-
随着城市化发展的不断加快,我国污水处理规模逐渐加大,而剩余污泥(WAS)作为污水处理过程的副产品,产量较大,成分复杂且难以处理。厌氧消化技术可有效降低污泥产量,并产出甲烷等生物能源,因此应用广泛[1]。然而,由于国内厌氧消化技术主要针对于含固率较低的污泥(TS<5%),通过常规厌氧消化技术产生的VFAs等可回收碳源浓度较低,难以满足反硝化碳源需求[2]。相比于传统厌氧消化技术,高固厌氧消化所需的池容较小,生物能源产出较高,弥补了传统厌氧消化的不足[3]。KARTHIKEYAN等[4]在研究厌氧发酵中生物能源回收时,将TS大于10%的污泥定义为高固污泥。当TS高于6%时,污泥的流动性减弱,黏度增大,絮体难以破解,故导致污泥水解过程受到限制,厌氧消化效率降低[5]。因此,如何促进高固污泥的水解过程成为提高消化反应效率的关键。
过硫酸钠(PS)预处理是一种高级氧化工艺(AOPs),成本低廉、使用安全、易于普及[6]。其作用机理是,在经过超声波、紫外线、还原性金属等作用下产生具有较高氧化还原电位的SO4-·,氧化裂解胞外聚合物(EPS),提高污泥水解产酸性能[7]。YANG等[8]采用过氧一硫酸盐(PMS)对污泥进行预处理,发现随着PMS投加量从0增长到0.09 g·g−1(以总悬浮固体计),VFAs产量由29.69增长至311.67 mg·g−1(以单位挥发性悬浮固体的COD计),类腐殖酸类物质在有机质中的占比也明显降低。LUO等[9]发现,铁粉活化PS可提高短链脂肪酸产量,在PS/Fe介入下,与VFAs生产相关的微生物丰度有所增加,提高了发酵液的可生化性。
本研究以污水处理厂脱水污泥(TS≥10%)为研究对象,采用成本较低的颗粒活性炭(GAC)作为PS的活化剂,以探究GAC活化PS预处理对污泥水解产酸性能的影响。本研究结果可为高固污泥厌氧消化技术的发展提供参考。
-
本实验采用的椰壳活性炭为商用活性炭,粒径为0.5~1.0 mm,比表面积为1 100 m2·g−1。高固污泥取自长沙市某污水处理厂的脱水机房,取回后置于4 ℃冰箱保存备用;种泥取自实验室长期培养的碱性厌氧消化反应器,其基本性质如表1所示。
-
为探究不同剂量GAC与PS对污泥厌氧消化的影响,在预实验确定的PS最佳投加量为1.50 mmol·g−1(以总固体计)基础上,本研究设置GAC投加量为0、2.5、5.0、10.0和20.0 g 5组反应器,与之对应的GAC相对投加量为0、0.16、0.33、0.65及1.31 g·g−1(以总固体计),分别命名为PS、PS-GAC 2.5、PS-GAC 5、PS-GAC 10、PS-GAC 20组。另设置不添加PS与GAC的对照组和仅有种泥而无待处理污泥的空白组。将140 g含固率为10.93%的高固污泥加入500 mL血清瓶中,并添加不同剂量PS与GAC,将上述血清瓶置于温度37 ℃、转速170 r∙m−1的摇床中预处理2 h,随后加入160 g含固率为11.32%的种泥。为提高发酵过程中VFAs产量,同时降低产甲烷菌对于VFAs的消耗,在整个发酵过程中使用高浓度NaOH溶液调节混合液pH至10[10],使其始终处于碱性发酵条件。实验开始前及每次取样后,均通入氮气5 min以保证无氧环境。最后,将所有反应器密封并置于摇床中发酵14 d,期间每天监测并调节pH,定时测定VFAs、SCOD、蛋白质及多糖等指标。
-
蛋白质采用Folin-Lowry法测定、多糖测定采用蒽酮硫酸法,化学需氧量通过“三五法”[11]进行测定,液相中挥发性脂肪酸(包括乙酸、丙酸、丁酸、戊酸及己酸)的质量浓度通过气相色谱-火焰离子化检测器进行定量[12](气相色谱仪7820A,安捷伦科技有限公司)。在实验进行到14 d时,采集污泥EPS样品,应用三维激发-发射-基质荧光光谱法(Horiba Aqualog,法国HORIBA Jobin Yvon公司)表征污泥发酵体系中EPS的变化,发射波长为250~600 nm,数据间隔1 nm,激发波长为220~600 nm,数据间隔5 nm,激发和发射狭缝保持在5 nm,扫描速率设定为1 200 nm·min−1。
-
在不同剂量GAC+PS条件下,厌氧污泥中VFAs变化情况如图1(a)所示。随着不同剂量GAC的参与,VFAs的累积情况有所不同。与对照组相比,单独投加PS对产酸性能有一定的抑制作用,该组最大VFAs产量(2.76 g·L−1)仅为对照组(4.08 g·L−1)的67.64%(P<0.05)。随着GAC介入厌氧发酵体系中,上述PS的抑制作用得到改善。当GAC投加量达到10.0 g时,发酵前2 d的VFAs产生速率为1.55 g·d−1,相比于对照组显著提升了341.43%(P<0.05),其VFAs最大产量达到5.24 g·L−1,与对照组相比提高28.43%(P<0.05)。但当GAC投加量增长到20.0 g时,污泥产酸性能逐渐降低。碱性环境下单独投加PS会生成大量的·OH及SO42−[13],而硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)以乙酸等VFAs为电子供体还原硫酸盐并生成硫化物[14]。该过程不仅会消耗反应器中已生成的VFAs,产生的硫化氢等副产物还可通过自由扩散进入细胞内,抑制产酸菌活性[15]。GAC介入上述体系后,因其特有的碳结构和表面官能团,会促使PS以自由基和非自由基两种途径活化生成具有强氧化性的SO4−·和单线态氧(1O2)[16],可有效破解污泥絮体并提高反应体系中可利用底物的质量浓度。然而,当GAC过量时,会与已生成的SO4−·发生猝灭反应[13],降低污泥的破解效果。此外,GAC表面含有大量的碱性官能团如吡喃酮(环酮)及其衍生物等[17],可吸附大量的VFAs、水解酶等物质,减少了污泥絮体与水解酶的接触机会,从而导致污泥产酸性能的下降。
VFAs作为优质碳源[18],其中各短链脂肪酸的占比决定了发酵液的实用价值。因此,考察了炭活化PS预处理对VFAs组成的影响。如图1(b)所示,各反应器中,乙酸与丙酸均占据主导地位,随着PS与GAC的参与,VFAs的成分占比发生一定的变化。乙酸与丙酸作为主要产物,在对照组中分别占VFAs产量(4.08 g·L−1)的75%与11%,而PS-GAC 10组(5.24 g·L−1)中乙酸占比上升到87%(P<0.05),丙酸占比降低4%,其余各组中VFAs成分占比类似。乙酸质量浓度的提高可能是因为,经GAC活化后的PS产生的SO4−·可强化污泥絮体的破解效果,提高了反应器中可降解小分子有机物的质量浓度,从而促进了产乙酸菌自身代谢与利用过程[9]。同时,其他如丙酸、丁酸等发酵产物可在产氢产乙酸过程中进一步转化为乙酸,提高了乙酸的产量[19]。上述结果与樊雅欣等[20]对过硫酸盐协同硫酸盐还原菌强化剩余污泥产酸的研究相似,他们发现零价铁粉协同PS可有效促进乙酸的生成,其占比可提高34.20%。
-
图2为高固污泥在厌氧发酵过程中SCOD的变化情况。除对照组的SCOD在整个厌氧发酵过程始终处于上升趋势外,其余各组的SCOD均在第9 d达到最大值后逐渐降低。具体而言,PS、PS-GAC 2.5及PS-GAC 20组的SCOD质量浓度在发酵过程中始终较低,与对照组相比,其最大值分别降低了10.70%、17.23%及29.32%。而PS-GAC 10组在发酵至第9 d时,SCOD的质量浓度增加了49.29%,比对照组显著提高了30.41%(P<0.05);在第12 d时,PS-GAC 10组SCOD质量浓度下降到14 594 mg·L−1,但仍然高于对照组(13 986 mg·L−1)。可见,控制GAC投加量可有效促进污泥水解过程。
PS在GAC参与时产生的具有强氧化能力的SO4−·(E=2.5−3.1 V)主要通过氢原子提取、加成以及电子转移3种方式分别与污泥中醇类、烷烃、烯烃及芳香族化合物等有机物进行反应[21]。在碱性环境下单独投加PS生成的·OH氧化性较弱,与液相中溶解性还原物质反应导致SCOD质量浓度降低[13]。少量的GAC可与S2O82−生成具有氧化性更强的SO4−·,与溶解性有机物反应后进一步降低了SCOD的质量浓度。然而,过量的GAC可与SO4−·发生猝灭反应,减弱了污泥絮体的破解效果[22]。另外,大量的GAC对污泥中有机物质的吸附也可能是SCOD质量浓度较低的原因之一。
-
在厌氧发酵过程中,水解酶将蛋白质与多糖分解为小分子氨基酸及单糖等物质供酸化菌利用,因此溶解性蛋白质与多糖是污泥产酸的关键中间产物[23]。图3(a)为各反应器厌氧过程中溶解性蛋白质的变化情况。随着GAC投加量的提高,各反应器中溶解性蛋白质质量浓度变化情况有所不同。在发酵前期,对照组、PS组及PS-GAC 2.5组的溶解性蛋白质质量浓度表现为先升高后下降的趋势,均在第9 d达到最大值后又逐渐下降;继续提高GAC投加量,反应器中溶解性蛋白质的质量浓度在发酵期间一直呈单调下降趋势,并在第12 d降至最低值。由此可知,当GAC投加量为5.0和10.0 g时,相比对照组产酸情况较好。此时,反应器中产酸微生物对溶解性蛋白质的利用率较高,故导致蛋白质的生成速率低于消耗速率,降低了其在反应器中的质量浓度[24]。而当GAC投加量达到20.0 g时,过量GAC将反应器中的蛋白酶吸附在其表面,减少了蛋白酶与污泥絮体的接触,减弱了水解效果,从而导致溶解性蛋白质质量浓度随发酵过程的进行不断下降[25]。
图3(b)为溶解性多糖的变化情况。除对照组在发酵后期略有下降外,各反应器多糖质量浓度在发酵期间一直处于上升趋势。其中,PS组中多糖在发酵前6 d急剧上升,后期逐渐平稳。当投加GAC后,各反应器中多糖质量浓度在整个发酵过程中增速显著放缓,直到第12 d达到最大值。由此可知,在碱性环境下,仅投加PS时,生成的·OH破坏了污泥絮体的胞外结构,致使聚糖等难降解糖类物质释放于溶液中,且反应器中微生物活性受硫化物副产物影响,对溶解性有机物利用程度较低,导致PS组中VFAs产量降低,多糖物质出现累积现象[26]。GAC的介入,减弱了微生物受到的抑制作用,实验前期产生的多糖更易于被微生物利用转化为VFAs,因此其质量浓度增幅较小。然而,发酵后期由于反应器中累积了大量不易分解的肽聚糖类多糖物质,故导致其质量浓度有所升高。
-
三维荧光光谱技术被广泛应用于表征EPS及可溶性微生物产物等[27],通过测定发酵液中的溶解性有机物可以评价PS与GAC预处理对污泥水解产酸的影响。图4为不同预处理条件下污泥溶解性有机物(DOM)的三维荧光光谱。从图中可以看出,对照组出现的3个峰分别为A峰(I区酪氨酸类物质(220/320))、B峰(II区类芳香族蛋白质(240/380))与较弱的C峰(IV区类色氨酸物质(270/340))[28]。这3个峰在经过不同条件的预处理后,峰的位置及荧光强度发生了变化。产酸性能受限的PS组中A、C峰被掩盖,B峰及代表V区类腐殖酸物质(300/380)的D峰荧光强度增强。这说明,在此条件下,酪氨酸、色氨酸类物质占比较小,腐殖酸类物质质量浓度较高,可能对厌氧发酵过程产生了一定的抑制作用[29]。产酸性能较好的PS-GAC 5组与PS-GAC 10组中,A、B、C峰强度均小于对照组。这可能是产酸菌对酪氨酸类物质、类芳香族蛋白质、类色氨酸物质等溶解性物质利用率较高。相较于PS-GAC 10组,PS-GAC 20组中A峰和D峰荧光强度均有所增强。这表明,反应器中腐殖质类有机物未充分降解而产生累积。
对不同预处理条件下剩余污泥DOM的三维荧光光谱进行面积积分发现,对照组III区富里酸类物质、V区腐殖酸类物质占比分别达到了18.28%、6.27%,而PS组中III、V区占比提高到28.94%、8.96%。这表明,该组中大量的腐殖酸与富里酸类物质等含有含氧官能团的高分子有机物难以被降解,对污泥产酸过程有一定的抑制作用[30]。当GAC投加量达到10.0 g时,II、IV区占比分别达到37.04%、15.11%,分别略高于对照组的33.92%和13.70%,而III、V区占比较小。据此可以推测,PS和GAC预处理促进了污泥水解过程,类蛋白质物质大量出现,腐殖酸类物质被降解,厌氧发酵性能得到提升。PS-GAC 20组中II区占比达到37.30%,高于对照组,而III(17.48%)、V(5.45%)区占比低于对照组。其原因可能是,GAC对水解酶的吸附作用导致酶与蛋白质类物质的接触减少,而微生物不能直接利用大分子有机物产酸发酵,导致反应器中溶解性有机物发生累积。
目前,国内外污泥处理处置领域的研究对象主要是含固量为2%~5%的低固污泥。WEI等[31]利用玉米秸秆生物炭提高污泥中甲烷产量,得出当生物炭剂量为1.82~3.06 g·g−1(以总固体计)时,甲烷产量提高8.6%~17.8%。章钦等[32]探讨了生物炭对污泥厌氧发酵性能的影响,发现当生物炭投加量为2.25 g·g−1(以总悬浮固体计)时,污泥中VFAs累计质量浓度最大。本研究以高固污泥为对象,采用GAC与PS组合对其厌氧消化性能进行研究,发现当GAC投加量为0.65 g·g−1(以总固体计)时,反应器中VFAs产量可提高28.43%。相比于传统厌氧消化反应器,炭活化PS预处理高固污泥不仅提高了污泥发酵液的可生化性,并在降低成本、提高效率等方面有着明显的优势,在实际应用中可有效减小污泥消化池体积。
-
1)当GAC投加量为0.65 g·g−1(以总固体计)、PS投加量为1.50 mmol·g−1(以总固体计)时,反应器VFAs产量提升28.43%。其中,乙酸的质量浓度提高了48.98%。
2)GAC的投加量达到1.31 g·g−1(以总固体计)时,由于SO4−·被过量GAC消耗,未对污泥絮体起到有效的破解作用。同时,GAC表面对VFAs的吸附也导致产酸量下降。
3)三维荧光分析表明适量的GAC活化PS预处理污泥可有效降解抑制污泥产酸的腐殖酸类物质,提高溶解性有机物占比,改善反应器厌氧发酵性能。
椰壳颗粒活性炭活化过硫酸钠预处理促进高固污泥水解产酸性能
Coconut shell granular carbon activated sodium persulfate pretreatment elevates the performance of hydrolysis and acid production from high-solid sludge digestion
-
摘要: 为探究椰壳颗粒活性炭活化过硫酸钠(PS)预处理对高固污泥厌氧发酵水解产酸性能的影响,通过调节挥发性脂肪酸(VFAs)产量、溶解性化学需氧量(SCOD)、溶解性蛋白质及多糖等指标,探究了不同剂量颗粒活性炭(GAC)与PS预处理对高固污泥产酸发酵的最佳条件。结果表明,当PS和GAC投加量分别为1.50 mmol·g−1(以总固体计)和0.65 g g−1(以总固体计)时,在发酵前期产酸速率相比于对照组提高了341.43%,后续发酵过程中,VFAs最大产量相比于对照组提高了28.43%。其中,乙酸作为优质碳源,其质量浓度增加了48.98%;继续增加GAC剂量时,反应器厌氧发酵性能下降,其原因可能是过量GAC会消耗已生成的SO4−·,降低污泥水解作用,同时GAC表面对VFAs的吸附也导致产酸量下降。三维荧光分析表明,在产酸量较高的反应器中,氨基酸、芳香族蛋白质等溶解性有机物的质量浓度较低,这说明适量椰壳颗粒活性炭活化PS预处理方式可提高高固厌氧发酵中微生物对于水解底物的利用率,从而提高污泥的厌氧产酸性能。本研究结果可为炭活化PS预处理技术在高固污泥厌氧消化中的应用提供参考。Abstract: To analyze the effect of coconut shell granular activated carbon activated sodium persulfate (PS) pretreatment on the performance of anaerobic fermentation and hydrolysis of high-solid sludge for acid production, the optimal conditions with different doses of granular activated carbon (GAC) and PS were explored by the yield of volatile fatty acids (VFAs), soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD), soluble protein and polysaccharide. When the dosage of PS and GAC were 1.50 mmol·g−1 (based on the total solids) and 0.65 g·g−1 (based on the total solids), respectively, the acid production rate in the early fermentation stage increased by 341.43%. With the progress of fermentation, the maximum production of VFAs increased by 28.43% and the acetic acid as the high-quality carbon source increased by 48.98% compared with the control group. Increasing the dosage of GAC would lead to the decline of anaerobic fermentation performance of the reactor, which might be due to the consumption of the generated SO4−· by excessive GAC in the pretreatment process, resulting in the reduction of hydrolysates, and the adsorption of VFAs on the surface of GAC leads to the decrease of acid production simultaneously. Three-dimensional fluorescence analysis showed that the concentrations of soluble substances, such as amino acids and aromatic proteins, were relatively low in the reactor with high acid production, indicating that appropriate amount of coconut shell granular carbon activated PS pretreatment could improve the utilization rate of hydrolyzed substrates, and improve the anaerobic digestion performance of sludge. The results can provide a theoretical reference for the application of carbon-activated PS pretreatment technology in anaerobic digestion of high-solid sludge.
-
随着人类生产活动的加剧、臭氧层破坏日益严重,生活在地球表面的生物可能遭受紫外线的过度辐射,由此所导致的皮肤晒伤、老化、甚至癌变等问题越来越受到人们的关注[1]. 为了缓解这一问题,紫外防晒剂被广泛应用,通常被添加到个人护理品如防晒霜、沐浴露、身体乳等日用护肤品中[2],同时紫外防晒剂也常被添加在塑料、橡胶、油漆等长期暴露在阳光直射环境的工业产品中以延缓老化. 据统计,全球防晒剂的年消耗量由2016年的4.4万吨增长至2021年的5.2万吨,年均增长率约4%. 随着这些个人护理品和工业产品的大量使用及逐渐老化,添加于其中的防晒剂逐渐被释放进入环境,成为一类新污染物,广受关注. Casas-Beltran等[3]的研究预估了2007年至2025年间当地居民和游客使用防晒霜将给墨西哥金塔纳罗奥水体排入近
4367.25 吨的化学物质.二苯甲酮类(BPs)化合物是有机防晒剂家族中的重要成员,由于其防晒谱广、致敏性低、价格便宜,在实际生产生活中应用广泛. 二苯甲酮的骨架结构是由羰基相连的两个苯环. 苯环上取代基种类、数量、位置的不同,衍生出一系列二苯甲酮类防晒剂,常见二苯甲酮类防晒剂的分子结构如表1所示.
表 1 常见二苯甲酮类化合物Table 1. Common benzophenone compounds名称Name 化学式Chemical formula 名称Name 化学式Chemical formula 二苯甲酮(Benzophenone) 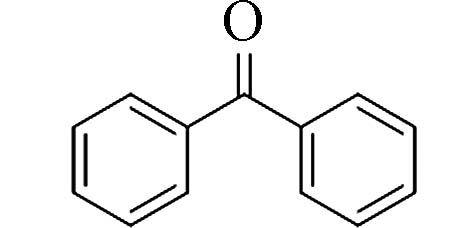
2-羟基二苯甲酮(2-Hydroxy-benzophenone) 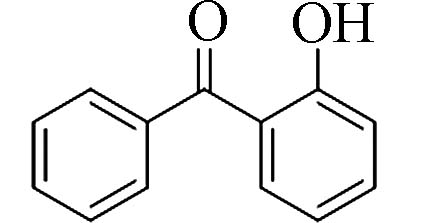
3-羟基二苯甲酮(3-Hydroxy-benzophenone) 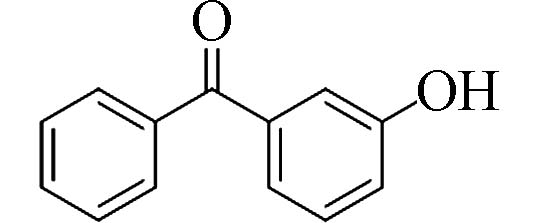
4-羟基二苯甲酮(4-Hydroxy-benzophenone) 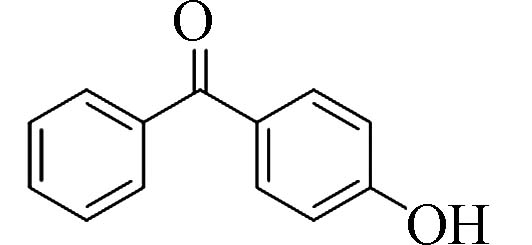
2,2´-二羟基二苯甲酮(2,2´-Dihydroxy-benzophenone) 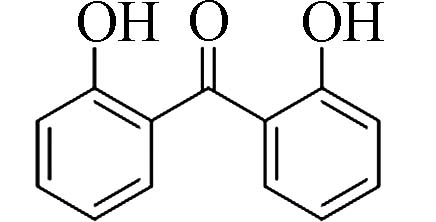
4,4´-二羟基二苯甲酮(4,4´-Dihydroxy-benzophenone) 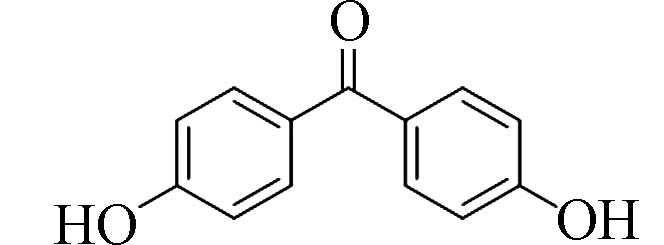
2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮(2,4-Dihydroxy-benzophenone) 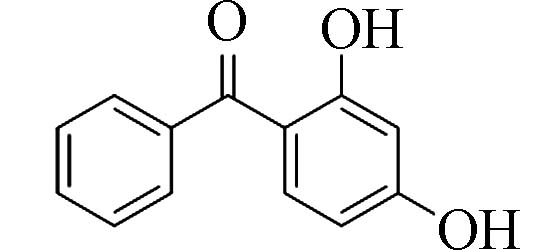
2,4,4´-三羟基二苯甲酮(2,4,4-Trihydroxy-benzophenone) 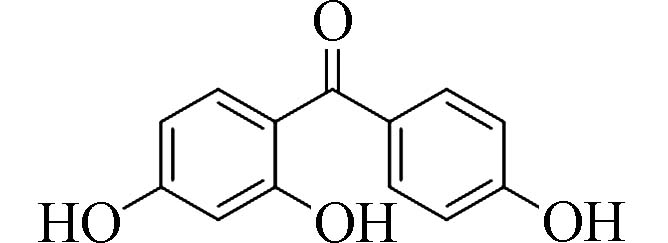
2,3,4-三羟基二苯甲酮(2,3,4-Trihydroxy-benzophenone) 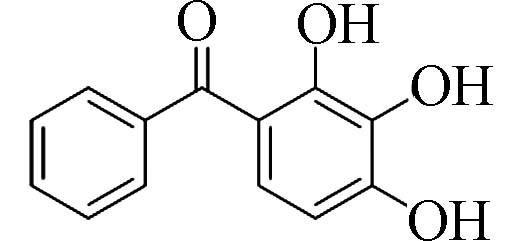
2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮(2,2 ́,4,4 ́-Tetrahydroxy-benzophenone) 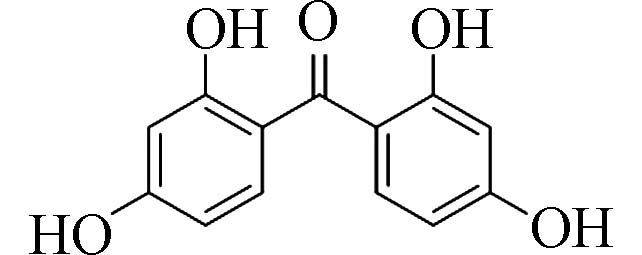
2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone) 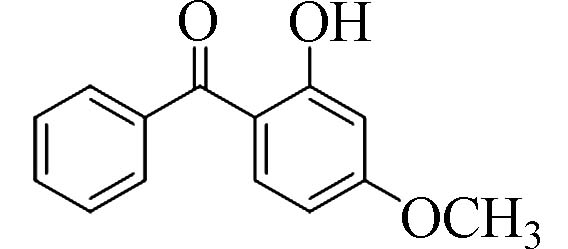
2-羟基-4-辛氧基二苯甲酮(2-Hydroxy-4-octyloxy-benzophenone) 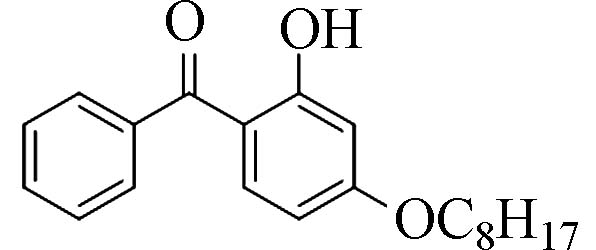
2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸(2-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid) 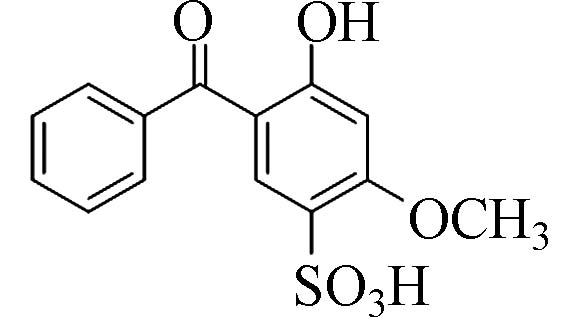
2,2´-二羟基-4,4´-二甲氧基二苯甲酮(2,2 ́-Dihydroxy-4,4 ́-dimethoxy-benzophenone) 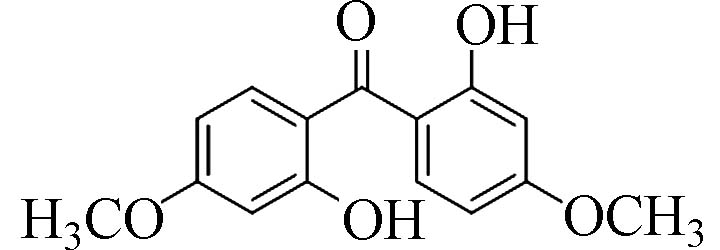
2-羟基-5-氯二苯甲酮(2-Hydroxy-5-chloro-benzophenone) 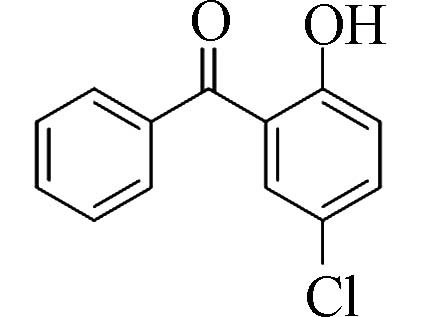
2,2´-二羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮(2,2 ́-Dihydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone) 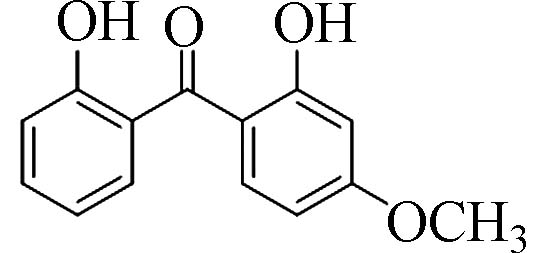
2,2'-二羟基-4,4'-二甲氧基苯甲酮-5,5'-二磺酸(2,2'-Dihydroxy-4,4'-dimethoxy-benzophenone-5,5'-disulfonic acid) 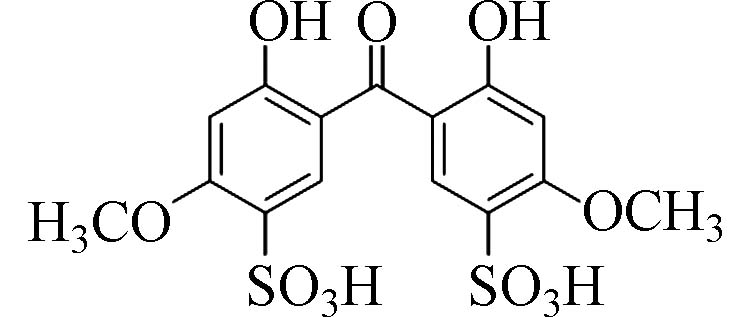
2,2´-羟基-4-甲氧基-4'-甲基二苯甲酮(2,2 ́-Hydroxy-4-methoxy-4'-methyl-benzophenone) 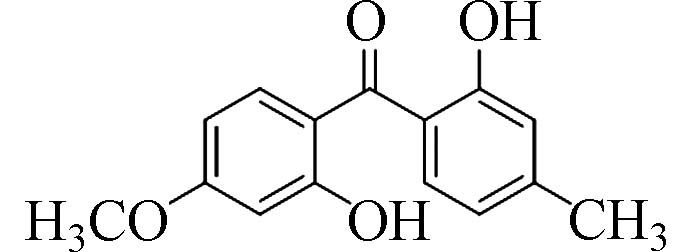
随着二苯甲酮类化合物的广泛使用,排入环境的量也在逐年增加. 目前已经在几乎所有的环境介质中发现了BPs类防晒剂的残留,甚至在部分居民尿液、乳汁、血液中检测出了BPs,其含量水平大致在0.08 ng·mL−1至1.9 ng·mL-1[4]. 环境中BPs的来源广泛,如防晒霜生产企业的废水排放、居民日常洗漱和娱乐活动的排放等[5]. 由于BPs类化合物的化学性质相对稳定,进入水环境后不容易被降解去除,导致其在水环境中的残留水平呈逐渐升高的趋势[6]. 在中国香港某热门海滩水体中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的检出浓度超过
1000 ng·L−1,汕头和潮州的地表水中浓度为50 ng·L−1[7]. 特别是在美国圣约翰岛的夏季海水中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的浓度高达1.395 mg·L−1[8]. BPs的污染问题逐步成为国内外环境领域的研究热点之一.环境中BPs类化合物备受关注的主要原因是其潜在的内分泌干扰效应. 调查结果表明人精液中BPs的检出限为0.22—2.35 ng·mL−1. 其中二苯甲酮、2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮和2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的检出率分别为17.8%、18.5%和27.3%,它们会导致精子数量减少和前向运动精子比例降低[9 − 11]. 体外毒性实验结果表明,BPs表现出雌激素效应、抗雌激素效应、抗孕激素效应和抗雄激素效应等多种负面生物效应[12]. 此外,BPs还具有一定的急性毒性、亚急性及慢性毒性、生长发育毒性和光致毒性. 2022年发表于Science的研究揭示了2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的糖基化代谢产物是导致珊瑚漂白和死亡的主要毒性物质[13]. 毒理学实验结果表明,即使防晒霜的暴露剂量低至 10 μL·L−1,也能导致硬珊瑚在96 h内完全白化[14]. 已有一些研究者对BPs类防晒剂在水处理相关过程中的转化行为进行了探讨,但多数研究仅关注单个二苯甲酮化合物在实验条件下的降解动力学以及降解产物,对于该类化合物的转化机理缺乏系统的认知. 因此,本文主要梳理二苯甲酮类化合物在氧化/消毒等水处理相关过程中的转化反应机理,为其风险评价和控制管理提供理论支持.
1. 氧化反应(Oxidation reactions)
氧化反应是指氧化剂与还原性底物之间发生的化学反应,在氧化反应中氧化剂将部分还原性官能团转化为氧化性官能团. 除了传统的氧化反应外,高级氧化技术近年来在水处理领域应用较广,主要借助光、声、电、磁等物理和化学过程中所产生的具有强氧化作用的活性氧自由基与底物发生反应. 羟基自由基(·OH)是活性氧自由基中的一种,具有高的电负性和电极电位(2.8 V),其氧化能力远远超过普通的化学氧化剂. 利用·OH作为氧化剂可以与大多数有机污染物及晶体材料发生氧化还原反应,可将水中的有机物降解成小分子有机物或完全矿化成CO2和H2O,实现污染物的高效去除[15 − 17].
Wang等研究了紫外防晒剂2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮在臭氧氧化处理中的转化特征[18]. 由于臭氧(O3)分子是由O2分子携带一个O原子构成,是一种性质活泼的暂存状态. 臭氧本身也是一种氧化还原电位很高的氧化剂(2.07 V),其氧化反应有两种方式,一种是O3分子直接进攻有机物形成臭氧化中间产物,并进一步分解;另一种是O3在紫外光诱导下,生成更为活泼的·OH.
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) Wang等发现2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮的氧化转化主要涉及两条转化路径[18]. 路径Ⅰ:由于2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮分子中C(7)原子的电子云密度较低,C(1)—C(7)和C(1´)—C(7)键容易断裂生成中间产物P1和P2,在O3和·OH存在的情况下,·OH攻击并取代羧基,P1也可以转化为P2. P2的苯环上有3个羟基官能团,很容易被臭氧继续氧化导致C(4)—C(5)键断裂,生成新的中间产物P3. P3的C(2)—C(3)键断裂被进一步氧化生成P4(草酸),是臭氧氧化过程的最终产物.
路径Ⅱ:BPs分子中与C(3´)相连的氢质子被·OH取代生成P6,由于P6具有与2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮相似的结构,其中C(1´)—C(7)键也可以被O3和·OH破坏而生成P7,但实验中发现中间产物P7的浓度始终低于其他产物,进一步研究发现P7可以继续与臭氧发生反应,转化为含氧杂环化合物(P9)和一些有机羧酸(P8, P10). 由于在整个实验过程中不断补充臭氧,中间产物有机羧酸(P8和P10)可以进一步氧化为更小分子的酸,如P11和P4. 另外,与P2相似,P6苯环上的3个羟基也很容易被继续氧化生成P12,并进一步发生苯环断裂生成羧酸类化合物(P13). 若反应体系中有羟基自由基,将进一步进攻P13发生脱羧反应生成P14,其C(1)—C(7)和C(1´)—C(7)键可以被O3和·OH继续进攻,在反应开始的4 min内大量生成P11和P4,而P11也会被羟基自由基进攻导致C—C断裂最终生成P4(图1a)[18].
 图 1 BPs类化合物的氧化反应途径Figure 1. Oxidation pathways of BPsa. 2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮的臭氧氧化过程;b. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的过硫酸盐活化转化过程;c. 氯代2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化体系中的Baeyer-Villiger氧化机理;d. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮氧化为2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮的过程(Ox:氧化反应)a. Ozone oxidation of 2,2 ́,4,4 ́-tetrahydroxy-benzophenone; b. Persulfate activation oxidation of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone; c. Baeyer-Villiger oxidation of chloro-2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in a chlorinated system; d. The oxidation of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone to 2,4-dihydroxy-benzophenone(Ox:Oxidation)
图 1 BPs类化合物的氧化反应途径Figure 1. Oxidation pathways of BPsa. 2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮的臭氧氧化过程;b. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的过硫酸盐活化转化过程;c. 氯代2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化体系中的Baeyer-Villiger氧化机理;d. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮氧化为2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮的过程(Ox:氧化反应)a. Ozone oxidation of 2,2 ́,4,4 ́-tetrahydroxy-benzophenone; b. Persulfate activation oxidation of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone; c. Baeyer-Villiger oxidation of chloro-2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in a chlorinated system; d. The oxidation of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone to 2,4-dihydroxy-benzophenone(Ox:Oxidation)过硫酸盐活化氧化也是近年研究较多的一种高级氧化处理技术,过硫酸盐可以诱导产生多种强氧化性自由基,如硫酸根自由基、羟基自由基等,利用这些自由基实现对污染物的高效降解甚至矿化. Pan等在光活化过硫酸盐降解2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的研究中提出了两条主要反应路线[19],如图1b所示. 其中路线Ⅰ是由诱导产生的·OH攻击2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮分子中的C(1)—C(7)键一侧的苯环,生成键裂解产物P1. 途径Ⅱ主要涉及羟基化反应,生成了一系列连续羟基化产物2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮→P2→P6→P7. 在这个过程中,中间产物P2还可以发生去甲基化生成P5. 此外,P2还可以通过直接氧化进一步转化为P3和P4. 除臭氧氧化、过硫酸盐氧化法外,高级氧化法还有光催化氧化法[20]、芬顿氧化法[21]、超声氧化法[22]等,这些方法都能生成·OH,可以降解水体中难以被普通氧化剂氧化的污染物.
在水的消毒处理中,需要向水中投加氧化性消毒剂(如次氯酸钠、臭氧等)以杀灭病原微生物,但这些消毒剂不仅仅和病原微生物反应,还可以和水中的还原性化学物质发生氧化还原反应. Zhang等所在的研究团队系统研究了多种BPs类防晒剂在氯化消毒过程中的转化反应[23],发现BPs类化合物在氯化消毒中大多会发生Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应[24]. 具体而言,在强氧化剂次氯酸的作用下,可以将BPs分子中的酮羰基氧化生成酯基衍生物,即Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应. 这些生成的酯基化合物还可以继续发生一系列反应生成氯代苯酚类产物,其在次氯酸体系中还可以继续发生氧化反应,生成苯醌类化合物,经过氧化开环,最后生成氯代乙酸、三氯甲烷类小分子高毒性消毒副产物. 一般而言,BPs防晒剂分子中羰基的化学性质比较稳定,但正是由于发生了Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应,改变了羰基的稳定性,才导致后续一系列反应的发生. 由此可见,Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应是BPs和其他含有酮羰基芳香族化合物氯化过程中形成氯仿等高毒性消毒副产物的关键环节(图1c)[25].
在2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的氧化、消毒等处理过程中发现,无论在酸性条件还是碱性条件下2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮分子中的甲氧基都会被·OH攻击发生脱甲基反应,转化为新产物2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮(图1d)[26 − 28]
在氧化、消毒处理过程中,BPs转化主要涉及的氧化反应分为普通的分子氧化反应和高级的自由基氧化反应. 普通氧化反应主要在臭氧氧化过程中发生,臭氧分子会直接和BPs发生反应使其转化. 而高级氧化反应存在于多种处理方式中,诱导生成的羟基自由基、硫酸根自由基等强氧化性自由基参与反应. 此外, Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应可高效的将酮类化合物转化为酯类化合物,这对氯消毒至关重要,可将BPs转化为相对分子质量较小的产物.
2. 取代反应(Substitution reactions)
取代反应是指化合物分子中某原子或原子团被试剂中相似类型的其它原子或原子团所替代的反应[29],可用通式表示为:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) 式中R-L为反应基质,A为进攻试剂,R-A为取代产物,L为离去基团.
芳香族化合物的取代反应从机理上可分为亲电取代、亲核取代以及自由基取代. 芳环亲电取代是指芳环上的氢原子被亲电试剂所取代的反应,如硝化、卤化、磺化、烷基化和酰基化等. 如果与芳环反应的试剂为亲核试剂,则发生芳环亲核取代. 从BPs类化合物的分子结构出发,其在氧化、消毒过程中可能发生亲电卤代反应和亲核水解反应.
2.1 亲电卤代反应
在氯化消毒处理中,投加的消毒剂次氯酸分子容易在水中发生极化形成Clδ+和OHδ−,其中带部分正电荷的Clδ+扮演亲电试剂的角色,容易进攻BPs分子中电子云密度更高的原子而发生亲电取代反应. 由于BPs类化合物分子中有多个电子云密度较高的区域,在氯化消毒处理中可生成多种氯代产物(图2a).
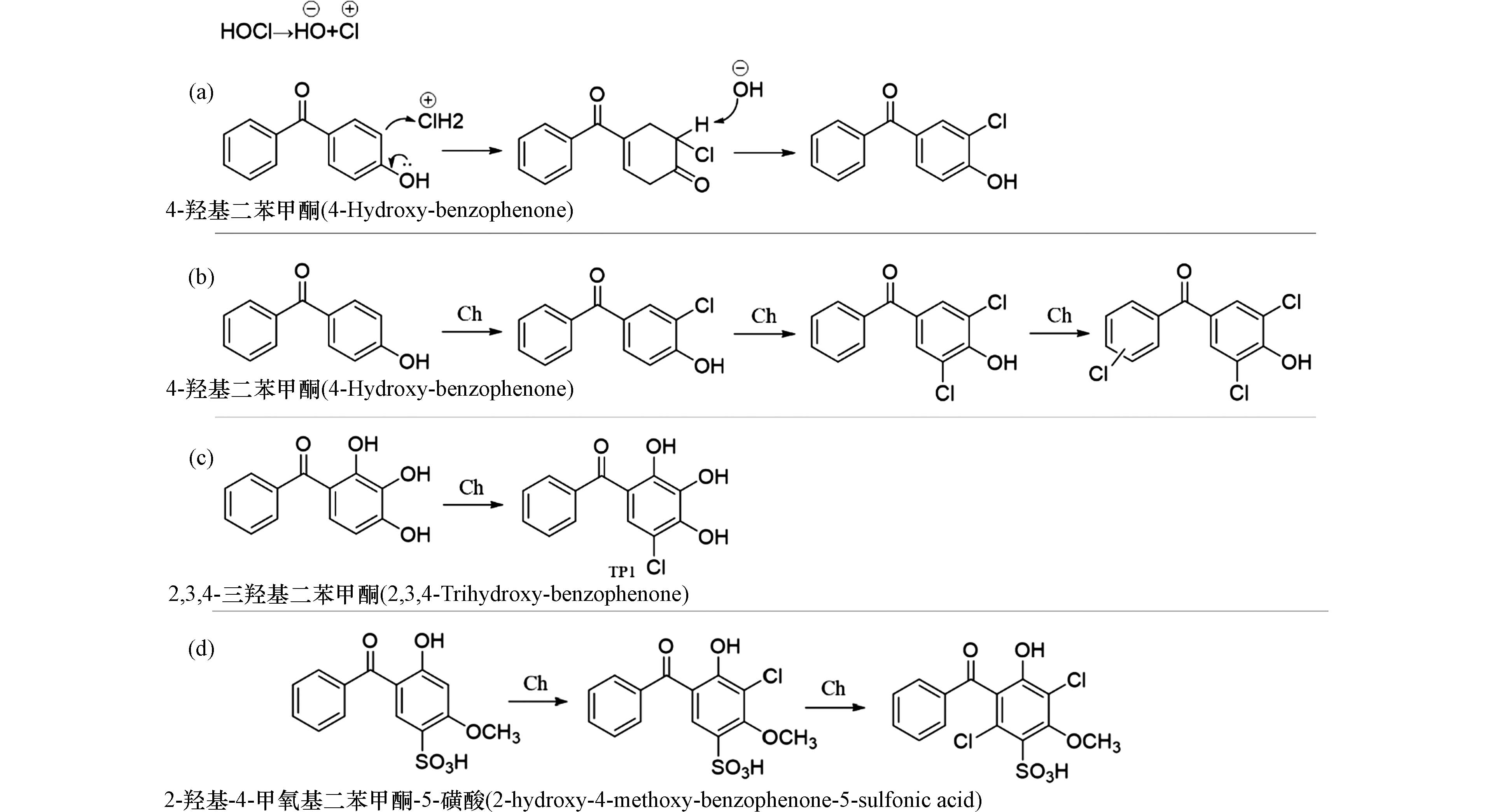 图 2 BPs类化合物的氯化转化途径Figure 2. Chlorination transformation pathways of BPsa. 4-羟基二苯甲酮的亲电氯化反应机理;b. 4-羟基二苯甲酮在氯化体系中的转化机理;c. 2,3,4-三羟基二苯甲酮在紫外-氯化体系中的转化机理;d. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化体系中的转化机理(Ch:氯化反应)a. Electrophilic chlorination mechanisms of 4-hydroxy-benzophenone; b. Transformation mechanisms of 4-hydroxy-benzophenone in chlorinated system; c. Transformation mechanisms of 2,3,4-trihydroxy-benzophenone in UV-chlorinated systems; d. Transformation mechanisms of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in chlorinated system(Ch:Chlorination)
图 2 BPs类化合物的氯化转化途径Figure 2. Chlorination transformation pathways of BPsa. 4-羟基二苯甲酮的亲电氯化反应机理;b. 4-羟基二苯甲酮在氯化体系中的转化机理;c. 2,3,4-三羟基二苯甲酮在紫外-氯化体系中的转化机理;d. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化体系中的转化机理(Ch:氯化反应)a. Electrophilic chlorination mechanisms of 4-hydroxy-benzophenone; b. Transformation mechanisms of 4-hydroxy-benzophenone in chlorinated system; c. Transformation mechanisms of 2,3,4-trihydroxy-benzophenone in UV-chlorinated systems; d. Transformation mechanisms of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in chlorinated system(Ch:Chlorination)在4-羟基二苯甲酮的氯化消毒过程中发现,无论是在酸性、中性、还是碱性条件下,苯环上的多个氢原子能被Clδ+连续取代,生成单氯取代、二氯取代、三氯取代产物(图2b)[30]. 在另一项紫外-氯联合处理2,3,4-三羟基二苯甲酮的研究中发现底物有两条可能的转化途径(图2c)[31]. 途径1中,氯取代首先发生在2,3,4-三羟基二苯甲酮的芳环上,形成单氯代产物TP1. 除了次氯酸作为消毒剂之外,氯胺也是在实际水消毒处理中常用的消毒剂,研究表明,2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮和2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸被氯或者氯胺消毒时都可以被Clδ+进攻发生氯取代反应,且2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化和氯胺化过程中遵循相似的反应途径,生成了氯代产物. 由于次氯酸的反应活性高于氯胺,氯化反应比氯胺化反应更快. 另外,由于2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸分子中含有吸电子官能团磺酸基,其与氯、氯胺的反应活性低于2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮(图2d)[32].
卤素离子是水体中,特别是沿海地区水体中常见无机离子,除了含量最高的氯离子外(约数十至数百 mg·L−1),溴离子和碘离子的浓度也可以达到ng·L−1—μg·L−1水平. 当向含有Br−、I−的水中投加次氯酸钠进行消毒处理时,可以将它们氧化为次溴酸、次碘酸,它们的性质与次氯酸相似,也能快速地与底物发生卤代反应[33]. 研究发现溴离子存在时,2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的氯化消毒处理过程中生成了12种溴代化产物[34]. 相似地,若碘离子存在时,检出了4种碘代产物[35]. 溴离子、碘离子的存在增加了氯化体系中的竞争反应,消耗了部分次氯酸,抑制了2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的转化效率. 但是,研究表明溴代产物、碘代产物往往具有比氯代产物更高的毒性,其所导致的健康风险更高.
2.2 水解反应
水解反应是指水分子作为亲核试剂,攻击化合物中的原子或原子团形成新物质的过程[36 − 37]. 通过水解反应,羟基(·OH)被引入化合物中,羟基属于供电子官能团,使化合物更容易进一步转化[38]. 如前所述,BPs属于酮类化合物,经过Baeyer-Villiger反应转化为酯类中间体,其与水分子发生亲核水解,形成苯酚类和苯甲酸类产物.
此外,就消毒处理中所投加的消毒剂次氯酸钠而言,属于弱酸强碱盐,其在不同pH条件下也会发生水解. 比如在较强酸性条件下,次氯酸钠将水解为次氯酸. 图3a中4-羟基二苯甲酮生成二氯取代产物后,发生Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应后生成酯类化合物,经水解反应生成了酚类产物P3 [30].
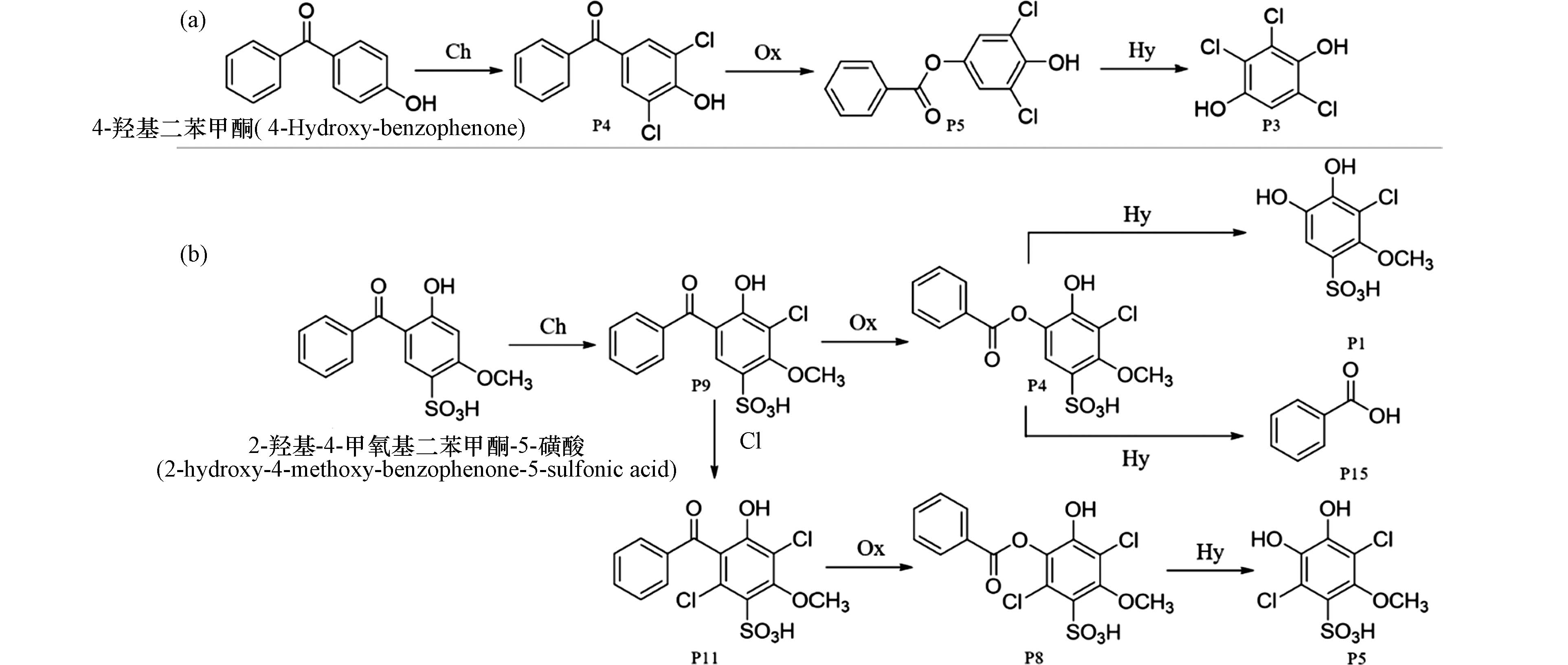 图 3 BPs类化合物的氧化及水解反应途径Figure 3. Oxidation and hydrolysis reaction pathways of BPsa. 4-羟基二苯甲酮在氯化体系中的转化机理;b. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化体系中的转化机理(Ch:氯化反应;Ox:氧化反应;Hy:水解反应)a. Transformation pathways of 4-hydroxy-benzophenone in chlorinated system; b. Transformation pathways of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in chlorinated system(Ch:Chlorination;Ox:Oxidation;Hy:Hydrolysis)
图 3 BPs类化合物的氧化及水解反应途径Figure 3. Oxidation and hydrolysis reaction pathways of BPsa. 4-羟基二苯甲酮在氯化体系中的转化机理;b. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在氯化体系中的转化机理(Ch:氯化反应;Ox:氧化反应;Hy:水解反应)a. Transformation pathways of 4-hydroxy-benzophenone in chlorinated system; b. Transformation pathways of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in chlorinated system(Ch:Chlorination;Ox:Oxidation;Hy:Hydrolysis)如前所述,次氯酸钠在较强酸性pH条件下的主要赋存形态为次氯酸,在中性、碱性pH条件下次氯酸电离生成次氯酸根离子,是一种强亲核试剂,可使2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的Baeyer-Villiger氧化所得的酯产物(P4和P8)继续发生亲核水解,生成酚类产物(P1和P5)和苯甲酸(P15)(图3b)[25].
由于2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸分子中既含有甲氧基又含有磺酸基官能团,在活化过硫酸盐氧化降解中发现由于水解反应的发生,生成了脱磺基、脱甲氧基的羟基取代产物[39]. 并且发现2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸分子在溴离子、碘离子存在下的氯化体系中会发生卤代反应生成卤化产物. 再发生Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应生成酯,进水解反应[34 − 35]. 大量研究表明,BPs的降解过程中,Baeyer-Villiger氧化是水解反应发生的重要前提.
3. 脱羧反应(Decarboxylation reactions)
脱羧反应是指羧酸分子中失去羧基放出二氧化碳的反应,该反应广泛应用于化工、医药等领域,是一种非常重要的化学转化,常用来构建新的C—C键和 C—X键,可以制备许多反应中间体[40]. 其反应通式为:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) 由于羧酸分子中的羧基为吸电子取代基,化学性质较为稳定,一般情况下不易发生脱羧反应,但在特殊条件下,羧酸能脱去羧基(失去二氧化碳)而生成烃. 脱羧反应通常不需要特殊的催化剂,在加热、碱性条件及光照等条件下即可发生. 当反应体系中有光催化剂存在时,催化诱导产生的活性自由基在脱羧过程中发挥关键作用[41]. 比如在紫外活化过硫酸盐处理2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸时,其中间产物会被·OH、SO4−·进攻氧化脱去羧基形成新的转化产物(图4a)[39]. 研究发现单独紫外[42]或紫外-过氧化物[43]降解BPs时也会发生脱羧反应,但紫外活化过硫酸盐对2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的降解速率远远大于其他两种,这说明可能是因为诱导产生的SO4−·加速了脱羧反应.
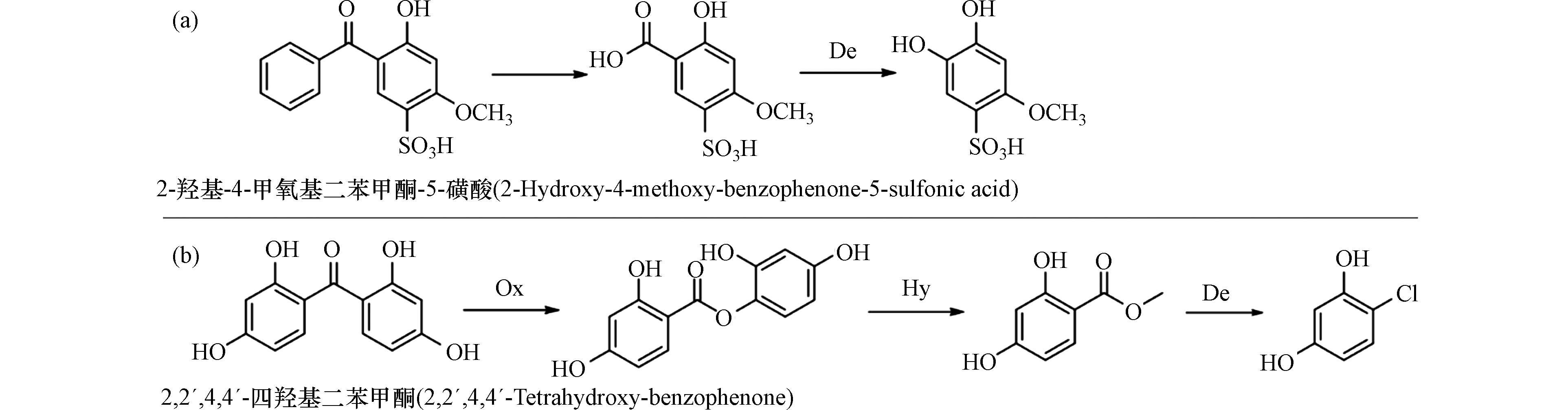 图 4 BPs类化合物转化中间产物的脱羧反应途径Figure 4. Decarboxylation pathway of BPs conversion intermediatesa. 紫外/过硫酸盐活化体系中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的转化机理;b. 2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮在氯化体系中的转化机理(Ch:氯化反应;Ox:氧化反应;Hy:水解反应;De:脱羧反应)a. Transformation mechanisms of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in UV/persulfate-activated system; b. Transformation mechanisms of 2,2 ́,4,4 ́-tetrahydroxy-benzophenone in a chlorinated system (Ch:Chlorination;Ox:Oxidation;Hy:Hydrolysis;De:Decarboxylation)
图 4 BPs类化合物转化中间产物的脱羧反应途径Figure 4. Decarboxylation pathway of BPs conversion intermediatesa. 紫外/过硫酸盐活化体系中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的转化机理;b. 2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮在氯化体系中的转化机理(Ch:氯化反应;Ox:氧化反应;Hy:水解反应;De:脱羧反应)a. Transformation mechanisms of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in UV/persulfate-activated system; b. Transformation mechanisms of 2,2 ́,4,4 ́-tetrahydroxy-benzophenone in a chlorinated system (Ch:Chlorination;Ox:Oxidation;Hy:Hydrolysis;De:Decarboxylation)在BPs的氯化处理过程中,也发现了脱羧反应形成酚类产物,比如,2,2´,4,4´-四羟基二苯甲酮在氯化处理中发生Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应生成苯甲酸苯酯类衍生物,进而发生亲核水解反应生成苯甲酸类产物,其在次氯酸作用下继续发生氯代脱羧反应. 值得注意的是,氯代脱羧反应促进了酚类产物的不断形成[23]. 酚类产物的生成促进了氯仿的大量生成(图4b). 而且在Larson和Rockwell等的研究中也发现取代苯甲酸在氯化过程中可发生脱羧并形成氯酚[44].
除上述常见的几种反应外,在氧化、消毒处理过程中BPs还会发生其他一些反应. 比如,2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮被过硫酸盐氧化时·OH进攻苯环,导致形成羟基化产物P5A,进而通过羟基缩合反应转化为P1(图5a)[45]. 2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮及羟基化产物P229和P245在紫外和TiO2存在下发生Norrish Ⅰ反应,化合物中羰基的α-碳键被破坏形成只含有一个苯环的P94、P109和P122(图5b)[46]. 2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸在酸性的氯化处理过程中,先经过连续的氯化反应生成二氯代产物P11. 随着Baeyer-Villiger反应的发生转化为酯化产物P8,进一步水解为酚类产物P5. 类儿茶酚水解产物P5在酸性氯化体系中进一步氧化缩合,形成五元杂环类呋喃产物P6(图5c)[25].
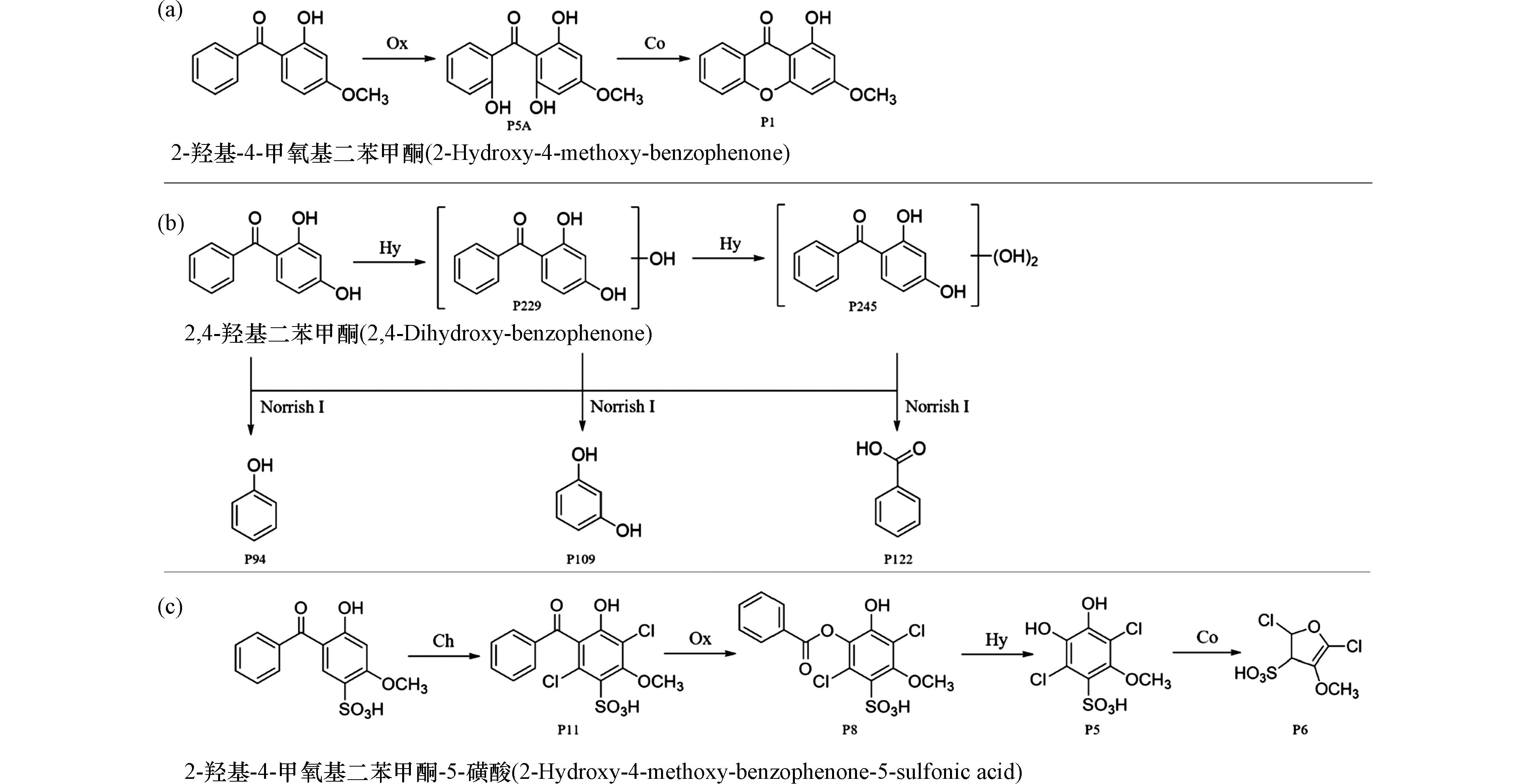 图 5 BPs类化合物其他反应的反应途径Figure 5. Some other transformation pathways of BPsa. 过硫酸盐活化体系中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的转化机理;b. 紫外/TiO2氧化体系中2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮的转化机理;c. 氯化体系中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的转化机理(Ox:氧化反应;Hy:水解反应;Co:缩合反应)a. Transformation pathways of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone in persulfate activation system; b. Transformation pathways of 2,4-dihydroxy-benzophenone in UV/TiO2 oxidation; c. Transformation pathways of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in chlorinated system(Ox:Oxidation;Hy:Hydrolysis;Co:Condensation)
图 5 BPs类化合物其他反应的反应途径Figure 5. Some other transformation pathways of BPsa. 过硫酸盐活化体系中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮的转化机理;b. 紫外/TiO2氧化体系中2,4-二羟基二苯甲酮的转化机理;c. 氯化体系中2-羟基-4-甲氧基二苯甲酮-5-磺酸的转化机理(Ox:氧化反应;Hy:水解反应;Co:缩合反应)a. Transformation pathways of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone in persulfate activation system; b. Transformation pathways of 2,4-dihydroxy-benzophenone in UV/TiO2 oxidation; c. Transformation pathways of 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy-benzophenone-5-sulfonic acid in chlorinated system(Ox:Oxidation;Hy:Hydrolysis;Co:Condensation)由于这些反应的相关研究报道较少,本文没有展开详细论述. 但需要特别说明的是,在氧化、消毒处理过程中由于反应复杂,研究者所提出的转化反应路径中的中间产物并非全部检出,导致很难完整描述某化合物的转化路径. 加之,由于转化的中间产物产率低、生成量少,难以分离获得纯净的产物,很多研究者往往只是通过质谱信息推测产物的结构,进而推断可能的反应机理. 众所周知,质谱信息只能给出准确的相对分子质量,不能确定官能团(如羟基、氯离子、甲氧基等)在化合物分子中的确切取代位置,难以确定产物的绝对分子结构. 因此,在实验研究过程中需要密切观察不同反应阶段中间产物的生成规律,并且分离或制备相应的产物,借助高分辨质谱、核磁共振等多种方式确定产物的绝对分子结构. 确切的产物分子结构为科学准确地揭示底物在氧化、消毒处理中的转化机理提供支撑.
4. 结论(Conclusion)
BPs类紫外防晒剂应用广泛,其潜在的负面生物学效应备受关注,因此研究它们在水处理过程中的转化特征非常必要. 氧化和消毒是最常用的水处理技术,本文总结了BPs类防晒剂在氧化和消毒处理中的转化机理,为该类污染物的风险管理和控制提供科学依据.
BPs的分子中含有不饱和的芳香苯环、酮羰基、羟基、甲氧基等官能团,其在氧化、消毒等水处理过程中最主要的转化机制是氧化反应,羟基自由基、硫酸根自由基等是最主要的活性氧化物种,可以促进BPs类物质的快速转化[47]. 此外,氯化消毒处理中的Baeyer-Villiger氧化反应可高效地将酮类化合物转化为酯类化合物,为后续的水解反应、脱羧反应、以及氧化开环提供了可能,大大促进了小分子高毒性消毒副产物的生成.
也正是由于BPs的分子中含有羰基、磺酸基等吸电子取代基,以及羟基、甲氧基等供电子取代基,BPs在氯化消毒处理中非常容易发生亲电取代反应,生成一系列单卤代、二卤代、三卤代产物,由于卤代产物的显著毒性效应,其潜在的生态与健康风险值得关注. 此外,BPs类化合物的Baeyer-Villiger氧化的酯类中间产物在次氯酸消毒体系中也容易发生亲核水解反应生成苯甲酸类产物,进一步与次氯酸发生取代脱羧反应.
由此可见,现有关于BPs类防晒剂在水处理中的转化主要涉及氧化反应、取代反应、脱羧反应等,虽然处理的方法不尽相同,但所涉及的反应类型大体相似. 因此,从反应机理出发,选择适当的处理方法,实现提高处理效率的目标,为该类污染物的风险管控提供科学依据.
-
表 1 污泥主要性质
Table 1. Main characteristics of the sludge
供试污泥品种 TCOD/(mg·L−1) SCOD/(mg·L−1) 含水率/% TS/% VS/% pH 种泥 63 000±300 9 500±300 88.28 11.32 3.81 10 高固污泥 65 000±600 9 700±300 89.53 10.93 4.35 5.5 -
[1] ZHAO J, LIN G, WANG Q, et al. Aged refuse enhances anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2017, 123: 724-733. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.026 [2] LIAO X, LI H, CHENG Y, et al. Process performance of high-solids batch anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Technology, 2014, 35(21-24): 2652-2659. [3] MUMME J, LINKE B, TöLLE R. Novel upflow anaerobic solid-state (UASS) reactor[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(2): 592-599. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.08.073 [4] KARTHIKEYAN O, VISVANATHAN C. Bio-energy recovery from high-solid organic substrates by dry anaerobic bio-conversion processes: a review[J]. Reviews in Environmental Science & Bio/technology, 2014, 45(26): 257-284. [5] ZHANG Y Y, LI H, CHENG Y C, et al. Influence of solids concentration on diffusion behavior in sewage sludge and its digestate[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 152: 674-677. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2016.06.058 [6] ZHEN G, LU X, ZHAO Y, et al. Enhanced dewaterability of sewage sludge in the presence of Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 116: 259-265. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.170 [7] SHI Y, YANG J, YU W, et al. Synergetic conditioning of sewage sludge via Fe2+/persulfate and skeleton builder: Effect on sludge characteristics and dewaterability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 270: 572-581. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.122 [8] YANG J, LIU X, WANG D, et al. Mechanisms of peroxymonosulfate pretreatment enhancing production of short-chain fatty acids from waste activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2018, 148: 239-249. [9] LUO J Y, ZHANG Q, WU L J, et al. Improving anaerobic fermentation of waste activated sludge using iron activated persulfate treatment[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 268: 68-76. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.080 [10] FANG W, ZHANG X, ZHANG P, et al. Overview of key operation factors and strategies for improving fermentative volatile fatty acid production and product regulation from sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 87: 93-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.027 [11] 吴福满. 亚硝酸盐预处理剩余污泥厌氧发酵产酸研究[D]. 大连; 大连理工大学, 2018. [12] 陈哲柯. 基于厌氧发酵的剩余污泥产中链脂肪酸研究[D]. 长沙; 湖南大学, 2019. [13] 何海洋, 王鲁, 马军. 过硫酸盐在污泥处理中的应用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41: 126-131. [14] 段妮娜. 污泥厌氧消化系统中硫转化的主要途径及影响因素[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(12): 129-133. [15] 任守军, 孙永明, 王瑶, 等. 硫酸盐对厌氧降解糖蜜酒精废水的影响机理及处理工艺研究进展[J]. 新能源进展, 2015, 3(5): 346-351. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-560X.2015.05.005 [16] 赵迎新, 麻泽浩, 杨知凡, 等. 污泥生物炭催化高级氧化过程进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(7): 11. [17] 王晓琳. 污泥基生物炭强化污泥厌氧产酸的机理研究[D]. 长沙; 湖南大学, 2018. [18] ELEFSINIOTIS P, LI D. The effect of temperature and carbon source on denitrification using volatile fatty acids[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2006, 28(2): 148-155. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2005.10.004 [19] HE Z W, YANG C X, WANG L, et al. Feasibility of short-term fermentation for short-chain fatty acids production from waste activated sludge at initial pH10: Role and significance of rhamnolipid[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 290: 125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.01.033 [20] 樊雅欣. 过硫酸盐预处理协同硫酸盐还原菌强化剩余污泥厌氧发酵产酸研究[D]. 太原; 太原理工大学, 2019. [21] 李志军. 负载Fe(Ⅱ)颗粒性活性炭活化过硫酸盐处理老龄垃圾渗滤液的研究[D]. 长沙; 湖南大学, 2016. [22] ROMERO A, SANTOS A, VICENTE F, et al. Diuron abatement using activated persulphate: Effect of pH, Fe(II) and oxidant dosage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2010, 162(1): 257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.05.044 [23] GOEL R, MINO T, SATOH H, et al. Enzyme activities under anaerobic and aerobic conditions in activated sludge sequencing batch reactor[J]. Water Research, 1998, 32(7): 2081-2088. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00425-9 [24] YANG Y, ZHANG Y, LI Z, et al. Adding granular activated carbon into anaerobic sludge digestion to promote methane production and sludge decomposition[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 149(15): 1101-1108. [25] 亓信石. 污泥预处理强化及厌氧消化特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨; 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016. [26] 李哲, 林嘉薇, 胡勇有. 热碱解-水解预处理剩余污泥的效果研究[J]. 华南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 51(1): 42-48. [27] CHEN Y, LIU K, SU Y, et al. Continuous bioproduction of short-chain fatty acids from sludge enhanced by the combined use of surfactant and alkaline pH[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2013, 140(3): 97-102. [28] WEN C, PAUL W, LEENHEER J A, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2003, 37(24): 5701-5710. [29] ZHENG H, YE C. Photodegradation of Acetochlor and Butachlor in Waters Containing Humic Acid and Inorganic Ion[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 2001, 67(4): 601-608. [30] 杨黎俊. 亚硝酸预处理协同烷基糖苷处理剩余污泥产酸的研究[D]. 太原; 太原理工大学, 2019. [31] WEI W A, WG A, HHN A, et al. Enhanced high-quality biomethane production from anaerobic digestion of primary sludge by corn stover biochar - ScienceDirect[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 306: 123159. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123159 [32] 章钦, 罗景阳, 操家顺, 等. 生物炭对剩余污泥厌氧发酵产酸的影响[J]. 环境科技, 2019, 32(1): 1-6. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:





