-
近年来,随着我国教育、科研快速发展,高等院校、科研院所、科技企业或工业园区每年实验室废液产生量快速增长,成为环境污染的重要风险之一[1]。实验室废液污染物组分、浓度与开展的研究工作有关,成分复杂,以其“腐蚀性、爆炸性、高毒性”等危害性而被纳入《国家危险废物名录》。实验室废液有较大的环境风险,且由于污染物种类、含量、性质各异,处理处置困难,目前主要通过暂存或委托具有危险废物处置资质的企业进行废液收集、转运与处置[2]。上述处理处置模式导致科研机构危险废液处置费用逐年增加,难以维系。此外,部分省区危险废物处置能力近乎饱和,且可能由于某些废物处置资质受限问题(如含汞废物)而导致废液长期贮存,产生极大安全隐患。研制高效、可行、稳定的实验室废液减量化处理与达标排放技术和设备,对于创新性解决我国实验室废液污染问题、控制环境风险具有重要意义。
依据废液理化特性,实验室废液一般可分为无机类废液、有机类废液等[3],具体包括废溶剂、有机废液和重金属-有机复合类的酸/碱废液。其中,高浓度有毒有机废液、重金属-有机物络合物的废液处置极其困难,解决此类废液处理难题的关键在于高毒组分降解/脱毒和多元重金属-有机络合物破络-解络。酸/碱废液常采用扩算渗析回收法[4]、中和法、直接稀释法处理,重金属废液处理方法包括化学沉淀法[5]、铁氧体法[6-7]、电化学法[8]和吸附法[9]等,有机废液处理方法有生物法、高级氧化法[10-12]、溶剂萃取法[13]和焚烧法[14]等。事实上,单一处理方法并不能实现废液稳定处理与达标排放,“分类预处理+物化处理+生化处理”工艺、“螯合-混凝沉淀”方法可使处理出水主要指标达到市政污水纳管排放标准[12-13]。此外,依据《危险废物鉴别标准通则》,实验室废液在处理过程中产生的污泥、残渣仍属于危险废物,处置费用仍相对较高,但前人研究较少考虑处理过程产生的危险废物污泥及其安全处置问题[15]。因此,研究建立实验室废液处理与减量化、达标排放与环境风险控制的技术方法具有重要意义。
全文HTML
-
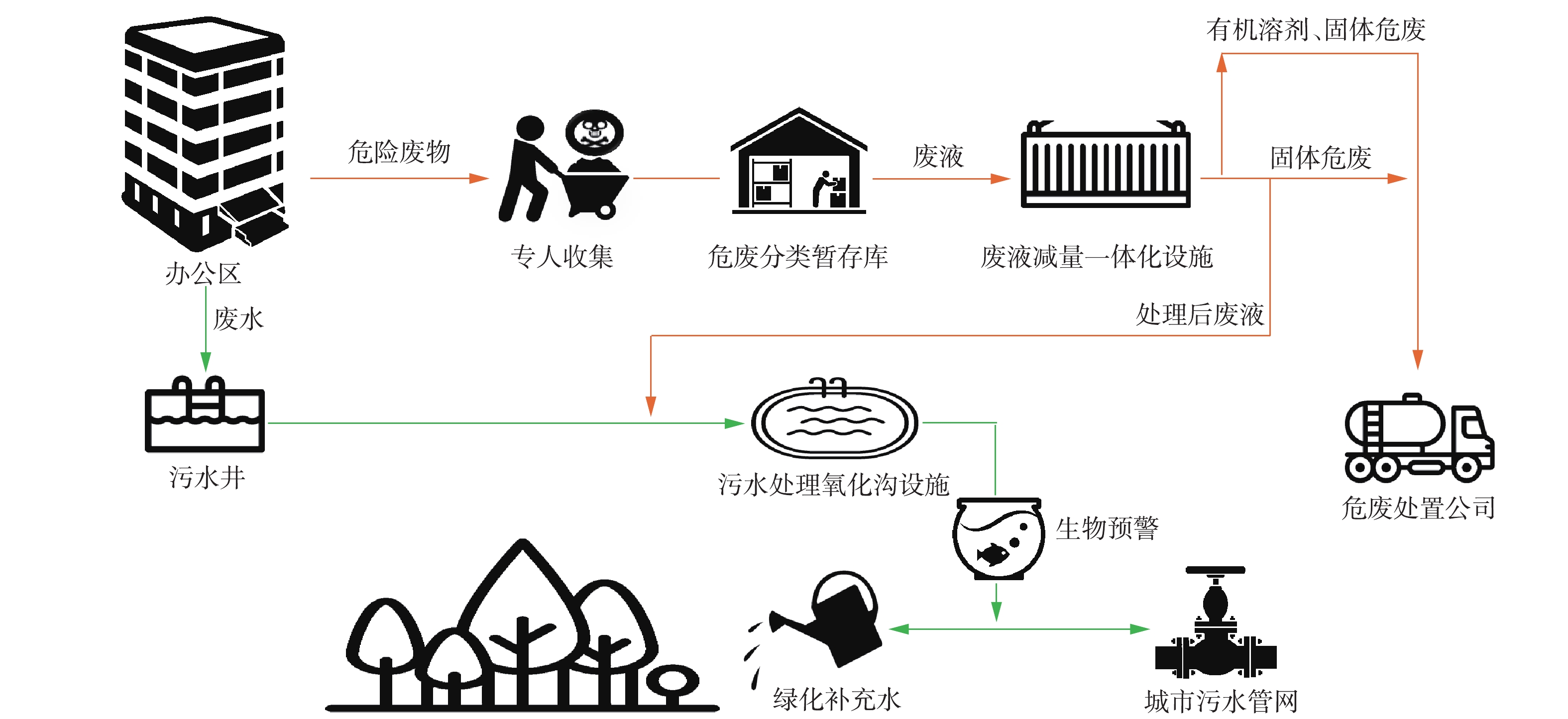
本研究以北京市某研究所收置的实验室废液为对象,2018年该研究所外委处置的危险废物近50 t,废液年产量增长率约为15%。结合实验室废液分类管理办法,提出“分类预处理+二级处理+末端吸附”的实验室废液一体化处理与减量化工艺思路,实现处理出水I类污染物浓度达到《水污染物综合排放标准》(DB 11/307-2013)“车间或生产设施废水排放口”的限值要求。废液处理工艺达标出水可纳入社区中水净化与回用系统(图1),实现废液减量化、无害化和资源化,最终系统排放出水COD、氮、磷、重金属等指标可达到北京市《水污染物综合排放标准》(DB 11/307-2013)纳管标准要求。
-
不同实验室废液依据危险废物标签信息,可大致分为疏水有机溶剂类废液、亲水有机物废液、无机废酸/碱、重金属废液、专项废液等,不同实验室收集的同类废液可混合后进行统一处理。含有I类有机污染物的废液不在此工艺处理范围内。
-
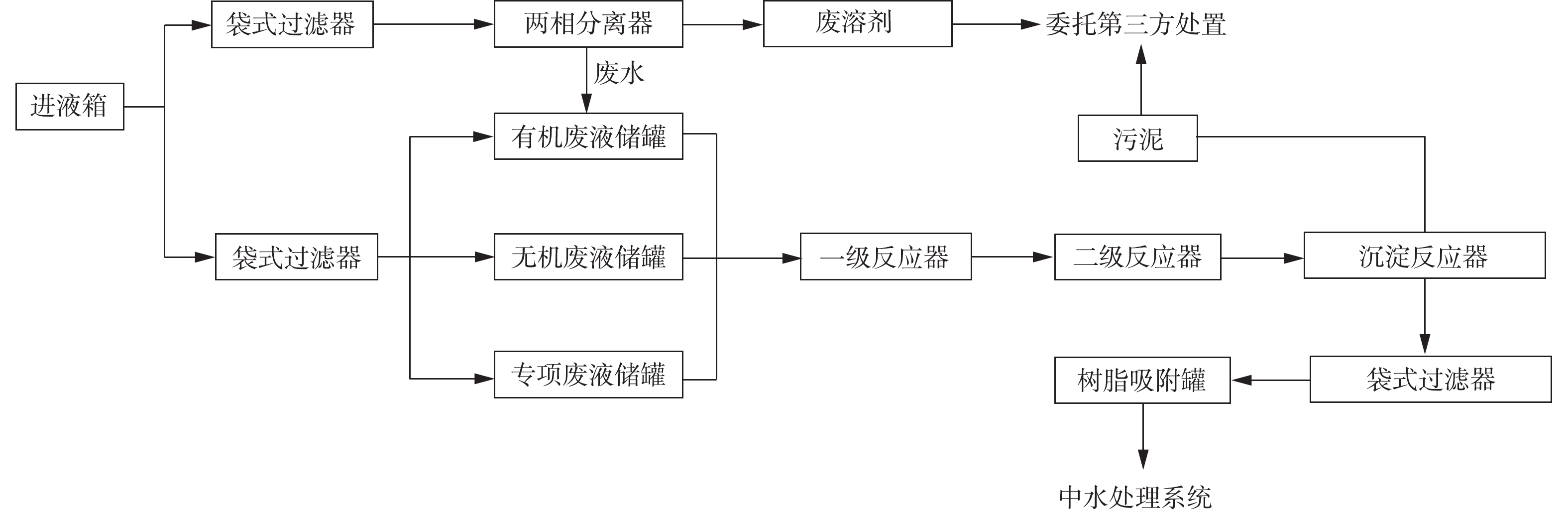
“分类预处理+二级处理+末端吸附”实验室废液一体化降危减量化处理工艺流程如图2所示。以实验室废物标签信息为基础,结合水质快速分析仪,可快速对所收置的废液进行定性分析,不同类别实验室废液采取不同的处置思路。
疏水有机溶剂废液包括疏水溶剂相和废水相2部分。废液首先通过袋式过滤器除杂,随后进入两相分离器内依据相似相溶原理实现溶剂相和废水相的萃取分层,分层后的疏水溶剂排出系统委托第三方转运处置,也可采取焚烧、湿式氧化等处理单元;废水排入亲水有机物废液的储罐进行后续处理。
亲水有机物废液含油类、重金属、有机物等污染物。废液首先在袋式过滤器除杂后,随后进入一级反应器完成乳化液破乳、络合态重金属破络/解络、难降解有机污染物氧化等过程,出水废液进入二级反应器进行化学沉淀,之后进入沉淀反应器固液分离去除重金属等I类污染物,产生的污泥经压滤脱水后委外处置,滤液则经袋式过滤器过滤后进入树脂吸附单元进一步去除微量强络合态重金属。
无机废液主要含强酸、强碱和重金属等污染物,废液与亲水有机废液共用处理单。废液首先经袋式过滤器除杂后,随后进入一级反应器进行重金属破络/解络,出水进入二级反应器进行化学沉淀,然后进入沉淀反应器固液去除重金属等I类污染物,产生的污泥及滤液的处理方法同上。
专项废液主要是某些组成性质较稳定、数量较大的一类废液。如含氰化物的废液和测COD所用的哈希(HACH)预制试剂。废液与亲水有机废液共用处理单元,首先经袋式过滤器除杂后,废液进入一级反应器进行银离子与汞离子化学沉淀、六价铬还原、氰化物破氰等过程,出水进入二级反应器进行化学沉淀,之后进入沉淀反应器进行固液分离。产生的污泥及滤液处置方法同上。
根据实验室废液管理和处置特点,废液需分类处理,从而可共用处理单元,减少占地面积,整个系统采取间歇运行模式,利用PLC自动控制确保设备稳定运行。实验室废液成分、含量、性质的复杂性,导致其难以利用在线检测仪器分析数据进行实时设备运行优化,这增大了设备运行操作和参数调控(如反应时间、投药量等参数)的难度。因此,在调试过程中,须确定对污染物去除范围较大、适应性较强、可实现稳定达标的运行参数,作为设备推荐的最优运行参数。最后,整个系统设置末端吸附单元,采用串级有机物吸附树脂、重金属鳌合树脂等,以确保系统出水中汞、镍、铅、钴等重金属浓度达到设计标准要求,然后再纳入社区中水处理系统,经混合后,利用生物处理单元,进一步去除有机物、氮磷等污染物,使废水最终处理回用或排放。
-
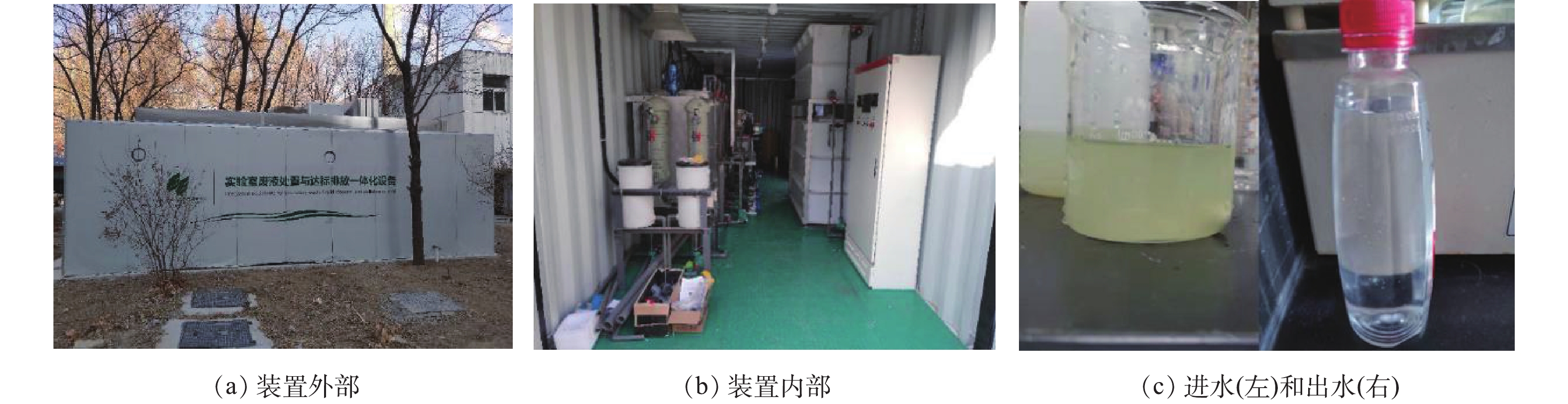
实验室废液降危减量一体化设备设计处理能力为1 t·d−1,所有处理单元置于标准集装箱(长×宽×高= 9 200 mm×2 700 mm×2 400 mm)中。一体化设备包括10个单元。
1)进液箱1个,有效容积3.5 L,配置1台离心泵。
2)袋式过滤器2个,配置2台离心泵。
3)两相分离器1个,配置1台机械搅拌器。
4)废液储罐3个,有效容积500 L,配置2台流量计和2台离心泵;储罐内设液位传感器。
5)机械反应器2个,有效容积500 L,配置2台搅拌器;储罐内设pH、ORP和液位传感器。
6)固液分离反应器1个,配置1台气动隔膜排泥泵,内设上清液溢流储存箱,储罐内设液位传感器。
7)吸附罐进水预处理器1个,配置2台离心泵。
8)树脂吸附罐4个,串联连接,配置自动再生反洗。
9)树脂再生液储罐1个。
10)板框压滤机1台,板框面积5 m2。
-
COD采用快速消解分光光度法测定,Ag、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni和Pb等重金属浓度采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-AES)测定,As、Hg等重金属浓度采用电感耦合等离子体-质谱法(ICP-MS)测定,pH、氧化还原电位(Eh)和电导率等指标采用便携式多功能水质测定仪进行测定。
2.1. 废液种类
2.2. 分类处置工艺设计
2.3. 净化单元
2.4. 分析方法
-
实验室废液降危减量一体化设备经调试后投入3个月试运行(图3)。在试运行过程中,设备稳定,出水I类污染物浓度可稳定达到《北京市水污染物综合排放标准》(DB 11/307-2013)中《车间或生产设施废水排放口标准》的限值要求(见表1)。系统处理出水储存于排水储罐,检测达标后纳入社区中水处理系统。
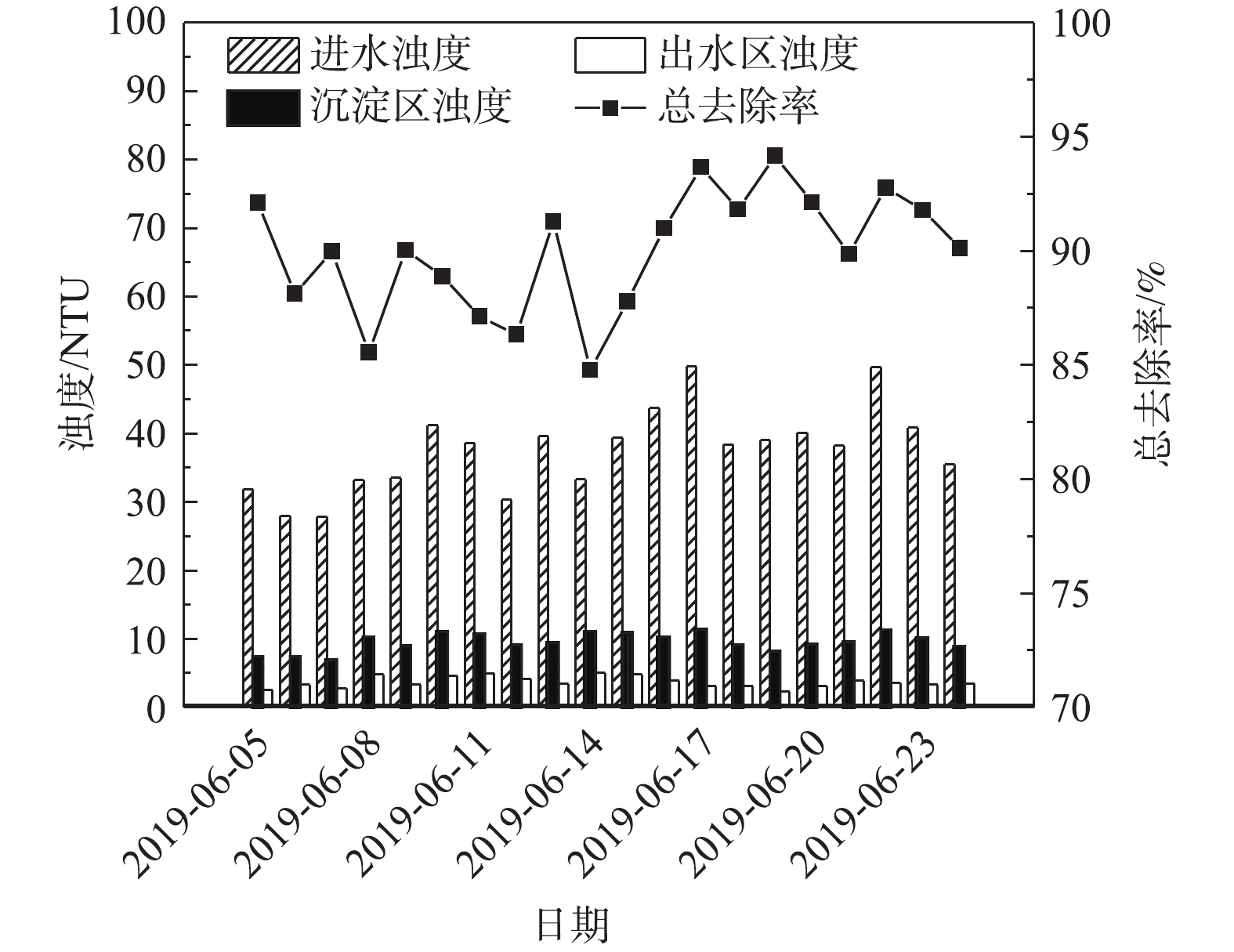
如表1所示,对比2个批次实验室废液进、出水水质,可以看出,混合废液酸性较强,中和用碱量较大;在总Cr、Ag2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Hg2+和Pb2+等重金属指标中,废液混合后浓度最高的I类污染物为总Cr,浓度为336 mg·L−1。对比而言,实验室废液中重金属浓度远低于传统工业危险废液,其重金属含量一般在0.1%以上。上述结果表明,对实验室废液首先开展产废园区的内减量化处理与环境风险控制,然后再将所产生的残渣委托第三方危险废物处置企业进行最终处置,这对于降低产废单位处置成本和减轻第三方危废处置企业负荷是可行的。
-
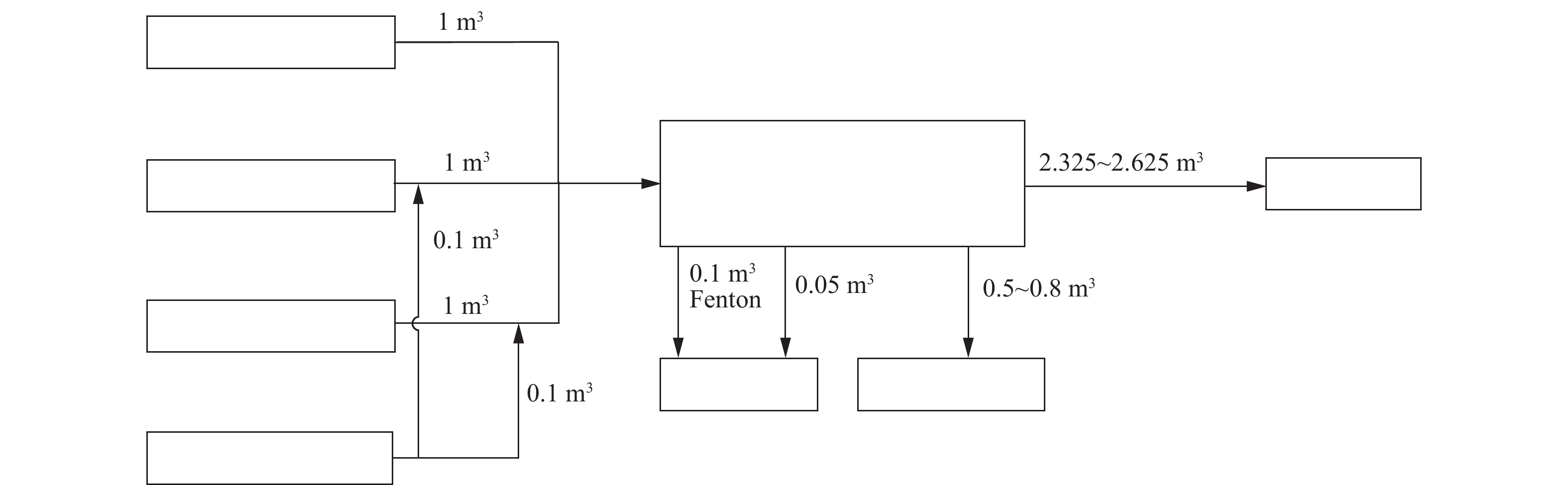
疏水有机溶剂类废液含水率为20%~50%,波动较大。在亲水性有机废液处理过程中,投加各类药剂溶液体积约占废液总体积的10%,且Fenton氧化过程污泥产量较大,压滤后污泥含水率约50%,为原废液体积10%左右。在无机废液处理过程中,投加各类药剂溶液体积约为废液总体积的10%,污泥产量约为废液体积的5%(含水率50%)。综上分析可知,通过处理后,疏水性有机废液可减量50%~80%,亲水性有机废液和无机废液可减量90%。实验室废液减量化处置过程中物料衡算如图4所示。
-
该装置运行成本主要包括电费、药剂费和污泥外委处置费等,其中污泥与废液的委托处置费接近。采用实验室废液降危减量一体化装置,1 t亲水性有机废液和无机废液处理时间约为8 h,处置成本较委托处置降低85%。这对于产废单位降低废液处置成本、确保危废安全无害化处置、控制环境风险具有重要意义。
3.1. 处理效果分析
3.2. 物料平衡分析
3.3. 经济性分析
-
1)实验室废液混合后重金属等I类污染物浓度较传统工业危险废液低。对实验室废液采取减量化处理,有机溶剂、含I类有污物废液及处理后的污泥等交由第三方危险废物处置企业处置,可显著降低产废单位的处置成本,或可减少第三方处置企业的处理压力。
2)“分类预处理+二级处理+末端吸附”的废液降危减量一体化处理工艺可实现I类重金属污染物稳定达到生产设施排放口标准,可有效控制实验室废液的环境风险。
3)相对于直接委托处置,直接减量化处置综合成本降低85%,具有很好的经济效益和环境效益。



 下载:
下载: