-
长期以来,水环境问题一直备受关注,《2018年中国生态环境状况公报》显示,我国地表水中Ⅳ、Ⅴ类水质占22.3%,劣Ⅴ类占6.7%;浅层地下水中Ⅳ类占29.2%,Ⅴ类占46.9%,其中,氮磷污染物超标问题较为严重[1-2]。因此,高效脱氮除磷依然是我国当前污水处理领域的研究热点。市政污水处理主要采用以絮状活性污泥法为核心的传统生物脱氮除磷工艺,存在处理能力低、占地面积大、运行成本高等问题[3]。如何提高传统活性污泥法的效率,如何在较小的范围内实现更高的污水处理效率、同时降低能耗,已成为目前全球范围内污水处理领域所面临的共性技术难题。
好氧颗粒污泥(AGS)技术起源于20世纪90年代末期[4],是当前最具应用价值的污水生物处理新技术之一。AGS是由微生物在特定水力条件下自凝聚形成的颗粒状活性污泥,具有沉降性能好、处理负荷高等优点[5-6],脱氮除磷原理与絮状污泥类似,即通过硝化-反硝化过程脱氮,通过聚磷菌(PAOs)的释磷和吸磷过程除磷。但AGS由于自身特殊的结构使得其自表面向内部存在溶解氧梯度,由此构建了明显的好氧区、缺氧区和厌氧区,硝化菌、反硝化菌和PAOs等功能菌群沿径向分布于不同层级,从而实现在同一反应器中进行同步硝化反硝化以及同步脱氮除磷[7-8]。好氧颗粒污泥系统一池式的反应理念和较高的污泥浓度可以降低20%~25%的运行费用,23%~40%的电耗和50%~75%的构筑物占地面积[9],同时减少化学药剂的消耗量[10-11]。目前,该技术被荷兰DHV公司初步在工程中应用,据报道[12],在世界范围内已有30多座好氧颗粒污泥厂在运行。
然而,中国生活污水水质和欧美等国家具有显著的差别,我国生活污水普遍呈现出低碳氮比和低COD特点。据统计[13],在全国127个污水处理厂中,大多数水厂原水BOD5/TN<2.59,80%的污水处理厂BOD5/TN<3.6,仅有10%的污水处理厂BOD5/TN>4。一般将COD低于200 mg·L−1,C/N低于8的污水成为低碳氮比污水[14]。据报道[15],世界范围内市政污水处理厂的典型进水C/N在10.5~12.6,COD值也显著高于中国的市政污水。因此,该技术在中国的推广应用还未获得实质性的突破。
目前,利用AGS处理生活污水的研究大多以实验室配水为基质,无法完全模拟生活污水的典型特征[16-17],而利用好氧颗粒污泥处理低碳氮比实际生活污水的研究较少,限制了AGS技术的进一步推广与应用。本研究利用AGS技术处理实际低碳氮比生活污水,研究了AGS的形成过程、N和P等污染物的同步去除过程和去除效率,可为该技术在中国的推广应用奠定基础。
全文HTML
-
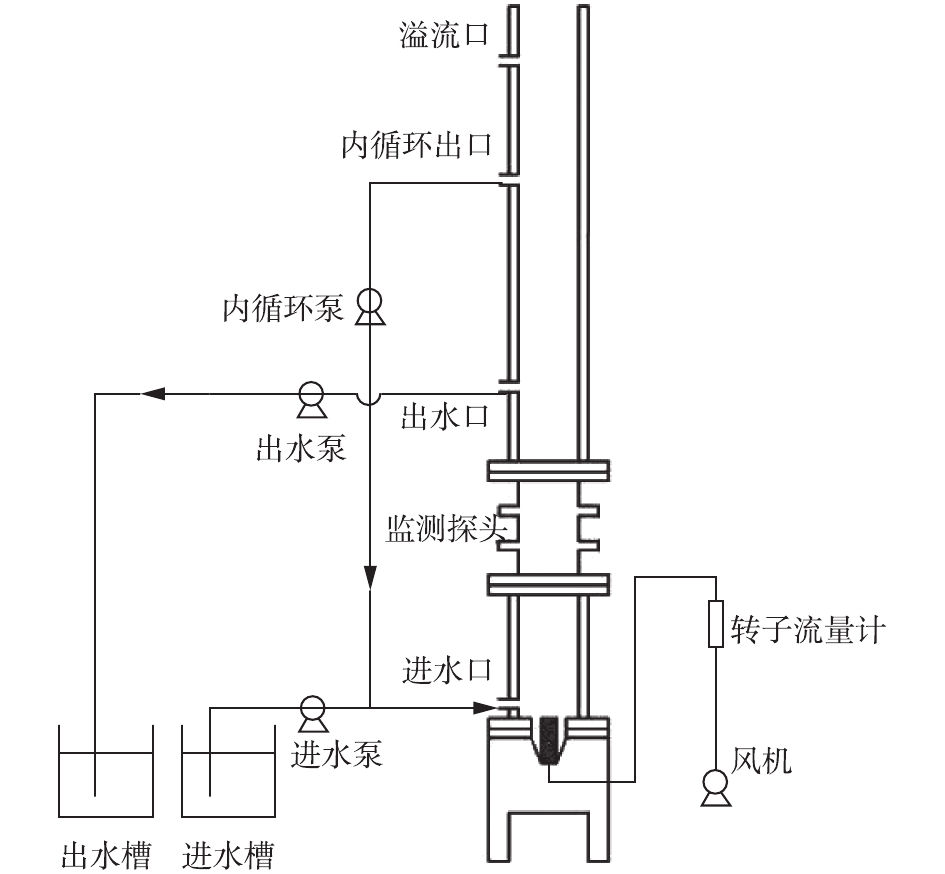
本研究采用SBR(序批式活性污泥法)作为实验装置,反应器整体为有机玻璃结构,外设循环水浴夹套,通过循环水浴装置保证冬季反应器温度不低于25 ℃。反应器内径为80 mm,高为1 400 mm,其中有效水深高度为1 200 mm。在运行过程中,SBR由PLC自动控制,气泵和微孔曝气头供气,由转子流量计控制气量,通过蠕动泵进出水,装置如图1所示。
反应器运行过程包括进水、厌氧循环、曝气、沉淀、出水5个阶段。在反应器运行的过程中,随着沉降时间的缩短,逐渐调整运行工况,增加排水比,并逐步缩短反应时间以增加周期数,反应器运行工况如表1所示。
-
本实验接种污泥取自济南某市政污水处理厂的曝气池,该厂采用A/A/O工艺,实验启动时的污泥接种浓度(MLSS)为5 400 mg·L−1。原水采自污水处理厂集水井,原水水质:COD 300~500 mg·L−1;氨氮40~70 mg·L−1;TN 50~80 mg·L−1;TP 4~7 mg·L−1。
-
实验过程中所使用的主要分析仪器包括:Hach DR1900分光光度计;HachDRB200快速消解仪;WTW Multi 3630 IDS便携水质监测仪。
1.1. 实验装置和运行方式
1.2. 接种污泥与实验用水
1.3. 分析方法
-
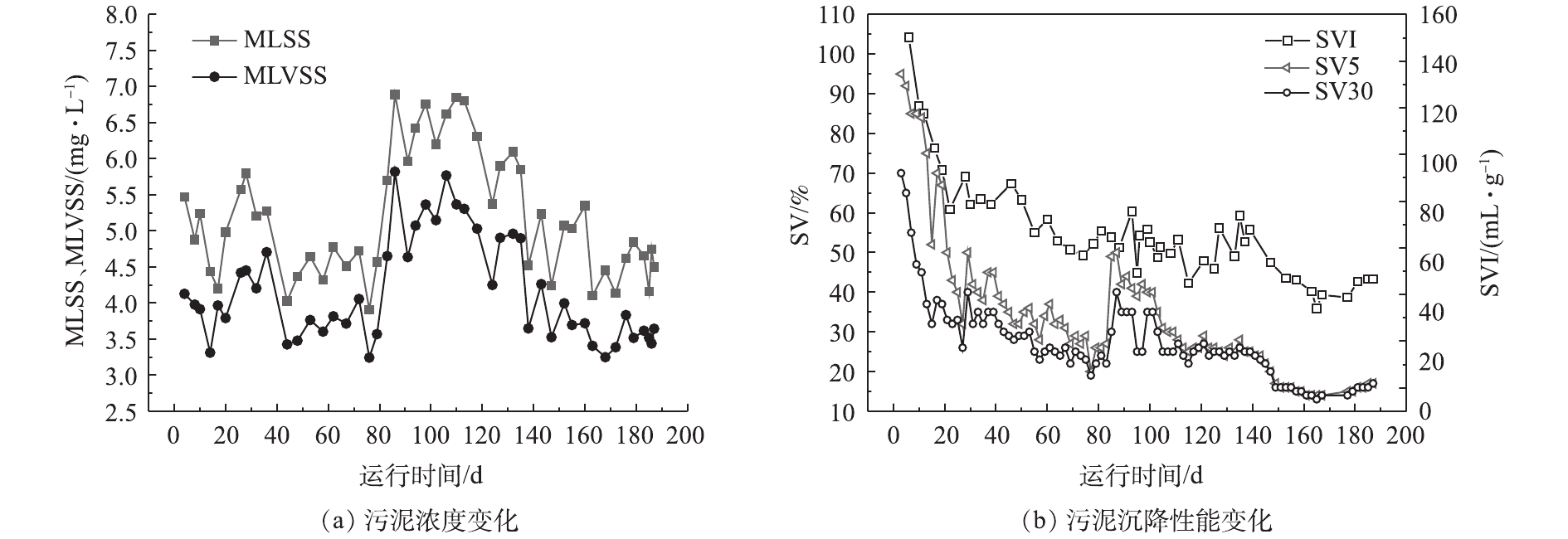
系统污泥浓度与沉降性能变化情况如图2所示。由图2(a)可见,反应器启动接种污泥浓度为5 500 mg·L−1。随着反应器的运行,采取不断缩短沉降时间的方式培养AGS,由此不断排出沉降性较差的污泥。在运行初期,由于污泥被筛选淘汰,污泥浓度整体上呈小幅下降趋势,7 d后微生物量开始缓慢增长,污泥浓度逐渐提升。在反应器运行至40 d左右时,由于当地进入多雨季节,雨水随管网汇入污水中,进水污染物浓度下降,反应器中生物量出现短暂的降低,但MLSS基本保持在4 000 mg·L−1以上,系统可稳定运行。在夏季结束后,原水中基质浓度开始升高,加之进水量的增大,在短时间内污泥浓度得到快速提升,絮状污泥一度获得一定竞争优势,随后又被逐渐筛选出体系之外。在反应器运行第80天后,继续降低沉降时间,污泥MLSS和MLVSS基本稳定在4 000~5 000 mg·L−1和3 000~4 000 mg·L−1;而有研究[18-19]表明,较高进水浓度(人工模拟废水)可使反应器污泥浓度达7 000~10 000 mg·L−1。由于实际生活污水COD值和C/N低,会导致生物量增值受限,从而维持相对低的污泥浓度[20]。
污泥容积指数(SVI)能综合反映沉降与污泥浓度之间的关系。由图2(b)可见,从SV5、SV30及SVI在好氧颗粒污泥形成过程总体上均呈下降趋势,接种絮状污泥SV5和SV30分别为95%和70%,在30 d后SV5与SV30差别明显缩小,系统沉降时间已由启动时26 min下降至8 min。相比其他利用实际污水培养好氧颗粒污泥的研究,在无外加药同时能够保持较高生物量的前提下,取得了更好的沉降性改善结果[21]。一般认为,实际污水培养好氧颗粒污泥所需的时间要大于人工配水(约30 d)[22];但实验过程中,以实际污水为基质所实现的颗粒化速度与人工配水培养所需的时间相比并无较大差距。反应器运行至100 d后,二者数值上已无显著差别。一般污泥的SV5与SV30相差小于10%时,可认为反应器内颗粒污泥占主导。反应器中污泥SVI值整体呈下降趋势,最终稳定在40~50 mL·g−1左右;而一般活性污泥的SVI为90~150 mL·g−1。由此可见,实际生活污水培养的好氧颗粒污泥具有良好沉降性能。
-
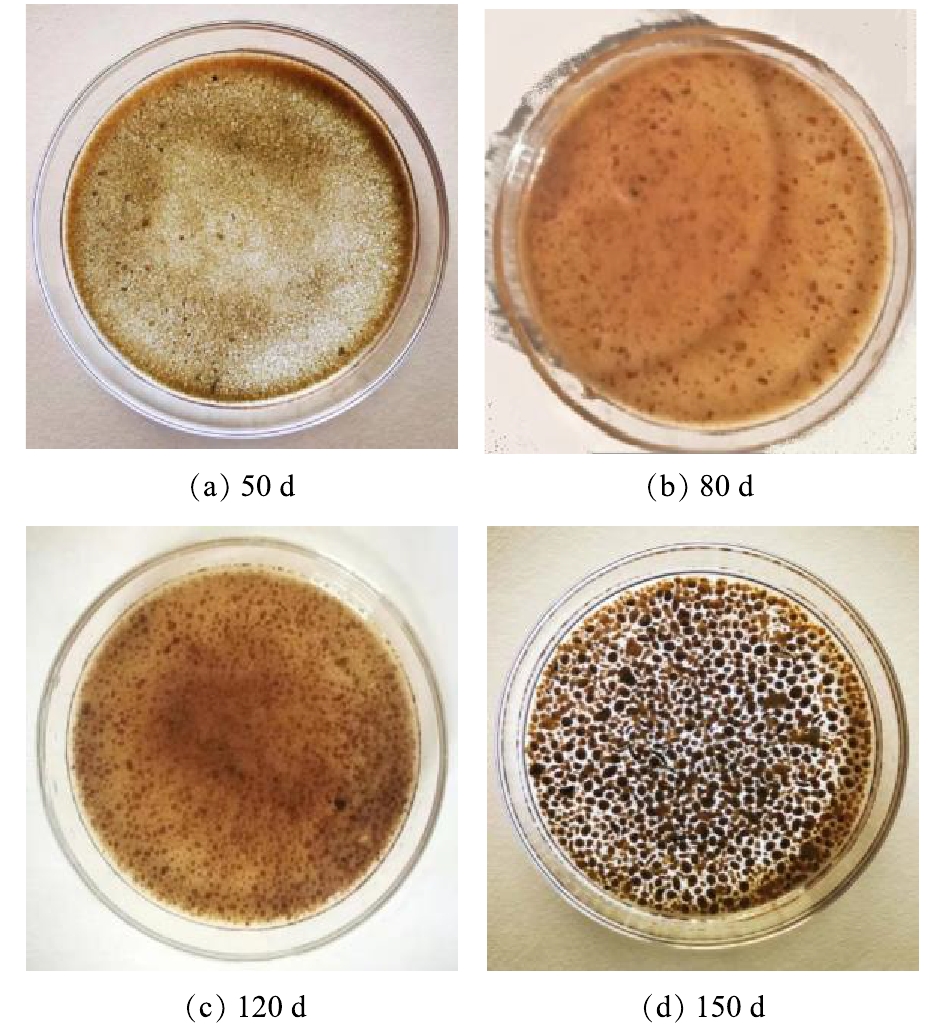
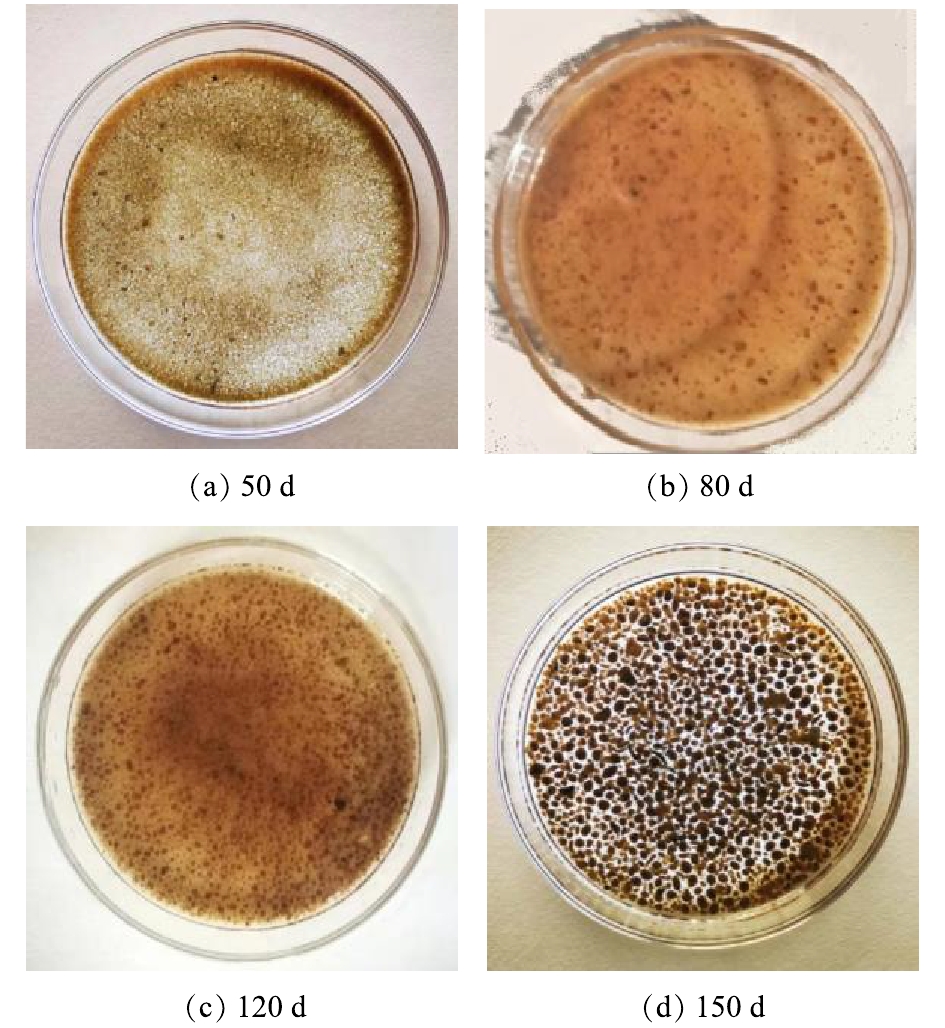
图3为反应器不同运行阶段污泥外观的变化情况。由图3可以看出,随着反应器的运行,在污泥中颗粒的比例逐渐增大,且颗粒粒径逐渐增大,呈现出与接种初期污水处理厂絮状污泥完全不同的形态。随着沉降时间的缩短,沉降性较差的污泥随出水排至反应器外,而反应器中沉降性较好的污泥则被逐渐筛选,从絮状演化为不规则的小颗粒,进而继续增大,最终形成饱满紧致、椭球形、边缘清晰的颗粒污泥。
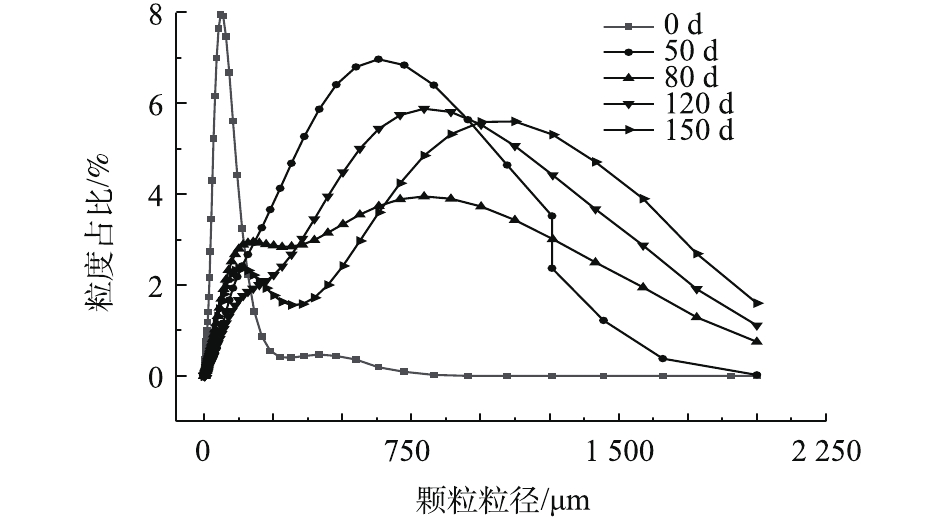
图4给出了培养过程中颗粒污泥粒径的变化情况,颗粒粒径及不同粒径的分布情况由Malvern Panalytical Mastersizer 2000 激光粒度仪测得。在反应器启动阶段,接种絮状污泥平均粒径为80.5 μm。随着反应器的运行,颗粒粒径逐渐增大,50 d后平均粒径增至378.3 μm,运行至80 d,污泥平均粒径为434.3 μm,粒径在500 μm以上的颗粒污泥约占总量的39.0%;在120 d左右,体系已基本处于稳定状态,此时颗粒污泥平均粒径为599.5 μm,基本实现完全颗粒化;反应器运行至150 d,体系中粒径超过500 μm 的颗粒污泥约占56.9%,可见颗粒污泥已占主导。
-
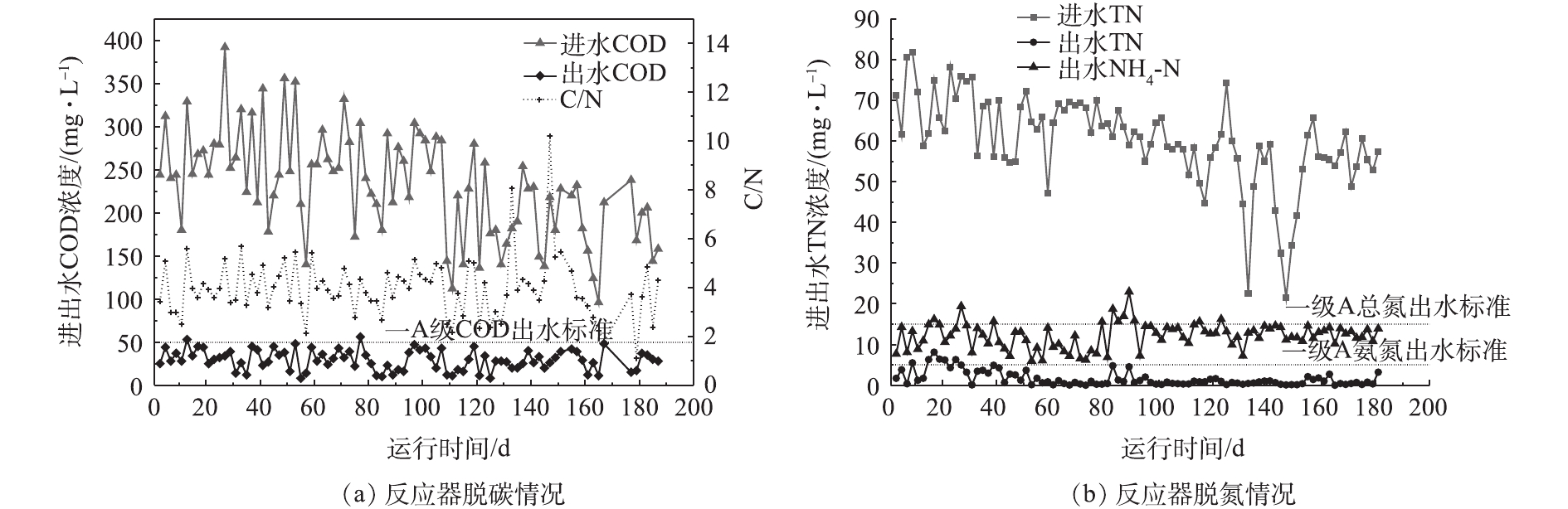
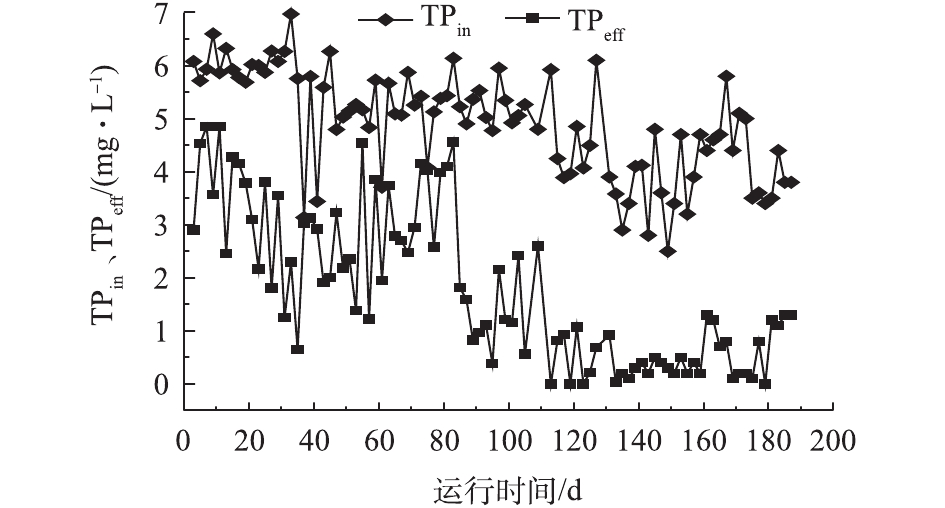
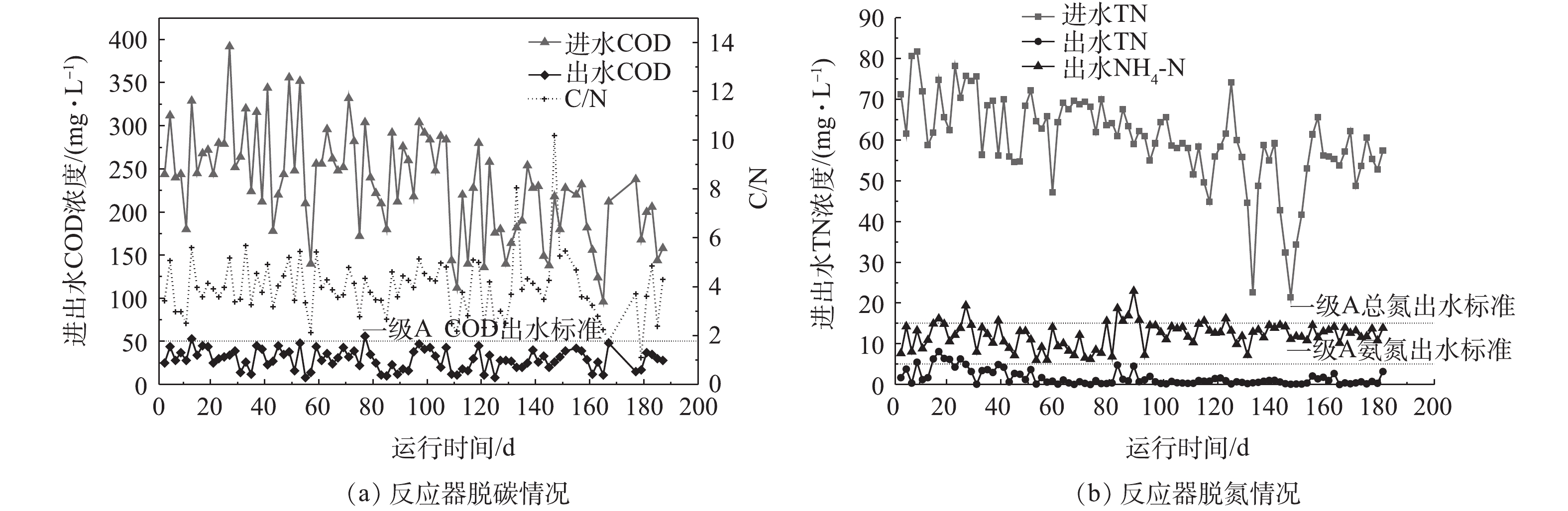
实验考察了反应器COD与TN的去除情况,反应器对碳和氮的去除效果见图5。进水取自城市生活污水处理厂集水井,在运行过程中,反应器进水碳氮比基本在2~6,属于典型的低C/N污水[3]。由图5可见,反应器启动初期受雨季影响,进水COD值总体上呈下降趋势,而出水COD值可基本保持在50 mg·L−1以下,平均去除率为89.5%,满足《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准,达标时间占比为98.9%。从整个运行过程的数据可见,除启动阶段及80 d左右因水质突变引起系统不稳定之外,反应器出水总氮基本能达到一级A标准,平均脱氮效率为78.5%,达标时间占比91.2%,而氨氮的时间天数高于98%。相较而言,传统活性污泥处理工艺在处理低C/N污水处理过程中,常需额外添加碳源以保证出水总氮达标,但添加碳源会导致运行成本和污泥产量增加,此外硝化液回流也会导致能耗增高以及占地面积增大。而好氧颗粒污泥系统以SBR为基础,利用更简单、紧凑的工艺模式,以不添加碳源的实际污水为基质,在跨越了从春季至秋季、从旱季至雨季的整个运行过程中,所达到的处理效率充分体现出好氧颗粒污泥技术在处理低C/N污水所具有的独特优势。
反应器除磷情况如图6所示。在反应器运行的前期阶段,除磷效果一直不理想,前80 d,除磷效率仅为42%,这是由于有机质浓度过低,致使聚磷菌在前期并未占据优势造成的结果。颗粒污泥在形成的过程中,需要保证存在周期性的“饥饿期”与“盛宴期”来刺激活性污泥在表面分泌胞外聚合物(EPS)来促进其团聚,并最终形成颗粒[7]。在进水之后,由于饥饿期的存在,大量碳源进入体系的瞬间即被各类微生物吸附或吸收。在这个阶段,如果聚磷菌不能获得足够的碳源作为营养物质,则会降低后续吸磷效率。而过量的排泥虽然能够提高除磷效率,但会造成生物量的损失,对体系中微生物种群的构建起到不良的影响。反应器运行90 d后,系统内颗粒污泥逐渐占据优势,除磷效果有所提高,此时反应器出水总磷基本可控制在2 mg·L−1左右。随着体系的进一步稳定,开始强化对污泥龄的把控,将其控制在7~12 d,除磷效果得以提升。130 d后,出水总磷可以保持在1 mg·L−1左右,甚至0.5 mg·L−1以下,达到一级A标准规定,这一阶段平均除磷率在70%以上。
-
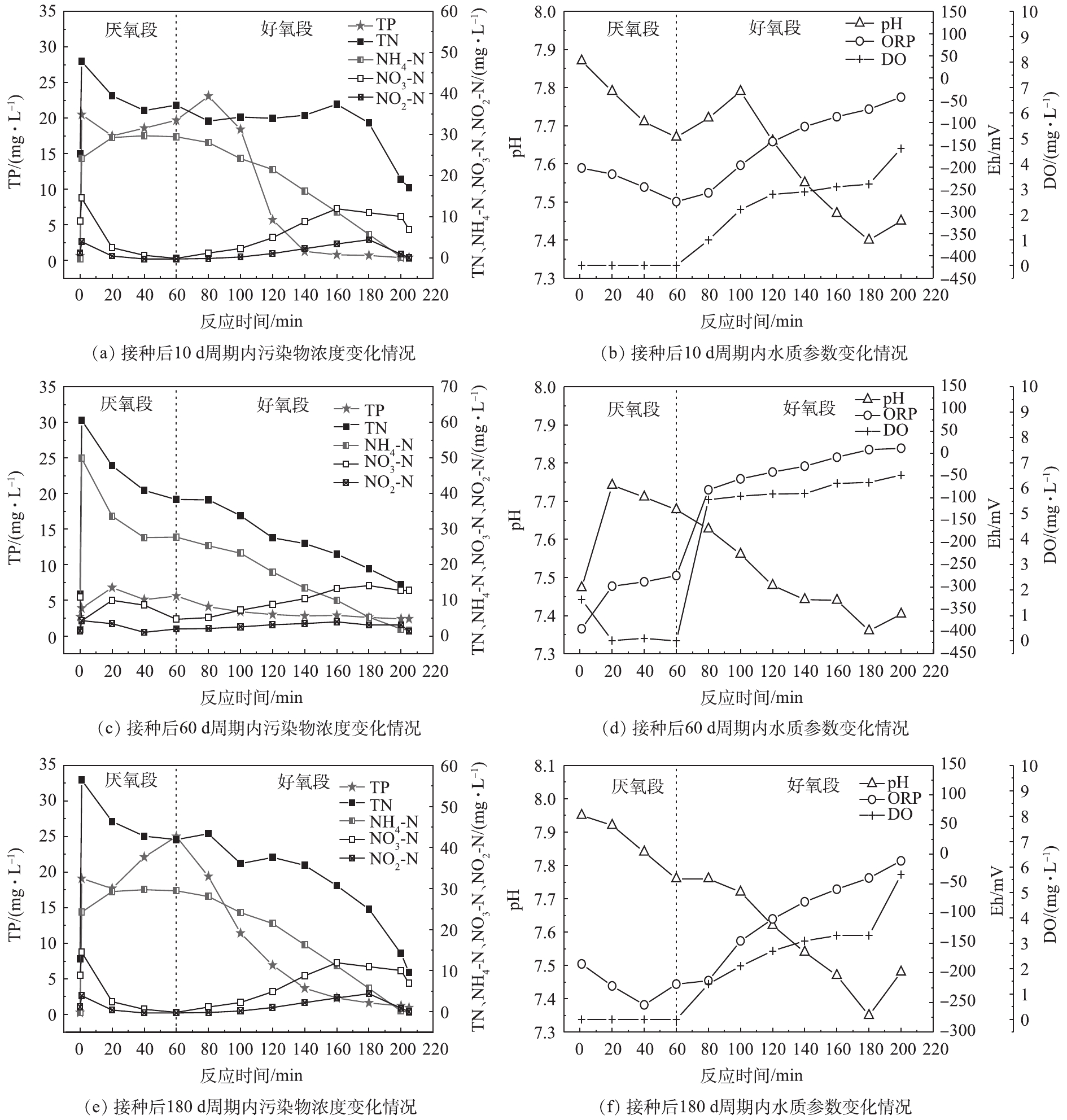
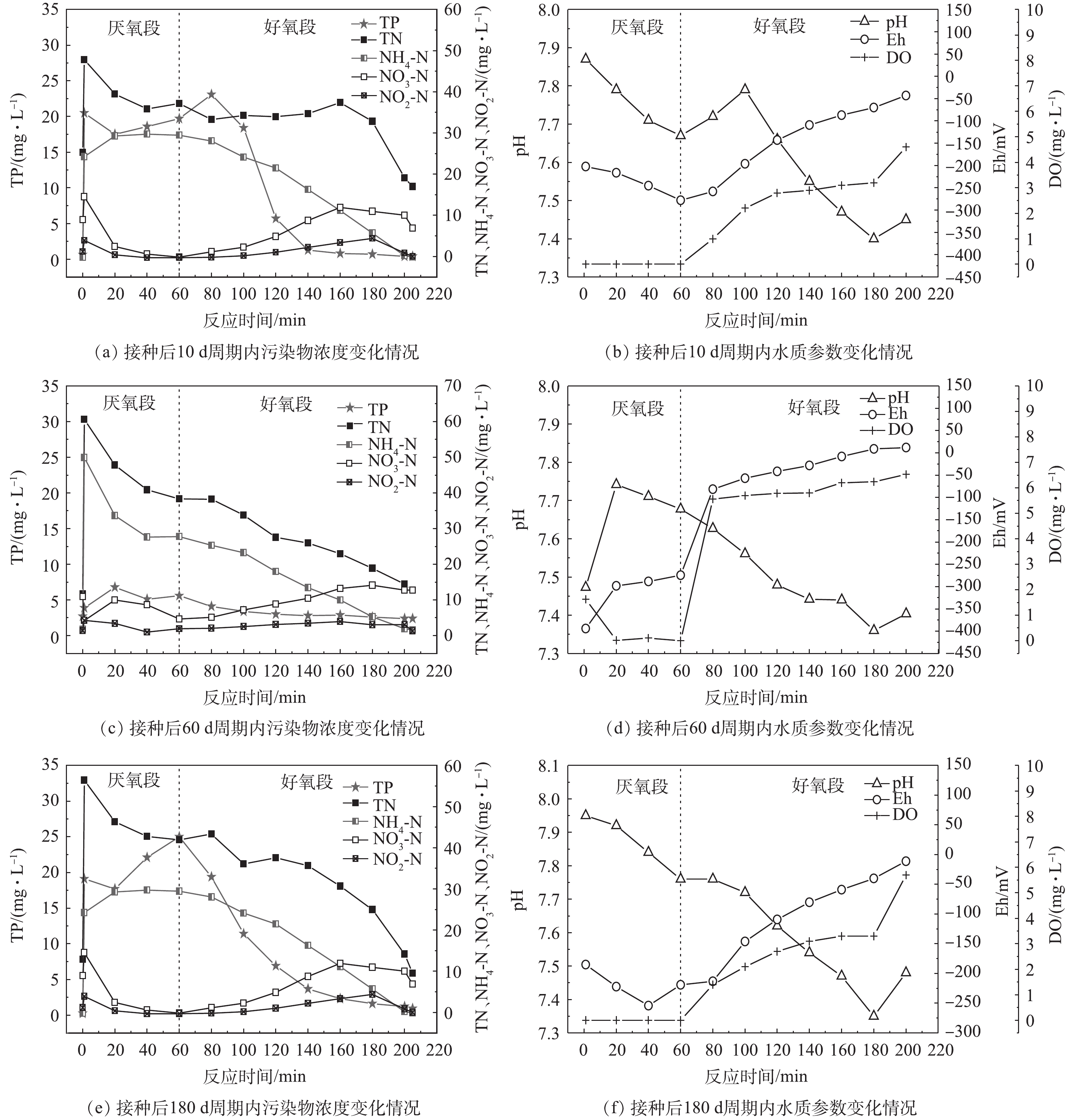
将反应器的运行模式分为进水、厌氧循环、曝气、沉淀4个阶段。在反应过程中,自进水后每隔20 min取样一次,经定性滤纸过滤掉悬浮物及少量污泥后,测定水中各污染物指标的浓度,同时在取样时记录取样口附近电极的pH、DO、Eh。不同运行阶段典型周期内污染物浓度与水质参数变化情况如图7所示。在反应器启动后,随着系统内污泥的不断筛选和淘洗,反应器中的微生物群落组成开始发生变化,其污染物降解过程也随之改变。由图7(a)可见,在接种后10 d,由于沉降性能较差的污泥被不断排出,污泥龄处在一个较小的范围内(7~10 d),此时系统除磷能力较好。但脱氮效率则很不理想,随着反应的进行,总氮在曝气100 min内没有明显的降低,氨氮和部分有机氮转化为硝态氮和亚硝态氮后积累在体系中,直至氨氮几乎被代谢完毕。这一阶段体系中无法发生同步硝化反硝化作用,出水总氮也超过20 mg·L−1。
在反应器运行60 d时,颗粒污泥在体系中占据主导地位。由图7(c)可见,在单个周期内,总氮随时间整体呈下降趋势,同步硝化反硝化作用已经开始显现,但在好氧过程中微生物对溶解氧的利用率不高,溶解氧浓度也处在一个较高的水平(图7(d))。在这一阶段,颗粒污泥逐渐架构自身微生物群落结构,因此,在低C/N进水的前提下,脱氮除磷存在明显的竞争,此时聚磷菌在竞争中处于劣势,厌氧阶段释磷量较低,故好氧段吸磷效果并不出色,出水总磷为2.4 mg·L−1,除磷效率较差。当反应器运行至180 d时,如图7(e)所示,此时各项运行参数接近稳定,系统中污泥处于完全颗粒化的状态,且颗粒的群落构建基本满足脱氮除磷要求。在这一阶段,能够观察到磷量明显,且系统除磷效果良好,出水总磷为0.9 mg·L−1。同时系统中总氮整体呈下降趋势,硝酸盐积累量很低,同步硝化反硝化作用明显,出水总氮为9.5 mg·L−1,可实现总氮达标出水。
根据生物脱氮原理,在硝化过程中,微生物将消耗碱度,从而引起pH降低;在反硝化过程中则会生成碱度,导致pH回升。颗粒污泥自身拥有特殊的外部好氧-内部缺氧的结构,能够保证在曝气阶段,外部好氧层进行硝化反应的同时内部仍然能够保持缺氧状态,通过反硝化作用将NOx-N转化为氮气,实现同步硝化反硝化[7]。另外,由于外部水体为有氧环境,且水体中存在大量的氨氮,硝化速度与反硝化速度很难达成同步。在曝气阶段初期,硝化速度大于反硝化速度,此时系统的pH开始下降,溶解氧开始提升。在曝气过程中,由于微生物不断消耗溶解氧,溶解氧不会快速到达饱和水平,直至水体内氨氮与COD近乎被氧化完全,此时好氧菌代谢程度降低,溶解氧再无大量消耗,因此,曝气阶段后期溶解氧有一个明显的陡增。同时由于硝化作用接近完全,反硝化速率将超过硝化速率,碱度开始被补偿,故pH出现一回升过程,pH的拐点以及DO的陡增点可以作为硝化作用接近结束的指示指标。
在整个体系中,由于多种物质以及不同的生化反应同时存在,因此,所测得的Eh不应简单视为一个热力学概念或某种氧化物(还原物)的浓度指标,而是整个体系所处的氧化还原状态的综合指标。Eh的大小往往与体系中不同功能菌代谢有关,一般来说,有机物氧化过程常发生在−50~200 mV,反硝化过程则发生在−50~50 mV,厌氧释磷过程发生在−200~0 mV[23]。在有机物被氧化的过程中,还原性物质不断被消耗,Eh有所升高,特别是有机物基本氧化完全,DO浓度大幅提高,此时Eh也会有进一步的跃升。此外,在硝化过程中,
NH+4 -N不断被氧化为氧化态的NO−x -N,导致体系的Eh也会升高;在相应的在反硝化过程中,NO−x -N被不断还原为N2,Eh则会降低。如图7(b)和图7(d)所示,在这一阶段,由于前一周期系统曝气阶段DO浓度较高,致使进水完成后余留溶解氧将原水中的NH+4 -N以及少量有机物氧化,Eh在厌氧阶段呈上升状态,此后由于溶解氧耗尽,产生的NO−3 -N又被迅速还原,因而上升的趋势有所减弱。这一特殊过程的出现造成碳源在这一阶段被大量消耗,聚磷菌未能得到充足的碳源,故其释磷效果较差,进而影响了好氧吸磷过程。在曝气阶段,DO浓度迅速升高,Eh也随之升高。因此,Eh的变化是系统中正在发生的各生化反应的综合体现,不正常的Eh变化对系统运行状况是否正常具有重要的指示性作用。
2.1. 污泥沉降性能变化
2.2. 污泥形态与粒径变化
2.3. 污染物去除情况
2.4. 反应周期内脱氮除磷过程
-
1)以低C/N市政污水为基质,在不添加碳源的前提下,可以培养出成熟的好氧颗粒污泥,通过合理调控运行工艺参数能够实现高效脱氮除磷过程。
2)好氧颗粒污泥与普通活性污泥对氮的降解过程有明显区别,其特殊的理化性质能保证以同步硝化反硝化的方式高效处理低C/N污水。
3)好氧颗粒污泥体系中DO、pH、Eh的大小及其变化趋势对系统运行调控及状态变化具有指示性作用。





 下载:
下载: