-
纳米银颗粒(silver nanoparticle,AgNPs)因其抗菌广谱、高效和不易产生耐药性等特点,广泛应用于医药、个人护理、家纺和家电等行业[1]。包含AgNPs的产品在其生产、加工、储存、使用和废弃等过程中,不可避免地直接或间接释放到环境中。据估算,约有60%的AgNPs通过污水管网进入市政污水处理厂[2],因此,污水处理系统是AgNPs重要的环境归趋。HOQUE等[3]的研究结果表明,污水中AgNPs的质量浓度一般在100~200 ng·L−1;ZHOU等[4]检测到活性污泥系统污泥中Ag质量分数可达到1.6 mg·kg−1。随着含有AgNPs材料的广泛应用,进入市政污水处理厂的AgNPs浓度会不断增加。活性污泥工艺是目前应用最广泛的污水生物处理技术,该工艺利用活性污泥(微生物聚集体)去除水中的各种污染物[5-6],包含AgNPs的污水可对活性污泥微生物活性产生抑制作用、降低出水水质、给水生生态系统带来负面影响[7-8]。
微生物群体感应(quorum sensing,QS)是指细菌自发产生、释放一些特定的信号分子,并能感知细菌群体中细胞密度变化进行种内或种间信息交流,从而调节微生物的群体行为[9]。作为高菌群密度的生态系统,活性污泥细菌的群体感应对环境变化非常敏感,可参与调控外来污染物胁迫下的自身应激代谢反应[10-11]。在污水处理系统中,细菌可分泌和释放酰基高丝氨酸内酯类(acyl-homeserine lactones,AHLs)信号分子,诱导生物膜形成并促进生物脱氮等过程[12-16]。HAN等[17]的研究表明,活性污泥系统中假单胞菌属细菌分泌AHLs并参与胞外聚合物分泌、种间竞争与脱氮等过程。污水中氮的去除是污水处理厂运行的首要目标之一[18-19]。外源投加信号分子[20-22]和群感菌[23-24]是目前利用微生物群体感应现象强化污水生物脱氮的主要方法。DE CLIPPELEIR等[20]发现,向活性污泥系统中添加适量外源AHLs信号分子可提高氨氧化速率和污泥中氨氧化菌的丰度。目前,关于AgNPs胁迫下活性污泥污水处理系统中微生物分泌AHLs信号分子的变化,以及这种变化与改进系统污染物去除效率间的关系研究鲜有报道。
因此,研究AgNPs胁迫下活性污泥污水生物处理系统的脱氮性能、AHLs对AgNPs胁迫的响应及外源添加AHLs对活性污泥脱氮效率恢复的调控,对阐明活性污泥系统中AgNPs对微生物的胁迫效应,采取可行的调控污泥微生物活性的生物措施具有重要意义。
全文HTML
-
以序批式反应器(sequencing batch reactors,SBRs)模拟活性污泥污水处理系统。SBRs有效容积为1.6 L,曝气系统包括空气泵和曝气头,空气流速为2.0 L·min−1。SBRs每日运行2个周期,每周期5 h,包括进水15 min、搅拌90 min、曝气90 min、静置90 min和排水15 min,非运行期的SBRs处于静置状态。SBRs启动第20 天,污泥浓度(mixed liquor suspended solids,MLSS) 和污泥容积指数(sludge volume index,SVI)分别达到(6 503±39) mg·L−1和(52.6±0.8) mL·g−1,活性污泥系统运行稳定。这时在进水中分别添加AgNPs和Ag+,开始实验。SBRs中活性污泥混合液在一个运行周期内的溶解氧(dissolved oxygen,DO)和pH分别为0.2~7.0 mg·L−1和7.5~8.4,每个运行周期内均有厌氧-好氧-缺氧交替的生境,有利于SBRs对有机物、氮、磷等污染物的去除[25]。预备实验结果表明,在1 mg·L−1 AgNPs胁迫下,AHLs在SBRs泥水混合液中的浓度常常低于文中所用UPLC-MS/MS的检测限。为了准确检测AgNPs胁迫下微生物分泌AHLs的变动,实验进水中分别添加了10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1的AgNPs。活性污泥系统分为5组,每组SBRs设置3个重复,5组SBRs分别为CK(进水中不添加AgNPs,也不添加Ag+),进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs,进水中分别添加3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+ (对应10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs溶解释放的Ag+浓度)。活性污泥系统运行周期内换水率为50%。
实验用AgNPs溶液购自北京德科岛金科技有限公司,AgNPs颗粒表面包被聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(polyvinyl pyrrolidone,PVP),平均粒径为10~12 nm。AgNPs经超声仪(KQ-700DE,昆山市超声仪器公司)(100 W,40 kHz)超声5 min后,加入SBRs进水中。反应器进水中添加的Ag+以AgNO3配制(进水中的
NO−3 -N进行相应扣减),AgNPs在纯水中溶解释放的Ag+浓度依照孙秀玥采用超滤法测得的结果[26]。 -
实验中,采用南京某市政污水处理厂浓缩池污泥作为接种污泥。实验所用污水为人工模拟中等强度的城市污水,统一用纯水配置,具体组成参见孙秀玥的研究论文[26]。配制污水所用试剂购于阿拉丁(上海)有限公司,均为分析纯。
根据《水和废水监测分析方法》[27],水质指标
NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N、NO−2 -N和TN采用可见-紫外分光光度计(Shimadzu,UV-1800,Japan)测定。DO和pH分别使用便携式溶解氧仪(JPB-607A,上海雷磁仪器厂)和pH测定仪(PB-10,赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司)测定。泥水混合液MLSS和SVI采用水和废水标准监测方法测定[28]。化学需氧量(chemical oxygen demand,COD)采用HACH COD 快速测定仪(HACH,DR1010,USA)测定。 -
将活性污泥混合液分为污水(水相)和污泥(泥相)2个部分,分别测定污水和污泥中的Ag浓度。取曝气结束前30 min的泥水混合物,利用低温高速离心机(Centrifuge 5810R,Eppendorf,Germany)在4 ℃和20 000 r·min−1条件下离心30 min,过0.45 μm 醋酸纤维滤膜(Whatman,USA),滤液即为污水。将剩余部分即污泥置于110 ℃烘箱中烘干至恒重,冷却至室温后研磨,过100目筛后备用[29]。在污泥中加入4 mL浓盐酸和1 mL浓硝酸,采用石墨炉消煮仪(SH220,上海海能仪器股份有限公司)消解。消煮残渣置于20 mL体积分数为50%的氨水中浸泡。污泥中的Ag浓度为消煮污泥中Ag浓度与消煮残渣的浸泡液Ag浓度之和。采用ICP-MS/MS (NexION 300,PerkinElmer,USA)测定污水和污泥中Ag浓度,加标回收率在96%以上。
-
采用DNA提取试剂盒(MoBIO Laboratories,Inc,USA)提取活性污泥中细菌DNA,提取成功后涡旋混匀,用微量分光光度计(Thermo,NanoDrop 2000c,USA)测定DNA浓度(核酸纯度A260/A280>1.8),DNA样品保存于-20 ℃冰箱。
活性污泥DNA样品由MiSeq平台进行Illumina高通量测序(上海凌恩生物科技有限公司)。PCR扩增通用引物为515F(GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGG)和907R(CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT)。使用QIIME(quantitative insights in microbial ecology)软件对所得序列进行生物信息学处理。利用UCLUST分类器对有效序列进行聚类,将相似性高于97%的序列归为一个分类单元(operational taxonomic units,OTU)。OTU采用贝叶斯算法(http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/)与Silva(SSU123)核糖体数据库进行对比进行聚类分析和物种分类学分析,利用R Studio进行分析并作图。
-
将SBRs中的泥水混合物于4 ℃和20 000 r·min−1下离心30 min,收集50 mL上清液,过0.45 μm醋酸纤维滤膜,采用固相萃取(solid-phase extraction,SPE)对上清液AHLs进行提纯和富集[30]。具体步骤为:依次向Oasis HLB固相萃取柱(Waters,上海)加入5 mL甲醇和5 mL超纯水活化萃取柱;50 mL过膜(0.45 μm)后的上清液以<1 mL·min−1的流速过柱;采用5 mL体积分数为10%的甲醇水溶液淋洗萃取柱;氮气吹干;最后加入5 mL乙腈洗脱,收集洗脱液,氮气吹洗脱液至近干,加入1 mL乙腈重新溶解,洗脱液过0.22 μm有机滤膜后,密封遮光保存于−20 ℃冰箱,用于后续检测分析。
采用UPLC-MS/MS超高效液相色谱串联质谱仪(Xevo TQ-Smicro,Waters,USA)定量检测活性污泥混合液水相中N-丁酰基-高丝氨酸内酯(N-butanoyl-L-homoserine lactone,C4-HSL)、N-己酰基-高丝氨酸内酯 (N- hexanoyl -L -homoserine lactone,C6-HSL)、N-辛酰基-高丝氨酸内酯 (N- octanoyl -L -homoserine lactone,C8-HSL)、N-癸酰基-高丝氨酸内酯(N- decanoyl -L -homoserine lactone,C10-HSL)、N-十二烷酰基-高丝氨酸内酯 (N- dodecanoyl -L -homoserine lactone,C12-HSL)和N-十四烷酰基-高丝氨酸内酯 (N- tetradecanoyl -L -homoserine lactone,C14-HSL) 6种信号分子。液相色谱柱BEH C18(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7μm;Waters),运行时间为4 min,柱温为40 ℃,流动相A为含甲酸的超纯水(体积分数0.1%),B为含甲酸的乙腈(体积分数0.1%),采用梯度洗脱,流速为300 μL·min−1。质谱采用双通道多反应检测模式,离子源采用正离子模式,去溶剂气体为氮气,流量为992.0 L·h−1,锥孔气体为氩气,流量为1.0 L·h−1,离子源温度为149 ℃,去溶剂化温度为497 ℃,进样量为3 μL。活性污泥混合液中6种信号分子的加标回收率为51.22%~137.71%。
-
在反应器运行第65 天,向5组反应器中分别一次性加入浓度均为10 nmol·L−1的C6-HSL、C8-HSL和C12-HSL混合溶液,并以1.1节中相同的运行方法继续运行SBRs。
-
所有数据均采用3次重复的平均值±标准偏差来表示。数据统计和分析使用Excel 2016,采用Origin 9.2软件绘图。
1.1. 模拟活性污泥污水处理系统
1.2. 进水水质及水质指标分析方法
1.3. SBRs系统中水相和泥相Ag浓度的测定
1.4. 细菌DNA提取与16S rDNA高通量测序
1.5. SBRs中污水AHLs提取与检测
1.6. 外源添加AHLs类信号分子
1.7. 数据统计和分析方法
-
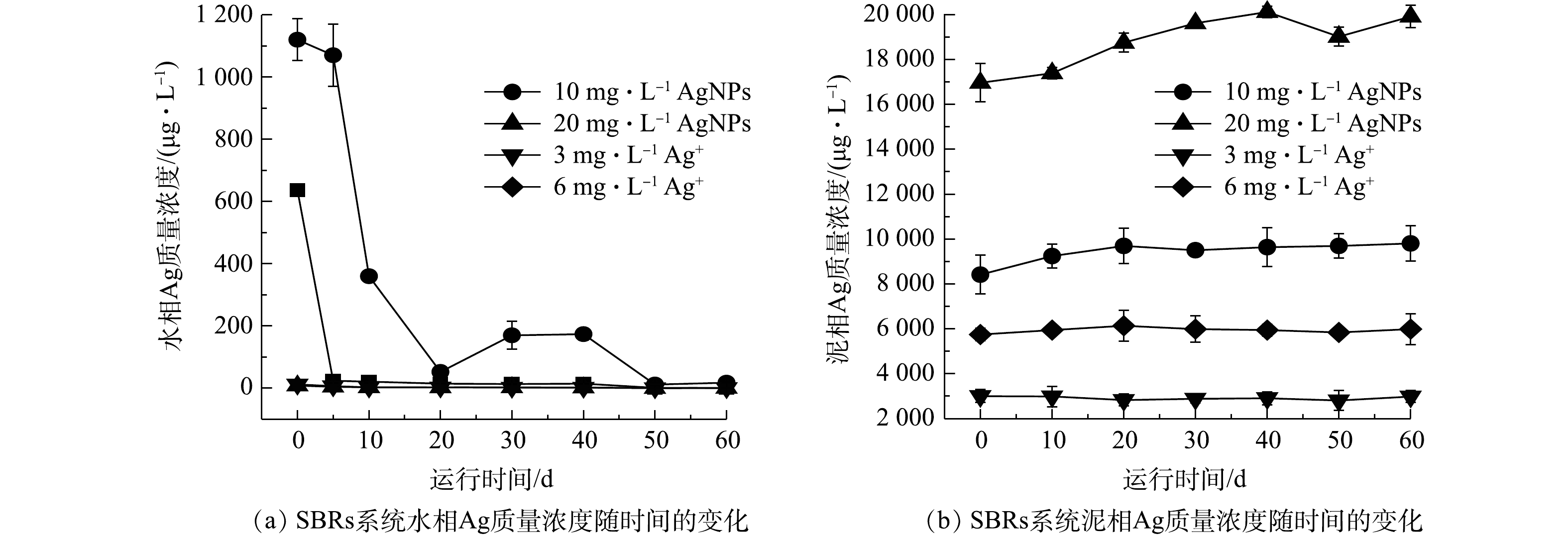
1) SBRs泥水混合液中水相和泥相中Ag浓度的比较分析。取CK及进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs,3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的SBRs第1、5、10、20、30、40、50和60 天曝气阶段的泥水混合物,分别测定水相和泥相中Ag质量浓度,减去CK反应器泥水混合液中水相和泥相Ag质量浓度,结果如图1所示。SBRs运行初期,各反应器水相中Ag质量浓度分别为(636.59±1.59)、(1 120.54±66.78)、(8.13±0.60)和(11.81±1.75) μg·L−1(图1(a)),运行期间,各反应器水相中Ag质量浓度呈下降趋势。SBRs运行至第60 天,进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1 AgNPs,3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+,反应器中水相平均Ag质量浓度均降至0.25 μg·L−1以下,进水中添加20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的反应器中水相平均Ag质量浓度降至17.40 μg·L−1。
由图1(b)可知,进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs,3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的反应器污泥中Ag质量浓度运行期内较稳定,分别为8 418.88~9 806.72、16 966.49~20 118.67、2 829.25~3 002.99、5 747.96~6 140.47 μg·L−1,SBRs污泥中Ag质量浓度与理论Ag添加量相近。由此可推断,进入活性污泥系统的AgNPs和Ag+主要存在泥相中[26]。
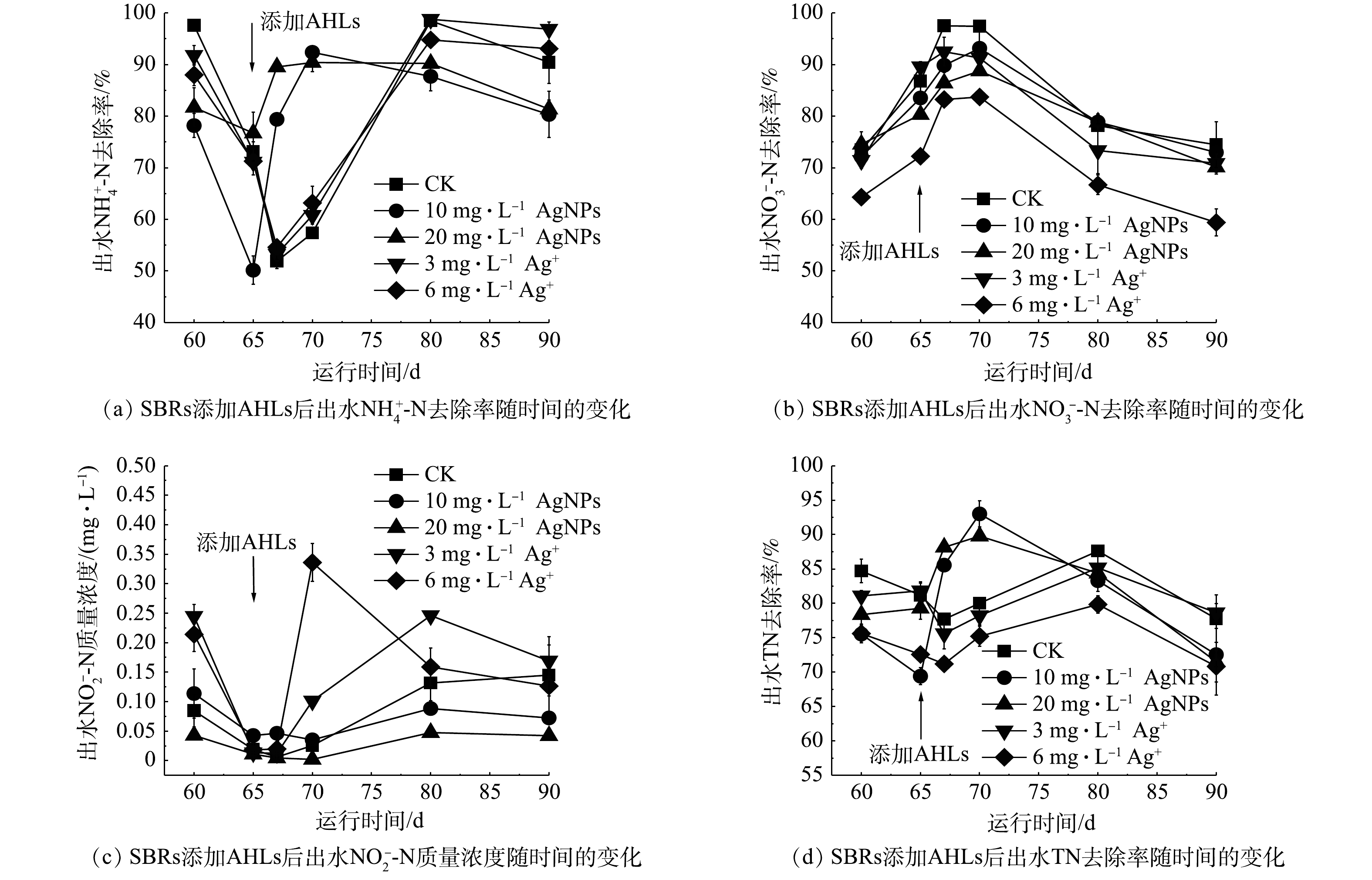
2) AgNPs和Ag+对SBRs中氮去除效率的影响。SBRs连续运行60 d后,
NH+4 -N、NO−3 -N和TN去除率以及出水NO−2 -N质量浓度变化如图2所示。由图2(a)可知,进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的SBRs在运行期间,NH+4 -N平均去除率与CK相比分别降低了5.51%~19.62%和8.23%~36.91%;而进水中分别添加3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的反应器与CK相比,NH+4 -N平均去除率没有显著差异,均高于84.73%。这说明AgNPs对活性污泥硝化反应的抑制作用比其溶解释放出的Ag+作用更显著。其他研究者也有类似发现,如ZHANG等[18]发现,进水中分别添加1 mg·L−1和10 mg·L−1 AgNPs导致SBRs对NH+4 -N的去除率由98.8%分别降低至71.2%和49.0%,AgNPs对NH+4 -N去除有显著抑制作用。LIANG等[31]发现,1 mg·L−1 AgNPs和1 mg·L−1 Ag+使SBRs中活性污泥的比耗氧速率硝化作用(活性污泥混合液中添加NH+4 -N为底物,分别测定1 mg·L−1 AgNPs和1 mg·L−1 Ag+胁迫下活性污泥的比好氧速率,以此来代表硝化作用)分别降低了41.4%和13.5%,在相同的Ag浓度下,AgNPs对硝化作用的胁迫效应高于Ag+。由图2(b)可知,与CK相比,进水中分别添加3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的SBRs对
NO−3 -N平均去除率分别降低了2.03%~8.55%和9.17%~12.73%;而与CK相比,进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的反应器对NO−3 -N的去除率无显著差异。自第10 天后,5组SBRs的出水NO−2 -N平均质量浓度均低于0.49 mg·L−1,结果见图2(c)。由图2(d)可知,与CK相比,运行至第10 天后,进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs,3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的SBRs中,TN平均去除率分别下降了0.93%~9.22%、3.34%~8.36%、1.87%~6.05% 和1.95%~9.14%。在60 d的运行期间内,进水中添加20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的反应器对TN去除率显著低于CK。SBRs运行至第60 天时,CK与进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs,3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的活性污泥系统对COD的平均去除率分别为93.93%、71.84%、47.25%、93.49%和92.07%。从实验结果来看,进水中添加AgNPs对活性污泥微生物硝化作用的抑制影响更明显,导致NH+4 -N去除率下降,因而转化成NO−3 -N的比例降低;Ag+对活性污泥微生物反硝化作用的抑制效应较明显,但很有可能因为AgNPs抑制NH+4 -N转化为NO−3 -N,使得微生物反硝化作用的底物减少,从而导致表观上外源添加AgNPs对NO−3 -N去除率的抑制影响低于Ag+;AgNPs对活性污泥微生物去除有机碳的抑制效应明显高于其溶解释放的Ag+。 -
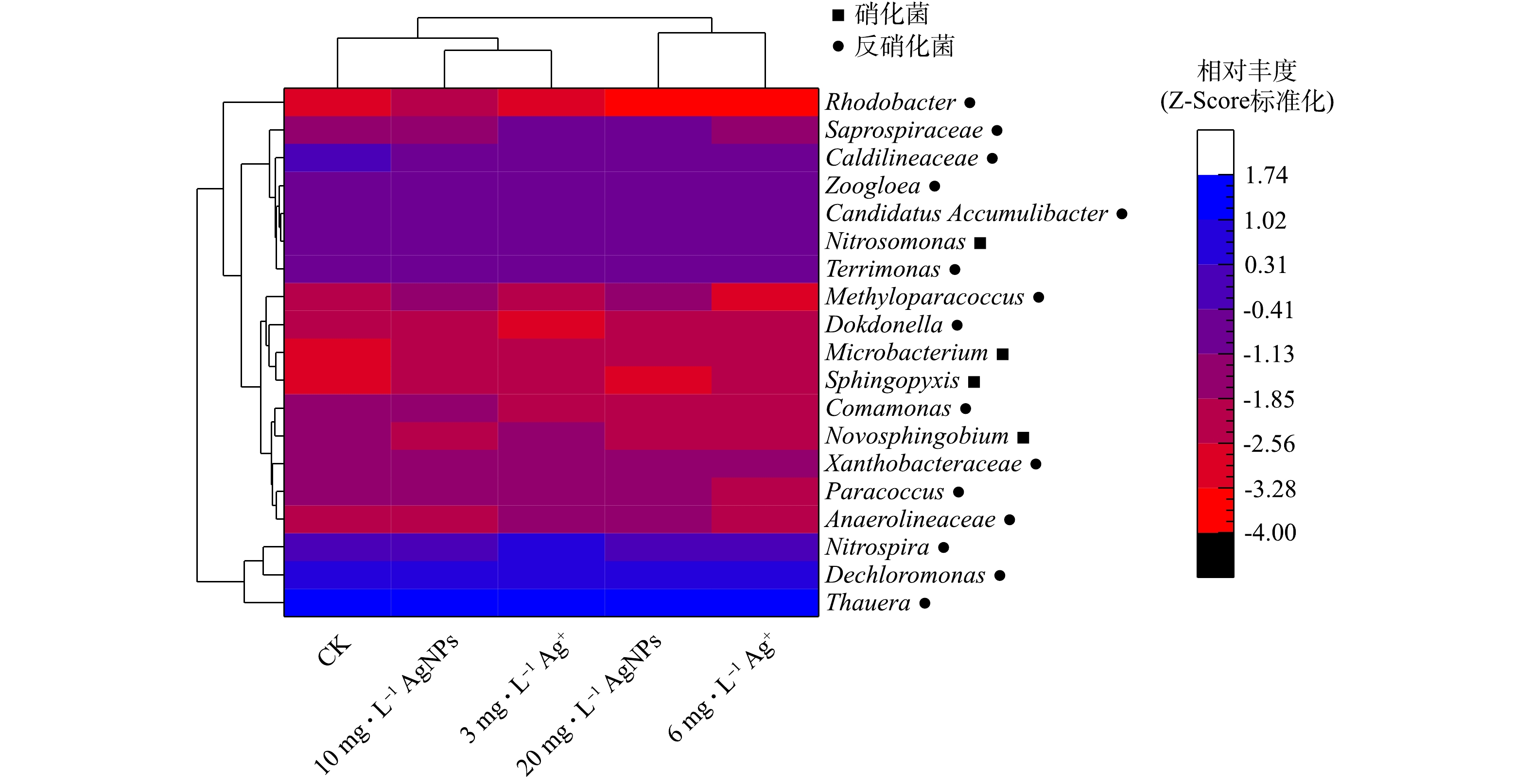
为了研究AgNPs及其释放出的Ag+对SBRs脱氮效率影响的原因,采用16S rDNA高通量测序法分析了活性污泥微生物群落结构。图3为反应器运行至第60 天时,相对丰度>0.010%的典型硝化和反硝化细菌属水平热图。CK与进水中添加20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的SBRs中亚硝酸菌属Nitrosomonas[32]的平均相对丰度分别为0.160%和0.070%;进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的SBRs中具有硝化功能的Novosphingobium[33]的平均相对丰度从CK反应器的0.034%下降到0.005%和0.002%,AgNPs对活性污泥硝化菌的胁迫作用与浓度有关;进水中分别添加3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的反应器与CK相比,反硝化菌Dechloromonas和Caldilineaceae[34]的平均相对丰度分别由6.100%和0.270%下降到4.700%和4.700%,0.180%和0.110%。动胶菌属zoogloea可以硝酸盐作为电子受体进行反硝化反应[35],进水中分别添加3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的反应器中zoogloea平均相对丰度从CK反应器的0.220%下降到0.090%和0.090%。AgNPs及其释放出的Ag+可以通过影响硝化菌和反硝化菌的相对丰度,从而影响活性污泥系统的脱氮效率。
-
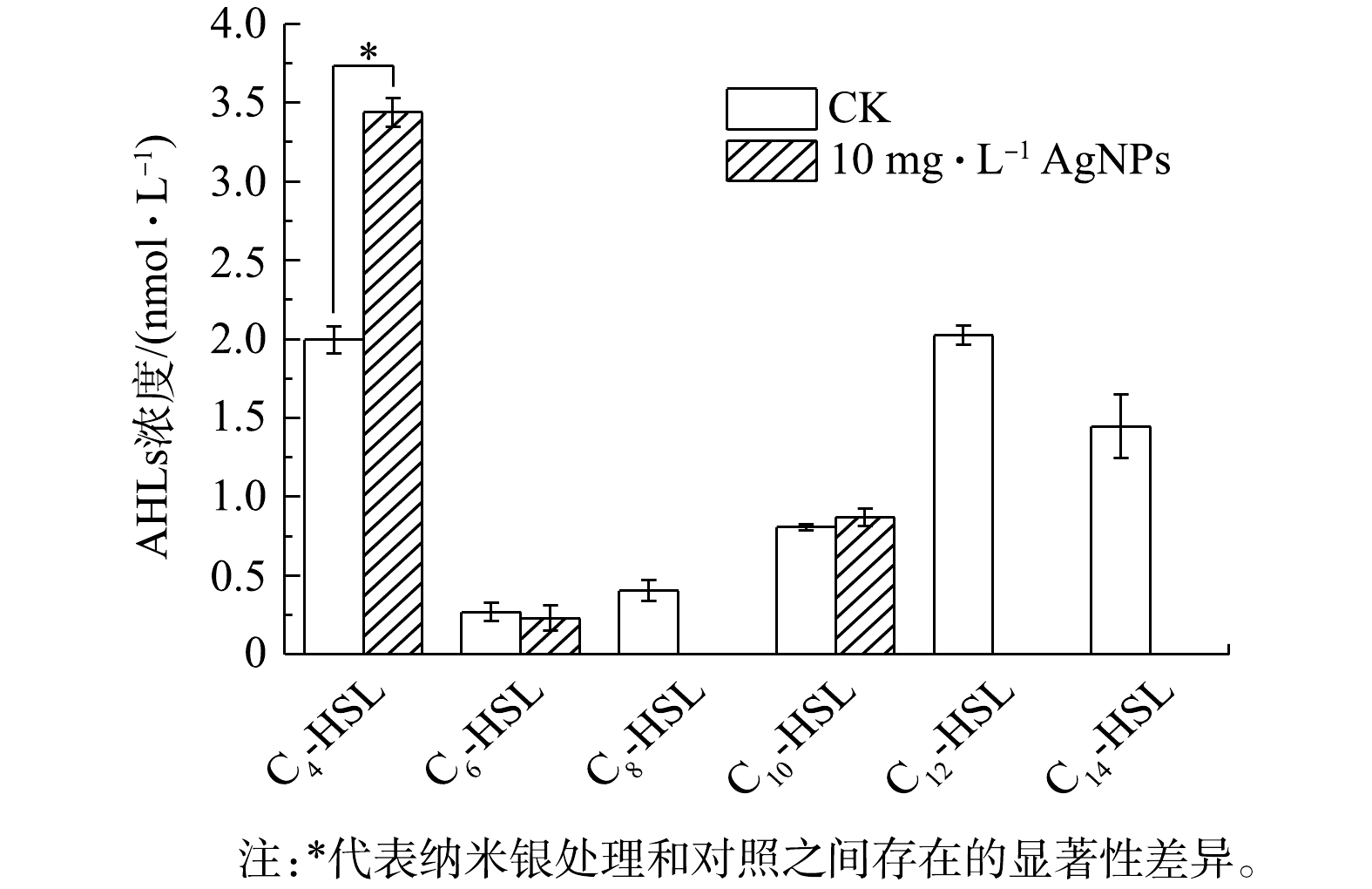
采用UPLC-MS/MS分别检测运行至第60天时的CK与进水中添加10 mg·L−1 AgNPs反应器中活性污泥微生物分泌的6种AHLs信号分子的浓度,结果如图4所示。CK中C4-HSL、C6-HSL、C8-HSL、C10-HSL、C12-HSL和C14-HSL的浓度分别为(2.00±0.08)、(0.27±0.06)、(0.41±0.06)、(0.81±0.02)、(2.02±0.06)和(1.45±0.21) nmol·L−1。WANG等[36]检测离心后生物膜中C4-HSL和C12-HSL的最高浓度为0.6 nmol·g−1;SUN等[37]检测到活性污泥中含量最高的AHLs信号分子为C8-HSL,浓度达1.3 nmol·L−1。进水中添加10 mg·L−1 AgNPs反应器中只检测到C4-HSL、C6-HSL和C10-HSL 3种信号分子,其平均浓度分别为CK反应器中的1.7、0.8和1.1倍。因而,10 mg·L−1 AgNPs添加于SBRs进水中可导致活性污泥微生物分泌AHLs信号分子的数量发生变化,C4-HSL平均浓度显著增高,也可导致AHLs信号分子种类减少,其中C8-HSL、C12-HSL和C14-HSL均未检出。
-
反应器运行至第65天时,外源加入混合AHLs。与加入前(第60 天)相比,CK与进水中分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs,3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+的反应器对
NH+4 -N平均去除率分别降低了24.52%、28.04%、5.01%、20.73%和16.76%;对NO−3 -N平均去除率分别增加了13.33%、11.41%、5.82%、18.25%和8.06%;各反应器出水NO−2 -N浓度均有所降低,降低幅度最大的SBRs(进水分别添加3 mg·L−1和6 mg·L−1 Ag+)中出水NO−2 -N平均质量浓度降低了0.21 mg·L−1。外源加入AHLs后,进水分别添加10 mg·L−1和20 mg·L−1 AgNPs的反应器中的TN平均去除率升高,运行至第70 天时,TN平均去除率达到最大值,分别为93.01%和89.82%(图5)。综合上述结果可知,外源加入混合AHLs可在5~10 d内导致AgNPs和Ag+胁迫下反应器对NH+4 -N平均去除率降低,对NO−3 -N的平均去除率升高,且可显著提高AgNPs胁迫下反应器对TN的平均去除率。朱颖楠等[38]指出,C6-HSL可调控生物膜修复和强化脱氮。张向晖等[39]发现,外源添加0.5 g·L−1的C6-HSL和C8-HSL会抑制厌氧氨氧化菌群生长,但能提高活性污泥的脱氮性能。外源加入混合AHLs的种类、数量对其调控污水处理反应器中微生物的脱氮性能都有影响。
2.1. AgNPs和Ag+对SBRs污染物去除性能的影响
2.2. AgNPs和Ag+对活性污泥中脱氮细菌相对丰度的影响
2.3. AgNPs对活性污泥微生物分泌AHLs信号分子浓度的影响
2.4. 外源加入AHLs信号分子对SBRs中污染物去除效能的影响
-
1)进入活性污泥系统中的AgNPs及其释放的Ag+主要存在污泥中,可影响活性污泥中硝化细菌和反硝化细菌相对丰度,抑制活性污泥微生物硝化和反硝化作用,从而降低活性污泥对TN的去除效率。
2) AgNPs胁迫影响活性污泥微生物分泌AHLs信号分子的数量和种类。10 mg·L−1 AgNPs胁迫下反应器中C4-HSL平均浓度与CK相比显著提升1.7倍,而C8-HSL、C12-HSL和C14-HSL 3种信号分子浓度则低于检测限。
3) 10 mg·L−1 AgNPs胁迫下的活性污泥反应器在外源加入混合AHLs 5 d后TN平均去除率由69.41%提高至93.04%,但AHLs的调节作用受种类、数量等因素影响,需要进一步开展研究。



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: