-
随着点源污染的有效控制和管理,面源污染日渐成为水环境污染的主要贡献源。尤其是农业面源污染,是导致河流健康状况持续下降的主要原因,威胁着水生态系统的完整性和多样性[1-3]。河流生态缓冲带是保护河流水质的一道屏障,通过建立和恢复河流生态缓冲带来拦截面源污染,被认为是一项行之有效的措施和管理途径[4-6],也是河流水质保护的重要手段,对维系河流生态系统的健康起着重要作用[7-8]。
缓冲带(buffer zone,BZ),亦称植被过滤带(vegetative filter strips,VFS)、植被缓冲带(vegetative buffer strips, VBS)、保护缓冲带(conservation buffer strips,CBS)等,是指利用植被拦截污染物或有害物质的条带状保护区域[9-11]。从狭义上讲,河流生态缓冲带指河岸植被缓冲带,它具有截留污染物以净化水质、提供生物栖息地以保护物种多样性、调节河流微气候、稳固河岸、连接廊道、美化景观等生态功能,具有独特的生物化学循环特征和生态水文功能[5, 12]。从广义上讲,具有水质净化、降低氮磷污染物入河作用的河道两岸湿地缓冲区、养分拦截沟、生态围堰等水生态处理系统,以及具有土壤固碳、改善水质等多种生态服务功能的河道两岸的农田区非农生境的条状植被覆盖带,也可归入河流生态缓冲带范围[13-14]。
河流生态缓冲带的研究在国外已有较长历史,其研究内容从19世纪末期到20世纪60年代单纯的水土保持,发展到后来的保护陆地生态系统、提高生物多样性等方面。尤其是20世纪80年代以来,欧美等国家在缓冲带功能、植被类型及其净化效果、缓冲带宽度确定模型的构建、缓冲带管理等方面开展了大量研究。在20世纪90年代末,美国农业部国家资源保护局(USDA-NRCS)提出了国家保护性缓冲带倡议(National Conservation Buffer Initiative),从此开启了以控制面源污染为目标,保证水系周边地带稳定性、提高生态环境整体质量的生态恢复与保护的新阶段[15-18]。
我国对河流生态缓冲带的研究起步较晚。近年来,尽管在缓冲带功能及构建技术方面开展了一些初步研究[19-22],但仍停留在概念、功能和管理等方面的定性描述。而如何结合我国流域水环境的实际情况,在科学划定河流生态缓冲带的范围、构建缓冲带生态修复模式方面还存在明显不足。为此,本文对河流生态缓冲带在农业面源污染阻控方面的研究进行了系统梳理和分析,旨在为我国河流生态缓冲带的科学划定、生态构建及生态系统管理提供参考和借鉴。
-
面源污染是指通过降雨径流的冲刷和淋溶,使大气、地面和土壤中的污染物进入水体而造成的水环境污染,其中农业面源污染是引起水体富营养化的主要原因[23-24]。河流生态缓冲带作为一种成本低廉且有效阻控农业面源污染汇入周边河流的带状植被系统,通常分布在产生污染物的源区(即农田)内,或源区与受纳水体(河流、河道及湖泊等)之间,其可通过滞留、下渗、吸附、吸收和降解等过程促进泥沙沉降,并截留地表径流中的污染物。根据河流生态缓冲带的分布位置和主要作用,一般将其分为阻控农田面源污染的田间缓冲区(in-field buffers)、田边缓冲区(edge of field buffers)和“田后”保护缓冲区(after-field conservation buffers) [13-14, 25]。基于农业面源污染阻控的河流生态缓冲带分类如图1所示。
-
田间缓冲区是建立在农田区内的具有一定密度的人工或天然的条带状植被屏障,主要包括植草水道、等高缓冲带和防风缓冲带(如图2所示)。
1) 植草水道。植草水道是指在农田区内由规划建造或自然生长的植被所覆盖的沟渠(如图2(a)所示)。一方面,植草水道利用植物根系生长作用增加水分下渗,减缓地表径流流速,有助于过滤氮磷组分和污染物,截留颗粒物,同时也可防止沟壑和细沟侵蚀;另一方面,植草水道还可营造田间生物岛屿和野生生物资源库。
2) 等高缓冲带。等高缓冲带是指沿着等高线构建的一种狭长的永久植被带,与耕作带之间交替分布(如图2(b)所示),即将大面积耕地分割成若干等高带状的小地段。类似的布局有助于降低片区和细沟侵蚀,拦蓄部分地表径流,减轻土壤冲刷[13, 26]。等高缓冲带是按照农田斜坡的轮廓与等高线呈一定角度构建的植被屏障,适合面积大且相对平坦的坡耕地。由于其分布特征,等高缓冲带的入渗能力得以提升,人为产生一个比降,能安全疏导多余径流,通过改善渗透来截留泥沙和污染物。
3) 防风缓冲带。防风缓冲带亦称“防风林”“防护带”或“草本防风屏障”,其能保护作物免受强风和破坏性风吹动,以及防止裸露土壤造成的风蚀[27-28](如图2(c)所示)。这些缓冲带由一排或多排树木组成,按照一定宽度、结构、走向、间距的林带栽植在农田田块边缘,可分隔田地、降低风速,并有助于减少该地块农药的漂移。若林带垂直于斜坡栽植,也有助于减少径流污染。另一种防风缓冲带是草本防风植被带,通常由高草组成。这些草本植物沿着垂直于一般风向的方向一排排种植,可降低风速,从而拦截随风传播的氮磷组分和农药。
-
田边缓冲区即位于农田区和水体之间的植被区域,包括农田边界缓冲带和河岸植被缓冲带(如图3所示)。
1) 农田边界缓冲带。农田边界缓冲带是指建立在农田边缘的永久性植被带(见图3(a))。其功能一方面是为了抑制风蚀和水蚀,提供授粉、害虫控制等,同时亦为野生动物提供栖息地[29];另一方面,这类缓冲带还可以减少农田径流中的农药和氮磷组分的越界迁移和污染水体,且当径流水流过这些边界时,可截留吸附农药的颗粒物。
2) 河岸植被缓冲带。河岸植被缓冲带是被研究最多的缓冲带类型,是分布在农田与水体之间的区域。它是指水生生态系统和陆地生态系统之间的能量、物质交换的过渡带,一般由水域区、河岸区和相邻土地区等3部分组成(见图3(b)和3(c))。良好的河岸植被缓冲带可有效截留、消除农业面源污染中的氮磷和农药等物质[30-32]。鉴于河岸植被缓冲带在控制农业面源污染方面的重要作用,后文主要讨论的对象为河岸植被缓冲带。
按照河岸植被缓冲带的植被组成可划分为河岸林地缓冲带、草地缓冲带和几种植被构成的复合缓冲带。不同的植被类型对于陆源污染物的阻控能力不同。
河岸林地缓冲带亦称“河岸管理区”“林地缓冲区”“河岸森林”等,指在河流水体沿岸构建的由各类树木林带或灌木林为主的区域组成。河岸林地缓冲带不仅能防止引起水体富营养化和水质恶化的土壤氮磷组分、农药、流失泥沙、牧畜粪便、大气降尘等进入临近水体,而且还能降低和维持水温,从而起到改善水生物种平衡的作用,有助于恢复原生河岸植物群落,同时还可增加植物生物量和土壤中的碳储量。
河岸草地缓冲带通常是指沿着常年或季节性水体构建的旱地和水生栖息地之间的过渡带。在缓坡耕地沿等高线种植缓冲草带,可减少坡耕地土壤与氮磷的流失,是一种被广泛采用的土地和生物保护性措施[31-32]。河岸草本植物缓冲带的构建,一方面可为鱼类和野生动物提供栖息地,保护栖息地走廊和原生植物群落,同时亦可改善水质;另一方面,草地缓冲带对拦截农田地表径流中的颗粒物和污染物效果显著,同时能减少河道能量,从而可阻止河岸被侵蚀。
河岸复合缓冲带是指利用多种林草植物构建不同配置模式而形成的具有一定缓冲功能的植被带。为达到更好的面源污染防治效果,通常将缓冲带植被进行合理配置,如构建从水体岸边向岸坡延伸的乔木、灌木和草本组成的缓冲区域。这样能更好防止地表径流、地下径流、废水排放等携带的氮磷、有机质和其他污染物等汇入水体。有研究表明,采用2种及以上植被组成的复合型缓冲带的截留效率更高,缓冲带植物的种类、植被的组分和密度等均会影响缓冲带截留效果[33-34]。
-
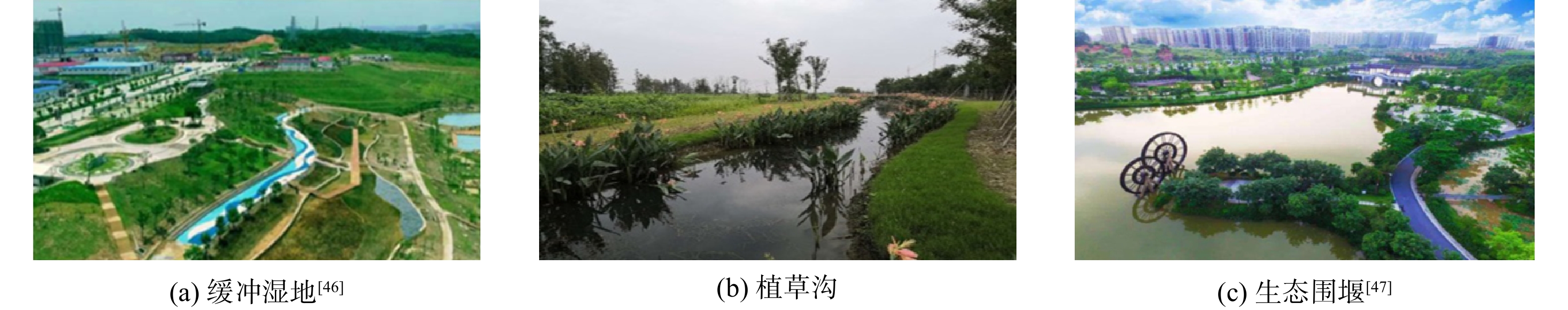
人工湿地、生态围堰、植草沟等虽然不是典型的植被缓冲带,但这些生态处理设施可在污染物排入河流之前,起到截留污染物、水质净化、降低氮磷入河等作用。尤其是将上述设施与植被缓冲区相结合,还可带来额外的生态环境效益。因此,这些生态处理设施也可归入生态缓冲带范围(如图4所示)。
1) 缓冲湿地。缓冲湿地一般由基质和生长在基质上的水生植物组成,形成基质-植物-微生物生态系统。虽然这类湿地不是典型的植被缓冲带,但其可利用湿地中填料、水生植物和微生物之间的相互作用,通过一系列物理、化学及生物过程实现对污染物的去除和对污水的净化(见图4(a))。有文献报道,人工湿地可将排放污水中总氮负荷降低37%[35]。也有研究者发现,湿地对氮的去除率可达到79%,对其中硝态氮的去除率可高达96%[36-37]。湿地对磷的截留是通过滞留颗粒物来实现的,这一过程包括沉积、吸附和络合等作用,对磷的去除率为25%~98%[38-39]。缓冲湿地去除污染物以改善水质的效果主要受到湿地与流域面积之比、水在湿地中滞留时间及湿地位置等因素的影响。湿地与流域面积比越大,湿地截留污染物、改善流域水质的能力就越强[38-40]。
2) 植草沟。植草沟指种有植被的地表浅沟,其利用沟渠和植物的协同作用来实现面源径流的收集、转输及净化(见图4(b))。当面源径流以较低流速经植草沟持留、植物过滤和渗透,径流中的颗粒态污染物和部分溶解态污染物会被有效去除,故植草沟是实现径流总量控制、污染物总量削减、地下水补充等的重要技术手段[41-42]。植草沟分为传输型植草沟、渗透型干植草沟及常有水湿式植草沟。各类植草沟可分别提高径流总量和径流污染控制效果。传输型植草沟是开阔的浅植被性沟渠,主要起到收集、转输径流的作用,可将集水区的径流(如农田退水)引导和传输到其他地表水处理设施。干植草沟是植被覆盖的沟渠,包括人工改造的土壤过滤层和过滤层底部铺设的地下排水系统,以增强植草沟的处理和传输能力。湿植草沟与传输型植草沟类似,只是设计为沟渠型的湿地处理系统,以增强处理效果。有研究结果表明,干植草沟的污染物去除率明显高于传输型植草沟和湿植草沟[42-44]。适当增加植草沟的长度、降低坡度或阶梯式边坡的设计、土壤渗透性改进、延长径流与植物的接触时间或增加径流和植草沟沉淀及渗透过程等,均可提高污染物去除效果[45]。
3) 生态围堰。生态围堰即基于传统的水利工程建设中围堰的概念,结合水生态修复的理念,在围堰构建中添加功能性吸附填料并种植水生植物,以达到拦截、降解面源径流中污染物目的,同时恢复水生态功能。围堰湿地就是一种生态围堰,即在河流岸边通过建设围堰形成围堰区,再经过相应生态化处理形成生态围堰(见图4(c))。
-
河岸植被缓冲带主要是通过一定宽度的水-土壤-植被系统的沉淀、过滤、渗透、吸收、降解转化等物理、化学和生物作用,控制或减少面源污染物,达到净化水质、保护河湖水体健康的目的。其主要作用机制包括截留径流中颗粒物及其携带的污染物、植被的吸收、土壤对污染物的吸附,以及土壤微生物对污染物的降解作用(如图5所示)。
-
农业生产活动降低了地表的水土保持能力,使得农田中的颗粒态和溶解态污染物随降雨径流经过植被缓冲区进入河流水体。在此过程中,缓冲带中的植被可有效增加径流阻力、减缓地表径流速度,使更多地表径流通过土壤空隙渗入,从而变成渗流。这样大多数携带污染物的固体颗粒逐渐淀积下来,径流中的泥沙等颗粒态污染物或悬浮物得到有效过滤和拦截[13]。与此同时,渗流中的可溶性污染物通过植被缓冲带内深厚的枯落物层和疏松的土壤渗透到更深层的土壤中,从而可降低地表径流对可溶性污染物的转运能力[48]。已有研究表明,缓冲带能去除大约90%的颗粒物[49-51]。其中,草本植物过滤带可明显降低颗粒物流失量,如当径流中颗粒物浓度为20、40和60 g·L−1时,植被过滤带对颗粒物的拦截效率分别为95%、93%和85%[52]。在天然降雨条件下,7.1 m宽的单一柳枝稷缓冲带能拦截径流中95%的颗粒物、80%的总氮(TN)、62%的硝态氮(NO3−-N)、78%的总磷(TP)和58%的PO43−-P;随着缓冲带宽度增加(如16.3 m),且植被由单一柳枝稷改变为柳枝稷/林木复合植被缓冲带时,其对污染物的去除效率随之提高(即拦截97%的颗粒物、94%的TN、85%的NO3−-N、91%的TP和80%的PO43−-P)[53]。因此,植被缓冲带对颗粒物及其携带污染物的拦截作用,主要是通过颗粒物的沉积及其运移能力削弱的共同作用实现。在此过程中,颗粒物及附着于颗粒物上的污染物沉降至过滤带内,进而被滞留去除。
-
缓冲带中,植物根系可提高土壤的纵向水力传导度,从而促进径流下渗。当携带着污染物的径流经过植被缓冲带时,溶解态的污染物会随着入渗水流进入土壤,并被植物根系吸收。缓冲带的植被根系越发达、生物量越高(如灌木、乔木过滤带),越能促进植物根系吸收和微生物降解,从而提高对径流中污染物的截留效率[54-56]。河岸植被缓冲带对氮具有明显的削减效果,草林复合植被缓冲带对氮的去除率可达89%[57-58],宽度为10~13 m的牧场植被缓冲区可拦截地表径流中80%以上的悬浮物和颗粒态氮,对溶解态氮的去除率达67%[59]。随着时间的推移,缓冲带对磷的截留效率逐渐降低。植被缓冲带对磷的去除存在一个饱和值[9, 60]。植被缓冲带中植物本身亦可吸收农药类污染物,并促进农药的降解,而农药的降解是植被过滤带去除农药的一个重要途径。许多禾木科草本植物对阿特拉津具有明显的吸收作用,在这些草本植物的根和茎叶中均能检测到阿特拉津及其代谢产物。其中,柳枝稷为缓冲带候选植物之一,其体内的阿特拉津有94.3%被分解转化为各种代谢物[61-62]。
-
土壤中不同有机和无机成分对污染物的吸附是植被缓冲带截留转化污染物的主要机理之一。土壤吸附污染物的效果取决于其结构、组成和特性。结构简单的沙土渗透率很强,但截留污染物能力较差。而黏土下渗速率小,并且通过离解、吸附、同晶型置换等一系列作用,使得土壤颗粒带有正负电性。这种带电性可增强其吸附性能,从而提高土壤对径流中可溶性污染物的吸附拦截能力[63]。此外,土壤中不仅会发生一系列的物理、化学和生物反应,还可能累积更多的有机物质成为氮磷沉积场,这样有利于土壤对径流中农药的吸附及降解[64-65];同时,有机物的积累也为微生物的活动和生长提供了所需能量,从而也会促进农药等污染物的生物降解。
-
土壤中存在大量微生物。尤其是在根际土壤微区,由于该区域植物能量和物质代谢最活跃,其中的微生物量、微生物活性及各种酶的活性均高于非根际土壤。截留在植被缓冲带中的污染物经过一段时间后被根际土壤微生物介导发生微生物降解作用,转化成不同形态的物质。在不同类型的植被缓冲带中,这类微生物降解作用的强度存在一定差异[66-68]。另外,由于植物根系能分泌出多种酶,这些酶可通过生物过程分解和降解农药类污染物,因此,在植物根际土壤中微生物降解也是植被缓冲带去除农药的一个重要途径[69]。
-
在农业生产中,化肥、农药的大量使用导致氮、磷成为农业面源污染的主要污染物。通过上述分析可知,河岸植被缓冲带通过沉积、植物吸收、土壤吸附、微生物反硝化作用等途径,可有效削减氮磷等面源污染物。
1) 氮的削减途径。通常地表径流中含有可溶态氮及与土壤颗粒结合的吸附态氮。当地表径流流经河岸植被缓冲带时,植物对径流的阻力会使径流速度降低,从而增加了地表径流中吸附态氮的沉积和可溶态氮的入渗。入渗水流中部分溶解态氮经过植物根区时,可被植物根系吸收并转运到植物体内,并在植物体内转化成有机氮,使得氮在植物体中长期积累[56]。在植被过滤带中,滨水地带的土壤干湿交替频繁,有利于土壤中微生物的生长。微生物在好养条件下将有机氮转化为氨态氮(NH4+-N),氨态氮进一步被氧化为硝态氮(NO3−-N)或亚硝态氮(NO2−-N);在厌氧条件下,吸附在植被根系和土壤中的硝态氮和亚硝氮在反硝化细菌的作用下,被还原成氮气和氮氧化物并被释放到大气中,反应过程如式(1)~(3)所示 [67-68]。因此,河岸植被缓冲带中的反硝化作用被认为是彻底去除地表径流中氮的最佳途径。
2) 磷的削减途径。河岸植被过滤带对磷的去除机制取决于径流中磷的形态。颗粒结合态磷可通过植被的拦截作用沉积在河岸植被过滤带中,而可溶态磷随径流入渗进入土壤后可被植物根系和微生物同化吸收,并在植物体内转化为有机磷,同时还经过渗透作用进入地下水中。河岸植被缓冲带对磷的截留转化作用与氮不同,除了被植物根系吸收利用外,主要途径是物理过程 [53, 60]。例如,地表径流中颗粒物对磷的吸附、渗透到土壤中被土壤吸附,均使得地表径流中的磷被削减。
-
河岸植被缓冲带是截留农业面源污染物的有效手段,具有较高的氮磷截留转化效率。然而,河岸植被缓冲带对污染物削减效果受各种因素的影响,主要包括河流两岸水文地质特征、河岸带陆域土壤状况、污染物种类、河岸植被缓冲带的坡度/宽度、河岸带植物组成状况等。不同因素可通过影响缓冲带的下渗能力、径流的入流速度、植被的吸收特性、微生物的降解能力等造成不同缓冲带面源污染物阻控效果的明显差异。
-
水文地质条件具有内在可变性,其对植被缓冲带截留效果的影响主要体现在对土壤和植被的影响。当地下水位较高时,缓冲带植被的根系和土壤可与径流充分接触,从而提高植被缓冲带对径流中氮磷污染物的拦截效率;当地下水位较低时,则大大降低植被缓冲带的拦截效率[56, 63]。土壤的温度对土壤中有机氮的降解有明显影响。在夏季,土壤温度较高,植物缓冲带中反硝化作用相对活跃,氮素转化后更易被植被缓冲带截留、转化和吸收;而到冬季,当温度较低时,就限制了土壤中氮素的转化速率,导致植被缓冲带的污染物截留能力明显下降[70-71]。
径流强度和流速是影响缓冲带截留效率的另一个重要因素。降雨强度越高,径流量越大,缓冲带中污染物的流失越明显;且径流流速越高,径流通过缓冲带时越不利于污染物与土壤植被的接触,影响污染物的下渗过程,从而降低了阻控污染物的效率[58,72]。另外,不同径流流态也是影响缓冲带阻控效果的关键因素。当径流以集中流状态流过缓冲带时,污染物的去除率明显高于均匀流流过缓冲带时的截留效率。这主要是由于,径流流态为集中流时,增加了缓冲带系统内污染物在植被-土壤-微生物间的相互作用,从而有利于截留效率的提高[72]。
-
缓冲带中土壤的特性,如有机碳含量、土壤质地、土壤微生物含量、土壤结构和pH值等都是影响缓冲带污染物截留效率的关键因素。这些因素的变化可改变缓冲带中径流流速和路径,引起土壤的渗透性、吸附污染物的能力及微生物活性的差异,进而影响缓冲带各生态功能的发挥[48, 63-65]。有研究结果表明,土壤有机质含量越高,越有利于径流中疏水性污染物的吸附,而被吸收后的污染物,可通过土壤微生物作用而降解或矿化[68-69]。通常,以沙质土为基质的缓冲带比黏质土为基质的缓冲带能截留更多氮磷,且其矿化过程受到土壤矿物质含量的影响。污染物的矿化作用表现为矿物质含量低的细质土高于矿物质含量高的粗质土[73-74]。由于颗粒较小的土壤具有较大的比表面积,因此,可有效吸附径流中更多的污染物,缓冲带截留效率会更高。此外,土壤pH和土壤微生物的含量,均会影响污染物的降解能力。土壤pH升高和微生物含量越高,越有利于污染物的矿化。土壤的含水性直接影响着土壤的渗透性和吸附性,间接影响微生物活性,从而影响缓冲带截留效果[75]。
-
农业面源污染来源广泛,主要来自于养殖业废水排放、农药化肥流失,以及水土流失和暴雨径流下土壤中氮磷等流失。污染物来源、种类和形态不同,缓冲带对其阻控效率也有所不同。其中,氮素通常以硝态氮、氨态氮等可溶性氮,以及与颗粒物结合的吸附态氮和有机残体的有机态氮等形式存在;磷素主要有可溶性磷、颗粒态磷和有机态磷;农药包括溶解态和颗粒物吸附态。当径流中的这些污染物通过缓冲带时,颗粒吸附态污染物的削减率最高,而溶解态污染物的阻控效率最低[49, 51, 53]。具有强吸附性的农药污染物,由于其易被颗粒物吸附,其被截留的效率较高;而弱或中度吸附性农药污染物被吸附的可能性小,缓冲带对其截留的效率相对较低[64-65, 69]。
-
缓冲带坡度是农业面源污染物削减的重要影响因素。为有效阻控面源径流中的污染物,可依据地形需要来设定坡度不尽相同的植被缓冲带。坡度影响着地表径流速度和地表下渗量,由于受到重力作用,坡度增大,地表径流流速加快,缓冲带的拦截效果降低;若坡度过大,将造成地表径流流速不均,导致坡面水流形成集中水流,则会增大对地表的侵蚀;而适宜的坡度有利于延长地表径流在缓冲带中的滞留时间,从而提高对地表径流中污染物的吸附、沉淀、过滤和降解的效果[76]。为保持一定的截留效率和缓冲带宽度,缓冲带的坡度不应高于15%,适宜的坡度为2%~8%[29, 31-32]。
-
河岸植被缓冲带宽度是影响其农业面源污染阻控功能的最主要因素。如果宽度较窄,则达不到截留污染物效果;而缓冲带越宽,可供径流下渗的面积则越大,能截留悬浮颗粒物的植被越多,对径流中污染物的阻控效果也越明显,但同时也会造成土地资源浪费和管护成本提高,因而不利于社会经济的可持续发展。众多学者针对污染物截留效率对缓冲带宽度要求进行了相关研究,但对植被缓冲带最适宽度仍存在争议。有研究者认为,当缓冲带宽度达到10~50 m时即可明显阻控地表径流中的氮磷组分,而通过现场实验发现,当河岸植被缓冲带宽度增加到10~60 m时,即可阻控颗粒物和污染物进入水体;也有学者认为,较窄的植被缓冲带亦能改善部分水质指标[48, 77-78],植被缓冲带宽度不是减小径流污染的最重要的影响因素之一,而植被密度和入渗能力更加重要[59, 79]。河岸植被缓冲带的这些特性和性能取决于立地条件和区域环境状况,其中,坡面坡度、土壤类型和植被类别等因素决定着最适宽度的大小。因此,需要结合实际的立地条件、区域环境状况、气候条件等因素,因地制宜地设定植被缓冲带宽度。
-
缓冲带植物种类、植被覆盖度和植物不同的生长阶段均会影响缓冲带对污染物的截留效率。按照缓冲带植被组成的不同,可将其划分为草地缓冲带、灌木缓冲带、乔木缓冲带,以及上述至少2种植被构成的复合缓冲带。草本植被对颗粒泥沙和附着颗粒物的污染物拦截效果明显;而乔木或灌木植被,由于其根茎系统相对较深,对径流中溶解态氮磷的吸收效果优于草本植被[80-82]。由于磷的溶解性差,草本植被对其拦截效率更高,而乔木植被缓冲带比草本类型的缓冲带吸收滞留的氮素更多。草本植被缓冲带中,不同种类的草本对径流污染物的去除率也存在差异,如百慕大草皮>白花三叶草>高羊茅草[82]。
缓冲带的植被布局包括横纵2个层面。最优纵向结构分层表现为不同生活型的乔木、灌木、草本植物的分布。横向植物配置考虑不同物种的密度和不同物种植物共存。植被越稠密,根茎分布越广泛,其水分蒸发量越大,从而可吸收更多的径流量,污染物截留效率更高[58, 80-82]。
-
要构建一个合理的河岸植被缓冲带,其核心问题是确定最佳宽度。河岸植被缓冲带的污染物截留效率与其宽度密切相关:其宽度越宽,截留污染物和颗粒物的效率就越高。国内外学者已从不同角度提出了基于面源污染阻控的河岸植被缓冲带宽度的确定方法,其中包括经验值法、现场实测分析法、数学模型计算法等。
1) 经验值法
以面源污染阻控和保护水质为目的,针对小流域不同河岸植被缓冲带规划和构建,最早采用经验值法确定河岸植被缓冲带的实际划定宽度,如在美国内布拉斯加州某小流域河岸边,采用经验值法划定的9~35 m河岸植被缓冲带[83]。经验值法适用于立地条件不确定和数据资料缺乏的小流域,该方法简单、实用、可操作性强。但由于并未考虑缓冲带宽度与河岸生态功能的内在联系,该方法的划定结果存在很大不确定性。
2) 现场实测分析法
现场实验确定河岸植被缓冲带宽度,通常指在野外实验区内,通过模拟自然降雨过程中对不同宽度缓冲带截污效率进行实测研究,并结合实测数据建立模型,拟合计算出河岸植被缓冲带宽度。污染物截留效率的测定与评价通常采用2种方式。一种是通过比较输入和输出缓冲带的污染物含量差异确定其截留效率;另一种是比较输出缓冲带和对照试验两者之间的污染物含量差异来评价其拦截能力[34, 84]。
3) 数学模型计算法
模型计算法是确定河岸植被缓冲带宽度的最常用方法。常用的数学模型主要包括:基于河岸带物理过程的复杂模型,如VFSMOD (The Vegetative Filter Strip Model)模型、REMM (Riparian Ecosystem Management Model)模型和CREAMS (The Chemicals Runoff and Erosion from Agricultural Management Systems)模型[85-87];基于不同参数的简单模型,如Phillips水文模型和时间模型、Mander模型、Nieswand模型和SWAT模型[16, 88-91];基于GIS的数学模型法。
VFSMOD模型由MUNOZ-CARPENA等[85]于1999年开发,并在美国北卡罗莱纳州得到验证、测试和应用,对不同宽度缓冲带的泥沙过滤效果进行了模拟研究。该模型主要包括入渗模块、地表径流模块和泥沙过滤3个模块,其主要功能是计算缓冲带的下渗水量、出流水量和泥沙截留效果,对颗粒物去除效果的模拟较为全面,而不能模拟泥沙吸附态污染物削减效果。REMM是综合考虑影响河流生态系统健康多种因素的河岸植被缓冲带划定模型,是目前河岸植被缓冲带发展较为成熟的计算模型。该模型能精确模拟自然坡面缓冲径流条件下缓冲带的水文特征、营养物迁移、植物生长等多种过程,已在美国Georgia地区进行了参数校正研究和应用[86]。REMM模型适用于自然坡面缓冲径流条件的河岸植被缓冲带,而在城市区域或建设有管网的地区,还未得到有效应用。另外,该模型的运行需要气候、田间、河岸带、土壤和植被等较多基础资料,需要多达200个参数,且忽略了河流纵向连接性及过滤效率的季节变化,故其应用推广受限。CREAMS是用于田块尺度的河岸植被缓冲带划定模型,它包括水文模型、侵蚀模型和污染物转化3个模块,通过模拟田块径流、侵蚀和农用污染物流失过程,确定河岸植被缓冲带宽度与颗粒物及污染物去除率的关系。该模型的局限性在于,参数之间会相互影响,忽略了缓冲带因其流量和峰值的变化,故只适用于土壤与降雨均匀、土地利用与耕作单一的“田块尺度”,不能在大尺度范围内应用[87]。
一些学者还开发了多种简单数学模型,以确定河岸植被缓冲带宽度。NIESWAND等[90]在曼宁公式的基础上,将坡度和宽度作为河岸侵蚀、截留颗粒物的最主要影响因子建立了一个以坡度为自变量、宽度为因变量的单因子回归方程。但该公式不适合在坡度大于15%和不透水地表面区域应用。Mander模型是综合考虑了地表径流强度、坡度、粗糙度系数、入渗速率、土壤吸附能力和特定坡长等因素建立的以宽度为因变量、多因素为自变量的回归方程,其中,特定坡长为流域面积与河流段长度的比值或河流到流域边界的距离。由于不同流域立地条件存在差异,坡长参数为经验值且无法反映实际条件,因此,该方法在应用时需进行修正[89]。CHANG等[91]利用SWAT模型,将宽度和坡度作为缓冲带截留效率的影响因素建立了回归方程。在利用该回归方程确定缓冲带宽度时,需采用现场实测数据对缓冲带的不同植被、宽度和坡度的相应系数进行校正。Phillips模型包括水文模型和时间模型。这2个模型均先设立参考缓冲带,再将现状立地条件与参考缓冲带进行比较,得出规划缓冲带的宽度。同时,在这2个模型的构建中均考虑了河岸两侧土地利用类型、土壤条件以及地形条件等因素对河岸植被缓冲带宽度的影响。但2个模型的不同点在于,Phillips水文模型是针对颗粒物附着的污染物去除机制,将能量损失代表污染物去除效率,建立的与河流两侧坡度、饱和导水率、曼宁系数的数学方程,由于仅考虑物理过程,其模拟的污染物去除率偏低;而Phillips时间模型是基于溶解态污染物去除机制,综合考虑了缓冲带对污染物的吸收和转换,以滞留时间衡量污染物除效率建立的与河流两侧坡度、饱和导水率、曼宁系数、土壤储水能力等之间的数学方程[16, 88],尽管该模型结合了物理过程和微生物作用,但考虑拦截效率的影响因素不全面。
另外,基于GIS的数学模型法是在大尺度流域河岸植被缓冲带划定及管理中应用较为广泛的方法,是在综合考虑流域地形地貌、水文功能、土壤特征、土地利用和土地覆盖等影响因素基础上建立的空间信息库的河岸植被缓冲带划定模型,其所需基础数据资料较多。例如,以Phillips时间模型为基础,结合基于GIS技术所建立的流域自然地理信息、生态水文功能等信息库,将模型所需数据叠加,通过GIS计算得出缓冲带宽度,并应用于美国北卡罗来纳州山岛湖流域缓冲带研究中[92]。
综上所述,不同数学模型法划定河岸植被缓冲带宽度具有各自的优缺点和适用范围。复杂的数学模型法,能较为全面地解释缓冲带的作用机理和模拟污染物和颗粒物拦截过程,但模型运算需要较多的数据和资料;而简单数学模型法虽涉及的空间变量较少、所需流域的基础资料少,但因未充分考虑流域的立地条件,使得缓冲带宽度计算结果准确度不够。基于GIS的数学模型法,可通过GIS技术完成大量数据的管理和计算,从而降低计算结果的误差,可实现快速和科学地确定大尺度流域缓冲带宽度。
-
河岸植被缓冲带的植被选取要遵循自然规律,应尽量选择对农业面源污染物(如氮、磷等)去除能力较强、用途广泛、经济价值较高、观赏性强的土著优势物种,慎重引进外来植物品种,同时要考虑常绿树种与落叶树种混交、深根系植物和浅根系植物搭配、乔木-灌木-草本植物相结合的方式 [14]。通常,植物搭配采用草本-乔木、草本-灌木、草本-灌木-乔木3种配置方式构成的复合过滤带 [93-94]。
按照河岸植被缓冲带的横向空间结构,通常有邻水区域、中间过渡区和近陆区域。邻水区域位于河溪水陆交错区,以乔木林带为主,起到保护堤岸、去除污染物等作用,同时为野生动物提供栖息地。中间过渡区域属岸坡缓冲区,以乔灌木树种为主,同时要考虑植物的多样性组合,以减少河岸侵蚀,截留泥沙,吸收滞纳氮磷污染物,增加生物多样性和野生动物栖息地,在洪水期减缓水流。近陆区域位于外侧远离河岸的区域,属岸边缓冲带,主要以草本类植物为主,可配置一些灌木类,用于阻滞地表径流中来自农业面源污染的沉积物,吸收氮磷和降解农药等污染物[14, 94]。
对于植被树(或草)种选择,通常选择根系发达、耐水湿水淹、抗土壤侵蚀能力强的植物种类,同时还要考虑物种的耐盐碱性和培肥改土能力,合理搭配草本-灌木-乔木植被物种[14]。因此,在邻水区,应选择种植根系发达、生长量大、固土能力强,耐水淹的乔灌树种;在过渡区域,应选择种植根量多、根系分布广、改良土壤作用强、生长量大、生长稳定、抗逆性强的乔灌树种和草本植物;而在近陆区域,应选择种植根系发达、生长旺盛、固土力强、能大量拦截径流中沉淀物和氮磷污染物的草本植物。
-
1) 河流生态缓冲带是一个复杂的结构体系,包括陆域、水体、堤岸、动物、植被以及微生物等,不同要素之间存在相互作用。在河流生态缓冲带类型选择与构建中,需要综合考虑立地条件与污染物类型,将河岸植被缓冲带与强化措施相结合,从而达到更好的污染物去除效果。
2) 河岸植被缓冲带截留污染物的影响因素复杂多变,缓冲带污染物截留效果存在较大差异。因此,急需探索适合各地区特点的方法,对缓冲带的空间结构、截留过程,以及各影响因子间的作用机制进行研究。另外,前人对植被缓冲带污染物去除机制的研究大多针对氮磷及颗粒物等,而对农药等其他污染物的去除机理研究较少,相关研究应进一步拓展和深入。
3) 尽管国内外已经对河岸植被缓冲带的最小宽度进行了大量的实验和模型模拟研究,但由于影响因素的多样性和复杂性,仍很难准确定量确定缓冲带的最佳宽度。因此,亟待开发实用的、准确的、适合我国特点的数学计算模型,同时结合工程投资、可持续发展等其他因素,以实现工程实施的生态环境和经济效益最大化。
4) 河流缓冲带具有独特的生物化学循环特征和生态水文功能,目前对其效果的评估仍基于短期的研究结果。因此,应建立长期动态的监测体系,充分考虑气候条件变化、植被生长过程等对径流污染物去除的影响,更加科学地反映和评价缓冲带在径流污染物削减、生物多样性和水生态系统健康恢复中的作用。
5) 由于径流中污染物在缓冲带中的截留及长期积累,若管理不善,可能会使缓冲带成为“污染源”。因此,还应根据各地实际条件开展植被缓冲带的管理机制研究。只有建立植被缓冲带管护制度和措施,才能可持续地发挥其正常功能。
以农业面源污染阻控为目标的河流生态缓冲带研究进展
Research progress in riverine ecological buffer zone for control of agricultural non-point source pollution
-
摘要: 河流生态缓冲带是河流生态系统的重要组成部分,一些国家已将河流生态缓冲带的构建与维护作为控制流域面源污染的关键措施。针对河流生态缓冲带的农业面源污染阻控功能,梳理了河流生态缓冲带的研究进展。基于河流生态缓冲带类型的划定,重点总结了河岸植被缓冲带的阻控机制及影响阻控效果的主要因素、氮磷削减途径和缓冲带生态构建模式,并就植被缓冲带对污染物的削减机理及量化方法、缓冲带的设计理念与构建模式、缓冲带的长期效果评估和管理机制等方面提出了展望,以期为我国河流生态缓冲带的科学划定、生态构建以及生态系统管理提供参考。Abstract: As an important part of river ecosystem, riverine buffer zone has been regarded as one of the best ways for river basin governance and also employed globally as a key technical measure to control non-point source pollution. On the basis of literature review, this article summarized the recent research progress on riverine buffer zone for control of agricultural non-point source pollution to improve water quality, in particular to the types of riverine buffer zone, the pollution control mechanism of typical riparian vegetation buffer zone, the main impact factors on the retention effect of pollutants in runoff, removal pathway of N and P, as well as ecological construction mode of riparian buffer zone. Moreover, based upon recent research status in riverine buffer zone, prospects were put forward in terms of the mechanism and quantization method of pollutant reduction, the design concept and construction mode, and the long-term effect evaluation and management mechanism of buffer zone, so as to provide reference for the scientific delimitation, ecological construction and system management of riverine buffer zone in China.
-
近年来,随着人们生活水平的提高,我国餐厨垃圾产生量以每年10%的速度增长,截至2018年,餐厨垃圾产生量突破了1×108 t,占城市生活垃圾的57%左右。餐厨垃圾含有的大量有机物质容易腐烂变质并携带病原菌,不仅污染环境而且威胁人体健康。同时,餐厨垃圾又富含碳水化合物、蛋白质和油脂,营养价值高,是有机废物厌氧能源化的理想底物[1]。氢能被广泛认为是未来最具潜力的绿色可再生能源之一[2],与传统的电解水、化石燃料制氢相比,暗发酵生物制氢具有运行成本低、能耗低、操作简单等特点,可实现餐厨垃圾等高浓度复杂有机废物的能源化利用,成为最具前景的氢能制备策略之一,符合我国绿色可再生能源的战略需求。
暗发酵制氢是产氢微生物利用氢酶的催化作用将有机物降解产生氢气,同时生成挥发性脂肪酸(VFA)、乙醇等代谢产物的过程。当末端产物为乙酸时,葡萄糖的理论产氢量为4 mol·mol−1,但实际产氢量不足2 mol·mol−1,底物的氢能转化效率不足50%[3]。有研究[4-7]表明,暗发酵制氢与[2Fe-2S]铁氧化还原蛋白和[4Fe-4S]氢酶的活性密切相关,铁氧还原蛋白可作为氢化酶的电子载体参与氢分子的产生过程,其中,铁是其重要组成部分,能够影响微生物的产氢潜力[8]。此外,铁离子的种类和含量也会影响微生物的产氢功能基因表达,进而影响复杂底物的产氢性能[9]。因此,如何克服高浓度有机废物暗发酵制氢过程的代谢障碍,提高复杂底物的利用效率和产氢潜力是制约暗发酵生物制氢技术的瓶颈问题。
有研究[10-12]发现,投加纳米零价铁(NZVI)和零价铁(ZVI)可以提高暗发酵制氢过程中的微生物活性,进而提高暗发酵制氢潜力和底物的利用效率。ZVI以其低成本成为氢发酵中最具吸引力的添加剂,能够降低发酵系统中的氧化还原电位(ORP),可以为发酵菌提供更有利的环境[13]。ZHANG等[14]研究了ZVI对葡萄糖发酵产氢量的影响,当ZVI浓度为400 mg·L−1时,最大产氢量为1.22 mol·mol−1,比对照组高出了37.1%。ZHU等[15]发现,ZVI的浓度为16 g·L−1时,产氢量从3.8 mol·mol−1提高到8.7 mol·mol−1。NZVI具有较高的催化活性和较大的表面积,从而提高了暗发酵制氢过程的效率[16]。NATH等[17]采用NZVI强化葡萄糖间歇暗发酵产氢,发现当NZVI为100 mg·L−1时,最大产氢量可达到1.9 mol·mol−1,比未加NZVI的对照组高出1倍。ZADA等[18]发现,在加入250 mg·L−1 NZVI条件下,水葫芦的产氢量从31.7 mL·g−1增加到57 mL·g−1。可见,投加NZVI和ZVI添加剂均可提高产氢性能,且具有操作简单、能耗低的优点。目前,研究主要集中在投加NZVI与ZVI对以葡萄糖、蔗糖等单一底物暗发酵制氢性能的影响,而以餐厨垃圾等复杂有机废物为底物,深入研究暗发酵制氢过程中铁离子转化规律和产氢酶活性的影响还鲜有报道。本研究通过投加不同浓度的NZVI和ZVI,研究了其对餐厨垃圾在(55±1) ℃高温条件下的暗发酵制氢潜力、末端代谢产物变化规律的影响,通过分析发酵前后铁离子组成及浓度变化、氢化酶和脱氢酶活性表达,探究了NZVI与ZVI强化餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢的作用机制,以期为餐厨垃圾等复杂有机废物的绿色能源化提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
本实验所用的餐厨垃圾取自北京市某大学食堂,分拣出餐厨垃圾中骨头、塑料袋等杂质后破碎至5 mm,经90 ℃水热预处理30 min,离心去油(去油可提高餐厨垃圾的水解效果,利于提高产气潜力[19]),置于4 ℃冰箱备用[20]。接种污泥取自北京某生活垃圾综合处理厂的干式厌氧发酵剩余污泥。实验材料的基本理化指标如表1所示。
表 1 实验材料基本理化指标Table 1. Basic physical and chemical indexes of experimental materials分析项目 TS/% VS/% VS/TS/% 含水率/% pH COD/(mg·L−1) C/% N/% 餐厨垃圾(水热后) 22.55 20.59 91.31 77.45 6.07 107 100 53.10 3.94 接种污泥 15.13 7.59 50.15 84.87 7.20 7 600 22.13 2.27 1.2 实验设计
将11.65 g经水热去油预处理的餐厨垃圾与50 g接种污泥混合放入500 mL广口瓶中,接种比为0.63∶1(VS∶VS),分别加入不同浓度(0、100、200和300 mg·L−1)的NZVI和ZVI,实验反应器情况记为:NZVI-0、NZVI-1、NZVI-3和ZVI-0、ZVI-1、ZVI-2、ZVI-3。加去离子水定容至200 mL,有机负荷为6 g·(L·d)−1(以VS计),采用1 mol·L−1 HCl与1 mol·L−1 NaOH调节初始pH为6,通氮气10 min排除反应装置内空气。在(55±1) ℃的高温条件下进行暗发酵制氢,搅拌速度为120 r·min−1,采用排水法收集产生的气体。实验编号如表2所示。
表 2 暗发酵产氢动力学分析Table 2. Dynamic analysis of dark fermentation hydrogen production实验组 Pmax/mL Rmax/(mL·h−1) λ/h R2 NZVI-0 220.72 38.41 1.95 0.999 55 NZVI-1 259.25 49.43 3.27 0.999 35 NZVI-2 224.87 47.04 2.66 0.999 85 NZVI-3 248.70 76.48 6.02 0.996 37 ZVI-0 308.51 216.07 5.72 0.998 48 ZVI-1 425.72 66.32 4.59 0.998 44 ZVI-2 350.91 70.96 5.58 0.998 90 ZVI-3 459.24 77.67 4.72 0.989 22 注:Pmax代表最大产氢量潜力,Rmax代表最大产氢速率,λ表示反应启动时间。 1.3 分析方法
铁离子浓度采用GB/T 12496.19-2015邻菲啰啉分光光度计法测定;氢化酶、脱氢酶活性采用辛红梅等[21]方法测定。VFA和乙醇浓度测定采用9790II气相色谱仪分析测定,色谱条件为:色谱柱采用CP-Wax(FFAP)25 m×0.32 mm×0.2 μm毛细管柱,FID氢火焰离子检测器,进样量1 μL,柱温箱初始温度为80 ℃,保持5 min,以10 ℃·min−1速率升温至190 ℃;进样口和检测器温度为250 ℃;高纯氮气为载气,流速为1.5 mL·min−1。气体成分测定采用上海天美公司GC7900气相色谱仪分析发酵气相产物和含量,色谱条件为:色谱柱采用填充柱,TCD热导检测器,分析柱1为2 m hayesep Q,分析柱2为5 A分子筛3 m;柱温箱120 ℃,进样口和检测器温度为150 ℃,电流为30 mV,载气为高纯氩气,进样量为1 mL。以峰面积定量,校正归一法计算气体含量。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢性能的影响
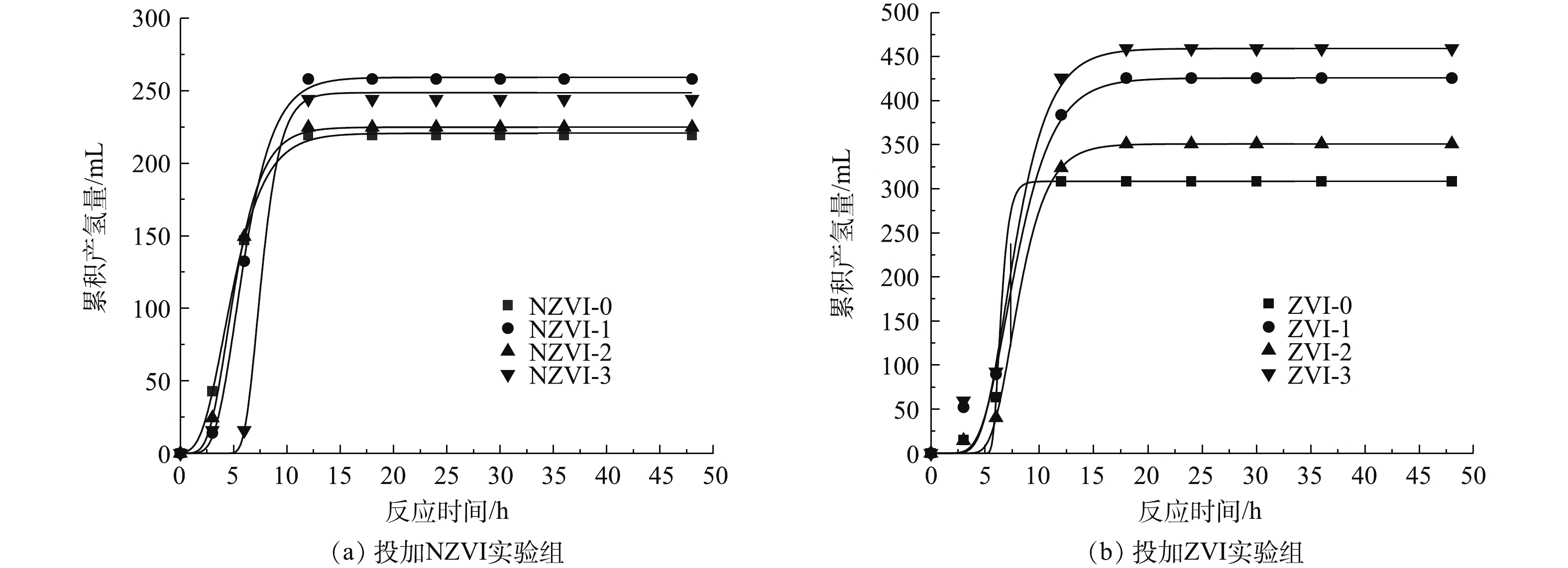
1) NZVI和ZVI对暗发酵制氢性能的影响。图1为不同浓度NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾高温暗发酵累积产气量和氢气百分含量的影响结果。结果表明,所有实验组在暗发酵前18 h累积产气量显著提高,之后累积产气量增加趋势变缓直至趋于稳定。在暗发酵产氢的过程中,氢气百分含量呈现先升高后降低的趋势。在投加NZVI添加剂时,浓度为100 mg·L−1的NZVI-1组的暗发酵制氢性能最好,累积产气量和氢气百分含量在12 h和30 h达到最大值,分别为676 mL(单位VS产气量为281.68 mL)和83.76%,是未投加NZVI实验组的1.08倍和1.1倍。其次为NZVI-0实验组,累积产气量和氢气百分含量分别为625 mL(单位VS产气量为260.43 mL)和79.16%。由此可见,与未投加NZVI相比,NZVI-1组最多可提高产气量51 mL(单位VS产气量为21.25 mL),提高氢气百分含量8.53%。
在投加ZVI添加剂时,暗发酵产氢性能较好的实验组为投加浓度300 mg·L−1的ZVI-3组和浓度100 mg·L−1的ZVI-1组,获得累积产气量分别为798 mL和732 mL(单位VS产气量分别为332.51 mL和305.01 mL),最大氢气百分含量分别为72.79%和81.95%,从节省添加剂的角度考虑,暗发酵产氢性能最好的是添加ZVI浓度为100 mg·L−1的ZVI-1组。由此可见,与未投加ZVI相比,投加100 mg·L−1 ZVI最多可提高产气量90 mL(单位VS产气量为37.50 mL),提高氢气百分含量2.74%。
2)NZVI和ZVI产氢动力学分析。在累积产气量和氢气百分含量分析基础上,利用修正过的Gompertz模型对暗发酵产氢过程的累积产氢量进行动力学拟合,产氢动力学分析结果如图2和表2所示。由图2可知,除NZVI-3实验组外,投加NZVI实验组的启动时间均比投加ZVI实验组短,但ZVI组的最大产氢潜力和最大产氢速率均比NZVI组高。在投加NZVI实验组中,NZVI-0实验组启动时间最短,为1.95 h,但最大产氢潜力和最大产氢速率均为最低,分别为220.72 mL和38.41 mL·h−1。浓度为100 mg·L−1的NZVI-1组最大产氢潜力最高为259.25 mL,浓度为300 mg·L−1的NZVI-3实验组的最大产氢速率最高,为76.48 mL·h−1。虽然NZVI-3实验组的最大产氢速率值最高,但其启动时间(6.02 h)是NZVI-1实验组(3.27 h)的1.84倍。NZVI-3实验组的最大产氢潜力(248.70 mL)也小于NZVI-1实验组(259.25 mL)。由此可见,投加NZVI可以提高最大产氢速率和最大产氢潜力,且投加浓度为100 mg·L−1时达到的效果最好。
投加ZVI的实验组的产氢潜力均高于未投加ZVI的ZVI-0实验组(308.51 mL)。其中,ZVI-3实验组的最大产氢潜力最高,为459.24 mL,ZVI-1实验组次之,为425.72 mg·L−1。此外,ZVI-1实验组的启动时间最短,为4.59 h。当ZVI投加量为100 mg·L−1时,餐厨垃圾最大产氢潜力是投加NZVI实验组的1.64倍。可见投加ZVI可有效提高产氢微生物对底物的利用效率和产氢潜力。
2.2 NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢发酵途径的影响
乙醇和VFAs是暗发酵制氢的重要末端代谢产物,根据其浓度和组成可将暗发酵制氢的代谢类型分为乙醇型发酵、丁酸型发酵、丙酸型发酵和混合酸发酵[22]。投加不同浓度的NZVI和ZVI后,餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢末端乙醇和VFAs各组分占比如图3所示。结果表明,末端代谢产物中以乙醇、乙酸和丁酸为主,其中乙醇占比最高(53.71%~77.09%),发酵类型是以乙醇型发酵为主的混合型发酵。与未投加ZVI的实验组相比,投加浓度为300 mg·L−1的ZVI-3实验组中的乙醇浓度提高了7.04%。
在投加NZVI的实验组中,乙酸在NZVI-1、NZVI-2、NZVI-3组中末端代谢产物中的占比分别为18.04%、16.89%、14.22%,均高于NZVI-0对照组(9.42%)。而对于投加ZVI的实验组,ZVI-1、ZVI-2、ZVI-3实验组中乙酸在末端代谢产物中的占比分别为6.44%、7.70%、6.62%,均低于ZVI-0对照组(8.18%)。由此可见,与投加ZVI相比,投加NZVI更有利于乙酸的转化,但产氢潜力和速率有所较低。可能由于发酵过程中产生的乙酸使体系pH降低,产生过剩的NADH+H+,未能被氧化为NAD+,影响微生物酶活或酶合成,进而抑制NADH/NAD+平衡产氢[23]。
投加NZVI的实验组相比未投加NZVI的实验组(67.7%),其中乙醇的占比均有所降低。对应投加NZVI的实验组,随着NZVI投加量的增加,乙醇占比由53.71%逐渐升高至63.50%,同时累积产气量和氢气百分含量有所下降,这说明NZVI在一定程度上改变了产氢细菌的代谢产氢途径,产生了更多的乙醇副产物和更少的乙酸副产物,投加低浓度的NZVI有利于产氢,浓度过高可能对微生物活性产生了抑制作用。投加ZVI的实验组相比未投加ZVI的实验组(70.05%),其中乙醇的占比略有提高。随着ZVI投加量的增加,乙醇占比由72.65%升高至77.09%,同时在ZVI-3实验组中的累积产气量大于ZVI-1实验组。发酵过程中所产生的乙醇可以氧化过多的NADH+H+,有利于产氢潜力的提高[23]。对于投加NZVI和ZVI的实验组,暗发酵末端代谢产物中乙醇的占比均有所升高,但累积产气量的变化趋势却相反,这可能是由于2种添加剂对与产氢相关的关键酶影响有所不同。
2.3 NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢ORP的影响
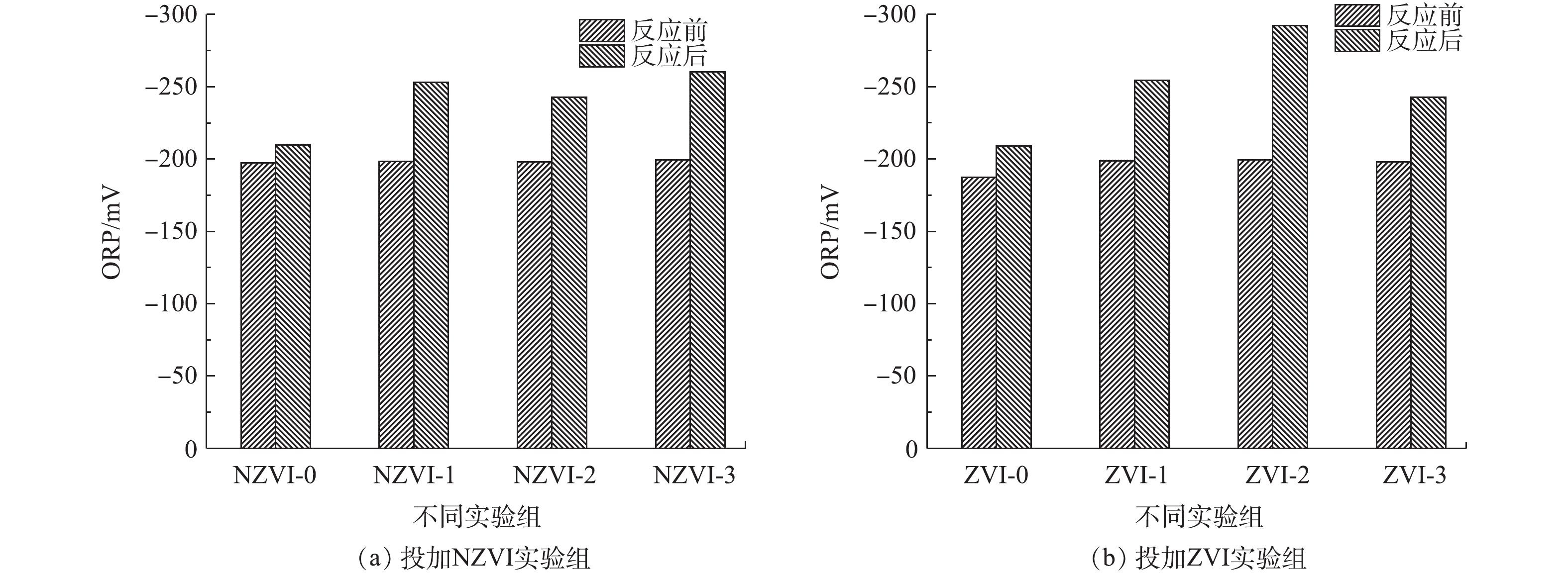
在发酵过程中,ORP是控制微生物代谢和增殖的重要参数之一[24-25]。其可以通过还原/氧化NAD(NADH/NAD+)来改变细胞内外的ORP,从而调控微生物代谢。一般认为,厌氧微生物所需ORP的最适范围为-180~-260 mV[26]。
暗发酵产氢前后体系中的ORP变化结果如图4所示。结果表明,投加与未投加NZVI和ZVI的实验组在反应结束后ORP均有所下降,其中投加NZVI与ZVI的实验组中ORP下降更为显著。投加NZVI的实验组,NZVI-3实验组ORP下降最大,由反应前的−199.6 mV下降至−260.1 mV,是未投加NZVI实验组的1.24倍。其次是NZVI-1实验组,由反应前的−198.5 mV下降至−253 mV,是未投加NZVI实验组的1.20倍。对于投加ZVI的实验组,ZVI-2实验组的ORP下降最大,由反应前的−199.4 mV下降至−292.2 mV,是未投加ZVI实验组的1.39倍。其次是ZVI-1实验组,由反应前的−198.8 mV下降至−254.3 mV,是未投加ZVI实验组的1.21倍。
结合产氢潜力结果分析可知,产氢效果好的NZVI-1实验组(−253 mV)与ZVI-1实验组(−254.3 mV)ORP值相近,均在厌氧微生物最适ORP的范围内,从而有利于产氢性能的提高。分析原因可能是:反应器内的ORP迅速降低,说明分子氧等氧化剂被消耗掉,这可能由于投加的NZVI和ZVI被用作电子供体,铁可作为底物诱导因子,作用于细菌代谢途径中,既能参与细菌的生物氧化过程,又能使反应器内的ORP迅速降低,使ORP维持在产氢的最适范围内,从而提供更好的还原条件[27-29];另一方面,氢化酶活性和NAD+/NADH平衡产氢均需要较低的ORP[30]。
2.4 NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢过程中铁离子浓度的影响
图5表示投加NZVI和ZVI进行暗发酵制氢前后,各实验组发酵液中Fe2+和Fe3+浓度的变化情况。由图5可知,在餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢前,体系中Fe2+和Fe3+的浓度较低,分别为23.74 mg·L−1和28.52 mg·L−1。反应结束后,未投加NZVI与ZVI的实验组中Fe2+和Fe3+的浓度有所下降,投加NZVI与ZVI的实验组中Fe2+浓度显著上升,而Fe3+浓度略有提升,这证明了NZVI和ZVI是作为电子供体而存在的。铁在产氢细菌的代谢机制中起着至关重要的作用,是形成氢化酶和铁氧还蛋白的重要成分[31]。Fe2+可以促进了生物量的增长和功能基因的表达,从而促进氢气的产生。对于投加NZVI的实验组,NZVI-3实验组中的Fe2+浓度最高,为43.78 mg·L−1,是未投加NZVI实验组的2倍,NZVI-2的Fe2+浓度次之,为42.47 mg·L−1,是未投加NZVI实验组的1.96倍。在投加ZVI的实验组,ZVI-1实验组的Fe2+浓度最高,为38.21 mg·L−1,是未投加ZVI实验组的1.96倍,ZVI-3的Fe2+浓度次高,为36.51 mg·L−1,是未投加ZVI实验组的1.87倍。
厌氧微生物可以将Fe3+还原为生物利用性更高的Fe2+。在投加NZVI的实验组中,NZVI-2实验组的Fe3+浓度最高,为15.99 mg·L−1,是未投加NZVI实验组的1.72倍,NZVI-1的Fe3+浓度次之,为14.21 mg·L−1, 是未投加NZVI实验组的1.53倍。在投加ZVI的实验组中,ZVI-3实验组的Fe3+浓度最高,为12.12 mg·L−1,是未投加ZVI实验组的1.30倍,ZVI-1的Fe3+浓度次之,为10.34 mg·L−1,是未投加ZVI实验组的1.28倍。
综上所述,在暗发酵制氢体系中投加NZVI和ZVI,可使Fe2+浓度升高,Fe3+浓度略有升高。一方面,这是由于投加的NZVI和ZVI有部分转化为了Fe2+;另一方面是由于微生物对Fe3+的利用将Fe3+还原成Fe2+。但投加NZVI与ZVI浓度过高,铁离子会与蛋白质结合生成难以被生物降解的螯合物,故使产氢潜力下降[32]。
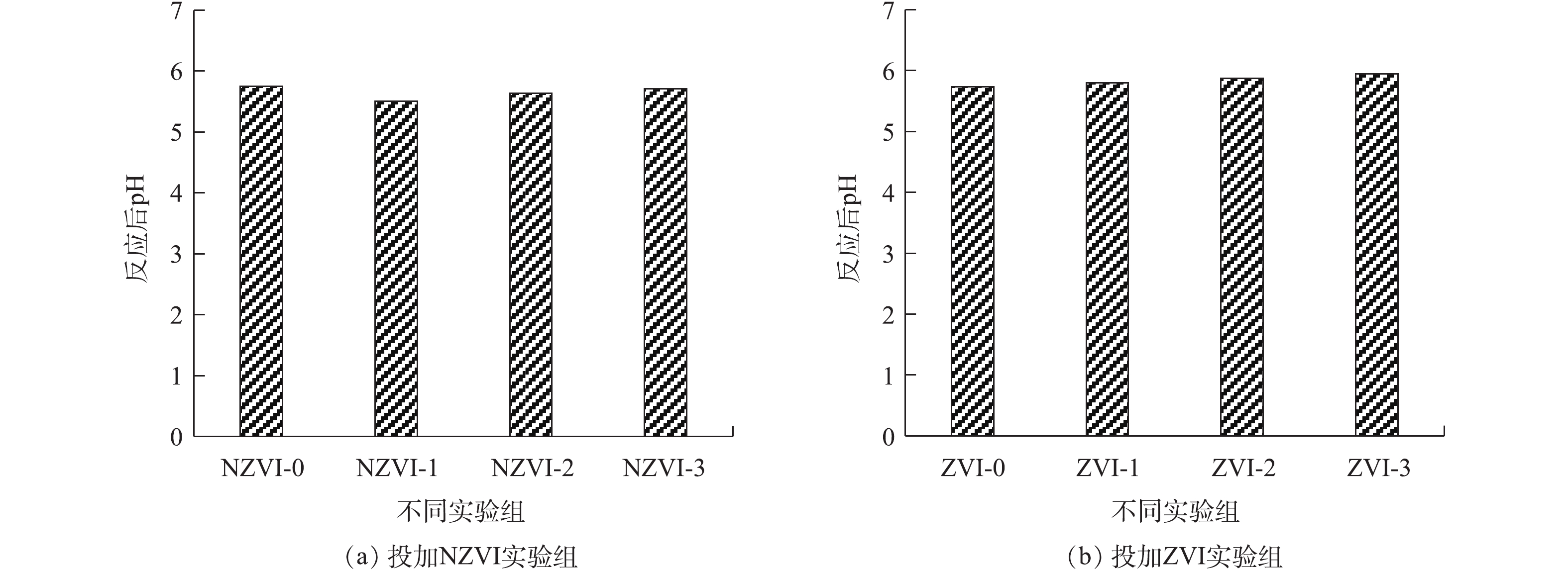
2.5 NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢过程pH的影响
反应结束时pH的变化情况如图6所示。由图6可知,NZVI和ZVI对反应器的pH的影响作用并不明显。在暗发酵制氢反应结束时,投加NZVI和ZVI的实验组的pH均在5.5~6.0。在投加NZVI实验组中,pH最高的实验组为NZVI-3实验组(5.71),最低的为NZVI-1实验组(5.51)。投加ZVI的实验组中,pH最高的为ZVI-3实验组(5.94),最低的为ZVI-1实验组(5.8)。随着投加NZVI和ZVI浓度的增加,pH也随升高。这可能是由于投加的NZVI和ZVI作为诱导因子作用于细菌代谢途径中,参与了产氢细菌的生物氧化过程,发酵类型为以乙醇型发酵为主的混合型发酵[33]。末端代谢产物中乙醇的占比随着NZVI和ZVI投加量的增加而增大,从而导致了pH的升高。投加NZVI的实验组在反应结束时pH低于未投加NZVI的实验组(5.75),投加ZVI的实验组在反应结束时pH高于未投加ZVI实验组,这说明与投加ZVI相比,投加NZVI更有利于乙酸的转化,产生的乙酸可使体系pH降低。
2.6 NZVI和ZVI对餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢过程中酶活性的影响
有机物的暗发酵制氢过程是在一系列酶和辅酶以及中间传递体的作用下完成的一种生物氧化过程。其中,氢化酶是一类能够高效可逆地催化产生氢气的酶,含有双核铁原子的铁氢化酶具有很高的催化活性。脱氢酶中的电子载体铁氧还蛋白是暗发酵生物氧化过程产生氢分子的重要功能蛋白。可见,铁是决定餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢过程氢化酶和脱氢酶活性的重要物质,对产氢微生物的生长代谢有着重要的影响。
投加不同浓度的NZVI和ZVI对氢化酶和脱氢酶活性的影响结果如图7所示。结果表明,对于未投加NZVI与ZVI的实验组,氢化酶活性分别为2.49 mL·(g·min)−1和2.76 mL·(g·min)−1(以VSS计)。在投加NZVI后,氢化酶活性有所提高,其中,NZVI-3组的氢化酶活性最高,为2.56 mL·(g·min)−1,是未投加NZVI实验组的1.02倍,NZVI-1实验组氢化酶活性次高,为2.55 mL·(g·min)−1。在投加ZVI后,氢化酶活性有显著提高。ZVI-3实验组氢化酶活性(3.96 mL·(g·min)−1)最高,是ZVI-0实验组的1.43倍。ZVI-1实验组次之,为3.54 mL·(g·min)−1。有研究[5]表明,NZVI可以降低培养基中溶解氧的水平,从而提高氢化酶的活性。李永峰等[33]提出金属元素在微生物生命活动中具有重要作用,其对酶的作用主要有2方面:一是作为酶的辅助因子,在酶促反应中运输转移电子、原子或某些功能基团参与氧化还原或运载酰基团作用;二是作为激活剂来提高酶的活性。铁作为铁氧还蛋白及氢化酶重要的组成成分,投加NZVI和ZVI可以提高铁氧还蛋白和氢化酶的活性,促进电子的转移,进而提高产氢效能。
对于NZVI-0和ZVI-0实验组,脱氢酶活性分别为128.32 μg·(g·min)−1和140.53 μg·(g·min)−1(以VSS计)。然而,投加NZVI的实验组脱氢酶活性出现了显著下降,由NZVI-0实验组的128.32 μg·(g·min)−1下降到NZVI-1实验组的34.37 μg·(g·min)−1,下降了73.2%。且随着投加NZVI浓度增加,脱氢酶活性继续下降,NZVI-3实验组中脱氢酶活性下降到最低,为8.40 μg·(g·min)−1。在投加ZVI的实验组中,脱氢酶活性有显著的提高。脱氢酶活性在ZVI浓度小于300 mg·L−1时,随着投加ZVI浓度的增加,其由140.53 μg·(g·min)−1提高到150.84 μg·(g·min)−1,提高了7.3%,但当ZVI浓度为300 mg·L−1时,脱氢酶活性下降到80.96 μg·(g·min)−1。这说明过高的ZVI浓度抑制了脱氢酶的活性。结合相关文献,其原因可能是因为铁的投加量过高超出了体系中产氢微生物的所需,而过剩的铁形成了铁盐或亚铁盐,从而使系统的渗透压升高,导致脱氢酶活性的降低[21]。
有研究[34]表明,当金属元素浓度维持在较低水平时,对微生物可以起到激活作用,但当浓度过高时,便会对微生物的酶活性产生抑制作用。由此可见,投加ZVI的同时提高了氢化酶和脱氢酶的活性。结合铁离子浓度变化趋势可知,投加的NZVI和ZVI会向系统环境中释放铁离子,为微生物提供生长代谢过程中所需的铁元素并提高氢化酶活性。但投加NZVI时虽然提高了氢化酶活性,脱氢酶活性却受到了抑制,这可能缘于纳米材料中活性氧的生成和氧化应激反应引起的生物毒性损害了微生物细胞结构,导致细胞死亡,进而影响微生物产氢能力[35]。
由此可见,投加100 mg·L−1 NZVI和ZVI均可有效提高氢化酶活性,投加ZVI还可提高脱氢酶活性,有利于产氢微生物的暗发酵制氢。
3. 结论
1)投加NZVI和ZVI均可显著提高餐厨垃圾暗发酵制氢性能,投加100 mg·L−1 ZVI效果最佳,最大产氢潜力和最大产氢速率分别为425.72 mL和66.32 mL·h−1,是投加NZVI实验组的1.64倍和1.34倍。投加NZVI与ZVI后,末端代谢产物以乙醇、乙酸和丁酸为主,其中乙醇占比最高(53.71%~77.09%),发酵类型是以乙醇型发酵为主的混合型发酵。
2)投加NZVI和ZVI可使反应体系中ORP显著下降,有利于暗发酵制氢的进行。反应结束后,未投加NZVI与ZVI的实验组中Fe2+和Fe3+的浓度较反应前均有所下降,投加NZVI与ZVI的实验组Fe2+浓度有显著上升,Fe3+浓度略有提升。在投加的NZVI和ZVI浓度为300 mg·L−1时,Fe2+浓度分别是未投加NZVI和ZVI实验组的2倍和1.87倍。
3)投加NZVI和ZVI均可有效提高氢化酶活性,投加100 mg·L−1 ZVI-1实验组氢化酶活性最佳,为3.54 mL·(g·min)−1,是NZVI-1实验组的1.38倍。投加ZVI可同时提高氢化酶和脱氢酶活性,有利于产氢微生物的暗发酵制氢。
-
-
[1] 李秀芬, 朱金兆, 顾晓君, 等. 农业面源污染现状与防治进展[J]. 中国人口资源与环境, 2010, 20(4): 81-84. [2] ZHANG W Q, JIN X, LIU D, et al. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen and phosphorus and eutrophication assessment for a typical arid river: Fuyang River in northern China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 55: 41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2016.07.004 [3] 刘同岩, 杨驰浩, 周宇澄, 等. 天目湖流域氮磷面源污染现状分析[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2020, 61(12): 2641-2643. [4] MANDER U, HAYAKAWA Y, KUUSEMETS V. Purification processes, ecological functions, planning and design of riparian buffer zones in agricultural watersheds[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2005, 24: 421-432. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.01.015 [5] DOSSKEY M G, VIDON P, GURWICK N P, et al. The role of riparian vegetation in protecting and improving chemical water quality in streams[J]. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 2010, 46: 261-277. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.2010.00419.x [6] TANG Q, BAO Y, HE X, et al. Sedimentation and associated trace metal enrichment in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 479-480: 258-266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.122 [7] WANG Q, LI C, CHEN C, et al. Effectiveness of narrow grass hedges in reducing atrazine runoff under different slope gradient conditions[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2018, 25(1/2): 7672-7680. [8] 刘威尔, 张鑫, 张娟, 等. 农田缓冲带规划建设与天敌保护效果研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(2): 172-179. [9] HICKEY M B C, DORAN B A. Review of the efficiency of buffer strips for the maintenance and enhancement of riparian ecosystems[J]. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 2004, 39(3): 311-317. doi: 10.2166/wqrj.2004.042 [10] KUO Y M, MUNOZ-CARPENA R. Simplified modeling of phosphorus removal by vegetative filter strips to control runoff pollution from phosphate mining areas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 378(3/4): 343-354. [11] GUMIERE S J, LE BISSONNAIS Y, RACLOT D, et al. Vegetated filter effects on sedimentological connectivity of agricultural catchments in erosion modeling: A review[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2011, 36: 3-19. doi: 10.1002/esp.2042 [12] LIN Y F, LIN C Y, CHOU W C, et al. Modeling of riparian vegetated buffer strip width and placement: A case study in Shei Pa National Park, Taiwan[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2004, 23: 327-339. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2004.11.006 [13] GENEA S M, HOEKSTRAB P F, HANNAMC C, et al. The role of vegetated buffers in agriculture and their regulation across Canada and the United States[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 243: 12-21. [14] 袁鹏, 刘瑞霞, 俞洁, 等. “浙江省河流缓冲带划定与生态修复技术指南(试行)”解读[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2021, 11(1): 1-5. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20210003 [15] DILLAHA T A, RENEAN R B, MOATAHIMI S, et al. Vegetative filter strips for agricultural non-point source pollution control[J]. Transactions of American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 1989, 32: 513-519. doi: 10.13031/2013.31033 [16] PHILLIPS J D. An evaluation of the factors determining the effectiveness of water quality buffer zones[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1989, 107: 133-145. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(89)90054-1 [17] MUSCUTT A D, HARRIS C L, BAILEY S W, et al. Buffer zones to improve water quality: A review of their potential use in UK agriculture[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 1993, 45: 59-77. doi: 10.1016/0167-8809(93)90059-X [18] USDA. Natural Resources Conservation Service, Buffer Strips: Common Sense Conservation[R]. Washington, D C: USDA, 1998. [19] 邓红兵. 河岸植被缓冲带与河岸带管理[J]. 应用生态学报, 2001, 12(16): 951-954. [20] 岳隽, 王仰麟. 国内外河岸带研究的进展与展望[J]. 地理科学进展, 2005, 24(5): 33-40. [21] 郭怀成, 黄凯, 刘永, 等. 河岸带生态系统管理研究概念框架及其关键问题[J]. 地理研究, 2007, 26(4): 789-798. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2007.04.016 [22] 郭二辉, 孙然好, 陈利顶. 河岸植被缓冲带主要生态服务功能研究的现状与展望[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(8): 1830-1837. [23] NANUS L, WILLIAMS M W, CAMPBELL D H, et al. Evaluating regional patterns in nitrate sources to watersheds in national parks of the Rocky Mountains using nitrate isotopes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42: 6487-6493. [24] DRISCOLL C T, LAWRENCE G B, BULGER A J, et al. Acidic deposition in the northeastern United States: Sources and inputs, ecosystem effects and management strategies[J]. BioScience, 2001, 51(3): 180-198. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0180:ADITNU]2.0.CO;2 [25] 余晓燕, 齐实, 李林英, 等. 美国的生物缓冲带[J]. 水土保持应用技术, 2007(6): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5366.2007.06.009 [26] SAHU M, GU R. Modeling the effects of riparian buffer zone and contour strips on stream water quality[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2009, 35: 1167-1177. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.03.015 [27] USDA. Natural Resources Conservation Service[R]. Nebraska: USDA. Inside Agroforestr. , 2001. [28] CLEUGH H. Effects of windbreaks on airflow, microclimates, and crop yields[J]. Agroforestry Systems, 1998, 41: 55-84. doi: 10.1023/A:1006019805109 [29] USDA. Natural Resouces Conservation Service, Conservation Practice Standard-Vegetative Barriers - Code 601[R]. Washington, D C: USDA, 2010. [30] Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. Field manual on buffer design in the Canadian Prairies[R]. Ottawa-Ontario: Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, 2010. [31] USDA. Natural Resouces Conservation Service Conservation Practice Standard-Riparian Herbaceous Cover - Code 390[R]. Washington, D C: USDA, 2015. [32] USDA. Natural Resources Conservation Service New York-Riparian Herbaceous Cover[R]. New York: United States Department of Agriculture, 2018. [33] Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. Eco-buffers: An alternative agroforestry design[R]. Ottawa-Ontario: Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, 2012. [34] DUCHEMIN M, HOGUE R. Reduction in agricultural non-point source pollution in the first year following establishment of an integrated grass/tree filter strip system in southern Quebec (Canada)[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2009, 131: 85-97. [35] KOVACIC D, DAVID M, GENTRY L, et al. Effectiveness of constructed wetlands in reducing nitrogen and phosphorus export from agricultural tile drainage[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2000, 29: 1262-1274. [36] RICKERL D H, JANSSEN L L, WOODLAND R. Buffer wet lands in agricultural landscapes in the prairie pothole region: Environmental, agronomic, and economic evaluations[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2000, 55(2): 220-226. [37] HAMMER D, KNIGHT R L. Designing constructed wetland for nitrogen removal[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1994, 29(4): 15-27. doi: 10.2166/wst.1994.0148 [38] WOHEMADE C J. Ability of restored wetlands to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in agricultural drdinage water[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2000, 55(3): 303-309. [39] VAN DER VALK A G, JOLLY R W, Recommendations for research to develop guidelines for the use of wetland to control rural non-point source pollution[J]. Ecological Engineering, 1992, 1(1/2): 115-134. [40] CHESCHEIR G M, SKAGGS R W, GILLIAM J W. Evaluation of wetland buffer areas for treatment of pumped agricultural drainage[J]. Transactions of the American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 1992, 35(1): 175-182. doi: 10.13031/2013.28585 [41] 戈鑫, 杨云安, 管运涛, 等. 植草沟对苏南地区面源污染控制的案例研究[J]. 中国给水排水, 2018, 34(19): 134-138. [42] 郭凤. 植草沟在道路地表径流传输入渗过程中的模拟研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2014. [43] 段进凯, 李田, 张佳炜. 强化浅基质层干植草沟对道路径流的脱氮效果[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 225-231. [44] 张佳炜, 李田, 张庭秀. 浅基质层干植草沟运行效果的现场实验[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9): 4105-4112. [45] 赵金辉, 陆毅, 赵晓莉, 等. 植草沟-湿地滞留塘控制农业径流污染效能[J], 环境科学与技术. 2014, 37(10): 117-120. [46] 李斌, 刘东, 刘瑞霞, 等. 南方城市黑臭水体综合治理: 以南宁市竹排江e段(那考河)为例[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(5): 702-710. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200107 [47] 王凡, 潘钧, 刘丹妮, 等. 贵阳市七彩湖黑臭水体治理案例分析[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(5): 726-732. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.20200108 [48] PROSSER R S, HOEKSTRA P F, GENE S, et al. A review of the effectiveness of vegetated buffers to mitigate pesticide and nutrient transport into surface waters from agricultural areas[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 261(110210): 1-13. [49] YUAN Y, DABNEY S M, BINGNER R L. Cost effectiveness of agricultural BMPs for sediment reduction in the Mississippi Delta[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2002, 57(5): 259-267. [50] WHITE M J, ARNOLD J G. Development of a simplistic vegetative filter strip model for sediment and nutrient retention at the field scale[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2009, 23(11): 1602-1616. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7291 [51] GILLIAM J W. Riparian wetlands and water quality[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1994, 23(5): 896-900. [52] 肖波, 萨仁娜, 陶梅, 等. 草本植被过滤带对径流中泥沙和除草剂的去除效果[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013, 29(12): 136-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.12.018 [53] LEE K H, ISENHART T M, SCHULTZ R C. Sediment and nutrient removal in an established multi-species riparian buffer[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2003, 58(1): 1-8. [54] MOSET V, HILLE S, RUBK G H. Indicators of biomass and methane yields in vegetated buffer strips[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 210: 907-915. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.337 [55] LAMBRECHTS T, FRANCOIS S, LUTTS S, et al. Impact of plant growth and morphology and of sediment concentration on sediment retention efficiency of vegetative filter strips: Flume experiments and VFSMOD modeling[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 511: 800-810. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.02.030 [56] HEFTING M M, CLEMENT J C, BIENKOWSKI P, et al. The role of vegetation and litter in the nitrogen dynamics of riparian buffer zones in Europe[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2005, 24(5): 465-482. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.01.003 [57] PETERJOHN W T, CORRELL D L. Nutrient dynamics in an agricultural watershed: Observations on the role of a riparian forest[J]. Ecology, 1984, 65(5): 1466-1475. doi: 10.2307/1939127 [58] 高军, 尤迎华, 谈晓珊, 等. 植被过滤带阻控径流污染的机制及研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(9): 91-97. [59] SMITH C M. Riparian pasture retirement effects on sediment, phosphorus, and nitrogen in channellised surface run-off from pastures[J]. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 1989, 23(1): 139-146. doi: 10.1080/00288330.1989.9516349 [60] DORIOZ J M, WANG D, POULENARD J, et al. The effects of grass buffer strips on phosphorus dynamics: A critical review and synthesis as a basis for application in agricultural landscapes in France[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2006, 117(1): 4-21. [61] HENDERSON K L, BELDEN J B, COATS J R. Fate of atrazine in a grass phytoremediation system[J]. Environmental Toxicology & Chemistry, 2007, 26(9): 1836-1842. [62] ALBRIGHT I V, MURPHY I J, ANDERSON J A, et al. Fate of atrazine in switchgrass-soil column system[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 90(6): 1847-1853. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.09.097 [63] 陈仲颐, 周景星, 王洪瑾. 土地力学[J]. 北京:清华大学出版社, 1994: 9. [64] BLANCHE S B, SHAW D R, MASSEY J H, et al. Fluometuron adsorption to vegetative filter strip components[J]. Weed Science, 2003, 51(1): 125-129. doi: 10.1614/0043-1745(2003)051[0125:FATVFS]2.0.CO;2 [65] AJR R, SHAW D R, KINGERY W L. Comparison of fluometuron sorption to soil from a filter strip and cropped field[J]. Weed Science, 2002, 50(6): 820-823. doi: 10.1614/0043-1745(2002)050[0820:COFSTS]2.0.CO;2 [66] NAEHER S, HUGUET A, ROOSE-AMSALEG C L, et al. Molecular and geochemical constraints on anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in a riparian zone of the Seine Estuary (France)[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2015, 123: 237-250. doi: 10.1007/s10533-014-0066-z [67] WANG S, WANG W, ZHAO S, et al. Anammox and denitrification separately dominate microbial N-loss in water saturated and unsaturated soils horizons of riparian zones[J]. Water Research, 2019, 162: 139-150. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.06.052 [68] QIN Y B, CHEN Z H, DING B J, et al. Impact of sand mining on the carbon sequestration and nitrogen removal ability of soil in the riparian area of Lijiang River, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 261: 114220. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114220 [69] 汪小勇, 张超兰, 姜文. 被农药污染的土壤植物修复研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2005, 21(7): 382-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6850.2005.07.112 [70] DAEBELER A, BODELIER P L E, HEFTING M M, et al. Soil warming and fertilization altered rates of nitrogen transformation processes and selected for adapted ammonia-oxidizing archaea in sub-arctic grassland soil[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 2017, 107: 114-124. [71] HU R, WANG X P, XU J S, et al. The mechanism of soil nitrogen transformation under different biocrusts to warming and reduced precipitation: From microbial functional genes to enzyme activity[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 722: 137849. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137849 [72] LEE K, ISENHART T, SCHULTZ R, et al. Multispecies riparian buffers trap sediment and nutrients during rainfall simulation[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2000, 29: 1200-1205. [73] DOSSKEY M G, HELMERS M J, EISENHAUER D E. A design aid for determining width of filter strips[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2008, 63(4): 232-241. doi: 10.2489/jswc.63.4.232 [74] LOBO G P, BONILLA C A. A modeling approach to determining the relationship between vegetative filter strip design and sediment composition[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2017, 237: 45-54. [75] ASMUSSEN L, WHITE A, HAUSER E, et al. Reduction of 2, 4-D load in surface runoff down a grassed waterway[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1977, 6: 159-162. [76] LIND L, HASSELQUIST M E, LAUDON H. Towards ecologically functional riparian zones: A meta-analysis to develop guidelines for protecting ecosystem functions and biodiversity in agricultural landscapes[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2019, 249: 109391. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109391 [77] HAWES E, SMITH M. Riparian Buffer Zones: Functions and Recommended Widths[R]. America: Eightmile River Wild and Scenic Study Committee, 2005. [78] 万成炎, 马沛明, 常剑波, 等. 三峡水库生态防护带建设的初步探讨[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2009, 26(1): 9-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2009.01.003 [79] 王秋光, 李永峰, 李春华, 等. 草林复合植被缓冲带结构功能及净化机理研究综述[J]. 中国水土保持, 2013(6): 39-42. [80] SYVERSEN N. Effect and design of buffer zones in the Nordic climate: The influence of width, amount of surface runoff, seasonal variation and vegetation type on retention efficiency for nutrient and particle runoff[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2005, 24(5): 483-490. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2005.01.016 [81] 孙金伟, 许文盛. 河岸植被缓冲带生态功能及其过滤机理的研究进展[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2017, 34(3): 40-44. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20160706 [82] 黄沈发, 唐浩, 鄢忠纯, 等. 3种草皮缓冲带对农田径流污染物的净化效果及其最佳宽度研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2009, 31(6): 53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2009.06.016 [83] DOSSKEY M G, HELMERS M J, EISENHAUER D E. Assessment of concentrated flow through riparian buffers[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2002, 57(6): 336-343. [84] YOUNG E O, BRIGGS R D. Shallow ground water nitrate-N and ammonium-N in cropland and riparian buffers[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2005, 109(3/4): 297-309. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2005.02.026 [85] MUNOZ-CARPENA R, PARSONS J E, GILLIAM J W. Modeling hydrology and sediment transport in vegetative filter strips[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1999, 214: 111-129. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(98)00272-8 [86] LOWRANCE R, ALTIER L S, WILLIAMS R G, et al. REMM: The riparian ecosystem management model[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2000, 55(1): 27-34. [87] WILLIAMS R D, NIEKS A D. Using CREAMS to simulate filter strip effectiveness in erosion control[J]. Joumal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1988, 43: 108-112. [88] PHILLIPS J D. Evaluation of north Carolina’s estuarine shoreline area of environment concern from a water quality perspective[J]. Coastal Management, 1989, 17(2): 103-117. doi: 10.1080/08920758909362079 [89] MANDER U, KUUSEMETS V, LOHMUS K, et al. Efficiency and dimensioning of riparian buffer zones in agricultural catchments[J]. Ecological Engineering, 1997, 8(4): 299-324. doi: 10.1016/S0925-8574(97)00025-6 [90] NIESWAND G H, HORDON R M, SHELTON T B, et al. Buffer strips to protect water supply reservoirs: A model and recommendations[J]. Water Resources Bulletin, 1990, 26(6): 959-966. doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.1990.tb01430.x [91] CHANG C L, HSU T H, WANG Y J, et al. Planning for implementation of riparian buffers in the Feitsui reservoir watershed[J]. Water Resources Management, 2010, 24: 2339-2352. doi: 10.1007/s11269-009-9554-7 [92] XIANG W. GIS-based riparian buffer analysis: injecting geographic information into landscape planning[J]. Landscape and Urban Planning, 1996, 34(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/0169-2046(95)00206-5 [93] 廖先容, 扈幸伟, 邬龙. 城市河流滨岸缓冲带生态修复模式研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2017, 48(10): 109-112. [94] 陶梅, 萨仁娜. 植被过滤带防治农业面源污染研究进展[J]. 山西农业科学, 2012, 40(1): 91-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2481.2012.01.27 -






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: