-
随着城镇化水平的不断提高,地表水体的污染负荷日益加重[1]。人工湿地作为污水处理技术之一[2],利用填料的吸附作用、微生物降解作用和植物吸收等作用去除水中的污染物。人工湿地进行磷的去除主要以填料吸附作用为主[3]。目前,人工湿地中常用的填料主要有砾石[4]、沸石[5]、石灰石[6]、钢渣[7]、粉煤灰砖[8-9]、陶粒[10]等。并且,填料的吸附作用除了与填料本身材质有关,还受到理化性质、吸附时间和pH的影响。因此,选择人工湿地的填料是至关重要的。
本研究结合西北地区地域气候特征,就地取材,以生物炭、混凝土渣为主要研究对象,从吸附动力学和热力学的角度研究了其对
PO3−4 -P的吸附特性。基于以上研究结果,构建了2种类型的潜流人工湿地,加入生活污水,考察了其对生活污水中磷的去除效果,并探究了填料对磷的吸附机理及其稳定性,以期为西北地区人工湿地选材及人工湿地的构建提供参考。
全文HTML
-
以废弃混凝土渣和生物炭为实验填料,将一部分进行研磨过筛,选择20~60目的填料,清洗烘干后备用。混凝土渣取自本地区某建筑工地。生物炭购买于本地区活性炭厂,该生物炭由农业秸秆经风干、破碎及炭化处理制备而成。2种材料物理化学特性[10-15]见表1。
-
在进行动力学实验时,各称取0.500 g填料于150 mL锥形瓶中,加入50 mg·L−1的磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)溶液50 mL,置于(25±1) ℃、转速为150 r·min−1的恒温振荡器中连续振荡,分别在0.17、0.33、0.5、1.0、1.5、3、5、10、18、24 h取出,取上清液过0.45 μm滤膜,测其
PO3−4 -P含量。在进行热力学实验时,各称取0.500 g填料于150 mL锥形瓶中,加入磷浓度为1.0、2.0、4.0、8.0、12.0、20.0、40.0、60.0 mg·L−1的KH2PO4溶液50 mL,置于(25±1) ℃、转速为150 r·min−1的恒温振荡器中振荡,由所得的平衡时间,取上清液过0.45 μm滤膜,测其磷含量。在15 ℃和35 ℃下使用同样的方法进行实验。
PO3−4 -P的测定采用钼酸铵分光光度法,具体操作步骤参见文献中的方法[16]。 -
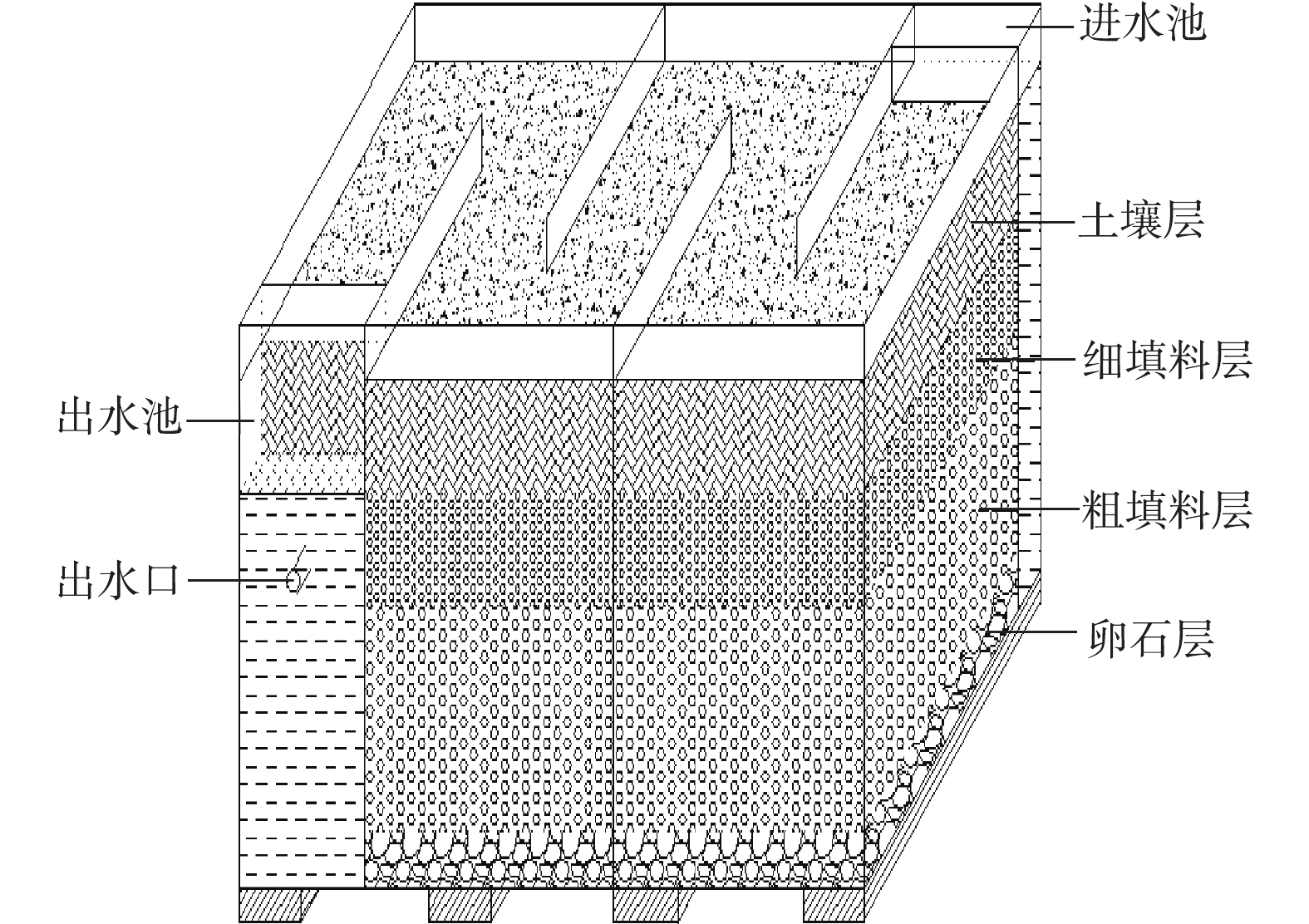
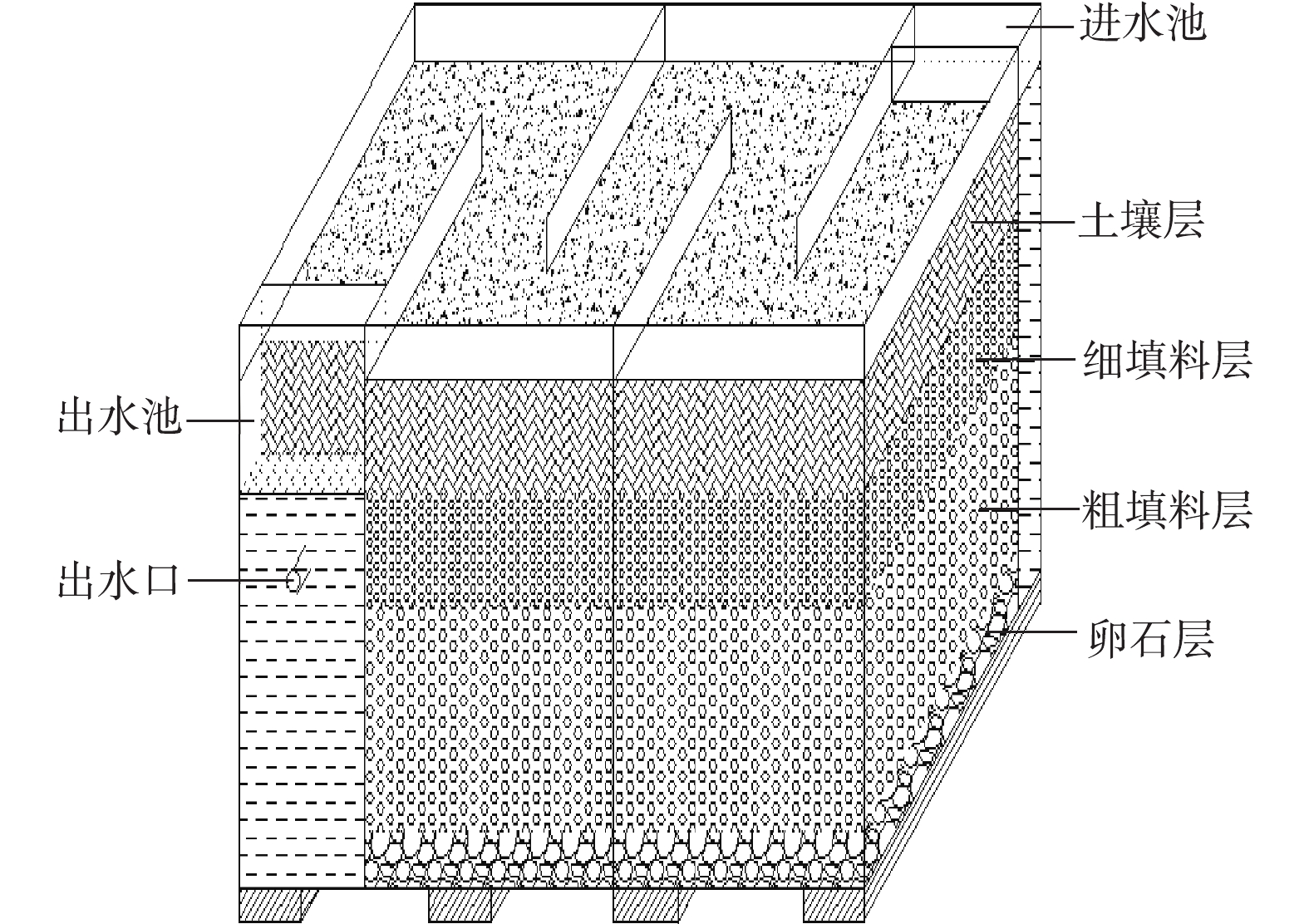
采用10 mm厚的有机玻璃,构建2种长宽高为100 cm×60 cm×50 cm的静态潜流人工湿地,其可处理污水容积为20 L。在垂直方向,湿地自下到上由厚度为5 cm的下垫层、30 cm填料层(下部为20 cm粗填料层,上部为10 cm细填料层)和10 cm土壤层构成,如图1所示。下垫层由粒径为15~25 mm的鹅卵石构成,粗填料层和细填料层分别由粒径为6~10 mm和3~5 mm的填料铺设而成,土壤层为过10目筛的均匀黄土。在水平方向,共设置5个长宽高为60 cm×20 cm×50 cm的隔室,进水来自居民生活污水,由湿地进水池均匀投配,经填料层到达湿地出水池后由收集管排出。水中pH为7.2~7.8,溶解氧为3.4~3.8 mg·L−1,
PO3−4 -P浓度为3.8~5.9 mg·L−1。 -
构建人工湿地,进行驯化培养,待运行稳定后,采用间隔配水方式。由图1可知,湿地有效表面积为0.6 m2,有效过流体积为0.02 m3,实测平均水力停留时间为24 h,计算获得有效水力负荷为0.034 m3·(m2·d)−1[17]。实验总计重复3次,控制水温为10~12 ℃,分别在6、12、24、36、48、60、72、84、96、108、120 h追踪测定出水磷含量,分析其运行参数和稳定性。
-
填料对磷的动力学吸附过程一般用准一级、准二级动力学模型、颗粒内扩散模型和Elovich模型进行拟合分析,如式(1)~式(4)所示。
式中:Ct为t时刻吸附溶液中
PO3−4 -P平衡质量浓度,mg·L−1;Qt为t时刻基质对PO3−4 -P的吸附量,mg·g−1;a为动力学常数,mg·L−1;k1为准一级动力学模型速率常数,mg·(L·h)−1;k2为准二级动力学模型速率常数,mg·(g·h)−1;k3为颗粒内扩散模型速率常数,mg·(g·h)−1;k4为Elovich模型速率常数,mg·(g·h)−1;t为反应时间,h。填料对磷的等温吸附过程一般用Langmuir和Freundlich等温曲线经验方程来描述,如式(5)和式(6)所示。
式中:Q为基质对
PO3−4 -P的吸附量,mg·g−1;Qm为基质对PO3−4 -P的饱和吸附量,mg·g−1;Cf为吸附平衡后滤液中PO3−4 -P浓度,mg·L−1;KL为Langmuir吸附特征常数,mg·L−1;KF为Freundlich特征常数,mg·g−1;n为Freundlich特征常数,g·L−1。研究结果均采用OriginPro8.0及Excel 2019软件进行数据显著性分析。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 实验方法及指标测定
1.3. 人工湿地的构建
1.4. 人工湿地运行效果实验测定
1.5. 数据分析方法
-
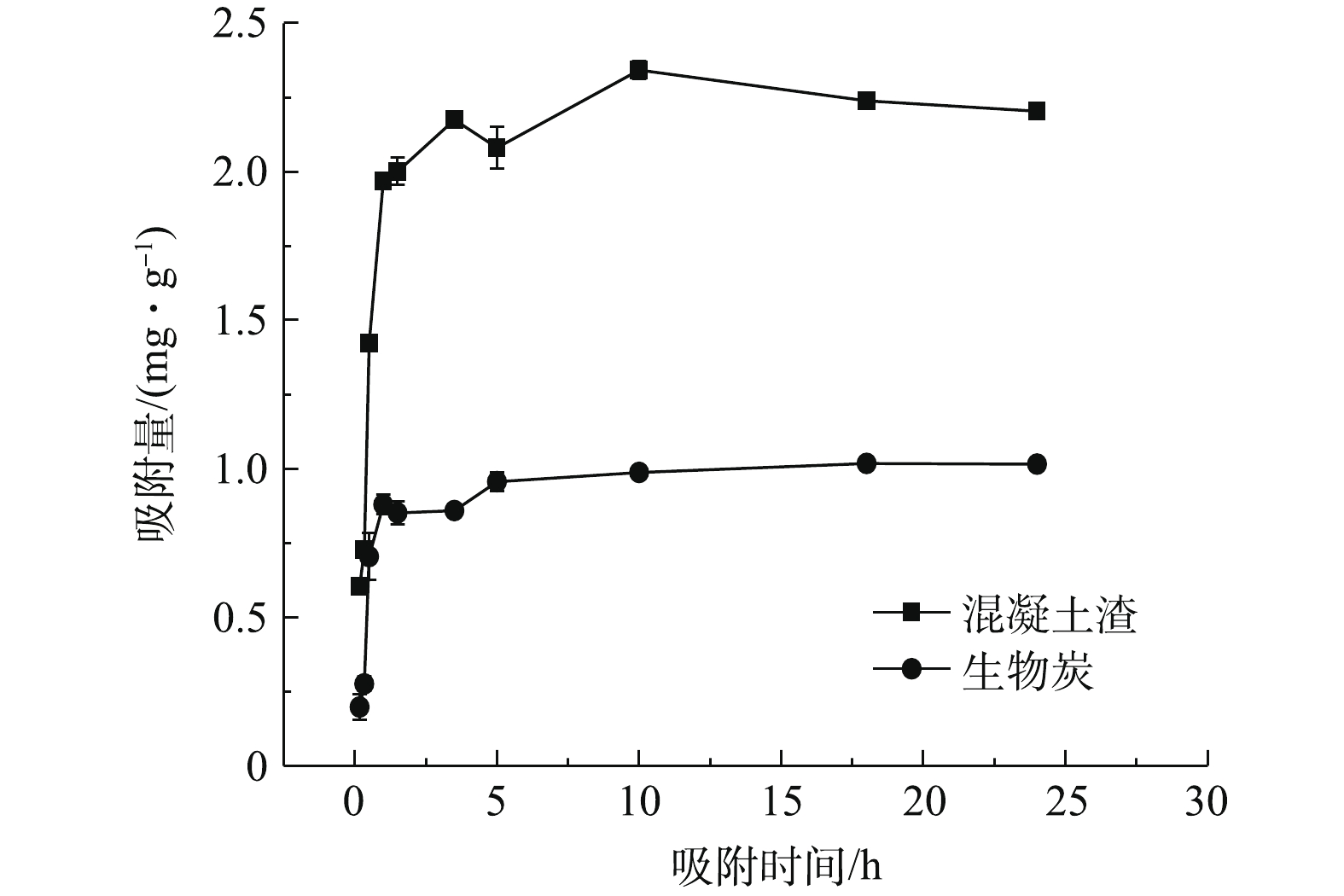
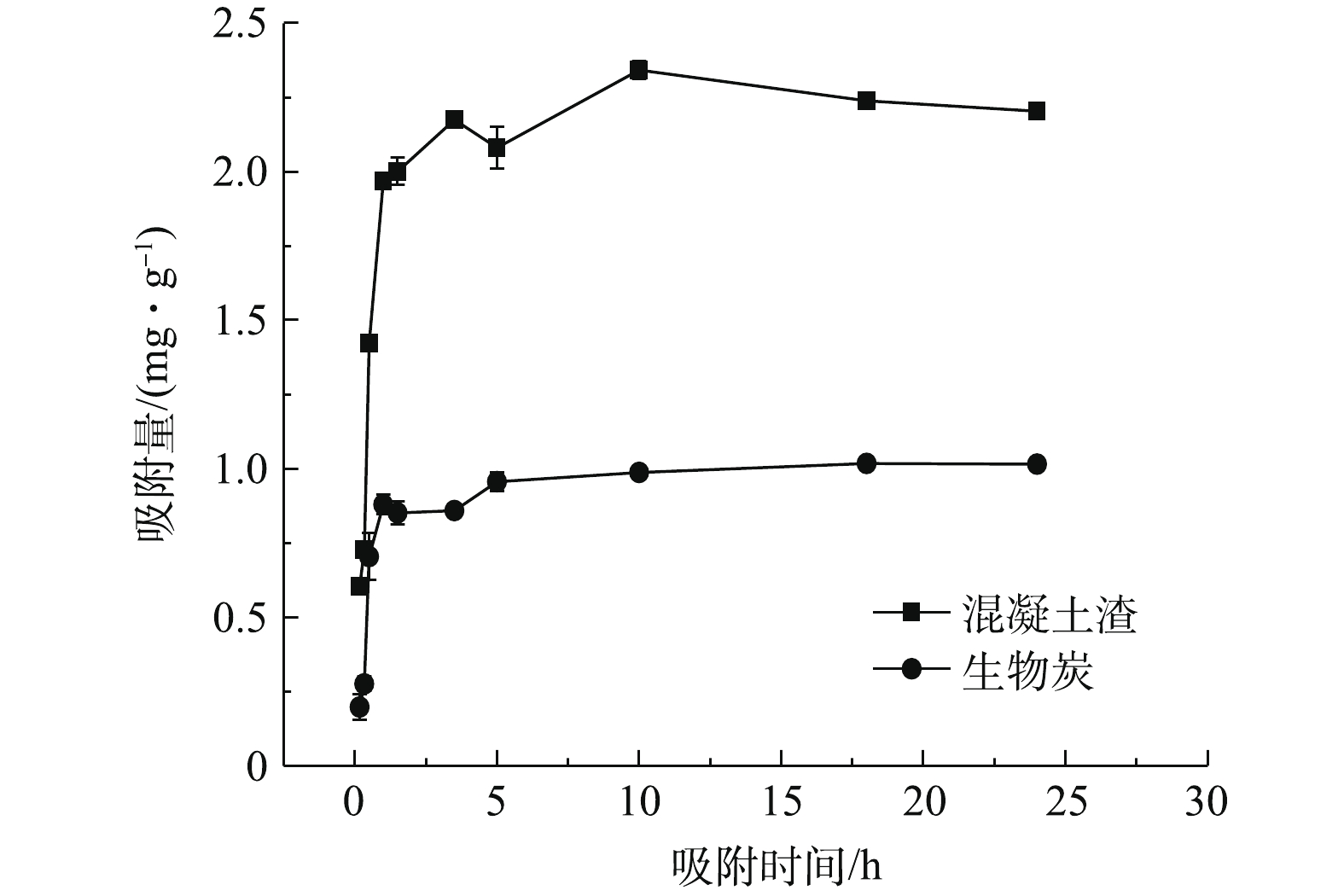
基于浓度为30 mg·L−1的KH2PO4的进水条件,实验设3个平行样,2种填料对
PO3−4 -P的吸附动力学实验结果如图2所示。混凝土渣和生物炭基质对磷的吸附量随着时间的延长而不断增加,在吸附时间为18 h时,2种填料均达到吸附的最大值,可以认为此时吸附达到平衡。这与张修稳等[12]在填料对磷的吸附特性比较中的研究结果相似。整体来看,混凝土渣的最大吸附量为2.206 mg·g−1,是生物炭最大吸附量的2.16倍。分析其原因为,填料除磷不仅和物理吸附有关,还与金属元素Al、Ca、Mg、Fe有关[18-19]。由表1可知,混凝土渣钙含量高达68.52%,这是因为混凝土渣在制作过程中需要加入大量的石灰石,使其具有丰富的氧化钙,而Ca元素容易磷酸根离子发生化学反应,形成钙结合态磷酸盐(Ca-P)沉淀,从而降低水中的磷含量[20],所以混凝土渣对磷的吸附量高于生物炭。由表1可知,生物炭虽然含有金属元素较少,但是其具有较高的比表面积,使其有利于物理吸附,以去除水中的磷。用准一级动力学方程、准二级动力学方程、颗粒内扩散力学方程和EIovich方程对磷的吸附动力学进行拟合,结果如表2所示。2种填料在动力学吸附过程中EIovich方程模拟拟合效果最佳,这说明在混凝土渣和生物炭对
PO3−4 -P的吸附过程中,主要包含了表面吸附、颗粒内部扩散和外部液膜扩散等多种吸附过程[9]。在EIovich方程中,k4是吸附速率随时间变化快慢的指标,其值越大,表示吸附速率下降越快。由表2可知,混凝土渣的吸附速率随时间下降的比生物炭缓慢,即混凝土渣对生活污水中磷具有更好的持续效应。 -
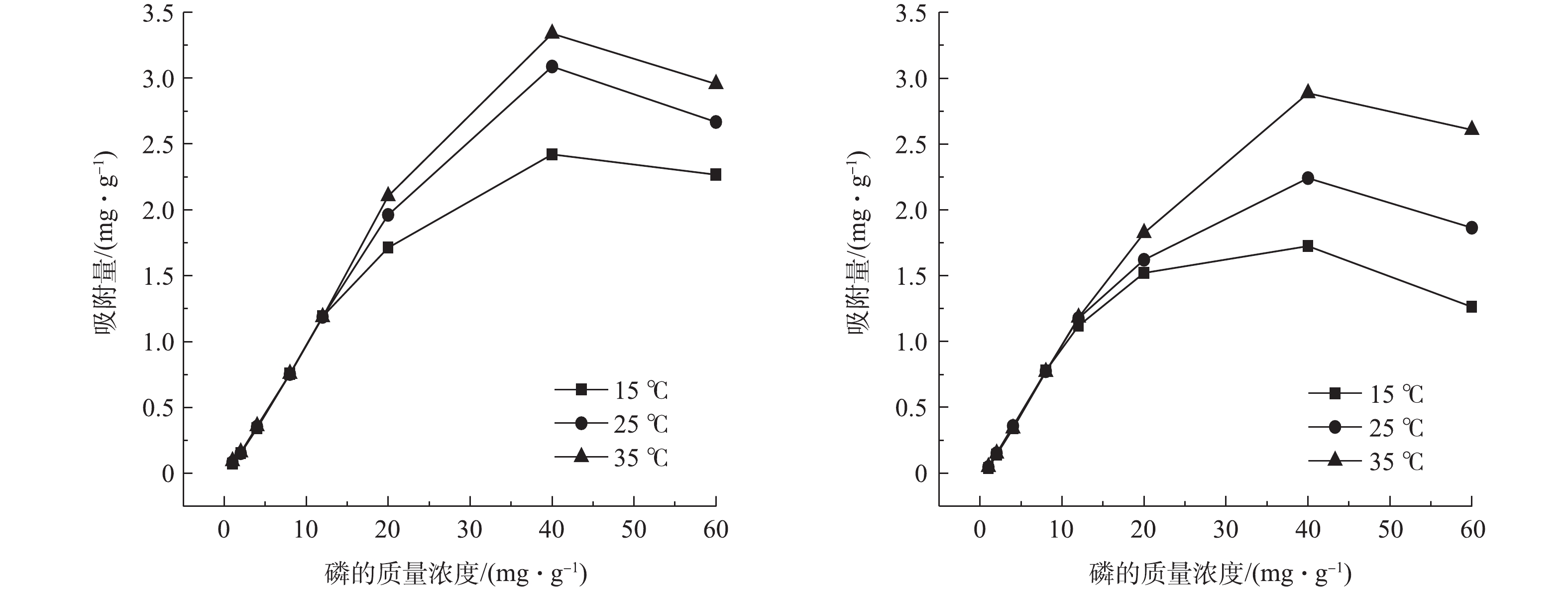
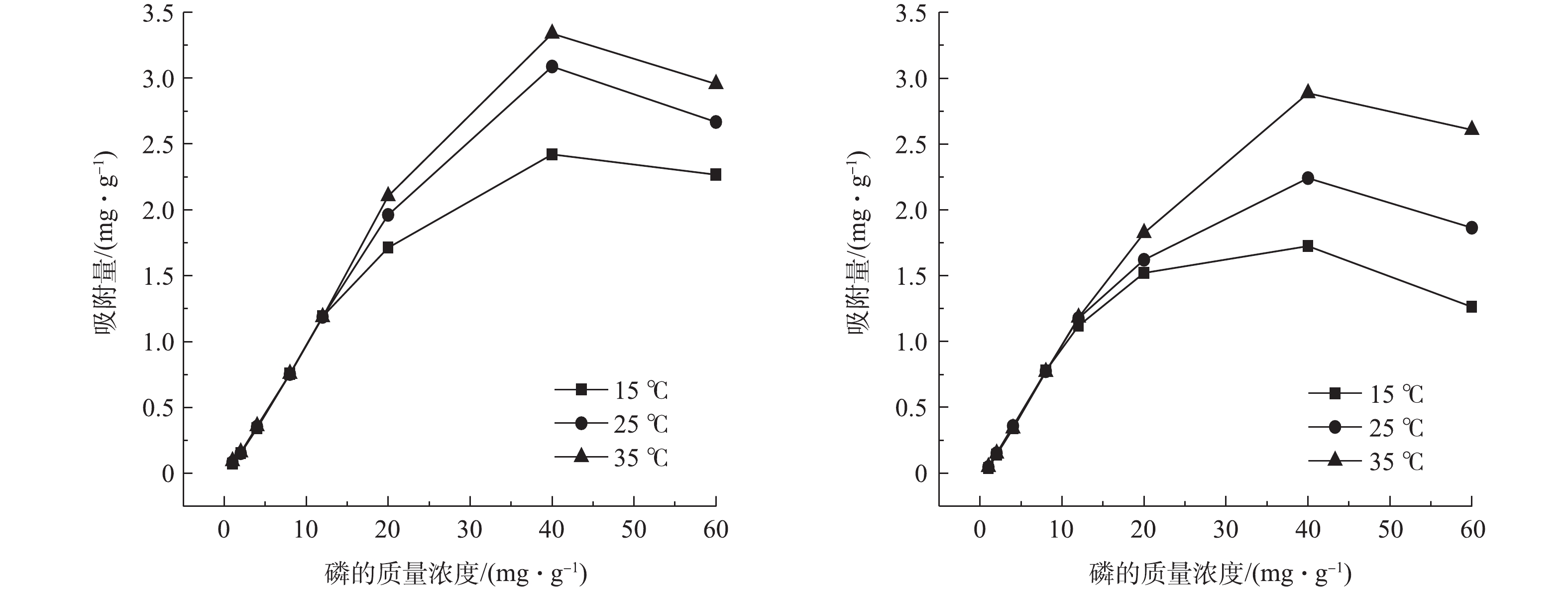
基于不同磷酸盐浓度,填料对
PO3−4 -P等温吸附实验结果见图3。由图3可知,随着温度的升高,在不同磷酸盐初始浓度胁迫下,吸附量整体呈上升趋势。这表明温度的升高对基质吸附有促进作用,同时,也表明混凝土渣和生物炭的吸附过程是吸热过程。混凝土渣和生物炭的吸附变化均呈现2个阶段:在第1阶段,2种填料均呈现急速上升的趋势,随着磷酸盐浓度的增加,吸附量开始快速增加;第2阶段中,当磷酸盐浓度达到40 mg·L−1时,2种基质的吸附量达到最大,吸附速率变得缓慢,且呈下降趋势。在磷酸盐浓度达到12 mg·L−1以上,混凝土渣较生物炭具有更好的吸附效应。这是由于混凝土渣具有较高的钙含量,使混凝土渣在磷的吸附过程中既有物理吸附过程,又伴有化学吸附过程。崔理华等[21]在人工湿地填料对磷的吸附特性研究中也证实了这一点,即含钙量多的填料,易与水中的磷生成难溶性盐,从而去除水中的磷。用Langmuir和Freundlich方程拟合混凝土渣和生物炭基质对磷的等温吸附效应,获得拟合值,结果如表3所示。通过比较2种等温方程的相关系数R2,发现混凝土渣对磷的吸附更符合Freundlich方程。这说明混凝土渣对磷的吸附既有单层吸附,又有多层吸附,且表面是非均匀的。另外,其非线性指数n大于1,表明混凝土渣的吸附容易进行,且为不可逆过程[22]。这进一步解释了混凝土渣对于磷吸附伴有化学吸附特征。对生物炭来说,Langmuir方程拟合效果更好,这说明生物炭对磷的吸附多为单分子层吸附。其中,KL·Qm的大小反映了固液体系中填料吸附溶质的缓冲能力的强弱[23],其值越大,表示缓冲能力越强。由表3可知,混凝土渣在磷的去除效应中具有更好的稳定性。
-
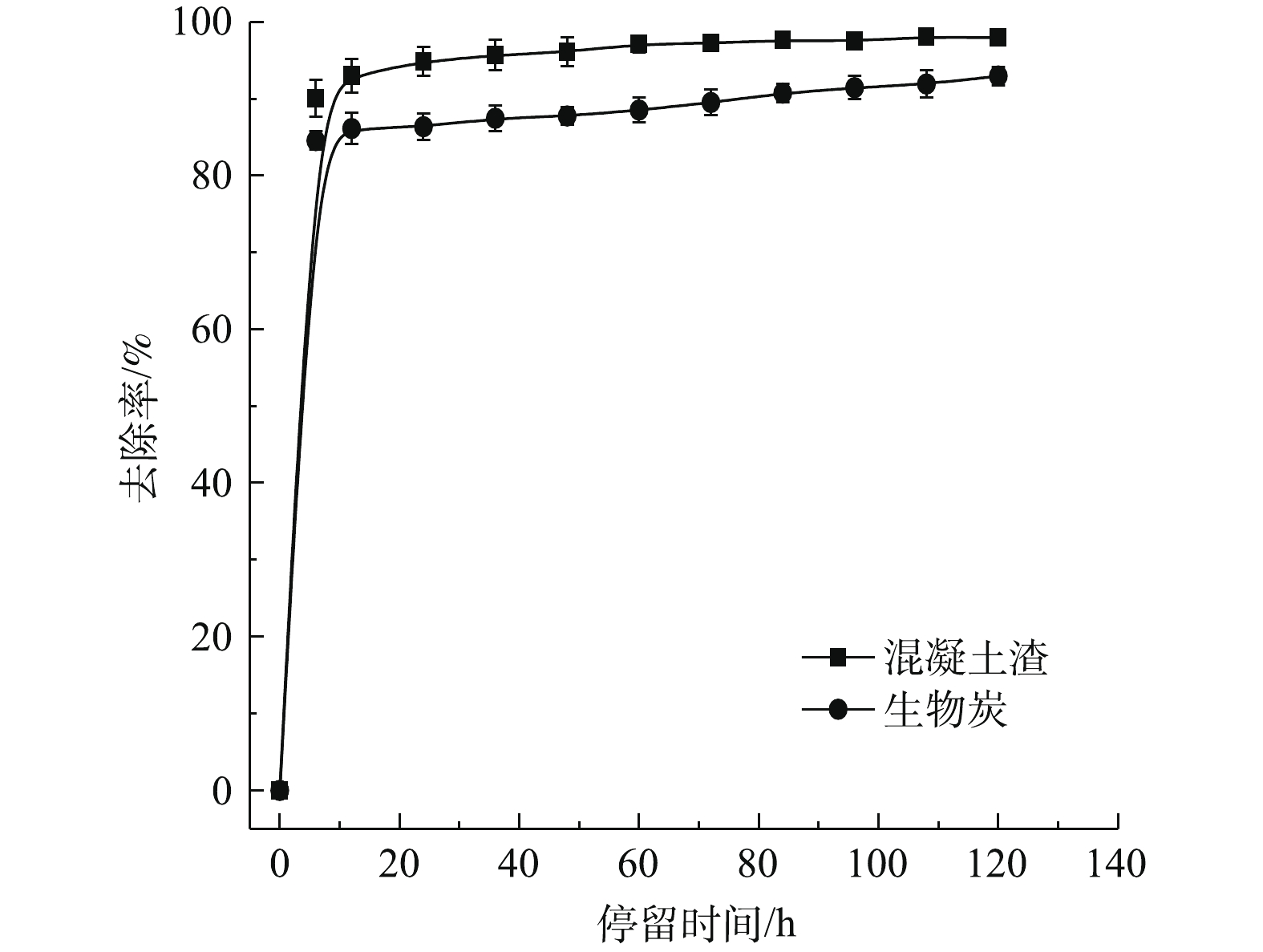
本研究构建了2种长、宽、高为100 cm×60 cm×50 cm的静态潜流人工湿地模型,以进行生活污水处理研究,其结构如图1所示。本研究首先对所建人工湿地进行驯化处理,待湿地模型运行稳定之后,然后探究HRT对
PO3−4 -P的去除效果。结合西北地区气候特征,湿地进水水温为10~12 ℃左右、pH为7.2~7.8、溶解氧为3.4~3.8 mg·L−1、水力负荷为0.034 m3·(m2·d)−1、初始加入生活污水PO3−4 -P浓度为3.8~5.9 mg·L−1。对3次重复实验所得去除率取平均值,进而绘制潜流人工湿地对PO3−4 -P的去除率随HRT的变化曲线。如图4所示,随着HRT的延长,湿地对PO3−4 -P的去除率迅速提高,并始终保持呈正相关性,当HRT达到24 h时,潜流人工湿地中的磷的去除效率增加幅度开始减慢。此时,混凝土渣湿地和生物炭湿地对磷的平均去除率分别为94.86%和86.37%。当HRT≥24 h时,湿地中填料对磷吸附速率趋于稳定。此时,由于水中溶解氧源于进水,溶解氧被消耗减少,聚磷菌活性降低,对磷的积累能力降低,反应速率变慢,使填料对污染物的吸附趋于平衡。综上所述,本研究选择24 h为最佳HRT,综合考虑2种人工湿地的除磷效果和经济成本等因素,认为宜选择混凝土渣为填料的人工湿地来处理西北地区生活污水中的磷。
2.1. 填料对磷的吸附动力学特性
2.2. 填料对磷的等温吸附特性
2.3. 2种填料在潜流人工湿地对磷的去除效果比较
-
1)混凝土渣和生物炭对磷的静态吸附平衡时间均为18 h,且混凝土渣的最大吸附量是生物炭最大吸附量的2.16倍。动力学吸附过程拟合结果表明,EIovich模拟方程对2种填料的拟合效果最佳,这表明2种填料对
PO3−4 -P的吸附有表面吸附、颗粒内部扩散和外部液膜扩散等多种吸附过程。混凝土渣的等温吸附特性与Freundlich方程拟合更好,生物炭更符合Langmuir方程,这表明混凝土渣对PO3−4 -P吸附既有单层吸附,又有多层吸附,表面是非均匀的,而生物炭对PO3−4 -P的吸附多为单层吸附。2)动力学吸附实验和等温吸附实验结果表明,混凝土渣对
PO3−4 -P的吸附既有物理吸附亦有化学吸附。3)与以生物炭为填料的湿地相比较,以混凝土渣为填料的静态潜流人工湿地除去污水中的磷效果更好。在HRT为24 h时,混凝土渣湿地和生物炭湿地对
PO3−4 -P的去除率分别达到了94.86%和86.37%。4)选用混凝土渣作为潜流人工湿地填料,能更好地达到有效处理西北地区农村生活污水中磷的目的。















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: