-
塑料制品的使用非常广泛,但在其给人们生活带来便利的同时,大量塑料废物也给环境带来很大压力。塑料废物是难物降解,会在环境中存留长达400~1 000年[1]。经过长时间的物理、化学和生物降解等作用,塑料在自然环境中断裂成塑料碎片或颗粒。当这些塑料碎片或颗粒的粒径小于5 mm时,被定义为微塑料[2]。除此之外,一些化妆品和清洁剂中也会添加微塑料[3]。微塑料广泛存在于生态环境中,与塑料相比,微塑料的化学性能更加稳定,更容易被生物吞食,并通过生物链发生传递、富集,甚至对人体产生危害[4]。因此,微塑料的污染问题逐渐成为研究热点和重点。
近年来,关于海洋环境中微塑料的研究日益增多。CORDOVA等[5]分析了印度尼西亚泗水海峡北岸微塑料的分布特征,发现聚苯乙烯为主要的微塑料类型。COLLIGNON等[6]发现,地中海北部水体中的微塑料丰度在强风事件前是强风事件后的5倍。内陆河流与湖泊环境与人类活动的关系更为密切,但是相关微塑料污染研究相对较少。JIANG等[7]分析了青藏高原河水和河流沉积物中微塑料的分布特征,发现在人类活动稀少的偏远地区微塑料污染程度小。WANG等[8]研究了浙江温瑞塘河沉积物中微塑料的分布特征,发现粒径小于300 μm的微塑料更容易积聚在河流沉积物中,从而使得进入海洋中的这类微塑料丰度减小。
白洋淀是我国华北平原最大的淡水湖泊,位于河北省东南部的保定市,地处太行山东麓、永定河冲积扇与滹沱河冲积扇之间的低洼地区,属海河流域大清河水系[9]。白洋淀淀区水域面积为366 km2,平均蓄水量13.2×108 m3,被称为“华北明珠”[10]。府河是白洋淀的最重要供水河流之一,全长62 km,流域面积781 km2[9]。府河沿岸居民众多,生活和农业生产中使用的塑料产品繁多。这些产品形成的塑料废物通过污水排放和地表径流等多种方式输送到府河,最终流入白洋淀或在河道中堆积。目前,还没有关于白洋淀地区微塑料污染状况的研究。本研究通过对府河入淀口段中沉积物进行采样并检测,分析沉积物中微塑料的污染现状及其来源,以期为白洋淀区域微塑料污染方面的治理提供参考。
全文HTML
-
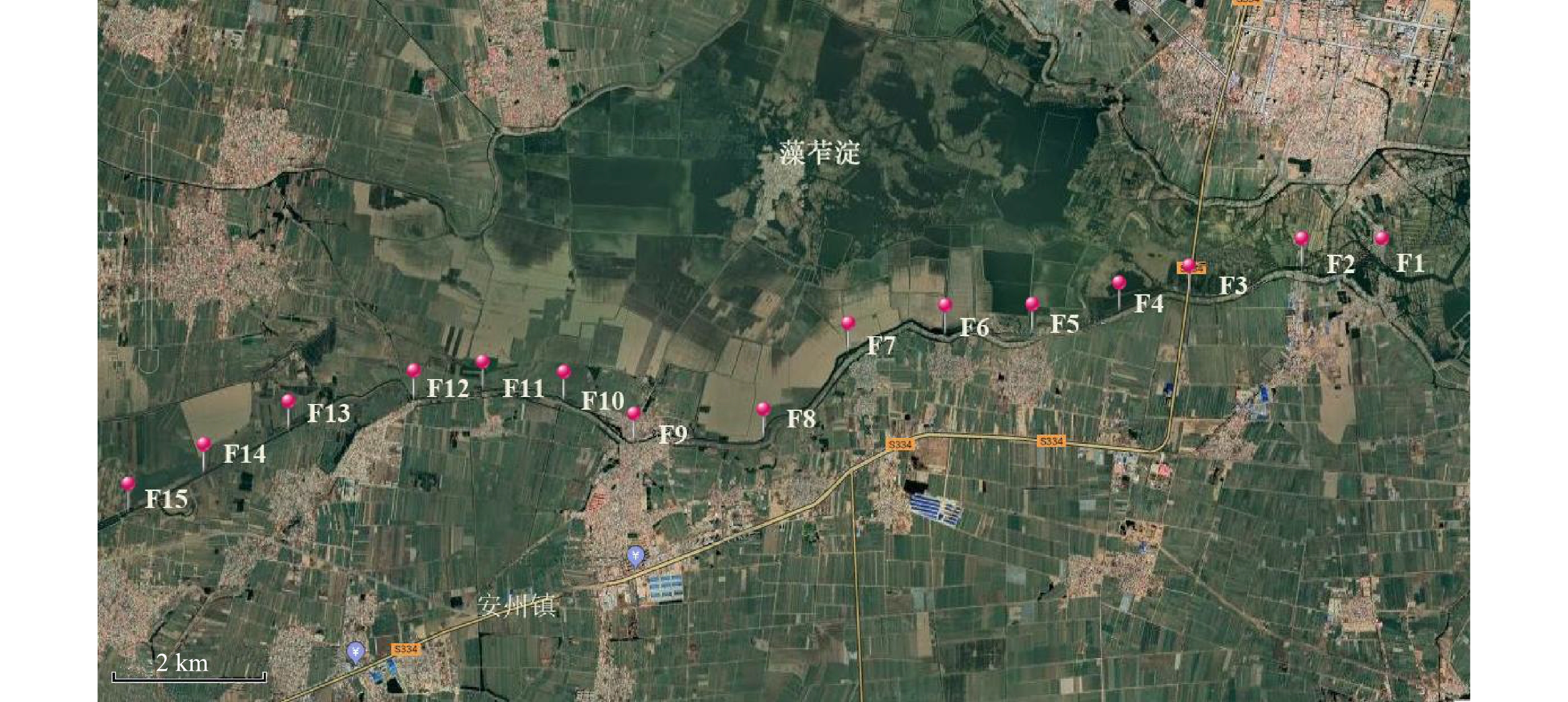
在府河入淀口设置15个采样点采集沉积物样品。每个采样点间隔2 km左右。采样点分布如图1所示,同时采用GPS进行定位。采样点南刘庄(F1)、旧大桥(F2)、新大桥(F3)、东向阳(F5)、西向阳(F6)、际头(F7)、大寨(F8)、桥北(F9)、白庄(F11)、建昌(F12)和李庄(F13)均为村庄附近或者人流较为密集区域,F4、F10、F14、F15这4个采样点附近多为农田,少村庄。用不锈钢柱状采样器在以上采样点采集深度为5 cm处的沉积物样品,每个位点分别取3个平行样。将样品分别装入玻璃瓶中密封保存,送回实验室进行进一步分析。
-
真空抽滤系统(SHZ-DIII,天津市予华仪器科技有限公司);体视显微镜(XTD-7045A,北京世纪科信仪器有限公司);傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Vertex 70,德国布鲁克科技有限公司)。
-
沉积物样品中微塑料提取采用密度浮选法[11-12]。取适量沉积物样品在50 ℃下烘干,至沉积物样品的质量恒定不再变化。称取50 g沉积物干样,加入1 L的饱和氯化钠溶液,摇晃均匀,室温下静置12 h。取上清液置于真空抽滤系统下抽滤,滤膜采用1 μm的混合纤维素滤膜。抽滤完成后,将滤膜置于干净的培养皿中进行下一步检测。将滤膜置于体视显微镜下观察,根据颗粒的外观、颜色等判断其是否为微塑料,拍照计数,测量微塑料的粒径。
-
选取50个颗粒进行红外光谱分析,检测其成分及类型,统计分析微塑料的丰度、形状和粒径大小。每个实验样品设置3个平行。沉积物样品中微塑料丰度以每千克干重沉积物中微塑料的个数计算。府河沉积物中微塑料的平均丰度值用(平均值±标准偏差)表示。
1.1. 实验原料
1.2. 实验装置
1.3. 实验方法
1.4. 分析方法
-
经过对沉积物样品的检测分析发现,在所有采样点的沉积物样品中均发现微塑料。15个采样点的微塑料平均丰度为(558.4±233.3)个·kg−1,各采样点的丰度见图2。墨水河沉积物中微塑料的丰度为0~170 个·kg−1[13];葡萄牙安图河沉积物样品中微塑料的丰度为100~629 个·kg−1[14];安大略湖沉积物中微塑料的丰度为20~27 830 个·kg−1,平均丰度为760 个·kg−1[15];乐安河沉积物中微塑料的平均丰度为1 366 个·kg−1[16]。与这些文献中报道河流中微塑料污染状况相比,府河入淀口沉积物中微塑料污染处于中等水平。
位点F7处微塑料的丰度最大,为1 049 个·kg−1。这是由于采样点位于南际头和北际头2个村庄附近,人口较其他采样点更多,有2 694人,而且离河道比较近,因此,河岸周围的生活垃圾与废水也较多,使得这个区域沉积物中微塑料累积量更大。位点F2和F3处的沉积物样品中微塑料丰度也很高,分别为642 和769 个·kg−1。这可能是由于F2和F3附近餐饮店较多,人类活动比较密集,容易造成一次性塑料垃圾的堆积,如矿泉水瓶、一次性包装袋等。除此之外,在F2和F3附近还有2座桥,桥墩会拦截河中的塑料垃圾,导致沉积物中微塑料积聚。F15处沉积物中微塑料的丰度最小,丰度值为212 个·kg−1,其次是F11(241 个·kg−1)和F10(270 个·kg−1)。F15周围少村庄、多农田,F10和F11附近的白庄村人口为824人,而且这3个采样点周围的村庄离河道远,附近人类活动少。
以上结果表明,河道沉积物中微塑料的丰度与周围人口密度和人类活动有关。在人口众多、工业发达的浙江温州温瑞塘河沉积物中,发现微塑料丰度高达(32 947±15 342)个·kg−1,而在人口稀少的西藏地区拉萨河流沉积物中,微塑料丰度仅为(180±42)个·kg−1[7-8]。一般来说,人口密度越大,人类活动越密集的地区,微塑料的丰度越大[5, 17-18],与本研究观察的结果一致。
-
府河沉积物中微塑料的形状主要为碎片、纤维、薄膜和球状4类,典型图像如图3所示。其中,碎片状微塑料占比最大,约为66.1%;其次为纤维状微塑料,占比为26.4%;薄膜状和球状2种微塑料占比最小,分别为5.5%和2.0%(图4)。球状微塑料仅在3个采样点的沉积物样品中出现,且数量最少。这与文献报道的其他区域微塑料状态不同:如鄱阳湖南矶山支入湖段沉积物中微塑料以发泡类为主,发泡类微塑料多为白色,密度小,组成成分为聚苯乙烯,主要来源于渔民用的发泡浮子、泡沫包装箱和一次性泡沫餐具[1];墨河沉积物中微塑料以纤维状为主,主要来自周围纺织工业园和生活废水中的衣物纤维[13];三峡水库沉积物中微塑料以纤维状为主,主要来自附近渔民使用的捕捞工具以及生活污水中的衣物纤维[19];美国劳伦森大湖沉积物中微塑料以球状为主,主要来自清洁用品(如洗面奶)中的颗粒添加物[20]。这些都表明微塑料形状与研究区域周围环境及微塑料的来源有很大关系。府河周围多为居民村庄与农田,故府河沉积物中的微塑料污染主要来源于生活垃圾、生活污水和农田废物。
府河入淀口段碎片状的微塑料多为硬质塑料碎片和块/条状的塑料编织袋碎片。这些碎片状塑料大多数为塑料制品在自然条件下裂解成的小碎片,故碎片状微塑料以次生微塑料为主[21]。纤维状微塑料主要呈细线型,府河沉积物中纤维状微塑料主要来源于生活污水中的衣物纤维。除此之外,在农业生产中使用的化肥编织袋容易老化,也可能会断裂形成纤维状微塑料;薄膜状微塑料多为无规则的片状,质地轻,府河入淀口沉积物样品中薄膜多来源于废弃塑料包装袋以及农用地膜。球状微塑料多为个人日常护理产品和某些类型清洁剂中的添加物[22],在府河沉积物样品中的整体含量很少。大部分沉积物样品中碎片状微塑料占比最大,而在F7和F9处的沉积物中,纤维状微塑料的占比最大,其次是碎片状微塑料。这可能因为这2个采样点附近的村庄离河道比较近,生活污水大部分直接排入河中,造成衣物纤维的积累。
-
府河沉积物中微塑料粒径分布如图5所示。粒径为0.1~0.5 mm的微塑料占比最大,为44.7%;其次是0.5~1 mm 和1~5 mm的微塑料,占比分别为30.0%和18.5%;粒径小于0.1 mm的微塑料占比最小,为6.8%。府河沉积物中微塑料的粒径范围以0.1~1 mm为主,与大多数研究结果类似[23-26],如湘江、太湖、长江口、黄海和渤海沉积物中,粒径小于1 mm的微塑料占大多数。亓会英等[13]认为,粒径较小的微塑料颗粒容易在水力作用下随水流迁移,而粒径较大的微塑料更容易下沉,并积聚在沉积物中。除此之外,显微镜下目测挑选微塑料的方法尚存在局限性,不易检测出粒径较小的微塑料,故测得丰度值可能比实际丰度较低。研究表明,水生生物的摄食与微塑料的粒径有关,粒径小于1 mm的微塑料可能更易被吞食,通过食物链积累在其他生物体内,造成更大的威胁,这部分微塑料或许将成为未来的研究重点[1]。
进一步分析发现,府河沉积物中纤维状和薄膜状微塑料的粒径比其他2种形状的微塑料大,一般大于1 mm;球状微塑料的粒径较小,一般小于0.1 mm。这可能与塑料的原始状态有关,纤维状和薄膜状微塑料一般由较大的塑料裂解而成,而球状微塑料一般是清洁剂和化妆品的微小添加剂,故纤维状和薄膜状的微塑料粒径大于球状微塑料。
-
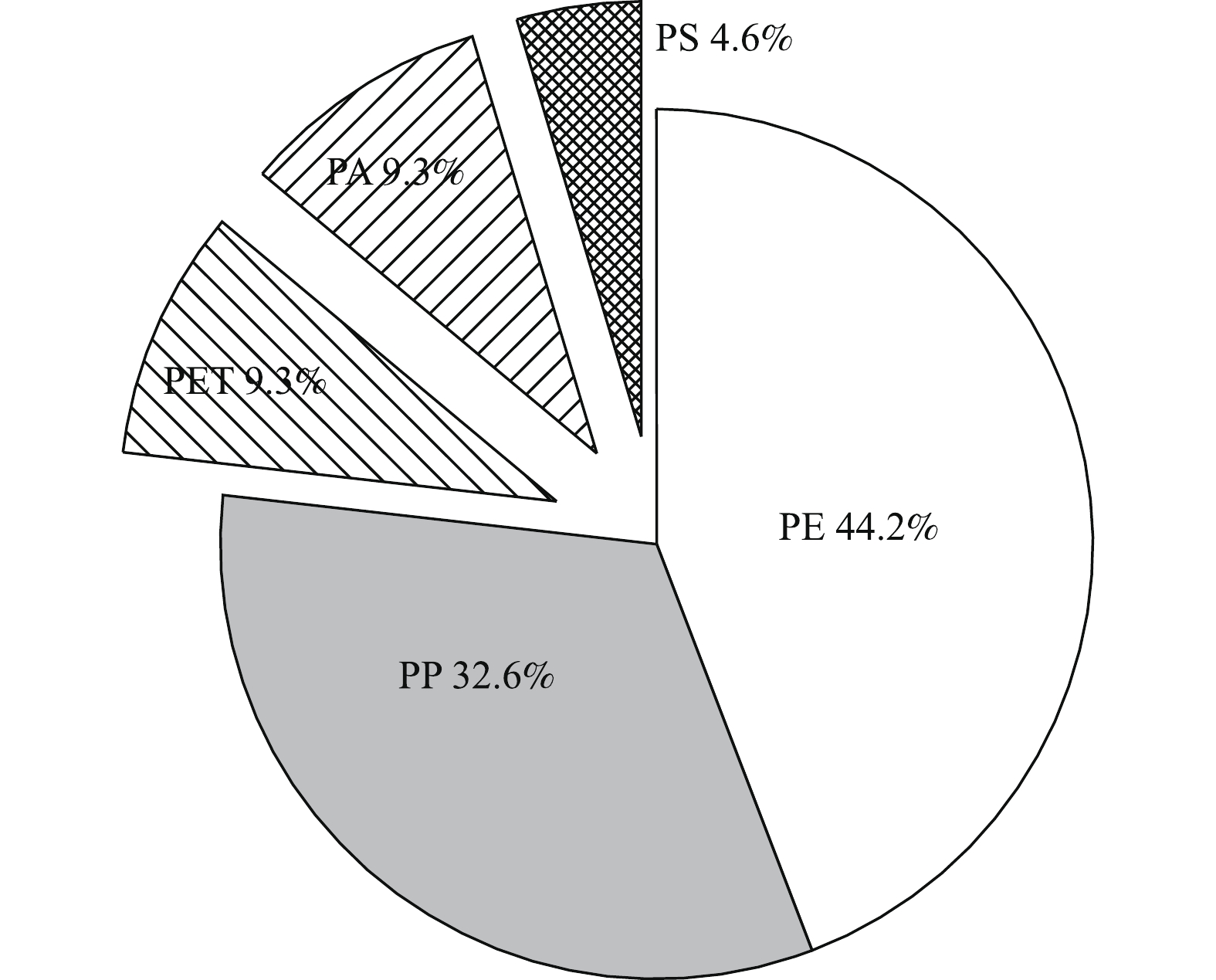
检测的50个颗粒中有43个是微塑料,并发现5种不同的类型。图6为5种微塑料的红外光谱特征图。占比最大的2种微塑料是聚乙烯(PE)和聚丙烯(PP),分别为44.2%和32.6%,其次是聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)、聚酰胺(PA)和聚苯乙烯(PS)(图7)。PE和PP因价格低廉、化学性能稳定等优点,在日常生活中被大量使用,所以许多研究中微塑料类型都以PE和PP为主[18, 27-29]。虽然PP和PE的密度低于河水密度,但微塑料表面可能由于生物污染附着和积累有机物、杂质,使其密度增大,进而积聚到沉积物中[8]。推测府河入淀口段沉积物中PE主要来自塑料包装盒和一次性产品;PP主要来自塑料编织袋和塑料袋;PET主要来自矿泉水瓶的分解,除此之外还可能来自一些衣服纤维;PA主要来自洗衣废水中的衣物纤维;PS主要来自废弃的泡沫塑料制品和清洁用品。沉积物中微塑料的类型与其来源密切相关,除PE和PP等一些常见的微塑料类型外,RODRIGUES等[14]在葡萄牙安图河沉积物样品中检测到聚乙酸乙烯酯(PVA),这类聚合物常用于水性涂料和胶粘剂中;罗雅丹等[30]在青岛海水浴场检测到丁二烯共聚物(SB),这可能来源于钓鱼时使用的泡沫浮子。
2.1. 府河沉积物中微塑料的丰度
2.2. 府河沉积物中微塑料的形状
2.3. 府河沉积物中微塑料的粒径分布
2.4. 府河沉积物中微塑料的类型
-
1)府河入淀口段沉积物样品中微塑料的丰度最大为1 049 个·kg−1,平均丰度为(558.4±233.3) 个·kg−1,与其他河流沉积物中微塑料的丰度值相比,府河入淀口段的微塑料污染处于中等水平。
2)府河入淀口段沉积物中微塑料主要有4种形状,分别为碎片状、纤维状、薄膜状和球状。其中碎片状微塑料占比最高,约占总数的66.1%。微塑料的粒径以0.1~1 mm为主,占总数的74.7%。微塑料的类型主要是聚乙烯和聚丙烯2种。
3)微塑料的污染情况与人类活动密切相关,府河入淀口段沉积物中微塑料主要来源于生活污水中的衣物纤维、日常塑料用品以及废弃化肥袋和农用地膜的分解。因此,建议加强对府河周围,甚至整个白洋淀地区生活垃圾的治理,从源头上减少微塑料的产生。





 下载:
下载: