-
“十三五”规划实施以来,我国对工业废水的处理要求日趋严格,尤其是“水十条”的出台,使脱硫废水零排放成为必然趋势[1-3]。目前,脱硫废水零排放处理工艺多采用预处理+浓缩减量+蒸发固化[4-9],其存在设备占地面积大、投资和运行成本高[10],直接蒸发固化工艺存在烟道腐蚀等风险[11];另一方面,当前电力环保新形势下电厂机组运行负荷普遍偏低,急需开发低成本的脱硫废水处理技术。利用渣水系统中的碱性炉渣处理脱硫废水中的重金属或酸性物质,以废治废,具有投资成本低,工艺改造简单等优势[12-16];但脱硫废水水质复杂,含盐量高,且pH较低,排入渣水系统后对渣水系统的腐蚀风险尚未可知。
本研究通过模拟实验,采用动态失重法和电化学法,系统地研究了添加不同比例脱硫废水的捞渣机补水混合液,对渣水系统中捞渣机、链条、水冷壁、关断门和冷灰斗等一系列直接接触混合液的关键部件金属材料的腐蚀影响,考察了温度、pH和电导率对材质的腐蚀规律;探讨了多因素共同存在下对金属材料的腐蚀规律;并提出了防腐蚀策略,本研究可为利用渣水系统处理脱硫废水提供理论指导和数据支持。
全文HTML
-
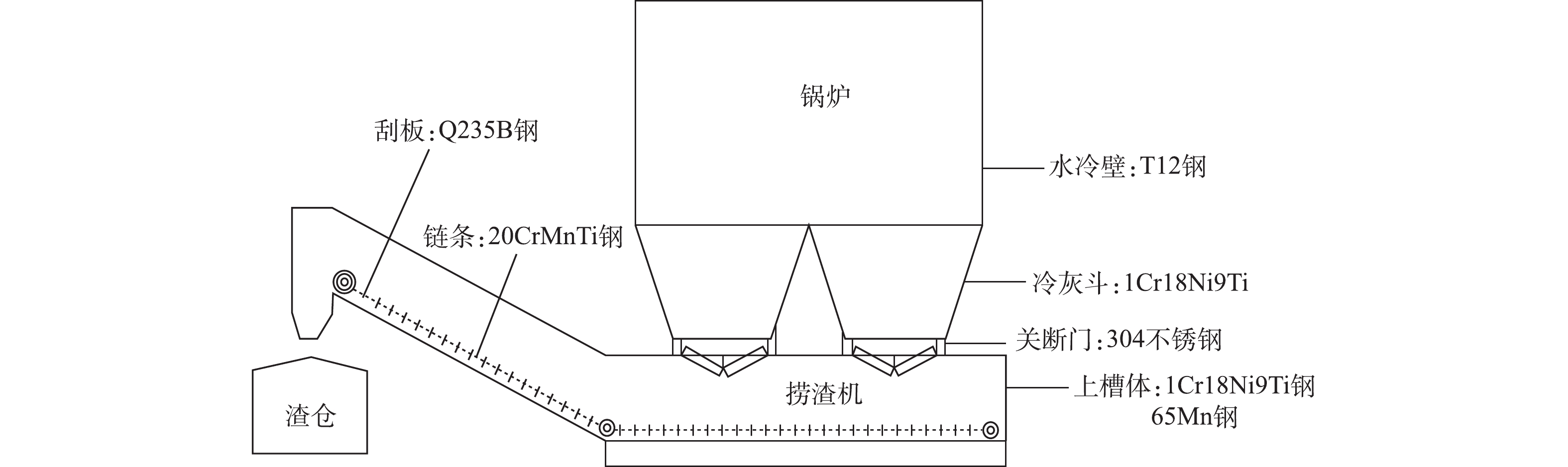
本研究系统研究了燃煤电厂渣水系统中与水直接接触的6种典型材质,对应的设备位置如图1所示,通过模拟挂片实验和电化学腐蚀实验分别直接和间接地进行各材质腐蚀行为研究。腐蚀实验的材质见表1。
-
研究[17-19]表明,影响金属腐蚀的主要因素包括工业水温度、pH、电导率和金属材料等。本研究采用正交法[20-21]设计实验,用极差法对实验结果进行分析,可直观地观察到各因素水平对腐蚀速率的影响,并得到不同因素对材质腐蚀速率的影响大小[22],另一方面,通过电化学方法研究不同材质的腐蚀规律。
1)腐蚀评价正交实验设计。腐蚀实验所用材质见表1,实验采用3因素3水平进行正交实验,其中,3因素分别为温度、pH、电导率,3水平为温度(50、65、80 ℃)、pH(5、7、9)、电导率(15、30、45 mS·cm−1),每个数据点作3个平行样。实验结果中系数K表示水平对腐蚀速率的影响强弱,K值越大,影响越强;极差R表示因素对腐蚀速率影响的显著性大小,R值越大,影响则越大。
3)腐蚀实验。样片上的防锈油脂先用滤纸擦拭干净,然后置于丙酮和无水乙醇中用脱脂棉擦洗,擦洗干净后用滤纸吸干,放入干燥器中4 h,再用分析天平(赛多利斯,型号:BSA224S)进行称重(精确到2 mg);待按实验要求配制好的实验水样达到指定温度时,挂入实验用试片,启动旋转挂片腐蚀实验仪(型号:RCC-111);达到实验指定时间时,取出试片进行外观观察及记录,然后将试片用毛刷刷干净,并在酸洗溶液中清洗30 s,接着取出用水冲洗后用滤纸擦拭吸干水分,于无水乙醇中浸泡3 min,取出置于滤纸上吸干,再放入干燥器中4 h后称质量(精确到2 mg)。同时做试片的酸洗空白实验,以矫正酸洗失重。实验流程如图2所示,具体实验步骤参照GB/T 18175-2014进行。通过对不同材质的腐蚀减重进行分析,筛选不同材质的最优工艺条件;在最优工艺条件下进行电化学实验(电化学工作站型号为Gamry 3000),对不同材质的腐蚀机理进行分析。
4)腐蚀速率计算。腐蚀速率按(1)式进行计算。
式中:v为腐蚀速率,mm·a−1。Δm为试片的质量损失,g;s为试片的表面积,cm2;ρ为试片的密度,g·cm−3;t为实验时间,h;8 760为与年相当的时间,h·a−1;10为与1 cm相当的长度,mm·cm−1。
5)耐腐性判定。根据腐蚀的3级标准判断材质的耐腐性能,当腐蚀深度小于0.1 mm·a−1时,耐蚀性等级为1,属耐蚀材质;当腐蚀深度为0.1~1.0 mm·a−1时,耐蚀性等级为2,属可用材质;当腐蚀深度>1.0 mm·a−1时,耐蚀性等级为3,属不可用材质。
6)材质的主要化学成分如表4所示。
1.1. 实验装置和材料
1.2. 实验方法
-
1)水冷壁-T12钢。T12钢的腐蚀正交实验结果如表5所示。极差R值的大小反映了各因素、水平对腐蚀速率的影响程度[22-23]。由表5可知,温度、pH、电导率的极差R值分别为1.590 6、0.677 2、2.474 1,3个因素中对T12钢腐蚀速率影响的显著性[24]最大的是电导率,其次是温度,最小的是pH。由于T12钢的化学成分组成可知,T13钢含碳量高且不含生成保护膜的元素,在高电导率废水中极易受到腐蚀;温度主要是影响腐蚀产物形成的防护层性能,不同材质对温度的敏感性不一样;由pH对腐蚀速率的影响可知,该材质对pH不敏感。
每个因素的不同水平对腐蚀速率的影响也各不相同,在温度因素中,K3>K2>K1;在pH因素中,K2>K1>K3;对电导率因素而言,K2>K1>K3。由此可推测,在温度50 ℃、pH=9、电导率为45 mS·cm−1的实验条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最小;在温度80 ℃、pH=7、电导率为30 mS·cm−1条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最大。
有研究[25-28]发现,通常情况下金属的腐蚀速度随温度的增加而增加;当在温度在较低的区间内,随着温度的升高,水中溶解氧下降幅度较下,但氧扩散速率的增加较为显著,因而到达金属表面的氧流量增加,导致金属腐蚀速率增加。相关研究[28-29]表明大多数金属材料在酸性较碱性条件更易被腐蚀,这主要取决于不同材料表面氧化层在酸性条件下稳定性。本研究中T12钢含碳量高,属碳素工具钢,在高氯离子腐蚀介质中,大量氯离子容易穿过金属表面的氧化层,侵蚀内部金属并产生氯化铁等腐蚀产物,这些氯化物向外扩散的速率较快[30],导致与基材分离。因此,T12钢在高氯离子溶液中更易受到腐蚀[31]。
2)冷灰斗、上槽体-1Cr18Ni9Ti钢。表6是1Cr18Ni9Ti钢的腐蚀正交实验结果。对表6的正交实验结果进行极差分析可知,温度、pH、电导率的极差R值分别为0.064 3、0.066 7、0.065 4,3个因素对1Cr18Ni9Ti钢腐蚀速率影响的显著性最大的是pH,其次是电导率,最小是温度。由1Cr18Ni9Ti钢的化学成分组成可知,1Cr18Ni9Ti钢的含碳量低且含有大量的Cr、Ni、Ti元素,其腐蚀产物保护膜具有高效的的防腐性能,因此,影响该材质腐蚀速率的主要原因是pH对腐蚀产物的溶解。
根据对3个因素的水平值进行分析可知,每个因素的不同水平对腐蚀速率的影响各不相同。在温度因素中,K3>K2>K1;在pH因素中,K1>K2>K3;对电导率因素而言,K3>K2>K1。因此,当温度50 ℃、pH=9、电导率为15 mS·cm−1的条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最小;而在当温度80 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最大。
1Cr18Ni9Ti钢含有Cr、Ni等元素,这些元素的腐蚀产物溶于酸性水溶液而不溶于碱性水溶液,则1Cr18Ni9Ti钢在低pH时腐蚀速率快,而在高pH时腐蚀速率慢。PANERU等[32]、LIU等[33]、HOLMBERG等[34]的研究表明,发生高温腐蚀或电化学腐蚀时,含有铬、镍、钛元素的不锈钢受腐蚀时会在表面生成一层致密的保护膜,更耐氯离子与复杂介质腐蚀。这也是1Cr18Ni9Ti钢在高pH与高电导条件下腐蚀速率低的原因。
3)关段门、管道-304不锈钢。表7是304不锈钢的腐蚀正交实验结果。由表7可知,温度、pH、电导率的极差R值分别为0.066 4、0.070 7、0.069 6,3个因素对304不锈钢腐蚀速度影响的显著性最大的是pH,其次为电导率,最小是温度。304不锈钢的化学性质成分与1Cr18Ni9Ti钢相近,皆具有良好的耐腐性能,对腐蚀速率影响的最大的因素是pH。
通过对3个因素的水平值进行分析可知,每个因素的不同水平对腐蚀速率的影响各不相同。温度因素中,K3>K1>K2;pH因素中,K1>K2>K3;对电导率因素而言,K3>K1>K2。因此,当温度为65 ℃、pH=9、电导率为30 mS·cm−1的条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最小;而当温度80 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最大。
304不锈钢中最为重要的元素是Ni、Cr,行业要求Ni含量须大于8%,Cr含量须大于18%。BORENSTEIN在《微生物腐蚀手册》中指出304不锈钢在水环境中能形成一种薄的、致密的、富含铬的氧化物保护膜,具有良好的耐腐蚀性,因此,在工业冷却水中得到了广泛的应用,特别是在发电厂和离岸工业[35],YUAN等[30]研究304型不锈钢在模拟海水中的腐蚀行为中所得到的结论也证实了这一观点。
4)上槽体-65Mn钢。表8为65Mn钢的腐蚀正交实验结果。由表8可知,温度、pH、电导率的极差R值分别为1.051 3、1.142 9、1.698 8;3个因素对65Mn钢腐蚀速度影响的显著性从大到小依次是电导率>pH>温度。65Mn钢同T12钢一样,缺少形成保护膜的元素,因此在高电导率介质中容易受到腐蚀;其腐蚀产物形成的保护膜易受在环境中溶解或脱落,使得腐蚀持续发生。这也是65Mn钢在高电导率和酸性条件下腐蚀速率高的原因。通过对3个因素的水平值分析可知:温度因素中,K2>K3>K1;pH因素中,K2>K3>K1;对电导率因素而言,K2>K1>K3。因此,当温度为50 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1的条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最小;而在当温度65 ℃、pH=7、电导率为30 mS·cm−1条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最大。65Mn钢含碳量少,强度较高,但相对于1Cr18Ni9Ti钢、304不锈钢,65Mn钢中因为缺少铬、镍、钛等形成保护膜的元素,耐腐性能较差。
5)刮板-Q235B钢。表9为Q235B钢的腐蚀正交实验结果。由表9可知,温度、pH、电导率的极差R值分别为3.257 4、2.241 2、1.617 0,3个因素对Q235B钢腐蚀速度影响依次是温度>pH>电导率。
通过对3种因素的水平值分析可知,每个因素的不同水平对腐蚀速率的影响各不相同。由表9可以看出,在温度因素中,K2>K3>K1;在pH因素中,K1>K2>K3;对电导率而言,K3>K2>K1。因此,当温度50 ℃、pH=9、电导率为15 mS·cm−1的条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最小;而在当温度65 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最大。Q235B钢同T12钢和65Mn钢,由于腐蚀介质中含有大量的侵蚀性离子(氯离子、硫酸根离子等)容易在金属表面造成点蚀,在酸性条件下腐蚀产物易溶解,无法形成保护膜,腐蚀进一步加剧[28],因此,Q235B钢在低pH和高盐条件下腐蚀速率高。
6)链条-20CrMnTi钢。表10为20CrMnTi钢的腐蚀正交实验结果。对20CrMnTi钢的实验结果进行极差分析可知,温度、pH、电导率的极差R值分别为0.641 7、0.697 5、1.563 3,3个因素对20CrMnTi钢腐蚀速率的影响大小依次是电导率>pH>温度。由材质的化学成分组成可知20CrMnTi钢同T12钢、65Mn钢一样缺少形成保护膜的元素,在高电导率和酸性条件下腐蚀速率较高。
对3个因素的水平值进行分析可知,每个因素的不同水平对腐蚀速率的影响各不相同。温度因素中,K3>K2>K1;pH因素中,K2>K3>K1;对电导率因素而言,K1>K2>K3。因此,当温度为50 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1条件下材质的腐蚀速率最小;而在当温度80 ℃、pH=7、电导率为15 mS·cm−1条件下,材质的腐蚀速率最大。
对比1Cr18Ni9Ti钢和304不锈钢,20CrMnTi钢的抗腐蚀性差,故其在相同实验条件下各实验组的腐蚀速率较高;但相对于T12钢、65Mn钢、Q235B钢,20CrMnTi钢的腐蚀情况较轻。
-
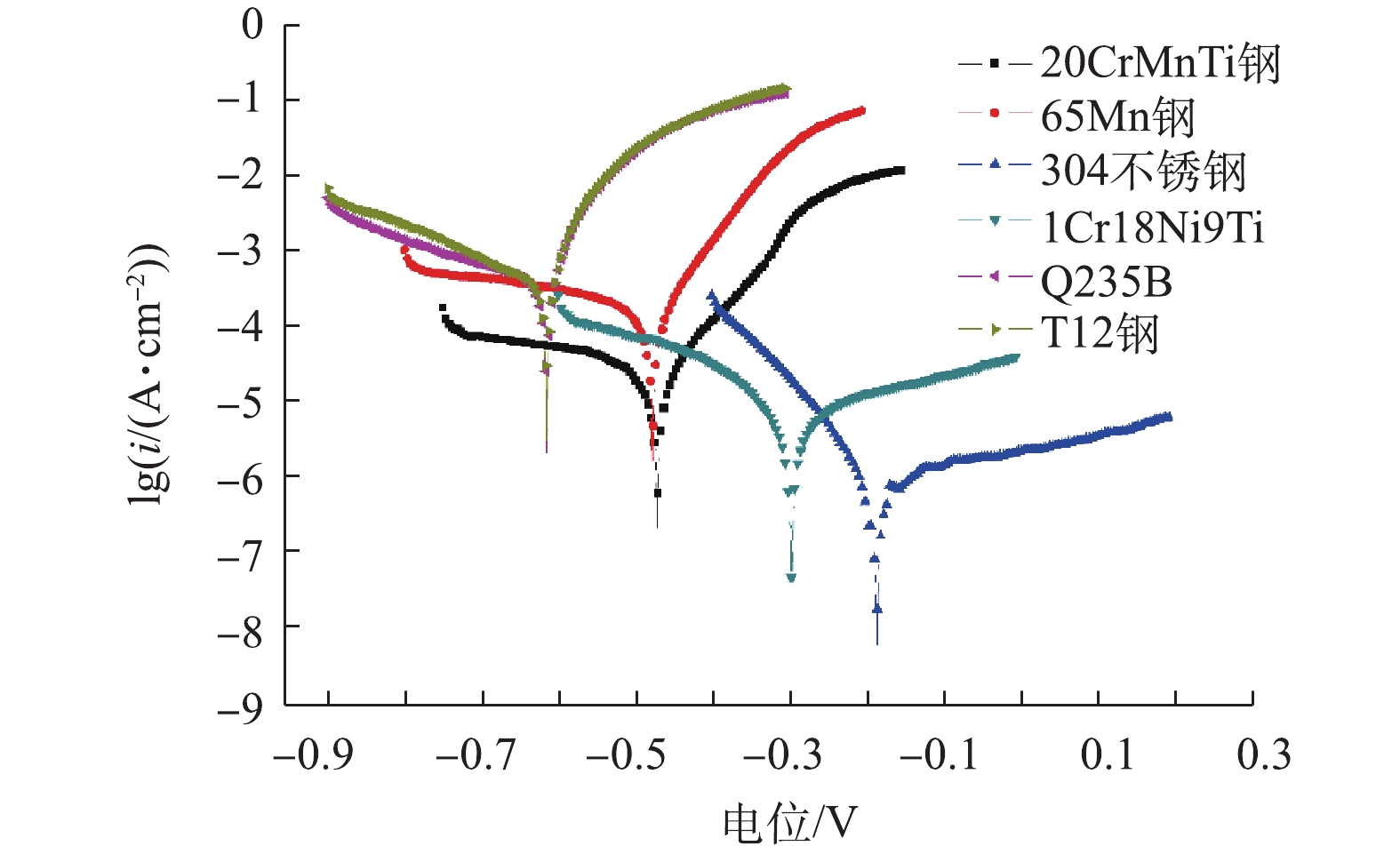
根据正交实验的结果,选择各材质腐蚀速率最小的最佳因素组合,应用电化学极化曲线法,对上述6种材质进行评价。各材质的最佳因素组合如下:1Cr18Ni9Ti钢温度为50 ℃、pH=9、电导率为15 mS·cm−1;T12钢温度为50 ℃、pH=9、电导率为45 mS·cm−1;304不锈钢温度为65 ℃、pH=9、电导率为30 mS·cm−1;65Mn钢温度为50 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1;Q235B钢温度为50 ℃、pH=9、电导率为15 mS·cm−1;20CrMnTi钢的温度为50 ℃、pH=5、电导率为45 mS·cm−1。各材质的相应的电化学参数见表11,极化曲线如图3所示。
金属自腐蚀电位越负,腐蚀倾向越大;其正值越大,腐蚀倾向越小[18]。金属的点蚀电位是指钝化膜开始发生破裂的电位,用于表征材料点蚀敏感性的特征参数之一,当其值为正值,且绝对值越大,表明金属材料对点蚀的敏感性越小。
由表11可知,1Cr18Ni9Ti钢、T12钢、304不锈钢、65Mn钢、Q235B钢、20CrMnTi钢对应的自腐蚀电位(单位V)可知,6种材质的耐腐性能大小为304不锈钢>1Cr18Ni9Ti>20CrMnTi>65Mn钢>T12钢>Q235B钢;1Cr18Ni9Ti钢、T12钢、304不锈钢、65Mn钢、Q235B钢、20CrMnTi钢的腐蚀电流分别为1.72×10−6、7.85×10−4、3.48×10−6、1.58×10−4、8.23×10−4、1.13×10−4 A·cm−2,结果表明,6种材质发生点蚀的敏感性为1Cr18Ni9Ti钢<304不锈钢<20CrMnTi钢<65Mn钢<T12钢<Q235B钢。由图3可知,1Cr18Ni9Ti钢与304不锈钢这2种材质的阴极Tafel斜率大于阳极Tafel斜率,说明这2种材质阴极反应的阻力较阳极反应大,即阴极氧气等的还原反应阻力大,阳极金属的氧化反应难以进行,因而表现为1Cr18Ni9Ti钢与304不锈钢比其他4种材质耐蚀性要好。电厂捞渣机上槽体的实际腐蚀情况也证实了这一点。结果表明,1Cr18Ni9Ti钢和304不锈钢具有良好的耐腐蚀性能,其可满足运行要求。
-
由实验结果可知,T12钢、65Mn钢、Q235钢、20CrMnTi钢等在实验与实际运行中腐蚀速率较高,应采取相应的防腐措施,保证设备和管道的安全运行。目前常用的防腐蚀方法有选用耐蚀金属材料、添加缓蚀剂、涂层防护等。具体防护措施如下。
1)耐蚀金属材料的选用。由实验结果可知,在脱硫废水中选用1Cr18Ni9Ti钢和304不锈钢,可满足系统耐蚀的要求;在经济允许的情况下,可考虑更换材质。
2)缓蚀剂的投加。投加缓蚀剂是相对简便易行的防腐蚀处理方案。缓蚀剂通过在金属表面形成保护膜,阻隔了金属和腐蚀介质而达到缓蚀的效果。缓蚀剂的选择需要综合考虑运营成本。
3)涂层防护。涂层防护是通过在金属表面形成的涂层使得金属免于腐蚀的技术,一般分为金属涂层和非金属涂层两大类。对于水冷壁(T12钢)、上槽体(65Mn钢)、刮板(Q235B钢)、链条(20CrMnTi钢)等长期需要浸泡在水中的设备可采用涂层保护,以有效降低设备运行风险。
2.1. 正交实验结果与讨论
2.2. 腐蚀评价的电化学极化曲线
2.3. 缓蚀策略
-
1) T12钢、65Mn钢、Q235钢、20CrMnTi钢的腐蚀速率大于1.0 mm·a−1,在本研究中属于不适用材质。
2) 1Cr18Ni9Ti钢和304不锈钢的腐蚀速率低于0.1 mm·a−1,属耐腐材质。
3)以T12钢做水冷壁、以65Mn作上槽体部件、以Q235B钢作为捞渣机刮板、以20CrMnTi钢作链条,在原运行条件不能有效耐受高温高盐水溶液对其的腐蚀,需定期检修与更换,或进行涂层防护。
4)以1Cr18Ni9Ti钢作冷灰斗和上槽体、以304不锈钢作关断门和管道能有效降低脱硫废水排入渣水系统后因腐蚀带来的机组运行风险与检修成本。



 下载:
下载: