧区MLSS为2 136 mg·L−1,因沉淀区表面频繁出现漂浮老化污泥并清理,故系统污泥量缓慢降低,启动第23天好氧区MLSS已降至1 500 mg·L−1左右。随着活性污泥对池内环境逐步适应,系统污泥量逐渐上升,启动培养42 d后好氧区MLSS恢复至1 876 mg·L−1。实验中取自污水厂氧化沟的接种污泥SVI高达145 mL·g−1,处于膨胀状态,沉降性能差,启动培养41 d后好氧区SVI降至107 mL·g−1,沉降性能显著改善。这表明工艺间歇运行模式可有效抑制污泥膨胀[11]。
启动期间工艺处理效果如图4所示。出水COD为(40.3±25.8) mg·L−1,大部分时间可达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。启动前10 d,出水NH4+-N为(17.7±3.3) mg·L−1;第11天出水NH4+-N快速下降至1.9 mg·L−1。硝化效率的快速增长得益于有机物在前端厌氧、缺氧区得到了充分去除,并且在好氧区中28.2 h的水力停留时间为硝化菌的生长提供良好环境[20-21]。在硝化效率得到提升时,出水TN随反硝化脱氮作用的增强而持续降低,启动17d后出水TN为(8.8±3.6) mg·L−1。TP变化不同于其他指标,启动前17 d出水TP低于0.5 mg·L−1,但伴随着出水TN的降低,出水TP却于第18天快速波动上升,最高值达到6.1 mg·L−1,远高于进水TP(3.1 mg·L−1),富集于污泥中的磷得到释放。
厌氧区未实现厌氧环境是出水TP超标的主要原因。曝气结束时好氧区DO为3.6 mg·L−1,而在污泥内外回流共同作用下,部分富氧污泥从沉淀区经缺氧区回流至厌氧区,由于DO与ORP值呈正相关[22],导致污泥回流后厌氧1区ORP值提升至-75.8 mV,破坏了厌氧环境,进而影响有机物的转化和厌氧释磷[23]。另一方面,启动10 d后硝化效率显著提升,大量NO3−-N 在高内外污泥回流比时,从好氧区依次回流至缺氧区、厌氧区,并于厌氧区发生反硝化,与厌氧释磷过程竞争碳源,从而导致内碳源PHA生成量减少[24],好氧区聚磷过程所需能量不足,因此,在出水TN浓度降低的同时,TP浓度大幅上升。
2.2 进水量2 m³·d−1参数优化对装置处理效能影响
为使出水TP达标,保持进水量为2 m³·d−1,调整气水比与污泥内回流比,以提供厌氧区厌氧释磷所需的环境条件。气水比在参数未优化的起始时刻和参数优化第3天由30分别降至25、20,气水比调整后好氧区DO降至(2.6±0.1) mg·L−1,厌氧区ORP值稳定低于−150 mV,满足厌氧释磷所需的厌氧区ORP低于-100 mV的条件[25-26]。
污泥内回流比在参数优化后的第7、24和41天由14分别降至12、9和7,内回流污泥NO3−-N 质量浓度保持在(5.5±0.5) mg·L−1,未发生显著变化,但回流总量降至初始的50%,携带至厌氧区NO3−-N量显著减少,因此,反硝化对厌氧释磷的碳源竞争减弱。装置运行中需通过一定的回流量维持厌氧区、缺氧区污泥悬浮所需的水力条件,避免污泥沉淀导致污泥厌氧发酵,因此,未进一步调低污泥内回流比。
参数优化期间工艺处理效果如图5所示。出水COD、TN、NH4+-N分别为(25.2±15.1)、(7.8±3.1)和(1.1±0.8) mg·L−1,稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。参数优化43 d后出水TP降至(2.1±0.3) mg·L−1,相较于进水平均降低0.5 mg·L−1,系统除磷性能有所恢复。
2.3 进水量3 m³·d−1参数优化对装置处理效能影响
参数未优化的起始时刻将进水量提高至3 m³·d−1,污泥内外回流量不变,但污泥内外回流比分别降至4.5、9.5,减少了反硝化对厌氧释磷过程碳源竞争的影响,同时兼顾了厌氧区和缺氧区混合液水力搅拌需求。
参数优化期间工艺处理效果如图6所示,出水COD、TN、NH4+-N分别为(26.1±12.9)、(7.3±1.6)和(1.2±0.6) mg·L−1,与2 m3·d−1优化运行期间出水水质相当,稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。参数优化后的第14天出水TP降至0.8 mg·L−1,去除率提升至71%,明显优于2 m3·d−1处理量时的TP去除率。
参数优化后的第14天分析了反应装置污染物浓度的沿程变化。在20 min运行周期内,分别考察曝气回流阶段(4 min)、污泥沉降中期(12 min)和污泥沉降末期(20 min,即单周期结束时)厌氧1区和2区、缺氧1区和2区上下层、好氧区进水和出水的水质变化,同时考察了曝气回流阶段(4 min)装置沿程水质。其中厌氧、缺氧折流区上下层水样采样点为每一单格水面以下0.1 m和池底以上0.1 m。由于多阶折流A2O工艺污泥内外回流比相较于常规活性污泥工艺更高[27],因此,对进水污染物稀释作用明显,各池污染物质量浓度变化较小。
厌氧区水质变化如图7(a)所示。曝气回流阶段上一周期的进水在内回流推流作用下,分布于厌氧区,厌氧1区下层和2区下层的COD分别为42.6 mg·L−1和38.3 mg·L−1。沉降阶段伴随着厌氧释磷和反硝化反应的进行,厌氧1区下层和2区下层COD分别降至28.1 mg·L−1和25.4 mg·L−1 。曝气回流阶段厌氧1区上层和2区上层NO3−-N 分别为3.9 mg·L−1和0.7 mg·L−1,降低了3.2 mg·L−1。沉降阶段厌氧1区上层和1区下层NO3−-N 分别降低2.1 mg·L−1和0.9 mg·L−1,表明厌氧1区是厌氧区脱氮反应主要区域。曝气回流阶段厌氧2区上层TP为4.4 mg·L−1,释磷比达到157.7%,满足后端超量吸磷需求[28]。沉降阶段由于厌氧区碳源供给充分,因此是主要厌氧释磷区域,释磷后厌2区下TP最高达到9.7 mg·L−1。
缺氧区水质变化如图7(b)所示。曝气回流阶段缺氧1区上层和2区上层TP和NO3−-N分别为 2.1、1.1 mg·L−1和3.9、3.0 mg·L−1,对应质量浓度分别下降1.0 mg·L−1和0.9 mg·L−1,反硝化除磷过程去除的磷与氮理论比
ΔPO43−/ΔNO3−−N= 好氧区水质变化如图7(c)所示。曝气阶段NH4+-N由3.2 mg·L−1降至0.5 mg·L−1,NO3−-N由3.0 mg·L−1升至5.5 mg·L−1,硝化效果良好。COD由17.2 mg·L−1升至31.4 mg·L−1,其主要原因是好氧区水力停留时间达到18.8 h,部分衰亡期污泥在曝气过程中氧化分解释放有机物[30],回流至缺氧区后也为缺氧区的反硝化提供了碳源。由于聚磷菌内碳源在缺氧区的反硝化除磷过程被消耗,好氧聚磷的能量不足,TP仅由1.1 mg·L−1降至0.9 mg·L−1。
曝气回流末期沿程水质变化如图7(d)所示。水中有机物在厌氧区和缺氧区消耗后降至12.4 mg·L−1,而因部分老化污泥曝气氧化分解,好氧区出水增至31.4 mg·L−1。厌氧释磷后厌氧区出水TP为4.4 mg·L−1,外回流污泥中TP为1.1 mg·L−1,外回流污泥与厌氧区出水按9.5:4.5比混合汇入缺氧区前端,因此缺氧区进水TP为2.1 mg·L−1,经反硝化除磷作用缺氧区出水降至1.1 mg·L−1,缺氧区对磷去除的贡献率为83.3%。厌氧区出水NH4+-N为7.7 mg·L−1,在外回流污泥稀释作用及少量同化作用下,缺氧区出水NH4+-N降至3.2 mg·L−1,经硝化作用好氧区出水NH4+-N进一步降至0.5 mg·L−1。好氧区出水NO3−-N为5.5 mg·L−1,而通过外回流污泥(回流比为9.5)和内回流污泥(回流比为4.5),NO3−-N被带回厌氧区和缺氧区进行脱氮反应,厌氧区内和缺氧区内去除的NO3−-N分别为3.2 mg·L−1和0.9 mg·L−1,厌氧区、缺氧区对氮去除的贡献率分别为62.7%、37.3%。
综上所述,厌氧区实现有机物转化和厌氧释磷的同时,承担了系统主要脱氮功能;缺氧区发生反硝化除磷,其除磷脱氮比与理论值接近,是系统主要除磷单元;好氧区通过硝化反应有效去除NH4+-N,基本实现了多阶折流A2O工艺设计的各分区污染物去除功能。
2.4 不同阶段单位质量污泥磷含量
自启动以来,仅清除厌氧区少量漂浮老化污泥,没有排出剩余污泥,进水TP为(2.7±0.7) mg·L−1,后期出水稳定低于1.0 mg·L−1。不同阶段单位质量污泥磷含量如表2所示,A、B、C分别为进水量2 m³·d−1参数优化开始、结束(53 d)和进水量3 m³·d−1参数优化结束(14 d)的装置沉淀区污泥样品,3份污泥样品TP含量为23.45~27.99 mg·g−1,较西藏地区污泥中TP含量平均值(15.9~16.2 mg·g−1)高60% [31],表明高原环境下多阶折流A2O工艺相较于其他工艺表现出更强的污泥储磷能力。随着时间的推移,单位质量污泥TP含量也在不断增高,进水量2 m³·d−1参数优化结束(B)较2 m³·d−1参数优化开始(A)增加1.87 mg·g−1,进水量3 m³·d−1参数优化结束(C)较2 m³·d−1参数优化结束(B)增加2.67 mg·g−1,好氧区MLSS由1 876 mg·L−1(A)提升至2 450 mg·L−1(C),单位质量污泥TP含量和污泥量的增加代表系统可储磷总量不断提高。在运行3~4个月后,可排出一部分污泥以维持系统稳定运行,并将磷移出系统外,长时段内集中排泥有利于污泥的处置管理,符合西藏地区污水厂运维技术薄弱现状。
表 2 不同阶段单位质量污泥磷含量及污泥质量浓度Table 2. Phosphorus content in per unit mass of sludge at different stages样品 TP/(mg·g−1) IP/(mg·g−1) NAIP/(mg·g−1) AP/(mg·g−1) OP/(mg·g−1) MLSS/(mg·L−1) A 23.45 17.46 11.46 6.52 4.62 1876 B 25.32 19.25 12.59 6.52 5.62 2368 C 27.99 22.36 16.69 5.54 5.11 2450 IP是污泥中总磷主要存在形态,IP在TP中的占比为74.5%~79.9%;而NAIP则是主要无机磷形态,NAIP的占比为65.4%~74.6%。本研究中,这2种磷形态占比与国内市政污水厂单位质量污泥磷形态占比统计结果一致[31]。生物有效磷也是与SMT磷分类法密切相关的指标,其为能够以溶解态磷酸盐释放,并被植物、藻类等生物生长利用的磷[32]。根据RUBAN等[18]提出的方法,生物有效磷可通过NAIP+OP粗略计算得出。本系统中单位质量污泥生物有效磷占TP比例为68.6%~77.8%,表明系统中大部分的磷可以被生物利用,可为阶段性排放的污泥通过堆肥实现资源化利用提供参考。
3. 结论
1)多阶折流A2O工艺启动运行稳定后,出水TN、NH4+-N和COD稳定达到《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。通过优化气水比、污泥回流比等参数,可为系统提供厌氧释磷和反硝化除磷环境。当进水量为3 m³·d−1、气水比为20、污泥内回流比为4.5、污泥外回流比为9.5时,在系统不排泥的情况下,出水TN、NH4+-N和COD稳定达到一级A标准,TP稳定达到一级B标准。
2)多阶折流A2O工艺中单位质量污泥TP含量较西藏污水厂平均水平高60%,其表现出更强的储磷能力,随着单位质量污泥TP含量和污泥量的增加,系统储磷总量不断提高,表明该工艺可用于高原城镇生活污水的处理。
-
表 1 实验进水水质
Table 1. Water quality of experimental influent
mg·L−1 统计值 COD NH4+-N TN TP 范围 126.2~227.0 15.9~29.1 20.3~36.4 1.9~3.4 平均值 167.1 21.9 27.8 2.8 表 2 不同阶段单位质量污泥磷含量及污泥质量浓度
Table 2. Phosphorus content in per unit mass of sludge at different stages
样品 TP/(mg·g−1) IP/(mg·g−1) NAIP/(mg·g−1) AP/(mg·g−1) OP/(mg·g−1) MLSS/(mg·L−1) A 23.45 17.46 11.46 6.52 4.62 1876 B 25.32 19.25 12.59 6.52 5.62 2368 C 27.99 22.36 16.69 5.54 5.11 2450 -
[1] 韩震. 高海拔地区改良型双污泥除磷脱氮工艺优化研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2020. [2] LIHUA N, YI L, PEIFANG W, et al. Altitude-scale variation in nitrogen-removal bacterial communities from municipal wastewater treatment plants distributed along a 3600-m altitudinal gradient in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 559: 38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.175 [3] 宗永臣. 西藏高原环境下A2/O工艺微生物特征及脱氮除磷机理研究[D]. 拉萨: 西藏大学, 2021. [4] 陈悦. 高海拔地区同步硝化反硝化—反硝化除磷系统工艺优化及氮磷去除特性研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2020. [5] ZENG R J, LEMAIRE R, YUAN Z, et al. Simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in a lab-scale sequencing batch reactor[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2003, 84(2): 170-178. doi: 10.1002/bit.10744 [6] 宗永臣. 西藏地区自然环境对污水处理效果的影响初探[J]. 市政技术, 2017, 35(3): 132-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7767.2017.03.041 [7] CAMPANI G, RIBEIRO M P A, HORTA A C L, et al. Oxygen transfer in a pressurized airlift bioreactor[J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2015, 38(8): 1559-1567. doi: 10.1007/s00449-015-1397-4 [8] 张培胜, 李轶, 王龙飞. 我国高原污水处理厂现存问题及其展望[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(5): 82-86. [9] YUFENG L, JUEJUN P, TANGRAN H, et al. Enhance the treatment of low strength wastewater at low temperature with the coexistence system of AnAOB and heterotrophic bacteria: Performance and bacterial community[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 714: 136799. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136799 [10] LIU Y, FANG H. Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on flocculation, settling, and dewatering of activated sludge[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2003, 33(3): 237-273. doi: 10.1080/10643380390814479 [11] 敖强. 城镇污水处理厂活性污泥丝状菌膨胀控制技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2020. [12] 李雪. 高原地区AAO氧化沟工艺污水厂提标改造技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. [13] 王利, 徐文国, 卢士香. 高原地区SBR法处理生活污水工程实例[J]. 水处理技术, 2012, 38(S1): 135-137. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2012.s1.037 [14] 吴永刚. 高原低温型城镇污水处理设计与体会[J]. 水处理技术, 2020, 46(12): 134-137. doi: 10.16796/j.cnki.1000-3770.2020.12.027 [15] 吕学斌, 李晓云, 田津, 等. 一种适用于高寒缺氧地区污水处理系统: CN201621396930.4[P]. 2017-07-25. [16] 韦佳敏, 刘文如, 程洁红, 等. 反硝化除磷的影响因素及聚磷菌与聚糖菌耦合新工艺的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(11): 4608-4618. doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2020-0179 [17] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [18] RUBAN V, LOPEZ-SANCHEZ J F, PARDO P, et al. Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments: A synthesis of recent works[J]. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 370(2/3): 224-228. [19] 俞振飞, 王国祥, 钱君龙, 等. SMT法测定沉积物标准样品有机磷形态分析方法探究[J]. 中国环境监测, 2013, 29(03): 117-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2013.03.024 [20] 王翠. 不同C/N比低浓度污水的A/O/N脱氮研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2006. [21] 李志华, 杨红亮, 赵雨. 小城镇污水处理厂CAST工艺启动及运行策略[J]. 中国给水排水, 2014, 30(18): 140-144. [22] 马勇, 彭永臻. 应用DO、pH和ORP在线控制A/O硝化过程[J]. 中国给水排水, 2005(11): 1-5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2005.11.001 [23] 苏高强, 彭永臻. 基于ORP的控制策略在废水生物处理中的应用[J]. 工业水处理, 2011, 31(8): 11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2011.08.003 [24] MEYER R L, ZENG R J, GIUGLIANO V, et al. Challenges for simultaneous nitrification, denitrification, and phosphorus removal in microbial aggregates: Mass transfer limitation and nitrous oxide production[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2005, 52(3): 329-338. doi: 10.1016/j.femsec.2004.11.011 [25] 涂航, 张军, 张文钊, 等. A/O-MBR耦合蠕虫床组合系统中试处理性能研究[J]. 给水排水, 2020, 56(S2): 29-36. [26] 边德军, 郑少杰, 李清哲, 等. AOA-SBR工艺污水处理效果及其强化生物除磷性能[J]. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2021, 22(2): 115-122. [27] 鲍任兵, 马民, 徐健, 等. AAO及改良型工艺耦合MBR工艺应用研究综述[J]. 净水技术, 2022, 41(3): 26-31. doi: 10.15890/j.cnki.jsjs.2022.03.004 [28] 张婧倩, 王淑莹, 唐旭光, 等. 低温对EBPR系统生物除磷特性的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(9): 2882-2886. [29] 汪林. 反硝化同步除磷动力学原理及其在改善MSBR性能中的应用[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2010. [30] 袁丽梅. 多点进水厌氧—多级缺氧/好氧—膜组合工艺处理生活污水的实验研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2007. [31] 王超, 刘清伟, 职音, 等. 中国市政污泥中磷的含量与形态分布[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(4): 1922-1930. [32] SONZOGNI W C, CHAPRA S C, ARMSTRONG D E, et al. Bioavailability of phosphorus inputs to lakes[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1982, 11(4): 555-563. -




 下载:
下载: