-
随着原油油品劣质化加剧,含油污水水质呈生物毒性大、高浓度、难降解的趋势发展[1];加之环保排放标准日趋严苛,环境承载负荷降低,含油污水处理压力不断增加[2]。针对含油污水中的悬浮物、油分及溶解性污染物等,目前普遍采取除油脱固预处理、生物处理和深度处理相结合的组合工艺。其中,除油脱固预处理单元工艺及设施相对固定,常规采取以气浮为核心的组合技术,利用絮凝和沉降相结合的方式去除油分和悬浮物[3-4],稳定调控生化进水中的油分和悬浮物质量浓度,但也普遍存在出水水质易受来水冲击产生波动、絮凝药剂消耗量大并产生大量的化学浮渣等危废、VOCs等臭气逸散、构筑物运行维护泥繁琐等弊端[5-7],极易诱发“环境临避效应”。
微通道分离是一种利用颗粒介质堆积形成的微通道,高效截滤去除污染物的方法。通过对0.5~1 mm无烟煤颗粒堆积形成的微通道进行Micro-CT扫描,得到微通道平均半径为17 μm[8-9]。针对含油污水常规气浮预处理过程的潜在弊端,利用介质深层截滤实现来水中油分及悬浮物物理分离的过滤技术能充分弥补其中的不足,但同时也存在因为油分和悬浮物对介质颗粒的粘附造成过滤分离效率持续衰减等问题。有研究表明,床层介质截滤的油分和悬浮物与介质颗粒的相互作用力是由毛细力、范德华力和分子间排斥力组成的合力模型[10-11]。如果能够促进颗粒介质表面及孔道内油类污染物的快速脱附,不断更新颗粒介质表面及孔道,将显著延长截滤床层的应用周期。目前,对于颗粒介质中石油类污染物的脱附主要有3种途径:减黏洗涤脱附[12-13];相似相溶脱附[14];高温脱附[15]。热脱附应用范围较广,适合处理多种有机物混合污染的工况,但处理大量颗粒介质时存在能耗高、效率低等问题[16];使用化学药剂淋洗可以显著降低油类污染物与颗粒间的表面作用力,降低污染物脱附难度,但存在产生二次污染、药剂消耗较高等问题[17]。颗粒在旋流场旋转剪切流作用下进行高速自公转耦合运动,从而产生自公转耦合离心力实现颗粒表面污染物脱附[18]。已有研究表明,颗粒在旋流器中频繁的碰撞和自公转耦合运动加强了粘附在过滤介质表面油的脱附[19-20],实现了废催化剂的再利用[21]。因此,旋流器具有强化过滤介质再生的潜在优势。
针对实际含油污水预处理过程中消耗大量化学絮凝药剂并产生浮渣等危废,常规过滤技术无法实现颗粒介质彻底再生等技术瓶颈,本研究通过开发微通道振荡脱附单元,研究了旋流振荡再生强度和振荡再生结构对微通道分离装置过滤介质再生效率的影响,由此集成研发沸腾床分离器,考察了装置对实际含油污水的分离效率,并分析了微通道振荡再生对沸腾床分离的强化原理以及装置的分离经济性,可为含油污水低成本高效预处理提供参考。
-
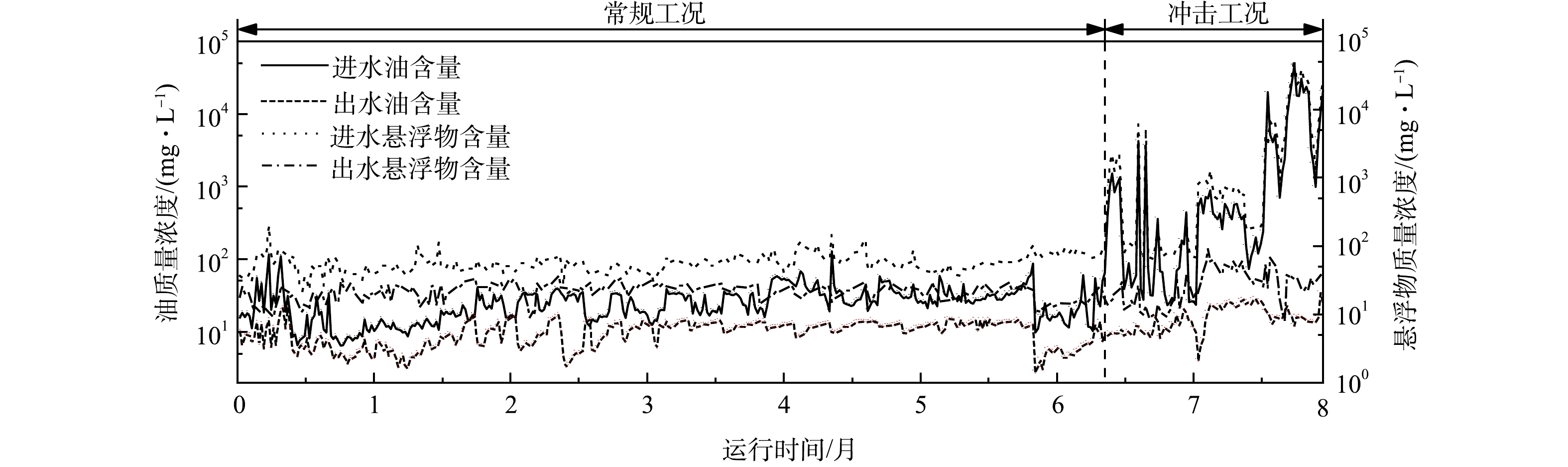
本研究所用含油污水来源于某石化公司污水处理厂均质调节罐出水,油及悬浮物质量浓度分布如图1所示。常规工况下,含油污水油质量浓度为30~200 mg·L−1、悬浮物质量浓度为40~230 mg·L−1;受上游装置波动或生产区异常影响,冲击工况下,来水中的油和悬浮物质量浓度接近50 000 mg·L−1。
-
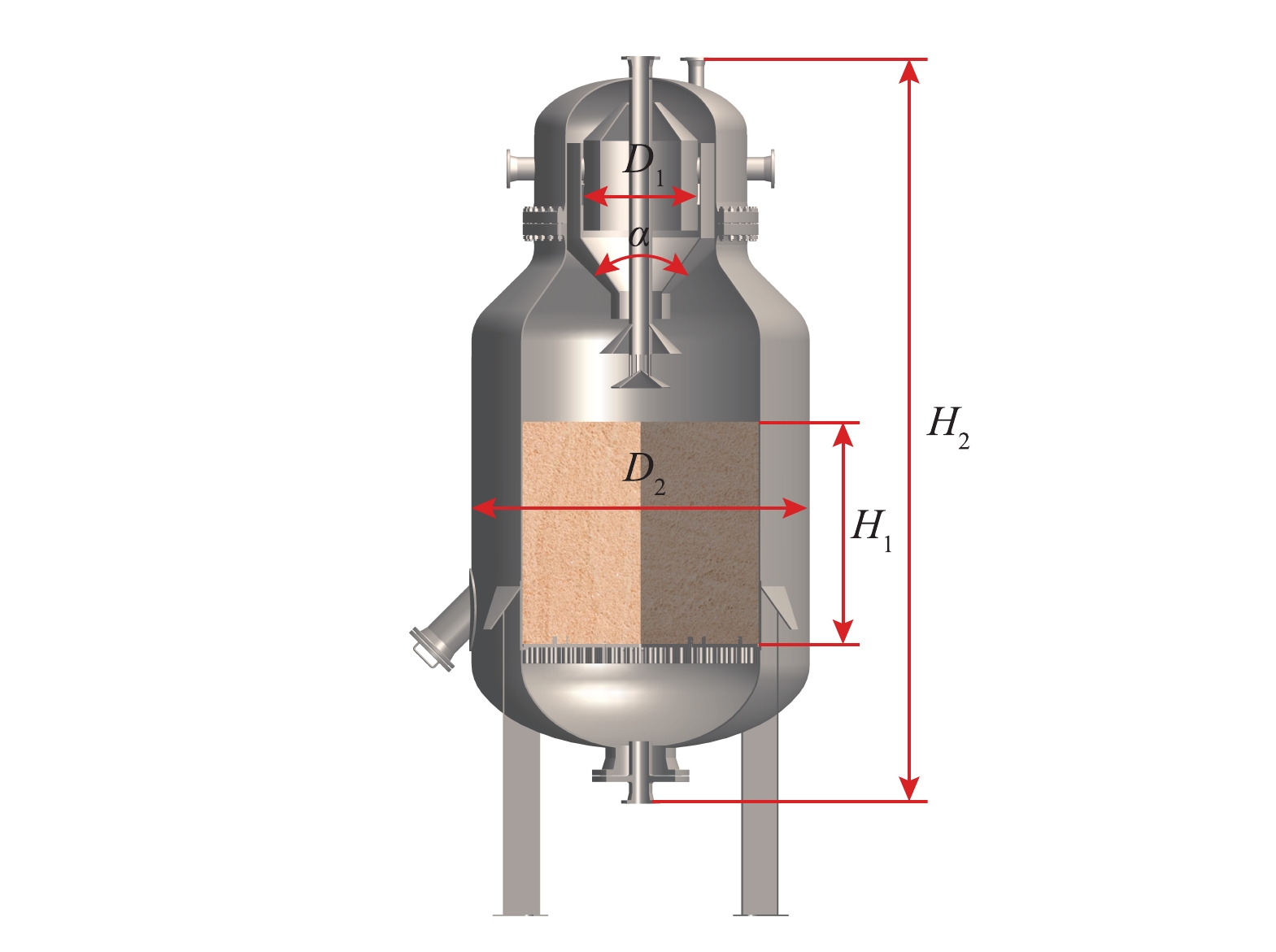
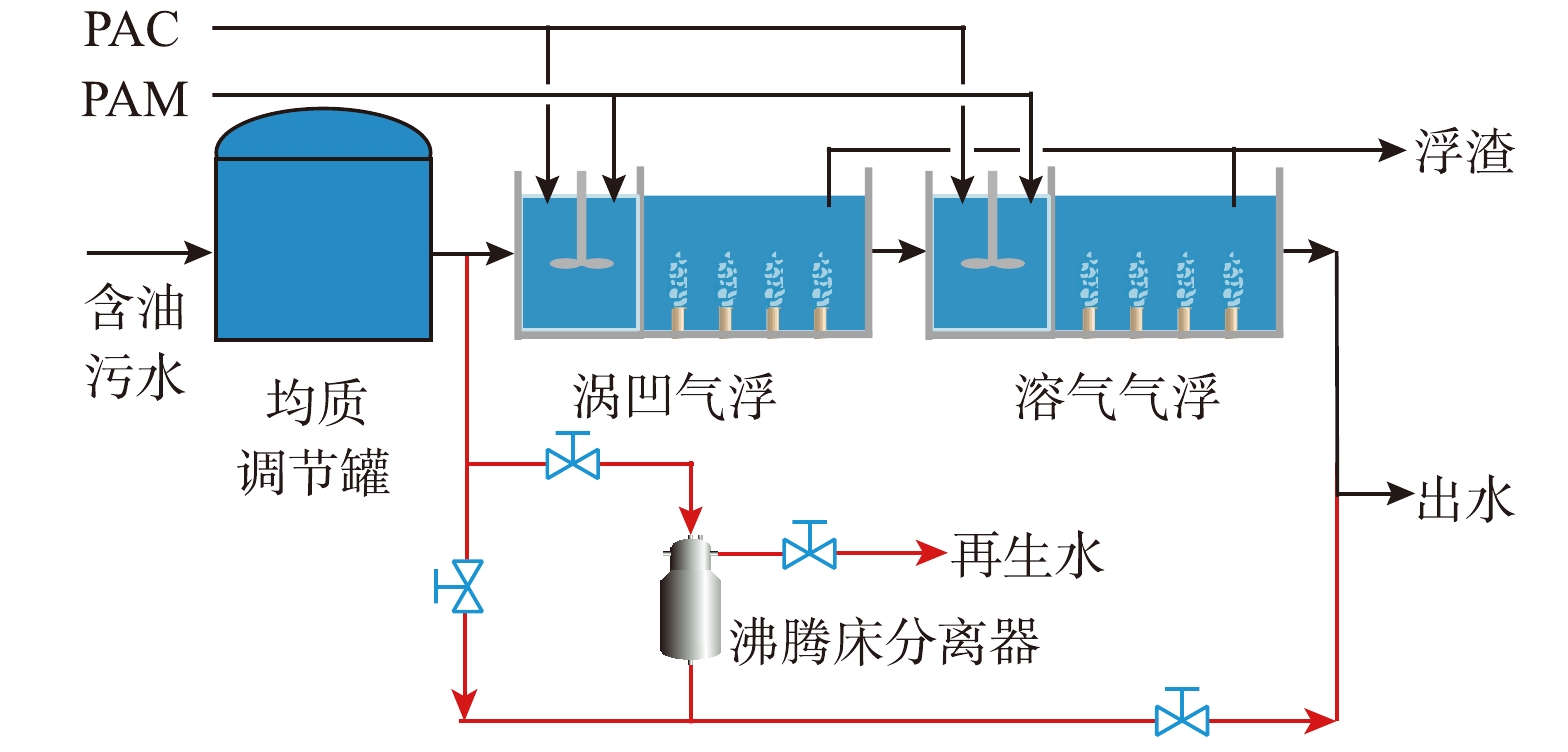
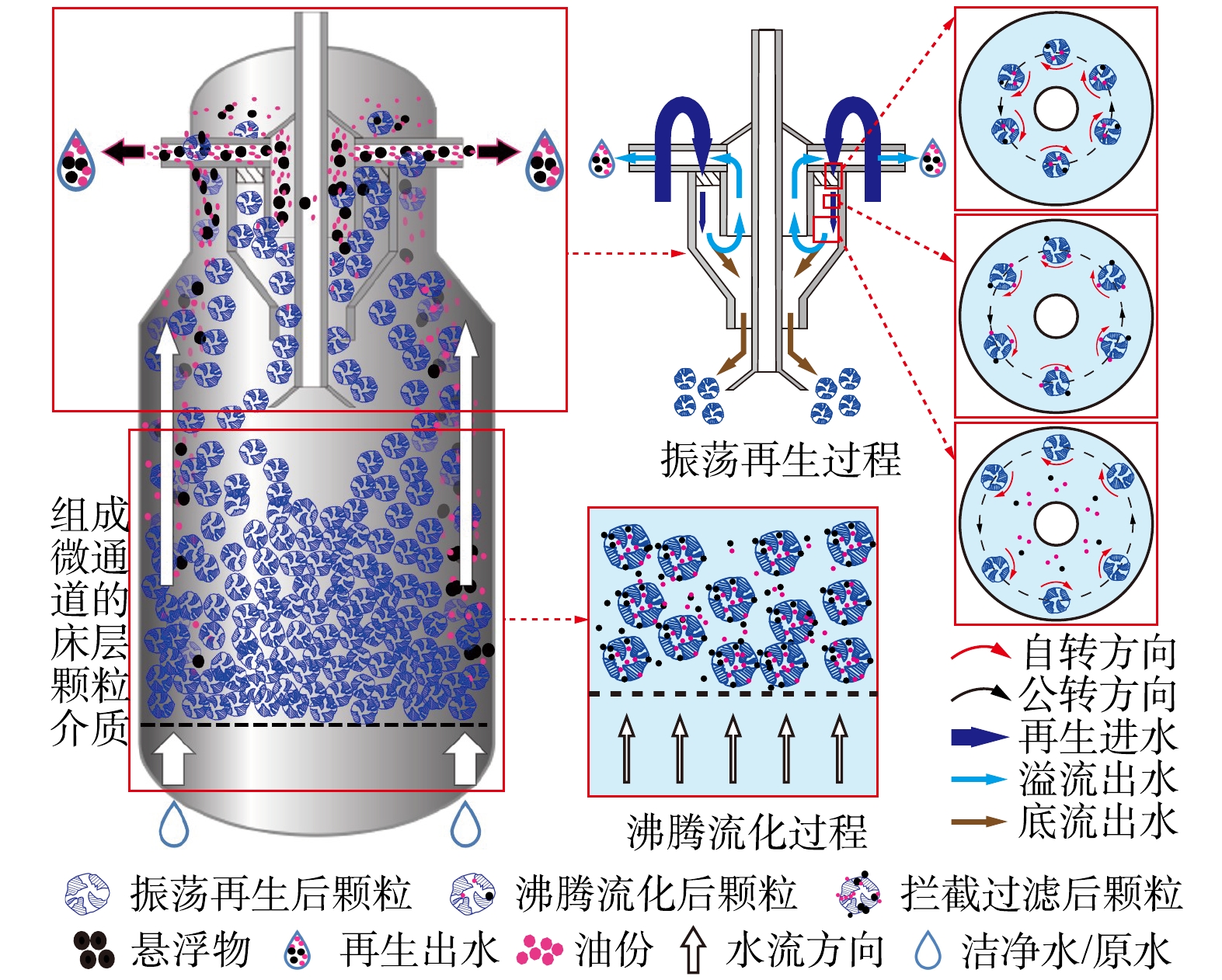
沸腾床分离器结构如图2所示,再生结构溢流口直径D1=450 mm,再生结构锥角α=90°,装置直径D2=1 000 mm,过滤介质装填比例H1/D2=1.2,装置高度H2=3 060 mm。沸腾床分离器在分离工况时,含油污水从装置顶部进口进入,经过过滤介质截滤后从装置底部出口流出。介质床层截滤饱和后,从装置底部出水口通入净水,将含油过滤介质和床层中截留的污染物同时冲入到装置顶部的旋流再生结构中,颗粒介质经过旋流再生结构充分脱附净化后返回设备床层,而油和悬浮物随再生水从再生出口排出。在现场实验中,沸腾床分离器与现场涡凹气浮+溶气气浮并联处理均质调节罐出水,如图3所示,以对比不同工艺的效率及经济性。
-
分别考察沸腾床分离器的再生强度和再生结构对再生效果的影响。实验内容及相关参数设置如表3所示。首先,保持再生时间为15 min[22],再生结构为轴向结构时,分别设置再生强度为3.5、4.2、5.0 L·(s·m2)−1,考察装置再生出水和再生后过滤出水的油和悬浮物质量浓度的变化,优选装置再生强度;然后保持相同的再生强度和再生时间,考察轴向再生结构和切向再生结构的再生出水水质差异,从而优选装置再生结构。
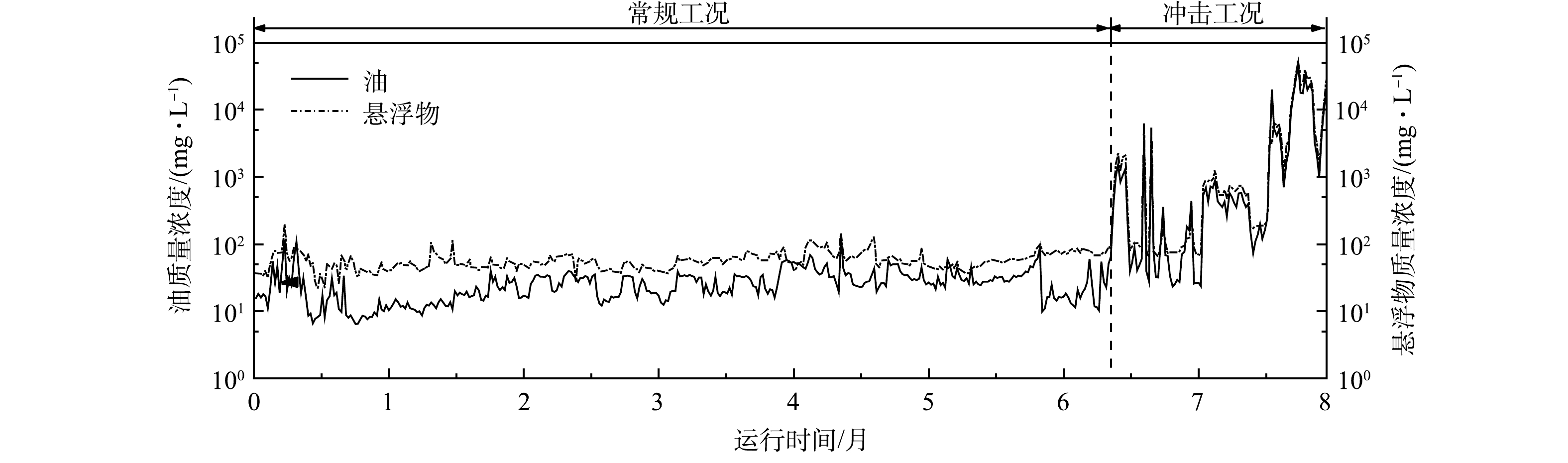
通过连续实验考察微通道振荡再生对沸腾床分离器连续处理实际废水的效果及稳定性。针对油质量浓度为25~200 mg·L−1的来水,沸腾床分离器连续运行8个月,测量装置出水油质量浓度和悬浮物质量浓度;连续实验过程中还存在油质量浓度接近50 000 mg·L−1的波动来水,以考察装置的抗冲击能力。
-
本实验分别采用重量法[23]和红外分光光度法[24]测量处理前后含油污水中的悬浮物质量浓度和油质量浓度。为避免采样后污油挂壁对后续测试分析造成影响,采用100 mL采样瓶采样,将四氯乙烯倒入采样瓶中充分萃取后测量。
-
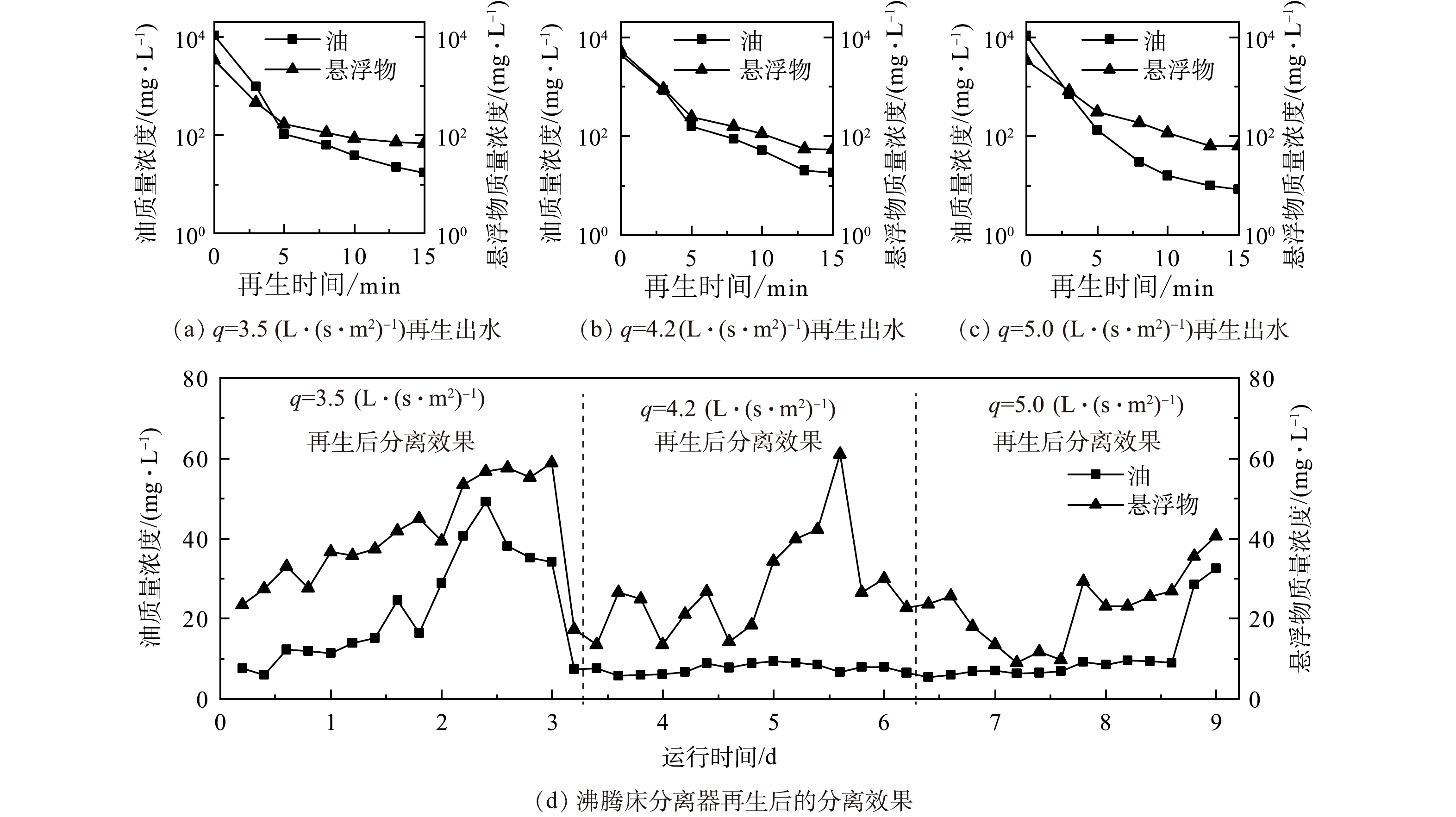
1)床层介质再生强度。为考察再生强度对再生效果以及再生后装置分离效果的影响,分别设置沸腾床分离器再生强度为3.5、4.2、5.0 L·(s·m2)−1,结果如图4所示。经过15 min再生,再生出水的油和悬浮物浓度均达到稳定,因此,实验选取再生时间为15 min。在3种再生强度下,装置再生出水油质量浓度分别从10 722、4 432、4 216 mg·L−1降至17.0、18.0、8.2 mg·L−1,而再生出水悬浮物质量浓度分别从3 388、5 240、6 768 mg·L−1降至67.7、52.5、62.68 mg·L−1;再生后装置分离出水的平均油质量浓度为28.2、8.3、10.6 mg·L−1,悬浮物平均质量浓度为41.2、37.6、22.6 mg·L−1。结果表明,当再生强度为5.0 L·(s·m2)−1、再生水压力为0.4 MPa、再生时间为15 min时,装置再生后投用,连续分离运行72 h,沸腾床分离器出水平均油质量浓度和悬浮物质量浓度分别小于20 mg·L−1和30 mg·L−1,满足后续生化单元进水油质量浓度低于20 mg·L−1的技术指标[25]。由此可见,装置再生强度的增大提高了再生水流的剪切作用力和颗粒间的摩擦力,实现了粘附在颗粒表面的污染物快速脱落,从而维持床层稳定的分离性能。
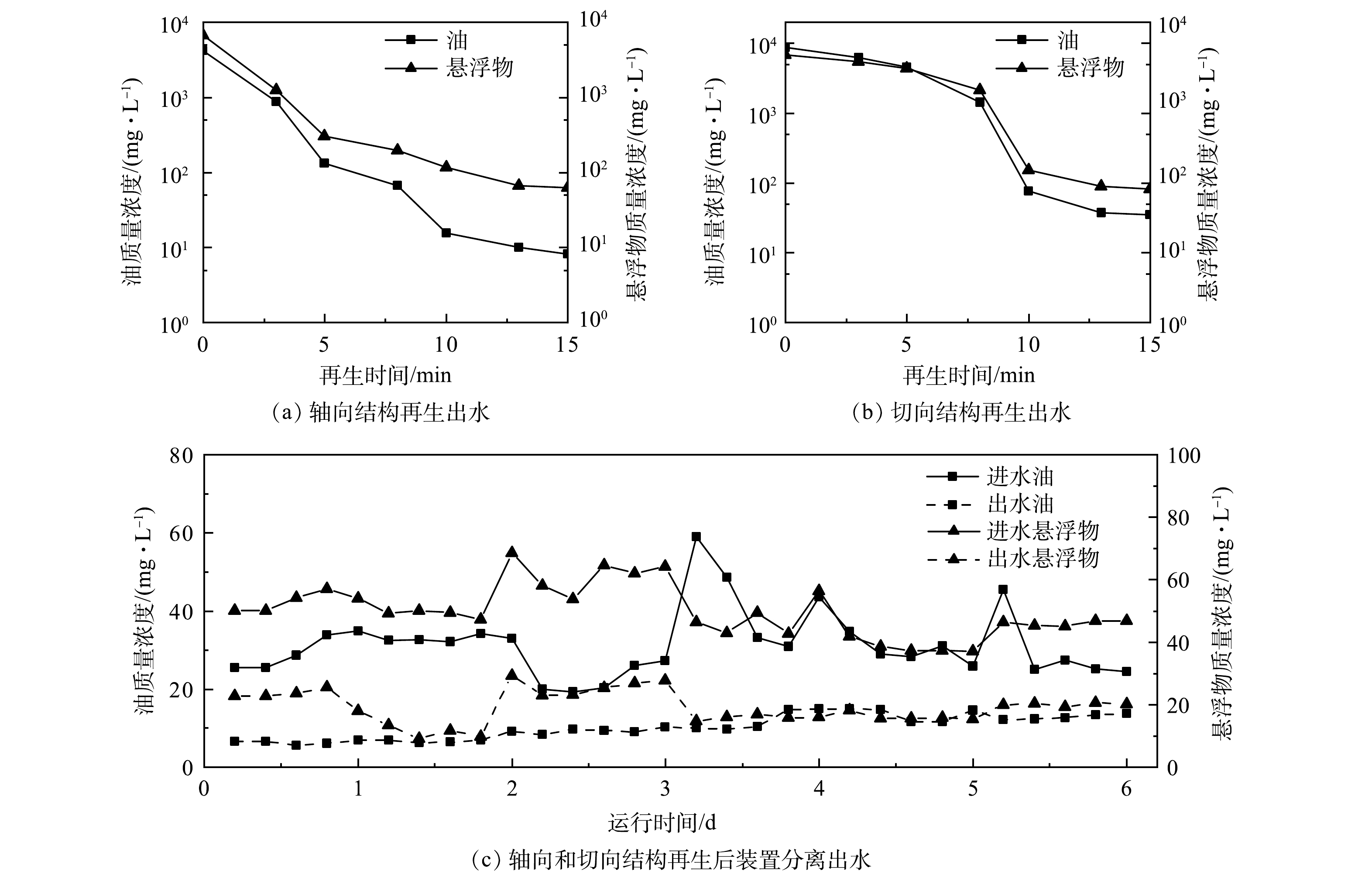
2)床层介质再生结构。实验设置两种介质振荡再生的旋流器以考察其介质脱附效果的差异。如图5所示,当再生强度为5.0 L·(s·m2)−1、再生时间为15 min时,采用轴向旋流再生结构的沸腾床分离器再生15 min后的瞬时再生出水油质量浓度为8.2 mg·L−1,悬浮物质量浓度为62.7 mg·L−1;采用切向旋流再生结构的沸腾床分离器再生15 min后的瞬时再生出水油质量浓度为34.9 mg·L−1,悬浮物质量浓度为81.8 mg·L−1。在相同再生工况条件下,轴向结构相比于切向结构的再生出水油质量浓度和悬浮物质量浓度分别降低了76.5%和23.3%。这是由于相较于切向再生结构,轴向再生结构增大了进口截面积,在相同再生时间条件下再生更多的颗粒介质,介质再生效果得到提升,再生出水油和悬浮物随之降低。
再生结束后,当过滤速度为13 m·h−1、过滤时长为72 h时,轴向再生结构装置进水平均油质量浓度为28.4 mg·L−1、平均悬浮物质量浓度为55.5 mg·L−1,出水平均油质量浓度为7.6 mg·L−1、平均悬浮物质量浓度为20.8 mg·L−1;而切向结构装置进水平均油质量浓度为34.1 mg·L−1、平均悬浮物质量浓度为44.0 mg·L−1,出水平均油质量浓度为12.8 mg·L−1、平均悬浮物质量浓度为17.4 mg·L−1。在相同操作条件下,轴向结构再生后装置分离出水平均油质量浓度相较于切向再生结构降低了40.6%。这是由于在相同的再生时间内,轴向再生结构能够再生更多的颗粒介质,再生后能够截滤更多的油分,使装置分离出水含油量降低。轴向再生结构装置的再生效果以及再生后装置的分离效果均较优,因此,轴向再生结构为沸腾床分离器的优选结构。
-
通过耦合旋流振荡再生单元,微通道分离过程的分离效率稳定性和设备寿命相应受到影响。经过连续8个月的实验验证,如图6所示,针对油质量浓度在30~200 mg·L−1、悬浮物质量浓度为25~200 mg·L−1的常规工况来水,采用再生强度为5.0 L·(s·m2)−1、再生时间为15 min的轴向结构周期性再生沸腾床分离器,出水平均油质量浓度降至为11.4 mg·L−1、平均悬浮物质量浓度为23.5 mg·L−1;其中,95%出水油质量浓度<20 mg·L−1,88%出水悬浮物质量浓度<30 mg·L−1。特定条件下,针对油质量浓度和悬浮物质量浓度在50 000 mg·L−1以内波动时,沸腾床分离器的出水平均油质量浓度降至15.9 mg·L−1、平均悬浮物质量浓度降至29.8 mg·L−1,出水水质持续维持稳定。结果表明,采用旋流振荡再生强化沸腾床分离能够有效实现颗粒介质表面污染物脱附,保障沸腾床分离器长周期稳定运行,且在冲击工况下快速再生过滤介质,恢复装置油水分离性能,使其具有良好的抗冲击能力。
-
有研究表明[26],旋流场中的颗粒不仅绕旋流中心做公转运动,同时在非匀速流体作用下产生非零转矩并引起颗粒做绕自身球心旋转的自转运动。因此,颗粒介质在旋流场中产生自转和公转的耦合运动,粘附在颗粒介质表界面上的污染物则受到由颗粒自公转耦合运动所产生的离心力作用[27],其大小如式(1)所示。
式中:
Fr 为自公转耦合离心力,N;Fz 为自转离心力,N;Fa 为公转离心力,N;t 为自转时长,s;r1 为孔道直径,m;l1 为孔道深度,m;ρ1 为孔隙中污染物的密度,kg·m−3;ωz 为颗粒自转角速度,rad·s−1;rp 为颗粒半径,m;ωa 为颗粒公转角速度,rad·s−1;Ra 为颗粒公转轨道半径,m。颗粒自转速度
ωz 与公转速度ωa 的大小由微流控和高速成像技术进行检测,ωz 大小在1 000 rad·s−1以上[18],Fz 方向均从颗粒中心向外,Fa 方向均从旋流中心指向壁面。由此,颗粒公转产生的将颗粒内部污染物脱离出孔道的离心力,在颗粒的高速自转运动作用下得到加强,且当颗粒自转时,颗粒上的每一处位置受到方向呈周期性变化的振荡离心力作用,其振荡周期如式(2)所示。随着颗粒的高速旋转,颗粒内污染物在振荡离心力的作用下,有可能克服颗粒表界面粘附力和孔道毛细作用力[28],使颗粒介质表界面污染物脱附,实现颗粒介质彻底再生。本文中含油颗粒再生时进入双切向与轴向再生结构中,流体在切向进口与导叶片的作用下产生旋转流场,使含油颗粒产生自公转耦合运动,从而使颗粒表面及孔道内的油类污染物受到振荡离心力的作用,实现含油颗粒的彻底再生。与传统颗粒介质再生技术[29]相比,微通道振荡再生技术通过引入旋流场的作用,一方面增强了颗粒表面应力作用,实现表面污染物的分离;另一方面,颗粒自公转耦合产生的振荡离心力,实现了颗粒孔隙中污染物的脱附。式中:T为振荡周期,s;
ωz 为颗粒自转角速度,rad·s−1。沸腾床分离器再生过程如图7所示。当截滤在沸腾床分离器中的油类污染物上升到一定量时,设备压降将达到设定值,需要对滤料介质进行再生,再生过程包括颗粒沸腾流化过程和振荡再生过程。通过将洁净水或原水从滤床底部通入设备中,使床层颗粒介质完全流化。流态化的含油颗粒介质相互碰撞和摩擦,释放出大部分截留的油类污染物。然后,含油颗粒介质和截留的油类污染物同时进入至设备顶部旋流再生结构中,在旋转湍流场作用下,含油滤料颗粒产生自公转耦合运动,进而诱导产生振荡离心力,强化颗粒表面及孔道内油类污染物脱附;颗粒介质颗粒经旋流器再生后,从旋流器底流中排出,再次形成微通道床层;而颗粒尺寸较小,密度较低的油类污染物及悬浮物随流体从旋流再生结构的液相出口排出。由此,以旋流振荡再生为核心的再生方式实现了微通道分离的长周期稳定运行,且与常规涡凹气浮和溶气气浮的组合预处理工艺相比,取消了化学药剂的消耗,具有良好的环保经济效益。
-
以200 m3·h−1含油污水预处理为例,对比分析沸腾床分离工艺与涡凹气浮+溶气气浮组合工艺的经济性差别,如表1所示。涡凹气浮和溶气气浮组合工艺装置总功率为37 kWh,其中包括两级气浮装置进水泵、曝气机、DAF回流泵、PAC药剂泵和PAM药剂泵的能耗,工业用电价格按0.8元·kWh−1计算,年装置能耗约为2.4×105元;每年在气浮处理过程中需添加PAC和PAM约为168 t和5 t,PAC和PAM单价按2 000 元·t−1和16 000 元·t−1计[30],年药剂成本约为4.2×105 元;处理过程中产生浮渣约为5 000 t(含水率98%),经脱水处理至含水率降至40%后外送处理,处理单价按3 000 元·t−1计[31],每年浮渣处理成本约为5.1×105 元。沸腾床分离工艺装置总功率为20 kW,其中包括沸腾床分离器进水泵能耗,年装置能耗约为1.3×105元;沸腾床分离器处理过程中,不使用化学絮凝药剂且不产生浮渣,因此,无药剂及危废处理消耗。
综上,相较于每年耗费约1.17×106元的涡凹气浮和溶气气浮的组合工艺,沸腾床分离工艺预期每年约节省1.04×106元的装置能耗、化学药剂及危废处理等成本。
-
1)沸腾床分离器再生强度为5.0 L·(s·m2)−1、再生时间为15 min、再生结构为轴向结构时,达到最佳处理效果。
2)通过集成旋流振荡以充分再生沸腾床分离器床层介质,确保沸腾床分离器长周期维持稳定、高效分离运行,其出水平均油分和悬浮物质量浓度分别降至11.4 mg·L−1和23.5 mg·L−1,基本满足后续生化单元进水要求;来水水质波动条件下沸腾床分离器出水也持续维持稳定。
3)基于微通道振荡分离的含油污水预处理工艺,避免了化学药剂的消耗,有效降低了浮渣产量。相对于处理量为200 m3·h−1的涡凹气浮和溶气气浮组合工艺,沸腾床分离工艺预期每年约节省1.04×106万元装置能耗、药剂消耗及危废处理等相关费用,具有显著的经济环保意义。
旋流诱导介质振荡再生增强含油污水微通道分离
Hydrocyclone-induced oscillation regeneration of filter medium for enhanced microchannel separation of oily wastewater
-
摘要: 受微通道分离介质再生后截滤残留污染物影响,常规微通道分离效率持续衰减,成为抑制微通道分离广泛高效应用的关键瓶颈。通过开发旋流振荡再生单元,研究了旋流振荡再生强度和振荡再生结构对微通道分离装置过滤介质再生效率的影响,由此集成研发沸腾床分离器,考察了装置对实际含油污水的分离效率,并分析了微通道振荡再生对沸腾床分离的强化原理以及装置的分离经济性。结果表明,当再生强度为5.0 L·(s·m2)−1时、再生15 min后采用轴向振荡再生结构,沸腾床分离器达到最佳再生工况。在最佳再生工况下开展10 m3·h−1实际含油污水连续处理实验,针对油质量浓度为30~200 mg·L−1、悬浮物质量浓度为25~200 mg·L−1的来水,装置出水平均油分和悬浮物质量浓度分别降至11.4 mg·L−1和23.5 mg·L−1,并可在来水最高油质量浓度和悬浮物质量浓度接近50 000 mg·L−1的冲击工况下,确保出水平均油分和悬浮物质量浓度降至15.9 mg·L−1和29.8 mg·L−1。利用沸腾床分离器再生结构中旋流诱导的过滤介质表界面污染物振荡运动,分离过程中截滤残留的油分和悬浮物等污染物被及时脱附,实现颗粒介质表界面彻底更新,确保装置长周期稳定运行。以200 m3·h−1规模实际含油污水处理为例,沸腾床分离工艺相对涡凹气浮和溶气气浮的组合工艺,可完全取消化学絮凝药剂消耗且不产生化学浮渣,且具有显著的经济环保效益。Abstract: Affected by the residual pollutants filtered after the regeneration of the microchannel separation medium, the separation efficiency of conventional microchannels separator continues to decline, which has become a key bottleneck inhibiting the widespread and efficient application of microchannel separator. A hydrocyclone oscillation regeneration unit was developed. The influence of the hydrocyclone oscillation regeneration intensity and the oscillating regeneration structure on the regeneration efficiency of the filter medium of the microchannel separation device was studied, and the ebullated bed separator was integrated and developed to investigate the separation efficiency of the device for actual oily wastewater, and to analyze the enhancement principle of the microchannel oscillation regeneration for the ebullated bed separation and the separation economy of the device. The results showed that when the regeneration intensity was 5.0 L·(s·m2)−1, the regeneration time was 15 min and the axial oscillating regeneration structure was adopted, the optimal regeneration conditions occurred for the ebullated bed separator. The continuous treatment experiment of 10 m3·h−1 actual oily wastewater was carried out under the optimal regeneration conditions. For the influent water with an oil content of 30~200 mg·L-1 and a suspended solids content of 25~200 mg·L−1, the average oil content and the suspended solids content in the effluent of the device decreased to 11.4 mg·L−1 and 23.5 mg·L−1, respectively. When the maximum oil and suspended solids contents in the influent were close to 50 000 mg·L−1, it can also ensure that the average oil and suspended solids content in the effluent could decrease to 15.9 mg·L−1 and 29.8 mg·L−1, respectively. Using the oscillating motion of the pollutants on the surface of the filter medium induced by the hydrocyclone in the regeneration structure of the ebullated bed separator, the pollutants such as oil and suspended solids remained in the filtration during the separation process could be removed in time, and the surface and interface of the particle medium could be completely regenerated to ensure a long-term stable operation of the device. Taking the actual oily sewage treatment at a scale of 200 m3·h−1 as an example, the ebullated bed separation process can abolish the consumption of chemical flocculation agents completely and does not produce scum, compared with the cavitation air flotation and dissolved air flotation, and has significant environmental benefits.
-
表 1 含油污水预处理工艺经济性分析
Table 1. Economic analysis of oily wastewater pretreatment process
指标 以200 m3·h−1规模计 涡凹气浮+溶气气浮 沸腾床分离器 备注 经济性指标 药剂消耗成本 PAC 168 t·a−1+PAM 5 t·a−1 0 4.2×105元·a−1 气浮浮渣产量 5 000 t·a−1 0 5 000 t·a−1 动力设备电耗 2.4×105 元·a−1 1.3×105 元·a−1 1.1×105 元·a−1 环保效益指标 出水指标 含油量<30 mg·L−1;含固量<50 mg·L−1 含油量<20 mg·L−1含固量<40 mg·L−1 — 外委危废处置 170 t·a−1(含水率40%) 0 5.1×105 元·a−1 VOCs逸散 略微 0 — 运维指标 人为操作 间歇性 全自动 — -
[1] TIAN X, SONG Y, SHEN Z, et al. A comprehensive review on toxic petrochemical wastewater pretreatment and advanced treatment[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 245: 118692. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118692 [2] JAFARINEJAD S, JIANG S C. Current technologies and future directions for treating petroleum refineries and petrochemical plants (PRPP) wastewaters[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2019, 7(5): 103326. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2019.103326 [3] MOOSAI R, DAWE R A. Gas attachment of oil droplets for gas flotation for oily wastewater cleanup[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2003, 33(3): 303-314. doi: 10.1016/S1383-5866(03)00091-1 [4] SANTO C E, VILAR V J P, BOTELHO C M S, et al. Optimization of coagulation–flocculation and flotation parameters for the treatment of a petroleum refinery effluent from a Portuguese plant[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 183: 117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.041 [5] SUN Y, LIU Y, CHEN J, et al. Physical pretreatment of petroleum refinery wastewater instead of chemicals addition for collaborative removal of oil and suspended solids[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 278: 123821. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123821 [6] SUN Y, LIU Y, XU B, et al. Simultaneously achieving high-effective oil-water separation and filter media regeneration by facile and highly hydrophobic sand coating[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 800: 149488. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149488 [7] SATHTHASIVAM J, LOGANATHAN K, SARP S. An overview of oil–water separation using gas flotation systems[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144: 671-680. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.087 [8] DAI L, TIAN J, FU P, et al. Purification of black alkali liquor by microchannel filtration to promote energy savings and consumption reduction in lye cleaning systems[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 774: 145116. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145116 [9] LIU B, WEI Q, MA H, et al. Cooperative physical separation of oil and suspended solids from methanol-to-olefin wastewater: A pilot study[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 311: 114841. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114841 [10] MEYERS P A, OAS T G. Comparison of associations of different hydrocarbons with clay particles in simulated seawater[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1978, 12(8): 934-937. [11] LIU Y, ZHANG S, ZOU C, et al. Quantitative measurement of interaction strength between kaolinite and different oil fractions via atomic force microscopy: Implications for clay-controlled oil mobility[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 133: 105296. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105296 [12] ABDEL AZIM A-A A, ABUDUL-RAHEIM A-R M, KAMEL R K, et al. Demulsifier systems applied to breakdown petroleum sludge[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2011, 78(2): 364-370. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2011.07.008 [13] MAMN M J. Full-scale and pilot-scale soil washing[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 1999, 66(1): 119-136. [14] AL-ZAHRANI S M, PUTRA M D. Used lubricating oil regeneration by various solvent extraction techniques[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2013, 19(2): 536-539. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2012.09.007 [15] 李一川, 王栋, 王宇, 等. 热化学清洗法洗涤油泥—回收石油的工艺条件研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2008: 39-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2008.03.012 [16] 周永贤, 王小峰, 褚维平, 等. 热脱附在石化行业中的应用与发展趋势[J]. 农家参谋, 2020: 165. [17] 王国伟, 李义连, 杨森, 等. 不同淋洗剂对砷污染土壤的淋洗试验研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2021, 28: 182-187. doi: 10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20201088 [18] HUANG Y, LI J P, ZHANG Y H, et al. High-speed particle rotation for coating oil removal by hydrocyclone[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 177: 263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.12.001 [19] FU P B, WANG H L, LI J P, et al. Cyclonic gas stripping deoiling and gas flow acceleration classification for the resource utilization of spent catalysts in residue hydrotreating process[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 190: 689-702. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.203 [20] WANG Y, CHANG Y L, LI J P, et al. Analysis of performance of novel hydrocyclones in ebullated bed reactor with different vortex finder structures[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2020, 158: 89-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2020.04.002 [21] LI J-P, YANG X-J, MA L, et al. The enhancement on the waste management of spent hydrotreating catalysts for residue oil by a hydrothermal–hydrocyclone process[J]. Catalysis Today, 2016, 271: 163-171. doi: 10.1016/j.cattod.2015.08.037 [22] 国亚东, 刘国荣, 隋克鹏. 深床过滤器部分反冲洗的试验研究[J]. 过滤与分离, 2005, 15(2): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8265.2005.02.007 [23] 国家环境保护局. 水质-悬浮物的测定-重量法: GB/T 11901-89 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1989. [24] 环境保护部. 水质-石油类和动植物油类的测定-红外分光光度法: HJ 637-2012 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012. [25] 环境保护部. 含油污水处理工程技术规范: HJ 580-2010 [S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2010. [26] SHI D, HUANG Y, WANG H, et al. Deoiling of oil-coated catalyst using high-speed suspending self-rotation in cyclone[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019, 210: 117-124. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.03.059 [27] HUANG Y, WANG H L, TIAN J, et al. Theoretical study on centrifugal coupling characteristics of self-rotation and revolution of particles in hydrocyclones[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 244: 116552. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116552 [28] FU P, YU H, LI Q, et al. Cyclone rotational drying of lignite based on particle high-speed self-rotation: Lower carrier gas temperature and shorter residence time[J]. Energy, 2022, 244: 123005. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.123005 [29] 于忠臣, 魏震, 董喜贵, 等. 场作用下的滤料反冲洗技术及发展[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2017, 48: 6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2455.2017.03.002 [30] 韩国义, 郑俊, 王正收, 等. 隔油/气浮/两段生化法处理炼油厂含油废水[J]. 中国给水排水, 2010, 26(2): 64-67. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2010.02.016 [31] 陈晓波. 浮渣处理及回炼难点分析及对策[J]. 中外能源, 2016, 21(5): 74-77. -




 下载:
下载: