-
垃圾收运是垃圾从产生到最终处理中必有的关键环节,且垃圾收运成本占垃圾处理总成本的50%以上[1]。如何对垃圾收运路径进行优化是城市及农村固废管理的重点难点之一。目前的垃圾收运路径往往只采用数学规划算法进行规划,以路径最短为唯一优化目标。但现实中,堵车、人流量、路面平整度、道路宽度、装车时间等实际因素造成了路况复杂多变[2],这种方法无法避免由复杂路况带来的垃圾收运成本高昂,同时对人居环境与自然生态造成了不可逆的负面影响。
启发式算法、元启发式算法、超启发式算法等仿自然体算法比追求精确结果的数学规划算法更适用于解决垃圾收运路径优化问题[3]。启发式算法在可接受的计算时间和空间下给出待解决组合优化问题每一个实例的一个可行解[4];元启发式算法不借助于某种问题的特有条件,从而能够运用于更广泛的方面[5];超启发式算法提供了某种高层策略,通过操纵或管理一组低层启发式算法,以获得新启发式算法[6]。其中,元启发式算法比启发式算法更不易陷入局部最优,而超启发式算法的研究处于起步阶段,尚未有成熟的应用。蚁群算法是元启发式算法的代表性算法,十分适用于解决垃圾收运类路线优化问题[7]。蚁群算法模仿了自然蚁群中蚂蚁返回时间最快的路径为最优路径的原理,还可以将从收集到处理中各环节的社会、经济、环境、生态、市政等多元数据也需要被纳入改进蚁群算法程序语言中。因此,对蚁群算法中的信息素更新规则、期望函数进行改进,可以有效减少垃圾收运成本及对周边人群健康与生态环境质量的不良影响。
本研究通过多元大数据融合、遥感数据可视化、多指标赋予权重、对传统蚁群算法加以改进,建立了垃圾从垃圾收集点到垃圾焚烧厂的收运路径优化模型,拟解决生活垃圾收运成本过高导致垃圾无害化程度较低的问题。
-
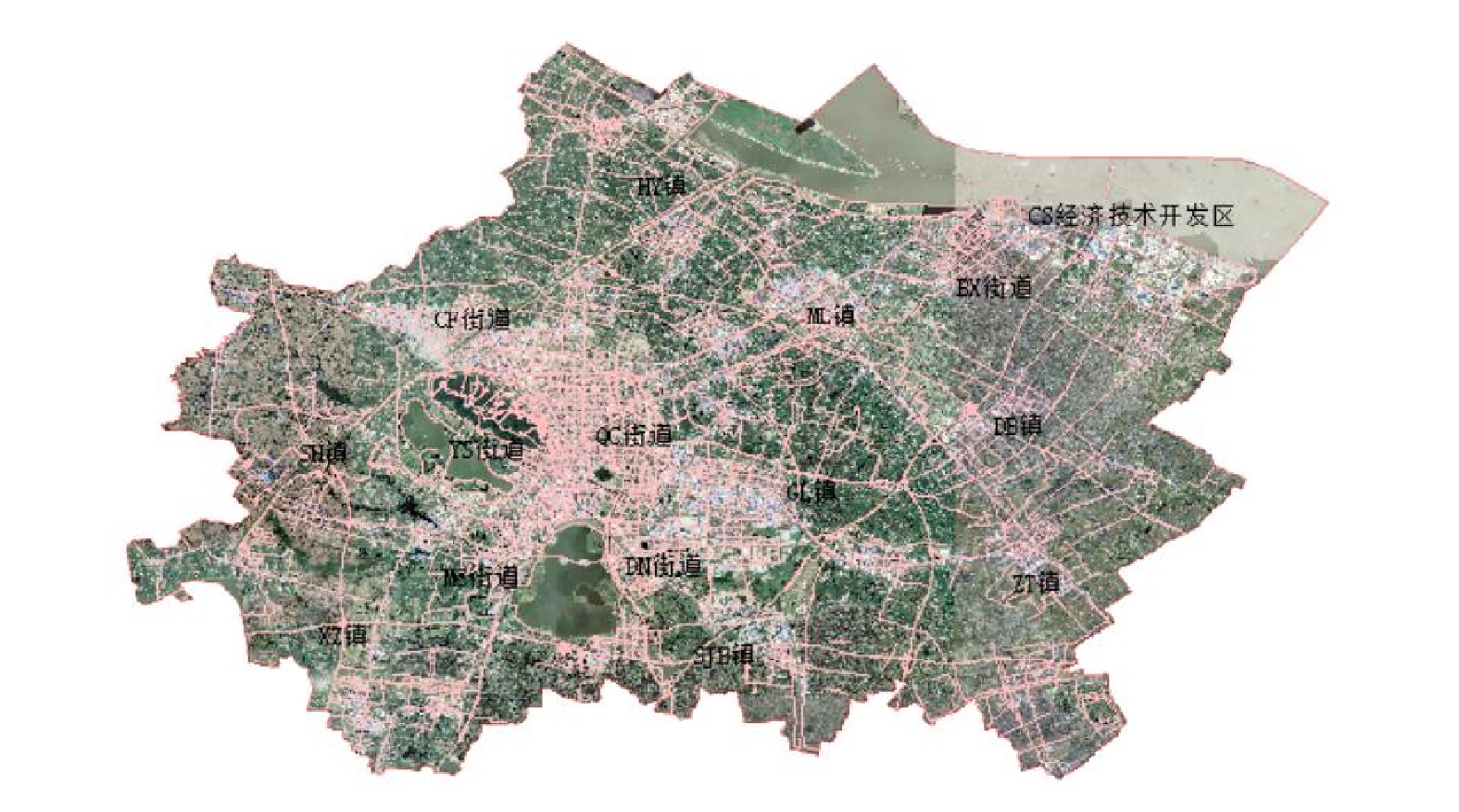
研究区域为我国东南部某县级市。该县级市总面积超过1
× 106 m2,常住人口超过1× 106,该地包含6个街道和8个镇,基础设施建立完备,交通系统稠密完善。该县级市已实施垃圾分类政策,但在垃圾处理方面的人力资金投入与需求相比仍然不足,要求后续垃圾收运工作充分考虑到生活垃圾分类方法。此外,该县级市内的野生动植物资源丰富,应在进行市政规划管理时给予保护意识与足够重视。研究对象为该县级市的其他垃圾,其处理方式为:先从垃圾收集点由垃圾收集车收集至经垃圾中转站进行压缩预处理后,然后由垃圾运输车运输至垃圾焚烧厂。经实际调研与网络查询,当地具有329个垃圾收集点、40个垃圾中转点、3个垃圾焚烧厂。
-
本研究所需路网分布、道路长度、道路等级、道路限速等数据信息来源于Open Street Map网站的2020年全国路网矢量图[8],经过裁剪后得到研究区域路网图如图1所示。环境成本中包含的土地保护需求指标数据来源于500 m全球土地退化态势评价数据集[9],影响人口规模指标的数据来源于2020年中国人口密度分布图[10],降噪物密度指标的数据来源于中国-东盟1 km分辨率植被覆盖度数据集[11],生态不可分割度指标的数据来源于2020年中国土地利用图[12]。
-
本研究将传统蚁群算法中的“往返时间”概念扩大至“成本”,在ArcGIS 10.7软件中的Python拓展模块实现蚁群算法,其步骤为:1)首先,进行路网处理,将道路以节点为界限划分路段,且对节点进行编号;2)之后,在Python拓展模块中编写程序,程序中对传统蚁群算法中的期望函数与信息素更新规则进行改进,以体现道路对生态环境的恶劣影响与改进经济成本代表指标。
基本蚁群算法涉及到2个过程。第一个过程是状态转移,蚁群算法中的状态转移概率函数由节点间距离与信息素浓度共同决定。i及j节点之间状态转移概率函数Pijm的计算方式如式(1)所示。
式中:m为蚂蚁数量;α为信息启发因子,表示信息素浓度的重要性,取值为0~5;β为期望启发因子,表示节点之间成本的重要性,取值为0~5;τij为i、j节点之间的信息素浓度;ηij为从i节点到j节点的期望值。传统蚁群算法中期望函数ηij的计算方式如式(2)所示。
第二个过程是信息素更新,(t+1)时刻i、j节点之间路段上信息素浓度τij(t+1)的计算方式如式(3)、式(4)所示。
式中:ρ为信息素挥发系数;1-ρ为信息素残留系数;Δτij(t)为t时刻所有蚂蚁在节点i、j间留下的信息素浓度;Δtijk(t)为t时刻第k只蚂蚁在节点i、j间带来的信息素增量。
信息素增量的计算方式有3种:蚁周模型、蚁量模型、蚁密模型。本研究选择不容易陷入局部最优的蚁周模型为信息素更新规则。传统蚁群算法中的信息素更新规则如式(5)所示。
式中:Q为信息素总量,取值范围为10~10 000;lij为i、j节点之间的道路长度。
-
本研究利用 SPSS 软件实现 CRITIC 法与熵权 TOPSIS 法对综合成本指标的权重分配,其步骤为:1)建立综合成本评价指标体系;2)获取评价所需数据并建立道路数据集;3)以 CRITIC 法对环境成本指标下各子指标进行权重分配;4)以熵权 TOPSIS 法对综合成本指标下的时间成本与环境成本进行权重分配,环境成本权重与时间成本权重的比值即为新定义的环境干扰因子。
客观权重赋值法与以层次分析法等为代表的主管权重赋值法相比,只关注指标数据之间的差异,仅从数据中生成属性权重,而不需要从使用者中获取任何偏好信息[13],也可有效降低决策方法的复杂性与非直观性[14]。其中,CRITIC算法考虑了各指标自身的对比强度及指标间的冲突性,能够较全面的衡量各指标重要性,因而被作为一种相对完善赋权算法,被广泛使用。熵权法可用于分析对象之间存在较大差异的指标。它们均可用于整合社会影响评估和不同标准的确定。
-
本研究利用客观权重赋值法中的CRITIC权重法与熵权TOPSIS 法建立道路综合成本评价体系,在体系中纳入道路交通对自然生态、人居环境的影响,并将该体系应用于所研究县级市路网中,以获得各路段的综合成本数值,为下一步计算得到综合成本最低的垃圾收运路径方案做好数据准备。
首先,考虑到数据的可达性与时效性,本研究取道路长度与限速之比为时间成本;环境成本由土地保护需求、影响人口规模、降噪物密度、生态不可分割度确定。
本研究使用时间成本与环境成本作为综合成本Cij的2大指标,其计算方式如式(6)所示。
式中:tij为i、j节点之间道路的时间成本;γ为环境干扰系数;eij为i、j节点之间道路的环境成本。
时间成本tij的计算方式如式(7)所示。
式中:lij为i、j节点之间道路的长度,km;vij为i、j节点之间的车速,km∙h−1,由道路限速与车辆最高行驶速度确定。
环境成本eij的计算方式如式(8)所示。
式中:λ1为土地退化态势的权重,0~1;eij,1为i、j节点之间道路穿行的土地退化态势;λ2为人口密度的权重,0~1;eij,2为i、j节点之间道路穿行地区的人口密度;λ3为植被覆盖度的权重,0~1;eij,3为i、j节点之间道路穿行地区的植被覆盖度;λ4为生态抗扰度的权重,0~1;eij,4为i、j节点之间道路穿行地区的生态抗扰度。
利用CRITIC法赋予环境成本中各指标权重,并利用熵权法计算环境干扰因子。时间成本由道路长度与道路限速之比得到。之后,编辑路网数据集,添加“时间”字段,通过字段计算器算的每段道路通过所需花费的时间。
-
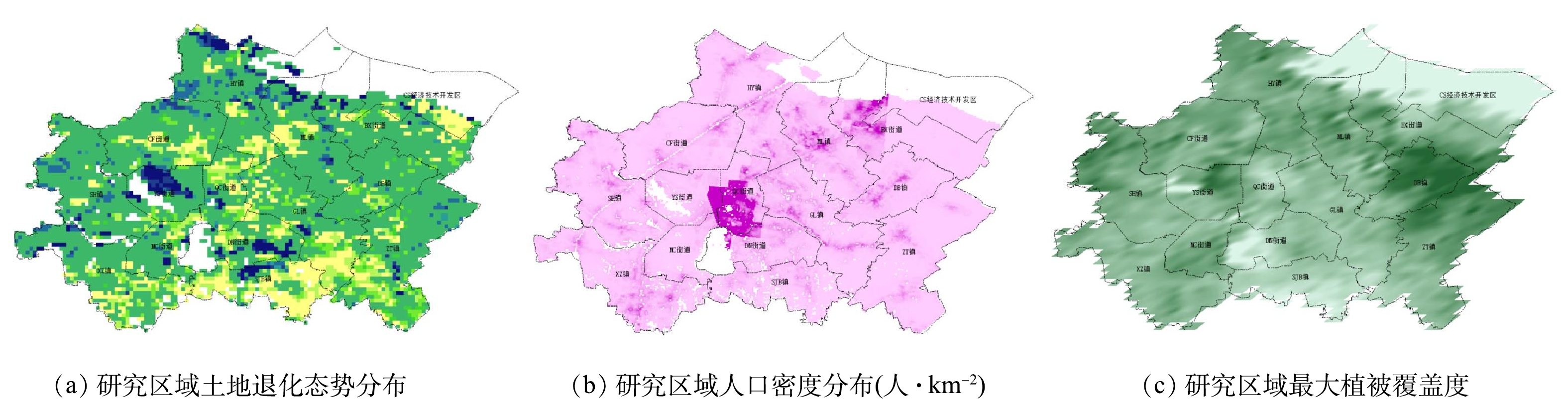
垃圾运输对运输区域的生态干扰程度主要由土地保护需求、影响人口规模以及降噪物密度决定。本研究利用土地退化态势来确定土地保护需求。土地退化态势数据集中,将全球的土地退化态势分为2级评价系统。在第1级,将土地退化态势评价划分为3种类型:退化类型、改善类型和无变化类型。第2级,将土地退化态势评价划分为9种类型。下载土地退化态势数据集后,在ArcGIS软件中打开,并根据研究区域行政区划线要素矢量数据图对其裁剪,得到如图2(a)所示的研究区域土地退化态势分布栅格图,图中颜色越浅表示土地退化越严重。
影响人口规模由人口密度分布确定。将人口密度分布栅格数据经过裁剪与符号化后标注于研究区域地图,通过识别功能得到各垃圾中转站所处位置的人口密度。研究区域人口密度栅格图像如图2(b)所示。图中颜色越深,表明人口密度越大。
降噪物密度由植被覆盖度确定。植被覆盖度数据的处理方式同土地退化态势分布图,结果如图2(c)所示。图中颜色越深,表示植被覆盖度越大。
-
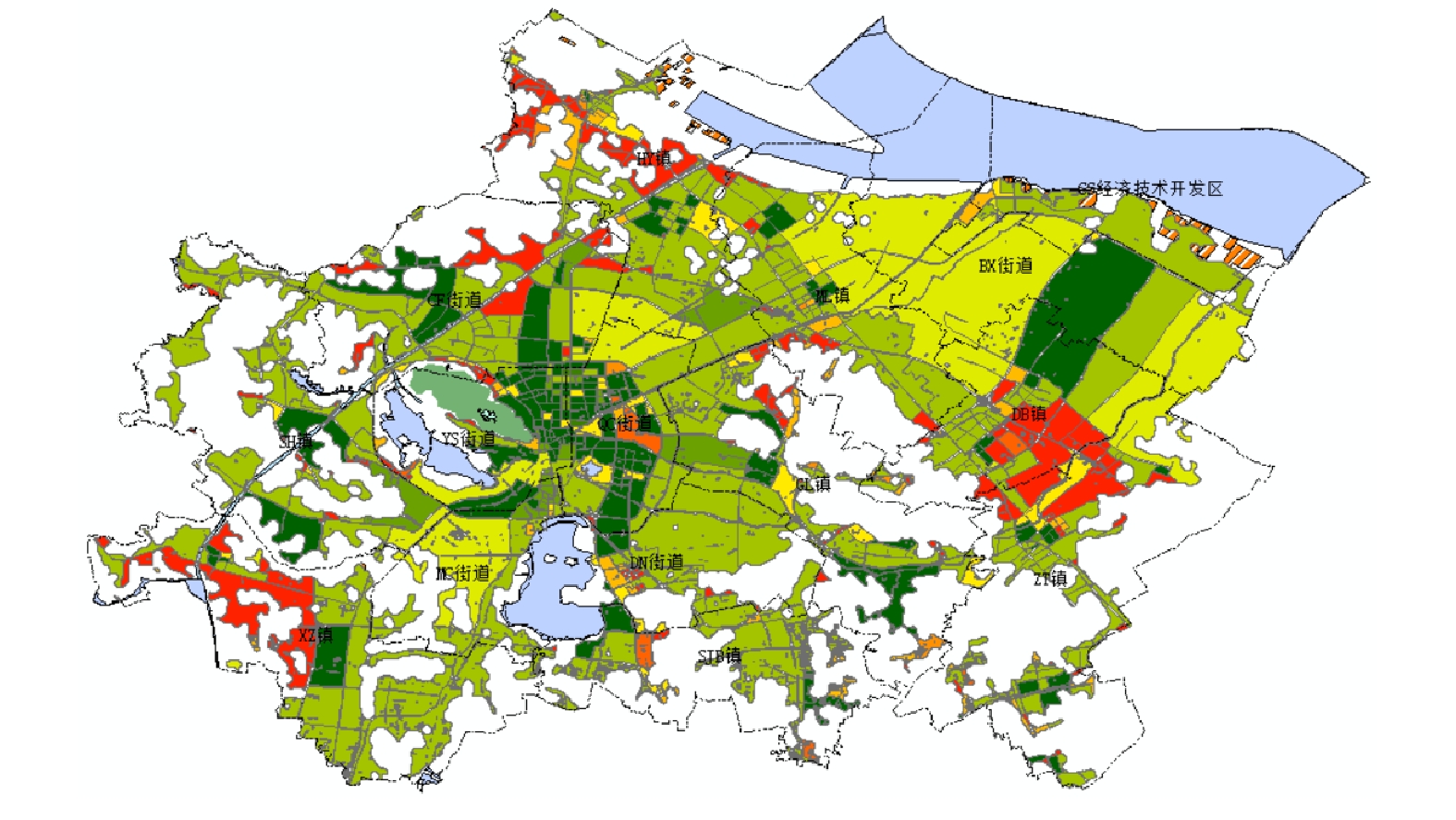
在环境成本保护的各指标中,生态不可分割度为本研究根据生物丰度指数含义进行改进得到的指标,旨在评价道路交通沿线周边生态系统对道路切割的抵抗力,以减少堵路交通对沿线周边造成的不可逆性深远影响。生态不可分割度越高,往往当地生态系统所含的食物链就越复杂,则道路交通对当地生态环境切割与生物栖息地破碎化的负面影响就越深。根据我国生态环境部颁布的《生态环境状况评价技术规范(HJ 192-2015)》[15]的标准,定义生态抗扰度的打分方式如表1所示。利用空间地理数据云的2020年中国土地利用图矢量数据计算生态不可分割度,经过裁剪,其结果如图3所示。图中颜色越接近红色,城市化程度越高,生态不可分割度得分越低。
-
在环境成本的所有指标中,土地利用类型为矢量数据,其匹配方式为,选中路网文件,选择“连接和关联”中的“连接”,并基于空间位置来连接土地利用类型图层。其余的指标均为栅格数据,只需要在已有的路网矢量数据添加上相对应的栅格数据值即可。至此,研究区域各路段已被赋予环境成本数值。之后,在SPSSAU平台上利用CRITIC权重法计算环境成本中各指标权重。计算结果如表2所示。据此可得到各路段取值为0~1的环境成本数值。
对于环境干扰因子的取值,首先使用熵权法对时间成本与环境成本的权重进行赋值,其次取环境干扰因子的值为环境成本与时间成本权重的比值。在SPSSAU平台上进行熵权法计算后,结果如表3所示:
环境干扰因子取值为0.1116。据此计算研究区域路网中所有路段的综合成本,之后在ArcGIS里的路段属性表中添加综合成本字段,完善路网数据集。
-
为考察综合成本对垃圾收运路径规划的影响,本研究先基于传统蚁群算法进行垃圾收运路径规划设计,然后与以改进蚁群算法为原理的规划路径作对比分析。传统蚁群算法中将“距离”作为经济成本的代替数据,以路径最短作为计算目标。
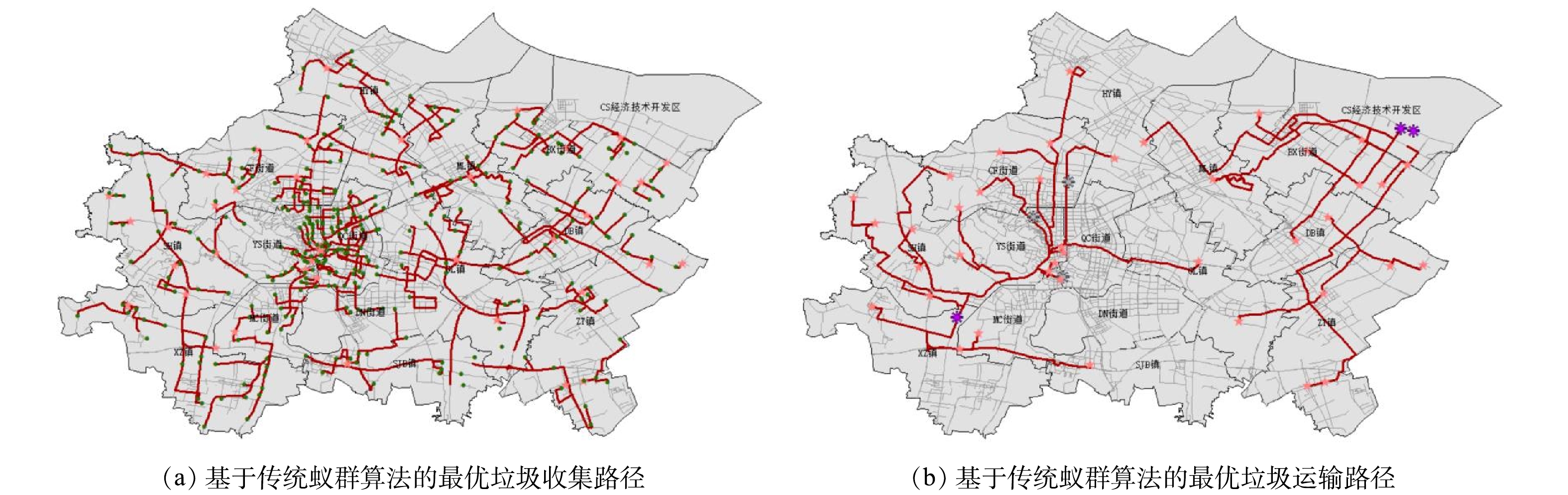
本研究中蚁群算法的实现依托于ArcGIS10.7 软件中的Python拓展模块。本研究区域的垃圾收集点与垃圾中转点数较多,所以用PyPy代替Python中的解释器CPython,将源代码直接转换为机器汇编语言,以大幅提升程序运行效率。程序运行后,输出最佳路径的节点编号。将节点选择结果标记至ArcGIS 10.7中的路网图上,得到基于传统蚁群算法的综合成本最低的收集路径、运输路径。结果如图4(a)、(b)所示。
-
为了修正传统蚁群算法对计算目标设定与指标选取的局限性,本研究以改进传统蚁群算法中期望函数定义与信息素浓度更新规则的方式,在蚁群算法计算最优路径时引入时间成本与环境成本,以改正原路径计算方法用“距离”代表经济成本、忽略环境影响的缺陷。其中,改进蚁群算法中期望函数的计算方式如式(9)所示。
式中:cij为i、j节点之间的综合成本。
本研究选择不容易陷入局部最优的蚁周模型为信息素更新规则,并结合将“成本”代替“路径长度”的理念,规定信息素更新规则为信息素总量与成本之比。其计算方式如式(10)所示。
式中:Q为信息素总量;Ck为蚂蚁k在本次遍历中所走路径小号的综合成本。
综合成本Ck的计算方式如式(11)所示。
式中:Tk为蚂蚁k在本次遍历中所走路径消耗的时间成本;Ek为蚂蚁k在本次遍历中所走路径消耗的环境成本。
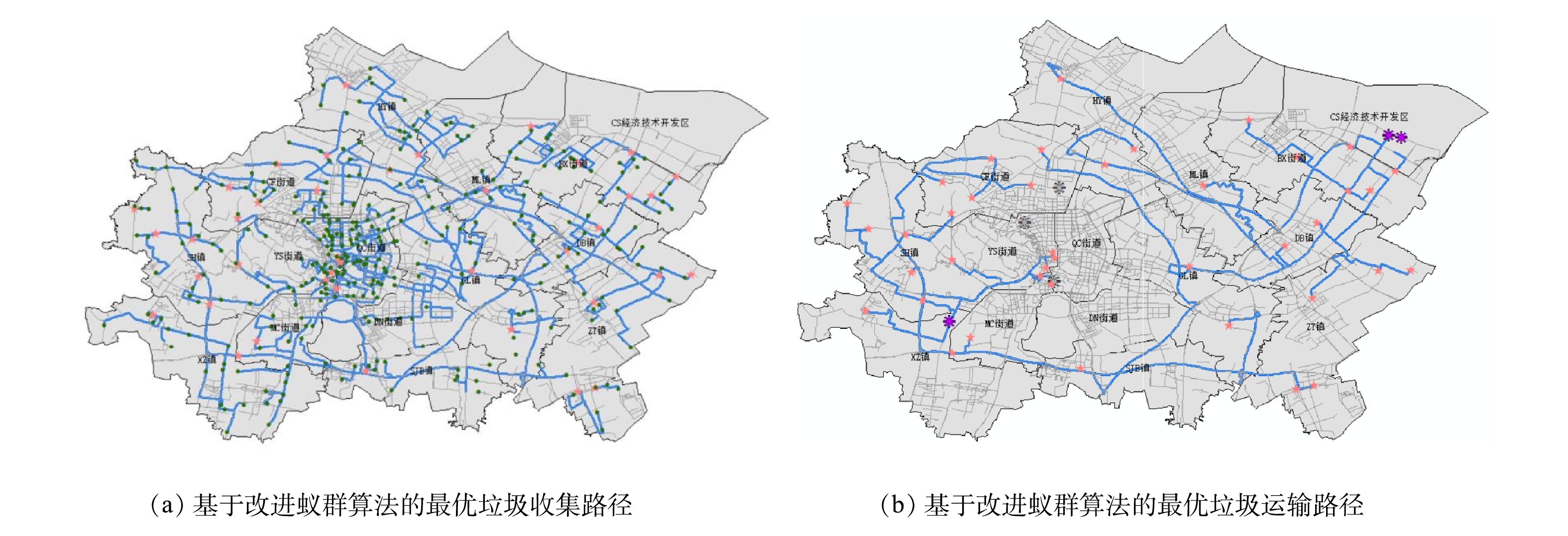
实现改进蚁群算法需要基于路段的综合成本属性,所以需要构建新的网络数据集。与传统蚁群算法相比,改进蚁群算法需要在新的数据集指定属性时添加综合成本,并在配置网络行驶方向时设置阻抗为综合成本,其余步骤与之前相同。程序运行后,根据运算所得到的节点选择相应结果,标记路网地图,得到基于改进蚁群算法的综合成本最低的收集路径与运输路径,结果如图5(a)、(b)所示。从图可以看出,基于改进蚁群算法得到的垃圾收集路径与垃圾运输路径均与基于传统蚁群算法计算得到的结果有明显不同。
-
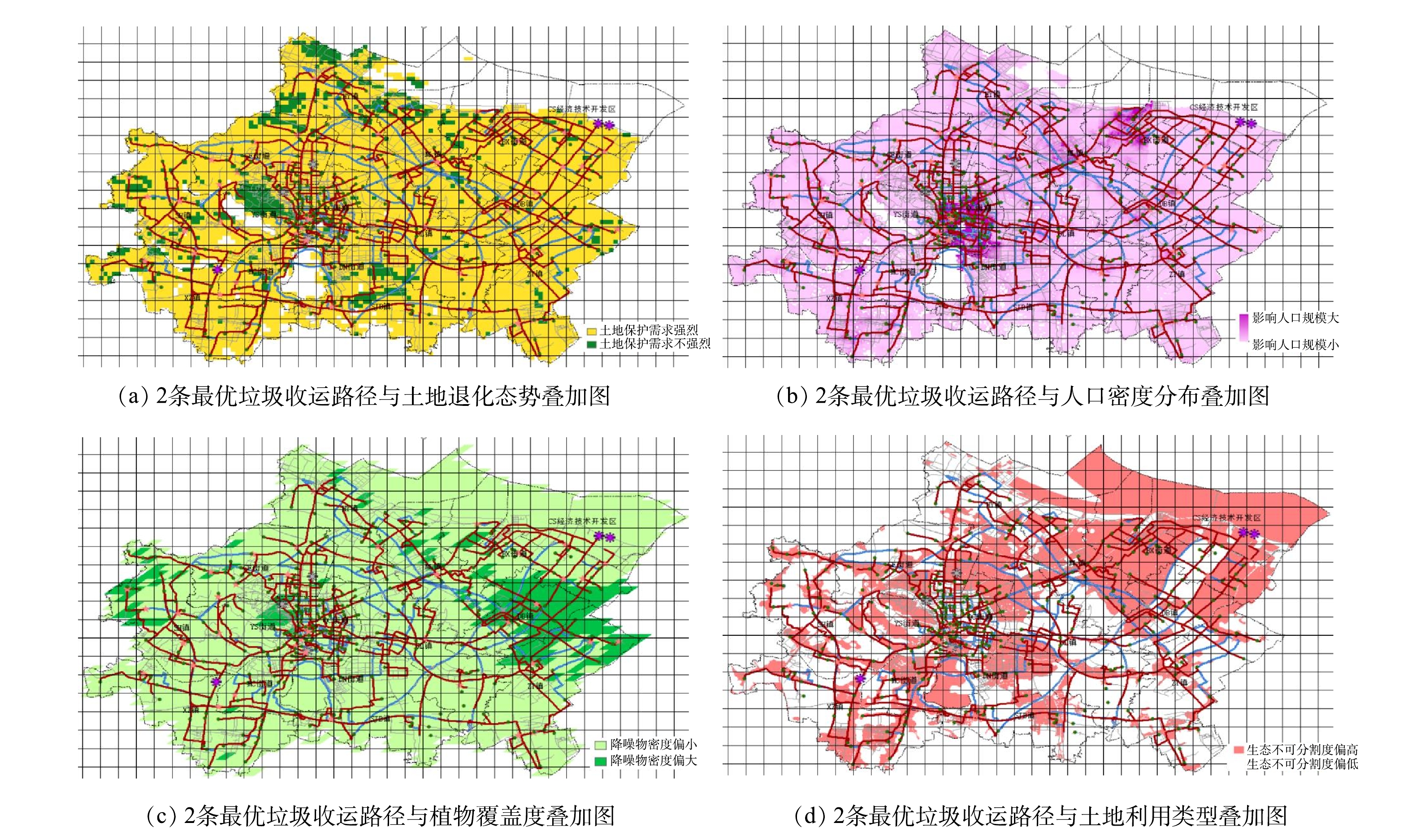
为进一步分析利用 CRITIC 法与熵权 TOPSIS法构建的路径综合成本评价体系对垃圾收运路径规划的影响,本节分别以环境成本中纳入的4项环境成本指标数据图为底图,用分辨率为1 km×1 km 的表格划分研究区域,定义被规划路径穿行的敏感区域(后面将分别定义)所占格子个数与规划路径穿行格子总数之比为规划路径对敏感地区的穿行率。计算基于2种蚁群算法算出的垃圾收运路径规划结果的穿行率并进行对比,讨论考虑环境成本后的最优垃圾收运路径与仅考虑经济成本的结果有何不同。如图4和图5所示,红色路径均为基于传统蚁群算法求得的最优垃圾收运路径,蓝色路径均为基于改良蚁群算法求得的最优垃圾收运路径。
将基于传统蚁群算法与改进蚁群算法得到的最优垃圾收集路径、运输路径均标记在土地退化态势图中,结果如图6(a)所示。底图的颜色越浅,表示土地退化越严重。定义土地退化态势为负数的区域为土地保护需求强烈区域(敏感区域),则分析图6(a)可知,红线对土地保护需求强烈区域的穿行率为81%,蓝线对土地保护需求强烈区域的穿行率为48%,蓝线较红线而言土地保护需求强烈区域穿行率减少了41%。可见,红线比蓝线更集中于土地退化严重的区域,而蓝线多分布于土地质量正在改善或不退化的区域。将土地保护需求纳入垃圾收运路径规划后,可有效缓解垃圾收运交通对土地退化的进一步恶劣影响,从而促进了退化土地恢复与土地质量改善。
将基于传统蚁群算法与改进蚁群算法得到的最优垃圾收集路径、运输路径均标记在人口密度分布图中,结果如图6(b)所示。底图的颜色越深,表示人口密度越大。定义人口密度大于中位数 311 人∙km−2的区域为影响人口规模偏大区域(敏感区域)。分析图6(b)可知,红线对影响人口规模偏大区域的穿行率为2%,蓝线对影响人口规模偏大区域的穿行率为18%。与红线相比,蓝线影响人口规模偏大区域穿行率减少了44%。可见,红色线条比蓝色线条更集中于人口密集区域,而蓝色线条多分布于人口密度较小的地方,整体布局也更加均匀。人口规模大的区域往往交通繁忙,将影响人口规模纳入垃圾收运路径规划后,不仅能绕开人口密度大的居住地从而改善人居环境,还能有效缓解拥堵路段,从而缩减垃圾收运时间、提高垃圾收运效率、减少车辆运行造成的环境污染。
将基于传统蚁群算法与改进蚁群算法得到的最优垃圾收集路径、运输路径均标记在植物覆盖度图中,结果如图6(c)所示。底图的颜色越深,表示植物覆盖度越大,对车辆噪音的削减能力越强。定义植物覆盖度小于中位数192的区域为降噪物密度偏小区域(敏感区域)。分析图6(c)可知,红线对降噪物密度偏小区域的穿行率为76%,蓝线对降噪物密度偏小区域的穿行率为54%,蓝线较红线而言降噪物密度偏小区域穿行率减少了9%。可见,红线比蓝线更集中于难以被植物削减噪音的区域,而蓝线多分布于容易被植物削减噪音的区域。将降噪物密度指标纳入垃圾收运路径规划后,可将垃圾收运路径更多转移至植物密度高的地方,使车辆通行产生的噪音得到更大程度的削减,从而减轻了垃圾收运交通噪音对人类的影响,提高了人居环境质量。
将基于传统蚁群算法与改进蚁群算法得到的最优垃圾收集路径、运输路径均标记在土地利用类型图中,结果如图6(d)所示。图中颜色越接近红色,城市化程度越高,生态不可分割度得分越低。定义生态不可分割度大于中位数40的区域为生态不可分割度偏大区域(敏感区域)。分析图6(d)可知,红线对生态不可分割度偏大区域的穿行率为83%,蓝线对生态不可分割度偏大区域的穿行率为49%,蓝线较红线而言生态不可分割度偏大区域穿行率减少了41%。可见,红线比蓝线更集中于不应被人为分割的区域,而蓝线多分布于已进行过人为建设的区域,即红线比蓝线更集中于生态不可分割度高(城市化程度高)的区域。将生态不可分割度纳入垃圾收运路径规划后,可有效减轻垃圾收运交通对周边生态环境的切割程度,减少了人类活动对自然度高的区域的进一步干扰,从而在一定程度上保护了物种多样性与生态稳定性。
-
1)以“耗时”作为经济成本的衡量指标,将限速情况等路况因素考虑在内,可以充分体现包括路径长度在内的耗油量、人力成本等额外经济成本,从而更利于道路交通经济成本的控制。
2)基于人口密度分布等数据,将道路交通对周边人群健康、生态环境质量的影响纳入对道路交通的综合成本评价当中,对蚁群算法进行了因地制宜的改良,将规划路径对土地保护需求强烈区域、影响人口规模偏大区域、降噪物密度偏小区域、生态不可分割度偏大区域的穿行率分别降低了41%、44%、29%、41%。
基于GIS与改进蚁群算法的垃圾收运路径规划
Garbage collection and transportation path planning based on GIS and improved ant colony algorithm
-
摘要: 针对传统垃圾收运路线成本高昂、对人居环境与自然生态造成不可逆负面影响的问题,提出了一种基于GIS技术与改进蚁群算法的垃圾收运路径规划方法。采用CRITIC法、熵权TOPSIS法及改进的蚁群算法,以时间成本及环境成本作为优化目标,实现从垃圾收集点到最终处理厂的最优路径规划设计,从而有效降低垃圾收运成本与收运对周边生态环境的危害。结果表明,将道路交通对周边人群健康、生态环境质量的影响纳入对道路交通的综合成本评价当中,运输路径对土地保护需求强烈区域、影响人口规模偏大区域、降噪物密度偏小区域、生态不可分割度偏大区域的穿行率分别降低了41%、44%、29%、41%,有效降低了垃圾收运路径对生态敏感区域的干扰程度。本研究结果可为GIS 技术与蚁群算法在垃圾车收运路径规划中的应用提供参考。Abstract: The high cost of garbage collection and transportation limits the garbage disposal rate, and the transportation often causes irreversible negative impact on the human settlement environment and natural ecology. This paper proposed a method of garbage collection and transportation path planning based on GIS technology and improved ant colony algorithm. CRITIC method, entropy weight TOPSIS method and improved ant colony algorithm were used to realize the optimal path planning and design from the garbage collection point to the final treatment plant, thereby effectively reducing the cost of garbage collection and transportation and the harm to the surrounding ecological environment. The results showed that when the impacts of road traffic on the human settlement environment and natural ecology were included in the evaluation indicators of the garbage collection and transportation path, economic costs and ecology impact were reduced significantly. The transit rates of areas with strong demand for land protection, areas with large affected population size, areas with low noise reduction density, and areas with high degree of ecological inseparability had been reduced by 41%, 44%, 29%, and 41%, respectively. It reduced the disturbance of the garbage collection and transportation route to ecologically sensitive areas significantly. The results of this study could provide a reference for GIS technology and ant colony algorithm in garbage truck collection path planning.
-
Key words:
- domestic waste /
- path optimization /
- ant colony algorithm /
- CRITIC method /
- entropy weight TOPSIS method
-
表 1 土地利用类型与生态不可分割度得分的映射关系
Table 1. Mapping relationship between land use type and ecological indivisibility score
土地利用类型 基础分数 结构类型 修正系数 土地利用类型 基础分数 结构类型 修正系数 林地 100 有林地 1 耕地 31 水田 1 灌木林地 0.75 旱地 0.67 疏林地和其他林地 0.5 建筑用地 11 城镇建设用地 0.75 草地 60 高覆盖度草地 1 农村居民地 1 中覆盖度草地 0.75 其他建设用地 0.75 低覆盖度草地 0.5 未利用地 3 沙地 0.67 水域湿地 80 河流 0.5 盐碱地 1 湖泊(库) 0.75 裸土地 1 滩涂湿地 1 裸岩石砾 0.67 表 2 CRITIC法计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of CRITIC method
考察项目 指标变异性 指标冲突性 信息量 权重系数 土地退化态势 0.239 2.604 0.622 22.87% 人口密度 0.069 2.802 0.195 7.16% 植被覆盖度 0.178 2.833 0.505 18.56% 生态不可分割度 0.446 3.133 1.398 51.41% 表 3 熵权法计算结果
Table 3. Calculation results of Entropy Weight TOPSIS method
考察项目 信息熵值e 信息效用值 权重系数 时间成本 0.817 7 0.182 3 89.96% 环境成本 0.979 6 0.020 4 10.04% -
[1] SULEMANA A, DONKOR E A, FORKUO E K, et al. Optimal Routing of Solid Waste Collection Trucks: A Review of Methods[J]. Journal of Engineering, 2018, 2018: 1-12. [2] SULEMANA A, DONKOR E A, FORKUO E K, et al. Effect of optimal routing on travel distance, travel time and fuel consumption of waste collection trucks[J]. Management of Environmental Quality:An International Journal, 2019, 30(4): 803-832. [3] ASSAF R, SALEH Y. Vehicle-Routing Optimization for municipal solid waste collection using genetic algorithm: the case of southern nablus city[J]. Civil and Environmental Engineering Reports, 2017, 26(3): 43-57. doi: 10.1515/ceer-2017-0034 [4] 樊莹莹. 高速铁路列车运行调整及时空稳态分析研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2018. [5] 周祺森. 车辆路径问题的算法综述[J]. 甘肃科技纵横, 2020, 49(8): 75-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6375.2020.08.024 [6] 张艳梅, 姜淑娟, 陈若玉, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法的类集成测试序列确定方法[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(4): 931-945. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.00931 [7] PELLERIN R, PERRIER N, BERTHAUT F. A survey of hybrid metaheuristics for the resource-constrained project scheduling problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 280(2): 395-416. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.01.063 [8] Open Street Map funding(OSMF). Open Street Map [EB/OL]. [2021-05-12].https://www.openstreetmap.org/#map=4/36.99/104.15, 2021. [9] 高志海, 李增元, 孙斌, 等. 500m全球土地退化态势评价数据集(2000-2018)[M]. 北京: 全球变化科学研究数据出版系统, 2019. [10] 人口网. 中国人口密度分布地图. [EB/OL]. [2019-05-20]. https://www.renkou.org.cn/hot/pic/2019/0520/91714.html, 2021. [11] 穆西晗, 柳钦火, 阮改燕, 等. 中国-东盟1km分辨率植被覆盖度数据集[J]. 全球变化数据学报, 2017, 3(1): 45-51. [12] OSGeo中国中心. 中国土地利用在线地图[EB/OL]. [2020-02-14], https://www.osgeo.cn/map/m01ba, 2021. [13] ZHOU M, LIU X-B, YANG J-B, et al. Evidential reasoning approach with multiple kinds of attributes and entropy-based weight assignment[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 163: 358-375. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.08.037 [14] GOU X, XU Z, LIAO H. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic entropy and cross-entropy measures and alternative queuing method for multiple criteria decision making[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 388: 225-246. [15] 中国环境监测总站, 环境保护部南京环境科学研究所, 上海市环境监测中心, 等. 生态环境状况评价技术规范: HJ 192-2015[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2015. 期刊类型引用(11)
1. 吴金亮,何航,黄佳音,陈益人,张伟军,王东升. 印染污泥基炭材料制备及其对疏浚余水中溶解性有机质的吸附特性研究. 安全与环境工程. 2022(02): 174-182 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蒋玉柱,惠贺龙,刘弘毅,丁广超,卢文义,李松庚. 印染污泥基生物炭吸附处理难降解有机废水. 环境工程. 2022(10): 32-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 姬江浩,胥思勤. 污泥生物炭制备及应用研究进展. 科技创新与生产力. 2021(05): 41-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘连鑫,马彦彪,刘哲,王芳,崔建国,李红艳. 优化食用菌渣活性炭制备及其对亚甲基蓝去除特性. 工业水处理. 2021(06): 252-257 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵迎新,麻泽浩,杨知凡,杨凯超,邱潇洁. 污泥生物炭催化高级氧化过程进展. 化工进展. 2021(07): 3984-3994 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吴钦岳,刘和,郑炜,刘宏波,郑志永,张衍,张翠翠. 制药污泥热解制备生物炭及对制药废水的吸附处理性能分析. 环境工程. 2021(11): 103-109 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 裴轩瑗,任宏宇,任南琪,刘冰峰. 污泥生物炭处理水环境新兴污染物研究进展. 给水排水. 2021(S2): 545-552 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 许思涵,王敏艳,张进,刁韩杰,李彦铭,单胜道,曹玉成. 热解时间对污泥炭特性及其重金属生态风险水平的影响. 环境工程. 2020(03): 162-167 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 黄蓉,刘立恒,何东薇,汤传武. 热解条件对硫酸钙/污泥基生物炭中Pb、Ni形态分布及生态风险的影响. 环境污染与防治. 2020(07): 849-853 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 李文斌,叶勇,邓红艳,胡亚菲,王丹,陈星宇,何海霞,易会宇. 不同炭基两性黏土对紫色土吸附Cu~(2+)的影响. 地球与环境. 2020(05): 558-566 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 吴善斌,汪清环,郑育毅,孙启元. 再生污泥基生物炭对膜浓缩液COD吸附性能的影响. 泉州师范学院学报. 2020(06): 13-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(11)
-






 下载:
下载: