-
稀土元素(Rare Earth Elements, REEs)具有独特的核外电子结构和变价特征,物理性能优异[1],已成为国民经济可持续发展不可或缺的重要战略资源[2-3]。稀土在工业催化剂中应用广泛。2014年,全球流化催化裂化(Fluid Catalytic Cracking,FCC)催化剂供应量约为8.4×105 t[4]。由于有机物和重金属的影响,FCC催化剂在使用过程中结构被破坏并失活,最终变为废FCC催化剂,废FCC催化剂中的稀土主要为镧(La)和铈(Ce),且稀土质量分数约为2%~4%[5]。2015年,我国废FCC催化剂产生量约为1.43×105 t,折合稀土(La、Ce)约为2.86×103~5.72×103 t[6]。寻找合理、高效的方法来回收其中的稀土元素迫在眉睫。
目前,国内外回收稀土元素的主要方式是溶剂萃取法[7]。INNOCENZI等[8]对溶剂萃取法和选择性沉淀法进行了比较,发现溶剂萃取法对主杂质铝(Al)的萃取率较低,有利于提高La和Ce的回收率和最终产品质量。溶剂萃取法由浸出、萃取和反萃取3部分组成。对于浸出过程而言,浸出酸的选择是关键。BORRA等[9]发现,与有机酸相比,盐酸、硫酸和硝酸等无机酸更利于稀土的浸出。在萃取剂的选择上,目前对废FCC催化剂中稀土进行回收,研究最多的萃取剂是二(2-乙基己基)磷酸(P204)和2-乙基己基膦酸单2-乙基己基酯(P507)。YE等[10]研究了使用皂化的P507从废FCC催化剂中回收稀土的方法,当皂化率为20%时,La和Ce的萃取率可达100%。秦玉芳等[11]将废FCC催化剂用盐酸溶解,并用体积分数为60%的P204-煤油混合有机相萃取浸出液,当浸出液初始pH=2,萃取相比为2∶1时,萃取效果最好,稀土回收率达到91.76%。
用溶剂萃取法回收废FCC催化剂中的稀土时,会将一部分杂质Al萃取出来。铝是非常弥散的元素,在溶液中的赋存状态较为复杂,由于铝的两性,回收废FCC催化剂时去除铝的方法主要有碱法、酸法和萃取法[12]。目前,研究较多的主要是碱法和酸法,这2种方法工艺复杂,成本较高[13-14]。然而,对萃取法的研究鲜有报道,ZHAO等[15]研究了P507和P204对废FCC催化剂中稀土的萃取效果,发现P204对La和Ce的萃取效果较好,同时也会萃取出大量的Al,而P507对La和Ce的萃取效果比P204差,但萃取出的Al更少。
为进一步探索从废FCC催化剂中回收稀土时萃取法对铝的去除效果,本研究对萃取的过程和条件进行优化,选择常用的稀土萃取剂P204和P507作为萃取剂,着重研究了浸出过程、单一溶剂萃取过程和P204-P507复合萃取过程,以期为从废FCC催化剂中回收高纯度稀土提供有益参考。
-
本实验使用的废FCC催化剂来自于华东某炼油厂。盐酸(HCl, 36%~38%)、硝酸(HNO3, 65%~68%)和硫酸(H2SO4, 95%~98%)、氨水(NH3·H2O, ≥26%)、P204(C16H35O4P, 98%)、P507(C16H35O3P, 95%)、磺化煤油均为分析纯。
-
采用热重分析(TGA,DSC1型,梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司)仪测定废FCC催化剂样品中有机物的质量分数,并确定其最佳煅烧温度。废FCC催化剂样品先在105 ℃下干燥,冷却后过200目筛,然后在最佳煅烧温度下,马弗炉内煅烧2 h,冷却后储存于干燥器中备用。通过X射线衍射分析仪(XRD,D/max 2550V型,日本RIGAKU公司)对焙烧前后的废FCC催化剂的晶相结构进行分析。通过X射线荧光分析(XRF,XRF-1800型,日本岛津)初步确定样品的组成,然后用王水在180 ℃下对废FCC催化剂样品消解30 min并通过电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES,Agilent 710型,美国安捷伦科技有限公司)定量测定消解液中Ce、La、Al的质量浓度[16]。
-
1)浸出过程实验。首先,分别配制1、2、3、4、5 mol·L−1的盐酸、硝酸和硫酸,在浸出温度为60 ℃、固液比为1∶10、浸出时间为4 h的条件下,对550 ℃煅烧后的废FCC催化剂样品进行浸出,以确定最佳浸出酸及其最佳浓度。之后,采用控制变量法,控制其余条件为前一步所得最佳浸出条件,依次研究浸出时间(持续反应6 h,每间隔1 h取1次样)、浸出温度(控制温度分别为40、50、60、70、80 ℃)、固液比(控制固液比分别为1∶5、1∶10、1∶15、1∶20、1∶25)对Ce和La浸出率的影响。浸出过程在恒温水浴震荡箱中进行,并对锥形瓶进行加盖处理。将浸出液在转速为5 000 r·min−1条件下离心分离5 min并稀释至合适的倍数,用ICP-OES测定浸出液中Ce和La的质量浓度。
2)萃取过程实验。在最佳条件下浸出550 ℃焙烧后的废FCC催化剂样品,制得浸出液,其中Ce、La和Al的质量浓度分别为1 027 mg·L−1、657 mg·L−1和2 997 mg·L−1。分别配制浓度为0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5 mol·L−1的P204和P507萃取剂,并用氨水调节浸出液初始pH分别为1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5和3.0,探索单一溶剂萃取的最佳萃取条件。在最佳萃取条件下,控制P507在(P204+P507)混合萃取剂中的体积比分别为0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8和1.0,研究P204-P507复合萃取体系对浸出液中稀土和Al的萃取效果。所有萃取过程均在室温(25.0±0.2) ℃下进行,有机相与水相的体积比为1∶1。萃取过程平衡后,通过ICP-OES分析检测离心后上清液(水相)中Ce、La、Al的质量浓度。有机相中3种元素的质量浓度通过质量平衡法计算得出。
3)反萃取过程实验。使用2 mol·L−1的盐酸溶液作为反萃取剂,保持有机相和水相的体积比为1∶1,在室温(25.0±0.2) ℃下对有机相进行反萃取。反萃取过程平衡后,用ICP-OES检测上清液(水相)中Ce、La、Al的质量浓度。
金属浸出率的计算如式(1)所示。金属萃取率的计算如式(2)所示。金属回收率的计算如式(3)所示。
式中:n为稀释倍数;c为ICP-OES检测水相中金属离子的质量浓度,mg·L−1;v为上清液体积,mL;m为废FCC催化剂样品质量,g;w为废FCC催化剂样品中金属元素的质量分数;C0和Ce分别为初始和平衡时金属离子在水相中的质量浓度,mg·L−1;E'为反萃取率;W为金属回收率。
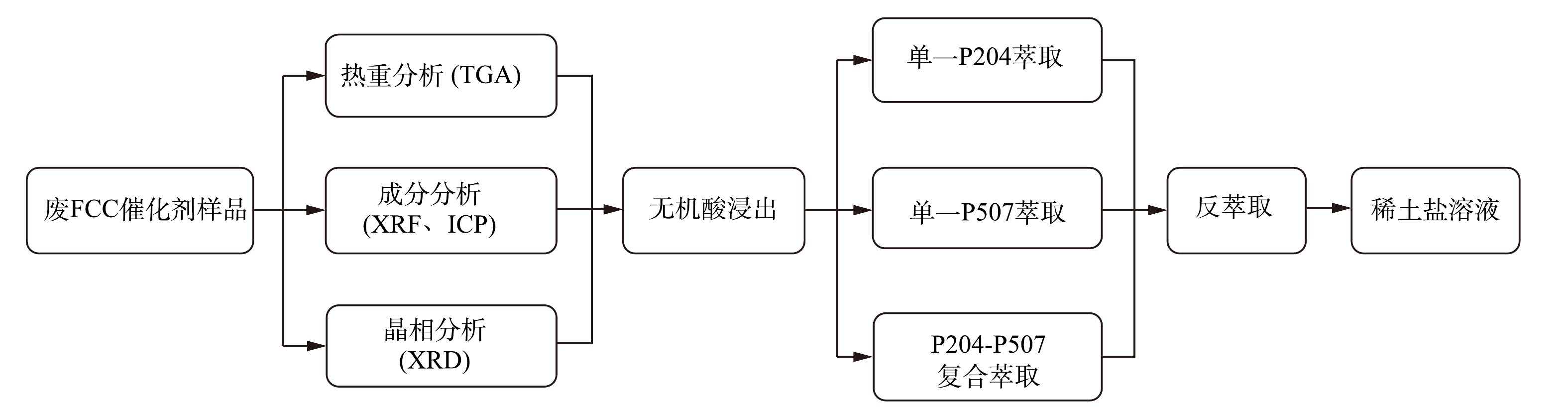
每组实验进行3次。实验数据为3次实验的平均值,误差线为标准差。详细工艺流程图见图1。
-
对废FCC催化剂进行了XRF分析,并处理数据得到各元素的质量分数,样品中主要元素为Al和Si,质量分数分别为36.33%和24.19%;稀土元素为Ce和La,质量分数分别为7.23%和3.84%。废FCC催化剂ICP-OES分析测定的Ce和La质量分数分别为1.56%和1.01%,REEs总质量分数为2.57%。据文献报道,废FCC催化剂中的REEs质量分数为2%~4%[17]。后续实验以ICP-OES测定的数据为准。
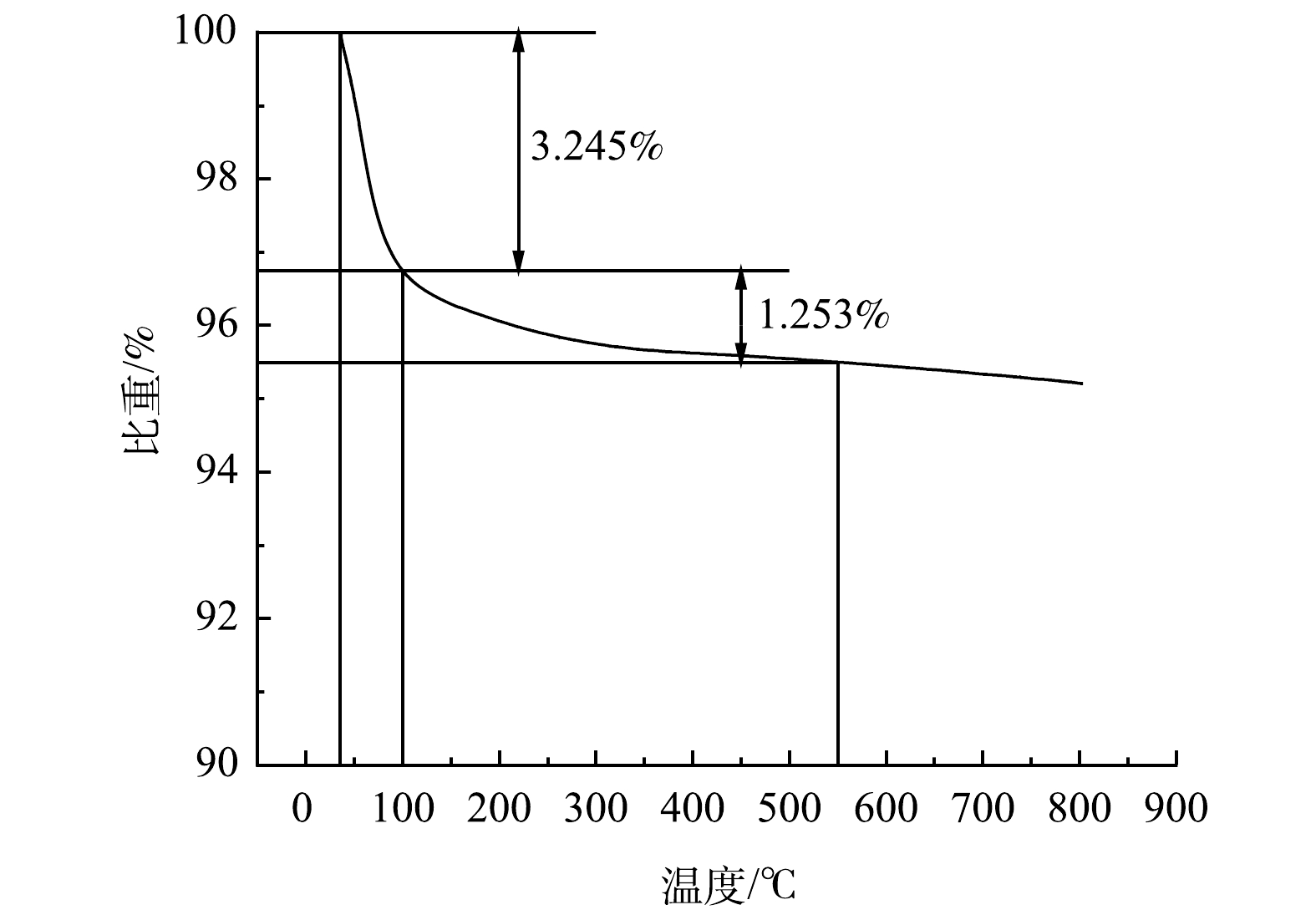
为确定废FCC催化剂中有机物的质量分数,对其进行了TGA分析,结果如图2所示。一般认为100 ℃左右失重是由于催化剂样品的脱水引起的。从图2可看出,废FCC催化剂中水分的质量分数为3.245%,有机物质量分数为1.253%。当温度高于550 ℃时,样品的重量几乎没有减少,可以认为550 ℃是最佳的焙烧温度。
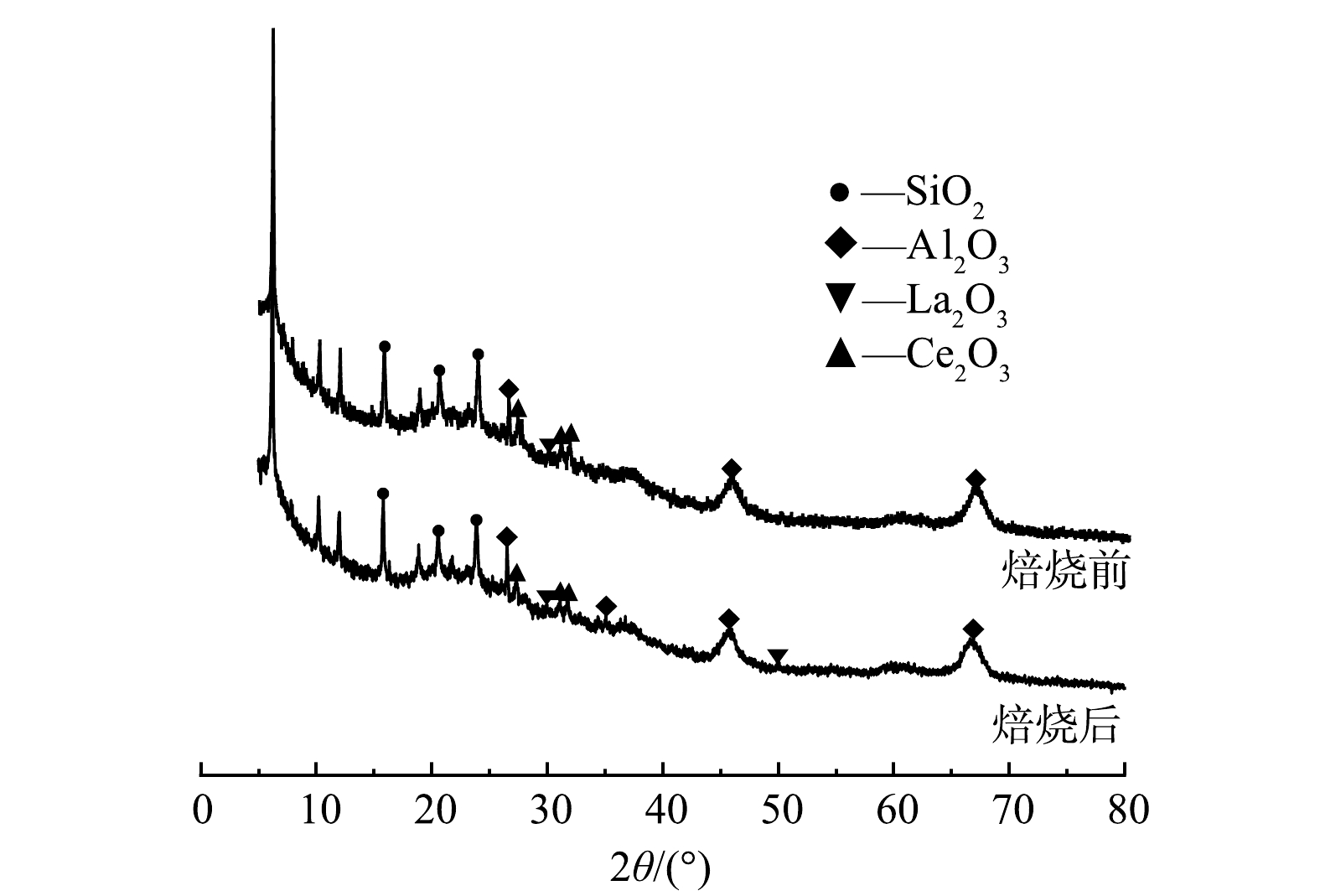
焙烧前后废FCC催化剂的XRD分析如图3所示。从图3可看出,焙烧对废FCC催化剂的晶相结构几乎不产生影响。废FCC催化剂中的金属主要是以金属氧化物的形式存在,且大多存在于非结晶相中,主要矿物成分为SiO2和Al2O3。观察到图中有较多的衍射峰,在2θ=15.88°、20.66°和23.78°时,发现明显的SiO2的特征峰;在2θ=26.5°、35.0°、45.9°和66.6°时,发现明显的Al2O3的特征峰。由于废FCC催化剂中La和Ce的质量分数较低,仅能观察到微弱的La2O3和Ce2O3特征峰。
-
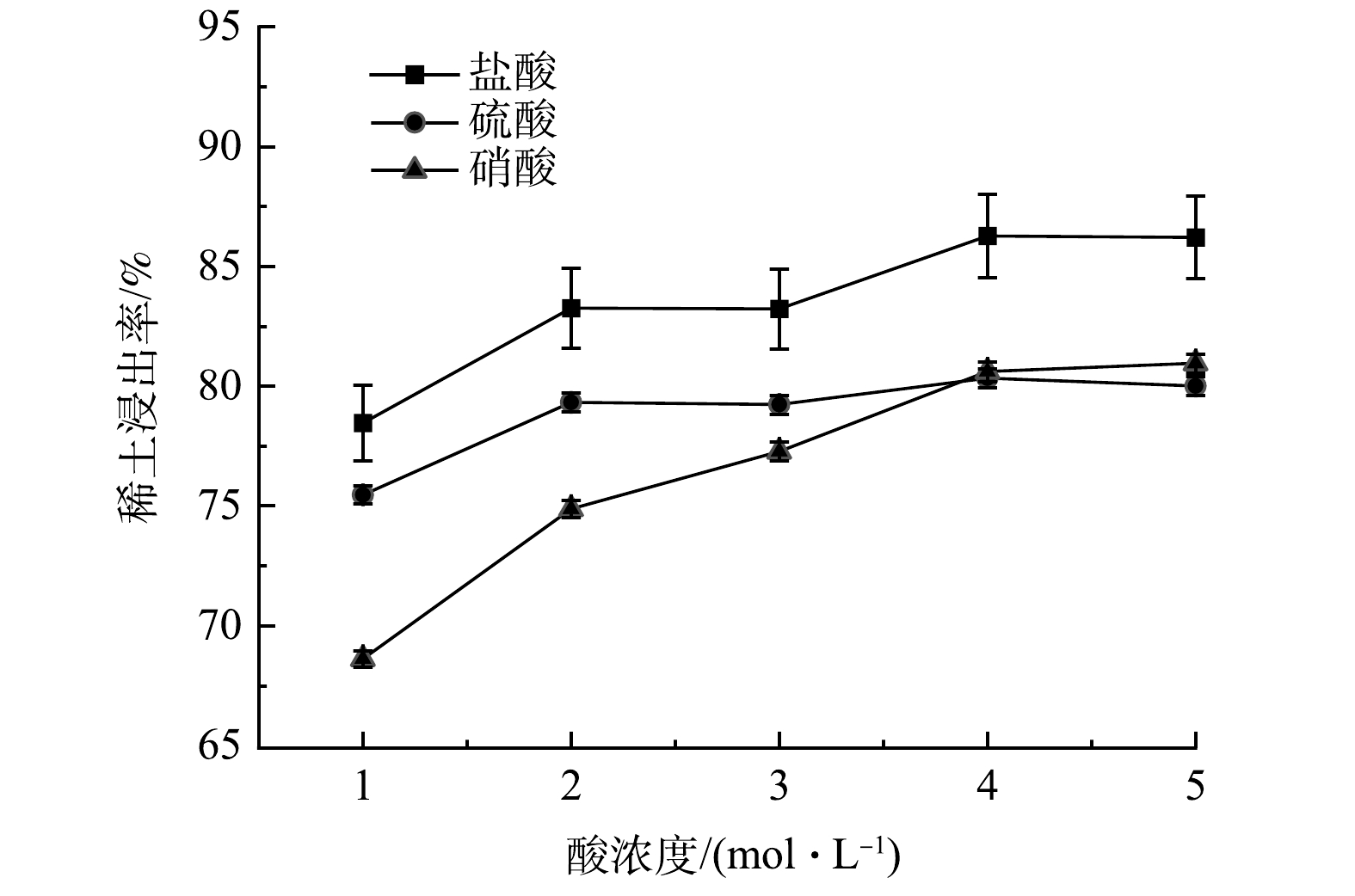
1)浸出酸的影响。不同种类和浓度的无机酸对REEs浸出率的影响如图4所示。由图4可看出,在相同条件下,盐酸对样品中REEs的浸出率明显优于硫酸和硝酸。其原因可能是,Cl−比NO3−和SO42−更易与稀土离子形成配位,且NO3−和SO4−可与稀土离子、Na+、K+形成稀土复盐沉淀,使浸出液中稀土的质量浓度降低[18]。当无机酸浓度从1 mol·L−1增加至4 mol·L−1时,REEs的浸出率迅速提高,最高浸出率可达86.3%。当无机酸浓度大于4 mol·L−1时,REEs浸出率的增加不明显。根据实验结果,后续稀土浸出实验采用4 mol·L−1盐酸溶液。
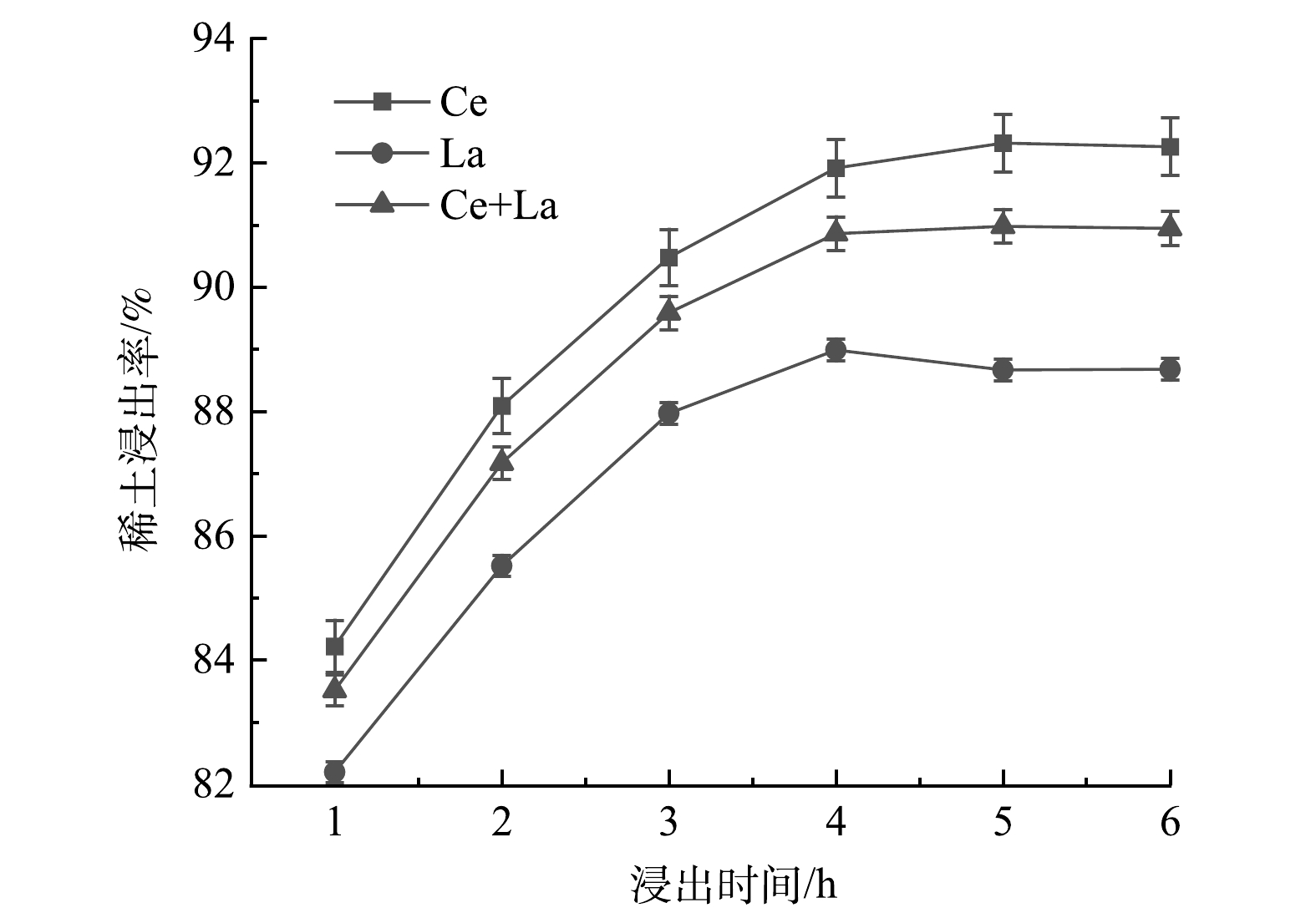
2)浸出时间的影响。图5显示了浸出时间对REEs浸出率的影响。由图5可看出,随着浸出时间的增加,REEs的浸出率逐渐提高。当反应时间超过4 h时,REEs浸出率的增加趋于缓慢。其原因可能是,在反应开始时,高浓度的反应物使反应剧烈,随着反应的进行,反应物的浓度逐渐降低,反应趋于平衡。当反应时间达到4 h时,La的浸出率达到最大为89.0%;当反应时间为5 h时,Ce的浸出率达到最大为92.3%。反应时间从4 h增加到6 h,Ce和La的总浸出率稳定在90.9%,因此,选择4 h作为浸出稀土的最佳时间。
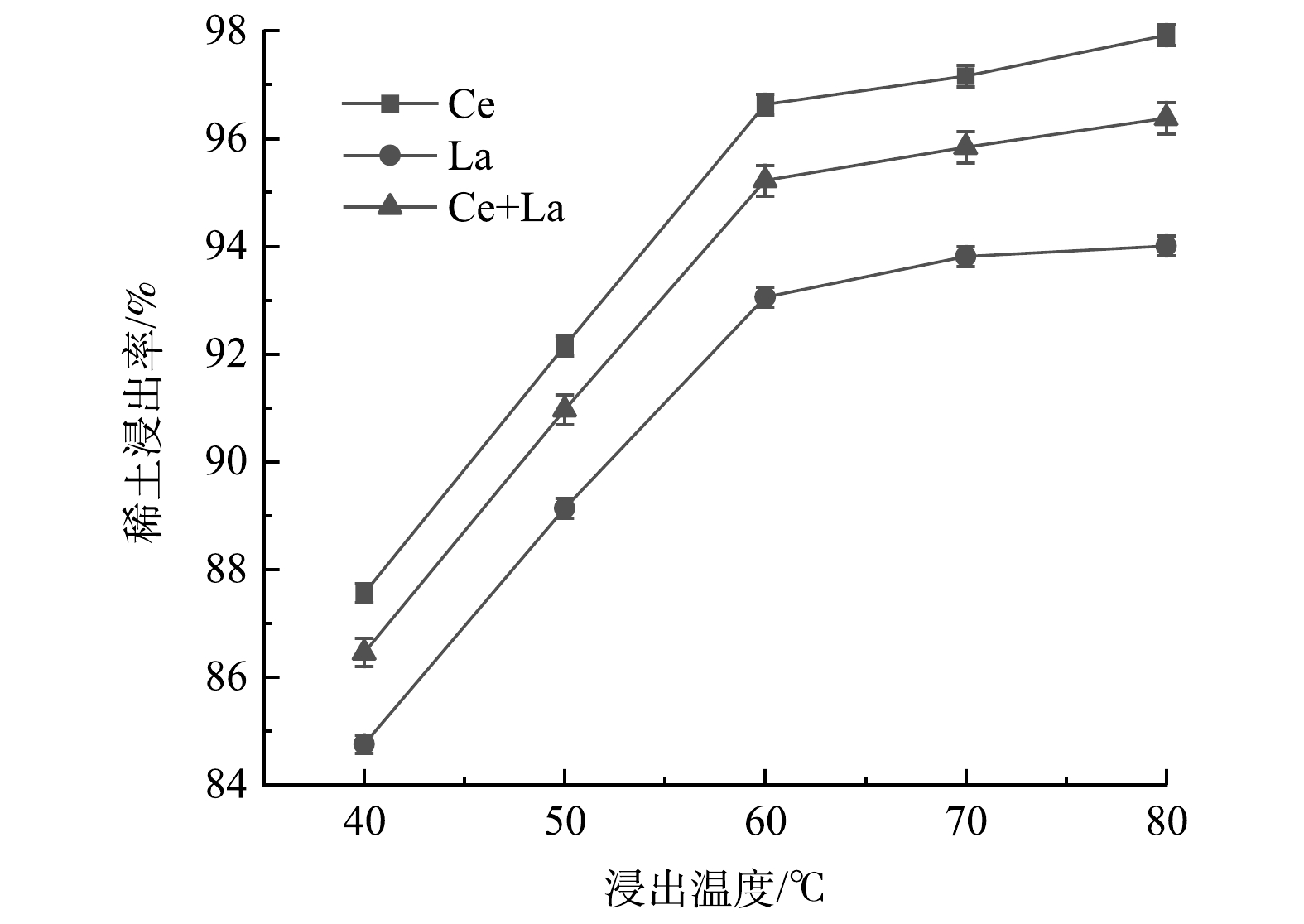
3)浸出温度的影响。图6显示了温度对REEs浸出率的影响。由图6可看出,当浸出温度从40 ℃上升到80 ℃时,La和Ce的浸出率分别从84.8%和87.6%提高到94.0%和97.9%,Ce和La的总浸出率从86.5%提高到96.4%。其原因可能是,较高的浸出温度加强了溶液中离子的运动,并有助于酸在催化剂间隙中扩散,从而促进酸与废FCC催化剂之间的反应。当温度大于60 ℃时,浸出率基本保持稳定。为节省成本,选择60 ℃作为最佳浸出温度。
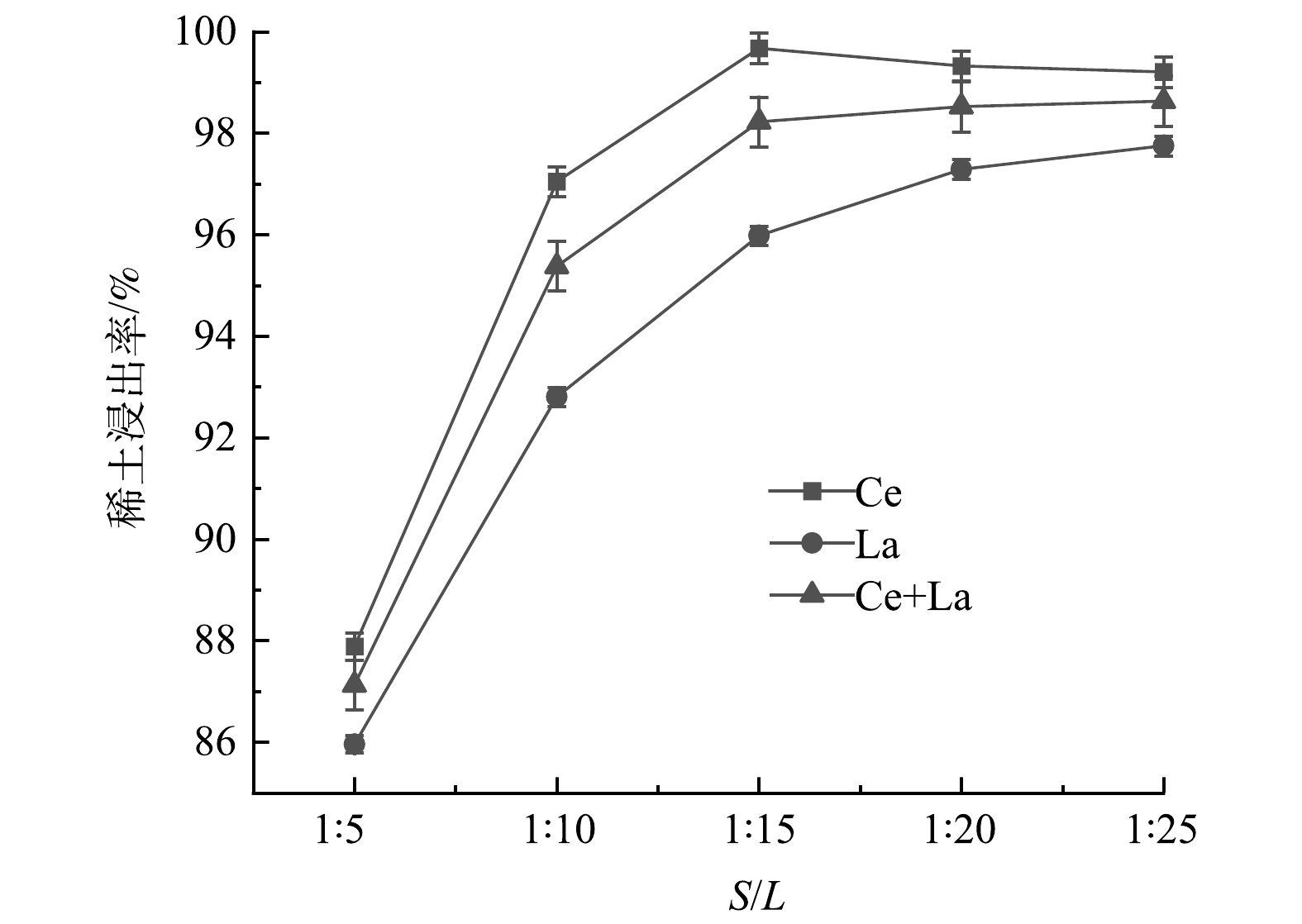
4)固液比的影响。废FCC催化剂样品与盐酸溶液的质量比为固液比(S/L)。固液比对REEs浸出率的影响如图7所示。从图7可看出,当固液比从1∶5降低到1∶15时,La和Ce的浸出率随着固液比的下降而快速增加。当固液比从1∶15降低至1∶25时,La和Ce的浸出率变化不大,La和Ce的浸出率最大值分别达到97.7%和99.7%,La和Ce的总浸出率稳定在98.5%左右。其主要原因是,随着固液比的降低,废FCC催化剂样品与酸溶液的接触面积变大,有利于反应的发生。考虑到酸液的消耗,选择1∶15作为最佳固液比。
-
溶剂萃取的关键是萃取剂的选择。分别采用P204和P507从浸出液中萃取REEs,反应机理[15]如式(4)所示。在盐酸介质中萃取稀土离子的机理属于离子交换,当pH在1.0至3.0时,稀土离子以Ce3+和La3+的形式存在[19],1个REE3+与萃取剂二聚体中的3个H+交换,通过萃取剂从稀土浸出液中萃取出来,达到提纯分离的目的。
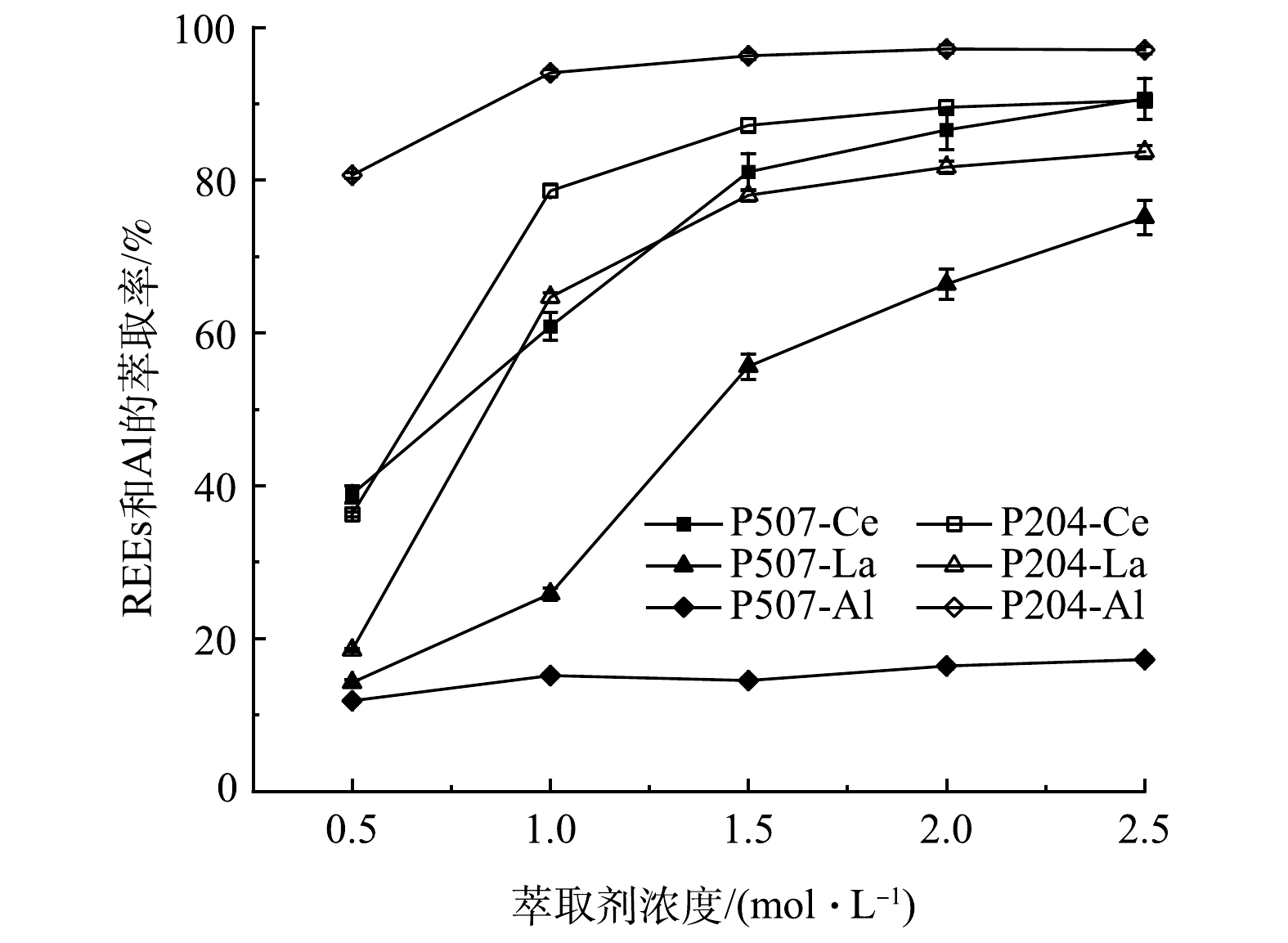
1)萃取剂浓度对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。图8显示了萃取剂浓度对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。从图8可看出,P204对稀土La和Ce的萃取率均高于P507。其主要原因是,P204和P507都属于酸性磷型萃取剂,其萃取能力取决于酸性强弱,P507分子中存在1个烷基,酸性弱于P204,萃取能力更弱[20]。
同种萃取剂对Ce和La的萃取能力也不同,P204对Ce和La的萃取率最高分别为90.0%和83.7%,P507对Ce和La的萃取率最高分别为90.0%和75.1%。其主要原因是,当被萃取稀土离子的价数相同时,离子半径越小,形成的配合物越稳定,由于“镧系收缩”,Ce3+半径小于La3+,更容易被萃取[21]。
萃取剂浓度从0.5 mol·L−1增加至1.5 mol·L−1时,Ce和La的萃取率有较大提高,当萃取剂浓度大于1.5 mol·L−1时,随着萃取剂浓度的增加,Ce和La萃取率增长开始变缓,且实验过程中发现,当萃取剂浓度达到2.0 mol·L−1时,由于有机相的粘度过高,2种萃取剂都会出现乳化现象,故导致有机相和水相难以分离。综合考虑,后续实验萃取剂浓度选择1.5 mol·L−1。
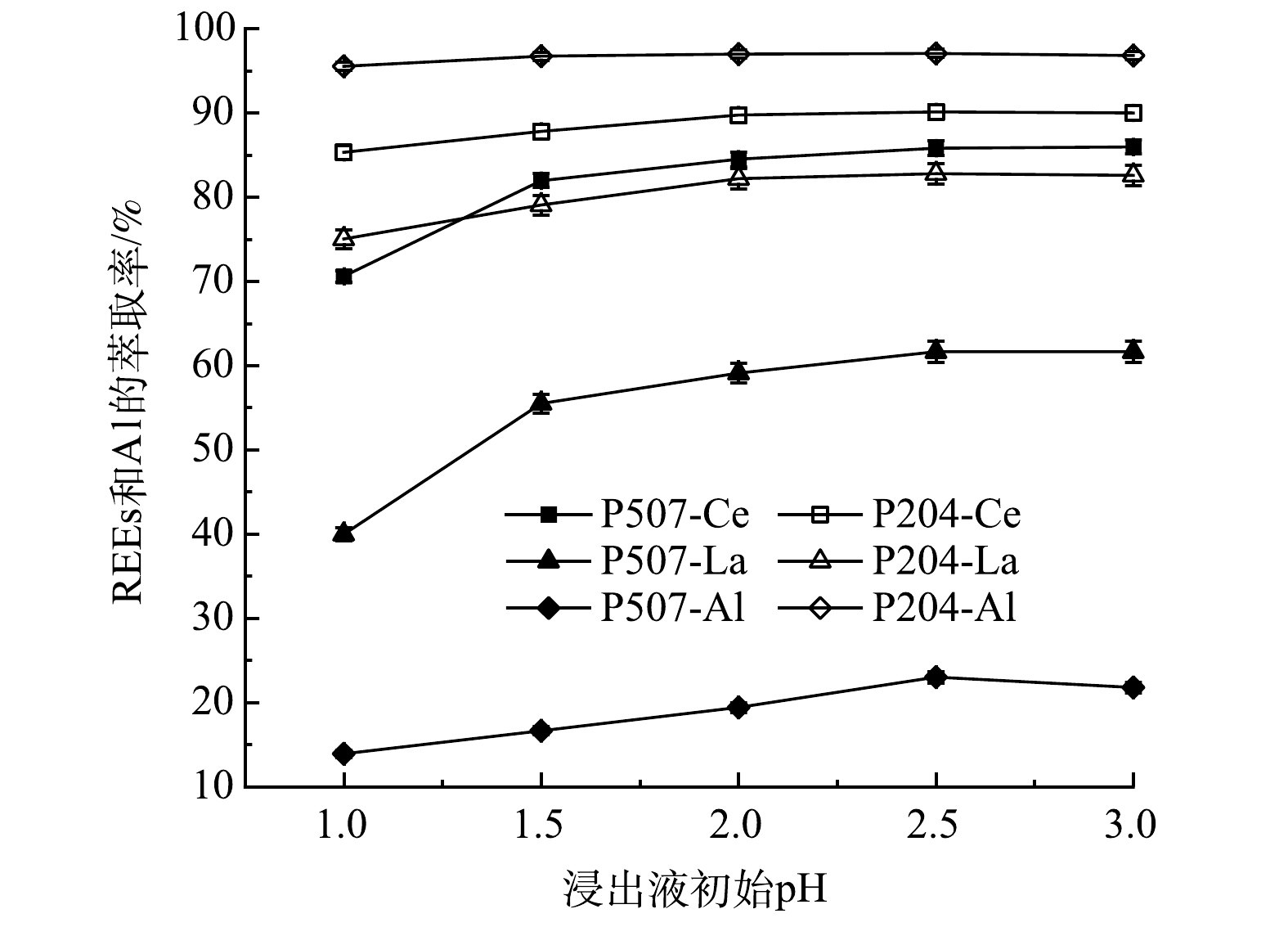
2)浸出液初始pH对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。图9显示了浸出液初始pH对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。由图9可看出,当浸出液初始pH从1.0增加至2.5时,P204对REEs的萃取率变化不大,而P507对REEs的萃取率受pH影响较大。其主要原因是,P507酸性弱于P204,更适合在弱酸性条件下萃取,当pH增大时,溶液酸性减弱,P507萃取能力更强[22]。当pH大于2.5时,2种萃取剂对稀土元素的萃取率达到最大并保持稳定。P507和P204对La和Ce的最大萃取率分别为61.7%、85.8%和82.8%、90.2%,稀土总萃取率分别为76.4%和87.3%。自实验中观察到,当pH为3.0时会引起乳化。这是因为,Al离子在体系中的存在形式较多,当pH大于2.5时,Al2(OH)24+、Al6(OH)153+等铝的多聚体形式含量增多,降低萃取体系的稳定性,故引起乳化[23]。因此,最佳的浸出液初始pH为2.5。
-
从单一溶剂萃取过程中发现,P204对REEs和Al都有较高萃取率,P507对REEs的萃取率略低于P204,而对Al的萃取率远低于P204。结合2种萃取剂本身的优缺点,向P204中加入适量的P507,以探索P204-P507复合萃取体系对REEs和Al的萃取效果。
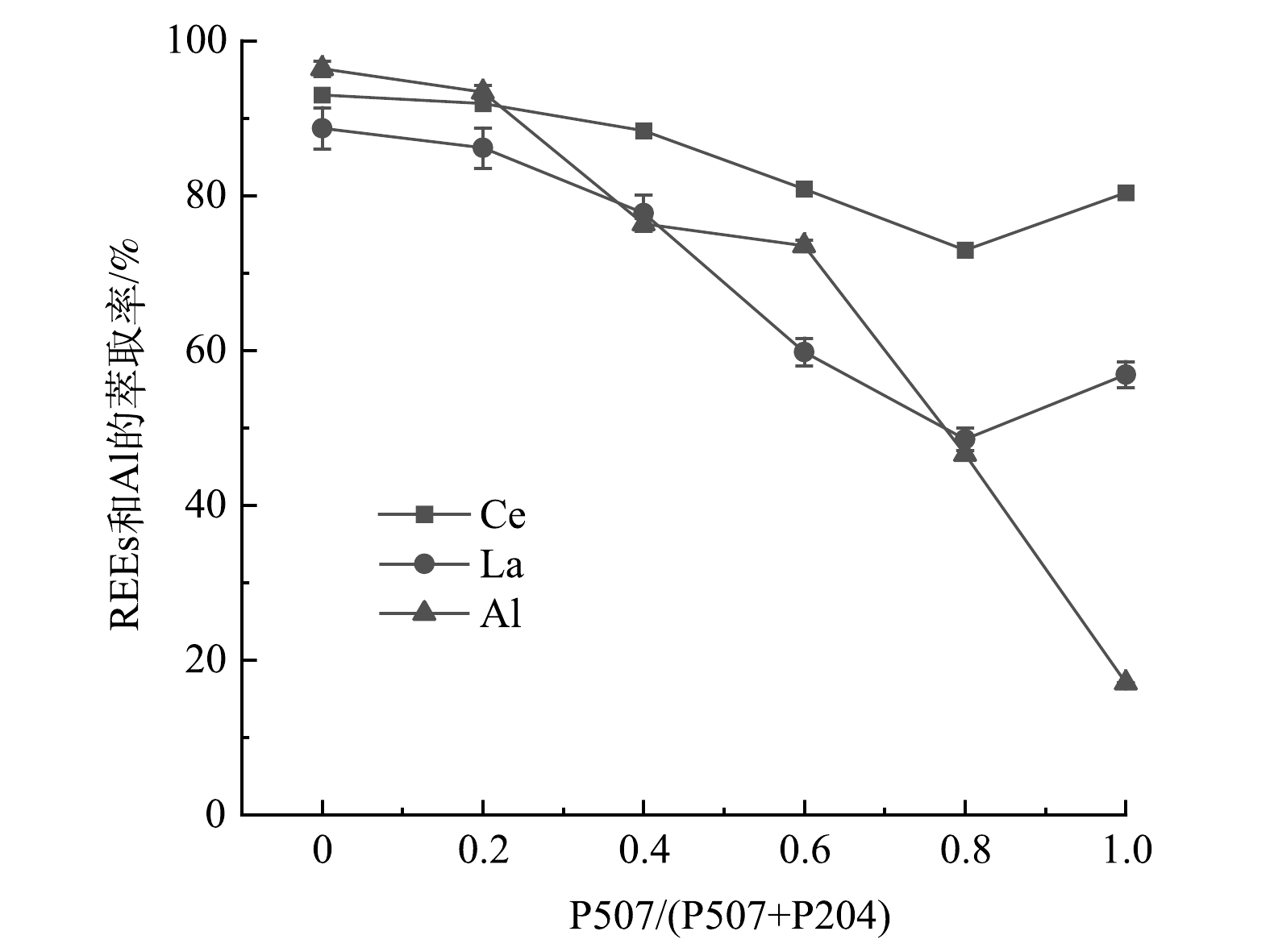
1)P507体积比对REEs和Al萃取的影响。图10显示了P507体积比对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。从图10可看出,随着P507体积比的增加,复合萃取体系对Al的萃取率快速降低,当P507/(P507+P204)=1.0即P507=1.5 mol·L−1、P204=0 mol·L−1时,Al的萃取率降到最低为17.1%。而La和Ce的萃取率先下降后升高,在P507/(P507+P204)=0.8即P507=1.2 mol·L−1、P204=0.3 mol·L−1时下降到最低点,分别为48.5%和72.9%,然后略有回升。其原因可能是,P507结构中存在1个烷基,因电子在P-C键上的传递速率较P-O上慢,降低了P-O-H、P-O-C-H上H+与其他金属离子的交换速率,进而体现出较弱的萃取能力,与P204混合后,使整个萃取体系的萃取能力下降。
P204和P507萃取Al的机理为阳离子交换,简要反应过程如式(5)所示[24]。当水相pH为1.0至2.0时,Al在溶液中主要是以Al3+的形式存在,当水相pH大于2.0时,随着pH的增加,Al3+的水解聚合反应逐渐发生,形成Al2(OH)24+、Al3(OH)45+、Al6(OH)153+和其他具有亲水性基团的低聚物[25]。P507和P204均属于酸性萃取剂,且P507的酸性较弱,随着复合萃取体系中P507的体积比逐渐增大,可能会使平衡时体系的酸性逐渐减弱,pH逐渐增大,更多的Al3+发生水解聚合反应,Al3+的萃取逐渐被抑制,从而使Al的萃取率迅速降低。
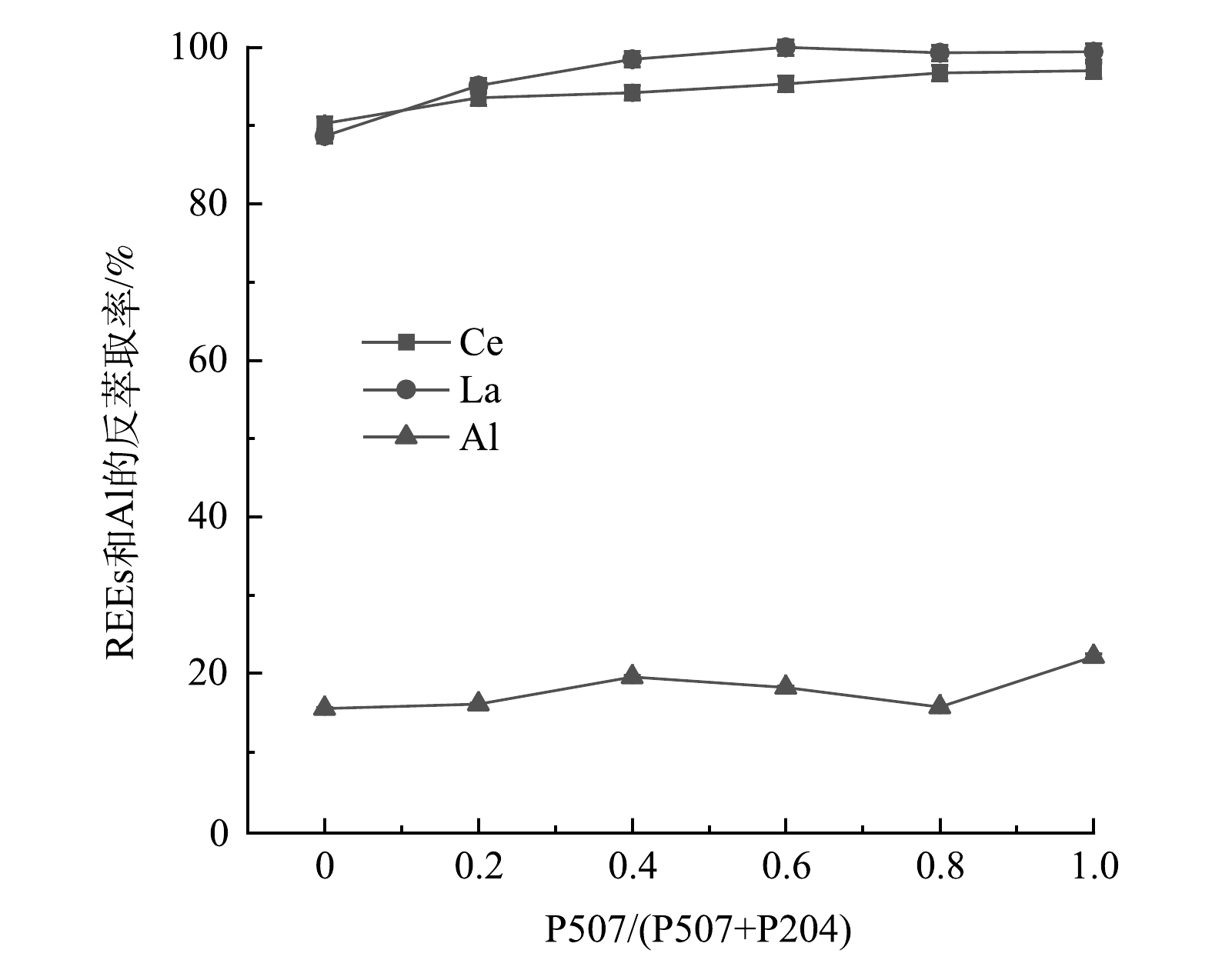
2) P507体积比对REEs和Al反萃取的影响。图11显示了P507体积比对REEs和Al反萃取率的影响。从图11可看出,P204-P507复合萃取体系对La和Ce的反萃取效果明显,反萃取率在90.0%以上,且随着P507体积比的增加而提高,La的反萃取率最高可达到100%,Ce的反萃取率最高可达到97.0%。而P204-P507复合萃取体系对Al的反萃取效果不明显,当P507/(P507+P204)从0增加到0.8时,对Al的反萃取率稳定在20.0%以下,当P507/(P507+P204)=1.0即P507=1.5 mol·L−1、P204=0 mol·L−1时,Al的反萃取效果略微提高,最高为22.1%。这表明反萃取可以很好的将REEs与Al分离。
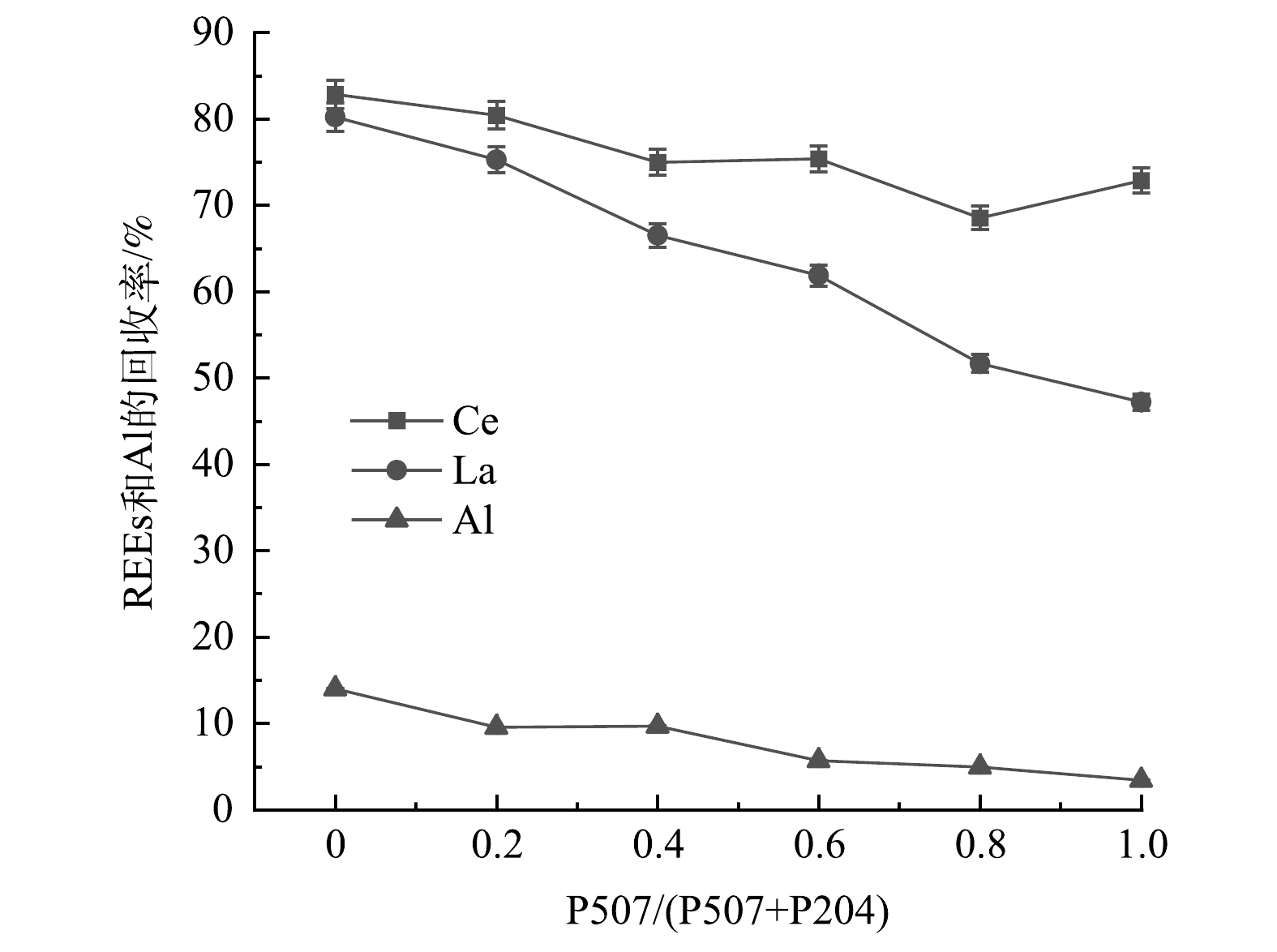
图12显示了P507体积比对REEs和Al回收率的影响。由图12可看出,随着P507体积比的增加,P204-P507复合萃取体系对La、Ce和Al的回收率逐渐降低,当P507/(P507+P204)=0.2即P507=0.3 mol·L−1、P204=1.2 mol·L−1时,La和Ce的回收率与单一P204萃取时相比略微下降,分别为75.3%和80.4%,Ce和La的总回收率为78.4%。然而,此时P204-P507复合萃取体系对Al的萃取率小于10.0%,在保证REEs高回收率的同时,降低了回收液中杂质Al的质量分数,提高了回收稀土的纯度。
-
1)与硫酸和硝酸相比,盐酸为最佳浸出剂。在最佳浸出条件(4 mol·L−1盐酸溶液、浸出时间为4 h 、60 ℃、固液比为1∶15)下,Ce和La的浸出率分别为99.7%和97.7%,Ce和La的总浸出率为98.5%。
2)最佳条件下,P507和P204对La和Ce的萃取率均较高,分别为61.7%、85.8%和82.8%、90.2%,但P507对Al的萃取率远低于P204。
3)当P204-P507复合萃取体系中P507的体积比为0.2时,对Ce和La的回收率分别为80.4%和75.3%,Ce和La的总回收率为78.4%,而杂质Al的回收率小于10.0%,有效降低了废FCC催化剂回收稀土中Al的质量分数。
P204-P507-HCl体系回收废FCC催化剂中稀土的优化
Recovery of rare earth elements from spent FCC catalysts in P204-P507-HCl system
-
摘要: 针对废流化催化裂化(FCC)催化剂的资源化利用问题,采用溶剂萃取法从废FCC催化剂中高效回收稀土。对无机酸浸出过程、二(2-乙基己基)磷酸(P204)和2-乙基己基膦酸单2-乙基己基酯(P507)单独萃取稀土过程以及P204-P507复合萃取稀土过程分别进行了研究。结果表明,盐酸为最佳浸出剂,在最佳浸出条件(4 mol·L−1盐酸溶液、浸出时间为4 h、60 ℃、固液比为1∶15)下,Ce和La的浸出率分别为99.7%和97.7%。萃取过程的最佳条件为萃取剂浓度1.5 mol·L−1、浸出液初始pH=2.5,P204和P507对Ce和La的萃取率均较高,而P507对杂质铝的萃取率远低于P204。P204-P507复合萃取体系中P507体积比为0.2时,Ce和La的回收率分别达到80.4%和75.3%,略低于纯P204萃取体系,而杂质铝的回收率小于10.0%。P204-P507复合萃取体系能有效降低回收稀土中杂质铝的萃取量。本研究可为从废FCC催化剂中回收高纯度稀土提供参考。Abstract: Aiming at the problem of resource utilization of spent fluidized catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts, the solvent extraction method is used to efficiently recover rare earths from spent FCC catalysts. The process of inorganic acid leaching, single extraction of bis (2-ethylhexyl) phosphoric acid (P204) and single 2-ethylhexyl phosphonate (P507) and composite extraction of rare earth by P204-P507 were studied. The results showed that hydrochloric acid was the best leaching agent. Under the optimal leaching conditions (4 mol·L−1 hydrochloric acid solution, leaching time of 4 h, 60 ℃, solid-liquid ratio of 1:15), the leaching rates of Ce and La were 99.7% and 97.7%, respectively. The optimal extraction conditions were as follows: the concentration of extractant was 1.5 mol·L−1, the initial pH of leaching solution was 2.5, and the extraction rates of Ce and La were both higher for P204 and P507, while the extraction rates of aluminum for P507 were much lower than that for P204. When the volume ratio of P507 in P204-P507 was 0.2, the recovery of Ce and La reached 80.4% and 75.3%, respectively, slightly lower than that of pure P204, while the recovery of aluminum was less than 10.0%. The P204-P507 composite extraction system can effectively reduce the content of aluminum impurities in the recycled rare earth, providing a useful reference for the recovery of high purity rare earth from the waste FCC catalyst.
-
稀土元素(Rare Earth Elements, REEs)具有独特的核外电子结构和变价特征,物理性能优异[1],已成为国民经济可持续发展不可或缺的重要战略资源[2-3]。稀土在工业催化剂中应用广泛。2014年,全球流化催化裂化(Fluid Catalytic Cracking,FCC)催化剂供应量约为8.4×105 t[4]。由于有机物和重金属的影响,FCC催化剂在使用过程中结构被破坏并失活,最终变为废FCC催化剂,废FCC催化剂中的稀土主要为镧(La)和铈(Ce),且稀土质量分数约为2%~4%[5]。2015年,我国废FCC催化剂产生量约为1.43×105 t,折合稀土(La、Ce)约为2.86×103~5.72×103 t[6]。寻找合理、高效的方法来回收其中的稀土元素迫在眉睫。
目前,国内外回收稀土元素的主要方式是溶剂萃取法[7]。INNOCENZI等[8]对溶剂萃取法和选择性沉淀法进行了比较,发现溶剂萃取法对主杂质铝(Al)的萃取率较低,有利于提高La和Ce的回收率和最终产品质量。溶剂萃取法由浸出、萃取和反萃取3部分组成。对于浸出过程而言,浸出酸的选择是关键。BORRA等[9]发现,与有机酸相比,盐酸、硫酸和硝酸等无机酸更利于稀土的浸出。在萃取剂的选择上,目前对废FCC催化剂中稀土进行回收,研究最多的萃取剂是二(2-乙基己基)磷酸(P204)和2-乙基己基膦酸单2-乙基己基酯(P507)。YE等[10]研究了使用皂化的P507从废FCC催化剂中回收稀土的方法,当皂化率为20%时,La和Ce的萃取率可达100%。秦玉芳等[11]将废FCC催化剂用盐酸溶解,并用体积分数为60%的P204-煤油混合有机相萃取浸出液,当浸出液初始pH=2,萃取相比为2∶1时,萃取效果最好,稀土回收率达到91.76%。
用溶剂萃取法回收废FCC催化剂中的稀土时,会将一部分杂质Al萃取出来。铝是非常弥散的元素,在溶液中的赋存状态较为复杂,由于铝的两性,回收废FCC催化剂时去除铝的方法主要有碱法、酸法和萃取法[12]。目前,研究较多的主要是碱法和酸法,这2种方法工艺复杂,成本较高[13-14]。然而,对萃取法的研究鲜有报道,ZHAO等[15]研究了P507和P204对废FCC催化剂中稀土的萃取效果,发现P204对La和Ce的萃取效果较好,同时也会萃取出大量的Al,而P507对La和Ce的萃取效果比P204差,但萃取出的Al更少。
为进一步探索从废FCC催化剂中回收稀土时萃取法对铝的去除效果,本研究对萃取的过程和条件进行优化,选择常用的稀土萃取剂P204和P507作为萃取剂,着重研究了浸出过程、单一溶剂萃取过程和P204-P507复合萃取过程,以期为从废FCC催化剂中回收高纯度稀土提供有益参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
本实验使用的废FCC催化剂来自于华东某炼油厂。盐酸(HCl, 36%~38%)、硝酸(HNO3, 65%~68%)和硫酸(H2SO4, 95%~98%)、氨水(NH3·H2O, ≥26%)、P204(C16H35O4P, 98%)、P507(C16H35O3P, 95%)、磺化煤油均为分析纯。
1.2 催化剂表征
采用热重分析(TGA,DSC1型,梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司)仪测定废FCC催化剂样品中有机物的质量分数,并确定其最佳煅烧温度。废FCC催化剂样品先在105 ℃下干燥,冷却后过200目筛,然后在最佳煅烧温度下,马弗炉内煅烧2 h,冷却后储存于干燥器中备用。通过X射线衍射分析仪(XRD,D/max 2550V型,日本RIGAKU公司)对焙烧前后的废FCC催化剂的晶相结构进行分析。通过X射线荧光分析(XRF,XRF-1800型,日本岛津)初步确定样品的组成,然后用王水在180 ℃下对废FCC催化剂样品消解30 min并通过电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP-OES,Agilent 710型,美国安捷伦科技有限公司)定量测定消解液中Ce、La、Al的质量浓度[16]。
1.3 实验方法
1)浸出过程实验。首先,分别配制1、2、3、4、5 mol·L−1的盐酸、硝酸和硫酸,在浸出温度为60 ℃、固液比为1∶10、浸出时间为4 h的条件下,对550 ℃煅烧后的废FCC催化剂样品进行浸出,以确定最佳浸出酸及其最佳浓度。之后,采用控制变量法,控制其余条件为前一步所得最佳浸出条件,依次研究浸出时间(持续反应6 h,每间隔1 h取1次样)、浸出温度(控制温度分别为40、50、60、70、80 ℃)、固液比(控制固液比分别为1∶5、1∶10、1∶15、1∶20、1∶25)对Ce和La浸出率的影响。浸出过程在恒温水浴震荡箱中进行,并对锥形瓶进行加盖处理。将浸出液在转速为5 000 r·min−1条件下离心分离5 min并稀释至合适的倍数,用ICP-OES测定浸出液中Ce和La的质量浓度。
2)萃取过程实验。在最佳条件下浸出550 ℃焙烧后的废FCC催化剂样品,制得浸出液,其中Ce、La和Al的质量浓度分别为1 027 mg·L−1、657 mg·L−1和2 997 mg·L−1。分别配制浓度为0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5 mol·L−1的P204和P507萃取剂,并用氨水调节浸出液初始pH分别为1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5和3.0,探索单一溶剂萃取的最佳萃取条件。在最佳萃取条件下,控制P507在(P204+P507)混合萃取剂中的体积比分别为0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8和1.0,研究P204-P507复合萃取体系对浸出液中稀土和Al的萃取效果。所有萃取过程均在室温(25.0±0.2) ℃下进行,有机相与水相的体积比为1∶1。萃取过程平衡后,通过ICP-OES分析检测离心后上清液(水相)中Ce、La、Al的质量浓度。有机相中3种元素的质量浓度通过质量平衡法计算得出。
3)反萃取过程实验。使用2 mol·L−1的盐酸溶液作为反萃取剂,保持有机相和水相的体积比为1∶1,在室温(25.0±0.2) ℃下对有机相进行反萃取。反萃取过程平衡后,用ICP-OES检测上清液(水相)中Ce、La、Al的质量浓度。
金属浸出率的计算如式(1)所示。金属萃取率的计算如式(2)所示。金属回收率的计算如式(3)所示。
η=ncvmw×10−6×100% (1) E=C0−CeC0×100% (2) W=η×E×E′ (3) 式中:n为稀释倍数;c为ICP-OES检测水相中金属离子的质量浓度,mg·L−1;v为上清液体积,mL;m为废FCC催化剂样品质量,g;w为废FCC催化剂样品中金属元素的质量分数;C0和Ce分别为初始和平衡时金属离子在水相中的质量浓度,mg·L−1;E'为反萃取率;W为金属回收率。
每组实验进行3次。实验数据为3次实验的平均值,误差线为标准差。详细工艺流程图见图1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 废FCC催化剂的表征
对废FCC催化剂进行了XRF分析,并处理数据得到各元素的质量分数,样品中主要元素为Al和Si,质量分数分别为36.33%和24.19%;稀土元素为Ce和La,质量分数分别为7.23%和3.84%。废FCC催化剂ICP-OES分析测定的Ce和La质量分数分别为1.56%和1.01%,REEs总质量分数为2.57%。据文献报道,废FCC催化剂中的REEs质量分数为2%~4%[17]。后续实验以ICP-OES测定的数据为准。
为确定废FCC催化剂中有机物的质量分数,对其进行了TGA分析,结果如图2所示。一般认为100 ℃左右失重是由于催化剂样品的脱水引起的。从图2可看出,废FCC催化剂中水分的质量分数为3.245%,有机物质量分数为1.253%。当温度高于550 ℃时,样品的重量几乎没有减少,可以认为550 ℃是最佳的焙烧温度。
焙烧前后废FCC催化剂的XRD分析如图3所示。从图3可看出,焙烧对废FCC催化剂的晶相结构几乎不产生影响。废FCC催化剂中的金属主要是以金属氧化物的形式存在,且大多存在于非结晶相中,主要矿物成分为SiO2和Al2O3。观察到图中有较多的衍射峰,在2θ=15.88°、20.66°和23.78°时,发现明显的SiO2的特征峰;在2θ=26.5°、35.0°、45.9°和66.6°时,发现明显的Al2O3的特征峰。由于废FCC催化剂中La和Ce的质量分数较低,仅能观察到微弱的La2O3和Ce2O3特征峰。
2.2 从废FCC催化剂中浸出REEs
1)浸出酸的影响。不同种类和浓度的无机酸对REEs浸出率的影响如图4所示。由图4可看出,在相同条件下,盐酸对样品中REEs的浸出率明显优于硫酸和硝酸。其原因可能是,Cl−比NO3−和SO42−更易与稀土离子形成配位,且NO3−和SO4−可与稀土离子、Na+、K+形成稀土复盐沉淀,使浸出液中稀土的质量浓度降低[18]。当无机酸浓度从1 mol·L−1增加至4 mol·L−1时,REEs的浸出率迅速提高,最高浸出率可达86.3%。当无机酸浓度大于4 mol·L−1时,REEs浸出率的增加不明显。根据实验结果,后续稀土浸出实验采用4 mol·L−1盐酸溶液。
2)浸出时间的影响。图5显示了浸出时间对REEs浸出率的影响。由图5可看出,随着浸出时间的增加,REEs的浸出率逐渐提高。当反应时间超过4 h时,REEs浸出率的增加趋于缓慢。其原因可能是,在反应开始时,高浓度的反应物使反应剧烈,随着反应的进行,反应物的浓度逐渐降低,反应趋于平衡。当反应时间达到4 h时,La的浸出率达到最大为89.0%;当反应时间为5 h时,Ce的浸出率达到最大为92.3%。反应时间从4 h增加到6 h,Ce和La的总浸出率稳定在90.9%,因此,选择4 h作为浸出稀土的最佳时间。
3)浸出温度的影响。图6显示了温度对REEs浸出率的影响。由图6可看出,当浸出温度从40 ℃上升到80 ℃时,La和Ce的浸出率分别从84.8%和87.6%提高到94.0%和97.9%,Ce和La的总浸出率从86.5%提高到96.4%。其原因可能是,较高的浸出温度加强了溶液中离子的运动,并有助于酸在催化剂间隙中扩散,从而促进酸与废FCC催化剂之间的反应。当温度大于60 ℃时,浸出率基本保持稳定。为节省成本,选择60 ℃作为最佳浸出温度。
4)固液比的影响。废FCC催化剂样品与盐酸溶液的质量比为固液比(S/L)。固液比对REEs浸出率的影响如图7所示。从图7可看出,当固液比从1∶5降低到1∶15时,La和Ce的浸出率随着固液比的下降而快速增加。当固液比从1∶15降低至1∶25时,La和Ce的浸出率变化不大,La和Ce的浸出率最大值分别达到97.7%和99.7%,La和Ce的总浸出率稳定在98.5%左右。其主要原因是,随着固液比的降低,废FCC催化剂样品与酸溶液的接触面积变大,有利于反应的发生。考虑到酸液的消耗,选择1∶15作为最佳固液比。
2.3 单一溶剂萃取过程
溶剂萃取的关键是萃取剂的选择。分别采用P204和P507从浸出液中萃取REEs,反应机理[15]如式(4)所示。在盐酸介质中萃取稀土离子的机理属于离子交换,当pH在1.0至3.0时,稀土离子以Ce3+和La3+的形式存在[19],1个REE3+与萃取剂二聚体中的3个H+交换,通过萃取剂从稀土浸出液中萃取出来,达到提纯分离的目的。
REEs3++mH2A2=REEA3(HA)2m−3+3H+ (4) 1)萃取剂浓度对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。图8显示了萃取剂浓度对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。从图8可看出,P204对稀土La和Ce的萃取率均高于P507。其主要原因是,P204和P507都属于酸性磷型萃取剂,其萃取能力取决于酸性强弱,P507分子中存在1个烷基,酸性弱于P204,萃取能力更弱[20]。
同种萃取剂对Ce和La的萃取能力也不同,P204对Ce和La的萃取率最高分别为90.0%和83.7%,P507对Ce和La的萃取率最高分别为90.0%和75.1%。其主要原因是,当被萃取稀土离子的价数相同时,离子半径越小,形成的配合物越稳定,由于“镧系收缩”,Ce3+半径小于La3+,更容易被萃取[21]。
萃取剂浓度从0.5 mol·L−1增加至1.5 mol·L−1时,Ce和La的萃取率有较大提高,当萃取剂浓度大于1.5 mol·L−1时,随着萃取剂浓度的增加,Ce和La萃取率增长开始变缓,且实验过程中发现,当萃取剂浓度达到2.0 mol·L−1时,由于有机相的粘度过高,2种萃取剂都会出现乳化现象,故导致有机相和水相难以分离。综合考虑,后续实验萃取剂浓度选择1.5 mol·L−1。
2)浸出液初始pH对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。图9显示了浸出液初始pH对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。由图9可看出,当浸出液初始pH从1.0增加至2.5时,P204对REEs的萃取率变化不大,而P507对REEs的萃取率受pH影响较大。其主要原因是,P507酸性弱于P204,更适合在弱酸性条件下萃取,当pH增大时,溶液酸性减弱,P507萃取能力更强[22]。当pH大于2.5时,2种萃取剂对稀土元素的萃取率达到最大并保持稳定。P507和P204对La和Ce的最大萃取率分别为61.7%、85.8%和82.8%、90.2%,稀土总萃取率分别为76.4%和87.3%。自实验中观察到,当pH为3.0时会引起乳化。这是因为,Al离子在体系中的存在形式较多,当pH大于2.5时,Al2(OH)24+、Al6(OH)153+等铝的多聚体形式含量增多,降低萃取体系的稳定性,故引起乳化[23]。因此,最佳的浸出液初始pH为2.5。
2.4 P204-P507复合萃取过程
从单一溶剂萃取过程中发现,P204对REEs和Al都有较高萃取率,P507对REEs的萃取率略低于P204,而对Al的萃取率远低于P204。结合2种萃取剂本身的优缺点,向P204中加入适量的P507,以探索P204-P507复合萃取体系对REEs和Al的萃取效果。
1)P507体积比对REEs和Al萃取的影响。图10显示了P507体积比对REEs和Al萃取率的影响。从图10可看出,随着P507体积比的增加,复合萃取体系对Al的萃取率快速降低,当P507/(P507+P204)=1.0即P507=1.5 mol·L−1、P204=0 mol·L−1时,Al的萃取率降到最低为17.1%。而La和Ce的萃取率先下降后升高,在P507/(P507+P204)=0.8即P507=1.2 mol·L−1、P204=0.3 mol·L−1时下降到最低点,分别为48.5%和72.9%,然后略有回升。其原因可能是,P507结构中存在1个烷基,因电子在P-C键上的传递速率较P-O上慢,降低了P-O-H、P-O-C-H上H+与其他金属离子的交换速率,进而体现出较弱的萃取能力,与P204混合后,使整个萃取体系的萃取能力下降。
P204和P507萃取Al的机理为阳离子交换,简要反应过程如式(5)所示[24]。当水相pH为1.0至2.0时,Al在溶液中主要是以Al3+的形式存在,当水相pH大于2.0时,随着pH的增加,Al3+的水解聚合反应逐渐发生,形成Al2(OH)24+、Al3(OH)45+、Al6(OH)153+和其他具有亲水性基团的低聚物[25]。P507和P204均属于酸性萃取剂,且P507的酸性较弱,随着复合萃取体系中P507的体积比逐渐增大,可能会使平衡时体系的酸性逐渐减弱,pH逐渐增大,更多的Al3+发生水解聚合反应,Al3+的萃取逐渐被抑制,从而使Al的萃取率迅速降低。
Al3++3HA(0)=AlA3(0)+3H+ (5) 2) P507体积比对REEs和Al反萃取的影响。图11显示了P507体积比对REEs和Al反萃取率的影响。从图11可看出,P204-P507复合萃取体系对La和Ce的反萃取效果明显,反萃取率在90.0%以上,且随着P507体积比的增加而提高,La的反萃取率最高可达到100%,Ce的反萃取率最高可达到97.0%。而P204-P507复合萃取体系对Al的反萃取效果不明显,当P507/(P507+P204)从0增加到0.8时,对Al的反萃取率稳定在20.0%以下,当P507/(P507+P204)=1.0即P507=1.5 mol·L−1、P204=0 mol·L−1时,Al的反萃取效果略微提高,最高为22.1%。这表明反萃取可以很好的将REEs与Al分离。
图12显示了P507体积比对REEs和Al回收率的影响。由图12可看出,随着P507体积比的增加,P204-P507复合萃取体系对La、Ce和Al的回收率逐渐降低,当P507/(P507+P204)=0.2即P507=0.3 mol·L−1、P204=1.2 mol·L−1时,La和Ce的回收率与单一P204萃取时相比略微下降,分别为75.3%和80.4%,Ce和La的总回收率为78.4%。然而,此时P204-P507复合萃取体系对Al的萃取率小于10.0%,在保证REEs高回收率的同时,降低了回收液中杂质Al的质量分数,提高了回收稀土的纯度。
3. 结论
1)与硫酸和硝酸相比,盐酸为最佳浸出剂。在最佳浸出条件(4 mol·L−1盐酸溶液、浸出时间为4 h 、60 ℃、固液比为1∶15)下,Ce和La的浸出率分别为99.7%和97.7%,Ce和La的总浸出率为98.5%。
2)最佳条件下,P507和P204对La和Ce的萃取率均较高,分别为61.7%、85.8%和82.8%、90.2%,但P507对Al的萃取率远低于P204。
3)当P204-P507复合萃取体系中P507的体积比为0.2时,对Ce和La的回收率分别为80.4%和75.3%,Ce和La的总回收率为78.4%,而杂质Al的回收率小于10.0%,有效降低了废FCC催化剂回收稀土中Al的质量分数。
-
-
[1] 季根源, 张洪平, 李秋玲, 等. 中国稀土矿产资源现状及其可持续发展对策[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(8): 9-16. [2] 刘贵清, 曲志平, 张磊. 从废催化剂中回收稀土的现状与展望[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2014, 32(6): 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2014.06.013 [3] 宋文飞, 李国平, 韩先锋. 稀土定价权缺失理论机理及制度解释[J]. 中国工业经济, 2011(10): 46-55. [4] INNOCENZ V, FERELLA F, MAGGIORE F. Oil refining spent catalysts: A review of possible recycling technologies[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2016, 108: 10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2016.01.010 [5] 赵哲萱, 邱兆富, 杨骥, 等. 从废FCC催化剂和废汽车尾气净化催化剂中回收稀土的研究进展[J]. 化工环保, 2015, 35(6): 603-608. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2015.06.010 [6] 刘腾, 邱兆富, 杨骥, 等. 我国废炼油催化剂的产生量、危害及处理方法[J]. 化工环保, 2015, 35(2): 159-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2015.02.010 [7] 叶阑珊, 吕灵灵, 杨驰, 等. 废催化裂化催化剂稀土元素回收方法综述[J]. 广州化工, 2018, 46(10): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.10.007 [8] INNOCENZ V, FERELLA F, DE M, et al. Treatment of fluid catalytic cracking spent catalysts to recover lanthanum and cerium: Comparison between selective precipitation and solvent extraction[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2015, 24: 92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2014.09.014 [9] BORRA C R, PONTIKES Y, BINNEMANS K, et al. Leaching of rare earths from bauxite residue (red mud)[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2015, 76: 20-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2015.01.005 [10] YE S S, JING Y, WANG Y D, et al. Recovery of rare earths from spent FCC catalysts by solvent extraction using saponified 2-ethylhexyl phosphoric acid-2-ethylhexyl ester(EHEHPA)[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2017, 35(7): 716-722. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(17)60968-2 [11] 秦玉芳, 许涛, 马莹, 等. 废催化剂中稀土资源的回收与综合利用[J]. 稀土, 2014, 35(1): 76-81. [12] 贾江涛, 张亚文, 吴声, 等. 铝在稀土萃取分离流程中的分布及分离方法研究(I)[J]. 稀土, 2001(2): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2001.02.004 [13] WANG J Y, XU Y, WANG L S, et al. Recovery of rare earths and aluminum from FCC catalysts manufacturing slag by stepwise leaching and selective precipitation[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017(5): 3711-3718. [14] 胡谷华, 韦世强, 杨桂林, 等. 一种从草酸沉淀稀土母液中回收稀土元素的方法: CN201510636320.0[P]. 2015-12-30. [15] ZHAO Z X, QIU Z F, YANG J, et al. Recovery of rare earth elements from spent fluid catalytic cracking catalysts using leaching and solvent extraction techniques[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017(167): 183-188. [16] 环境保护部. 固体废物 22种金属元素的测定电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法: HJ 781-2016[S]. 北京: 中国环境出版集团, 2016. [17] 张福良, 李雨潼, 李晓宇. 国内外稀土资源开发利用现状及新时期我国稀土管理建议[J]. 现代矿业, 2018, 34(12): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2018.12.003 [18] 黄礼煌. 稀土提取技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007. [19] WANG J Y, HUANG X W, WANG L S, et al. Kinetics study on the leaching of rare earth and aluminum from FCC catalyst waste slag using hydrochloric acid[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 171: 312-319. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.06.007 [20] 李晚霞. 从废FCC催化剂中回收稀土镧和铈的研究[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2014. [21] 杨华. 稀土萃取分离中的配位化合物[J]. 稀土, 2003(6): 74-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2003.06.020 [22] 李剑虹, 常宏涛, 吴文远. 酸度对P(204)-HCl-H3AOH体系萃取La(Ⅲ)的机理影响[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2010, 30(1): 15-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6952.2010.01.005 [23] WU W, LI D, ZHAO Z, et al. Formation mechanism of micro emulsion on aluminum and lanthanum extraction in P507-HCl system[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(1): 174-178. [24] 潜美丽. 铝对P507体系萃取稀土元素的影响[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2010. [25] ZHANG H Y, ZHAO L S, ZHENG X D, et al. Extraction mechanism and separation behaviors of low-concentration Nd3+ and Al3+ in P507-H2SO4 system[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2021.04.011. -






 下载:
下载: