-
烟气经湿法脱硫后会产生大量含可溶性物质的白色水雾[1],导致环境污染[2]。除雾方法主要是加装除雾器[3],如折流板除雾器[4]、丝网除雾器[5]、静电除雾器等[6]。为提高除雾器的气液分离作用,NARIMANI 等[7]运用CFD的方法优化了带倒钩的折流板除雾器结构;EL-DESSOUKY 等[8]研究了不同网层厚度下丝网除雾器的最佳过滤风速;袁惠新等[9]研究了旋风除雾器在引入静电场后对细水雾的脱除效果。然而,目前水雾排放浓度依然难以达到相关标准规定的排放限值[10]。因此,白色烟羽排放的有效控制已成为湿烟气深度净化的一个研究热点[11-12]。
烟气“脱白”技术鲜有突破,其原因是除雾工程应用限制了2个高效技术路径:要求成本低、能耗少、占地小,不宜采用湿电;要求压损小、无堵塞,不能采用过滤。因此,近年来利用空气动力分离的技术方法倍受关注[13-15]。然而,采用空气动力分离除雾,需要在细而长的螺旋管中带动整个气流高速旋转,导致能耗过高,而且细水雾易被高速气流带出除雾器。
为实现高湿烟气的高效除雾,笔者提出了自由旋线除雾方法[16-17],并开展了单层自由旋线除雾实验研究[18]。结果表明,自由旋线除雾器的压损小、效率高,并且发现在控制能耗情况下增加旋线根数比增加旋线转速的提效作用更显著。然而,关于自由旋线除雾器的除雾性能还缺乏基础理论研究。本研究将基于经典的单根柱状纤维捕集和旋流离心分离机理,建立自由旋线除雾器的除雾效率理论,并通过实验加以验证,进而揭示旋线根数和转速对自由旋线除雾作用的影响规律,以期为自由旋线除雾技术的发展及应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
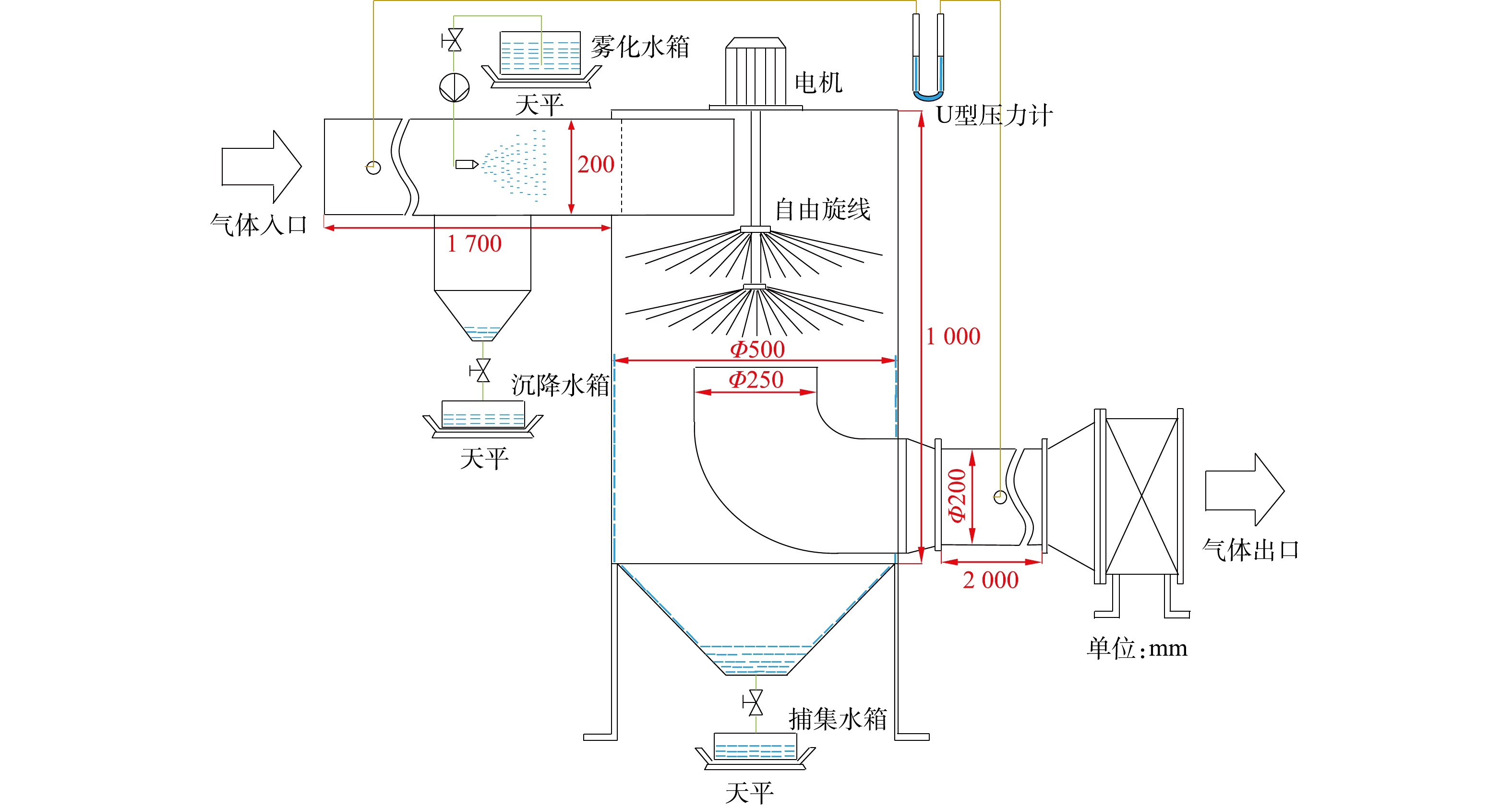
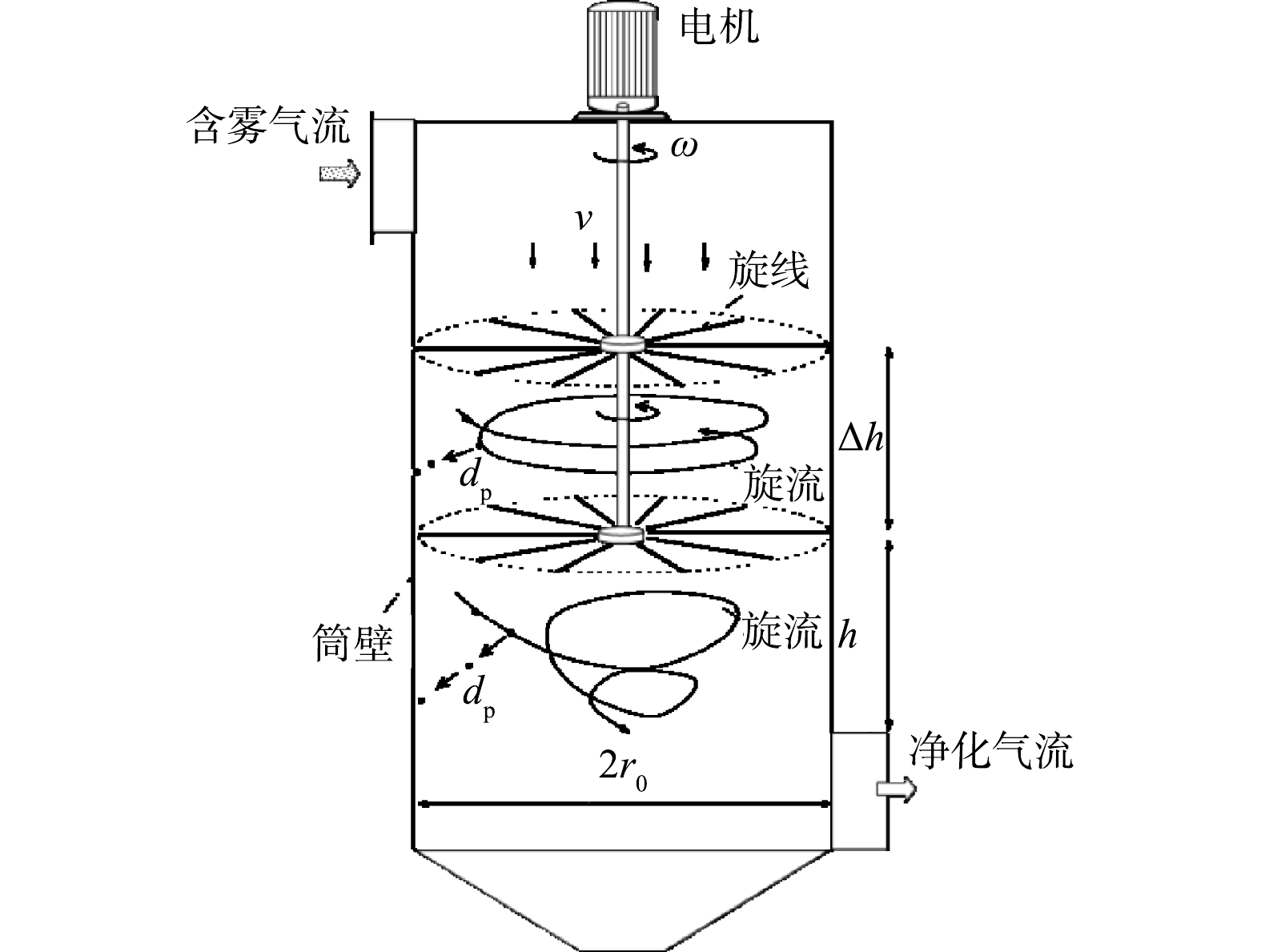
在旋线除雾器中布置有数以百计的纤维线(见图1)。纤维线的一端固定在电机的连接轴上,纤维线的另一端自由。电机启动前,纤维线在自重作用下自然下垂。电机启动后,高速旋转的纤维线(简称旋线)在离心力作用下呈伞形张开,并覆盖整个除雾器筒体过流断面。
当含雾气流进入除雾器,在通过旋线层时,柱状纤维旋线与液滴间产生拦截、惯性碰撞和扩散作用[19]。由于纤维线具有吸湿性,液滴会附着旋线表面或浸入旋线中,然后在离心力作用下甩向筒壁。筒壁上的液体在重力作用下最后流入除雾器底部的液斗中。另外,由于高速旋转的纤维线搅拌作用,使旋线层下方的气体形成旋流,进而对未被捕集的液雾产生离心分离作用,使旋线除雾器的净化效果得到进一步提升。所以,旋线除雾器的工作原理是旋线层过滤和旋流离心分离的协同作用。
-
当圆柱状纤维与垂直于来流方向颗粒物之间的相对速度相同时,基于孤立圆柱状捕集体对颗粒物的捕集机理来探索纤维层的捕集效率更容易[20]。但由于旋线与雾滴的相对速度是变化的,需先根据不同的捕集机理确定单根旋线的捕集量,然后由效率定义分别建立旋线层的拦截、惯性碰撞和扩散效率理论表达式。
-
分析纤维对颗粒物的拦截捕集作用首先要考虑绕捕集体流动的介质的流态。对于绕流问题,分为黏性流和势流。判断流态的依据是雷诺数(Re),具体见式(1)。
式中:ρ为空气密度,kg·m−3;v为空气流速,m·s−1;df为旋线直径,m;μ为气体动力黏性系数,常温常压下,μ=1.85×10−5 Pa·s。
当Re≤1时,柱状捕集体周围的流动可视为黏性流;而当Re>1时,可近似为势流[21]。在自由旋线除雾器中,旋线的切向速度可超过10 m·s−1,且旋线较粗(直径通常2~4 mm)。由此得出,气流绕旋线流动的雷诺数Re超过100,属势流。在势流情况下,单位长度孤立圆柱状捕集体对球形雾滴的拦截效率计算公式[22]见式(2)。
式中:ηr为单位长度孤立圆柱状捕集体对球形雾滴的拦截效率;G为拦截参数,计算式为式(3)。
式中:dp表示雾滴直径,m;df为旋线直径,m。
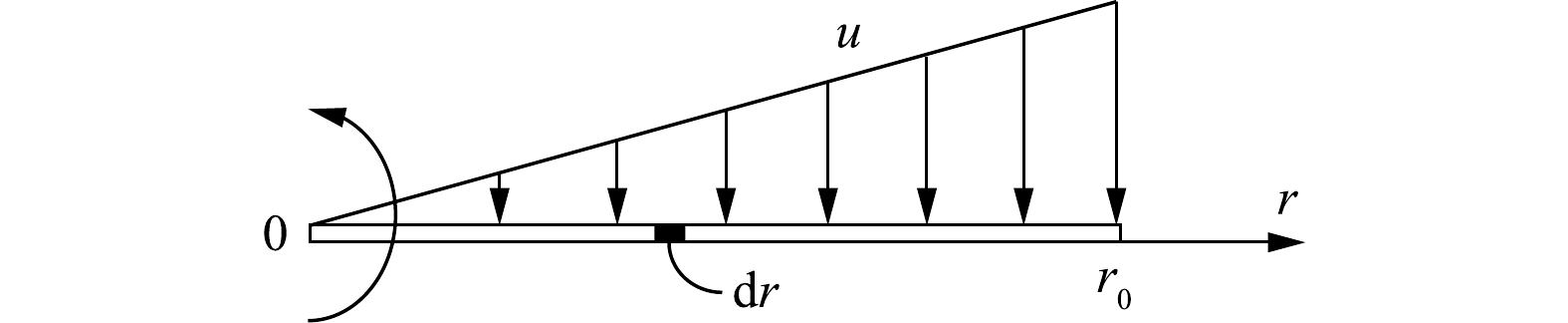
然而,沿旋线上的切向速度u是不均匀的,切向速度分布如图2所示。于是,旋线上任意点r与颗粒的相对运动速度见式(4)。
式中:u为旋线与颗粒的相对速度,m·s−1;ω为旋线旋转角速度,rad·s−1;r为旋线半径,m。
设气体中的颗粒初始浓度为c0,在图2所示的旋线微元长度dr上拦截的雾滴质量计算式见式(5)。
式中:dmR为微元dr上拦截的雾滴质量,kg;c0为气体颗粒浓度,kg·m−3。
对式(5)从0到旋线长度r0进行积分(见式(6)),得到单根旋线拦截作用捕集的雾滴质量。
因流向孤立旋线的雾滴总质量的计算式见式(7)。于是,单根旋线拦截作用的捕集效率可通过式(8)进行计算。
式中:M为来流雾滴总质量,kg;Q为气流流量,m3·s−1;c0为气体颗粒浓度,kg·m−3;v为通过旋线除雾器筒体断面的平均轴向速度,m·s−1;ηR为单根旋线拦截作用的捕集效率;mR为单根旋线捕集雾滴质量,kg。
-
当颗粒直径dp>1 µm,柱状捕集体的惯性碰撞效应是重要的。惯性碰撞效率是Stokes数St的函数,其表达式见式(10)。
式中:ρp为雾滴密度,kg·m−3;dp为雾滴直径,m;u为捕集体与颗粒的相对速度,m·s−1;μ为气体动力黏性系数,取μ=1.85×10−5 Pa·s;df为旋线直径,m。
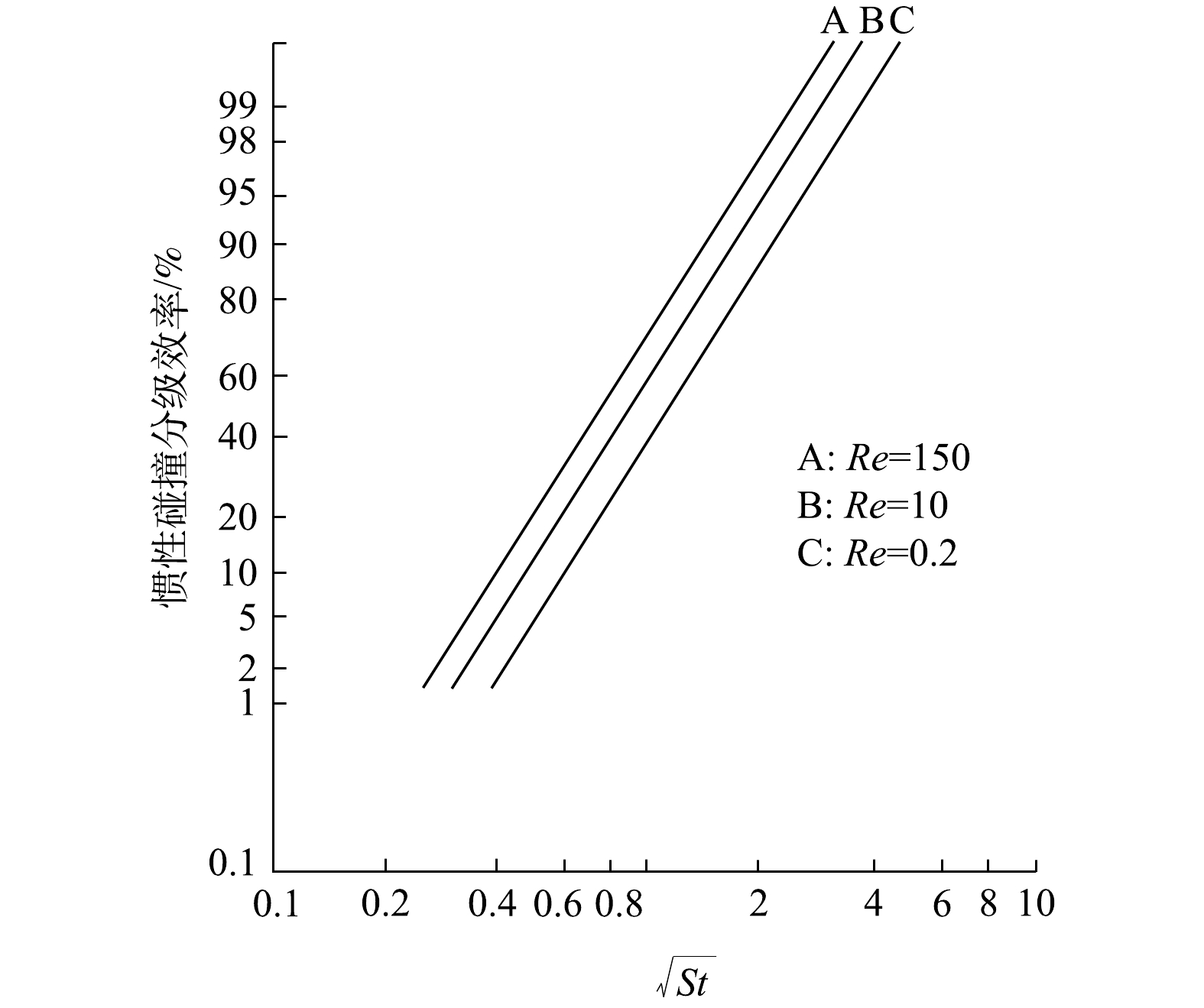
由于绕孤立柱状纤维流动的颗粒运动方程求解非常困难,至今没有分析解。虽然LANDAHL和HERMAN给出了惯性碰撞效率经验式[22],但在高雷诺数的势流情况下缺乏适用性论据。已有研究结果表明,在对数概率坐标纸上,单位长度孤立柱状捕集体的惯性碰撞效率随
√St 的变化呈一条直线[24],如图4所示。而能在对数概率坐标纸上具有直线分布特征的数学模型为对数正态分布。于是,惯性碰撞效率与
√St 的函数关系可用式(11)表示。式中:ηi为单位长度孤立圆柱状捕集体的惯性碰撞效率;σg为几何标准偏差;
(√St)50 为方根斯托克斯数中位值。对于旋线,符合Re≥150,满足曲线A,于是由图4可确定
(√St)50=0.7 。几何标准偏差计算式为式(12)。由此可推算孤立柱状捕集体的惯性碰撞效率计算式为式(13)。来流颗粒与旋线的相对运动速度是变化的,故单根旋线上惯性碰撞捕集的液滴质量可由积分(见式(14))来计算。单根旋线的惯性碰撞捕集效率计算见式(15),而气流中有N根捕集体的惯性碰撞效率计算式见式(16)。
式中:mI为单根旋线惯性碰撞作用捕集的液滴质量,kg;ηI为单根旋线的惯性碰撞捕集效率;ηIN为旋线层惯性碰撞捕集效率;N为旋线根数。
-
扩散效应适合于颗粒直径dp<1 µm的情况。但在水雾中,dp<1 µm液滴所占质量百分比极小,对总捕集效率的贡献很小,可忽略。
对于多机理同时存在的复合捕集效率,普遍采用RICHARD和SEINFELD 给出的算式[25] (见式(17))。于是,N根旋线的旋线层的拦截和惯性碰撞复合除雾效率计算式见式(18)。
上述研究表明,降低气流速度、增加转速,均有助于增强拦截和惯性碰撞的捕集作用,但增加旋线根数的提效作用更突出。
-
旋线除雾器可采用单层或多层布置。由于每层旋线布置的根数是受限的,当旋线除雾器无法满足水雾排放要求时,可通过增加旋线层数提效。当采用多层布置时,在两旋线层之间形成较规则的旋涡流,对雾滴产生离心分离作用。
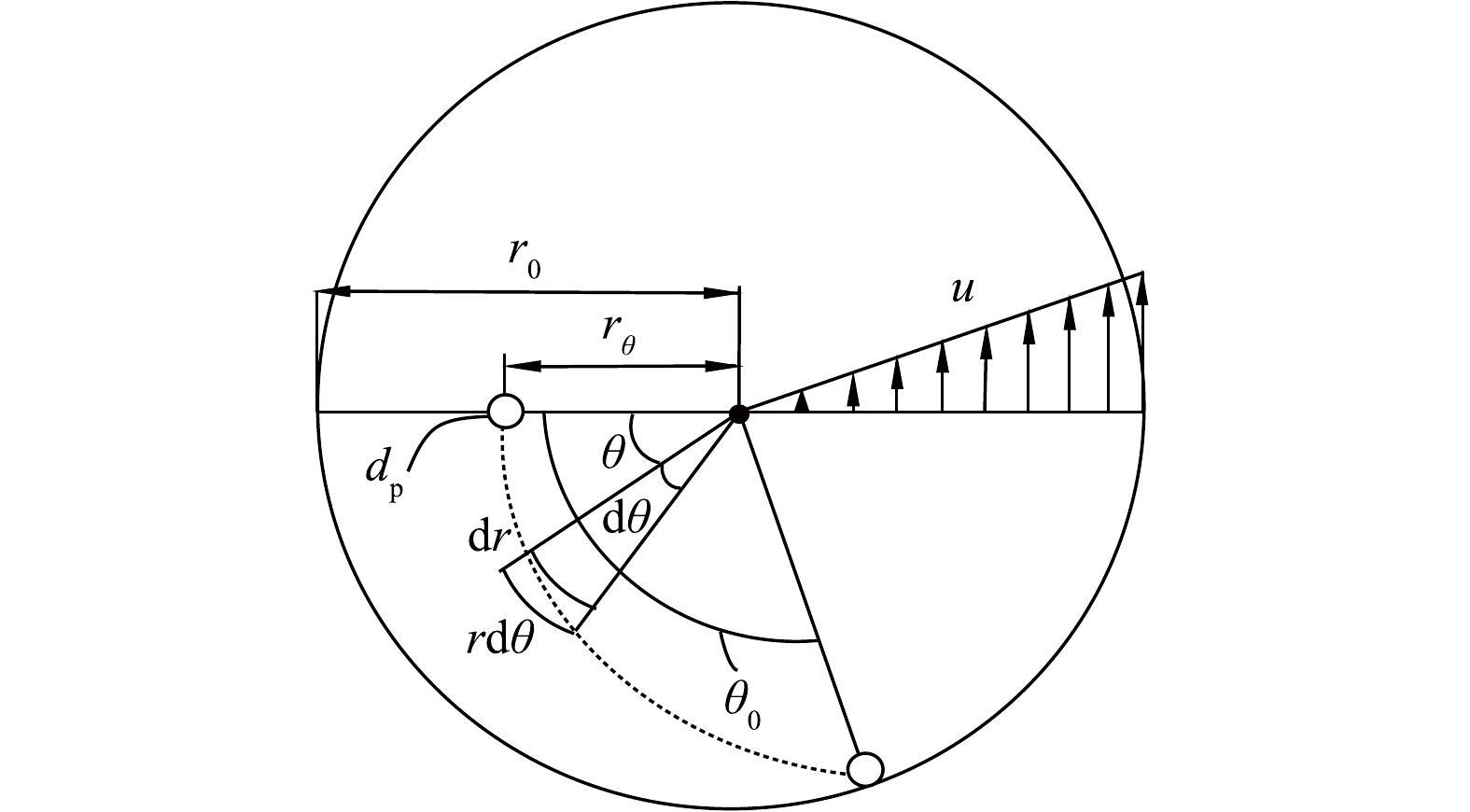
图1中,旋线层间的距离Δh应不小于旋线长度
r0 ,否则会发生相互干扰或缠绕。在切向上,在两层旋线高速同向旋转的拖曳下,Δh空间内的气体几乎以旋线相同的角速度ω旋转。在轴向上,其流速与下行流v相同。因此,旋流经过h距离的时间计算式见式(19)。在此期间,旋流的旋转角度计算式见式(20)。在图5所示的旋流场中,假定位于半径rθ直径为dp的雾滴随气流旋转θ角度后,沉降到r=r0的边壁上被捕集。
显然,对于位于rθ和r0之间直径为dp的所有雾滴将被捕集。因此,其旋流分离效率计算式见式(21)。
由式(21)可知,下面应确定rθ的计算方法。在图5所示的雾滴轨迹线的任意点(r, θ)上,雾滴在dt时间内径向和切向运动距离计算式见式(22)。
式中:雾滴的离心沉降速度w计算式见式(23)。
式中:τ为弛豫时间,计算式见式(24)。
式中:Cc 即Cunningham 滑移修正系数,对于dp>1 µm的粒子,Cc≈1。
由式(22)可换算得到式(25)。将式(23)代入式(25),得到式(26)。将式(4)代入式(26),积分得到式(27)。由式(27)得到式(28)。将式(28)代入式(21)得旋流离心分离效率计算式(29)。将式(20)代入式 (29),旋流离心分离效率还可由式(30)计算得到。
可见旋流离心分离除雾效率服从指数变化规律,且是雾径和转速平方的函数。在图1所示的第二层旋线下面仍有呈锥状收缩的旋流流动,但因接近气流出口,旋流衰减较快,故忽略其离心分离作用。
于是,双层旋线捕集和旋流离心分离协同除雾效率计算式为式(31)。
1.1. 旋线除雾器的工作原理
1.2. 旋线层的除雾效率
1.2.1. 拦截
1.2.2. 惯性碰撞
1.2.3. 扩散效应
1.3. 旋流离心分离
-
双层旋线除雾实验系统如图6所示。由除雾器本体、水泵、电机、旋线、风机、水箱构成。入口管均布4个雾化喷嘴,壳体采用8 mm厚有机玻璃,旋线长250 mm,材质采用3 mm聚酯纤维线。风机最大风量5 000 m3·h−1,全压300 Pa。
-
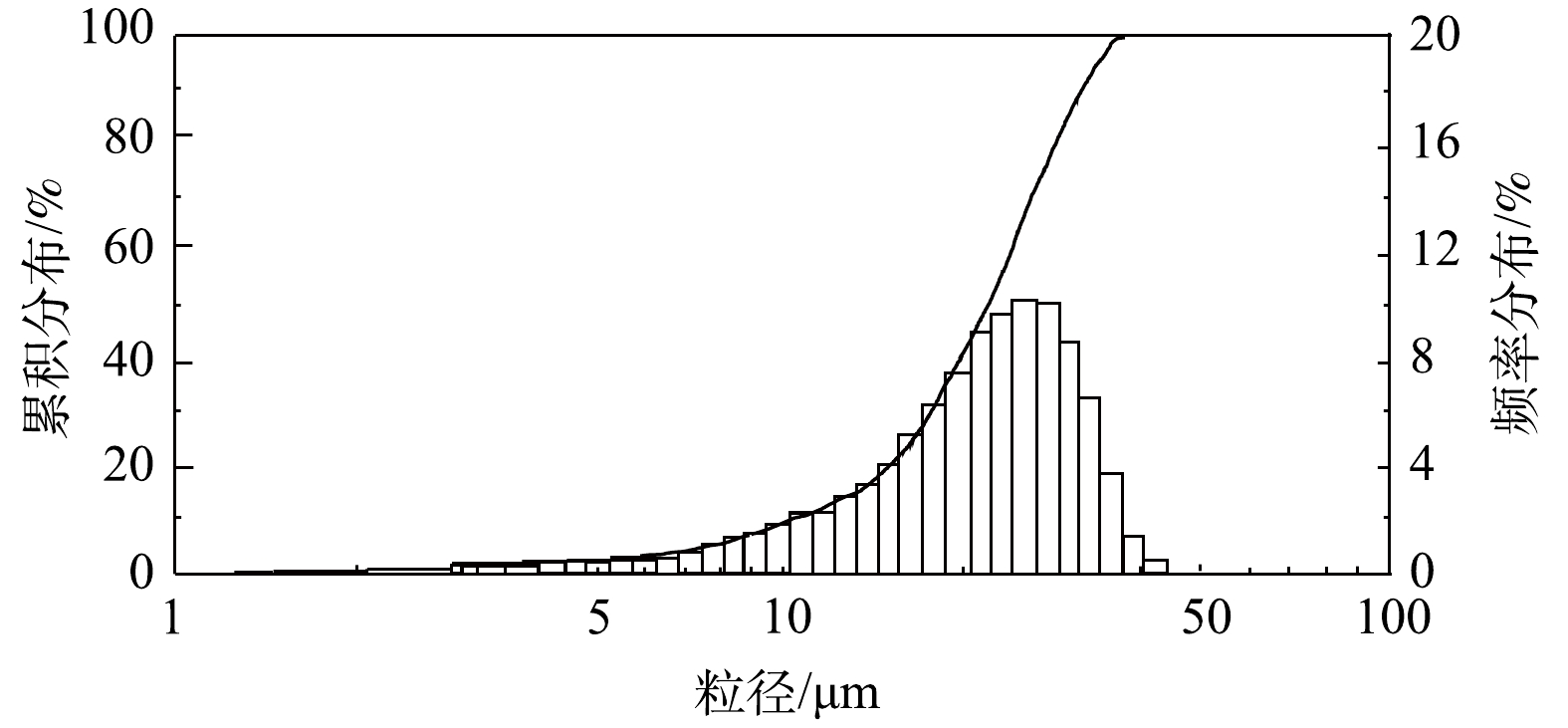
风量和旋线转速均采用变频器控制。通过调节水压改变水雾直径,采用Winner 318激光粒度分析仪测定实验水雾的粒径分布如图7所示。水雾中位径为20.1 μm,实验雾滴大小接近工业脱硫塔烟气夹带液滴的粒径范围[26]。
除雾效率的测定采用水平衡法[27]。在图6中,雾化水箱的失水量为喷嘴总喷水量m1,喷头喷出的雾化水雾随气流运动,喷到进气管壁上的雾滴汇入沉降水箱中,水量为m2。实际进入旋线除雾器筒体的总水雾量m0=m1−m2,被旋线旋线捕集的雾滴流入捕集水箱中,水量为mc,则除雾效率见式(32)。
-
实验在常温常压下进行,双层旋线除雾器每层旋线根数分别取100根和200根。考虑到现有静电除雾器的处理风速通常不超过2 m·s−1[28],为体现旋线除雾器的优势,实验风速取2.5 m·s−1。喷嘴的喷液量为1 355 kg·h−1,水雾浓度为4 100 mg·m−3。
-
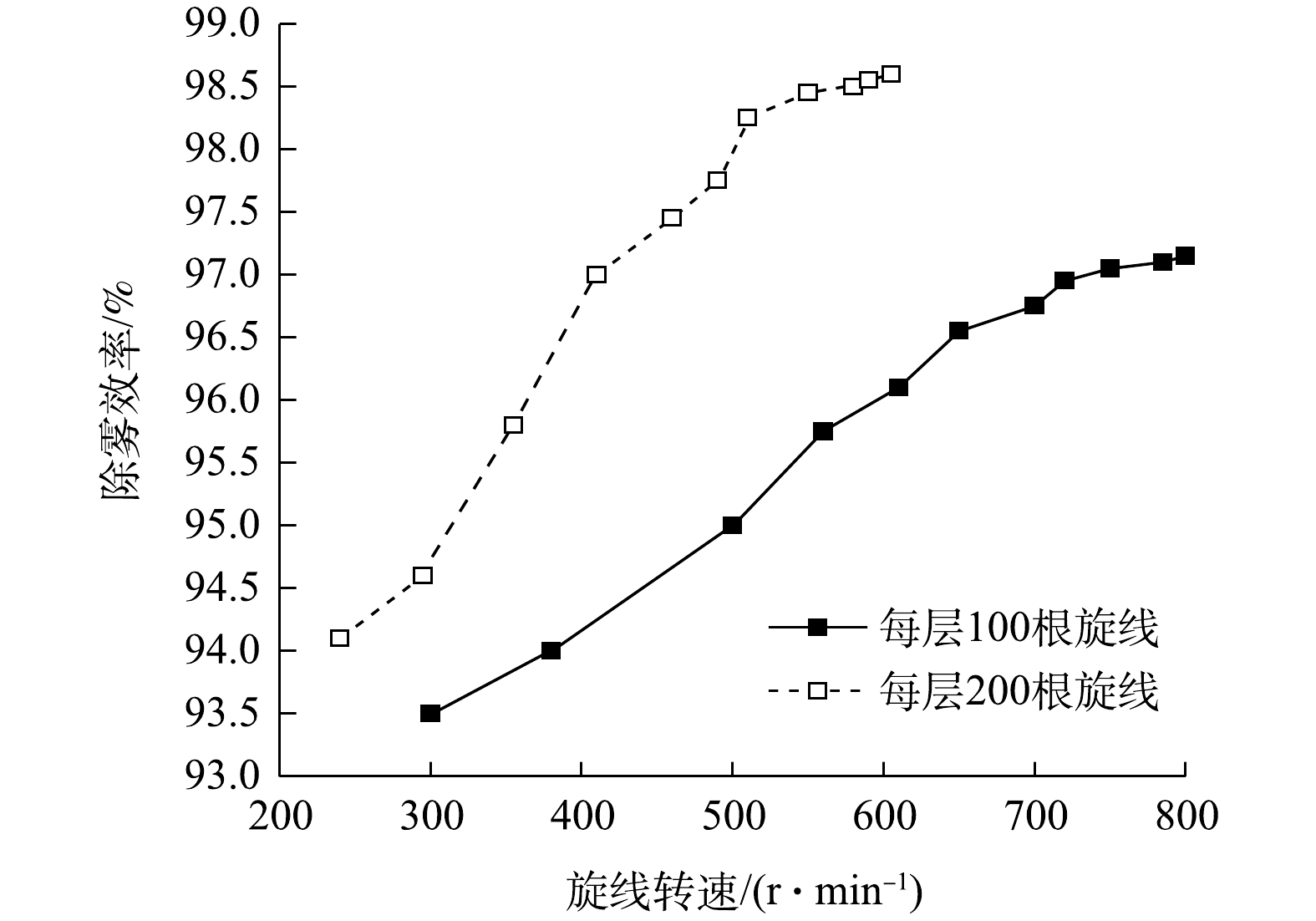
当每层旋线分别为100根和200根时,测得双层旋线除雾器的除雾效率与旋线转速的关系如图8所示。
结果表明,增加旋线根数的提效作用非常显著。采用直径3 mm旋线捕集中位径20.1 μm的水雾,当旋线转速500 r·min−1时,每层旋线为100根时除雾总效率约95%,当旋线增至每层200根时,除雾总效率为98.1%。
由于实验所测得的除雾效率是总除雾效率,所建立除雾效率理论式(31)是分级效率,二者无法比较。为将实验所得总效率与分级效率相联系以便于评价除雾器的性能,ZHAO等[29]通过大量实验数据和试错研究发现,颗粒群的总捕集效率和颗粒群中位径近似存在的关系如式(33)所示。
式中:ηT为总效率实验值;k0为待定系数;dp50为颗粒群中位径。
根据已知总效率实验值ηT和颗粒群中位径dp50,由式(33)可确定系数k0。于是,基于分级效率服从指数规律,ZHAO等[29]得出预估分级效率经验式(34)。
式中:ηe为预估分级效率。
作为验证性研究,仅讨论旋线转速500 r·min−1情况下分级效率理论值与分级效率经验预估值的吻合度。
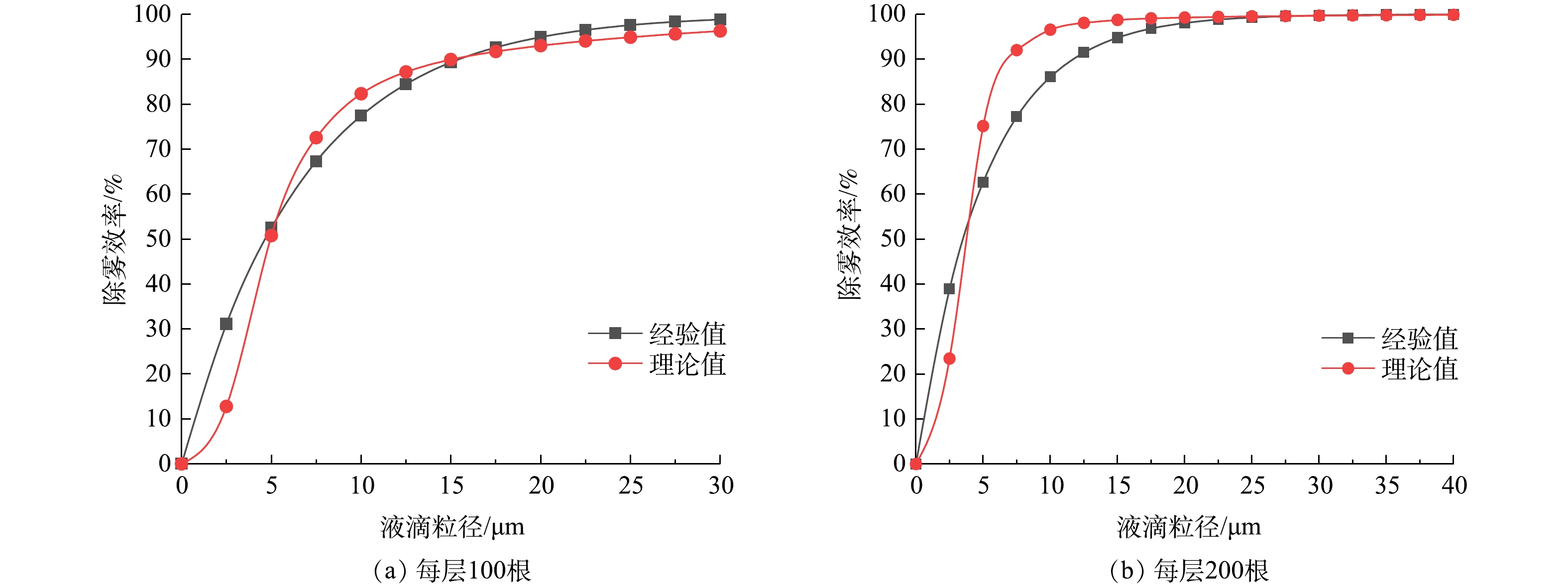
由总效率实验结果图8和式(33)得出的k0值(见表1)。由式(34)分别得出每层100根和200根时的分级效率经验值ηe,然后由式(31)得出双层旋线除雾器分级效率理论值ηC,将计算结果绘于图9中。
实验结果表明,当雾径小于5 μm,旋线除雾器分级效率理论值低于经验值;当雾径为5~20 μm时,理论值高于经验值,随后二者相互逼近。上述现象的原因是,当雾径小于5 μm,惯性碰撞效应较弱,而当雾径大于5 μm,惯性碰撞作用明显增强。总体看,旋线除雾器分级效率理论值与经验值相当吻合,在雾径为0~40 μm时,平均误差约1.4%,说明双层旋线的拦截、惯性碰撞与旋流离心分离复合除雾效率理论是比较准确的。
-
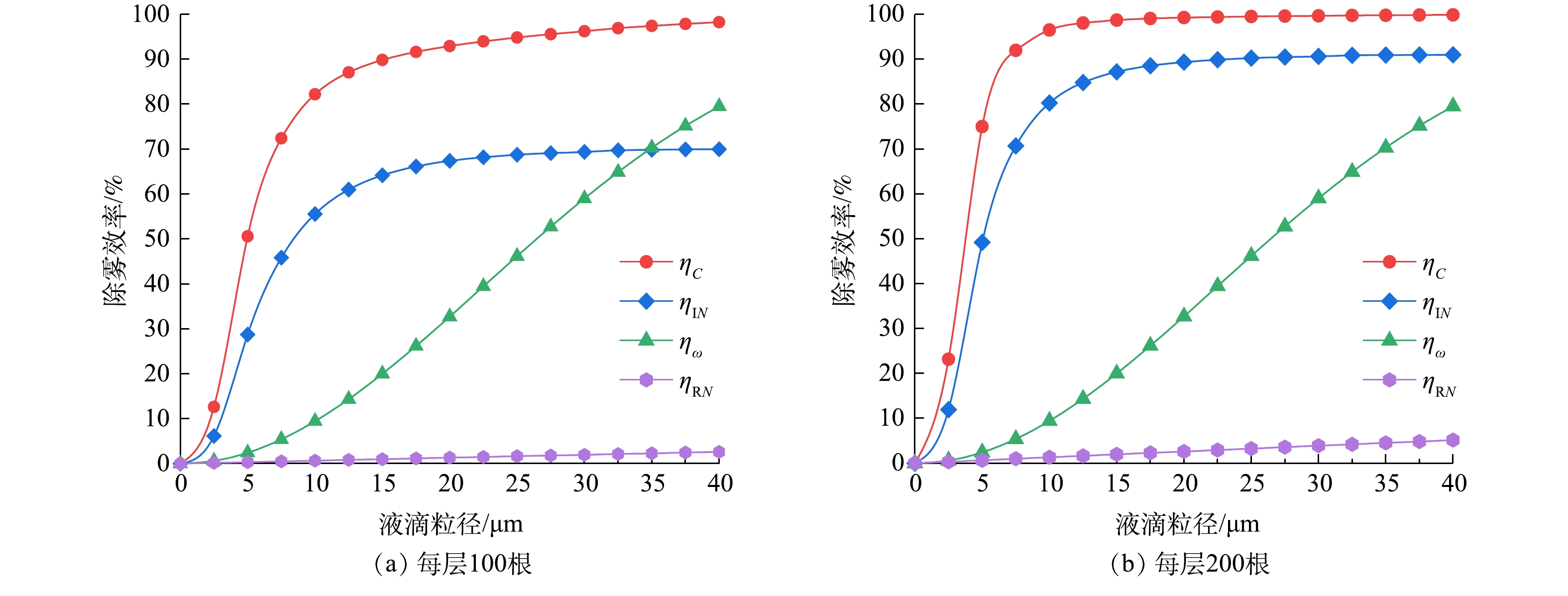
为明确各捕集机理在旋线除雾中的作用,取旋线转速500 r·min−1,将单层拦截ηRN、惯性碰撞ηIN、旋流离心分离ηω和双层复合除雾效率ηc的计算结果绘于图10中。由图10可看出,惯性碰撞效应起主导作用,旋流分离次之,拦截效率对旋线除雾器效率的贡献很小。如对20 μm雾滴,在每层旋线
N=200 根时,双层复合除雾效率已达98%,单层旋线惯性碰撞效率为89%,旋流离心分离效率为33%,而拦截效率仅2.5%左右。因此,拦截效率可忽略不计。在小雾径情况下,虽然离心分离作用小于惯性碰撞,但离心分离效率随雾径增加较快,对旋线除雾器具有明显提效作用。
2.1. 实验系统
2.2. 实验方法
2.3. 实验条件
2.4. 检验结果与讨论
2.4.1. 效率理论的检验
2.4.2. 不同机理的提效作用
-
1)旋线除雾器的除雾机理主要是拦截、惯性碰撞和旋线的高速旋转产生的旋流离心分离。理论研究表明,拦截和惯性碰撞随旋线转速和旋线根数的增加而提高,但增加旋线根数的提效作用更有效;旋流离心分离效率是雾径和转速的平方的函数,且服从指数规律。
2)双层旋线除雾器的理论分级效率的验证结果表明,在旋线转速500 r·min−1、旋线直径3 mm、每层旋线分别为100根和200根的情况下,在0~40 μm雾径范围内,旋线除雾器分级效率理论值与经验值基本吻合,平均误差约1.4%,说明双层旋线器的复合除雾效率理论是比较准确的。
3)对比各机理在旋线除雾器中的提效作用可看出,旋线的惯性碰撞效应起主导作用,特别是对小粒径的雾滴有较高的捕集效率;旋流离心分离作用次之,对于小粒径雾滴分离效率不高,但随着雾滴粒径的增加效率提升较快;旋线的拦截除雾效率较低,几乎可以忽略不计。



 下载:
下载: