-
在过去几十年中,农业和工业活动以及城市社区的污水导致了严重的水源污染[1]。面对越来越多的污染,衍生了各种新兴的污水处理技术。以电化学为基础的电化学高级氧化工艺受到了人们的青睐。在电化学高级氧化体系中可以通过阳极直接氧化、阴极还原或产生具有强氧化活性的物质,如羟基自由基(∙OH),将有机污染物矿化为CO2和H2O等[2-4]。但是在传统的电化学体系(二维电极体系)中存在电流效率低、电极面积小等缺点,三维粒子电极体系应运而生[5-6]。三维粒子电极是在二维电解槽中加入粒子电极,以此形成三维粒子电极系统。粒子电极的加入,可以通过增大电化学反应的面积,或形成一系列微电解池提高污染物去除效率,因此粒子电极的选择对于三维电极体系至关重要[7-8]。
蒙脱石是土壤中一种常见的黏土矿物,是膨润土的主要组成成分[9]。蒙脱石资源储量丰富,价格低廉。蒙脱石矿物表面常带有负电荷,为中和负电荷达到电荷平衡,在矿物层间吸附了大量的水合阳离子,使得层间具有大量的可交换阳离子[10-11]。因此,蒙脱石层间域除了具有交换吸附等性质,还具有层间柱撑的特性。以铁对蒙脱石进行改性作为催化剂已经有许多的研究报道,但是到目前为止,大部分研究更多集中于光-Fenton体系或作为非均相催化剂应用于Fenton体系中,将其作为粒子电极应用于电化学体系尚未见相关报道[9, 12-13]。而且铁改性蒙脱石多以粉末状作为催化形式,使用后回收困难,这限制了其应用[14]。因此,研究铁改性蒙脱石作为粒子电极的性能有助于拓宽污染物光/电复合降解体系的应用,解决催化剂难回收的问题,具有一定的实用意义。
本研究以铁改性蒙脱石(Fe-Mt)制备三维粒子电极,首先通过SEM-EDS和XRD表征对粒子电极进行了形貌与物相分析,并探究了pH、粒子电极投加量、槽电压以及进出水流量对电化学粒子电极体系的影响;然后通过与二维电极体系比较确定了Fe-Mt作为粒子电极的有效性,结合自由基抑制实验以及溶液中相关物质的检测初步探究了Fe-Mt粒子电极对亚甲基蓝去除的强化机理;最后进行了Fe-Mt粒子电极的稳定性实验。该研究有助于拓宽铁改性蒙脱石在污染物光/电复合降解体系的应用。
全文HTML
-
亚甲基蓝、无水碳酸钠(Na2CO3)、结晶硝酸铁(Fe(NO3)3·9H2O)、七水合硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)等试剂均购自天津市盛和化学试剂有限公司,以上试剂均为分析纯。
-
Fe-Mt催化剂和Fe-Mt粒子电极的制备。合成方法在参考文献基础上有所改进[15],步骤如下:高速搅拌条件下,将Na2CO3粉末缓慢加入0.2 mol·L−1的硝酸铁溶液中,控制好碱/铁比(OH/Fe摩尔比为1.0),将所得到的红褐色半透明铁柱撑液在室温下陈化24 h。然后,将适量蒙脱石加入去离子水中,制成2%的黏土浆液。在恒温水浴锅中保持60 ℃,缓慢滴入上述陈化好的铁柱撑准备液 (1 g蒙脱石样品滴加10 mmol Fe3+离子溶液)。持续搅拌2 h,所得的混浊液于室温下陈化24 h。陈化产物经无水乙醇洗涤3次,然后用去离子水离心-洗涤多次(至少6次)后在80 ℃下干燥至恒重为止,研磨过250目,密封备用。碱铁比为1.0样品标记为Fe-Mt。将制备好的Fe-Mt催化剂、黏土与成孔剂按照3∶6∶1配比在80 ℃烘干后,混合均匀,采用球磨机碾至粉末,加入适量水滚制成4~6 mm小球,然后在马弗炉中以600 ℃煅烧40 min,自然冷却至室温备用。
-
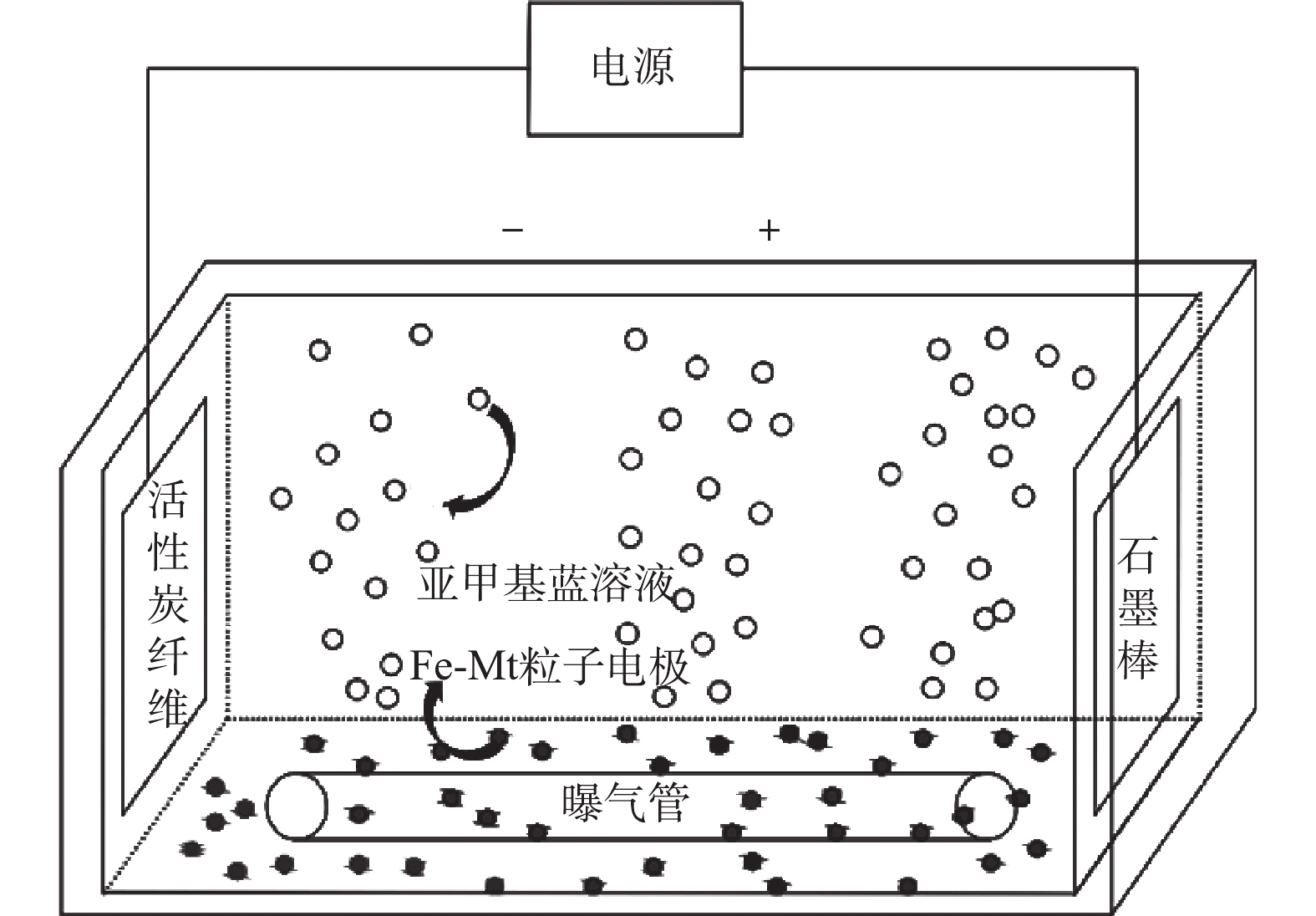
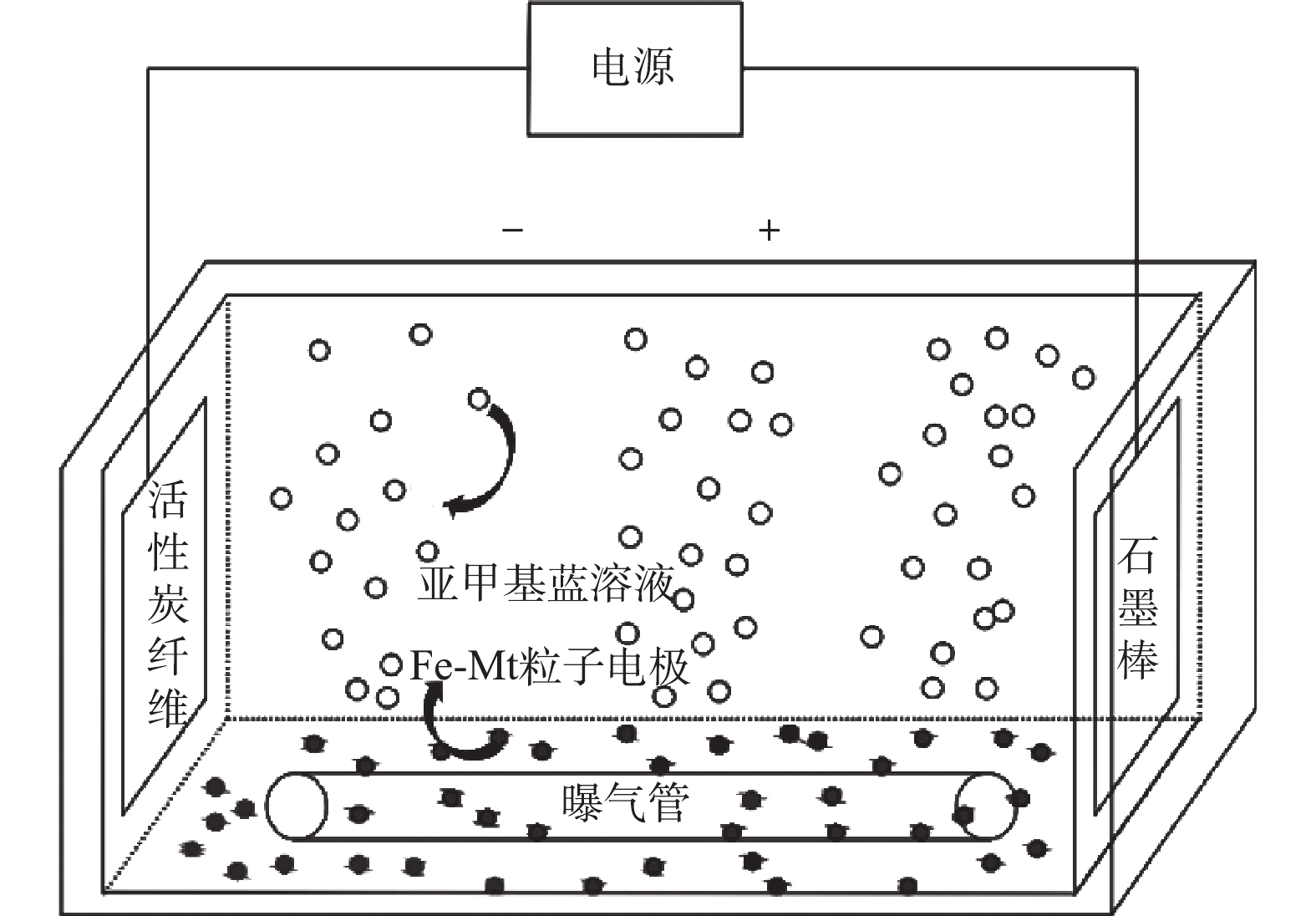
静态实验。实验在500 mL容器中进行(图1)。称取20 mg·L−1的亚甲基蓝溶液,使用H2SO4调节pH至3.0。加入以1.5 g·L−1的Na2SO4作为支持电解质,加入0.2 mmol·L−1的FeSO4·7H2O作为Fenton反应催化剂,充分溶解后倒入电解槽中。将一定量的粒子电极加入至电解槽中,以石磨棒与活性炭纤维分别作为阳极与阴极,电极板间距为6 cm,调节至电压为5 V进行电解。电解过程中曝气头持续在阴极进行恒流曝气,流量为3.0 L·min−1,粒子电极在使用前预先在亚甲基蓝溶液吸附达到饱和。
连续流实验。在静态实验装置的左右两端分别安装一台BT100-2J调速型蠕动泵,控制相同的进出水流量。采用配制好的浓度为20 mg·L−1的亚甲基蓝溶液作为进水电解液。
-
采用配有EDS分析系统的Quanta 200FEG型场发射环境扫描电镜对制备的样品进行形貌测试表与表面元素组成测试。D/max-IIIB型X-射线衍射光谱仪(日本)对样品物相进行表征测试。表征过程中的管电压为40 kV,管电流为30 mA。测试结果与JCPDS(粉末衍射标准联合会)标准卡片进行比对。电解液中的H2O2 浓度采用草酸钛钾比色法测定。采用1,10-邻菲罗啉分光光度法(HJ/T 345-2007)测定溶液中总溶解性铁离子浓度。YG900G10010型数字直流稳压稳流电源购自上海翼昇电子有限公司。SL1000便携式多参数分析仪购自美国HACH公司。电子分析天平购自梅特勒托利多仪器(上海)有限公司。KH-50B型超声波清洗器购自昆山禾创超声仪器有限公司。SB-178型恒流曝气泵购自Sobo公司。
1.1. 试剂与仪器
1.2. 材料制备
1.3. 电解实验
1.4. 表征与测试方法
-
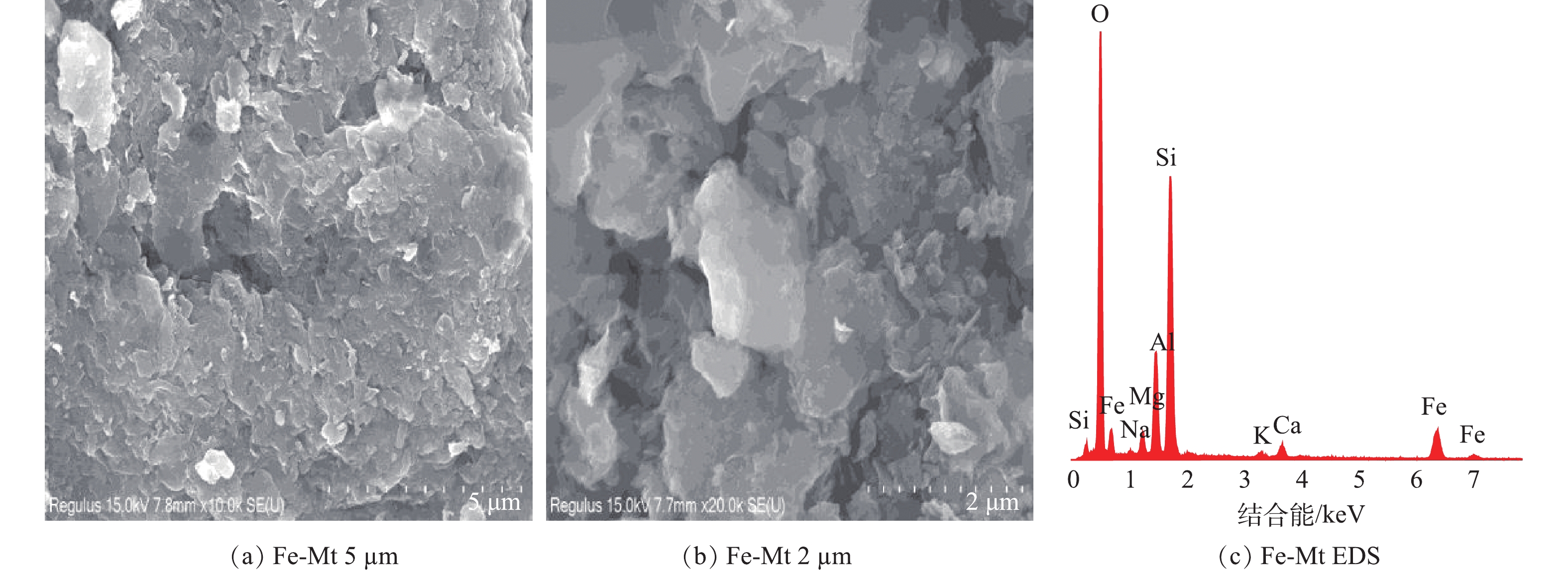
1) Fe-Mt粒子电极的表面形貌与元素表征。图2是Fe-Mt三维粒子电极的SEM-EDS表征结果。由图2(a)可见,制备出的三维粒子电极是一种形状较为规则的圆形小球,粒径为4~6 mm内。Fe-Mt三维粒子电极主要由浅黄色黏土与深红色Fe-Mt混合烧制而成,因此,Fe-Mt三维粒子电极呈深黄色。在前期粒子电极烧制过程中发现当煅烧温度过高,尤其在大于800 ℃时烧制成的粒子电极结构疏松,与水接触后结构发生塌陷现象,且粒径越大越明显。而根据5 µm下SEM影像显示,本研究在600 ℃煅烧成的 4~6 mm粒径的Fe-Mt三维粒子电极表面结构质密,进一步放大倍数显示粒子电极呈现不规整的乱石结构。EDS表征(图2(c))显示粒子电极所含元素种类较多,Si、Ca、Na、O与Mg等是蒙脱石与黏土常见的元素[16]。其中,O和Si所占权重最大,分别为53.78%和22.12%。根据EDS测试可以明显看出粒子电极含有一定量Fe元素,约占8.75%。
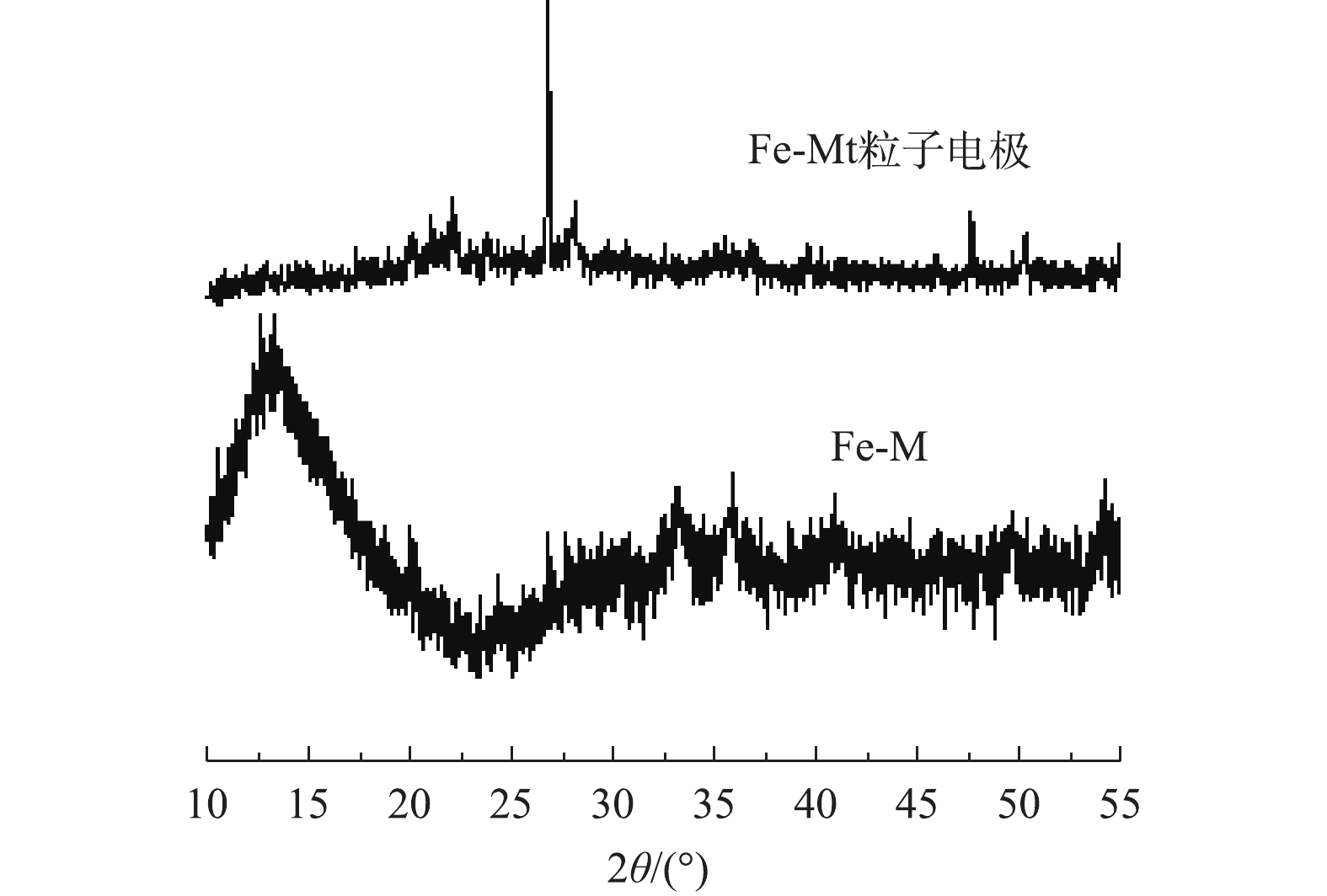
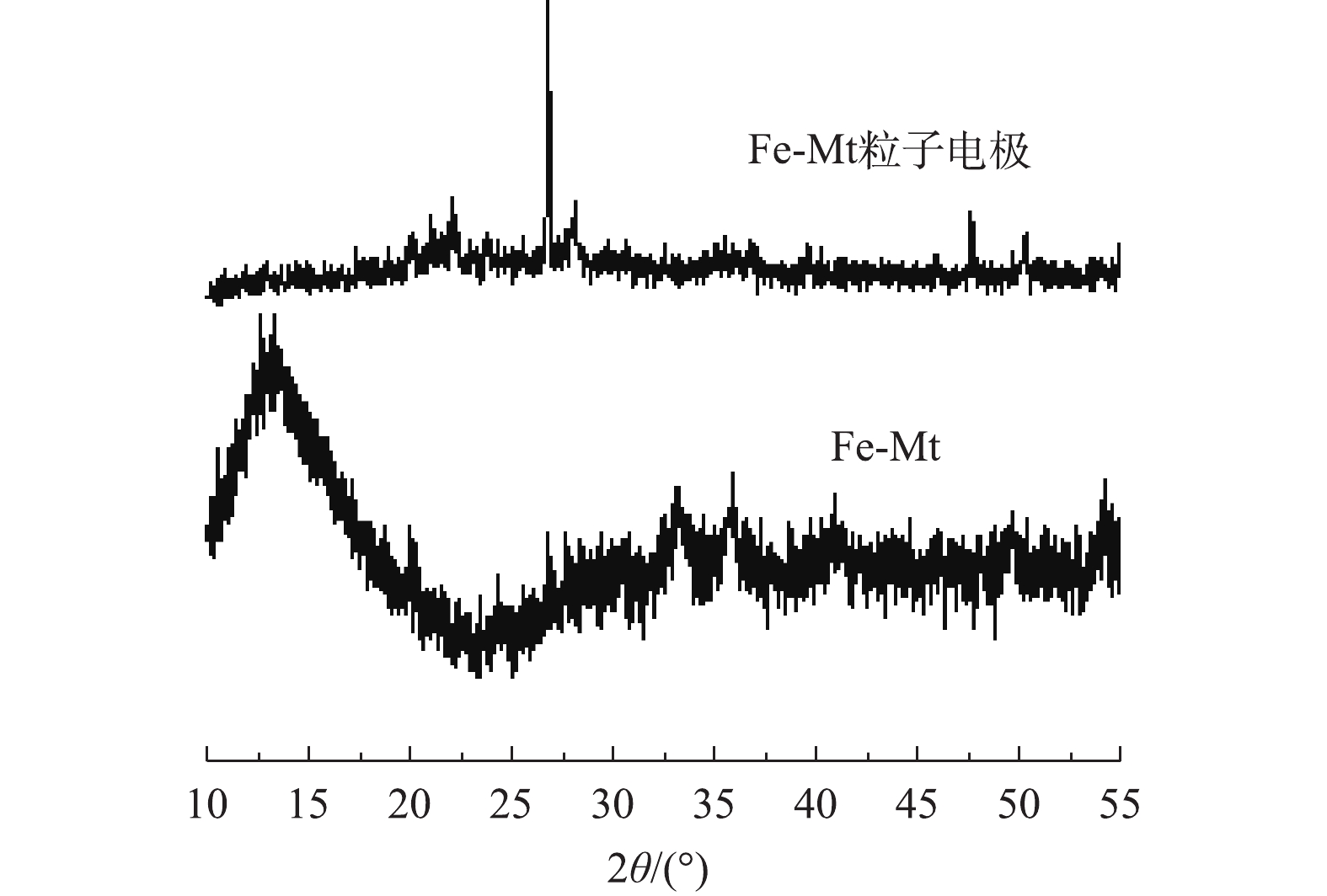
2)Fe-Mt粒子电极的XRD表征。图3分别是Fe-Mt与Fe-Mt粒子电极的XRD衍射图。可以清楚地观察到在2θ角分别为33.2°和35.7°的α-Fe2O3衍射峰[17]。然而Fe-Mt粒子电极的衍射图谱中α-Fe2O3衍射峰强度较弱,在20.8°与26.6°出现了衍射强度较高的特征衍射峰,通过对比pdf卡片,是SiO2的特征衍射峰,与EDS的表征结果一致。这说明制备成功的Fe-Mt粒子电极主要以SiO2为主要组成,这是其黏土组分占比较大导致的。
-
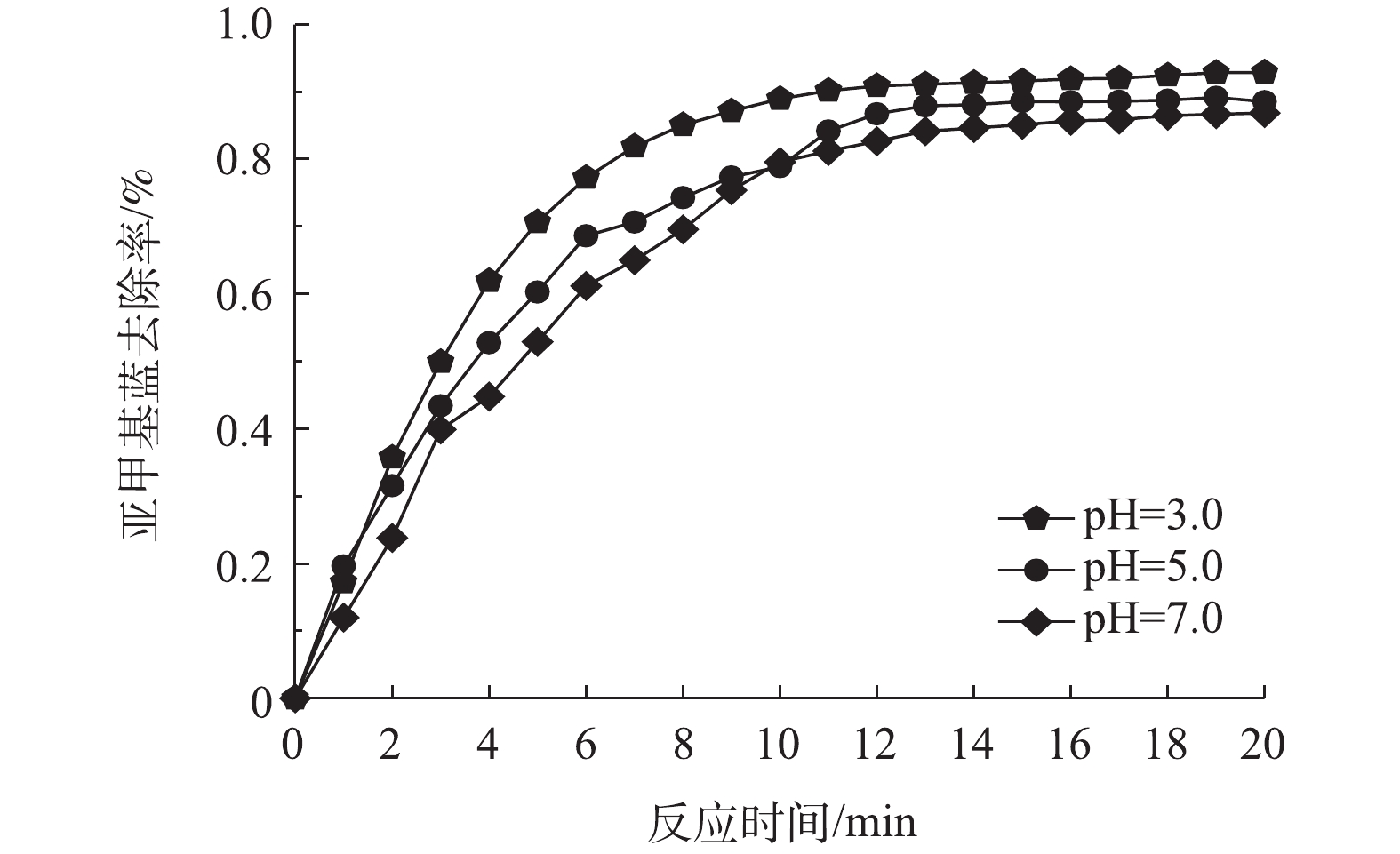
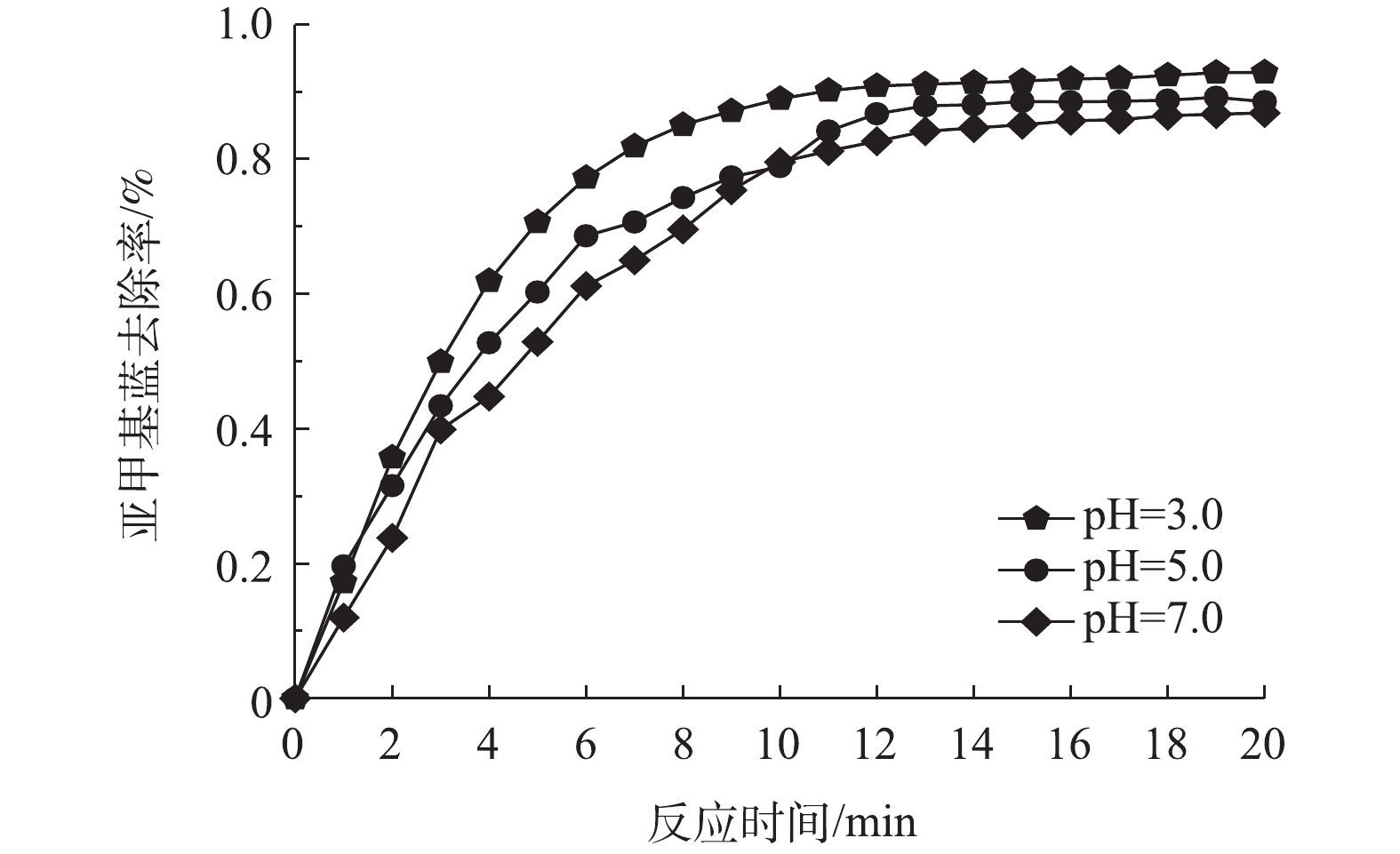
1) pH对亚甲基蓝去除率的影响。在电化学体系中,pH是影响污染物去除的主要影响因素之一[18]。酸性条件往往有助于污染物的去除,一方面,因为活性物质羟基自由基的氧化活性随pH升高而降低,另一方面,pH的增加会导致电化学体系中金属盐类催化剂的水解,从而降低污染物去除率[19-21]。图4显示了pH对Fe-Mt三维粒子电极的影响。可以看出随着pH增加,亚甲基蓝去除率降低。在前14 min左右亚甲基蓝去除率变化较明显,随着亚甲基蓝浓度的不断降低,去除率随时间变化逐渐变缓。在pH=3.0时,亚甲基蓝去除率最高为92.91%,比pH=7.0时提高了约7%,去除率变化幅度并不明显。因此,Fe-Mt三维粒子电极的投加有助于拓宽电化学体系pH的有效作用范围。Fe-Mt三维粒子电极的投加一方面能够增大电极反应面积,另一方面可以作为非均相催化剂,避免了金属离子催化剂的水解,因此,有效拓宽了降解亚甲基蓝的pH适用范围[22-24]。
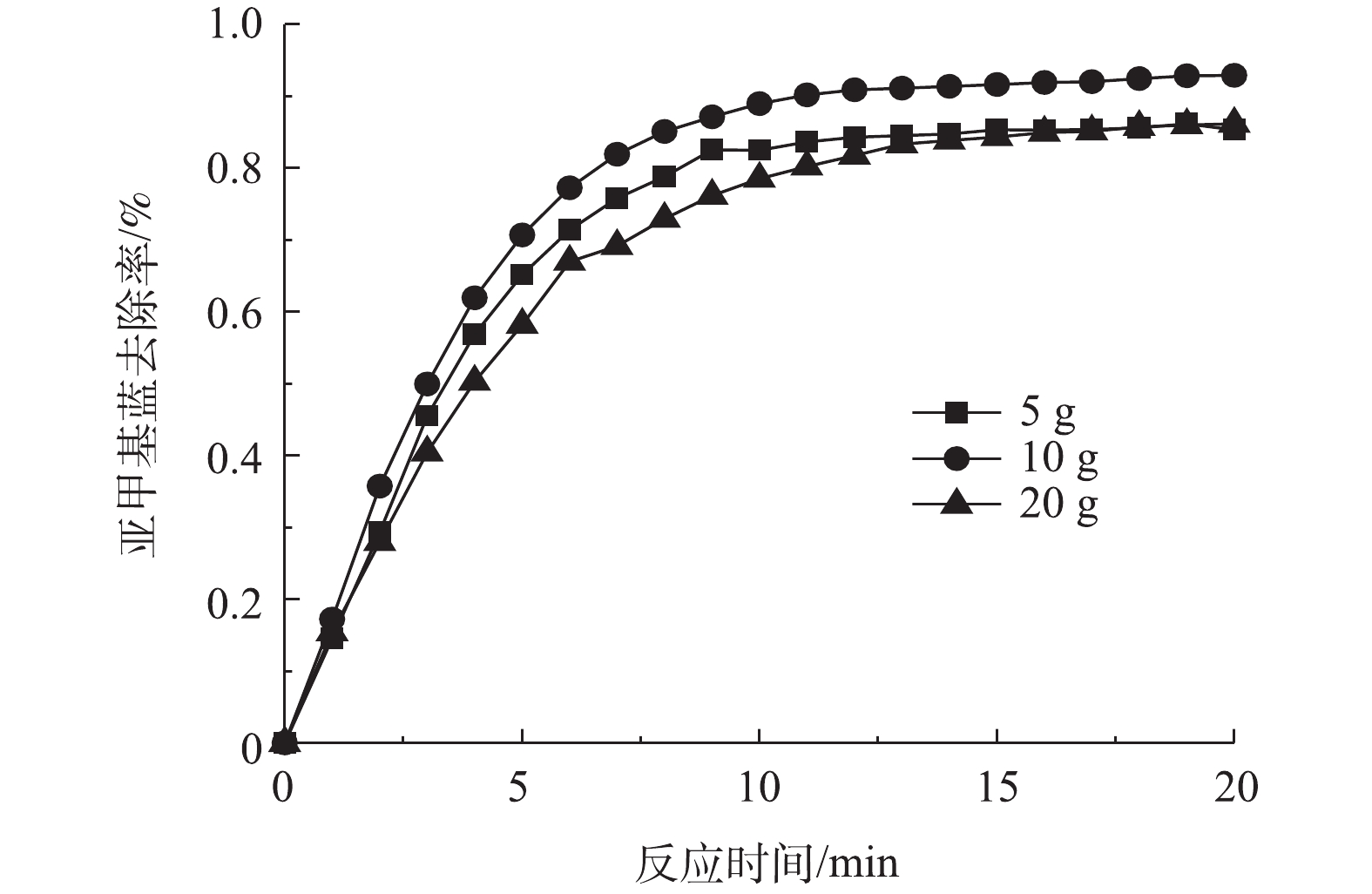
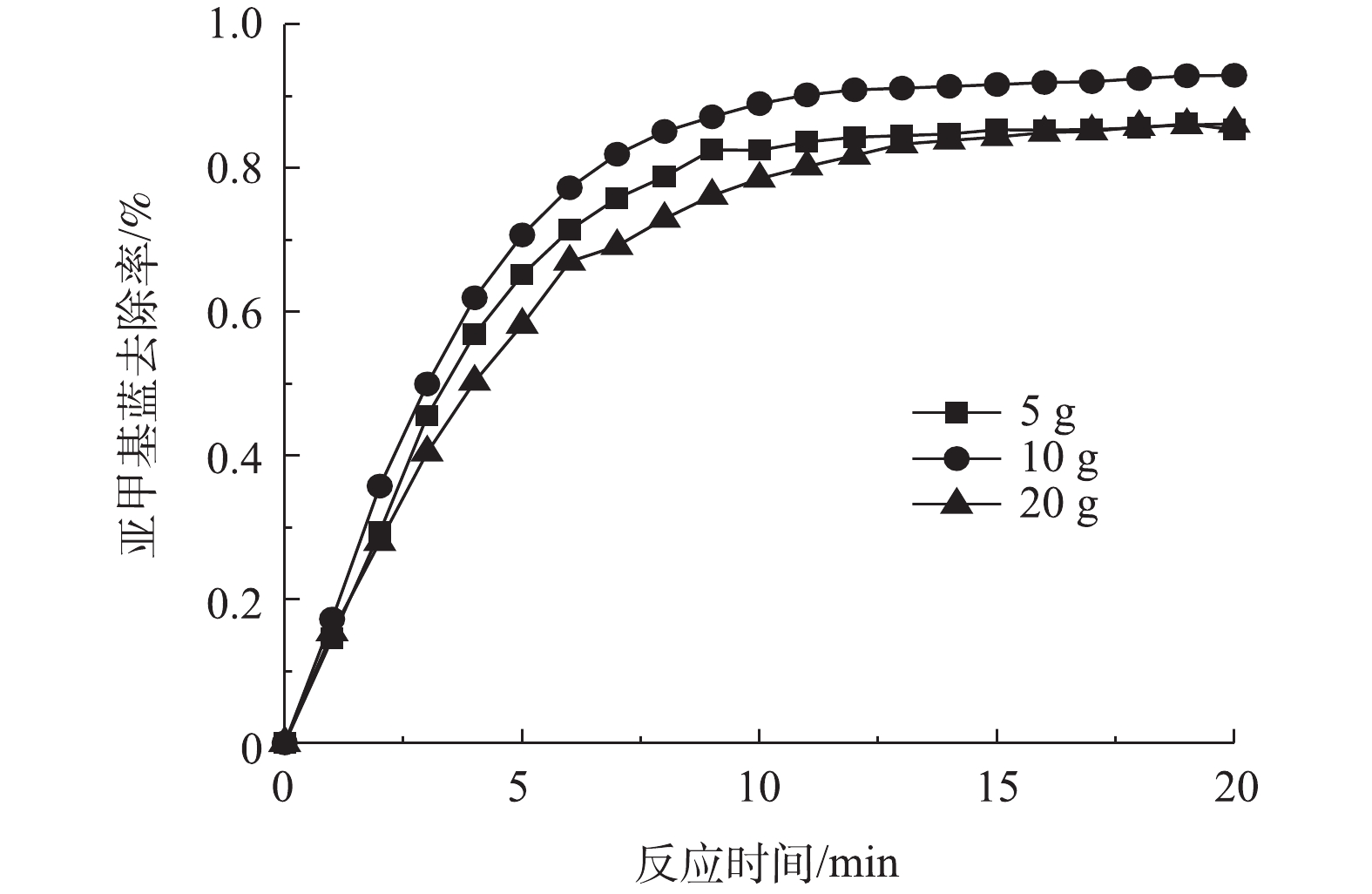
2)粒子电极投加量对亚甲基蓝去除率的影响。在槽电压5 V、pH=3.0、FeSO4·7H2O为0.2 mmol·L−1、支持电解质Na2SO4为1.5 g·L−1的条件下,改变Fe-Mt粒子电极投加量,探究投加量对三维粒子电化学体系的影响,结果如图5所示。可以看出,粒子电极投加量从5 g·L−1增加至10 g·L−1的过程中,亚甲基蓝去除率有所升高,继续增大粒子电极投加量至20 g·L−1,亚甲基蓝去除率反而降低。粒子电极的投加会在电化学体系形成3种电流,即短路电流、旁路电流和反应电流,而发挥有效作用的是反应电流。粒子投加量过多将占用反应体系空间,降低有机污染物传质效率,同时增加短路电流,降低电流效率[7, 25]。因此,该体系中最佳的粒子电极投加量是10 g·L−1。
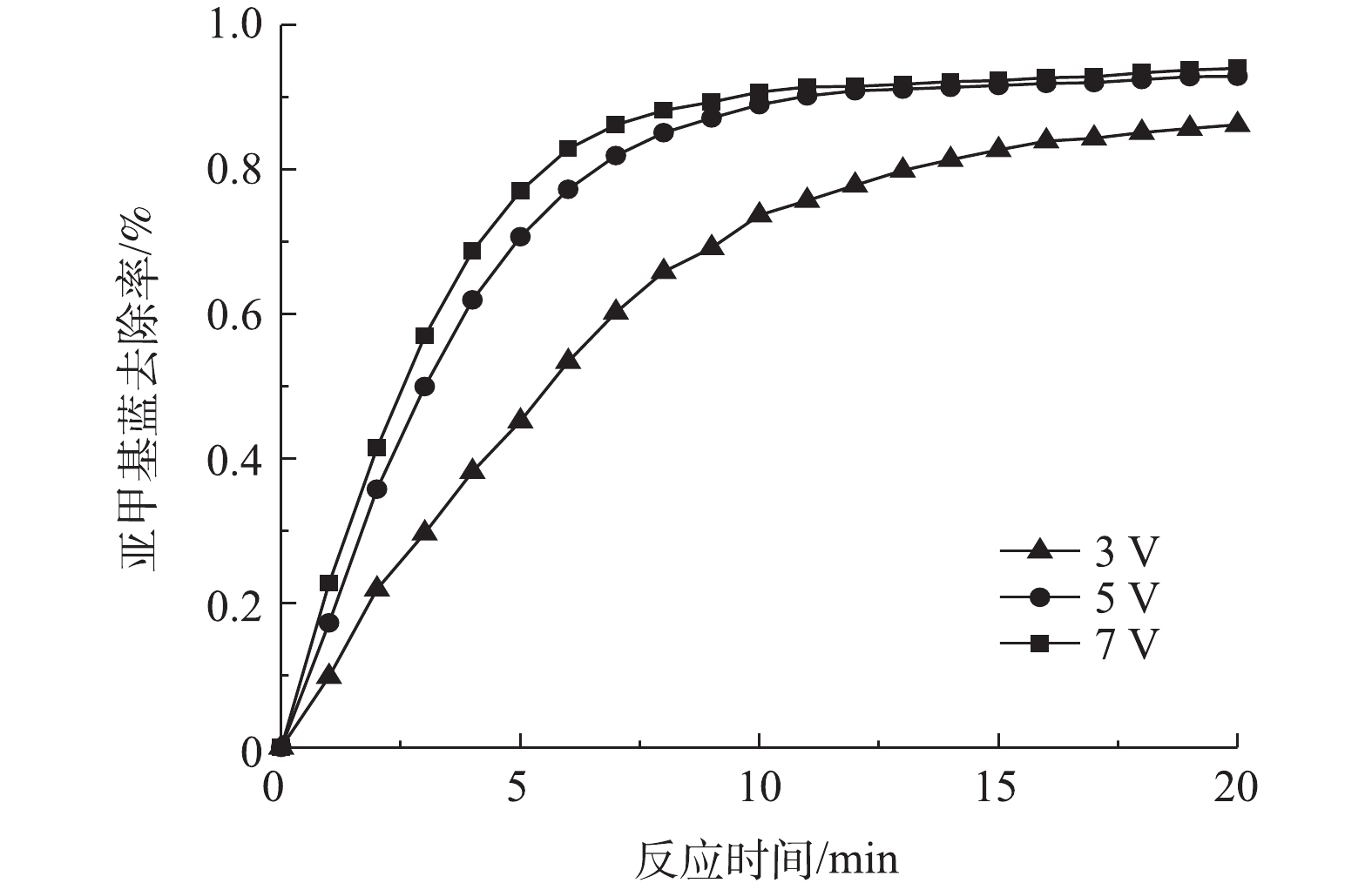
3)槽电压对亚甲基蓝去除率的影响。在电解体系不变的情况下,槽电压值会影响体系电流密度,进而影响亚甲基蓝去除率。因此,在粒子电极投加量为10 g·L−1、pH=3.0、FeSO4·7H2O为0.2 mmol·L−1、支持电解质Na2SO4为1.5 g·L−1的条件下,分别调节槽电压为3、5和7 V,探究了槽电压对三维粒子电极体系的影响,结果如图6所示。由图6可知,当槽电压从3 V升至5 V时,亚甲基蓝的去除率随之升高,但是继续增加槽电压至7 V后,亚甲基蓝的去除率升高幅度不大。这是因为在一定范围内增加槽电压,体系电流密度也会增大,阴极通过2电子反应产生的H2O2量也随之增大。H2O2的产生能够在粒子电极催化下产生活性物质去除亚甲基蓝。而当槽电压进一步增大时亚甲基蓝去除率增长不大,这与副反应的产生有关,如阴极的4电子反应与2电子反应竞争以及阳极对H2O2的直接氧化作用消耗了H2O2。因此,本研究中最适槽电压为5 V。
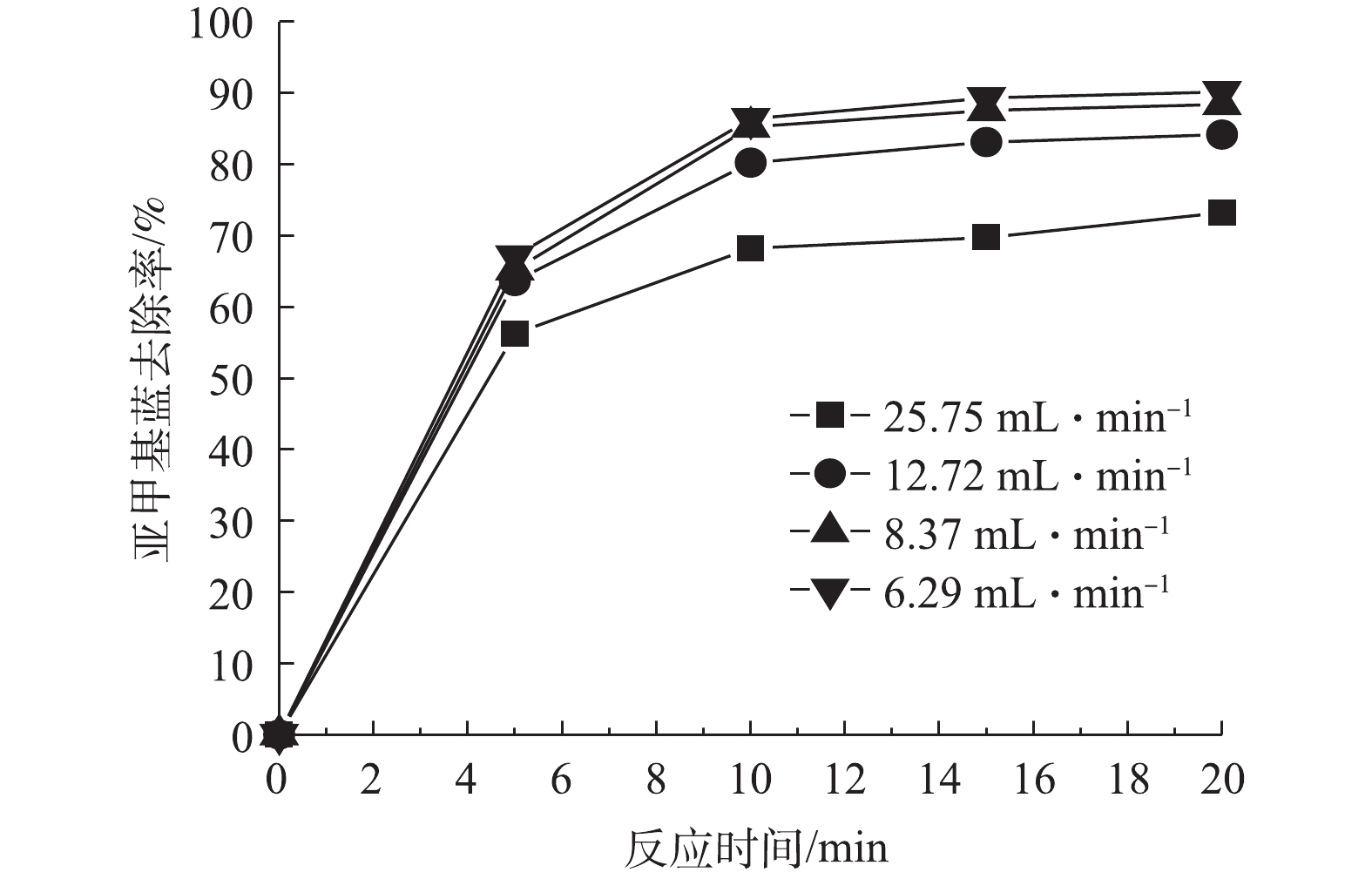
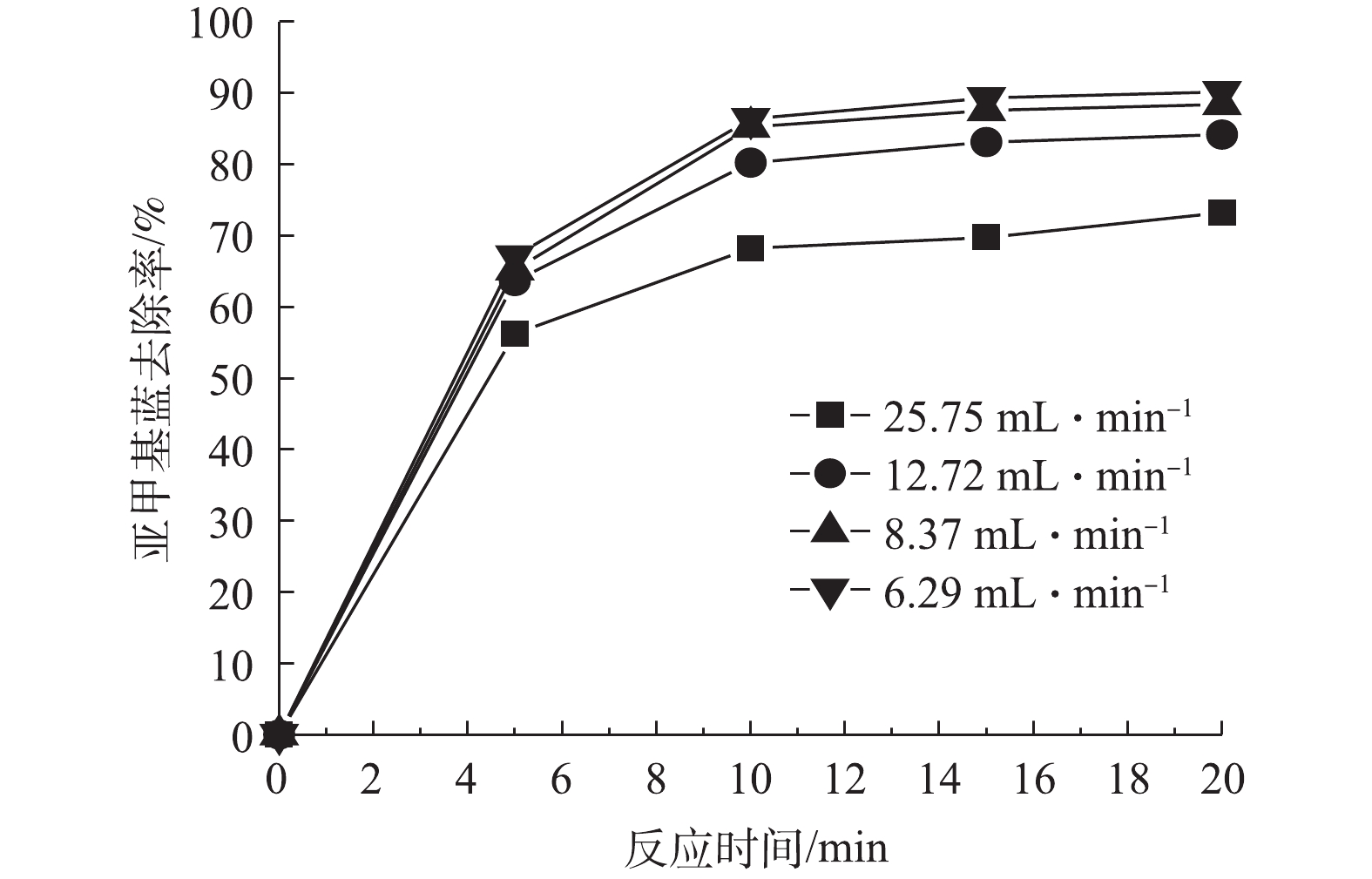
4)亚甲基蓝去除的连续流实验。连续流实验中的进出水流量能够影响水力停留时间,从而对亚甲基蓝去除率产生影响。因此,在Fe-Mt三维粒子电极体系中,以连续进出水的方式考察了进出水流量对亚甲基蓝的去除效果的影响,结果如图7所示。由图7可知,随着流量的不断减少,亚甲基蓝去除率逐渐升高。当流量由8.37 mL·min−1降低至6.29 mL·min−1时,亚甲基蓝去除率增幅较小。由此可见,进出水流量的调控对于反应体系的去除率起到重要的作用。
-
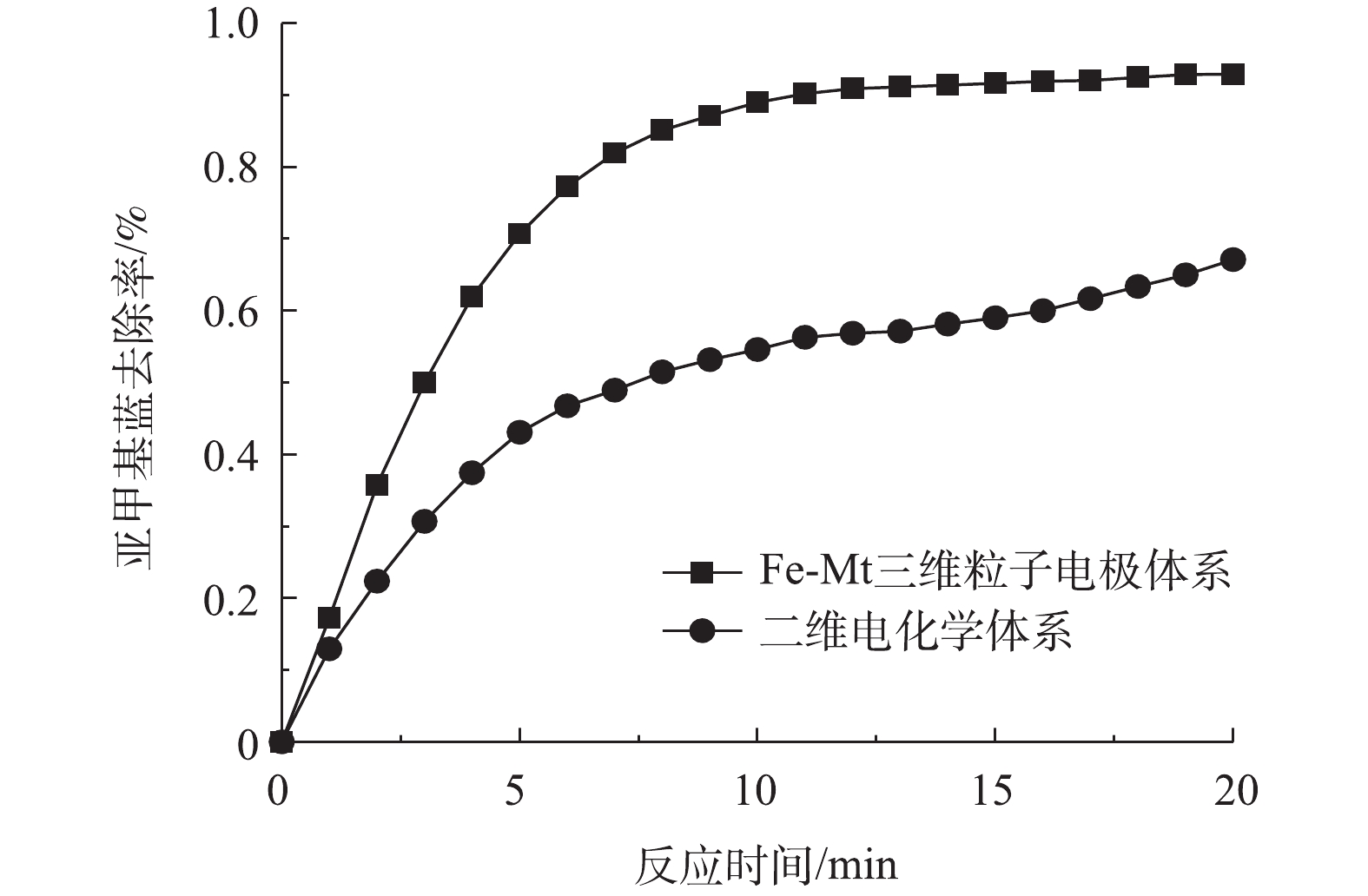
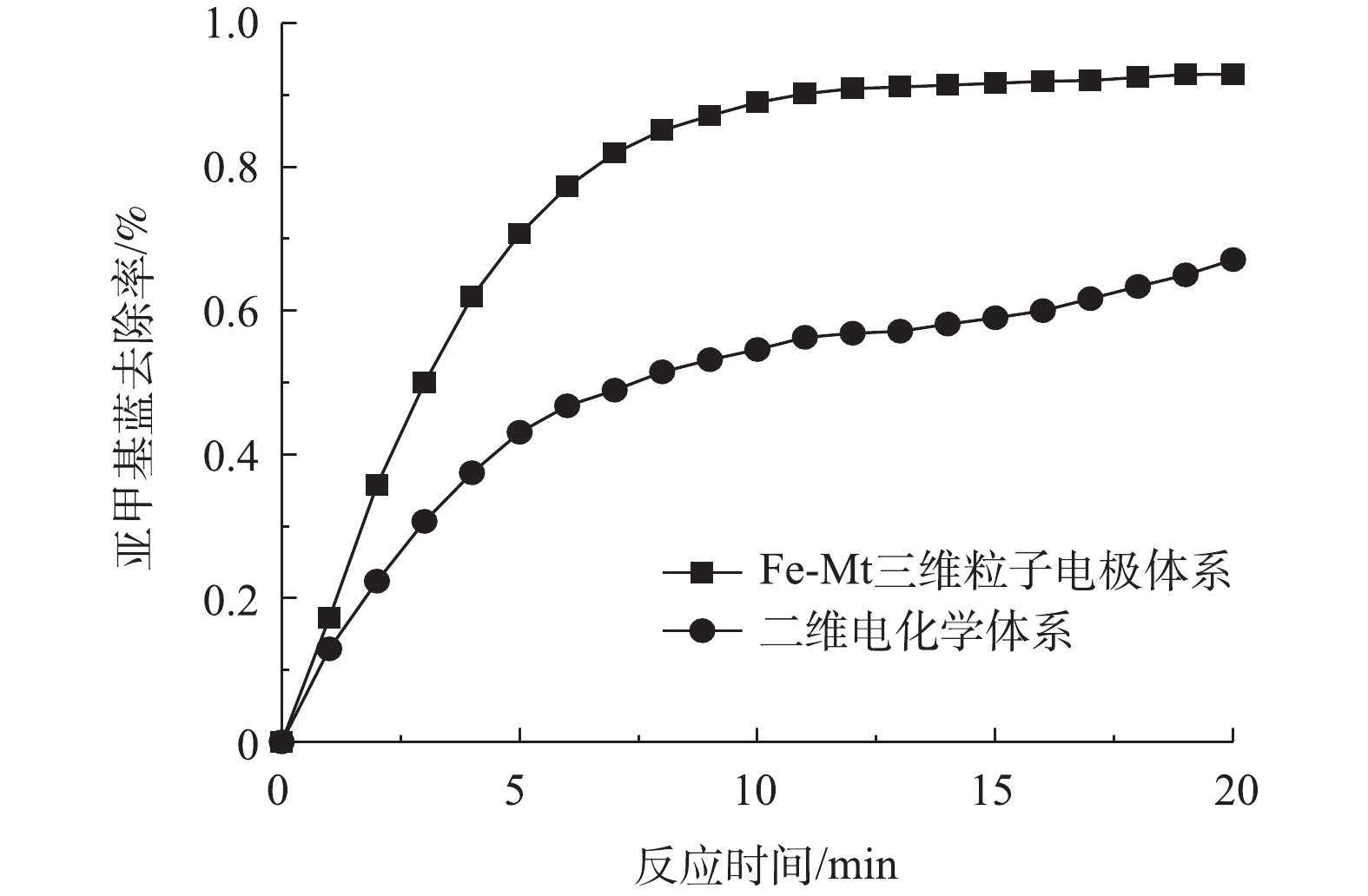
图8为在相同的电解条件下三维粒子电极体系与二维电化学体系对亚甲基蓝去除效果的对比。在Fe-Mt粒子电极投加量为10 g·L−1、电解20 min后,三维粒子电极体系较二维电化学体系对亚甲基蓝的去除率提高了约25%。因此,以Fe-Mt作为粒子电极应用于电化学体系是可行的。目前对于Fe-Mt的应用多集中于光-Fenton体系或非均相Fenton体系,其应用困难之一是Fe-Mt催化剂的回收性能。Fe-Mt作为催化剂投加量少,多以粉末状态分散在溶液中,应用过后难以回收[12-13]。该实验结论表明将其制作为三维粒子电极,可以有效发挥三维粒子电极的催化作用,有助于催化剂的回收。此外,Fe-Mt粒子电极也可以延伸作为光-Fenton体系的催化剂,对于光电复合体系的应用具有重要的价值。
-
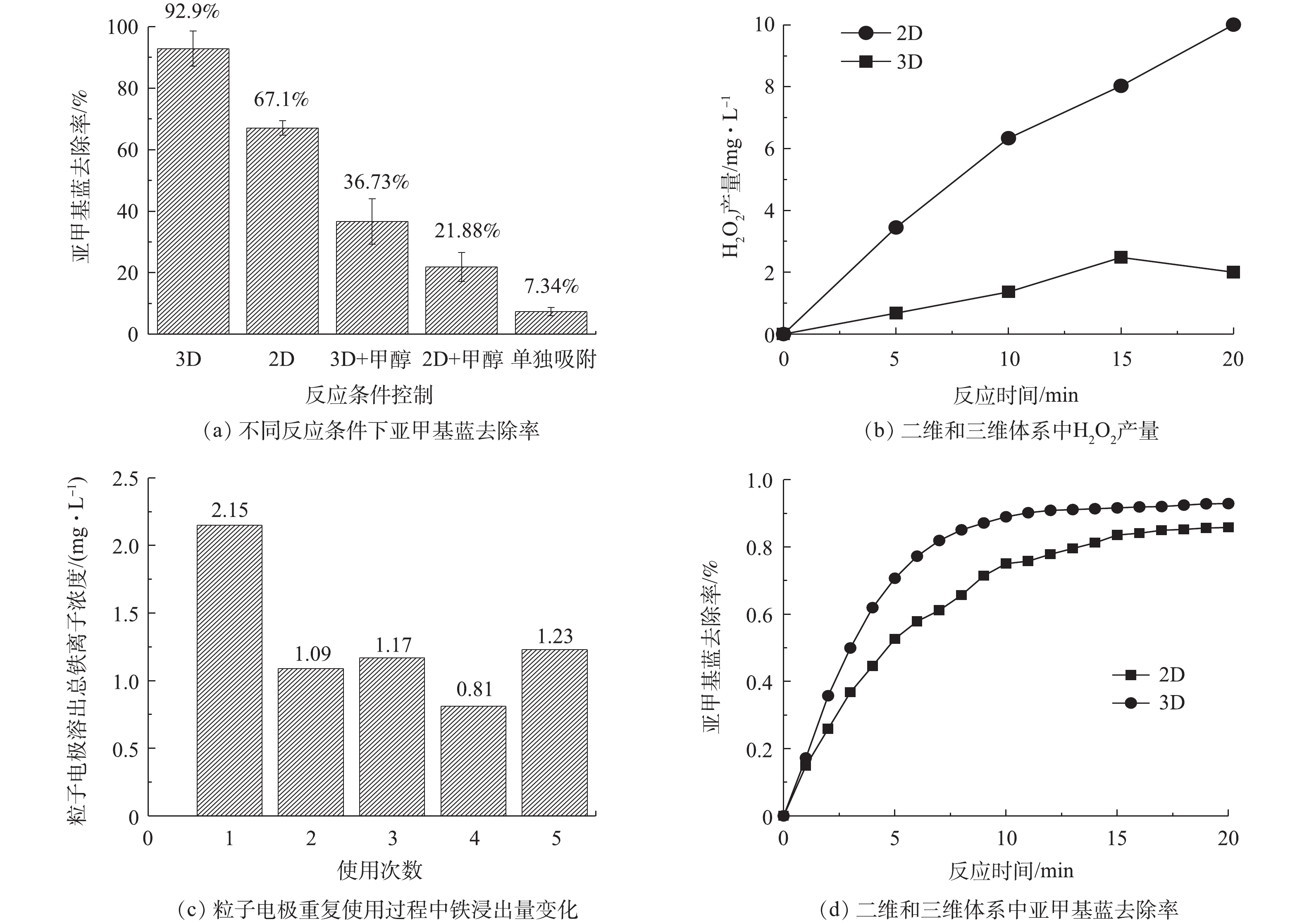
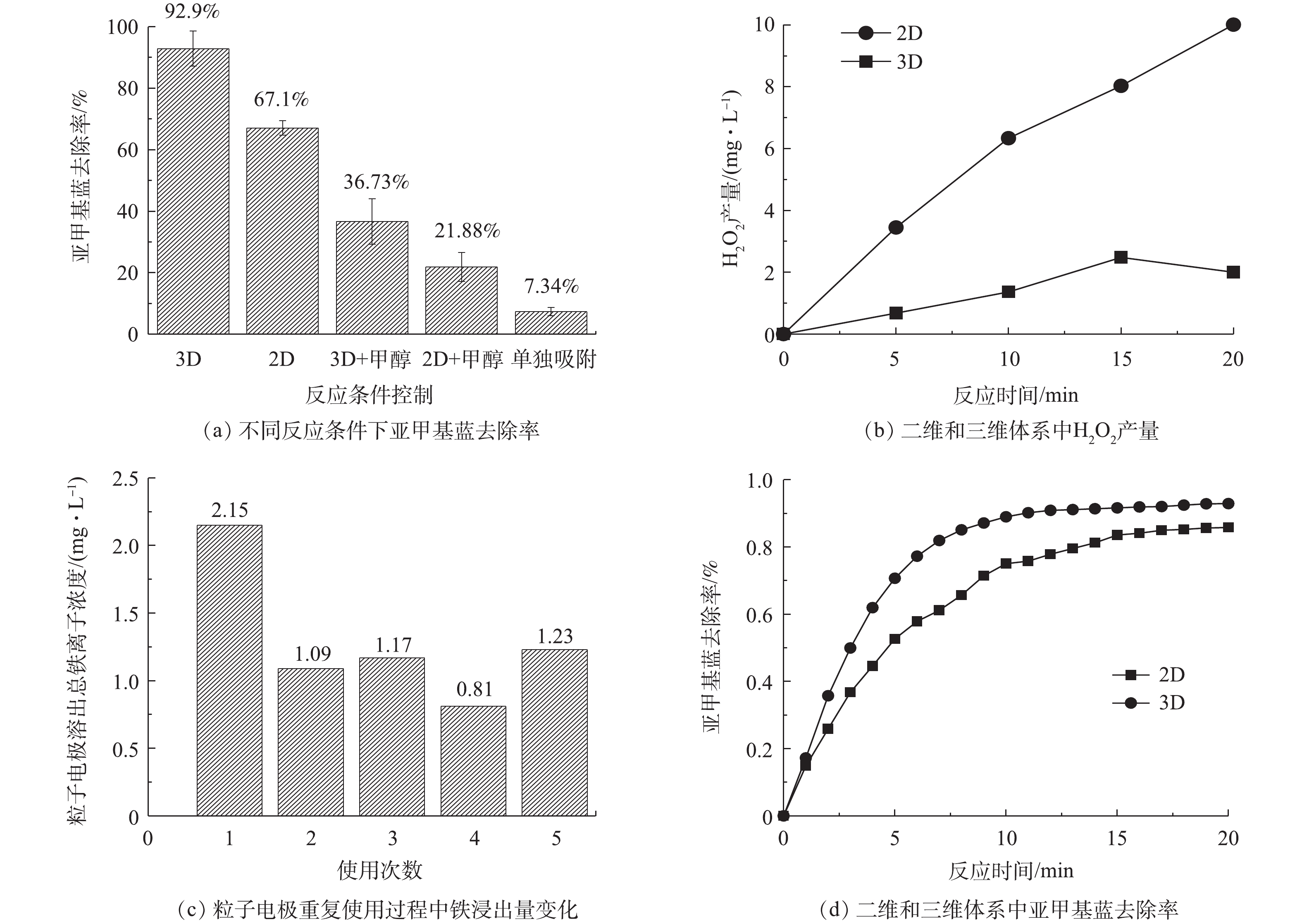
在Fe-Mt三维粒子电极体系中,对亚甲基蓝去除起作用的可能途径主要包括以下5条:在阳极直接氧化亚甲基蓝;溶液中添加的Fe2+(0.2 mmol·L−1)与阴极产生的H2O2反应产生∙OH氧化亚甲基蓝;在酸性条件下,粒子电极溶出额外的Fe2+,Fe2+与阴极产生的H2O2反应产生∙OH氧化亚甲基蓝;Fe-Mt粒子电极的吸附作用去除亚甲基蓝;Fe-Mt粒子电极直接催化H2O2产生∙OH氧化亚甲基蓝。针对这5种可能的路径,本研究通过向溶液加入∙OH抑制剂(甲醇)以及对H2O2和总溶解性铁离子的检测初步探究了Fe-Mt三维粒子电极体系对亚甲基蓝的去除机理,结果如图9所示。可以看出粒子电极的吸附作用对亚甲基蓝的去除作用十分有限,吸附20 min亚甲基蓝去除率仅7.34%(图9(a))。2D(二维电化学直接氧化,未加入Fe-Mt粒子电极)体系亚甲基蓝去除率约67.1%,当向2D体系加入∙OH抑制剂(甲醇)后,亚甲基蓝去除率下降至21.88%,这表明2D体系主要靠阳极直接氧化以及外加的Fe2+(0.2 mmol·L−1)与H2O2反应产生∙OH进而氧化亚甲基蓝。当向3D体系加入甲醇后,亚甲基蓝去除率下降至36.73%,这表明3D氧化体系除了依靠阳极对亚甲基蓝直接氧化外,体系产生的大量∙OH起到主导作用。图9(b)显示了3D体系与2D体系中H2O2产量随时间的变化。可以看出,2D体系H2O2产量明显高于3D体系,因此,可以确定在3D体系中,催化剂对H2O2活化效率明显高于2D体系。
为了进一步探明3D体系是依靠Fe-Mt粒子电极直接催化还是依靠额外的铁离子溶出对H2O2进行活化,对3D体系溶液中总溶解性铁离子的量进行了测定。在2D体系反应结束后总铁离子测量值约0.17 mmol·L−1(减少的铁离子浓度与铁离子的沉淀有关),因此,以3D体系总溶解性铁离子与0.17 mmol·L−1(约9 mg·L−1)的差值确定Fe-Mt粒子催化剂溶出的总铁离子浓度,结果如图9(c)所示。可以看出,在第1次使用时,3D体系产生了最高的溶解性总铁离子浓度,随着使用次数的增多,溶解性总铁离子浓度逐渐降低。因此,3D体系产生的溶解性铁离子对H2O2进行均相催化产生∙OH也是亚甲基蓝去除的途径之一。图9(d)为在向2D体系中加入0.25 mmol·L−1的Fe2+条件下与3D体系的亚甲基蓝去除效果的对比情况。可见即使向2D体系加入的Fe2+浓度大于3D体系溶解性的总Fe2+浓度,亚甲基蓝去除率依然低于3D体系。这表明3D体系溶出的铁离子不足以使其产生高的亚甲基蓝去除率。因此,Fe-Mt粒子电极对H2O2的直接催化也对亚甲基蓝去除产生作用。
综上所述,Fe-Mt三维粒子电极体系对亚甲基蓝去除的途径具有多样性。阳极的直接氧化能够去除一部分亚甲基蓝,而粒子电极的加入能够进一步提高亚甲基蓝的去除率。在酸性条件下,阴极能够通过2电子反应产生H2O2,H2O2能够被Fe-Mt粒子电极额外溶出的Fe2+催化而产生∙OH,再进一步氧化亚甲基蓝。Fe-Mt粒子电极本身具有一定的吸附作用,这加速了亚甲基蓝与粒子电极表面的传质过程。亚甲基蓝接近粒子电极表面后,Fe-Mt粒子电极直接催化H2O2产生∙OH,对亚甲基蓝进一步降解实现了吸附-氧化的协同作用。基于此,3D体系才比2D体系对亚甲基蓝具有更高的去除率。
-
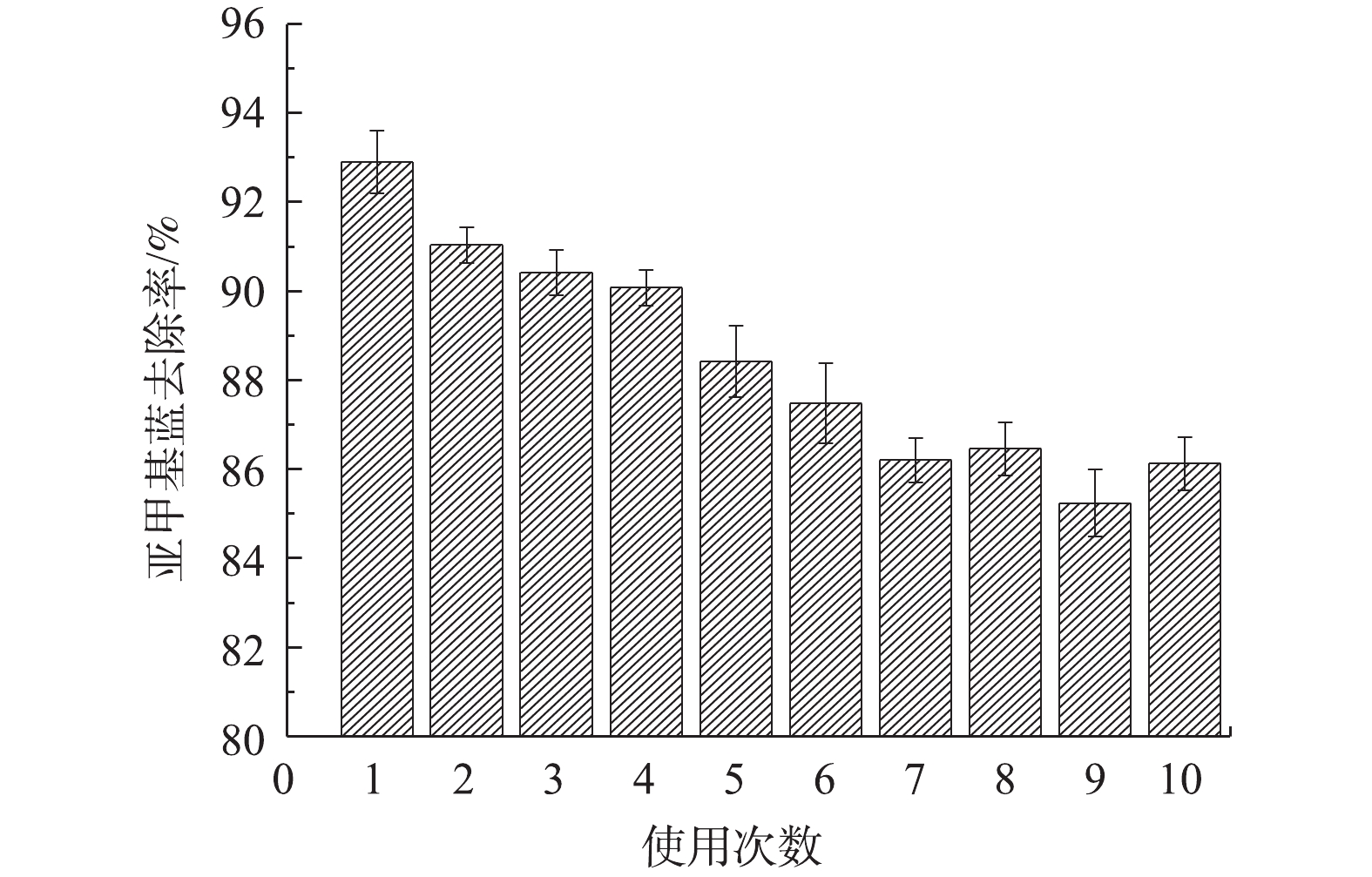
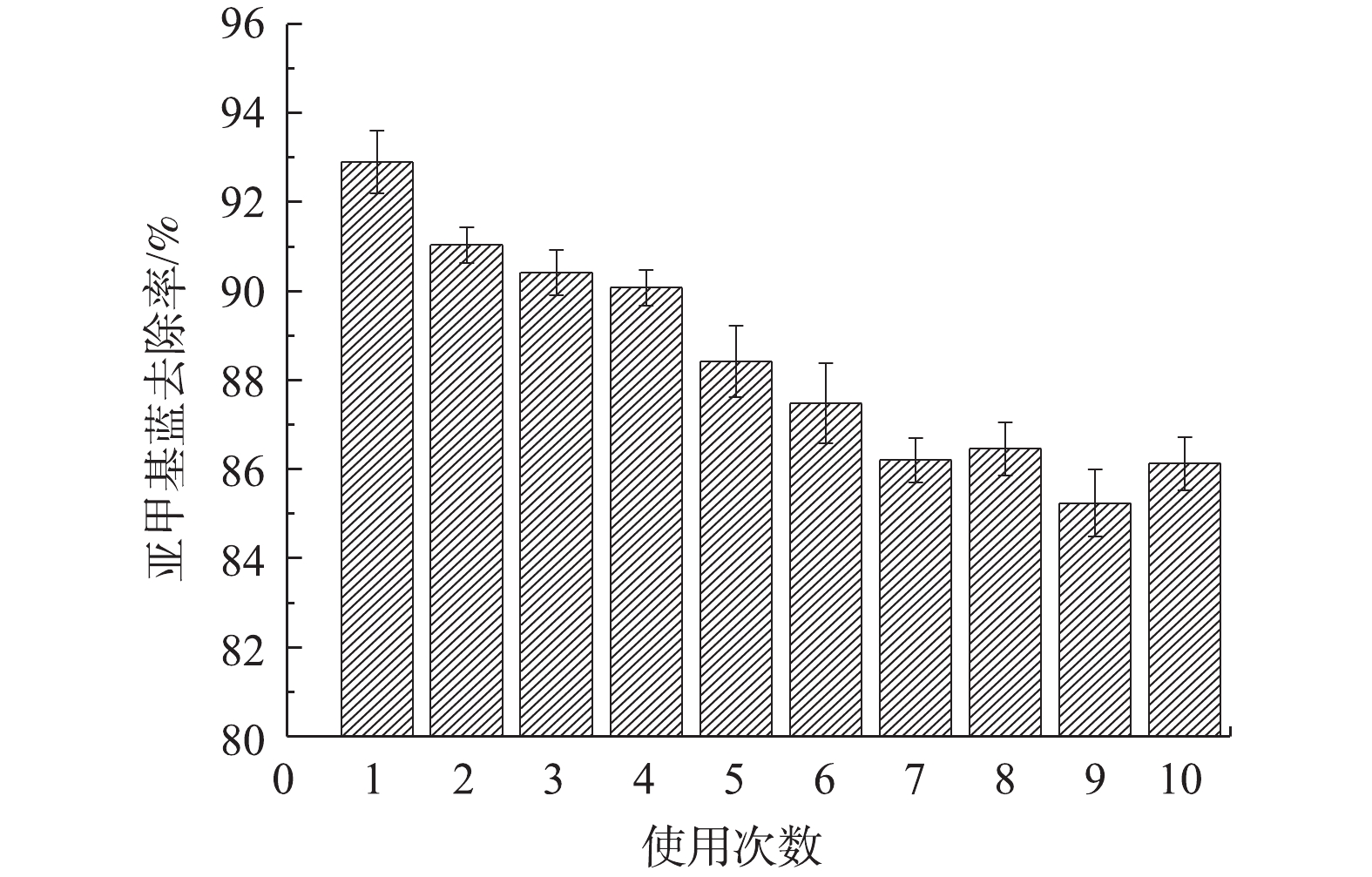
材料的稳定性是决定其应用性能的重要指标。图10为电极材料的使用次数对亚甲基蓝去除率变化的影响情况。可以看出,随着使用次数的增加,亚甲基蓝去除率呈下降趋势,重复使用至第10次后,去除率下降约7%,这说明Fe-Mt三维粒子电极具有良好的电化学催化活性。由图9(c)可知,在粒子电极重复使用的过程中,粒子电极表面的铁不断融出至溶液中,且随着使用次数的增加,铁离子溶出量减少,这表明粒子电极有效活性位点的减少。此外,粒子电极在重复使用过程中存在吸附-氧化耦合的过程,亚甲基蓝分子不断在粒子电极表面积累,其可能掩盖了粒子电极表面的活性位点,从而进一步降低了催化活性。
2.1. 粒子电极的表征
2.2. 对亚甲基蓝去除的影响因素分析
2.3. 不同体系对亚甲基蓝的去除效果对比
2.4. 三维粒子电极体系对亚甲基蓝的去除机理
2.5. 粒子电极的可重复利用性
-
1) Fe-Mt三维粒子电极体系能够将亚甲基蓝去除率提高约25%,这证明其作为粒子电极的有效性。
2)将pH由3.0增至7.0后,亚甲基蓝去除率降低了7%,表明Fe-Mt粒子电极的投加可拓宽电化学体系去除污染物的有效pH范围。
3)除了阳极对亚甲基蓝的直接氧化,Fe-Mt粒子电极还能够对H2O2实现直接与间接催化,并结合自身一定的吸附性能对亚甲基蓝实现吸附-氧化降解去除。



 下载:
下载: