-
根据2020年生态环境部对全国337个地级及以上城市的大气环境监测数据,环境空气质量超标的城市为135个,占全部城市数的40.1%。多数城市的首要污染物为PM10和PM2.5,年平均质量浓度分别为56 μg·m−3和33 μg·m−3[1]。扬尘污染是造成环境空气质量下降的重要因素,其主要来源包括裸露土壤、建筑施工、堆场扬尘、矿山开采、道路扬尘,以及已沉降扬尘的二次扬起等[2-3]。安欣欣等[4]在对北京城区PM2.5各组分污染特征及来源分析发现,春天风沙季扬尘源对PM2.5排放的贡献率为11%;李廷昆等[5]在研究城市扬尘污染主要成因时发现,扬尘源PM10排放量可对标其他所有人为源的排放总量。因此,扬尘污染的治理对于大气质量的提升具有重要意义。
目前,应用较广泛的抑尘手段主要有洒水抑尘、防尘网抑尘以及各类抑尘剂抑尘等[6-7]。洒水抑尘工艺简单,但效果持续时间短、操作频繁,且容易造成水资源浪费。防尘网在堆场、裸露土壤等场景应用较多,但抑尘效率较差且成本较高。相比而言,抑尘剂抑尘具有抑尘效率高、持续时间长等优势[8-9]。BAO等[10]利用丙烯酸和丙烯酰胺制备淀粉接枝共聚物,并采用化学改性法制备了一种高吸水性抑尘剂。LO等[11]研究出一种基于无毒材料的土壤稳定剂,可在土壤中形成韧性和持久的双网络,以提高土壤的机械韧性,从而抑制粉尘产生。王洁茹等[12]以海洋生物废弃物为原料制备出一种润湿性、粘结性良好的海洋生物型固土抑尘剂,与百喜草种子混合应用于黄河滩,起到了良好的固土作用和生态修复效果。
抑尘剂的研究虽已取得一定成效,但关于生态修复型抑尘剂的研究较少。我国的耕地面积广阔,农作物秸秆的总产量高达1.04×109 t,其中玉米秸秆占比高达32.5%。随着现代工业的发展,秸秆的传统应用价值被液化气、加工饲料等取代,因此被大量遗弃焚烧,造成资源浪费和环境污染。我国自2019年开始在全国范围内全面推进秸秆等生物质的资源化[13-15]。
本研究将高效抑尘和生态修复两个目标相结合,拟制备出一种常温下即可快速配制的生态修复环保型抑尘剂。以农业废弃物秸秆和绿色植物种子为主要原料,表面活性剂、碱和淀粉为抑尘剂,在抑尘固尘的同时利用种子生长实现修复。再通过粘度、分散度、表面张力等单因素指标的确定来探究各因素对抑尘剂抑尘性能的影响,以确定最优制备条件,并表征抑尘剂的结壳性能、抗风蚀与抗雨淋性能、抑尘效率和生态修复效果等,以期为绿色、可持续性的抑尘技术开发提供参考。
-
1) 制备原料。本研究抑尘剂的原料主要包括水、农业废弃物秸秆(华北地区农业固废)、淀粉(AR)、工业碱(例如NaOH (AR))、表面活性剂(AR)、草本植物种子等。
2) 制备设备。本研究实验过程中使用到的实验仪器与设备包括:精密分析天平 (BS210S) 、精密电动搅拌器(JJ-1)、粘度测定仪(Viscotester C)、全自动界面张力仪(JYW-200B)、接触角测试仪 (Dataphsics TP50) 、扫描电镜 (Hitachi S-4300) 、电热恒温鼓风干燥箱(DHG-9055A)、万能粉碎机(ZNH-180)、空压机(30L-750W)、便携式风洞(PISWERL)等。
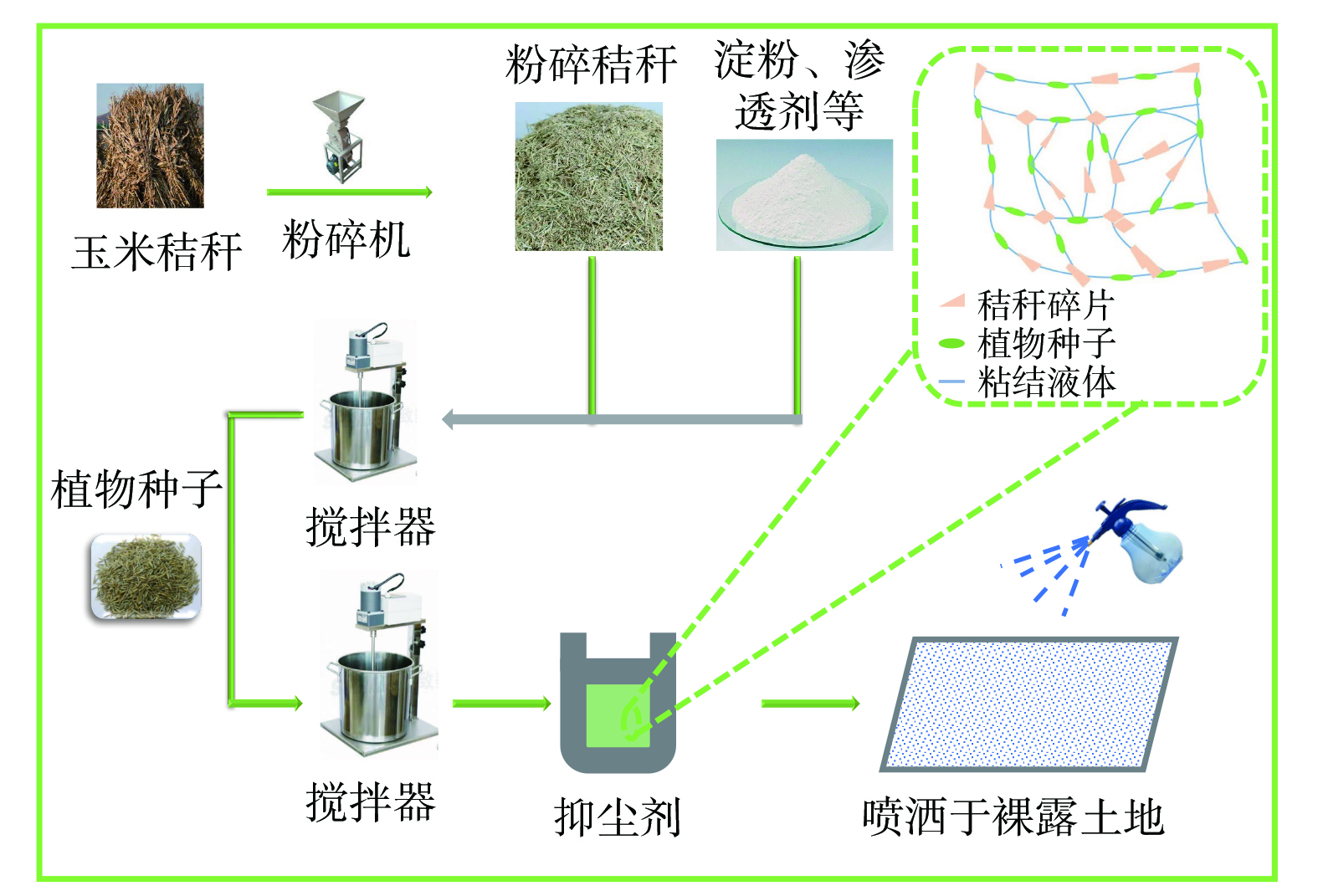
3) 制备工艺。首先用秸秆粉碎机将秸秆粉碎至2~3 mm,在容器中加入适量水,将淀粉、渗透剂、碱等按照一定质量比加入容器,待试剂充分溶解后向反应釜中加入一定质量比的秸秆碎片搅拌20 min,从而使得秸秆在碱性环境下的纤维素结构被破坏,然后将溶液与植物种子在搅拌器中混合均匀,即得到生态修复型抑尘剂。制备流程如图1所示。
-
秸秆是制备抑尘剂的主要原料,在抑尘剂中发挥链桥的作用。秸秆的加入可提高抑尘剂结壳后的强度,以增加整体结构的稳定性。同时,抑尘剂中植物种子的生长可起到生态修复效果,秸秆还可为植物种子的生长提供养料,从而同步实现有效抑尘和生态修复。
-
1) 粘度是抑尘剂的重要性能指标,用来衡量抑尘剂对于颗粒物的粘结效果。适当的粘度可增强抑尘剂分子间的联结性[16],从而使抑尘剂在喷洒后在抑尘面结壳更加紧实,以更好地发挥抑尘性能。本研究制备了一系列不同秸秆添加量的抑尘剂待测样品,采用Thermo Viscotester C 粘度测定仪测试了秸秆添加量对抑尘剂粘度的影响;选用常温下可溶解的淀粉作为抑尘剂粘结剂,向淀粉溶液中加入碱作为助剂,并对淀粉和碱的质量对抑尘剂体系粘度的影响进行了表征。
2) 抑尘剂需借助渗透剂提升其渗透性和润湿性。良好的渗透性能可增强抑尘剂在抑尘面的铺展能力,更好地与扬尘颗粒接触,从而达到抑尘目的[17]。本研究选用工业上常用的表面活性剂作为渗透剂,采用JYW-200B 全自动界面张力仪和Dataphsics TP50 接触角测试仪对溶液的表面张力和接触角进行测试。
-
在生态修复植物的选择时,首先需要遵循生态适应性、和谐性等原则,选用的植物要注意与周围环境相互协调,以保证植物形态与周围植物群落的相近性;其次,选用植物应具有耐旱、耐寒、耐热、耐贫瘠、耐盐碱、根系发达、生长周期短、成活率高等优点,从而保证在无人养护的条件下具有较强的存活力[18-20]。本研究选用了绿化植物种常见的高羊茅、胡枝子、早熟禾、紫花苜蓿、混播四季青和耐践踏四季青6种植物,将6种植物种子分别采取应用于抑尘剂后播种和直接播种的方式播种于托盘,对2种播种方式的植物生长情况及发芽周期进行记录。
-
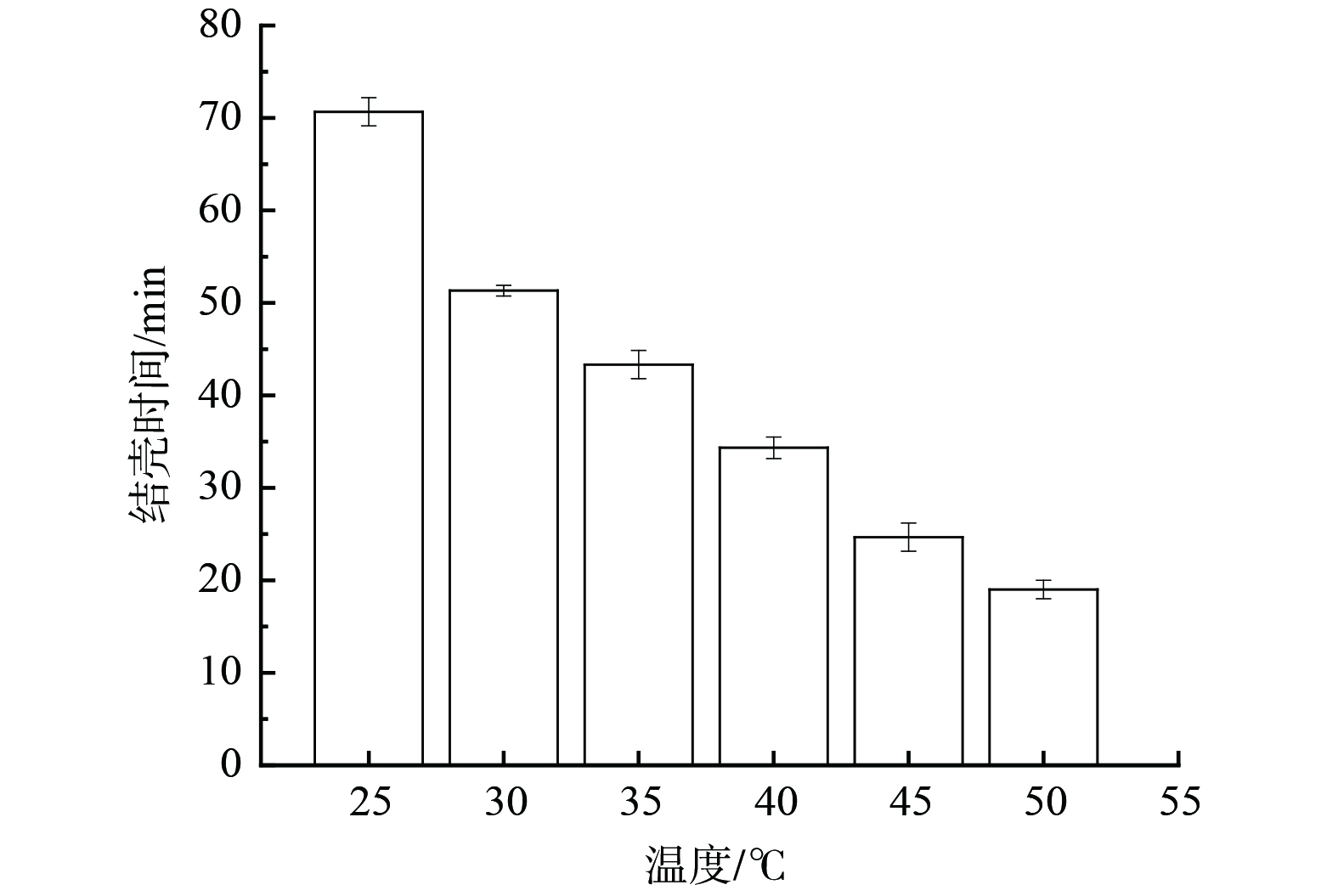
1) 结壳性能的表征。结壳时间是抑尘剂重要的应用指标之一,抑尘剂在喷洒后短时间内结壳,可在堆体表面形成一层覆盖壳体,以减少外界环境对粉尘的扰动,从而达到抑尘效果。考察了抑尘剂喷洒后在25 ℃、30 ℃、35 ℃、40 ℃、45 ℃和50 ℃温度下各表层干结成壳所需的时间,并使用扫描电镜对其结壳后的表面形貌进行了观察。
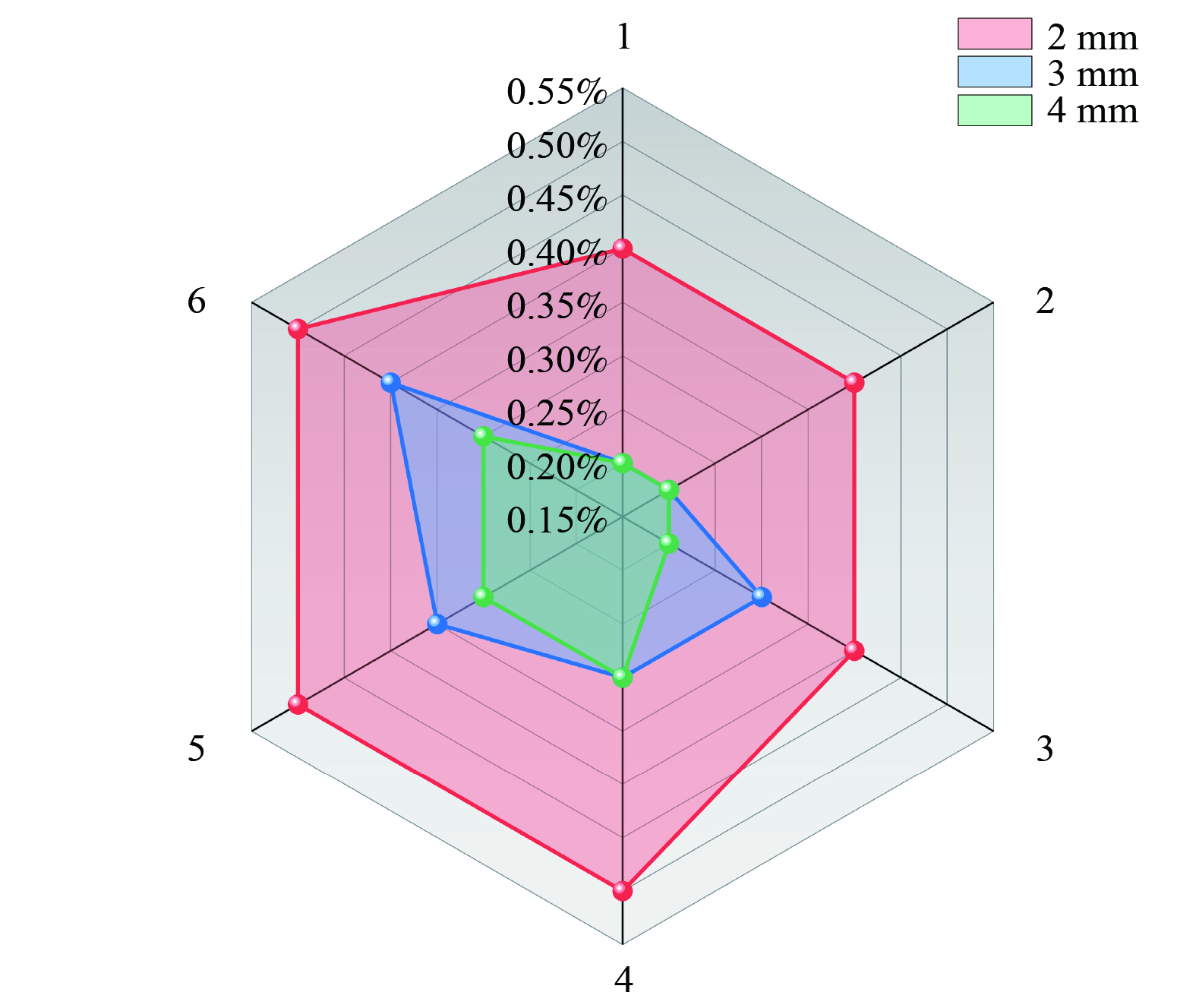
2) 抗风蚀与抗雨淋性能表征。抗风蚀性能是模拟在际应用中抑尘剂喷洒并结壳以后在大风天气下的形态变化。将尘土堆成圆锥体来模拟实际料场中的堆体,将抑尘剂以2 mm、3 mm和4 mm的喷洒厚度喷洒在圆锥体表面,待其干燥结壳后,在5级风(8~10 m·s−1)的条件下,持续吹6 h,分别记录其风蚀率。抗雨淋性能测试是模拟实际应用中抑尘剂在降雨条件下的形态变化:将尘土堆成底面直径为45 cm、高为 15 cm的圆锥体来模拟实际料场中的堆体;再将抑尘剂喷洒在堆体表面;待干燥结壳后,采用自制设备在堆体上方以均匀小孔覆盖来模拟自然降雨 (中雨条件下,即降雨量为20 mm·d−1) ;再次结壳后观察降雨前后表面形态的变化。
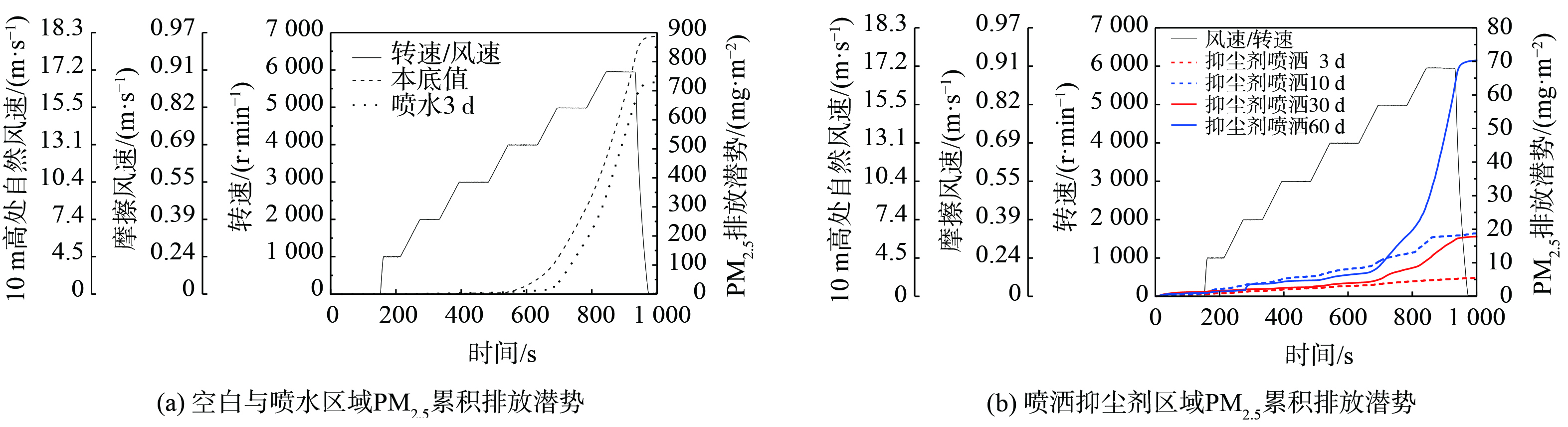
3) 抑尘效率的表征。抑尘效率是评价抑尘剂性能的重要指标。采用便携式风洞(PI-SWERL)对抑尘剂喷洒3 d、10 d、30 d和60 d后的抑尘效率进行表征,并与洒水的抑尘效率进行对比。装置由风洞腔体、旋转环、DustTrak8530智能粉尘仪、控制箱和电脑组成,如图2(a)所示。PI-SWERL可通过不同转速模拟不同等级的风在抑尘面的剪切力来侵蚀土壤释放扬尘,同时,对PM2.5质量浓度进行实时监测,并记录抑尘面的颗粒物累积排放潜势。在现场布置了5个测试区域 (1.2 m×1.2 m) ,并对测试区域表层2.5 cm的土壤进行平整以备测试,如图2(b)所示。将测试出的PM2.5累积排放潜势与喷水、未喷洒的裸地进行对比,并通过PM2.5质量浓度计算抑尘效率,计算方法如式(1)所示。
式中:
η 为抑尘效率,%;C1 为裸地区域PM2.5质量浓度,mg·m−3;Ci 为喷洒抑尘剂或水区域i天后的PM2.5质量浓度,mg·m−3。4) 生态修复效果的表征。通过研究植物生长情况发现,在植物种子中以混播四季青长势最好,其生长周期短,故选用混播四季青用于抑尘剂进行实际喷洒和生态修复效果研究。在校园内开辟了一块2 m×2 m的实验区域用于抑尘剂的喷洒,喷洒量为为2 L·m−2。观察植物的长势,如图3所示。
-
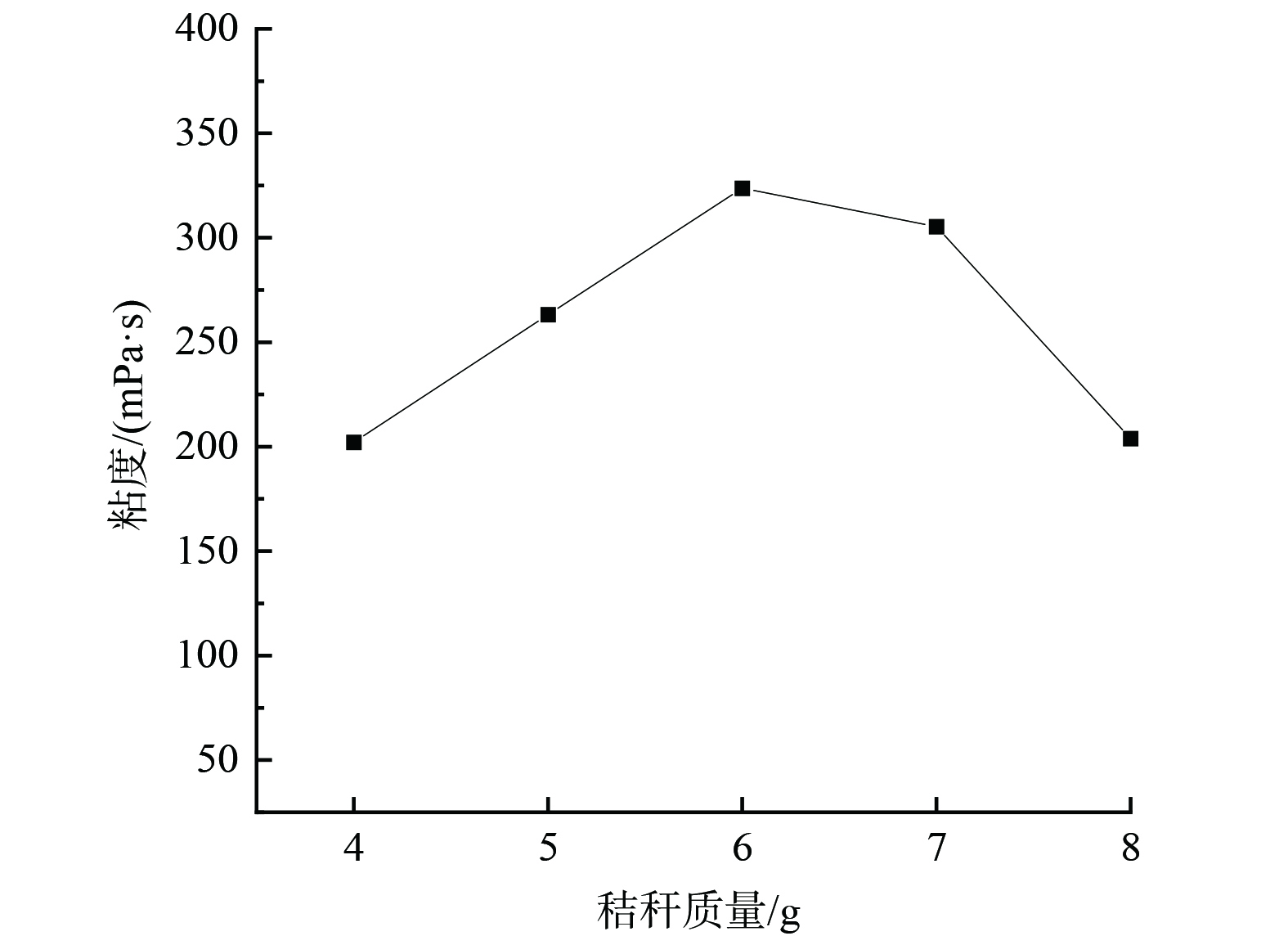
秸秆对抑尘剂性能影响测试结果如图4所示。随着秸秆质量的增加,粘度呈现出先增大后减小的趋势。这是由于秸秆的加入增强了液体分子间的交联性,因此粘度开始呈现增大的趋势。当秸秆的量继续增加,突破了交联的阈值,从而部分秸秆无法与抑尘剂液体有效交联。未交联的秸秆占据了抑尘剂分子的空间结构,因而粘度达到阈值后呈现出下降的趋势。表征结果表明,秸秆质量6 g即质量分数为2%是最佳秸秆添加量。
-
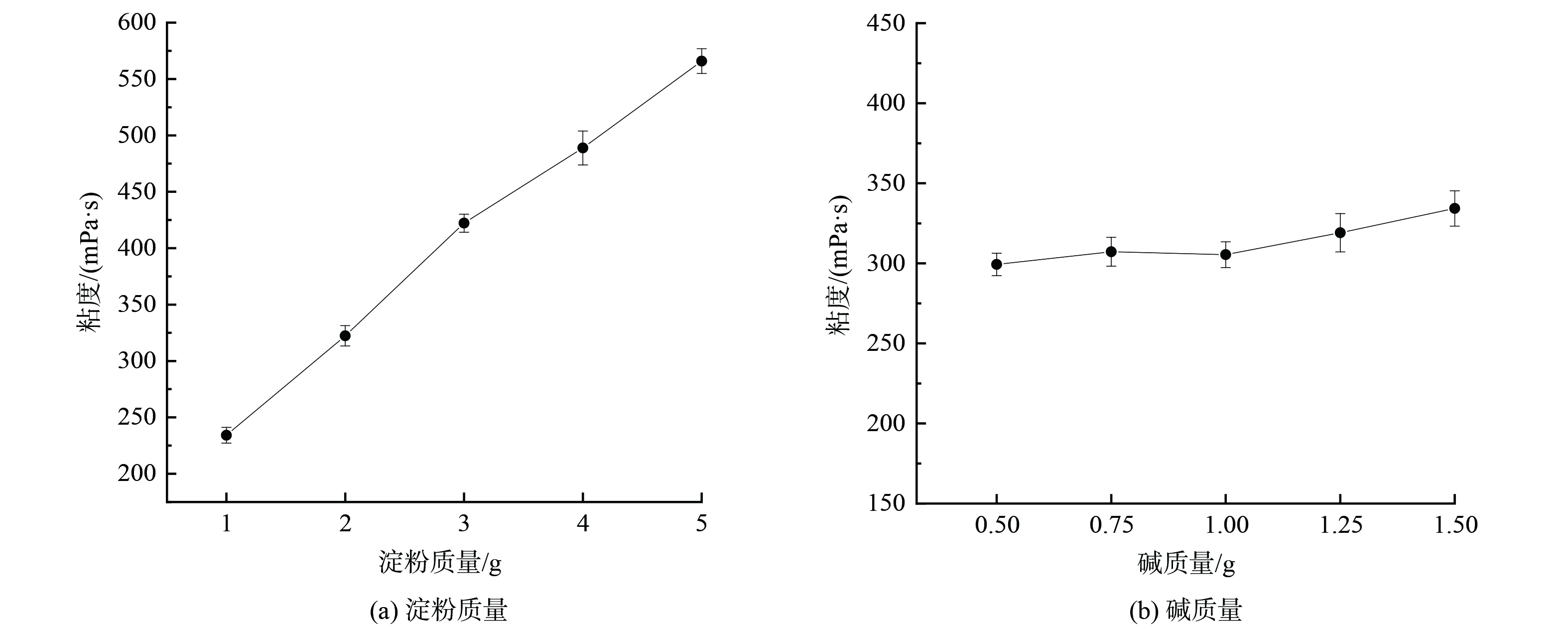
图5是粘结剂和碱对抑尘剂性能影响的测试结果。由图5(a)可知,随着淀粉质量的增加,抑尘剂的粘度越来越高。这是因为淀粉溶于水后有糊化作用,可显著增加溶液的粘度。由图5(b)可知,随着碱质量的增加,抑尘剂的粘度呈微量增加趋势,但对粘度影响有限。这是由于碱性环境有利于淀粉的水合溶解,加速纤维素化合物的降解过程,同时,碱性环境有利于秸秆纤维素结构的破坏、软化秸秆,从而增强溶液体系的韧性[21-22]。
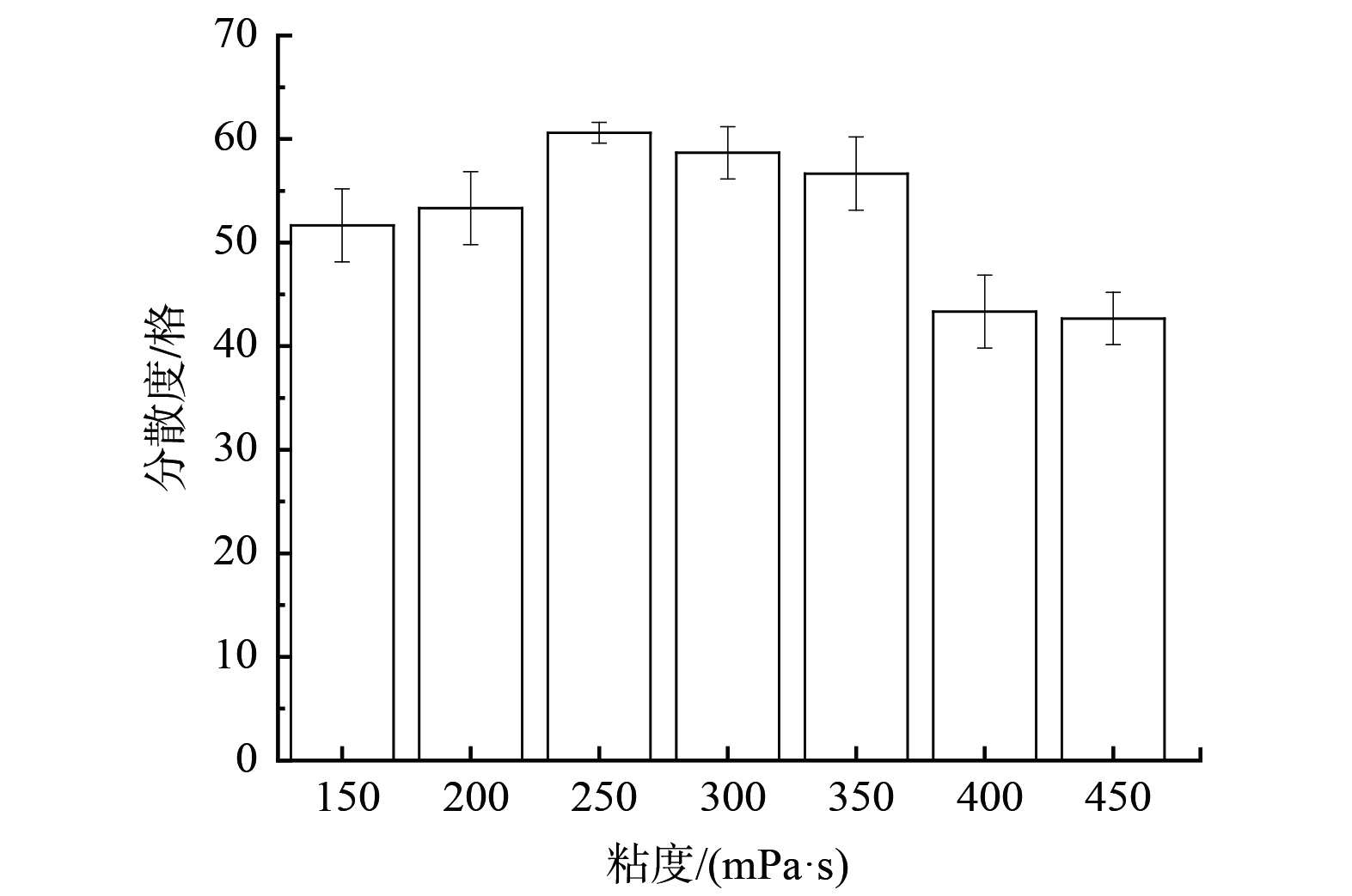
在实际应用中,适当的粘度有利于提高结壳强度、增强抑尘效果,而粘度过低或过高都不利于喷洒抑尘剂。图6表明,随着粘度的增加,分散性能先增加后降低。这是由于粘度过低会影响抑尘剂溶液整体的联结性,除不能有效粘结粉尘颗粒物外,也不能抵消秸秆在抑尘剂中的浮力,出现分层现象;粘度过高会导致抑尘剂溶液过于粘稠,影响喷洒的均匀性且易堵塞喷洒管路,降低抑尘效率。本研究中,当粘度为250~350 mPa·s时抑尘剂的分散度最好。因此,在抑尘剂制备材料中,确定淀粉的质量分数为0.7%、碱的质量分数为0.5%。
-
图7表明,随着表面活性剂质量分数的增加,溶液的表面张力和接触角呈现出先减小后趋于平缓的趋势。这是因为当表面活性剂分子进入水溶液后,疏水基与亲水基相互平衡,疏水基面向空气,亲水基插入水相;当表面活性剂分子浓度达到一定值时,分子富集在溶液表面,形成致密的界面膜,降低了表面张力[23-24]。另外,接触角越小,溶液在抑尘面的铺展能力越强,故表面活性剂的加入显著增强了抑尘剂的润湿性能,使其能有效润湿粉尘,使其粘附团聚、密度增加,从而达到抑尘目的。当达到表面活性剂的临界胶束浓度后,溶液的表面张力降至最低值,此时若再提高表面活性剂浓度只会导致体相浓度增加,而溶液表面张力不再降低[25]。在本研究中,接触角在表面活性剂质量分数为0.2%时达到拐点,此时的表面张力已达到阈值,说明此时抑尘剂具有良好的润湿性能。
-
表1表明,应用于抑尘剂后播种种子的发芽时间要晚于直接播种的种子。这是由于抑尘剂的粘度要远高于水,喷洒抑尘剂后土壤会出现结壳,从而导致该区域种子的发芽时间受到影响。图8表明,除早熟禾外,其他几种植物生长状况良好,且应用于抑尘剂后播种与直接播种种子的长势无明显差别。这说明本研究抑尘剂对于植物种子的生长无不良影响,可与多种绿色植物种子混合使用,亦可配合多种植物种子混播使用。此外,通过对植物生长情况的初步研究,在选取的植物种子中混播四季青长势最好,其生长周期短,且价格低廉,因此,初步选择混播四季青用于抑尘剂,并进行实际喷洒和生态修复效果的研究。
-
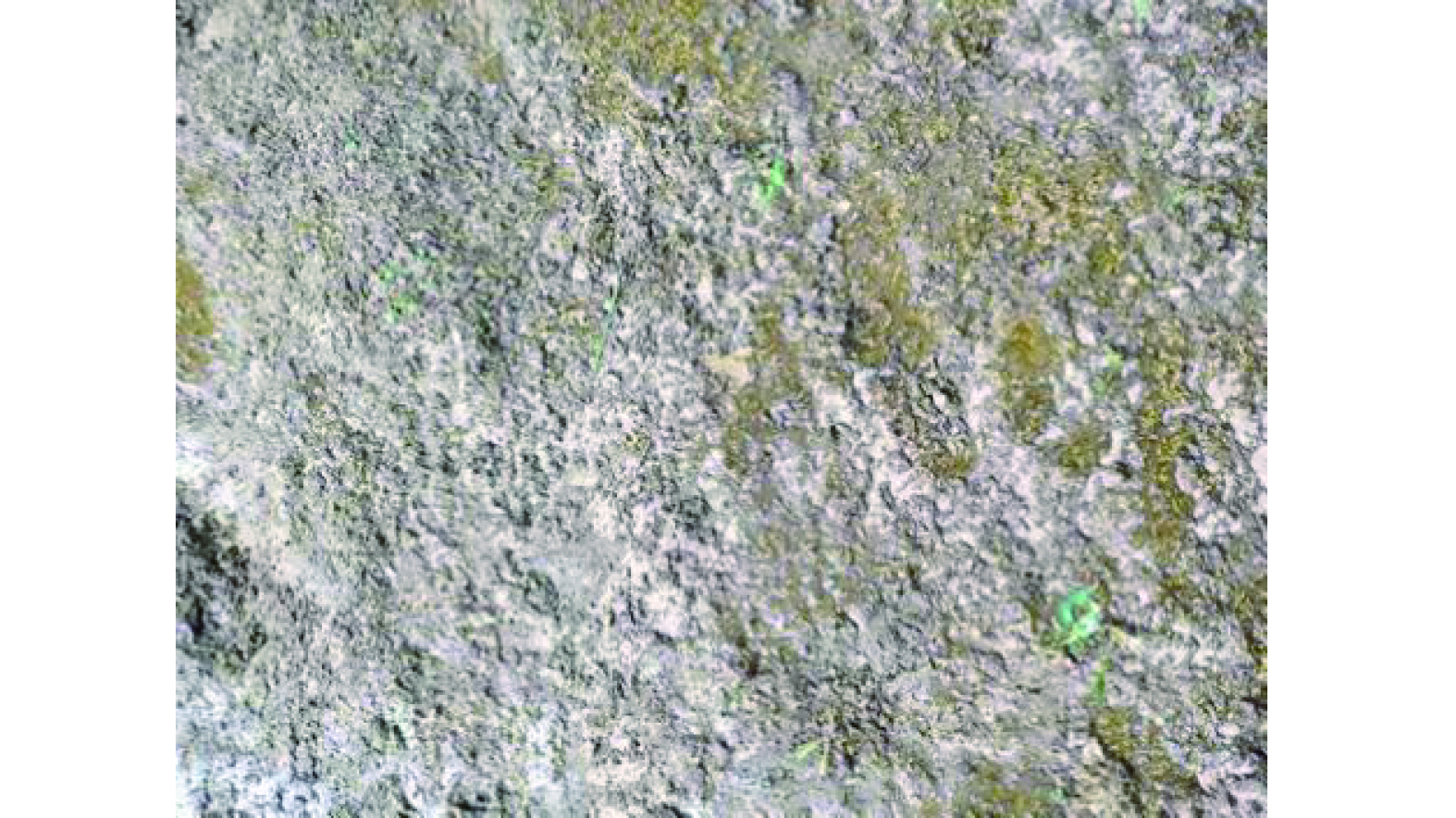
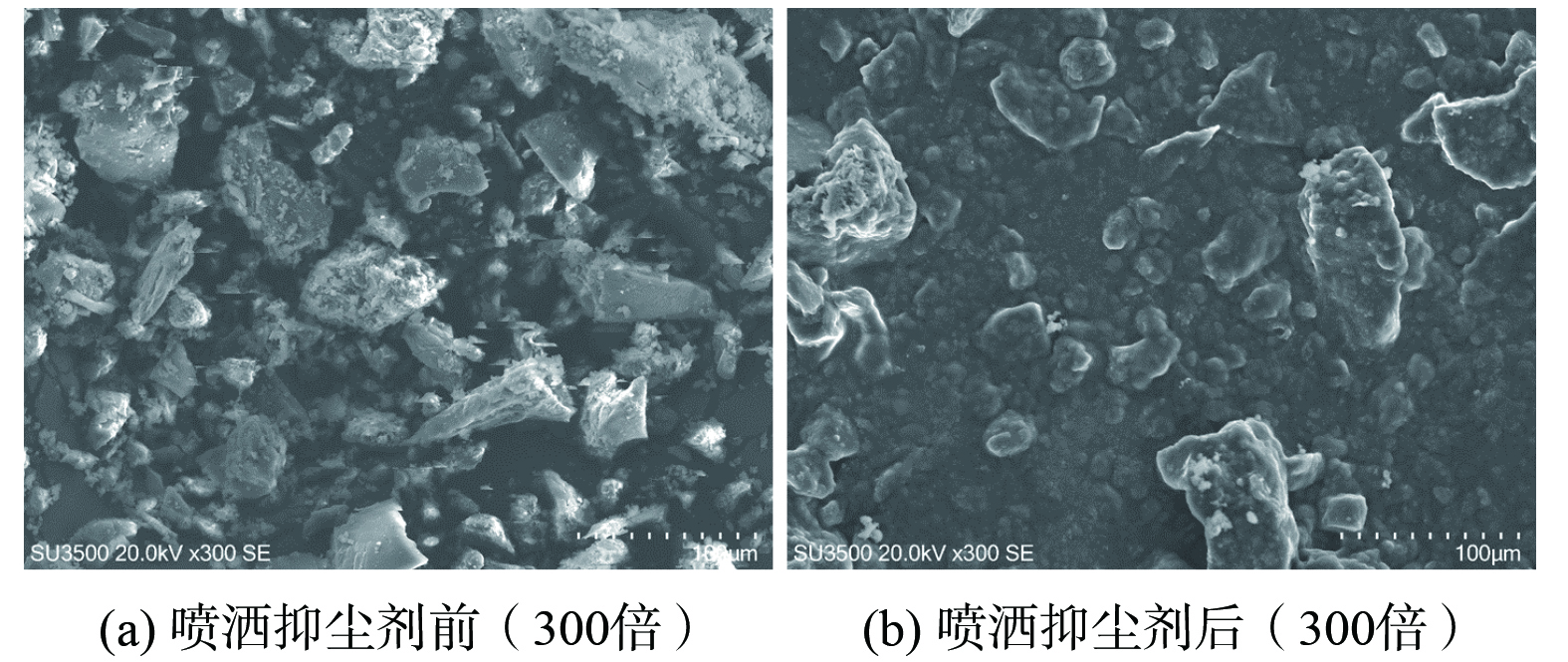
图9表明,在不同温度条件下,抑尘剂喷洒后的结壳时间会随着温度的升高而变得越来越短。在25 ℃下,结壳时间最长大于70 min;当气温在35 ℃左右时,结壳时间缩短至1 h以内;当温度达到50 ℃时,结壳时间最短,为20 min。这说明抑尘剂喷洒后可在短时间内干燥结壳,起到抑尘作用。通过扫描电镜 (SEM) 对抑尘面的微观结构表征结果(图10)发现,喷洒抑尘剂前后粉尘表面结构存在明显差异。在喷洒抑尘剂之前,粉尘总体呈现松散状态,颗粒之间存在大量间隙,缺乏致密性;在喷洒抑尘剂之后,喷施抑尘剂使得颗粒呈现紧密连接的网状结构,小颗粒粘在大颗粒上,明暗程度相对均匀,表现出较强的机械性能。这说明粉尘颗粒在表面活性剂的作用下得到了有效润湿,颗粒被黏附在抑尘面,即抑尘剂增强了整体结构的稳定性,使粉尘不易扬起。
-
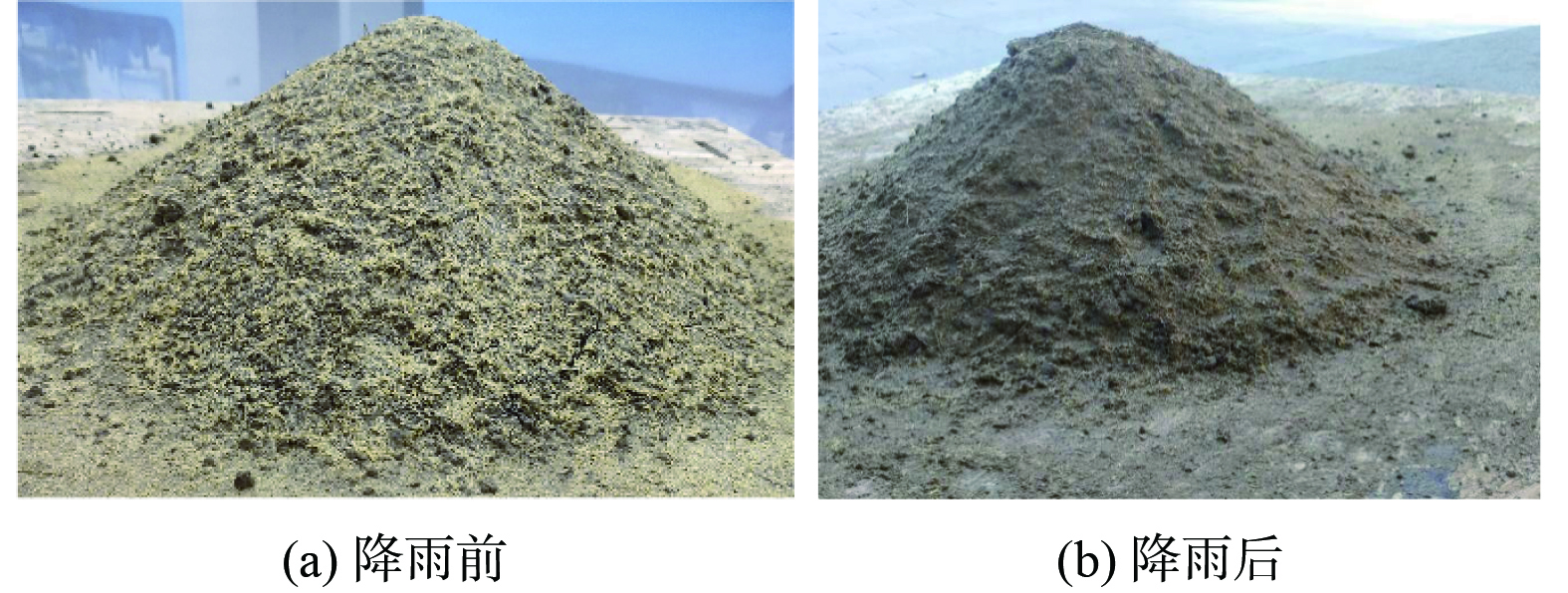
图11为抑尘剂抗风蚀性能测试结果。每条网线代表抑尘剂的风蚀率。当抑尘剂结壳后,在5级风(8~10 m·s−1)的条件下,持续吹6 h,喷洒量越厚、风蚀率越低。但3种喷洒厚度堆体风蚀率均不到1%,这说明抑尘剂干燥后形成的壳体正如SEM所示,粉尘颗粒得到有效润湿并黏附在一起,展现出较强的机械性能,具有良好的抗风蚀的能力,因此抑尘剂2 mm的喷洒厚度即可满足要求。经过在中雨条件(即降雨量为20 mm·d−1)下抗雨淋性能的测试,结果如图12所示。对比降雨前后堆体的表面形态发现,在初次干燥后堆体表层形成了一层保护壳体,壳体在经过雨淋后未出现松散现象;再次干燥后,表层壳体依旧紧实,覆盖性良好;雨淋前后壳体的厚度均为7 mm,未出现变化。这说明抑尘剂结壳后具有良好的抗雨淋性能。
-
各区域风蚀扬尘PM2.5的累计排放潜势如图13所示。空白区域在经过风洞腔体不同转速的连续侵蚀后,其PM2.5累计排放为887.07 mg·m−2,经过洒水处理的区域在相同条件下累计排放值为728.95 mg·m−2,相比于空白区域略有降低。而喷洒抑尘剂的区域PM2.5累计排放大幅降低,在喷洒3 d、10 d、30 d和60 d后,PM2.5累计排放分别为5.49 mg·m−2、17.80 mg·m−2、18.77 mg·m−2和70.27 mg·m−2。这说明PM2.5的排放得到有效控制,故抑尘剂喷洒结壳后可有效抵抗大风侵蚀。
由图13可知,在整个风蚀模拟过程中,占全年总天数约81.9%的极大风速(≤10.4 m·s−1,对应转速≤3 000 r·min−1)条件下,PM2.5累积排放潜势占总排放潜势的0.38%,而占比较小的极大风速(≥ 15.5 m·s−1s,对应转速≥ 5 000 r·min−1)条件下,对应的累积排放潜势占总排放潜势的86.91%。转速大于4 000 r·min−1后,累积排放潜势有了明显上升趋势,因此,本研究仅讨论PI-SWERL模拟极大风速≥ 13.1 m·s−1,对应转速≥ 4 000 r·min−1时,抑尘效率的变化。如表2所示,洒水的抑尘效率会随着风洞转速的提高而越来越低,当转速达到6 000 r·min−1时,抑尘效率仅为5.9%,且有效时间短;喷洒抑尘剂后,其在30 d内的抑尘效率可达99%以上,而60 d内抑尘效率略有降低,但仍可达到90%。抑尘剂的抑尘效率会随着转速的提高而增长,这是由于在低转速时,相同条件下的扬尘本底值较低,而随着转速提高,本底值出现了大幅上升,而喷洒抑尘剂的区域PM2.5浓度变化不大,因此,高转速时的抑尘效率要大于低转速时的抑尘效率。虽然风洞腔体模拟与实际抑尘场景存在差异,但所有的测试均在相同环境中进行,且检测数值稳定性好,所以能实现不同抑尘剂的抑尘效率在同一实验体系下进行比较和评价。测试结果表明,相比于相同方法测试的其他抑尘剂[26],本研究制备的抑尘剂抑尘效果更佳。
-
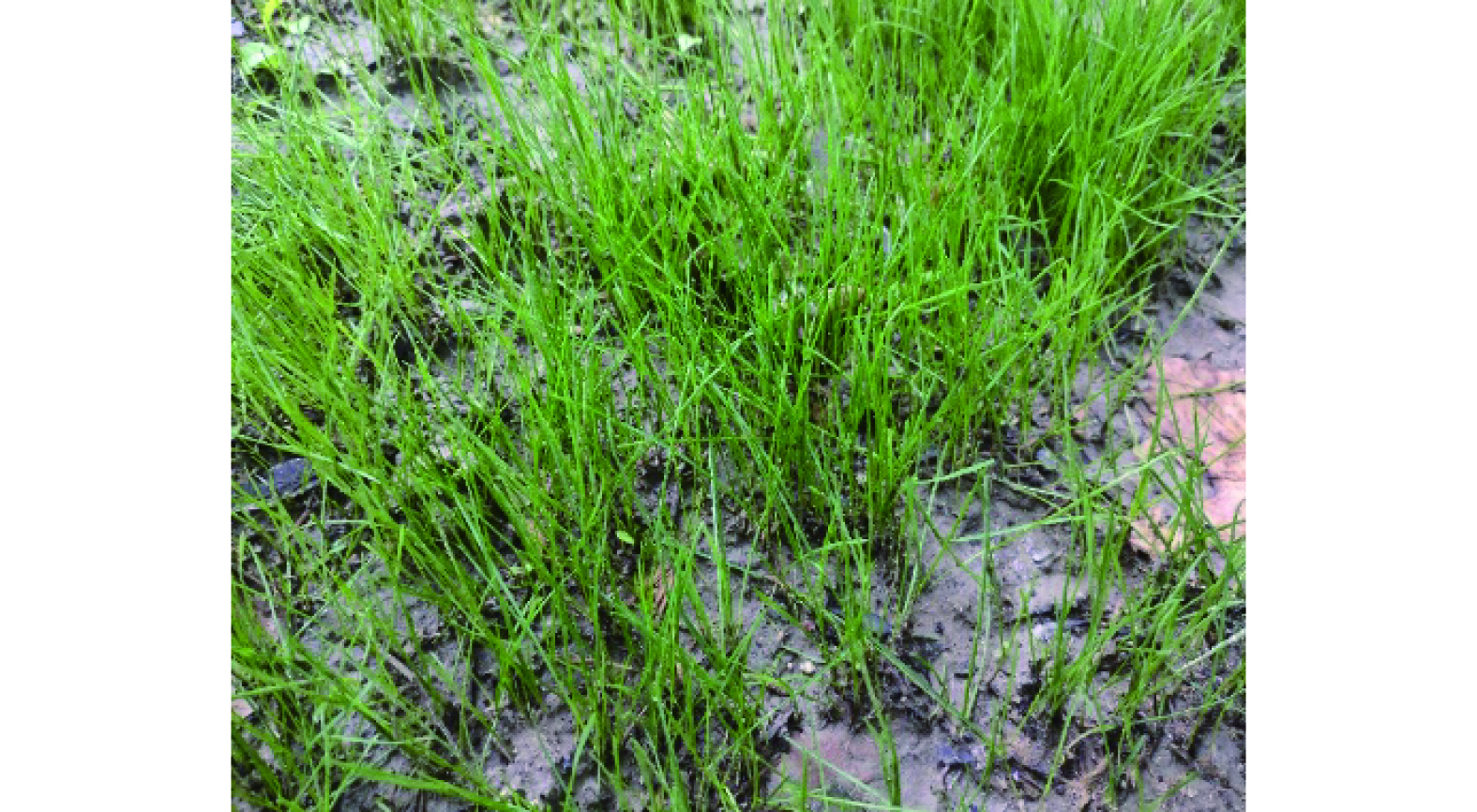
通过将混播四季青用于抑尘剂制备,并对实际喷洒后的生态修复效果进行研究,结果 (图14) 表明抑尘剂喷洒区域的植物生长状态正常。这说明抑尘剂对于植物的生长并无影响,本研究制备的抑尘剂与种子混合后具有良好的生态修复效果。实验区域内植物存在长势不均匀的情况,这是由于抑尘剂在喷洒时无法做到使植物种子分布绝对均匀,且植物种子也存在失活情况。草坪在形成的过程中亦需进行多次补播,因此,生长不均的情况可通过补播来改善。
-
1) 通过对所制备抑尘剂的性能评价,确定秸秆、淀粉、表面活性剂和碱的最质量配比为20∶7∶2∶5。该抑尘剂具有良好的渗透性能、抗风蚀和抗雨淋性能。
2) 制得抑尘剂的抑尘效果显著,在17.2 m·s−1风力条件下其抑尘效率可达到99.8%,在喷洒60 d以后,其抑尘效率亦可保持在90%以上。
3) 该抑尘剂具有良好的生态修复效果,多种常见的植物种子均可适用于此类型的抑尘剂。
4) 该抑尘剂制备工艺简单、成本低廉,解决了传统液体抑尘剂运输成本高、不便储存的难题,实现了废物资源的再利用。
以秸秆及植物种子制备的生态修复环保抑尘剂及其应用效果
Preparation and application of environmental dust suppressant prepared from straw and seed for ecological restoration
-
摘要: 以农业废弃物秸秆和绿色植物种子为主要原料,辅以少量淀粉、表面活性剂、碱等助剂,研制出一种常温下即可快速配制的生态修复型环保抑尘剂。通过对抑尘剂粘度、渗透性等性能的评价,确定抑尘剂制备原料秸秆、淀粉、表面活性剂和碱的最佳质量比为20∶7∶2∶5。抑尘剂的制备工艺简单、成本低廉,且抗风蚀抗雨淋效果较好。在5级风蚀条件下,抑尘剂的抗风蚀率大于99%。经过中雨 (降雨量20 mm·d−1) 雨淋后,喷洒抑尘剂的壳体依旧紧实,且结壳厚度未发生变化;对喷洒抑尘剂的场地进行生态修复效果表征,场地中所选种子生长茂盛,这表明其修复效果显著。进一步地,便携式风洞(PI-SWERL)测试结果表明,在抑尘剂喷洒60 d后,经过风速17.2 m·s−1的风力侵蚀,抑尘剂的抑尘效率仍可保持在90%以上。本研究可为开发绿色、可持续的抑尘技术提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 秸秆 /
- 抑尘剂 /
- 生态修复 /
- 便携式风洞(PI-SWERL).
Abstract: Using agricultural waste straw and green plant seeds as the main raw materials, supplemented with a small amount of starch surfactant alkali and other additives, a kind of environmental protection dust suppressant for ecological restoration was developed. Through the evaluation of viscosity permeability and other properties of dust suppressant, the optimal mass ratio of straw, starch, surfactant and alkali was determined to be 20:7:2:5. The preparation process of dust suppressant was simple, the cost was low, and the effect of wind erosion and rain resistance was significant. Under the condition of wind erosion at grade 5, the wind erosion resistance rate was more than 99%. After moderate rain (rainfall of 20 mm·d-1), the shell sprayed with dust suppressor was still compact, and the shell thickness did not change. The ecological restoration effect of the site sprayed with dust suppresor was characterized, and the selected seeds in the site grew luxuriant, which indicataed that the restoration effect was significant. Futhermore, the tese result of portable wind tunnel (PI-SWERL) showed that after 60 days of dust-suppressor spraying, the dust suppression efficiency remained more than 90% after wind erosion at a wind speed of 17.2 m·s-1.-
Key words:
- straw /
- dust suppressant /
- ecological restoration /
- portable wind tunnel (PI-SWERL).
-
磷是与能源和水并列的重要资源,具有单向流动和不可再生的特性[1-3]。依据美国地质调查局2010年数据,目前,磷矿资源可持续开采仅能维持50 a左右。一方面,由于磷矿不断受到镉、铀等放射性金属的污染以及富磷矿资源日益稀缺,致使开采难度逐年提高[4];另一方面,随着全球人口的增长以及社会经济的发展,对必须利用磷元素进行生产的产品需求也不断增大。磷矿的稀缺性和不可替代性使上述矛盾不断加剧,解决矛盾的方法之一就是从各种富磷废弃物中进行磷回收。
污泥磷回收技术主要是通过物理或化学的方法使污泥产生富磷上清液,通过投加金属盐类形成不溶性磷酸盐沉淀。磷的不同形态及其分布影响着污泥磷回收的效率。从污泥中回收磷的首要条件是污泥中的磷从固相转移到液相中[5]。目前,污泥磷溶出的方法主要有物理法、化学法和生物法等[6]。磷的溶出率基本上与其存在形态相关[7]。对于城市污泥中磷元素的研究,主要集中在污泥综合利用及其资源化利用等方面,包括农田林地应用和建筑材料应用等[8]。城市污泥中总磷含量为30 mg·g−1左右,大部分的磷随污泥进入填埋场所,仅有18.65%的磷被土地利用[9];同时,磷是水体富营养化的主要影响因子,水体中的磷含量增高易造成水华现象。因此,对污泥中磷的溶出过程进行研究十分必要。通过适当的提取方法,了解各形态磷占总磷的比例,对于研究污泥中磷的溶出规律以及污泥的资源化利用具有重要的意义。
自1990年起,化学连续提取法[10]在欧共体标准测量与检测局发起的欧洲标准测试计划框架下逐步发展,是一种标准化的沉积物磷形态分析方法。该方法操作简单,是目前广泛应用的磷形态连续分级提取方法[11],对污泥样品同样具有很好的实际操作性。该方法分3个步骤,采用盐酸和氢氧化钠进行提取,得到5种磷形态,包括总磷(TP)、无机磷(IP)、有机磷(OP)、非磷灰石无机磷(NAIP)和磷灰石无机磷(AP)[12]。
污泥磷溶出有多种方式,其中热解法和酸碱处理法是较为常用且高效的方法。热解法又分为高温预处理(一般温度高于100 ℃)[13]和低温预处理。考虑高温预处理成本较高,且pH对污泥磷溶出的影响一直是学者们的研究热点,而添加EDTA可以抑制金属离子在加热过程中对污泥磷溶出的影响,本研究通过SMT法提取污泥中不同形态的磷,分析磷的形态分布规律,并采用低温热解法、酸碱处理法和投加EDTA 3种方式研究北京市3座污水处理厂污泥中磷的溶出特性,为污泥资源化利用以及污泥磷回收提供技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
污泥为经污泥浓缩池处理后的脱水污泥。含水率低,易于储存,且含磷量较高。采自北京市高碑店(传统活性污泥法)、肖家河(A / O工艺)和清河(倒置A / A / O工艺)3座污水处理厂,含水率分别为36.48%、60.40%和74.42%。污泥样品在105 ℃下烘干12 h,经研磨后过 100 目筛,制成干污泥存于冰箱备用。
1.2 实验方法
1)污泥中磷的形态分析。以3座污水处理厂污泥中的磷为研究对象,应用SMT法[14]对污泥中各种形态的磷浓度进行检测,逐级提取,采用钼锑抗分光光度法对溶液中的磷进行测定。
2)污泥中磷的溶出实验。低温热解实验:分别取3种污泥0. 2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。将混合液置于恒温水浴锅中,温度分别控制在40、50、60和70 ℃,在中性pH条件下研究,低温热解6 h。投加酸碱实验:分别称取3种污泥0.2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。分别用浓度为1 mg·L−1的HCl和1 mg·L−1的NaOH调节溶液pH,pH分别控制为4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0、9.0和10.0,在常温条件下研究。反应24 h。投加EDTA实验:取3种污泥0.2 g于50 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mL去离子水后混匀。添加0、5、10和15 mmol·L−1的EDTA,在常温条件下研究。反应24 h。
以上实验平行3次,实验数据取平均值。反应结束后均取上清液于2 000 r·min−1离心15 min后测量磷酸根和总磷的浓度。磷酸根和总磷的测定采用钼锑抗分光光度法。
1.3 试剂及仪器
试剂包括氢氧化钠、盐酸、磷酸二氢钾、抗坏血酸、钼酸铵、酒石酸锑钾和氯化钠等,均为分析纯。仪器包括恒温振荡器(HY-2B)、紫外可见分光光度计(UV-2102C型)、离心机(TGL-16D)、恒温水浴锅(HH-WO)和台式pH计(Ohaus STARTER 3C)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 污泥中磷的组成和形态
污泥中总磷和各形态磷含量的测定结果如表1所示。各形态磷占总磷的百分比见图1。在SMT分级法中,总磷为有机磷和无机磷的总和,无机磷为非磷灰石态无机磷和磷灰石态无机磷的总和,可将其分别表示为TP=OP+IP,IP=NAIP+AP[15]。结果表明,高碑店、肖家河和清河3座污水处理厂污泥的TP浓度分别为47.12、34.03、31.35 mg·g−1,IP依次占TP的89.3%、71.7%、74.7%,这表明污泥中的磷主要以IP的形态存在;而在IP中,NAIP是主要的存在形态;OP含量较低,仅为3%~10%。
表 1 3座污水处理厂污泥中各形态磷的浓度和占比Table 1. Concentrations and proportions of different phosphorus species in sludge from three different sewage treatment plants不同形态的磷 高碑店 肖家河 清河 浓度/(mg·g−1) 占比/% 浓度/(mg·g−1) 占比/% 浓度/(mg·g−1) 占比/% 有机磷 1.56±0.03 3.3 3.32±0.07 9.8 1.95±0.05 6.2 非磷灰石态无机磷 14.64±0.01 31.1 16.17±0.05 47.5 18.70±0.05 59.7 磷灰石态无机磷 13.62±0.02 28.9 7.89±0.05 33.2 2.41±0.01 7.7 其他的无机磷 13.85±0.00 29.3 0.35±0.10 1.0 2.30±0.08 7.3 其他形态的磷 3.467±0.09 7.4 6.30±0.02 18.5 5.98±0.06 19.1 由图1可知,高碑店和肖家河污水处理厂污泥中的AP占比较高,占TP的30%左右,而清河污水处理厂污泥中的AP含量很低,仅占TP的7.7%,这是因为污水处理厂来水组成不同,致使污泥中各形态磷的占比不同[16]。经调查可知,高碑店和肖家河污水处理厂来水中均含有工业废水,AP是工业废水中磷的主要存在形态,因此,其占比较高;而清河污水处理厂来水为生活污水,因此,其占比相对较低。
2.2 污泥中磷的溶出实验
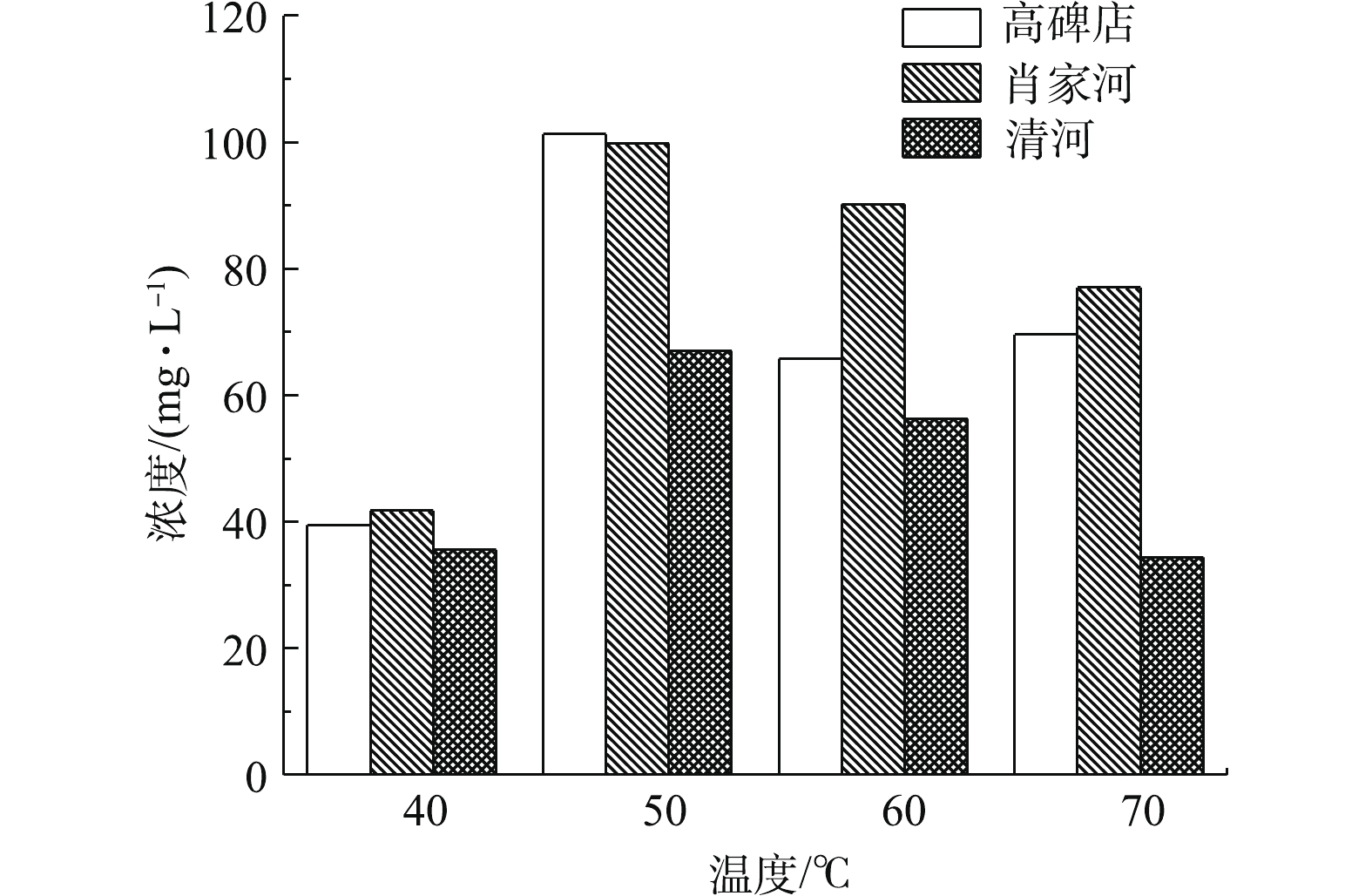
1)温度对污泥磷溶出的影响。经低温热解后,磷逐渐从污泥中溶出到上清液中,其中总磷浓度见图2。在不同温度下,3种污泥中的磷元素均有所溶出。这是由于升温破坏了污泥的表面结构,使污泥絮体分解,污泥中的大量磷得以溶出到上清液中。在50 ℃下,污泥总磷溶出率达到最高,此时高碑店污水处理厂、肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥上清液总磷浓度分别为101.24、99.80、67.02 mg·L−1,总磷溶出率分别为53.7%、73.3%、53.4%。
低温热解释放污泥中的磷,其原理是污泥细胞膜中的磷脂双分子层和细胞核中的DNA和RNA含有大量的磷元素,污泥絮体在加热过程中被破坏,可以有效地使其中的磷溶出[17]。因此,当温度从40 ℃升高到50 ℃时,污泥上清液中总磷的浓度升高;当温度从50 ℃升高到70 ℃时,污泥上清液总磷的浓度却呈下降趋势,这是因为温度升高致使污泥系统中的重金属不断释放,并与溶出的磷结合生成沉淀,导致污泥上清液总磷的浓度降低。
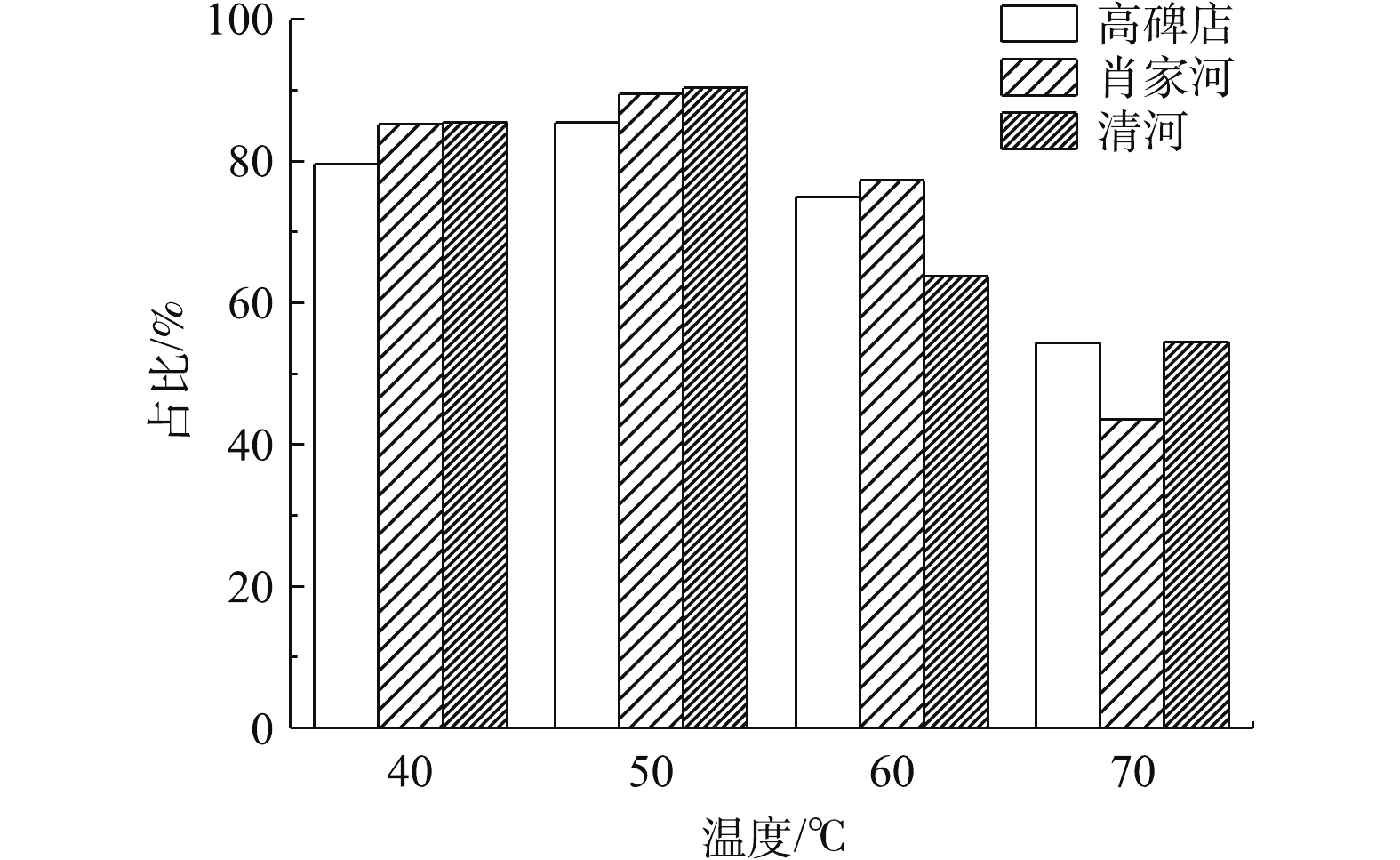
温度是影响污泥磷溶出的重要参数[18],温度过低时,污泥中的磷不能大量溶出;温度过高时,会影响污泥溶出的磷酸根占总磷的比例,而磷酸根的浓度占比越高,越有利于磷的回收[19]。由图3可知,低温热解实验中溶出来的磷以磷酸根为主,在不同温度条件下,3种污泥上清液中磷酸根占总磷的比例均在45%以上;当温度由50 ℃升高到70 ℃时,高碑店污水处理厂、肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥上清液中的磷酸根占总磷的比例均呈现下降的趋势,分别由86%下降到75%,89%下降到44%,90%下降到55%。这是因为污泥上清液中磷酸根占总磷的比例易受污泥中含有的重金属离子的影响,随着温度的升高,污泥中的重金属也不断溶出,从而与上清液中大量的磷酸根离子结合形成不溶性沉淀。
由于热解污泥时需要消耗大量能量,因此,从经济性和磷酸根的占总磷比例2方面进行考虑,在低温热解污泥时,温度并非越高越好。综上所述,确定低温热解温度为50 ℃。薛涛等[20]在处理污泥时,发现最佳的热处理温度为50 ℃,此时释放出来的总磷以磷酸根为主,约占95%。
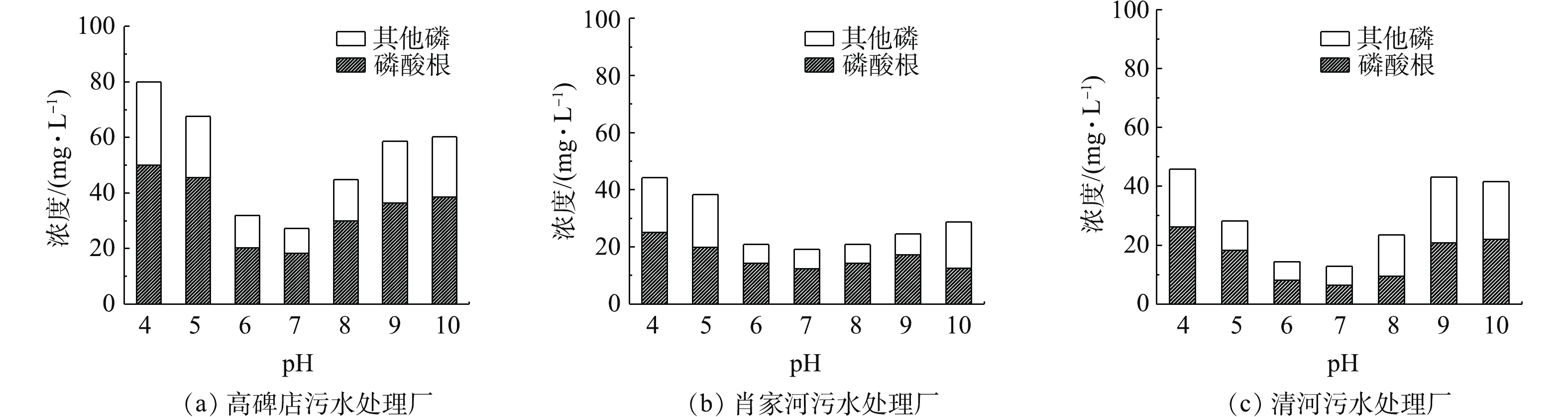
2) pH对污泥磷溶出的影响。pH是影响污泥中磷溶出的重要参数,同时改变磷酸盐沉淀的溶解状态,影响磷的溶解特性,从而改变磷的迁移转化过程[21]。污泥随着pH变化的磷溶出情况见图4,其中,柱状图表示总磷浓度变化,阴影部分为磷酸根浓度变化。结果表明,污泥中的磷在酸性、中性和碱性环境均有溶出。当pH小于7时,污泥上清液中磷的浓度均随着pH的增加而减小,当pH大于7时,污泥上清液中的磷浓度均随着pH的增加而增加。经酸碱处理后,污泥中的磷迅速溶出到上清液中,使磷酸根和总磷的浓度提高。在pH为4时,污泥中的磷达到了最大的溶出率。3种污泥上清液中的总磷含量分别为79.91、44.20、45.80 mg·L−1,总磷溶出率分别为42.4%、32.5%、33.6%。
在酸性条件下,由于酸的溶解作用[22],污泥中磷灰石态无机磷中的部分羟基磷灰石和弱吸附态磷迅速溶出,使得上清液中的磷浓度增加。且溶解作用随着酸性的增强而增强;在中性条件下,3种污泥上清液中的总磷含量最低;在碱性条件下,随着pH的升高,3种污泥上清液中的磷酸根浓度均有所下降,这是生成磷沉淀造成的[23]。
由图4可知,在碱性条件下(pH 8~10),清河污水处理厂污泥释放的总磷浓度均大于肖家河污泥,这是因为在pH较高的情况下,污泥中大部分非磷灰石态无机磷会大量溶出[24]。通过对污水处理厂污泥中的磷形态进行分析,清河污水处理厂污泥的AP含量较低,占污泥中TP的7.70%,而NAIP含量高,占污泥中TP的59.70%;肖家河污水处理厂污泥中AP含量高,占污泥中TP的33.20%,NAIP含量低,占污泥中TP的16.17%。NAIP主要是指铁结合态磷或铝结合态磷,是潜在的活性磷,不稳定,在碱性条件下易释放到水中[25]。AP主要是以钙的磷酸盐形式存在,常见于自然生长的磷灰石或湖泊沉积物中。其含量与陆源排放、沉积类型、沉积环境及间隙水中磷酸根含量等其他因素有关,钙结合态磷难溶于水,稳定性较高,只有在pH降低时有一小部分溶解[26]。因此,肖家河污水处理厂污泥在碱性条件下磷的溶出浓度要低于清河污水处理厂的污泥。
与中性pH条件下相比,投加酸或碱的污泥磷溶出效果均得到提高,且投加酸时的污泥磷释放效果优于投加碱时。综上所述,确定最佳pH为4。
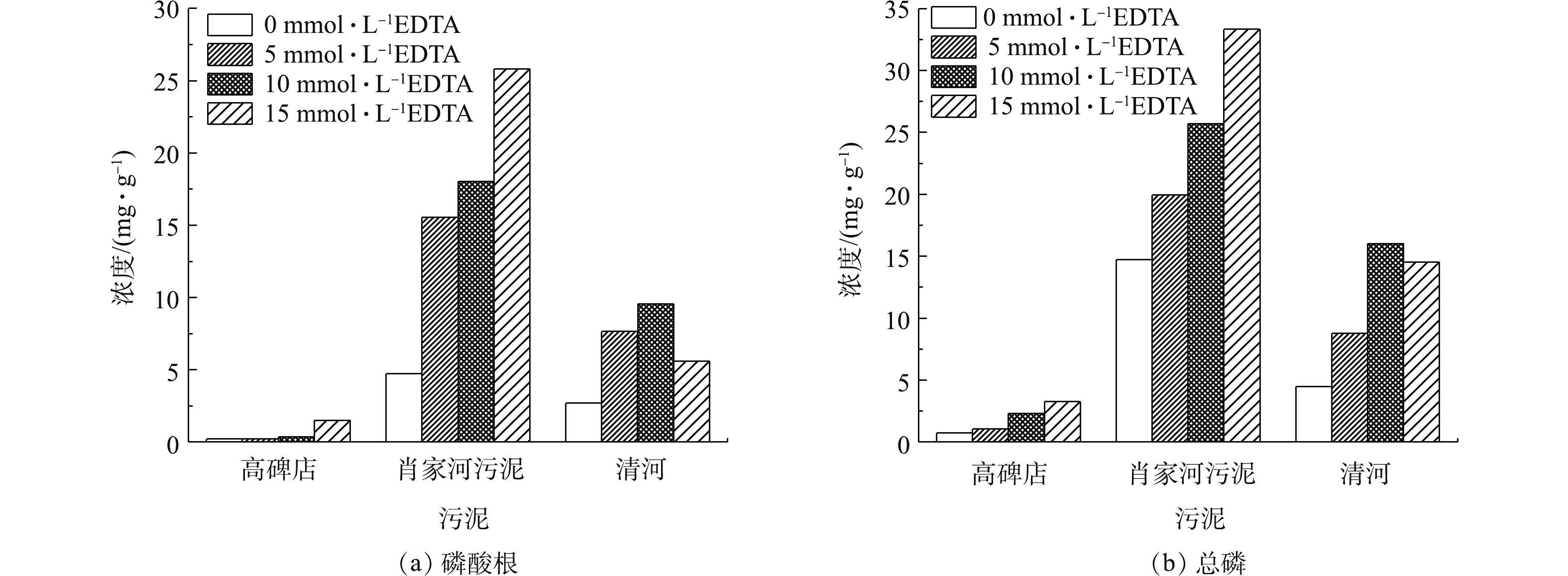
3) EDTA浓度对污泥磷溶出的影响。EDTA是一种重要的络合剂,易溶于水,可以与溶液中的金属离子络合形成稳定的水溶性化合物[27],因此,本研究通过添加EDTA来抑制金属离子对污泥磷溶出的影响。添加不同浓度的EDTA反应24 h后污泥中磷的溶出情况如图5所示。不添加EDTA时,有一部分总磷从污泥中释放出来,3种污泥总磷的溶出率分别为1.6%、43.3%、14.3%。EDTA均促进了污泥中磷的溶出,但对肖家河污水处理厂和清河污水处理厂污泥磷的溶出效果明显[28],当EDTA的浓度达15 mmol·L−1时,肖家河污水处理厂污泥中的磷几乎全部溶出到液相中,总磷溶出率可达97.9%。这是由于当EDTA的添加量达到一定程度时,破坏了污泥的稳定结构,从而使污泥中的生物细胞的表面结构暴露出来。此时细胞壁和细胞膜表面上与脂多糖和蛋白质结合的Ca2+和Mg2+会被EDTA所络合,导致污泥细胞内的磷释放出来[29]。
添加EDTA后,高碑店水厂污泥磷的溶出量并没有明显提高。这是因为其采用了生物除磷法的同时,也投加了大量的铁、铝等金属盐类,使废水中的磷转化为不溶性磷酸盐沉淀,使用的除磷药剂主要为液态硫酸铝[30]。EDTA致使污泥分解,细胞内的磷元素释放出来,同时,污泥上清液中聚集了大量的游离Al3+离子,Al3+与水中的OH−易形成Al(OH)3絮状胶体[31],胶体具有巨大的比表面积,能强烈的吸附磷酸盐。也有研究发现,铁与磷的比值越大,磷的释放量越小[32]。HOLDREN等[33]的研究表明,如果铁、磷的原子数量比大于1.8,那么磷酸盐能够由铁离子的氧化物所固定。上述2点原因阻碍了高碑店污泥中磷的溶出,使污泥上清液中磷酸根的浓度偏低。
对比肖家河和清河2个污水处理厂,发现肖家河污水处理厂污泥上清液总磷的浓度要明显大于清河污水处理厂对应的总磷浓度,分析其原因是由于肖家河污水处理厂污泥AP含量较高,而清河污水处理厂污泥AP含量较低,在EDTA浓度相同的情况下,AP的溶出率大于NAIP[31]。EDTA对不同污水处理厂污泥中磷的溶出率差异可能和不同磷酸盐化合物中金属离子的结合能大小有关。综合考察药剂投加的成本等因素,确定最佳EDTA浓度为10 mmol·L−1。
3. 结论
1)3种污泥中的磷主要以IP的形态存在,IP占TP的71.7%~89.3%;而在IP中,NAIP是主要的存在形态。
2)在50 ℃条件下,3座污水处理厂污泥总磷溶出率达到最高。在从40 ℃升高到70 ℃的过程中,污泥上清液总磷的浓度先升高再下降。低温使磷大量溶出,温度过高则会导致溶出的磷酸根占总磷的比例下降,影响后续磷回收。
3)污泥磷在酸或碱条件下的溶出效果均优于中性条件,且酸性条件最优。在碱性条件下,清河污水处理厂污泥溶出的总磷含量均大于肖家河污泥。原因之一是清河污水处理厂厂非磷灰石态无机磷占比大,污泥中大部分非磷灰石态无机磷会大量溶出。
4) EDTA的添加能够明显促进肖家河水厂污泥磷的溶出。在EDTA浓度相同的情况下,磷灰石态无机磷的溶出率大于非磷灰石态无机磷。
5)磷的形态影响着污泥磷的溶出,不同形态的磷在相同实验条件下溶出规律不同,结合磷形态找出合理的释磷条件,有利于提高溶出效率及后续的磷回收。考虑后期磷回收的可行性以及药剂投加成本等因素,确定处理污泥的最佳条件:温度为50 ℃,pH为4,EDTA为10 mmol·L−1。
-
表 1 喷洒后植物发芽时间的测试
Table 1. Test of germination time of plants after spraying
植物名称 喷洒抑尘剂的天数/d 喷洒水的天数/d 紫花苜蓿 7 4 混播四季青 9 6 耐践踏四季青 9 7 高羊茅 10 9 早熟禾 18 18 胡枝子 18 18 表 2 抑尘效率测试结果
Table 2. Dust suppression efficiency test results
转速/(r·min−1) 洒水后的抑尘效率η/% 喷洒抑尘剂后的抑尘效率η/% 喷洒3 d后 喷洒3 d后 喷洒10 d后 喷洒30 d后 喷洒60 d后 4 000 87.4 98.9 96.9 98.4 97.1 5 000 15.7 99.6 98.5 98.2 94.7 6 000 5.9 99.8 99.3 98.2 90.0 -
[1] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2020年全国生态环境质量简况[R], 北京, 2021.https://www.mee.gov.cn. [2] 胡敏, 唐倩, 彭剑飞, 等. 我国大气颗粒物来源及特征分析[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2011, 36(5): 15-19. [3] ASKARIYEH M H, VENUGOPAL M, KHREIS H, et al. Near-Road Traffic-Related Air Pollution: Resuspended PM2.5 from Highways and Arterials[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(8): 2851. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082851 [4] 安欣欣, 曹阳, 王琴, 等. 北京城区PM2.5各组分污染特征及来源分析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(5): 2251-2261. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202109142 [5] 李廷昆, 冯银厂, 毕晓辉, 等. 城市扬尘污染主要成因与精准治尘思路[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(3): 1323-1331. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202107092 [6] 李永强, 周亚萍, 杨晓娟, 等. 复合型道路抑尘剂在城市道路中的应用及经济分析研究[J]. 科学技术创新, 2020(27): 120-121. [7] 郭秀秀. 建筑施工扬尘对生态环境的污染及整治措施研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2021, 46(9): 123-127. [8] 王林凯, 郭红霞, 秦建平, 等. 风蚀扬尘抑尘剂制备及其抑尘效果[J]. 环境工程学报, 2020, 14(12): 3460-3467. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.202003008 [9] FAN T, ZHOU G, WANG J. Preparation and characterization of a wetting-agglomeration-based hybrid coal dust suppressant[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2018, 113: 282-291. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.10.023 [10] BAO Q, NIE W, LIU C Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of a binary‐graft‐based, water‐absorbing dust suppressant for coal transportation[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019, 136(7): 47065. doi: 10.1002/app.47065 [11] LO C, TIRKOLAEI H K, HUA M T, et al. Durable and ductile double-network material for dust control[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 361(C): 1-10. [12] 王洁茹. 海洋生物型固土抑尘剂的研制、性能表征及其在黄河滩区的应用研究[D]. 青岛: 山东大学, 2021. [13] 石祖梁, 贾涛, 王亚静, 等. 我国农作物秸秆综合利用现状及焚烧碳排放估算[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 2017, 38(9): 32-37. [14] 周治. 我国农业秸秆高值化利用现状与困境分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2021, 23(2): 9-16. doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2020.0410 [15] 候其东, 鞠美庭. 秸秆类生物质资源化技术研究前沿和发展趋势[J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48(18): 65-70. doi: 10.14026/j.cnki.0253-9705.2020.18.013 [16] FAN T, LIU Z Y, OUYANG J T, et al. Synthesis and performance characterization of an efficient coal dust suppressant for synergistic combustion with coal dust[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 269: 110854. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110854 [17] ZHOU Q, QIN B T, MA D, et al. Novel technology for synergetic dust suppression using surfactant-magnetized water in underground coal mines[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2017, 109: 631-638. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.05.013 [18] 符治明, 张晓龙, 李洪青, 等. 贵州高速公路岩石边坡常用绿化植物幼苗生长规律实验研究[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2012, 40(4): 24-29. [19] 孙盛年. 高速公路边坡绿化植物种类的搭配及应用[J]. 现代农业科技, 2019(24): 123-124. [20] 张锡国, 阿力坦巴根那, 余海龙. 赤通高速公路边坡生态恢复中的植物选择[J]. 防护林科技, 2010(4): 96-98. [21] 包秀春, 刘金炜, 赵栋梁, 等. 纤维素结晶度与粗糙度关系的研究[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(4): 83-86. [22] 李辉勇, 金密, 魏琴琴, 等. 弱碱性过氧化预处理对稻草秸秆酶解糖化的影响[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2011, 45(5): 11-16. [23] WANG P F, TAN X H, ZHANG L Y, et al. Influence of particle diameter on the wettability of coal dust and the dust suppression efficiency via spraying[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2019, 132: 189-199. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2019.09.031 [24] ZHOU G, QIU H, ZHANG Q, et al. Experimental investigation of Coal Dust Wettability Based on Surface Contact Angle[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 2016: 9452303. [25] 张晓光. 表面张力法和电导法对比测定表面活性剂临界胶束浓度[J]. 化学教育(中英文), 2021, 42(18): 134-136. [26] 秦建平, 李贝贝, 杨涛, 等. 风蚀扬尘抑尘剂效率测试方法与应用[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9): 3935-3941. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: