-
污水处理厂污泥是污水处理过程中的副产物。随着我国城市生活污水处理系统的发展,污泥产量逐年增加[1]。污泥富集了大量有机物、营养物质、病原微生物和重金属等有毒有害物质[2],在处理处置及储运过程中不可避免地释放恶臭气味,极易形成二次污染,在严重时可能会构成污染公害事件[3]。尽管污泥产量仅为污水总量的0.3%~0.5% (体积分数) [4],但污泥处理过程是污水处理厂恶臭释放的主要来源[5]。处理后的污泥若仍存在恶臭 (或较强烈异味) ,将在极大程度上限制污泥土地利用等多种处置方式的实施。除污水来源及其处理工艺外,污泥处理与处置工艺和实际运行对污泥的性质有较大影响,从而导致污泥在处理过程中和处置利用时的恶臭释放特征存在显著差异[6]。因此,污泥恶臭污染有效控制是提高污泥处理效率、实现污泥资源化利用必须解决的技术难题。由于我国污泥产量快速增加,对污泥恶臭污染控制的技术需求更为迫切。
基于此,本文以城市污水处理厂污泥在处理和处置过程中的恶臭污染为研究对象,分析整理近20年来有关污泥恶臭及其控制技术的文献报道,从污泥产臭关键环节的污染特征和发生机制入手,通过分析污泥恶臭减排的控制措施与策略,讨论污泥恶臭污染防治的复杂性和挑战,以期为防控污泥处理处置过程中的恶臭污染提供参考。
-
污泥处理处置过程释放的恶臭物质主要包括含硫化合物、含氮化合物、含氧有机物、烃类化合物和卤素及其衍生物。其中,分子质量为30~150且易挥发的物质较常见[7]。早期的研究多采用日本《恶臭防治法》中规定的六级恶臭强度评价法对城市污水处理厂释放的恶臭物质进行评估,发现其中含量排首位的是氨 (ammonia,NH3) ,其次是硫化氢 (hydrogen Sulfide,H2S) 、二甲基硫醚 (dimethyl sulfide,DMS) ;但甲硫醇 (methyl mercaptan,MT) 的臭气强度最大 (4.7级) ,其次是H2S (4.5级) ,均为强臭等级[8]。近期研究表明,除H2S和NH3外,多种浓度较低的挥发性有机硫化合物 (volatile organic sulfur compounds,VOSCs) 、含氮有机物和含氧有机物等挥发性物质,对污泥恶臭的形成具有重要贡献[9-10]。实际上,污泥释放的恶臭气体常包含数十至上百种挥发性物质,其中仅少部分是造成恶臭的主要物质。我国学者测定报道了40种典型恶臭物质嗅阈值[11],可能仍有许多致臭物质尚未明确[12]。其中,污泥处理处置过程中较常检出的恶臭物质嗅阈值及感官性质如表1所示。污泥释放的恶臭物质在成分组成上可能具有一定相似性,但由于不同性质的污泥释放的致臭物质在化学浓度相对含量上的差异,常导致污泥表现出明显不同的恶臭特征[13-15]。
污泥恶臭污染不仅会降低周边人群的工作和生活环境质量,长期接触还会对人群健康产生负面影响[16]。此外,部分恶臭物质为VOCs污染物,具有活泼化学性质的恶臭物质可与阳光或大气中的氮氧化物发生光化学反应及氧化反应,参与大气环境中臭氧和二次气溶胶的形成,是导致大气臭氧污染、酸雨和光化学污染等的重要前体物[17-18]。
-
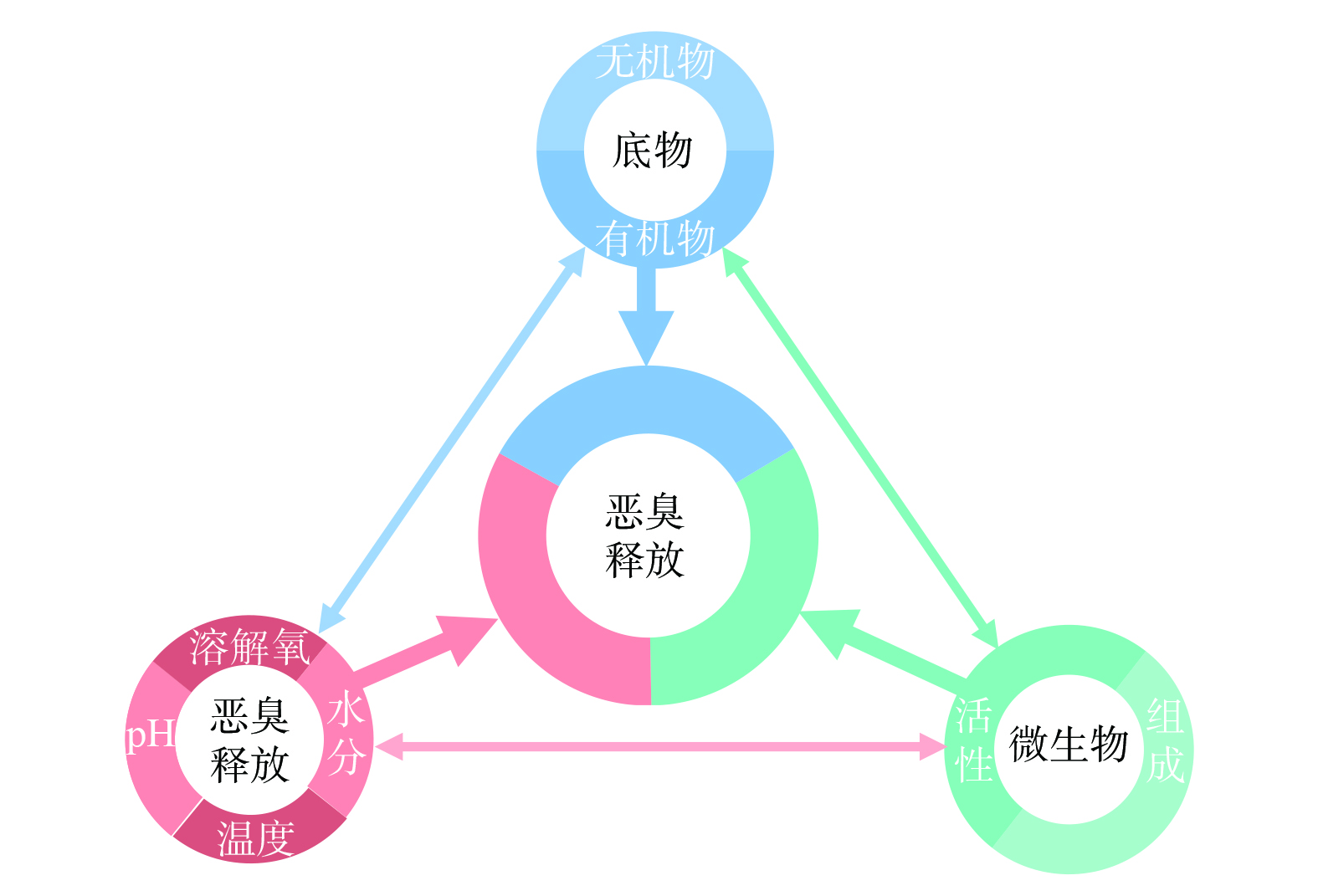
恶臭污染特征与污泥的性质密切相关[14]。污泥性质的差异体现在污泥中物质的组成和浓度,微生物群落结构,溶解氧、水分和pH等介质微环境条件3个方面 (图1) ,这些因素共同影响恶臭的产生和释放。因此,污泥恶臭物质的主要来源可归纳为底物释放和微生物代谢两大生成机制。
1) 底物释放。污水中存在多种恶臭物质和致臭前体物质,如有机质、硫化物和含硫蛋白质等[19],经污水处理过程 (如沉淀、吸附) 转移至污泥。这些底物在脱水、转移及运输等过程中,因受压或剧烈扰动等作用被释放出来[20]。此外,污水与污泥处理过程中加入的某些化学药剂可与污水或污泥中无异味物质发生反应转化为恶臭物质,或是增强部分恶臭物质的挥发性。如在污泥的石灰稳定化过程中,阳离子聚合物和蛋白质通过酶水解降解形成三甲胺 (trimethyl amine,TMA) 和二甲基二硫醚 (dimethyl disulfide,DMDS) ,随后加入的石灰导致污泥pH环境变化,促使TMA和DMDS释放[21]。
2) 微生物代谢。在缺氧或厌氧条件下,微生物降解有机物生成还原性硫化物、含氮有机物、挥发性脂肪酸等具有腐败或刺激气味物质,极易形成恶臭污染[22]。如H2S和MT主要由缺氧条件下硫酸盐还原菌 (sulfate-reducing bacteria,SRB) 和甲烷菌等微生物的生命活动形成[23]。含硫蛋白质在蛋白酶作用下分解为多肽,多肽再经肽酶作用分解为甲硫氨酸或半胱氨酸,然后在甲硫氨酸裂解酶和半胱氨酸裂解酶的作用下分别形成MT和H2S[24]。厌氧细菌又可将H2S和MT进行甲基化,分别生成MT和DMS[24]。挥发性含氮有机物 (如胺类、吲哚和粪臭素) 主要通过氨基酸脱羧作用和L-色氨酸降解代谢等过程产生[25]。水解细菌对污泥中的有机物 (如淀粉、纤维素、半纤维素和果胶等) 进行水解,形成小分子氨基酸、单糖和长链脂肪酸等有机成分。产酸菌利用这些水解产物进行厌氧发酵生成挥发性脂肪酸 (volatile fatty acids,VFAs) 、醇类、醛类和酮类等物质[26-27]。而好氧细菌则通过对含氮有机物及细胞物质进行氧化生成NH3和具有土霉味的物质[28-29]。二硫化碳 (carbon disulfide,CS2) 主要源于人为排放,无法由有机物降解或硫化物互相转化而产生[30],但在好氧和厌氧条件下可作为碳源被微生物降解,生成羰基硫 (carbonyl sulfide,COS) ,再转化为CO2和H2S[31]。
综上所述,底物挥发释放和微生物代谢是污泥恶臭物质产生的主要途径,并易受处理处置过程中环境条件的影响。从微生物的功能作用机制来看,微生物驱动的恶臭物质生成与转化过程由一个或多个功能基因参与完成[25]。
-
国内外常用的污泥处理技术有脱水、厌氧消化、好氧消化、干化等,处置技术有土地利用、填埋、堆肥和焚烧等[32]。我国污泥存在有机质含量低和含沙量高的特点,因此,形成了“厌氧消化-土地利用”、“好氧堆肥-土地利用”、“干化焚烧-灰渣填埋或建材利用”和“深度脱水-应急填埋”4条污泥稳定化处理与安全处置的主流技术[2]。由于经过不同处理和处置导致污泥性质存在差别,故形成的恶臭污染特征亦具有较大差异。FISHER等[13-14]比较了澳大利亚6个污水处理厂不同处理单元污泥释放的气味物质发现,浓缩、厌氧消化、脱水及储存过程中释放的挥发性物质差异明显,脱水和储存过程会释放浓度更高、种类更丰富的挥发性含硫化合物 (volatile sulfur compounds,VSCs) 、挥发性含氮化合物 (volatile nitrogen compounds,VNCs) 、卤代化合物、酮类和烃类等物质,从而揭示了不同污泥处理工艺对污泥释放恶臭的影响,以及污泥产臭的复杂性。本章分析讨论不同处理处置方式下,污泥的恶臭释放特征与产生机制。
-
浓缩是污泥处理的第一步,常采用重力浓缩、气浮浓缩和离心浓缩等工艺降低污泥含水率[33]。污水原有或生化过程中形成的NH3和VSCs等恶臭物质吸附在污泥中,并在浓缩过程中不断释放[34]。相对于污水处理厂中其他的功能区,污泥浓缩池和污泥脱水间产生的恶臭物质浓度通常较高。此外,浓缩过程较长的停留时间会形成缺氧环境,污泥中的微生物在厌氧条件下降解有机物形成恶臭物质。虽然污泥浓缩池常为密闭式,产生的污染物不易扩散,但浓缩过程中发生湍动会加剧恶臭气体逸出[12]。实际上,未经历长时间厌氧处理的剩余污泥并不具有强烈恶臭,污泥浓缩过程中微生物参与的厌氧反应是主要的恶臭产生途径。对于无污泥稳定化的处理工艺,污泥浓缩后还需进行机械脱水处理。目前,污泥脱水过程也常采用封闭运行工艺,对释放的恶臭气体进行收集处理,以避免造成严重的恶臭污染。
在污泥浓缩与脱水过程中,NH3和H2S的排放浓度较高[35],且具有夏、秋季高而冬、春季低的季节性特点。恶臭物质释放量随水温的升高而增加,而降雨可稀释污染物、降低水温和提高溶解氧浓度,从而降低恶臭污染物浓度[36]。同时,还存在一些浓度相对较低的DMS、DMDS、CS2、硫醇、苯乙烯和二甲苯等恶臭有机物[35,37]。LEHTINEN等[17]研究污水处理厂各单元VOCs释放特征发现,浓缩过程中乙醚和甲苯的释放量较大,其次才是DMDS和DMS。且苯系物的含量为所释放VOCs的80%以上[18]。又由于苯系物和醚类的嗅阈值较高,对恶臭贡献有限,则应归类为VOCs类污染物。
污泥脱水过程的恶臭气体释放量通常远高于浓缩过程[38-39],但对德国多个污水处理厂各处理单元恶臭污染贡献的研究发现,污泥脱水车间和污泥浓缩池的恶臭散发率分别为17%和26%,浓缩池比脱水车间的恶臭问题更突出[40]。这表明污泥浓缩与脱水过程中的产臭情况与工艺运行的具体参数密切相关,污泥水分、含氧量等参数的差异通过影响污泥中微生物的活性而在极大程度上决定着污泥产臭特征。
-
厌氧消化是污泥最终处置前最重要的稳定化处理方法[41]。厌氧消化指在厌氧条件下,利用微生物代谢降解蛋白质、碳水化合物和脂肪等有机物,产生甲烷、CO2和水等消化气[42],从而实现污泥的减量化、无害化、稳定化与资源化。由于我国不同地区污泥存在差异,传统厌氧消化工艺运行不理想[20],故多采用热水解预处理的改良型污泥厌氧消化或多段式厌氧消化等高级厌氧消化工艺来解决以上问题[43-44]。厌氧消化过程是封闭进行的,正常情况下消化气经妥当收集处理,不会造成严重的恶臭污染[20]。但由于厌氧消化气中存在较高含量的还原性硫化物 (尤其是H2S) ,不仅存在恶臭污染隐患,还可能造成设备腐蚀,降低设备安全稳定性和使用寿命[45]。因此,应注意防范污泥厌氧消化气泄露而引发的恶臭污染问题。此外,经厌氧消化处理后,污泥的恶臭强度有所降低[46],但污泥中残留的蛋白质在后续脱水和运输过程中会因受到剪切变得不稳定从而导致VSCs释放[42]。不同性质污泥在厌氧消化后储存时会释放恶臭物质。对比其特征后发现,初沉污泥释放的恶臭总浓度排在首位,其次为混合污泥 (初沉污泥和剩余污泥) 、剩余污泥[47]。
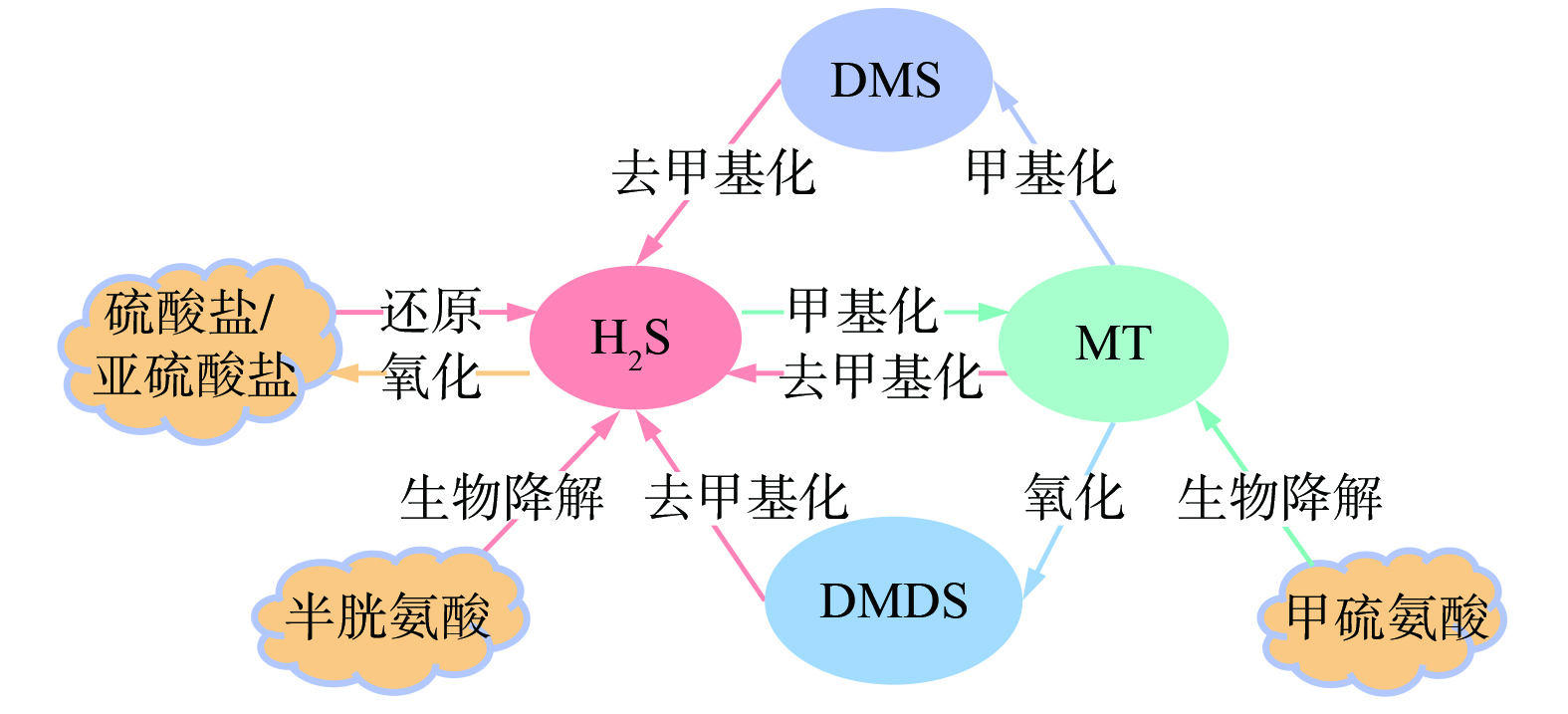
1) VSCs。传统厌氧消化和高级厌氧消化工艺释放的主要恶臭物质均以NH3、H2S和MT为主,而经热水解预处理的高级厌氧消化工艺会释放产生更高浓度的VSCs[48-49],推测是由于热水解预处理促进了含硫有机物的水解,使得其pH较低。厌氧条件下污泥VSCs循环途径可归纳如图2所示。H2S不仅可以由硫酸盐或亚硫酸盐等无机前体物在厌氧条件下经SRB转化为S2−,与H+结合形成,还可以由污泥中含硫有机物 (如含硫氨基酸) 厌氧分解生成MT、DMS和DMDS等有机硫化物发生去甲基化形成[24]。现有研究表明,在硫酸盐还原过程中,具有功能基因aprA编码腺苷5’-磷酸硫酸酐还原酶、dsrA/dsrB编码异化型亚硫酸盐还原酶的微生物可将硫酸盐、亚硫酸盐等还原为H2S等硫化物[25]。MT由甲硫氨酸降解或H2S生物甲基化反应生成,可经生物甲基化和氧化作用分别形成DMS和DMDS[24]。在厌氧条件下,污泥H2S和MT的释放与脱氢酶活性显著相关,脱氢酶活性可用于表征环境系统中微生物的活性,其值越大,恶臭释放潜力越大[23]。而CS2主要来源于非生物反应[31],故在厌氧消化过程中监测到的CS2一般由污泥自身携带。
在消化污泥短期储存期间,VOSCs可作为底物随产甲烷菌等微生物活性恢复而最终被转化为甲烷和H2S[50-51]。此外,有关消化气释放规律的研究表明,总VOSCs浓度随污泥厌氧消化停留时间的延长而降低[52];H2S、MT、DMS和DMDS的释放量随温度升高而增加,但温度对H2S影响较大,在高温消化 (55 ℃) 时污泥释放的H2S是中温消化 (35 ℃) 时的3倍[50]。
2) VNCs。厌氧消化工艺中NH3释放量最大 (741.60 g·t−1) ,远高于VSCs (277.27 g·t−1) [49]。但NH3的气味检测阈值比VSCs高2~3个数量级,并非关键恶臭物质,故很多研究都未对其进行监测[53]。NH3来源于具有功能基因ureC编码脲酶的微生物将污泥中的有机氮矿化转变为NH4+[25]并水解的过程。其释放量随温度升高而增加,在高温消化时污泥释放的NH3浓度是中温消化时的8倍[50]。厌氧消化污泥在脱水过程中释放的恶臭气体中偶尔可检测到具有低嗅阈值的TMA。TMA比单胺类物质更不易被微生物分解,故其释放量通常为其他胺类物质的7倍[54]。
3) 其他恶臭物质。厌氧消化过程形成的VFAs易被微生物降解[26],因此,VFAs的存在是产酸和产甲烷过程不平衡导致[55]。虽然高温消化时污泥释放的VFAs浓度为中温消化时的2~5倍,但仍低于其嗅阈值[50]。此外,厌氧消化污泥在长时间储存过程中也常持续释放多种恶臭有机物,主要有对甲酚、吲哚、甲苯、苯乙烯、乙苯、3-甲基吲哚和丁酸等[56]。这些VOCs主要通过污泥有机质 (如氨基酸) 分解产生,虽然释放量相对较低,但由于部分物质的嗅阈值较低且气味刺激性大,对污泥恶臭污染的形成具有重要贡献[57]。如色氨酸降解产生粪臭味的吲哚和3-甲基吲哚[47];酪氨酸降解产生对甲酚[58];苯丙氨酸在厌氧条件下降解产生甲苯、苯乙烯和乙苯,有氧条件下先转化为酪氨酸再形成对甲酚[56];而丁酸则是对甲酚的降解或转化的产物[59]。对甲酚和丁酸虽然是厌氧消化污泥脱水和储存过程释放的主要VOCs[13],但其对气味的贡献较低。吲哚和粪臭素作为产甲烷菌和SRB的底物[60-61],可在污泥长时间储存过程中随微生物活性降低而被释放。实际上,笔者近期研究发现,在脱水后的高级厌氧消化污泥中检出的吲哚和粪臭素的浓度均高于处理前的原泥,亦与上述推测一致[62]。
-
好氧消化工艺主要适合中小型污水处理厂的污泥处理[63],其工作原理与活性污泥法类似,通过对污泥进行长时间曝气,将污泥中的细胞物质和有机质降解为CO2等物质,实现污泥稳定化、无害化和减量化[64]。运行良好的好氧消化工艺会形成无臭、腐殖质状的污泥[65]。由于好氧消化产生的恶臭远低于厌氧消化过程,因此目前对该过程污泥恶臭释放的研究还十分有限[66]。当前对自热式高温需氧消化工艺 (autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion,ATAD) 释放恶臭气体的研究相对较多。该工艺在55~60 ℃条件下进行污泥消化,可减少高挥发性固体和病原体,实现污泥高度稳定[67]。但高温、高pH的环境条件和还原性硫化物的释放会导致恶臭污染。如ATAD反应器中pH升高会抑制硝化作用并促进NH3形成;在有机负荷过载的情况下产生VFAs,并在反应器中积聚导致恶臭[67]。且大多数ATAD系统不能始终保持有氧条件,会形成高浓度的NH3、VFAs和还原性硫化物 (如硫醇、H2S、DMS和DMDS) ,并随后从工艺废气、脱水和储存过程中释放出来[67-68]。此外,由于脱水方式与消化性能存在差异,在两个不同场所进行好氧消化工艺,其恶臭感官特征亦出现明显差异[66]。因此,污泥在某处理单元的产臭情况受其上游工艺和运行情况的影响,不同工艺进行合理组合是污泥恶臭污染防控的一个重要内容。
-
堆肥是一种简单且低成本的污泥处理处置技术,可分解有机物和杀灭病原体,最终形成类似腐殖质的稳定产物,将污泥转变为肥料或土壤改良剂[69-70]。堆肥过程恶臭物质的生成大多在厌氧条件下形成,其机制与厌氧消化过程类似。污泥好氧堆肥过程中释放的恶臭物质主要包括H2S、NH3和VOSCs,三者约贡献总气味的80%。其中,VSCs浓度虽相对较低,但对气味贡献大,为主要致臭物质[71]。大多数恶臭物质产生于中温期和高温初期,如挥发性无机物、VOSCs和苯,而降温期释放的恶臭物质主要为挥发性无机物[71]。不同的前处理过程会对污泥性质产生差异,导致在堆肥过程中的产臭特征存在明显差别。对比分析生污泥与厌氧消化脱水后污泥的堆肥产物恶臭释放特征发现,生污泥NH3和VOCs的排放量分别为19.37和0.21 kg·t−1,而厌氧消化污泥对应排放低得多,仅为0.16和0.04 kg·t−1;而且由于生污泥中可生物降解有机物含量较高,释放VOCs组分也更为多样[72]。除引发气味问题外,NH3的释放还造成了堆肥产品的氮素流失[73]。因此,降低NH3排放是提高污泥堆肥品质的关键。
1) VSCs。堆肥前期释放的VSCs (H2S、MT、DMDS、CS2和DMS) 占其总排放量的70%以上,且随环境温度的升高而增加[74]。VSCs的释放量虽然远小于NH3,但总的气味强度相当于甚至高于NH3,会造成较强烈的恶臭污染[75-76]。微生物产生的代谢物质会造成堆肥pH变化,影响恶臭物质的形成和释放。酸性代谢物质分解 (葡萄糖降解形成的有机酸) 和碱性代谢物质分解 (蛋白质降解产生的NH3) 会导致污泥pH降低和升高[77]。H2S主要由高温阶段污泥中的含硫化合物大量分解产生,同时伴随堆体pH升高[78]。当pH升至8.5时,H2S脱质子化为不易挥发的HS−[79]。此时的污泥呈碱性,还可中和部分H2S,并抑制SRB生长,减少H2S释放[80]。尽管DMDS和DMS是堆肥过程最主要的VOSCs[81],占总VSCs的80%以上,但其对气味的贡献小于H2S[74]。
2) VNCs。NH3排放浓度最大 (6 mg·kg−1以上) [76],占污泥堆肥所释放恶臭浓度的90%以上[82]。但受污泥性质的影响,其释放量会具有明显差异。如不同来源的生污泥与厌氧消化污泥脱水后进行堆肥累积的NH3排放量分别为0.04和0.23 g·kg−1,推测是消化污泥中易生物降解形式的氮初始含量较高所致[83]。对NH3释放规律的研究发现,堆体pH较高时,易造成大量NH3生成和挥发[77];高温阶段升高温度,NH3排放近指数增长[83];而提高堆肥含水率、降低通风速率可有效阻抑NH4+聚积与NH3释放[77]。相比于NH3,胺类物质对人体危害更大,在极低浓度下即可引发人类的嗅觉刺激。LAZAROVA等[82]发现,VSCs和TMA是堆肥过程中主要的恶臭物质,其次才是排放浓度最大的NH3。而堆肥过程中与TMA相关的鱼腥味只在堆肥初始阶段被检测到[84]。
3) 其他恶臭物质。在堆肥过程中还检测到芳香化合物、萜类、醛类、酮类和VFAs等恶臭物质[85]。其中,土臭素的释放量可作为污泥堆肥稳定化的指标[86]。大多数恶臭物质的释放量随堆肥温度的升高而增加[87];通风不足或污泥含水量较高会形成厌氧条件,进而产生VOCs和VFAs[72]。
-
简单的机械脱水并不能满足污泥处理要求,可采用干化技术实现污泥深度脱水[88]。污泥干化处理中,微生物活性在高温下受抑制,挥发性物质主要通过各种恶臭前体物的物理化学作用产生和释放。经不同前处理的污泥进行干化时,产臭特征会存在明显差异。如MURTHY等[15]对比了4种不同性质污泥进行干化的恶臭释放特征,发现在恶臭释放浓度、感官特征、持久性及强度方面均存在显著差异。
1) VSCs。污泥干化释放的VSCs有H2S、COS、MT、DMS、DMDS和CS2[15,89]。H2S释放分为2个阶段,当温度低于临界温度时,随着水分的蒸发,溶解在水中或吸附在污泥颗粒表面的经硫酸盐还原和含硫有机物脱硫形成的H2S被释放;当温度大于或等于临界温度时,含水率大大降低,使原本吸附在污泥颗粒表面的含硫有机物充分受热,导致H2S释放量急剧增加[90-91]。污泥pH对H2S释放也具有直接影响,中酸性污泥H2S的释放量远大于碱性污泥[91]。
2) VNCs。NH3释放量可达恶臭气体总浓度的88%[82],主要发生在干化早期,由游离氨、碳酸氢铵和蛋白质等物质的受热分解产生。NH3释放和水分挥发同时发生,存在于不同形态水中的氨,随污泥中游离水、毛细水和吸附水的蒸发而被释放[92]。溶于水的NH3可与酸性物质 (CO2、脂肪酸) 反应,转化为不挥发的NH4+ (如碳酸氢铵) 。碳酸氢铵热稳定极差,在污泥干化过程中几乎全部分解为NH3[93]。虽然NH3的释放随温度升高而增加,但当污泥含水率降低到一定程度时,其释放量会明显降低[94]。有机胺不仅是重要恶臭物质还是恶臭前体物。在高温干化条件下 (300~500 ℃) ,污泥中蛋白质裂解产生的有机胺可再通过脱氨和脱氢作用产生NH3[95]。
3) 其他恶臭物质。苯系物和VFAs也是污泥干化过程释放的主要VOCs,其释放量分别可达VOCs的50%~75%和15%~30%[96]。苯系物中各组分释放量的大小与污泥中含有的苯系物浓度呈正相关关系,升高温度会促进其释放[97]。VFAs主要有甲酸、乙酸和丙酸,可通过有机物 (如脂类) 的水热处理过程形成[98]。而在干化早期,VFAs排放量显著增加,但随含水量的下降而逐渐降低[94]。
污泥干化技术和机械脱水技术会对污泥性质造成明显改变,从而影响污泥在后续处置过程的恶臭特征。对比经不同脱水方式的厌氧消化污泥用于森林土地改良时两周内的恶臭释放特征,发现具有相似物理、化学和微生物特性的压滤和离心脱水污泥森林土地改良时释放的主要恶臭物质是NH3和DMDS,同时还释放少量DMS、CS2、TMA、丙酮和甲基乙基酮;而具有尘状结构和高表面积的干化污泥森林土地改良一周后的微生物活性远高于另2种污泥,两周内恶臭污染也更为严重;除上述物质外,还会释放硫醇和VFAs[99]。
-
随着土地资源的减少及能源需求的增加,焚烧被认为是一种相对成熟的城市污泥无害化处置技术[100]。有机物在高温焚烧过程中被完全氧化,产臭问题相对较轻。因此,目前对此过程污染物排放的研究主要集中在常规大气污染物 (氮氧化物、硫氧化物) 、重金属和多环芳烃等,对恶臭气体的研究相对较少[101]。亦有研究指出污泥焚烧工艺会释放NH3、H2S、TMA和乙醛等恶臭物质[101-102]。
-
尽管填埋不能实现对污泥的资源化利用,但过去几十年来仍是常见的工业污泥和市政污泥处置方式。目前,常将浓缩污泥与其他固体废物混合进行填埋[103]。混合填埋的污泥和其他有机废物在厌氧条件下分解产生的气体主要为甲烷和CO2,还包括醇类、烃类、卤代化合物和CS2等成分复杂的挥发性物质。尽管这些物质含量通常低于总排放量的1% (体积分数) ,但仍会形成恶臭[104-105]。通常,污泥填埋区NH3的释放量最大,但典型恶臭物质为VSC、有机酸及部分VOCs (胺类和醛类) 等[106-107]。DINCER等[104]比较了土耳其伊兹密尔垃圾填埋场5月和9月不同类型的气味源,发现污泥填埋区域释放的恶臭气体以卤代化合物、酮类和醛类化合物为主;9月份时由于氢氧化钙的加入及长时间高温蒸发使得VFAs、酯类和卤代化合物浓度降低。
-
土地利用和建材利用也是常见污泥处置方式。若污泥持续释放恶臭会严重影响污泥的资源化利用可接受度。污泥土地利用过程的恶臭释放特征受污泥性质和施用场地的影响。如对厌氧消化污泥和经厌氧消化的碱性稳定污泥土地利用时的恶臭释放特征进行研究时发现了DMDS、DMS、CS2、二甲基三硫醚、苯系物、萜烯和烷烃的释放,其中DMDS和二甲基三硫醚是主要的恶臭物质,但未发现NH3和含氮化合物的释放[108]。由于污泥中可能含有重金属、病原体和有毒有害有机物等污染物,土地利用可能造成土壤污染、植物毒性等对人类和环境产生风险的问题,因此污泥的农田施用被严格限制[109]。利用脱水污泥改良盐碱化土壤,污泥释放的恶臭气体有NH3、H2S、MT、DMDS和DMS;施用一周后释放的NH3和H2S质量浓度分别为0.18和0.0076 mg·m−3,均低于《居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度》 (TJ36-79) [110]。
污泥建材利用是将污泥干燥后,与粘土等硅铝原料充分混合,经过加热或烧制等工艺后制成水泥、砖和陶瓷颗粒等[111]。在此过程中,污泥会释放恶臭气体,对环境造成影响。粘土和污泥制成的陶瓷砖在烧结过程中会释放乙酸、乙腈、丙酮、CS2、二氯甲烷和MT等VOCs,但只有MT超过其嗅阈值,相对于污泥焚烧等其他过程产臭较轻[112]。也有研究将污泥与硅铝建筑材料混合,制备具有“大尺度-中尺度-小尺度-微尺度”结构的多尺度复合颗粒,可解决污泥用作建筑材料过程中VSCs释放和其他气味问题[111]。
-
污泥不同处理与处置过程释放的关键恶臭物质在成分组成上具有一定相似性,差异主要体现在各组分相对含量上。VSCs、VNCs和部分VOCs作为关键致臭物质通常具有高浓度稳定排放和低浓度波动排放2种模式;而部分污染物化学性质较不稳定,可发生转化,从而改变恶臭污染的特征。因此,解析识别关键污染物和污染特征是确定污泥恶臭治理方案的核心科学问题,并确保得出有针对性的恶臭污染治理手段。
污泥恶臭污染减排措施主要有4个方面:一是源头减量,即在恶臭产生的源头采取有效措施控制恶臭物质的形成;二是过程控制,通过恶臭收集、工艺优化与设备优选尽可能抑制恶臭气体的生成和泄露;三是末端处理,处理已产生的恶臭气体使其达标排放;四是排放管理,通过排放标准的制定实施实现对污染减排效果的最终管理和控制。现阶段,污泥恶臭气体的控制大多借鉴其他领域研究成果,尚处于发展的初级阶段,仍需不断加以完善、补充。源头减量与过程控制可有效遏制污泥处理处置过程中恶臭气体的生成与排放,从根本上更高效地解决污泥恶臭污染问题,而排放管理则是从系统管理的角度保证污泥恶臭污染防控全流程的实施质量。恶臭的有效控制需要从这4个方面协同开展,才能系统上解决污泥的恶臭污染问题。
-
热水解、机械预处理、酶预处理、化学调理和超声波技术等预处理技术可通过提高污泥稳定化效果从而减少污泥恶臭释放。热水解预处理通过在厌氧消化前对污泥施加高温 (140~170 ℃) 和高压 (600~900 kPa) ,以增强消化器的处理能力,从而实现污泥有机质的更深度降解,在工业中广泛应用了20多年仍在不断发展[113-114]。虽然厌氧消化过程中仍不能避免恶臭物质的产生,但脱水的高级厌氧消化污泥常以土霉味为主,其恶臭程度明显降低[62]。化学调理主要以提高污泥脱水效率为主要目的,兼顾减臭控臭功能。常用调理剂及其对污泥减臭控臭作用模式见表2[115]。虽然加入石灰[116]、FeCl3[116]、氧化钙[117]、明矾[118]和微生物菌剂[119]等调理剂在不同程度上可降低恶臭排放,但JOHNSTON等[57]将过氧化氢、泻盐和高锰酸钾等调理剂加入已脱水的厌氧消化污泥中,发现没有一种调理剂对减缓污泥暂存和储存期间恶臭气体的释放有效。因此,如何在保证调理效能的基础上有效减少调理过程及后续工艺中的污泥恶臭气体释放,仍需开展进一步研究。
除通过减量污泥有机质和调控介质环境条件参数外,还可通过添加微生物菌剂调整污泥微生物群落结构来改善恶臭释放。如将耐热科恩氏菌LYH-2 (Cohnella thermotolerans LYH-2) 接种到污泥中能有效控制H2S排放,并促进污泥堆肥腐熟[120]。近年来,微曝气技术、联合预处理技术也被应用于污泥处理以提高处理效能。微曝气技术应用于厌氧消化系统时,可强化污泥有机质水解、增强稳定化效果,从而减少H2S产生[121]。对污泥储槽中的浓缩污泥进行曝气可抑制产臭细菌的活性,从而减少VSCs等恶臭气体的释放[122]。超声波联合芬顿氧化预处理技术通过超声波处理促进了羟基自由基与污泥中H2S及含硫化合物的反应,使S2−浓度下降了1倍、SO42−浓度增加了近1倍,可有效减少污泥潜在的恶臭释放[123]。此外,化学调理与机械预处理技术进行联用也能显著降低污泥VSCs的释放[124]。然而,由于污泥密度和粘度较高,上述技术可能存在传质阻力带来的技术难点。因此,污泥恶臭的源头减量技术仍需进一步理论研究和应用验证。
-
1) 臭气收集。臭气收集系统需考虑管道选型、加盖密封和送风方式等。密闭式结构的构筑物或设备,设置抽风管道进行废气捕集即可。如规模较大的堆肥厂 (大于10 000~20 000 t·a−1) 应采用配备臭气处理系统的封闭式操作;而规模较小的堆肥厂可采用半透性覆盖层减少堆体恶臭释放或采用抽真空系统收集处理废气[125]。地上式臭气收集管道常选用玻璃钢材质,而地下式臭气收集管道往往选用不锈钢、内壁玻璃钢外壁混凝土或内壁玻璃钢外壁不锈钢材质[126]。对于需加盖密封以防止恶臭气体逃逸的构筑物或设备,主要的结构形式有钢筋混凝土顶板加盖、轻型骨架覆面加盖和钢支撑反吊膜结构加盖[127]。如污泥浓缩池一般采用钢筋混凝土顶板加盖,根据不同的直径和设备的差异,其加盖方式主要有钢筋混凝土盖板结合侧面推拉窗、玻璃钢盖板和钢支撑反吊氟碳纤膜[127]。送气方式分为适合密封效果好 (如除臭一体化设备) 的正压送气和密封效果略差 (如除臭滤池) 的负压送气[126]。
泄漏检测和修复 (leak detection and repair,LDAR) 技术是一种无组织VOCs控制技术,在石化行业广泛应用。该技术可对装备VOCs泄漏浓度实施定性或定量检测,及时修复发现的泄漏点,从而减少VOCs泄漏排放[128]。针对LDAR技术在4个炼油厂的应用发现,通过修复42%~81%的泄漏组件,VOCs排放量减少了42%~57%[129]。
2) 工艺优化。污泥停留时间、通风强度和剪切力等工艺参数会直接或间接影响含水率、温度和pH等污泥的性质参数及工艺环境,进而影响甚至直接决定污泥的产臭特征。如污泥厌氧消化停留时间为10 d和40 d时,污泥释放的VOSCs相较于生污泥分别减少了30%和50%[130]。然而,工艺参数的选择往往需要考虑综合效果,不能只针对单一的恶臭问题。如堆肥混合物料中污泥比例增加会导致NH3和H2S排放量增加,SUN等[131]兼顾温度、NH3、H2S和碳氮比等指标对污泥、树叶和稻草的混合比例研究就发现,尽管混合比为4:1:1时NH3和H2S排放量最低,但综合而言混合比为5:1:1时,其堆肥效果最好。
3) 设备优选。脱水是污泥处理过程中典型的产臭环节。脱水设备的选型不仅会影响工艺效果,还影响污泥恶臭排放。高固相离心脱水机的气味排放潜力要高于其他脱水设备[132]。这是由于离心脱水过程较大的剪切力导致污泥絮体破坏,并释放生物可利用蛋白,促进微生物产臭[133]。同时,污泥暴露在空气中,产甲烷菌活性降低使得VOSCs的降解被抑制,进一步导致恶臭释放量增加[133]。设备的选取也不能只针对单一的恶臭问题,需要根据实际情况做出适宜的选择。带式压滤机和板框压滤机为开放式,污泥恶臭问题虽然较为严重,但可在占地面积大,地理位置偏僻的污水处理厂采用;而离心脱水机和叠螺式脱水机是全封闭运行的,对环境影响小,可在位于市区内或靠近人口密集度高的污水处理厂采用[134]。近年来,随着智能化技术的深入发展,在强制通风静态垛工艺的基础上开发了智能控制好氧高温发酵工艺,对发酵过程中温度、氧气和臭气进行实时在线监测,并根据发酵状态进行反馈控制,代表了好氧发酵技术的发展方向[135]。秦皇岛市绿港污泥处理厂采用上述工艺进行实时在线监测和软件智能化控制,可有效控制H2S和NH3的大量产生和释放[136]。
-
1) 物理法处理。物理除臭法包括吸附法、液体吸收法和大气稀释扩散法等。吸附法适合处理低浓度、高净化要求的恶臭气体。其中,活性炭吸附法应用最为广泛,对VSCs的去除效果较好,但对VNCs的去除效果则稍差[12]。因此,目前研究集中在VSCs (尤其是H2S) 上,对VNCs和其他VOCs的关注较少[137]。泥炭、沸石、硅和污泥衍生吸附剂等也用于恶臭吸附[138],但有关吸附技术的研究重点是催化及改性活性炭技术。在活性炭吸附法基础上开发出的催化活性炭除臭技术将H2S和氧吸附在其表面并进行氧化,生成SO42−及少量SO32−和S,同时将NH3转化为NO3−或NO2−,对H2S、NH3及整体的臭气去除率分别为97.9%、86.7%和87.4%[139]。催化活性炭除臭技术对低浓度、多组分的恶臭气体具有较好的处理效果,但同样存在对除VSCs外的恶臭物质去除效果一般的缺点。活性炭吸附法的另一发展方向是通过对普通活性炭改性,制备出吸附性及稳定性更优良的活性炭材料。液体吸收法适合处理大气量、高浓度的臭气,具有简单、安全、可回收和低成本的优点,但目前大多采用不进行溶剂回收的工艺进行VOCs净化,因此寻找具有低挥发性、高热稳定性和可再利用的吸收剂是该技术的重点[140]。大气稀释扩散法将恶臭气体由烟囱排向大气,通过大气的稀释扩散以及氧化反应降低恶臭浓度[141],适用于处理中、低浓度有组织排放的恶臭气体,常与其他处理技术联用实现废气有组织达标排放。
2) 化学法处理。化学除臭法主要有化学洗涤法、化学氧化法、催化氧化法和直接燃烧法和催化低温燃烧法等。化学洗涤法是污水处理厂中最常用的恶臭减排技术之一[142],适用于处理大气量、高浓度的恶臭气体,如污泥稳定、干化和焚烧过程所产生的恶臭等。化学洗涤法通过使用酸液或碱液可有效去除NH3或H2S,但难以去除DMS、DMDS和CS2等疏水性VOCs[138]。而物理-化学溶剂法是目前处理天然气中VOSCs和酸性气体的常见方法[143],寻找脱除有机硫的稳定高效配方组份是其重要的发展方向。化学氧化法通过使用次氯酸钠、过氧化氢和高锰酸钾等氧化剂对还原性臭气物质进行处理[144]。如高锰酸钾等氧化剂已被用于处理小规模堆肥过程中产生的气味,低浓度的氧化剂直接散布在堆肥堆上,可杀死和抑制微生物,并随使用浓度改变堆肥过程[145]。直接燃烧法通过高温热解恶臭气体,较适合处理高浓度、高热值的废气,但初期设备投资较大,在城市污水除臭中应用较少[146]。在化学氧化法和直接燃烧法的基础上,通过使用催化剂开发了加快还原性臭气氧化速度的催化氧化法和降低臭气燃烧温度的催化低温燃烧法。然而,催化剂多为贵金属,其活性随使用时间逐渐下降甚至失活[141],延长高价催化剂的使用寿命是催化氧化法和催化低温燃烧法的关键。
近年来,一些高级氧化技术 (低温等离子技术和UV光催化技术) 被开发应用于恶臭治理领域。宁平团队[147]发现,在直流电晕放电等离子体反应器中,COS和H2S的化学键被破坏后通过自由电子、氧化自由基和臭氧进一步氧化为含碳化合物 (CO和CO2) 及含硫化合物 (S、SO2和SO42−) ,COS和H2S去除率分别为90%和98%。然而,低温等离子体技术存在电耗高和安全性等问题,在VOCs污染治理领域曾一度禁止使用或单一使用,目前应用相对较少。对北京某污水处理厂收集的臭气采用光催化技术进行处理,发现光催化剂比例WO3:TiO2为3.2:1时,对硫化物的去除率可超过90%[148]。而UV光氧化和光催化氧化技术存在停留时间短和氧化不彻底等问题,更适合于和其他技术联用。总的来说,物理或化学法存在运行费用高及二次污染的风险,很少单独应用。
3) 生物法处理。生物除臭法利用微生物将恶臭物质代谢成无臭无害的产物,如CO2、水、硫酸盐和硝酸盐。该技术具有成本低、操作简单、绿色安全等优点,是物理或化学法的替代方法[149],亦是污水处理厂最常用的除臭技术[150]。配备了恶臭处理系统的城镇污水处理厂有78%采用了生物除臭法。常规生物除臭法包括生物过滤法、生物滴滤法和生物洗涤法[151],可分别去除无量纲亨利系数等于或小于10、1和0.01的气态污染物[149]。
生物过滤法最早被应用于生物除臭[151],在污水处理厂恶臭治理中应用最为广泛[152],适用于去除流量大、浓度低的废气,对水溶性差的污染物去除效果较好[149]。如对NH3、H2S和甲苯3种混合污染物进行处理,去除率分别可达到98%、100%和40%[153]。相比于国外,国内对含氮恶臭有机污染物的研究还比较少,我国学者研究发现生物过滤法对TMA的去除率可达99%以上[154]。然而,生物过滤法处理H2S和有机物时会产生酸性物质,导致微生物活性抑制、填料酸化及设备腐蚀的问题,故需要对pH进行有效控制。此外,恶臭物质净化往往需要不同类型的微生物。如降解NH3和H2S的微生物通常为自养型,异养细菌易于降解亲水性物质,而真菌降解疏水性物质具有较大优势[155]。但传统生物过滤法常采用单一反应器,不同类型的微生物难以共存并共同发挥作用,去除物质类型及能力有限。因此,目前许多工艺采用两段生物除臭法进行恶臭治理。相比于生物过滤法,生物滴滤系统的结构更简单,建设和运行成本更低,对易导致生物系统酸化的VSCs的处理效果更好,但对水溶性较差的废气去除效果稍差,适用于处理质量浓度不高于500 mg·m−3的VOCs[156]。相较于以上2种生物除臭法,生物洗涤法可避免生物质增长导致填料堵塞的风险[149],对流量大、污染物质量浓度大于500 mg·m−3的恶臭气体及亲水性物质 (如醇、醛和脂肪酸) 处理效果更好,但对水溶性差的污染物去除效果较差,可通过在液相中加入吸收剂、吸附剂和生物表面活性剂等促进对烷烃等疏水化合物的去除[156]。
总的来说,上述生物除臭法仍存在滤床易堵塞、疏水性污染物处理效果不好或微生物活性易受影响等问题[156]。因此,有研究者提出采用活性污泥扩散法替代生物滤池等基于介质的处理系统,将收集的恶臭气体喷入污水处理厂的曝气池,通过吸收、吸附、冷凝及好氧微生物的生物降解作用处理恶臭气体[157];并针对疏水性物质开发了真菌生物反应器、膜生物反应器及双液相生物反应器[158];向生物滤池接种从富含H2S的土壤和污泥中筛选出的嗜酸氧化硫硫杆菌AZ11 (Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans AZ11) 后,H2S的去除率达99.9%[159]。目前,生物除臭技术研究仍集中于高效生物降解菌的筛选、反应器中物质传质效率提升、新型填料研发和反应器内部微生态调控等方面[156-158]。
4) 联用技术。单一除臭技术很难满足越来越严格的臭气排放标准,因此,合理采用多种恶臭控制技术形成较强的协同效应进行综合处理是进一步发展趋势。采用的联用技术一般以生物法为主,物理/化学法为辅。其中,活性炭吸附-生物联用技术 (如活性炭与生物滴滤法联用技术) 是污水处理厂中常用的恶臭控制方法,对处理高疏水性恶臭物质 (90%~99%) 方面具有优异性能[152,160]。然而,较高的吸附系统投资成本和运行费用,以及恶臭物质的复杂性和可变性仍是联用技术创新和应用的主要挑战。此外,两段生物除臭法联用、化学洗涤法-生物联用技术等也被广泛应用到污水处理厂中。近年来,有研究人员尝试将各种新兴处理技术与传统方法联用于恶臭废气处理,如非热等离子体-生物滴滤池联用、非热等离子体-UV光解联用等[161-162]。
-
目前,我国专门针对污泥恶臭污染执行的是《恶臭污染排放标准》 (GB14554—1993) ,其中规定了NH3、TMA、H2S、DMS、DMDS、MT、CS2和苯乙烯8种典型恶臭物质的排放限值。此外,还有一些地方、行业或污水处理企业的大气污染排放标准对恶臭指标有排放要求。但值得注意的是,这些标准的执行虽然在一定程度上缓解了恶臭污染造成的不利影响,但频发的民众投诉表明部分标准所规定的内容或限值已不能满足当前恶臭污染复杂形势的需要。
-
1) 我国污泥处理处置技术路线已形成“厌氧消化-土地利用”、“好氧堆肥-土地利用”、“干化焚烧-灰渣填埋或建材利用”和“深度脱水-应急填埋”四个主流方案。这些处理处置技术路线的实施都不能忽视恶臭污染问题。由于污泥恶臭物质的浓度低、成分复杂,准确的定性定量分析和影响评价比较困难,限制了对不同处理处置过程中污泥恶臭污染物释放规律的认识。因此,建立更先进的分析方法,将多种分析手段有机结合,从感官评价和仪器分析的不同角度表征恶臭的污染特征,准确识别关键的恶臭物质,是确定污泥恶臭治理方案的核心科学问题,对于研发污泥减臭控臭技术措施具有重要科学意义。
2) 污泥产臭特征与污泥性质密切相关,受环境条件的影响,微生物代谢发挥着尤其重要的作用。然而由于研究手段的限制和重视程度的不足,人们对污泥产臭机制的认识还非常有限。在准确识别关键恶臭物质的基础上,利用基因测序技术、PCR核酸技术等微生物分子生态学技术,深入理解不同处理和处置过程中污泥微生物介导的恶臭物质转化途径及相关机理,对认识污泥的产臭机制具有重要的理论意义,可为污泥恶臭的源头减排提供更可靠的科学依据。
3) 完整的污泥恶臭控制技术路线应从源头减量、过程控制、末端治理和排放管理四个方面综合考虑,其中应以源头减量和过程控制为主,最大限度减少恶臭释放和后续处理的压力。末端治理技术方面,化学洗涤法和生物过滤法仍是我国污泥恶臭治理的主要手段。但在实际的工程应用上,需要根据污泥恶臭释放特征、周边环境及除臭要求,针对性地选择一种或多种方法结合应用,有效提高恶臭综合去除效果。通过提高调理剂效能、调整污泥处理工艺运行参数和优化运行工况等手段从源头上减少污泥恶臭产生,开发应用新型除臭技术及联用技术,协调发挥各个环节的减臭控臭调控作用,实现污泥恶臭污染有效控制。在排放管理方面,由于我国恶臭污染防治事业起步较晚,有关污泥恶臭污染控制的技术方法和标准等还远远不够,需进一步进行研究并加强恶臭污染立法。
污水处理厂污泥处理处置过程中的恶臭污染特征与恶臭物质减排控制措施
Odor characteristics of wastewater treatment plant sludge during treatment and disposal and emission reduction control measures: A short review
-
摘要: 随着污水处理厂规模的不断扩大,污泥产量持续增加。虽然“重水轻泥”现象已有所改变,但污泥处理处置技术仍面临各种挑战。污泥处理处置过程中的恶臭污染会对周围环境和人群健康造成不利影响,极易引发民众投诉,是提高污泥处理效率、实现污泥资源化利用的难点之一。污泥释放的恶臭物质组分复杂,且影响污泥恶臭释放的因素较多,目前针对污泥处理处置过程中恶臭产生机制和释放规律的研究尚不深入,导致污泥控臭除臭处理的效果仍不理想。因此,在归纳总结污泥常见恶臭物质及其产生来源的基础上,详细阐述了不同处理处置方式下污泥的恶臭污染特征与产生机制,从源头减排、过程控制、末端治理、排放管理4个方面评述了污泥恶臭减排控制措施的原理和发展前景,讨论了污泥恶臭污染防治的复杂性和挑战,以期为污泥恶臭污染防控提供参考。Abstract: As the scale of sewage treatment plants expanded, the production of sludge continuously increased in China. Although the treatment of sludge has been gradually paid more attention, the development of sludge treatment technology is still facing various challenges. Odor pollution emitted from sludge treatment and disposal cause negative effects on the surrounding environment and public health, and easily lead to public complaints. The deodorization is one of the technical problems that must be solved to improve the sludge treatment efficiency and to implement the sludge resource utilization. The component of malodorous compounds emitted from sludge are variable and complex, affecting by many different factors including the physical-chemical properties of sludge and the surrounding conditions. However, due to the lake of knowledge in the generation mechanism of odorants and the principle of odor formation, the performance of sludge odor control is often unsatisfactory. Thus, based on summarizing the general production sources of odorous substances in sludge, the pollution characteristics and generation mechanism of sludge odor upon different processing methods were expounded. The principles and development of various odor control measures were then reviewed from the perspectives of source emission reduction, process control, end-of-pipe treatment and discharge management to show the complexity and challenges in the sludge odor pollution prevention.
-
Key words:
- sludge /
- sludge treatment /
- sludge disposal /
- odor characteristics /
- emission reduction control measures
-
污水处理厂污泥是污水处理过程中的副产物。随着我国城市生活污水处理系统的发展,污泥产量逐年增加[1]。污泥富集了大量有机物、营养物质、病原微生物和重金属等有毒有害物质[2],在处理处置及储运过程中不可避免地释放恶臭气味,极易形成二次污染,在严重时可能会构成污染公害事件[3]。尽管污泥产量仅为污水总量的0.3%~0.5% (体积分数) [4],但污泥处理过程是污水处理厂恶臭释放的主要来源[5]。处理后的污泥若仍存在恶臭 (或较强烈异味) ,将在极大程度上限制污泥土地利用等多种处置方式的实施。除污水来源及其处理工艺外,污泥处理与处置工艺和实际运行对污泥的性质有较大影响,从而导致污泥在处理过程中和处置利用时的恶臭释放特征存在显著差异[6]。因此,污泥恶臭污染有效控制是提高污泥处理效率、实现污泥资源化利用必须解决的技术难题。由于我国污泥产量快速增加,对污泥恶臭污染控制的技术需求更为迫切。
基于此,本文以城市污水处理厂污泥在处理和处置过程中的恶臭污染为研究对象,分析整理近20年来有关污泥恶臭及其控制技术的文献报道,从污泥产臭关键环节的污染特征和发生机制入手,通过分析污泥恶臭减排的控制措施与策略,讨论污泥恶臭污染防治的复杂性和挑战,以期为防控污泥处理处置过程中的恶臭污染提供参考。
1. 污泥恶臭物质的种类和来源
1.1 种类及其特点
污泥处理处置过程释放的恶臭物质主要包括含硫化合物、含氮化合物、含氧有机物、烃类化合物和卤素及其衍生物。其中,分子质量为30~150且易挥发的物质较常见[7]。早期的研究多采用日本《恶臭防治法》中规定的六级恶臭强度评价法对城市污水处理厂释放的恶臭物质进行评估,发现其中含量排首位的是氨 (ammonia,NH3) ,其次是硫化氢 (hydrogen Sulfide,H2S) 、二甲基硫醚 (dimethyl sulfide,DMS) ;但甲硫醇 (methyl mercaptan,MT) 的臭气强度最大 (4.7级) ,其次是H2S (4.5级) ,均为强臭等级[8]。近期研究表明,除H2S和NH3外,多种浓度较低的挥发性有机硫化合物 (volatile organic sulfur compounds,VOSCs) 、含氮有机物和含氧有机物等挥发性物质,对污泥恶臭的形成具有重要贡献[9-10]。实际上,污泥释放的恶臭气体常包含数十至上百种挥发性物质,其中仅少部分是造成恶臭的主要物质。我国学者测定报道了40种典型恶臭物质嗅阈值[11],可能仍有许多致臭物质尚未明确[12]。其中,污泥处理处置过程中较常检出的恶臭物质嗅阈值及感官性质如表1所示。污泥释放的恶臭物质在成分组成上可能具有一定相似性,但由于不同性质的污泥释放的致臭物质在化学浓度相对含量上的差异,常导致污泥表现出明显不同的恶臭特征[13-15]。
表 1 污泥处理处置过程中主要的恶臭物质嗅阈值及气味特征[11]Table 1. Odor threshold and sensory properties during sludge treatment and disposal[11]分类 物质名称 分子式 感官性质 嗅阈值/(mg·m−3) 含硫化合物 硫化氢 H2S 臭鸡蛋味 0.001 8 甲硫醇 CH3SH 烂菜心气味 0.000 1 二甲基硫醚 (CH3)2S 海鲜腥味 0.005 5 二甲基二硫醚 (CH3)2S2 洋葱味 0.046 3 含氮化合物 氨 NH3 强烈刺激性气味 0.227 7 三甲胺 (CH3)3N 鱼腥味 0.002 4 酸类 丙酸 CH3CH2COOH 刺激性气味 0.028 8 正丁酸 C3H7COOH 汗味、酸臭味 0.005 1 醛类 乙醛 CH3CHO 刺激性气味 0.035 4 丙醛 CH3CH2CHO 水果香味 0.041 5 苯系物 甲苯 C7H8 芳香气味 0.403 1 乙苯 C8H10 芳香气味 0.085 3 苯乙烯 C8H8 塑料味 0.158 1 对二甲苯 C8H10 芳香气味、水果香味 0.568 7 污泥恶臭污染不仅会降低周边人群的工作和生活环境质量,长期接触还会对人群健康产生负面影响[16]。此外,部分恶臭物质为VOCs污染物,具有活泼化学性质的恶臭物质可与阳光或大气中的氮氧化物发生光化学反应及氧化反应,参与大气环境中臭氧和二次气溶胶的形成,是导致大气臭氧污染、酸雨和光化学污染等的重要前体物[17-18]。
1.2 污泥恶臭物质的来源
恶臭污染特征与污泥的性质密切相关[14]。污泥性质的差异体现在污泥中物质的组成和浓度,微生物群落结构,溶解氧、水分和pH等介质微环境条件3个方面 (图1) ,这些因素共同影响恶臭的产生和释放。因此,污泥恶臭物质的主要来源可归纳为底物释放和微生物代谢两大生成机制。
1) 底物释放。污水中存在多种恶臭物质和致臭前体物质,如有机质、硫化物和含硫蛋白质等[19],经污水处理过程 (如沉淀、吸附) 转移至污泥。这些底物在脱水、转移及运输等过程中,因受压或剧烈扰动等作用被释放出来[20]。此外,污水与污泥处理过程中加入的某些化学药剂可与污水或污泥中无异味物质发生反应转化为恶臭物质,或是增强部分恶臭物质的挥发性。如在污泥的石灰稳定化过程中,阳离子聚合物和蛋白质通过酶水解降解形成三甲胺 (trimethyl amine,TMA) 和二甲基二硫醚 (dimethyl disulfide,DMDS) ,随后加入的石灰导致污泥pH环境变化,促使TMA和DMDS释放[21]。
2) 微生物代谢。在缺氧或厌氧条件下,微生物降解有机物生成还原性硫化物、含氮有机物、挥发性脂肪酸等具有腐败或刺激气味物质,极易形成恶臭污染[22]。如H2S和MT主要由缺氧条件下硫酸盐还原菌 (sulfate-reducing bacteria,SRB) 和甲烷菌等微生物的生命活动形成[23]。含硫蛋白质在蛋白酶作用下分解为多肽,多肽再经肽酶作用分解为甲硫氨酸或半胱氨酸,然后在甲硫氨酸裂解酶和半胱氨酸裂解酶的作用下分别形成MT和H2S[24]。厌氧细菌又可将H2S和MT进行甲基化,分别生成MT和DMS[24]。挥发性含氮有机物 (如胺类、吲哚和粪臭素) 主要通过氨基酸脱羧作用和L-色氨酸降解代谢等过程产生[25]。水解细菌对污泥中的有机物 (如淀粉、纤维素、半纤维素和果胶等) 进行水解,形成小分子氨基酸、单糖和长链脂肪酸等有机成分。产酸菌利用这些水解产物进行厌氧发酵生成挥发性脂肪酸 (volatile fatty acids,VFAs) 、醇类、醛类和酮类等物质[26-27]。而好氧细菌则通过对含氮有机物及细胞物质进行氧化生成NH3和具有土霉味的物质[28-29]。二硫化碳 (carbon disulfide,CS2) 主要源于人为排放,无法由有机物降解或硫化物互相转化而产生[30],但在好氧和厌氧条件下可作为碳源被微生物降解,生成羰基硫 (carbonyl sulfide,COS) ,再转化为CO2和H2S[31]。
综上所述,底物挥发释放和微生物代谢是污泥恶臭物质产生的主要途径,并易受处理处置过程中环境条件的影响。从微生物的功能作用机制来看,微生物驱动的恶臭物质生成与转化过程由一个或多个功能基因参与完成[25]。
2. 不同处理处置方式下污泥的恶臭污染特征与产生机制
国内外常用的污泥处理技术有脱水、厌氧消化、好氧消化、干化等,处置技术有土地利用、填埋、堆肥和焚烧等[32]。我国污泥存在有机质含量低和含沙量高的特点,因此,形成了“厌氧消化-土地利用”、“好氧堆肥-土地利用”、“干化焚烧-灰渣填埋或建材利用”和“深度脱水-应急填埋”4条污泥稳定化处理与安全处置的主流技术[2]。由于经过不同处理和处置导致污泥性质存在差别,故形成的恶臭污染特征亦具有较大差异。FISHER等[13-14]比较了澳大利亚6个污水处理厂不同处理单元污泥释放的气味物质发现,浓缩、厌氧消化、脱水及储存过程中释放的挥发性物质差异明显,脱水和储存过程会释放浓度更高、种类更丰富的挥发性含硫化合物 (volatile sulfur compounds,VSCs) 、挥发性含氮化合物 (volatile nitrogen compounds,VNCs) 、卤代化合物、酮类和烃类等物质,从而揭示了不同污泥处理工艺对污泥释放恶臭的影响,以及污泥产臭的复杂性。本章分析讨论不同处理处置方式下,污泥的恶臭释放特征与产生机制。
2.1 污泥浓缩与脱水过程
浓缩是污泥处理的第一步,常采用重力浓缩、气浮浓缩和离心浓缩等工艺降低污泥含水率[33]。污水原有或生化过程中形成的NH3和VSCs等恶臭物质吸附在污泥中,并在浓缩过程中不断释放[34]。相对于污水处理厂中其他的功能区,污泥浓缩池和污泥脱水间产生的恶臭物质浓度通常较高。此外,浓缩过程较长的停留时间会形成缺氧环境,污泥中的微生物在厌氧条件下降解有机物形成恶臭物质。虽然污泥浓缩池常为密闭式,产生的污染物不易扩散,但浓缩过程中发生湍动会加剧恶臭气体逸出[12]。实际上,未经历长时间厌氧处理的剩余污泥并不具有强烈恶臭,污泥浓缩过程中微生物参与的厌氧反应是主要的恶臭产生途径。对于无污泥稳定化的处理工艺,污泥浓缩后还需进行机械脱水处理。目前,污泥脱水过程也常采用封闭运行工艺,对释放的恶臭气体进行收集处理,以避免造成严重的恶臭污染。
在污泥浓缩与脱水过程中,NH3和H2S的排放浓度较高[35],且具有夏、秋季高而冬、春季低的季节性特点。恶臭物质释放量随水温的升高而增加,而降雨可稀释污染物、降低水温和提高溶解氧浓度,从而降低恶臭污染物浓度[36]。同时,还存在一些浓度相对较低的DMS、DMDS、CS2、硫醇、苯乙烯和二甲苯等恶臭有机物[35,37]。LEHTINEN等[17]研究污水处理厂各单元VOCs释放特征发现,浓缩过程中乙醚和甲苯的释放量较大,其次才是DMDS和DMS。且苯系物的含量为所释放VOCs的80%以上[18]。又由于苯系物和醚类的嗅阈值较高,对恶臭贡献有限,则应归类为VOCs类污染物。
污泥脱水过程的恶臭气体释放量通常远高于浓缩过程[38-39],但对德国多个污水处理厂各处理单元恶臭污染贡献的研究发现,污泥脱水车间和污泥浓缩池的恶臭散发率分别为17%和26%,浓缩池比脱水车间的恶臭问题更突出[40]。这表明污泥浓缩与脱水过程中的产臭情况与工艺运行的具体参数密切相关,污泥水分、含氧量等参数的差异通过影响污泥中微生物的活性而在极大程度上决定着污泥产臭特征。
2.2 污泥厌氧消化过程
厌氧消化是污泥最终处置前最重要的稳定化处理方法[41]。厌氧消化指在厌氧条件下,利用微生物代谢降解蛋白质、碳水化合物和脂肪等有机物,产生甲烷、CO2和水等消化气[42],从而实现污泥的减量化、无害化、稳定化与资源化。由于我国不同地区污泥存在差异,传统厌氧消化工艺运行不理想[20],故多采用热水解预处理的改良型污泥厌氧消化或多段式厌氧消化等高级厌氧消化工艺来解决以上问题[43-44]。厌氧消化过程是封闭进行的,正常情况下消化气经妥当收集处理,不会造成严重的恶臭污染[20]。但由于厌氧消化气中存在较高含量的还原性硫化物 (尤其是H2S) ,不仅存在恶臭污染隐患,还可能造成设备腐蚀,降低设备安全稳定性和使用寿命[45]。因此,应注意防范污泥厌氧消化气泄露而引发的恶臭污染问题。此外,经厌氧消化处理后,污泥的恶臭强度有所降低[46],但污泥中残留的蛋白质在后续脱水和运输过程中会因受到剪切变得不稳定从而导致VSCs释放[42]。不同性质污泥在厌氧消化后储存时会释放恶臭物质。对比其特征后发现,初沉污泥释放的恶臭总浓度排在首位,其次为混合污泥 (初沉污泥和剩余污泥) 、剩余污泥[47]。
1) VSCs。传统厌氧消化和高级厌氧消化工艺释放的主要恶臭物质均以NH3、H2S和MT为主,而经热水解预处理的高级厌氧消化工艺会释放产生更高浓度的VSCs[48-49],推测是由于热水解预处理促进了含硫有机物的水解,使得其pH较低。厌氧条件下污泥VSCs循环途径可归纳如图2所示。H2S不仅可以由硫酸盐或亚硫酸盐等无机前体物在厌氧条件下经SRB转化为S2−,与H+结合形成,还可以由污泥中含硫有机物 (如含硫氨基酸) 厌氧分解生成MT、DMS和DMDS等有机硫化物发生去甲基化形成[24]。现有研究表明,在硫酸盐还原过程中,具有功能基因aprA编码腺苷5’-磷酸硫酸酐还原酶、dsrA/dsrB编码异化型亚硫酸盐还原酶的微生物可将硫酸盐、亚硫酸盐等还原为H2S等硫化物[25]。MT由甲硫氨酸降解或H2S生物甲基化反应生成,可经生物甲基化和氧化作用分别形成DMS和DMDS[24]。在厌氧条件下,污泥H2S和MT的释放与脱氢酶活性显著相关,脱氢酶活性可用于表征环境系统中微生物的活性,其值越大,恶臭释放潜力越大[23]。而CS2主要来源于非生物反应[31],故在厌氧消化过程中监测到的CS2一般由污泥自身携带。
在消化污泥短期储存期间,VOSCs可作为底物随产甲烷菌等微生物活性恢复而最终被转化为甲烷和H2S[50-51]。此外,有关消化气释放规律的研究表明,总VOSCs浓度随污泥厌氧消化停留时间的延长而降低[52];H2S、MT、DMS和DMDS的释放量随温度升高而增加,但温度对H2S影响较大,在高温消化 (55 ℃) 时污泥释放的H2S是中温消化 (35 ℃) 时的3倍[50]。
2) VNCs。厌氧消化工艺中NH3释放量最大 (741.60 g·t−1) ,远高于VSCs (277.27 g·t−1) [49]。但NH3的气味检测阈值比VSCs高2~3个数量级,并非关键恶臭物质,故很多研究都未对其进行监测[53]。NH3来源于具有功能基因ureC编码脲酶的微生物将污泥中的有机氮矿化转变为NH4+[25]并水解的过程。其释放量随温度升高而增加,在高温消化时污泥释放的NH3浓度是中温消化时的8倍[50]。厌氧消化污泥在脱水过程中释放的恶臭气体中偶尔可检测到具有低嗅阈值的TMA。TMA比单胺类物质更不易被微生物分解,故其释放量通常为其他胺类物质的7倍[54]。
3) 其他恶臭物质。厌氧消化过程形成的VFAs易被微生物降解[26],因此,VFAs的存在是产酸和产甲烷过程不平衡导致[55]。虽然高温消化时污泥释放的VFAs浓度为中温消化时的2~5倍,但仍低于其嗅阈值[50]。此外,厌氧消化污泥在长时间储存过程中也常持续释放多种恶臭有机物,主要有对甲酚、吲哚、甲苯、苯乙烯、乙苯、3-甲基吲哚和丁酸等[56]。这些VOCs主要通过污泥有机质 (如氨基酸) 分解产生,虽然释放量相对较低,但由于部分物质的嗅阈值较低且气味刺激性大,对污泥恶臭污染的形成具有重要贡献[57]。如色氨酸降解产生粪臭味的吲哚和3-甲基吲哚[47];酪氨酸降解产生对甲酚[58];苯丙氨酸在厌氧条件下降解产生甲苯、苯乙烯和乙苯,有氧条件下先转化为酪氨酸再形成对甲酚[56];而丁酸则是对甲酚的降解或转化的产物[59]。对甲酚和丁酸虽然是厌氧消化污泥脱水和储存过程释放的主要VOCs[13],但其对气味的贡献较低。吲哚和粪臭素作为产甲烷菌和SRB的底物[60-61],可在污泥长时间储存过程中随微生物活性降低而被释放。实际上,笔者近期研究发现,在脱水后的高级厌氧消化污泥中检出的吲哚和粪臭素的浓度均高于处理前的原泥,亦与上述推测一致[62]。
2.3 污泥好氧消化过程
好氧消化工艺主要适合中小型污水处理厂的污泥处理[63],其工作原理与活性污泥法类似,通过对污泥进行长时间曝气,将污泥中的细胞物质和有机质降解为CO2等物质,实现污泥稳定化、无害化和减量化[64]。运行良好的好氧消化工艺会形成无臭、腐殖质状的污泥[65]。由于好氧消化产生的恶臭远低于厌氧消化过程,因此目前对该过程污泥恶臭释放的研究还十分有限[66]。当前对自热式高温需氧消化工艺 (autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion,ATAD) 释放恶臭气体的研究相对较多。该工艺在55~60 ℃条件下进行污泥消化,可减少高挥发性固体和病原体,实现污泥高度稳定[67]。但高温、高pH的环境条件和还原性硫化物的释放会导致恶臭污染。如ATAD反应器中pH升高会抑制硝化作用并促进NH3形成;在有机负荷过载的情况下产生VFAs,并在反应器中积聚导致恶臭[67]。且大多数ATAD系统不能始终保持有氧条件,会形成高浓度的NH3、VFAs和还原性硫化物 (如硫醇、H2S、DMS和DMDS) ,并随后从工艺废气、脱水和储存过程中释放出来[67-68]。此外,由于脱水方式与消化性能存在差异,在两个不同场所进行好氧消化工艺,其恶臭感官特征亦出现明显差异[66]。因此,污泥在某处理单元的产臭情况受其上游工艺和运行情况的影响,不同工艺进行合理组合是污泥恶臭污染防控的一个重要内容。
2.4 污泥堆肥过程
堆肥是一种简单且低成本的污泥处理处置技术,可分解有机物和杀灭病原体,最终形成类似腐殖质的稳定产物,将污泥转变为肥料或土壤改良剂[69-70]。堆肥过程恶臭物质的生成大多在厌氧条件下形成,其机制与厌氧消化过程类似。污泥好氧堆肥过程中释放的恶臭物质主要包括H2S、NH3和VOSCs,三者约贡献总气味的80%。其中,VSCs浓度虽相对较低,但对气味贡献大,为主要致臭物质[71]。大多数恶臭物质产生于中温期和高温初期,如挥发性无机物、VOSCs和苯,而降温期释放的恶臭物质主要为挥发性无机物[71]。不同的前处理过程会对污泥性质产生差异,导致在堆肥过程中的产臭特征存在明显差别。对比分析生污泥与厌氧消化脱水后污泥的堆肥产物恶臭释放特征发现,生污泥NH3和VOCs的排放量分别为19.37和0.21 kg·t−1,而厌氧消化污泥对应排放低得多,仅为0.16和0.04 kg·t−1;而且由于生污泥中可生物降解有机物含量较高,释放VOCs组分也更为多样[72]。除引发气味问题外,NH3的释放还造成了堆肥产品的氮素流失[73]。因此,降低NH3排放是提高污泥堆肥品质的关键。
1) VSCs。堆肥前期释放的VSCs (H2S、MT、DMDS、CS2和DMS) 占其总排放量的70%以上,且随环境温度的升高而增加[74]。VSCs的释放量虽然远小于NH3,但总的气味强度相当于甚至高于NH3,会造成较强烈的恶臭污染[75-76]。微生物产生的代谢物质会造成堆肥pH变化,影响恶臭物质的形成和释放。酸性代谢物质分解 (葡萄糖降解形成的有机酸) 和碱性代谢物质分解 (蛋白质降解产生的NH3) 会导致污泥pH降低和升高[77]。H2S主要由高温阶段污泥中的含硫化合物大量分解产生,同时伴随堆体pH升高[78]。当pH升至8.5时,H2S脱质子化为不易挥发的HS−[79]。此时的污泥呈碱性,还可中和部分H2S,并抑制SRB生长,减少H2S释放[80]。尽管DMDS和DMS是堆肥过程最主要的VOSCs[81],占总VSCs的80%以上,但其对气味的贡献小于H2S[74]。
2) VNCs。NH3排放浓度最大 (6 mg·kg−1以上) [76],占污泥堆肥所释放恶臭浓度的90%以上[82]。但受污泥性质的影响,其释放量会具有明显差异。如不同来源的生污泥与厌氧消化污泥脱水后进行堆肥累积的NH3排放量分别为0.04和0.23 g·kg−1,推测是消化污泥中易生物降解形式的氮初始含量较高所致[83]。对NH3释放规律的研究发现,堆体pH较高时,易造成大量NH3生成和挥发[77];高温阶段升高温度,NH3排放近指数增长[83];而提高堆肥含水率、降低通风速率可有效阻抑NH4+聚积与NH3释放[77]。相比于NH3,胺类物质对人体危害更大,在极低浓度下即可引发人类的嗅觉刺激。LAZAROVA等[82]发现,VSCs和TMA是堆肥过程中主要的恶臭物质,其次才是排放浓度最大的NH3。而堆肥过程中与TMA相关的鱼腥味只在堆肥初始阶段被检测到[84]。
3) 其他恶臭物质。在堆肥过程中还检测到芳香化合物、萜类、醛类、酮类和VFAs等恶臭物质[85]。其中,土臭素的释放量可作为污泥堆肥稳定化的指标[86]。大多数恶臭物质的释放量随堆肥温度的升高而增加[87];通风不足或污泥含水量较高会形成厌氧条件,进而产生VOCs和VFAs[72]。
2.5 污泥干化过程
简单的机械脱水并不能满足污泥处理要求,可采用干化技术实现污泥深度脱水[88]。污泥干化处理中,微生物活性在高温下受抑制,挥发性物质主要通过各种恶臭前体物的物理化学作用产生和释放。经不同前处理的污泥进行干化时,产臭特征会存在明显差异。如MURTHY等[15]对比了4种不同性质污泥进行干化的恶臭释放特征,发现在恶臭释放浓度、感官特征、持久性及强度方面均存在显著差异。
1) VSCs。污泥干化释放的VSCs有H2S、COS、MT、DMS、DMDS和CS2[15,89]。H2S释放分为2个阶段,当温度低于临界温度时,随着水分的蒸发,溶解在水中或吸附在污泥颗粒表面的经硫酸盐还原和含硫有机物脱硫形成的H2S被释放;当温度大于或等于临界温度时,含水率大大降低,使原本吸附在污泥颗粒表面的含硫有机物充分受热,导致H2S释放量急剧增加[90-91]。污泥pH对H2S释放也具有直接影响,中酸性污泥H2S的释放量远大于碱性污泥[91]。
2) VNCs。NH3释放量可达恶臭气体总浓度的88%[82],主要发生在干化早期,由游离氨、碳酸氢铵和蛋白质等物质的受热分解产生。NH3释放和水分挥发同时发生,存在于不同形态水中的氨,随污泥中游离水、毛细水和吸附水的蒸发而被释放[92]。溶于水的NH3可与酸性物质 (CO2、脂肪酸) 反应,转化为不挥发的NH4+ (如碳酸氢铵) 。碳酸氢铵热稳定极差,在污泥干化过程中几乎全部分解为NH3[93]。虽然NH3的释放随温度升高而增加,但当污泥含水率降低到一定程度时,其释放量会明显降低[94]。有机胺不仅是重要恶臭物质还是恶臭前体物。在高温干化条件下 (300~500 ℃) ,污泥中蛋白质裂解产生的有机胺可再通过脱氨和脱氢作用产生NH3[95]。
3) 其他恶臭物质。苯系物和VFAs也是污泥干化过程释放的主要VOCs,其释放量分别可达VOCs的50%~75%和15%~30%[96]。苯系物中各组分释放量的大小与污泥中含有的苯系物浓度呈正相关关系,升高温度会促进其释放[97]。VFAs主要有甲酸、乙酸和丙酸,可通过有机物 (如脂类) 的水热处理过程形成[98]。而在干化早期,VFAs排放量显著增加,但随含水量的下降而逐渐降低[94]。
污泥干化技术和机械脱水技术会对污泥性质造成明显改变,从而影响污泥在后续处置过程的恶臭特征。对比经不同脱水方式的厌氧消化污泥用于森林土地改良时两周内的恶臭释放特征,发现具有相似物理、化学和微生物特性的压滤和离心脱水污泥森林土地改良时释放的主要恶臭物质是NH3和DMDS,同时还释放少量DMS、CS2、TMA、丙酮和甲基乙基酮;而具有尘状结构和高表面积的干化污泥森林土地改良一周后的微生物活性远高于另2种污泥,两周内恶臭污染也更为严重;除上述物质外,还会释放硫醇和VFAs[99]。
2.6 污泥焚烧处置过程
随着土地资源的减少及能源需求的增加,焚烧被认为是一种相对成熟的城市污泥无害化处置技术[100]。有机物在高温焚烧过程中被完全氧化,产臭问题相对较轻。因此,目前对此过程污染物排放的研究主要集中在常规大气污染物 (氮氧化物、硫氧化物) 、重金属和多环芳烃等,对恶臭气体的研究相对较少[101]。亦有研究指出污泥焚烧工艺会释放NH3、H2S、TMA和乙醛等恶臭物质[101-102]。
2.7 污泥填埋过程
尽管填埋不能实现对污泥的资源化利用,但过去几十年来仍是常见的工业污泥和市政污泥处置方式。目前,常将浓缩污泥与其他固体废物混合进行填埋[103]。混合填埋的污泥和其他有机废物在厌氧条件下分解产生的气体主要为甲烷和CO2,还包括醇类、烃类、卤代化合物和CS2等成分复杂的挥发性物质。尽管这些物质含量通常低于总排放量的1% (体积分数) ,但仍会形成恶臭[104-105]。通常,污泥填埋区NH3的释放量最大,但典型恶臭物质为VSC、有机酸及部分VOCs (胺类和醛类) 等[106-107]。DINCER等[104]比较了土耳其伊兹密尔垃圾填埋场5月和9月不同类型的气味源,发现污泥填埋区域释放的恶臭气体以卤代化合物、酮类和醛类化合物为主;9月份时由于氢氧化钙的加入及长时间高温蒸发使得VFAs、酯类和卤代化合物浓度降低。
2.8 其他处置过程
土地利用和建材利用也是常见污泥处置方式。若污泥持续释放恶臭会严重影响污泥的资源化利用可接受度。污泥土地利用过程的恶臭释放特征受污泥性质和施用场地的影响。如对厌氧消化污泥和经厌氧消化的碱性稳定污泥土地利用时的恶臭释放特征进行研究时发现了DMDS、DMS、CS2、二甲基三硫醚、苯系物、萜烯和烷烃的释放,其中DMDS和二甲基三硫醚是主要的恶臭物质,但未发现NH3和含氮化合物的释放[108]。由于污泥中可能含有重金属、病原体和有毒有害有机物等污染物,土地利用可能造成土壤污染、植物毒性等对人类和环境产生风险的问题,因此污泥的农田施用被严格限制[109]。利用脱水污泥改良盐碱化土壤,污泥释放的恶臭气体有NH3、H2S、MT、DMDS和DMS;施用一周后释放的NH3和H2S质量浓度分别为0.18和0.0076 mg·m−3,均低于《居住区大气中有害物质的最高容许浓度》 (TJ36-79) [110]。
污泥建材利用是将污泥干燥后,与粘土等硅铝原料充分混合,经过加热或烧制等工艺后制成水泥、砖和陶瓷颗粒等[111]。在此过程中,污泥会释放恶臭气体,对环境造成影响。粘土和污泥制成的陶瓷砖在烧结过程中会释放乙酸、乙腈、丙酮、CS2、二氯甲烷和MT等VOCs,但只有MT超过其嗅阈值,相对于污泥焚烧等其他过程产臭较轻[112]。也有研究将污泥与硅铝建筑材料混合,制备具有“大尺度-中尺度-小尺度-微尺度”结构的多尺度复合颗粒,可解决污泥用作建筑材料过程中VSCs释放和其他气味问题[111]。
3. 污泥恶臭污染的减排控制措施及相关工艺研发应用现状
污泥不同处理与处置过程释放的关键恶臭物质在成分组成上具有一定相似性,差异主要体现在各组分相对含量上。VSCs、VNCs和部分VOCs作为关键致臭物质通常具有高浓度稳定排放和低浓度波动排放2种模式;而部分污染物化学性质较不稳定,可发生转化,从而改变恶臭污染的特征。因此,解析识别关键污染物和污染特征是确定污泥恶臭治理方案的核心科学问题,并确保得出有针对性的恶臭污染治理手段。
污泥恶臭污染减排措施主要有4个方面:一是源头减量,即在恶臭产生的源头采取有效措施控制恶臭物质的形成;二是过程控制,通过恶臭收集、工艺优化与设备优选尽可能抑制恶臭气体的生成和泄露;三是末端处理,处理已产生的恶臭气体使其达标排放;四是排放管理,通过排放标准的制定实施实现对污染减排效果的最终管理和控制。现阶段,污泥恶臭气体的控制大多借鉴其他领域研究成果,尚处于发展的初级阶段,仍需不断加以完善、补充。源头减量与过程控制可有效遏制污泥处理处置过程中恶臭气体的生成与排放,从根本上更高效地解决污泥恶臭污染问题,而排放管理则是从系统管理的角度保证污泥恶臭污染防控全流程的实施质量。恶臭的有效控制需要从这4个方面协同开展,才能系统上解决污泥的恶臭污染问题。
3.1 源头减量
热水解、机械预处理、酶预处理、化学调理和超声波技术等预处理技术可通过提高污泥稳定化效果从而减少污泥恶臭释放。热水解预处理通过在厌氧消化前对污泥施加高温 (140~170 ℃) 和高压 (600~900 kPa) ,以增强消化器的处理能力,从而实现污泥有机质的更深度降解,在工业中广泛应用了20多年仍在不断发展[113-114]。虽然厌氧消化过程中仍不能避免恶臭物质的产生,但脱水的高级厌氧消化污泥常以土霉味为主,其恶臭程度明显降低[62]。化学调理主要以提高污泥脱水效率为主要目的,兼顾减臭控臭功能。常用调理剂及其对污泥减臭控臭作用模式见表2[115]。虽然加入石灰[116]、FeCl3[116]、氧化钙[117]、明矾[118]和微生物菌剂[119]等调理剂在不同程度上可降低恶臭排放,但JOHNSTON等[57]将过氧化氢、泻盐和高锰酸钾等调理剂加入已脱水的厌氧消化污泥中,发现没有一种调理剂对减缓污泥暂存和储存期间恶臭气体的释放有效。因此,如何在保证调理效能的基础上有效减少调理过程及后续工艺中的污泥恶臭气体释放,仍需开展进一步研究。
序号 作用模式 调理剂 1 降低蛋白质生物利用度,降解蛋白质 明矾、亚硝酸盐、硫酸铁、泻盐 2 作为电子受体,促进缺氧条件下的降解 硝酸钙、硝酸钾 3 与硫化物、硫醇和蛋白质结合 FeCl3 4 抑制微生物活性,提高pH 石灰、灰 5 提高产甲烷菌活性 甲醇、生物增强剂 6 氧化有机物和恶臭物质 过氧化氢、高锰酸钾、次氯酸钙、次氯酸钠 7 吸附 活性炭、环糊精 除通过减量污泥有机质和调控介质环境条件参数外,还可通过添加微生物菌剂调整污泥微生物群落结构来改善恶臭释放。如将耐热科恩氏菌LYH-2 (Cohnella thermotolerans LYH-2) 接种到污泥中能有效控制H2S排放,并促进污泥堆肥腐熟[120]。近年来,微曝气技术、联合预处理技术也被应用于污泥处理以提高处理效能。微曝气技术应用于厌氧消化系统时,可强化污泥有机质水解、增强稳定化效果,从而减少H2S产生[121]。对污泥储槽中的浓缩污泥进行曝气可抑制产臭细菌的活性,从而减少VSCs等恶臭气体的释放[122]。超声波联合芬顿氧化预处理技术通过超声波处理促进了羟基自由基与污泥中H2S及含硫化合物的反应,使S2−浓度下降了1倍、SO42−浓度增加了近1倍,可有效减少污泥潜在的恶臭释放[123]。此外,化学调理与机械预处理技术进行联用也能显著降低污泥VSCs的释放[124]。然而,由于污泥密度和粘度较高,上述技术可能存在传质阻力带来的技术难点。因此,污泥恶臭的源头减量技术仍需进一步理论研究和应用验证。
3.2 过程控制
1) 臭气收集。臭气收集系统需考虑管道选型、加盖密封和送风方式等。密闭式结构的构筑物或设备,设置抽风管道进行废气捕集即可。如规模较大的堆肥厂 (大于10 000~20 000 t·a−1) 应采用配备臭气处理系统的封闭式操作;而规模较小的堆肥厂可采用半透性覆盖层减少堆体恶臭释放或采用抽真空系统收集处理废气[125]。地上式臭气收集管道常选用玻璃钢材质,而地下式臭气收集管道往往选用不锈钢、内壁玻璃钢外壁混凝土或内壁玻璃钢外壁不锈钢材质[126]。对于需加盖密封以防止恶臭气体逃逸的构筑物或设备,主要的结构形式有钢筋混凝土顶板加盖、轻型骨架覆面加盖和钢支撑反吊膜结构加盖[127]。如污泥浓缩池一般采用钢筋混凝土顶板加盖,根据不同的直径和设备的差异,其加盖方式主要有钢筋混凝土盖板结合侧面推拉窗、玻璃钢盖板和钢支撑反吊氟碳纤膜[127]。送气方式分为适合密封效果好 (如除臭一体化设备) 的正压送气和密封效果略差 (如除臭滤池) 的负压送气[126]。
泄漏检测和修复 (leak detection and repair,LDAR) 技术是一种无组织VOCs控制技术,在石化行业广泛应用。该技术可对装备VOCs泄漏浓度实施定性或定量检测,及时修复发现的泄漏点,从而减少VOCs泄漏排放[128]。针对LDAR技术在4个炼油厂的应用发现,通过修复42%~81%的泄漏组件,VOCs排放量减少了42%~57%[129]。
2) 工艺优化。污泥停留时间、通风强度和剪切力等工艺参数会直接或间接影响含水率、温度和pH等污泥的性质参数及工艺环境,进而影响甚至直接决定污泥的产臭特征。如污泥厌氧消化停留时间为10 d和40 d时,污泥释放的VOSCs相较于生污泥分别减少了30%和50%[130]。然而,工艺参数的选择往往需要考虑综合效果,不能只针对单一的恶臭问题。如堆肥混合物料中污泥比例增加会导致NH3和H2S排放量增加,SUN等[131]兼顾温度、NH3、H2S和碳氮比等指标对污泥、树叶和稻草的混合比例研究就发现,尽管混合比为4:1:1时NH3和H2S排放量最低,但综合而言混合比为5:1:1时,其堆肥效果最好。
3) 设备优选。脱水是污泥处理过程中典型的产臭环节。脱水设备的选型不仅会影响工艺效果,还影响污泥恶臭排放。高固相离心脱水机的气味排放潜力要高于其他脱水设备[132]。这是由于离心脱水过程较大的剪切力导致污泥絮体破坏,并释放生物可利用蛋白,促进微生物产臭[133]。同时,污泥暴露在空气中,产甲烷菌活性降低使得VOSCs的降解被抑制,进一步导致恶臭释放量增加[133]。设备的选取也不能只针对单一的恶臭问题,需要根据实际情况做出适宜的选择。带式压滤机和板框压滤机为开放式,污泥恶臭问题虽然较为严重,但可在占地面积大,地理位置偏僻的污水处理厂采用;而离心脱水机和叠螺式脱水机是全封闭运行的,对环境影响小,可在位于市区内或靠近人口密集度高的污水处理厂采用[134]。近年来,随着智能化技术的深入发展,在强制通风静态垛工艺的基础上开发了智能控制好氧高温发酵工艺,对发酵过程中温度、氧气和臭气进行实时在线监测,并根据发酵状态进行反馈控制,代表了好氧发酵技术的发展方向[135]。秦皇岛市绿港污泥处理厂采用上述工艺进行实时在线监测和软件智能化控制,可有效控制H2S和NH3的大量产生和释放[136]。
3.3 末端处理
1) 物理法处理。物理除臭法包括吸附法、液体吸收法和大气稀释扩散法等。吸附法适合处理低浓度、高净化要求的恶臭气体。其中,活性炭吸附法应用最为广泛,对VSCs的去除效果较好,但对VNCs的去除效果则稍差[12]。因此,目前研究集中在VSCs (尤其是H2S) 上,对VNCs和其他VOCs的关注较少[137]。泥炭、沸石、硅和污泥衍生吸附剂等也用于恶臭吸附[138],但有关吸附技术的研究重点是催化及改性活性炭技术。在活性炭吸附法基础上开发出的催化活性炭除臭技术将H2S和氧吸附在其表面并进行氧化,生成SO42−及少量SO32−和S,同时将NH3转化为NO3−或NO2−,对H2S、NH3及整体的臭气去除率分别为97.9%、86.7%和87.4%[139]。催化活性炭除臭技术对低浓度、多组分的恶臭气体具有较好的处理效果,但同样存在对除VSCs外的恶臭物质去除效果一般的缺点。活性炭吸附法的另一发展方向是通过对普通活性炭改性,制备出吸附性及稳定性更优良的活性炭材料。液体吸收法适合处理大气量、高浓度的臭气,具有简单、安全、可回收和低成本的优点,但目前大多采用不进行溶剂回收的工艺进行VOCs净化,因此寻找具有低挥发性、高热稳定性和可再利用的吸收剂是该技术的重点[140]。大气稀释扩散法将恶臭气体由烟囱排向大气,通过大气的稀释扩散以及氧化反应降低恶臭浓度[141],适用于处理中、低浓度有组织排放的恶臭气体,常与其他处理技术联用实现废气有组织达标排放。
2) 化学法处理。化学除臭法主要有化学洗涤法、化学氧化法、催化氧化法和直接燃烧法和催化低温燃烧法等。化学洗涤法是污水处理厂中最常用的恶臭减排技术之一[142],适用于处理大气量、高浓度的恶臭气体,如污泥稳定、干化和焚烧过程所产生的恶臭等。化学洗涤法通过使用酸液或碱液可有效去除NH3或H2S,但难以去除DMS、DMDS和CS2等疏水性VOCs[138]。而物理-化学溶剂法是目前处理天然气中VOSCs和酸性气体的常见方法[143],寻找脱除有机硫的稳定高效配方组份是其重要的发展方向。化学氧化法通过使用次氯酸钠、过氧化氢和高锰酸钾等氧化剂对还原性臭气物质进行处理[144]。如高锰酸钾等氧化剂已被用于处理小规模堆肥过程中产生的气味,低浓度的氧化剂直接散布在堆肥堆上,可杀死和抑制微生物,并随使用浓度改变堆肥过程[145]。直接燃烧法通过高温热解恶臭气体,较适合处理高浓度、高热值的废气,但初期设备投资较大,在城市污水除臭中应用较少[146]。在化学氧化法和直接燃烧法的基础上,通过使用催化剂开发了加快还原性臭气氧化速度的催化氧化法和降低臭气燃烧温度的催化低温燃烧法。然而,催化剂多为贵金属,其活性随使用时间逐渐下降甚至失活[141],延长高价催化剂的使用寿命是催化氧化法和催化低温燃烧法的关键。
近年来,一些高级氧化技术 (低温等离子技术和UV光催化技术) 被开发应用于恶臭治理领域。宁平团队[147]发现,在直流电晕放电等离子体反应器中,COS和H2S的化学键被破坏后通过自由电子、氧化自由基和臭氧进一步氧化为含碳化合物 (CO和CO2) 及含硫化合物 (S、SO2和SO42−) ,COS和H2S去除率分别为90%和98%。然而,低温等离子体技术存在电耗高和安全性等问题,在VOCs污染治理领域曾一度禁止使用或单一使用,目前应用相对较少。对北京某污水处理厂收集的臭气采用光催化技术进行处理,发现光催化剂比例WO3:TiO2为3.2:1时,对硫化物的去除率可超过90%[148]。而UV光氧化和光催化氧化技术存在停留时间短和氧化不彻底等问题,更适合于和其他技术联用。总的来说,物理或化学法存在运行费用高及二次污染的风险,很少单独应用。
3) 生物法处理。生物除臭法利用微生物将恶臭物质代谢成无臭无害的产物,如CO2、水、硫酸盐和硝酸盐。该技术具有成本低、操作简单、绿色安全等优点,是物理或化学法的替代方法[149],亦是污水处理厂最常用的除臭技术[150]。配备了恶臭处理系统的城镇污水处理厂有78%采用了生物除臭法。常规生物除臭法包括生物过滤法、生物滴滤法和生物洗涤法[151],可分别去除无量纲亨利系数等于或小于10、1和0.01的气态污染物[149]。
生物过滤法最早被应用于生物除臭[151],在污水处理厂恶臭治理中应用最为广泛[152],适用于去除流量大、浓度低的废气,对水溶性差的污染物去除效果较好[149]。如对NH3、H2S和甲苯3种混合污染物进行处理,去除率分别可达到98%、100%和40%[153]。相比于国外,国内对含氮恶臭有机污染物的研究还比较少,我国学者研究发现生物过滤法对TMA的去除率可达99%以上[154]。然而,生物过滤法处理H2S和有机物时会产生酸性物质,导致微生物活性抑制、填料酸化及设备腐蚀的问题,故需要对pH进行有效控制。此外,恶臭物质净化往往需要不同类型的微生物。如降解NH3和H2S的微生物通常为自养型,异养细菌易于降解亲水性物质,而真菌降解疏水性物质具有较大优势[155]。但传统生物过滤法常采用单一反应器,不同类型的微生物难以共存并共同发挥作用,去除物质类型及能力有限。因此,目前许多工艺采用两段生物除臭法进行恶臭治理。相比于生物过滤法,生物滴滤系统的结构更简单,建设和运行成本更低,对易导致生物系统酸化的VSCs的处理效果更好,但对水溶性较差的废气去除效果稍差,适用于处理质量浓度不高于500 mg·m−3的VOCs[156]。相较于以上2种生物除臭法,生物洗涤法可避免生物质增长导致填料堵塞的风险[149],对流量大、污染物质量浓度大于500 mg·m−3的恶臭气体及亲水性物质 (如醇、醛和脂肪酸) 处理效果更好,但对水溶性差的污染物去除效果较差,可通过在液相中加入吸收剂、吸附剂和生物表面活性剂等促进对烷烃等疏水化合物的去除[156]。
总的来说,上述生物除臭法仍存在滤床易堵塞、疏水性污染物处理效果不好或微生物活性易受影响等问题[156]。因此,有研究者提出采用活性污泥扩散法替代生物滤池等基于介质的处理系统,将收集的恶臭气体喷入污水处理厂的曝气池,通过吸收、吸附、冷凝及好氧微生物的生物降解作用处理恶臭气体[157];并针对疏水性物质开发了真菌生物反应器、膜生物反应器及双液相生物反应器[158];向生物滤池接种从富含H2S的土壤和污泥中筛选出的嗜酸氧化硫硫杆菌AZ11 (Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans AZ11) 后,H2S的去除率达99.9%[159]。目前,生物除臭技术研究仍集中于高效生物降解菌的筛选、反应器中物质传质效率提升、新型填料研发和反应器内部微生态调控等方面[156-158]。
4) 联用技术。单一除臭技术很难满足越来越严格的臭气排放标准,因此,合理采用多种恶臭控制技术形成较强的协同效应进行综合处理是进一步发展趋势。采用的联用技术一般以生物法为主,物理/化学法为辅。其中,活性炭吸附-生物联用技术 (如活性炭与生物滴滤法联用技术) 是污水处理厂中常用的恶臭控制方法,对处理高疏水性恶臭物质 (90%~99%) 方面具有优异性能[152,160]。然而,较高的吸附系统投资成本和运行费用,以及恶臭物质的复杂性和可变性仍是联用技术创新和应用的主要挑战。此外,两段生物除臭法联用、化学洗涤法-生物联用技术等也被广泛应用到污水处理厂中。近年来,有研究人员尝试将各种新兴处理技术与传统方法联用于恶臭废气处理,如非热等离子体-生物滴滤池联用、非热等离子体-UV光解联用等[161-162]。
3.4 排放管理
目前,我国专门针对污泥恶臭污染执行的是《恶臭污染排放标准》 (GB14554—1993) ,其中规定了NH3、TMA、H2S、DMS、DMDS、MT、CS2和苯乙烯8种典型恶臭物质的排放限值。此外,还有一些地方、行业或污水处理企业的大气污染排放标准对恶臭指标有排放要求。但值得注意的是,这些标准的执行虽然在一定程度上缓解了恶臭污染造成的不利影响,但频发的民众投诉表明部分标准所规定的内容或限值已不能满足当前恶臭污染复杂形势的需要。
4. 展望
1) 我国污泥处理处置技术路线已形成“厌氧消化-土地利用”、“好氧堆肥-土地利用”、“干化焚烧-灰渣填埋或建材利用”和“深度脱水-应急填埋”四个主流方案。这些处理处置技术路线的实施都不能忽视恶臭污染问题。由于污泥恶臭物质的浓度低、成分复杂,准确的定性定量分析和影响评价比较困难,限制了对不同处理处置过程中污泥恶臭污染物释放规律的认识。因此,建立更先进的分析方法,将多种分析手段有机结合,从感官评价和仪器分析的不同角度表征恶臭的污染特征,准确识别关键的恶臭物质,是确定污泥恶臭治理方案的核心科学问题,对于研发污泥减臭控臭技术措施具有重要科学意义。
2) 污泥产臭特征与污泥性质密切相关,受环境条件的影响,微生物代谢发挥着尤其重要的作用。然而由于研究手段的限制和重视程度的不足,人们对污泥产臭机制的认识还非常有限。在准确识别关键恶臭物质的基础上,利用基因测序技术、PCR核酸技术等微生物分子生态学技术,深入理解不同处理和处置过程中污泥微生物介导的恶臭物质转化途径及相关机理,对认识污泥的产臭机制具有重要的理论意义,可为污泥恶臭的源头减排提供更可靠的科学依据。
3) 完整的污泥恶臭控制技术路线应从源头减量、过程控制、末端治理和排放管理四个方面综合考虑,其中应以源头减量和过程控制为主,最大限度减少恶臭释放和后续处理的压力。末端治理技术方面,化学洗涤法和生物过滤法仍是我国污泥恶臭治理的主要手段。但在实际的工程应用上,需要根据污泥恶臭释放特征、周边环境及除臭要求,针对性地选择一种或多种方法结合应用,有效提高恶臭综合去除效果。通过提高调理剂效能、调整污泥处理工艺运行参数和优化运行工况等手段从源头上减少污泥恶臭产生,开发应用新型除臭技术及联用技术,协调发挥各个环节的减臭控臭调控作用,实现污泥恶臭污染有效控制。在排放管理方面,由于我国恶臭污染防治事业起步较晚,有关污泥恶臭污染控制的技术方法和标准等还远远不够,需进一步进行研究并加强恶臭污染立法。
-
表 1 污泥处理处置过程中主要的恶臭物质嗅阈值及气味特征[11]
Table 1. Odor threshold and sensory properties during sludge treatment and disposal[11]
分类 物质名称 分子式 感官性质 嗅阈值/(mg·m−3) 含硫化合物 硫化氢 H2S 臭鸡蛋味 0.001 8 甲硫醇 CH3SH 烂菜心气味 0.000 1 二甲基硫醚 (CH3)2S 海鲜腥味 0.005 5 二甲基二硫醚 (CH3)2S2 洋葱味 0.046 3 含氮化合物 氨 NH3 强烈刺激性气味 0.227 7 三甲胺 (CH3)3N 鱼腥味 0.002 4 酸类 丙酸 CH3CH2COOH 刺激性气味 0.028 8 正丁酸 C3H7COOH 汗味、酸臭味 0.005 1 醛类 乙醛 CH3CHO 刺激性气味 0.035 4 丙醛 CH3CH2CHO 水果香味 0.041 5 苯系物 甲苯 C7H8 芳香气味 0.403 1 乙苯 C8H10 芳香气味 0.085 3 苯乙烯 C8H8 塑料味 0.158 1 对二甲苯 C8H10 芳香气味、水果香味 0.568 7 -
[1] 戴晓虎, 张辰, 章林伟, 等. 碳中和背景下污泥处理处置与资源化发展方向思考[J]. 给水排水, 2021, 57(3): 1-5. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2021.03.001 [2] 戴晓虎. 我国污泥处理处置现状及发展趋势[J]. 科学, 2020, 72(6): 30-34. [3] CARRERA-CHAPELA F, DONOSO-BRAVO A, SOUTO J A, et al. Modeling the odor generation in WWTP: an integrated approach review[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2014, 225(6): 1-15. [4] 史昕龙, 陈绍伟. 城市污水污泥的处置与利用[J]. 环境保护, 2001(3): 45-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9705.2001.03.016 [5] JIANG G, MELDER D, KELLER J, et al. Odor emissions from domestic wastewater: A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 47(17): 1581-1611. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2017.1386952 [6] LEWKOWSKA P, CIEŚLIK B, DYMERSKI T, et al. Characteristics of odors emitted from municipal wastewater treatment plant and methods for their identification and deodorization techniques[J]. Environmental research, 2016, 151: 573-586. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.08.030 [7] KARAGEORGOS P, LATOS M, KOTSIFAKI C, et al. Treatment of unpleasant odors in municipal wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2010, 61(10): 2635-2644. doi: 10.2166/wst.2010.211 [8] 郭静, 梁娟, 匡颖, 等. 污水处理厂恶臭污染状况分析与评价[J]. 中国给水排水, 2002, 18(2): 41-42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2002.02.012 [9] BONNIN C, LABORIE A, PAILLARD H. Odor nuisances created by sludge treatment: problems and solutions[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1990, 22(12): 65-74. doi: 10.2166/wst.1990.0101 [10] DINCER F, MUEZZINOGLU A. Odor-causing volatile organic compounds in wastewater treatment plant units and sludge management areas[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 2008, 43(13): 1569-1574. doi: 10.1080/10934520802293776 [11] 王亘, 翟增秀, 耿静, 等. 40种典型恶臭物质嗅阈值测定[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(6): 348-351. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2015.06.072 [12] 杨庆, 李洋, 崔斌, 等. 城市污水处理过程中恶臭气体释放的研究进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(7): 2079-2087. [13] FISHER R M, LE-MINH N, SIVRET E C, et al. Distribution and sensorial relevance of volatile organic compounds emitted throughout wastewater biosolids processing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599: 663-670. [14] FISHER R M, LE-MINH N, ALVAREZ-GAITAN J P, et al. Emissions of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) throughout wastewater biosolids processing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616: 622-631. [15] MURTHY S, KIM H, PEOT C, et al. Evaluation of Odor Characteristics of Heat‐Dried Biosolids Product[J]. Water environment research, 2003, 75(6): 523-531. doi: 10.2175/106143003X141312 [16] SIRONI S, CAPELLI L, CÉNTOLA P, et al. Odour impact assessment by means of dynamic olfactometry, dispersion modelling and social participation[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2010, 44(3): 354-360. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.10.029 [17] LEHTINEN J, VEIJANEN A. Odour monitoring by combined TD–GC–MS–Sniff technique and dynamic olfactometry at the wastewater treatment plant of low H2S concentration[J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2011, 218(1): 185-196. [18] 唐小东, 王伯光, 赵德骏, 等. 城市污水处理厂的挥发性恶臭有机物组成及来源[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(4): 576-583. [19] KIM H, LEE H, CHOI E, et al. Characterization of odor emission from alternating aerobic and anoxic activated sludge systems using real-time total reduced sulfur analyzer[J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 117: 394-401. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.08.008 [20] 申翰彰. 城市污水处理厂污泥处理过程中恶臭气体排放特征和净化研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2020. [21] KIM H, MURTHY S, PEOT C, et al. Examination of mechanisms for odor compound generation during lime stabilization[J]. Water Environment Research, 2003, 75(2): 121-125. doi: 10.2175/106143003X140908 [22] 刘璐, 陈同斌, 郑国砥, 等. 污泥堆肥厂臭气的产生和处理技术研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2010, 26(13): 120-124. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2010.13.033 [23] CUI G, BHAT S A, LI W, et al. H2S, MeSH, and NH3 emissions from activated sludge: An insight towards sludge characteristics and microbial mechanisms[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2022, 166: 105331. [24] HIGGINS M J, CHEN Y C, YAROSZ D P, et al. Cycling of volatile organic sulfur compounds in anaerobically digested biosolids and its implications for odors[J]. Water Environment Research, 2006, 78(3): 243-252. doi: 10.2175/106143005X90065 [25] 吴伟霞, 席北斗, 黄彩红, 等. 有机固废堆肥中产臭及除臭技术的微生物作用机制研究进展[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(10): 2486-2496. doi: 10.13198/j.issn.1001-6929.2021.05.38 [26] SUFFET I H, BURLINGAME G A, ROSENFELD P E, et al. The value of an odor-quality-wheel classification scheme for wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(4): 25-32. doi: 10.2166/wst.2004.0211 [27] 李冬娜, 马晓军. 污泥厌氧发酵产酸机理及应用研究进展[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2020, 54(2): 51-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2020.02.008 [28] 沈玉君, 陈同斌, 刘洪涛, 等. 堆肥过程中臭气的产生和释放过程研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2011, 27(11): 104-108. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2011.11.036 [29] GOLUEKE C G, OSWALD W J. Biological conversion of light energy to the chemical energy of methane[J]. Applied microbiology, 1959, 7(4): 219-227. doi: 10.1128/am.7.4.219-227.1959 [30] WATTS S F. The mass budgets of carbonyl sulfide, dimethyl sulfide, carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2000, 34(5): 761-779. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00342-8 [31] 李若愚. 城市污水处理厂恶臭气体排放特征与扩散规律研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2021. [32] KELESSIDIS A, STASINAKIS A S. Comparative study of the methods used for treatment and final disposal of sewage sludge in European countries[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(6): 1186-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.01.012 [33] PARK M S, KISO Y, JUNG Y J, et al. Sludge thickening performance of mesh filtration process[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(8): 125-133. doi: 10.2166/wst.2004.0505 [34] HAN Z, QI F, LI R, et al. Health impact of odor from on-situ sewage sludge aerobic composting throughout different seasons and during anaerobic digestion with hydrolysis pretreatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249: 126077. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126077 [35] 黄力华, 刘建伟, 夏雪峰, 等. 城市污水处理厂典型气体污染物产生特性研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(3): 295-299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2015.03.059 [36] 眭光华, 李建军, 孙国萍. 城市污水处理厂恶臭污染源调查与研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2008, 2(3): 399-402. [37] RAS M R, BORRULL F, MARCÉ R M. Determination of volatile organic sulfur compounds in the air at sewage management areas by thermal desorption and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2008, 74(4): 562-569. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.06.017 [38] ZARRA T, NADDEO V, BELGIORNO V, et al. Instrumental characterization of odour: a combination of olfactory and analytical methods[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 59(8): 1603-1609. doi: 10.2166/wst.2009.125 [39] ZARRA T, NADDEO V, BELGIORNO V, et al. Odour monitoring of small wastewater treatment plant located in sensitive environment[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2008, 58(1): 89-94. doi: 10.2166/wst.2008.330 [40] FRECHEN F B. Odour emission inventory of German wastewater treatment plants-odour flow rates and odour emission capacity[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 50(4): 139-146. doi: 10.2166/wst.2004.0244 [41] LEITE W R M, GOTTARDO M, PAVAN P, et al. Performance and energy aspects of single and two phase thermophilic anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 86: 1324-1331. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2015.09.069 [42] MURTHY S, FORBES B, BURROWES P, et al. Impact of high shear solids processing on production of volatile sulfur compounds from anaerobically digested biosolids[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2002, 2002(9): 64-75. doi: 10.2175/193864702784162741 [43] YAN W, XU H, LU D, et al. Effects of sludge thermal hydrolysis pretreatment on anaerobic digestion and downstream processes: mechanism, challenges and solutions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 344: 126248. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126248 [44] KIM J, NOVAK J T, HIGGINS M J. Multistaged anaerobic sludge digestion processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011, 137(8): 746-753. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EE.1943-7870.0000372 [45] CHEN D, SZOSTAK P. Factor analysis of H2S emission at a wastewater lift station: a case study[J]. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 2013, 185(4): 3551-3560. doi: 10.1007/s10661-012-2809-4 [46] MURTHY S N, PEOT C, NORTH J, et al. Characterization and control of reduced sulfur odors from lime stabilized and digested biosolids[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2002, 2002(3): 1105-1124. doi: 10.2175/193864702785302195 [47] KACKER R. Identification and generation pattern of odor-causing compounds in dewatered biosolids during long-term storage and effect of digestion and dewatering techniques on odors[M]. Blacksburg: Virginia Tech, 2011. [48] LI X, CHEN S, DONG B, et al. New insight into the effect of thermal hydrolysis on high solid sludge anaerobic digestion: Conversion pathway of volatile sulphur compounds[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 244: 125466. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125466 [49] HAN Z, LI R, SHEN H, et al. Emission characteristics and assessment of odors from sludge anaerobic digestion with thermal hydrolysis pretreatment in a wastewater treatment plant[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 274: 116516. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116516 [50] WU G, PARKER W J. Development of a structured model for odour formation and emissions from anaerobic sludge digestion[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2004, 2004(11): 237-253. doi: 10.2175/193864704784136180 [51] LOMANS B P, VAN DER DRIFT C, POL A, et al. Microbial cycling of volatile organic sulfur compounds[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences CMLS, 2002, 59(4): 575-588. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8450-6 [52] VERMA N, PARK C, NOVAK J T, et al. Effects of anaerobic digester sludge age on odors from dewatered biosolids[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2006, 2006(12): 1119-1141. doi: 10.2175/193864706783749864 [53] FISHER R, BARCZAK R, GAITAN J P A, et al. Comparing static headspace and dynamic flux hood measurements of biosolids odour emissions[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2016, 54: 43-48. [54] ROSENFELD P E, HENRY C L, BENNETT D. Wastewater dewatering polymer affect on biosolids odor emissions and microbial activity[J]. Water environment research, 2001, 73(3): 363-367. doi: 10.2175/106143001X139380 [55] SPOELSTRA S F. Origin of objectionable odorous components in piggery wastes and the possibility of applying indicator components for studying odour development[J]. Agriculture and Environment, 1980, 5(3): 241-260. doi: 10.1016/0304-1131(80)90004-1 [56] CHEN Y C, HIGGINS M, MURTHY S, et al. Production of odorous indole, skatole, p-cresol, toluene, styrene, and ethylbenzene in biosolids[J]. Journal of Residuals Science and Technology, 2006, 3(4): 193-202. [57] JOHNSTON T, HIGGINS M, BRANDT R, et al. Effect of amendment addition on biosolids odors based on gas chromatography analysis and odor panel observations[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2009: 607-626. [58] MATHUS T L, TOWNSEND D E, MILLER K W. Anaerobic biogenesis of phenol and p-cresol from L-tyrosine[J]. Fuel, 1995, 74(10): 1505-1508. doi: 10.1016/0016-2361(95)00109-I [59] NOVAK J T, MURTHY S, HIGGINGS M J, et al. Ten years of odor research on biosolids-what have we learned[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2012, 2012(3): 527-541. doi: 10.2175/193864712811700633 [60] SHANKER R, BOLLAG J M. Transformation of indole by methanogenic and sulfate-reducing microorganisms isolated from digested sludge[J]. Microbial ecology, 1990, 20(1): 171-183. doi: 10.1007/BF02543875 [61] MA Q, MENG N, LI Y, et al. Occurrence, impacts, and microbial transformation of 3-methylindole (skatole): A critical review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 416: 126181. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126181 [62] GAO W, YANG X, ZHU X, et al. The variation of odor characteristics of wastewater sludge treated by advanced anaerobic digestion (AAD) and the contribution pattern of key odorants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022: 156722. [63] LIU S, ZHU N, LI L Y. The one-stage autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion for sewage sludge treatment: stabilization process and mechanism[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 104: 266-273. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.041 [64] DEMIRBAS A, COBAN V, TAYLAN O, et al. Aerobic digestion of sewage sludge for waste treatment[J]. Energy Sources, Part A:Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2017, 39(10): 1056-1062. doi: 10.1080/15567036.2017.1289282 [65] GANCZARCZYK J, HAMODA M F, WONG H L. Performance of aerobic digestion at different sludge solid levels and operation patterns[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(6): 627-633. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90120-7 [66] FISHER R M, BARCZAK R J, STUETZ R M. Identification of odorant characters using GC-MS/O in biosolids emissions from aerobic and anaerobic stabilisation[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2018, 2017(3): 736-742. doi: 10.2166/wst.2018.245 [67] LAYDEN N M, MAVINIC D S, KELLY H G, et al. Autothermal thermophilic aerobic digestion (ATAD)—Part I: Review of origins, design, and process operation[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering and Science, 2007, 6(6): 665-678. doi: 10.1139/S07-015 [68] BOWKER R P G, TRUEBLOOD R. Control of ATAD odors at the Eagle River Water and Sanitation District[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2002, 2002(5): 277-287. doi: 10.2175/193864702785139935 [69] WONG J W C, FANG M. Effects of lime addition on sewage sludge composting process[J]. Water Research, 2000, 34(15): 3691-3698. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00116-0 [70] MENG L, LI W, ZHANG S, et al. Effects of sucrose amendment on ammonia assimilation during sewage sludge composting[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 210: 160-166. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.094 [71] ZHU Y, ZHENG G, GAO D, et al. Odor composition analysis and odor indicator selection during sewage sludge composting[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2016, 66(9): 930-940. [72] MAULINI-DURAN C, ARTOLA A, FONT X, et al. A systematic study of the gaseous emissions from biosolids composting: Raw sludge versus anaerobically digested sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 147: 43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.118 [73] LI Y, LI W. Nitrogen transformations and losses during composting of sewage sludge with acidified sawdust in a laboratory reactor[J]. Waste Management & Research, 2015, 33(2): 139-145. [74] HAN Z, QI F, WANG H, et al. Emission characteristics of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) from a municipal sewage sludge aerobic composting plant[J]. Waste Management, 2018, 77: 593-602. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.05.049 [75] ZHAO S, YANG X, ZHANG W, et al. Volatile sulfide compounds (VSCs) and ammonia emission characteristics and odor contribution in the process of municipal sludge composting[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2019, 69(11): 1368-1376. [76] HAN Z, QI F, WANG H, et al. Odor assessment of NH3 and volatile sulfide compounds in a full-scale municipal sludge aerobic composting plant[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 282: 447-455. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.062 [77] LIANG Y, LEONARD J J, FEDDES J J, et al. A simulation model of ammonia volatilization in composting[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 2004, 47(5): 1667. doi: 10.13031/2013.17609 [78] 李明峰, 马闯, 赵继红, 等. 污泥堆肥臭气的产生特征及防控措施[J]. 环境工程, 2014, 32(1): 92-96. [79] ROSENFELD P E, SUFFET I H. Understanding odorants associated with compost, biomass facilities, and the land application of biosolids[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2004, 49(9): 193-199. doi: 10.2166/wst.2004.0569 [80] 翁焕新, 高彩霞, 刘瓒, 等. 污泥硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)与硫化氢释放[J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(10): 2094-2102. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.10.012 [81] SCHIAVON M, MARTINI L M, CORRÀ C, et al. Characterisation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released by the composting of different waste matrices[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 845-853. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.096 [82] LAZAROVA V, BOUCHY L, SENANTE E, et al. Fingerprint of odour creation potential of sludge treatment[J]. Water Practice and Technology, 2008, 3(4): wpt2008082. doi: 10.2166/wpt.2008.082 [83] PAGANS E, BARRENA R, FONT X, et al. Ammonia emissions from the composting of different organic wastes. Dependency on process temperature[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 62(9): 1534-1542. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.06.044 [84] MEL SUFFET I H, DECOTTIGNIES V, SENANTE E, et al. Sensory assessment and characterization of odor nuisance emissions during the composting of wastewater biosolids[J]. Water Environment Research, 2009, 81(7): 670-679. doi: 10.2175/106143008X390762 [85] EPSTEIN E, BOYETTE A, WU N. Odors and volatile organic compound emissions from composting facilities[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2000, 2000(3): 789-810. doi: 10.2175/193864700785303394 [86] LI H F, IMAI T, UKITA M, et al. Compost stability assessment using a secondary metabolite: Geosmin[J]. Environmental Technology, 2004, 25(11): 1305-1312. doi: 10.1080/09593332508618374 [87] KROGMANN U, BOYLES L S, MARTEL C J, et al. Biosolids and sludge management[J]. Water environment research, 1997, 69(4): 534-550. doi: 10.2175/106143097X134830 [88] LOWE P. Developments in the thermal drying of sewage sludge[J]. Water and Environment Journal, 1995, 9(3): 306-316. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-6593.1995.tb00944.x [89] WANG Y, WANG F, JI M. Characteristics of Emitted Odor and Discharged Condensate Water of Sludge Thermal Drying Project in Shenzhen Nanshan Thermal Power Plant//Advanced Materials Research[J]. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2013, 777: 127-132. [90] WU M, WANG Z, ZHOU J, et al. Release characteristics and control of hydrogen sulfide during thermal drying of municipal wastewater sludge[J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2018, 20(2): 946-954. doi: 10.1007/s10163-017-0657-6 [91] WENG H, DAI Z, JI Z, et al. Release and control of hydrogen sulfide during sludge thermal drying[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 296: 61-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.037 [92] 翁焕新, 章金骏, 刘瓉, 等. 污泥干化过程氨的释放与控制[J]. 中国环境科学, 2011, 31(7): 1171-1177. [93] 刘瓒. 污泥干燥处理中典型恶臭的释放特点[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007. [94] DENG W Y, YAN J H, LI X D, et al. Emission characteristics of volatile compounds during sludges drying process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(1): 186-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.022 [95] ZHANG J, TIAN Y, CUI Y, et al. Key intermediates in nitrogen transformation during microwave pyrolysis of sewage sludge: a protein model compound study[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 132: 57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.008 [96] DING W, LI L, LIU J. Investigation of the effects of temperature and sludge characteristics on odors and VOC emissions during the drying process of sewage sludge[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2015, 72(4): 543-552. doi: 10.2166/wst.2015.246 [97] WENG H X, JI Z Q, CHU Y, et al. Benzene series in sewage sludge from China and its release characteristics during drying process[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 65(3): 561-569. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1100-2 [98] SHANABLEH A, JONES S. Production and transformation of volatile fatty acids from sludge subjected to hydrothermal treatment[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2001, 44(10): 129-135. doi: 10.2166/wst.2001.0600 [99] ROSENFELD P E, HENRY C L, DILLS R L, et al. Comparison of odor emissions from three different biosolids applied to forest soil[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 2001, 127(1): 173-191. [100] ZHANG J, SUN G, LIU J, et al. Co-combustion of textile dyeing sludge with cattle manure: Assessment of thermal behavior, gaseous products, and ash characteristics[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 253: 119950. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119950 [101] LIANG Y, XU D, FENG P, et al. Municipal sewage sludge incineration and its air pollution control[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021: 126456. [102] SEO B S, JEON Y H. A Study on the Odor and Ventilation in Sludge Incineration Facilities[J]. Journal of the Korea Safety Management and Science, 2020, 22(2): 7-13. [103] O’KELLY B C. Sewage sludge to landfill: Some pertinent engineering properties[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2005, 55(6): 765-771. [104] DINCER F, ODABASI M, MUEZZINOGLU A. Chemical characterization of odorous gases at a landfill site by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A, 2006, 1122(1-2): 222-229. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2006.04.075 [105] ALLEN M R, BRAITHWAITE A, HILLS C C. Trace organic compounds in landfill gas at seven UK waste disposal sites[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 1997, 31(4): 1054-1061. [106] FANG J J, YANG N, CEN D Y, et al. Odor compounds from different sources of landfill: characterization and source identification[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(7): 1401-1410. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2012.02.013 [107] GAO S, ZHAO P, LI Y, et al. Characterization and influence of odorous gases on the working surface of a typical landfill site: A case study in a Chinese megacity[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2021, 262: 118628. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2021.118628 [108] LAOR Y, NAOR M, RAVID U, et al. Odorants and malodors associated with land application of biosolids stabilized with lime and coal fly ash[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2011, 40(5): 1405-1415. doi: 10.2134/jeq2010.0033 [109] LI S, ZHANG K, ZHOU S, et al. Use of dewatered municipal sludge on Canna growth in pot experiments with a barren clay soil[J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29(6): 1870-1876. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.12.007 [110] 王维思. 污泥改良盐碱化土壤臭气逸散研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012. [111] FAN H, LI L, LI Z, et al. Structure of sewage sludge-clay multiscale composite particles to control the mechanism of SO2 and H2S gas release[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(5): 1855. doi: 10.3390/ma15051855 [112] CREMADES L V, SORIANO C, CUSIDÓ J A. Tackling environmental issues in industrial ceramic sintering of sewage sludge: Odors and gas emissions[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2018, 20(4): 1651-1663. doi: 10.1007/s10668-017-9958-0 [113] PHOTHILANGKA P, SCHOEN M A, WETT B. Benefits and drawbacks of thermal pre-hydrolysis for operational performance of wastewater treatment plants[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2008, 58(8): 1547-1553. doi: 10.2166/wst.2008.500 [114] NGO P L, UDUGAMA I A, GERNAEY K V, et al. Mechanisms, status, and challenges of thermal hydrolysis and advanced thermal hydrolysis processes in sewage sludge treatment[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 281: 130890. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130890 [115] FISHER R M, ALVAREZ-GAITAN J P, STUETZ R M. Review of the effects of wastewater biosolids stabilization processes on odor emissions[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49(17): 1515-1586. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2019.1579620 [116] HIGGINS M J, MURTHY S N, NOVAK J T, et al. Effect of chemical addition on production of volatile sulfur compounds and odor from anaerobically digested biosolids[C]//Proceedings of Water Env. Fed. 75th Annual Conference. 2002. [117] VEGA E, MONCLUS H, GONZALEZ-OLMOS R, et al. Optimizing chemical conditioning for odour removal of undigested sewage sludge in drying processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2015, 150: 111-119. [118] GRUCHLIK Y, FOUCHÉ L, JOLL C A, et al. Use of alum for odor reduction in sludge and biosolids from different wastewater treatment processes: Gruchlik et al[J]. Water Environment Research, 2017, 89(12): 2103-2112. doi: 10.2175/106143017X15054988926406 [119] TEPE N, YURTSEVER D, DURAN M, et al. Odor control during post-digestion processing of biosolids through bioaugmentation of anaerobic digestion[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2008, 57(4): 589-594. doi: 10.2166/wst.2008.008 [120] CHEN L, LI W, ZHAO Y, et al. Isolation and application of a mixotrophic sulfide-oxidizing Cohnella thermotolerans LYH-2 strain to sewage sludge composting for hydrogen sulfide odor control[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 345: 126557. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126557 [121] NGUYEN D, KHANAL S K. A little breath of fresh air into an anaerobic system: How microaeration facilitates anaerobic digestion process[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2018, 36(7): 1971-1983. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2018.08.007 [122] LUO H, ZHANG D, TAYLOR M, et al. Aeration in sludge holding tanks as an economical means for biosolids odor control—A case study[J]. Water Environment Research, 2021, 93(10): 1808-1818. doi: 10.1002/wer.1582 [123] LIU N, GONG C, JIANG J, et al. Controlling odors from sewage sludge using ultrasound coupled with Fenton oxidation[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 181: 124-128. [124] DHAR B R, YOUSSEF E, NAKHLA G, et al. Pretreatment of municipal waste activated sludge for volatile sulfur compounds control in anaerobic digestion[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(4): 3776-3782. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.020 [125] SCHLEGELMILCH M, STREESE J, BIEDERMANN W, et al. Odour control at biowaste composting facilities[J]. Waste Management, 2005, 25(9): 917-927. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2005.07.011 [126] 许小平, 赵艳, 潘婷, 等. 污水处理厂除臭工艺收集系统的选择与分析[J]. 中国给水排水, 2012, 28(22): 54-58. [127] 王冬. 污水处理厂构筑物加盖(罩)除臭主要结构形式探讨[J]. 中国给水排水, 2010, 26(24): 47-50. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2010.24.012 [128] 张钢锋. 泄漏检测与修复(LDAR)技术在国内外的应用现状及发展趋势[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(9): 4621-4627. [129] KE J, LI S, ZHAO D. The application of leak detection and repair program in VOCs control in China’s petroleum refineries[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2020, 70(9): 862-875. [130] ERDAL Z K, FORBES JR R H, WITHERSPOON J, et al. Recent findings on biosolids cake odor reduction—Results of WERF phase 3 biosolids odor research[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A, 2008, 43(13): 1575-1580. doi: 10.1080/10934520802293792 [131] SUN X, TAN Z, HE X, et al. Initial active phase of in-vessel composting of sewage sludge, leaves and rice straw[J]. Nature Environment and Pollution Technology, 2022, 21(1): 83-90. doi: 10.46488/NEPT.2022.v21i01.009 [132] MURTHY S, HIGGINS M, CHEN Y C, et al. Influence of solids characteristics and dewatering process on volatile sulfur compound production from anaerobically digested biosolids[J]. Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation, 2003, 2003(1): 858-874. doi: 10.2175/193864703784292151 [133] CHEN Y C, HIGGINS M J, BEIGHTOL S M, et al. Anaerobically digested biosolids odor generation and pathogen indicator regrowth after dewatering[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(8): 2616-2626. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.02.014 [134] 陈丹丹, 窦昱昊, 卢平, 等. 污泥深度脱水技术研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(10): 4722-4746. [135] 陈俊, 陈同斌, 高定, 等. 城市污泥好氧发酵处理技术现状与对策[J]. 中国给水排水, 2012, 28(11): 105-108. [136] 陈俊, 高定, 陈同斌, 等. CTB污泥处理工艺的臭气控制效果研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2010, 26(9): 134-137. [137] LE-MINH N, SIVRET E C, SHAMMAY A, et al. Factors affecting the adsorption of gaseous environmental odors by activated carbon: A critical review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2018, 48(4): 341-375. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2018.1460984 [138] REN B, ZHAO Y, LYCZKO N, et al. Current status and outlook of odor removal technologies in wastewater treatment plant[J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2019, 10(6): 1443-1458. doi: 10.1007/s12649-018-0384-9 [139] 陈运进, 黄华, 温元洪, 等. 催化型活性炭除臭系统对污水泵站臭气的净化效果[J]. 中国给水排水, 2007, 23(15): 76-78. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4602.2007.15.020 [140] WANG W, MA X, GRIMES S, et al. Study on the absorbability, regeneration characteristics and thermal stability of ionic liquids for VOCs removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 328: 353-359. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.178 [141] 秦琛. 污水处理中恶臭对周边环境的污染及治理[J]. 环境工程, 2009, 27(S1): 291-293. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.2009.s1.063 [142] LEBRERO R, RODRÍGUEZ E, GARCÍA-ENCINA P A, et al. A comparative assessment of biofiltration and activated sludge diffusion for odour abatement[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 190(1/2/3): 622-630. [143] GHANBARABADI H, KHOSHANDAM B. Simulation and comparison of Sulfinol solvent performance with Amine solvents in removing sulfur compounds and acid gases from natural sour gas[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 22: 415-420. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2014.12.024 [144] DOMEÑO C, RODRÍGUEZ-LAFUENTE A, MARTOS J M, et al. VOC removal and deodorization of effluent gases from an industrial plant by photo-oxidation, chemical oxidation, and ozonization[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(7): 2585-2591. [145] BINDRA N, DUBEY B, DUTTA A. Technological and life cycle assessment of organics processing odour control technologies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 527: 401-412. [146] 沈东平, 方卫, 张甜甜. 城市污水厂除臭技术的应用综述[J]. 微生物学通报, 2009, 36(6): 887-891. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.2009.06.023 [147] WANG L, WANG X, NING P, et al. Simultaneous removal of COS, H2S, and dust in industrial exhaust gas by DC corona discharge plasma[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(18): 6568-6575. [148] LV J. Sewage odor elimination based on photocatalytic oxidation[J]. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2018, 68: 499-504. [149] BARBUSINSKI K, KALEMBA K, KASPERCZYK D, et al. Biological methods for odor treatment–A review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 152: 223-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.093 [150] SAHU S, LENKA R K. European developments for purification of biological waste gas[J]. European Journal of Molecular Clinical Medicine, 2020, 7(11): 703-708. [151] KENNES C, VEIGA M C. Technologies for the abatement of odours and volatile organic and inorganic compounds[J]. Chemic. Engin. Transac, 2010, 23: 1-6. [152] LEBRERO R, BOUCHY L, STUETZ R, et al. Odor assessment and management in wastewater treatment plants: a review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 41(10): 915-950. doi: 10.1080/10643380903300000 [153] PARK B G, SHIN W S, CHUNG J S. Simultaneous biofiltration of H2S, NH3 and toluene using an inorganic/polymeric composite carrier[J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 2008, 13(1): 19-27. doi: 10.4491/eer.2008.13.1.019 [154] 万顺刚, 李桂英, 安太成. 固定化微生物技术在大气恶臭污染物处理中应用研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(10): 1575-1584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.10.032 [155] 刘建伟, 马文林, 赵玉柱, 等. 两段生物滤池处理城市污水厂恶臭气体中试研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(8): 1825-1830. [156] 贾体沛, 王灿, 张亮, 等. 城镇污水处理厂生物除臭技术的关键影响因素及案例分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2022, 16(4): 1074-1082. [157] FAN F, XU R, WANG D, et al. Application of activated sludge for odor control in wastewater treatment plants: Approaches, advances and outlooks[J]. Water Research, 2020, 181: 115915. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2020.115915 [158] 杨凯雄, 李琳, 刘俊新. 挥发性有机污染物及恶臭生物处理技术综述[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(03): 107-111. doi: 10.13205/j.hjgc.201603022 [159] LEE E Y, LEE N Y, CHO K S, et al. Removal of hydrogen sulfide by sulfate-resistant Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans AZ11[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2006, 101(4): 309-314. doi: 10.1263/jbb.101.309 [160] SEMPERE F, GABALDÓN C, MARTÍNEZ‐SORIA V, et al. Evaluation of a combined activated carbon prefilter and biotrickling filter system treating variable ethanol and ethyl acetate gaseous emissions[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2009, 9(4): 317-323. doi: 10.1002/elsc.200900011 [161] WEI Z S, LI H Q, HE J C, et al. Removal of dimethyl sulfide by the combination of non-thermal plasma and biological process[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 146: 451-456. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.114 [162] ANDERSEN K B, FEILBERG A, BEUKES J A. Use of non-thermal plasma and UV-light for removal of odour from sludge treatment[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2012, 66(8): 1656-1662. doi: 10.2166/wst.2012.367 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: