-
湖泊是一种生物与环境、生物与生物之间相互依存与制约的复杂系统。一般情况下,这个系统是处于相对平衡的状态,过于频繁的人类活动会打破原本的平衡状态。2018年中华人民共和国生态环境部发布的关于湖库富营养化现状调查结果[1]显示,在所有被调查的湖库中,中营养占比为61.7%,中营养以上占比为29%,仅有9.3%营养化程度为贫营养。底泥是湖泊水体重要的营养源,在湖泊自净能力范围内,沉积物表现为营养物的“源”,超过其承载力时则表现为“汇”。由于浅水湖泊具有环境比较封闭、流动性差、水深较浅、易污染等特点,所以外界环境极易对湖泊水环境造成干扰,使得沉积物中的污染物释放到水体中形成二次污染。
氮磷过量输入是导致湖泊富营养化的直接原因,进入湖泊水体的氮磷来源于2个方面:一是外源的直接输入;另一重要来源则是底泥向上覆水的内源释放。近年来,国内外学者在对非洲的东非湖[2]、美国的太浩湖[3]、中国的乌梁素海[4]和太湖梅梁湾[5]等研究中,也证实了底泥污染物质对水质有较大的影响,因此,对因底泥营养盐释放引起水体二次污染的问题进行了极大的关注,并展开了一系列的相关研究。这些研究主要包括沉积物中污染物含量及分布[6]、污染程度评价[7]、底泥的释放机理[8]等。掌握污染物在沉积物-上覆水间的迁移对内源污染防治至关重要,迁移作用主要包括扩散、吸附-解吸、矿化、溶解和分解等。在这些过程中,pH[9]、溶解氧[10]、温度[11]、盐度[12]、微生物或藻类[13]、扰动(包括物理和生物扰动)[14]等因素会影响沉积物-上覆水间物质的交换。目前,关于此方面的研究多是从单因素角度定性地对环境因子和污染物释放间的关系进行分析[15-16]。张强等[17]在研究中发现,高扰动强度增加了TN和COD的释放通量,缩短了TP的吸附-解吸平衡时间,而对氨氮的影响较小。实际上各因子是协同作用的,也有部分学者通过设计正交实验,揭示了多因子共同作用下底泥的释放规律。张茜[18]通过正交实验得出温度、pH、溶解氧对总氮和总磷释放速率有着显著的差异,沉积物中总氮和总磷的释放与环境因子间的显著性排序为pH>温度>溶解氧。张硕等[19]研究发现,温度和溶解氧交互作用对正磷酸盐交换通量影响显著,对氨氮和硝氮交换通量无显著影响。但正交实验也存在一定的局限性,其分析的是离散型数据,所求得的因素最佳组合只能局限在所设计的工况中,但在现实情况中,各因子的变化是连续的,离散型数据会降低所得结果的精度。
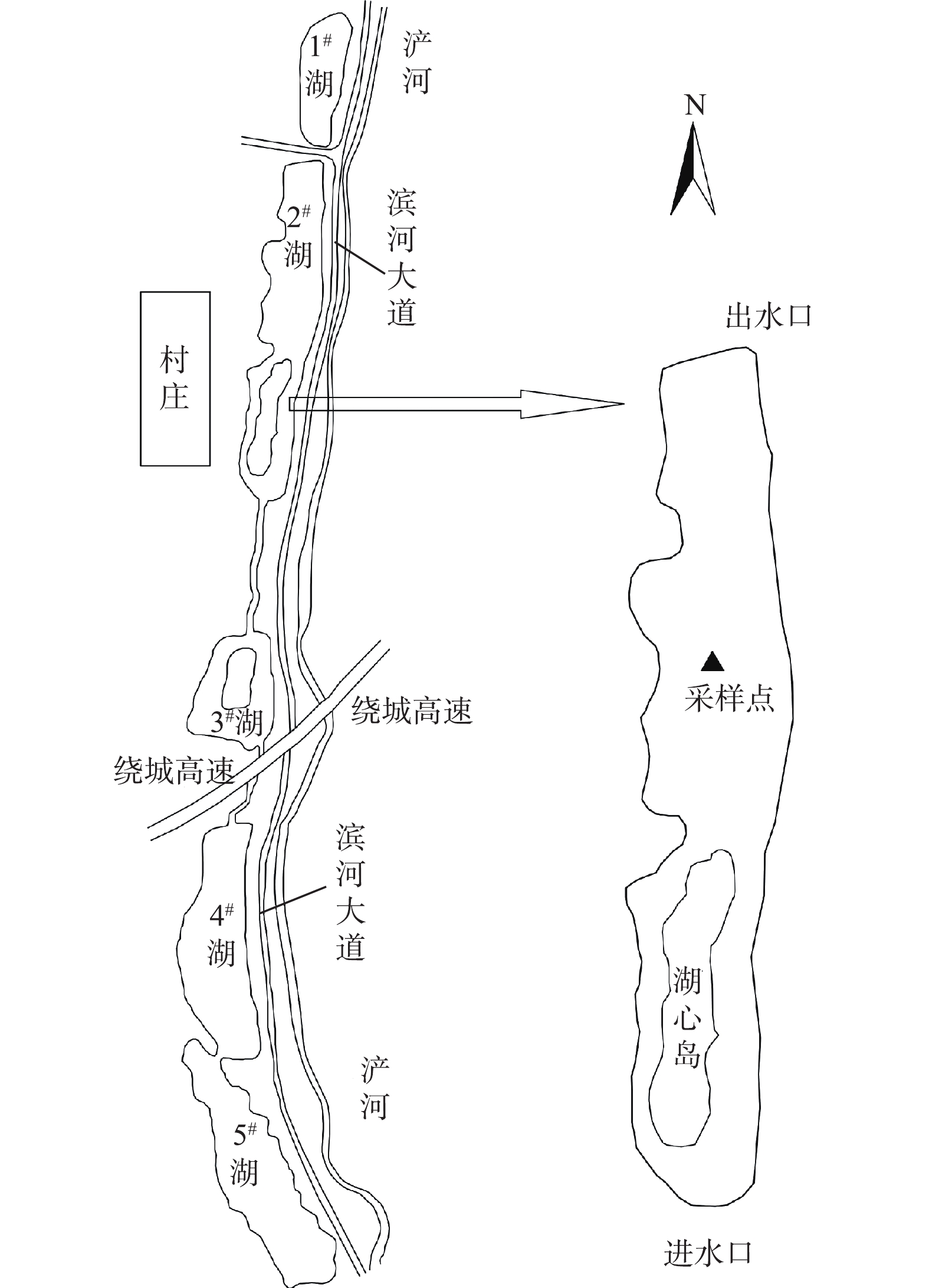
雁鸣湖2#湖(图1)位于西安市,属于浅水人工湖,从浐河引水,属于河道外湖泊。湖西面为黄土源,雨季时雨水夹带着塬上的污染物会流入2#湖,加上受污染的浐河水体会直接进入2#湖,这些因素都会导致湖泊水环境受到污染。在进行本研究前,监测发现,2#湖底泥和水体已经受到一定程度的污染,底泥颜色呈现深褐色至黑色,并散发有难闻气味,水体中TN、TP已经远超过国际上规定的富营养化发生的阈值[20](TN为0.2 mg·L−1,TP为0.025 mg·L−1)。针对雁鸣湖内源污染的研究很少,然而污染现状已不容忽视。本研究以雁鸣湖为研究对象,在单因子实验的基础上,结合响应面法,分别考察了温度、溶解氧、pH对沉积物-上覆水界面氮磷释放规律的影响,此实验方法规避了正交实验工况离散、回归精度较低等不足,分析了单因子作用及交互作用对界面氮磷释放的影响,并通过建立回归模型量化反映环境因子与释放量间的对应关系,研究结果对雁鸣湖富营养化防治具有一定的参考价值。
-
于2019年秋季进行样品采集,实验所用底泥采自西安市雁鸣湖2#湖中心,具体位置见图1。底泥通过抓斗式采样器获得,上覆水通过有机玻璃采样器获得。将采集的上覆水装入水桶,底泥装进自封袋迅速带回实验室备用。
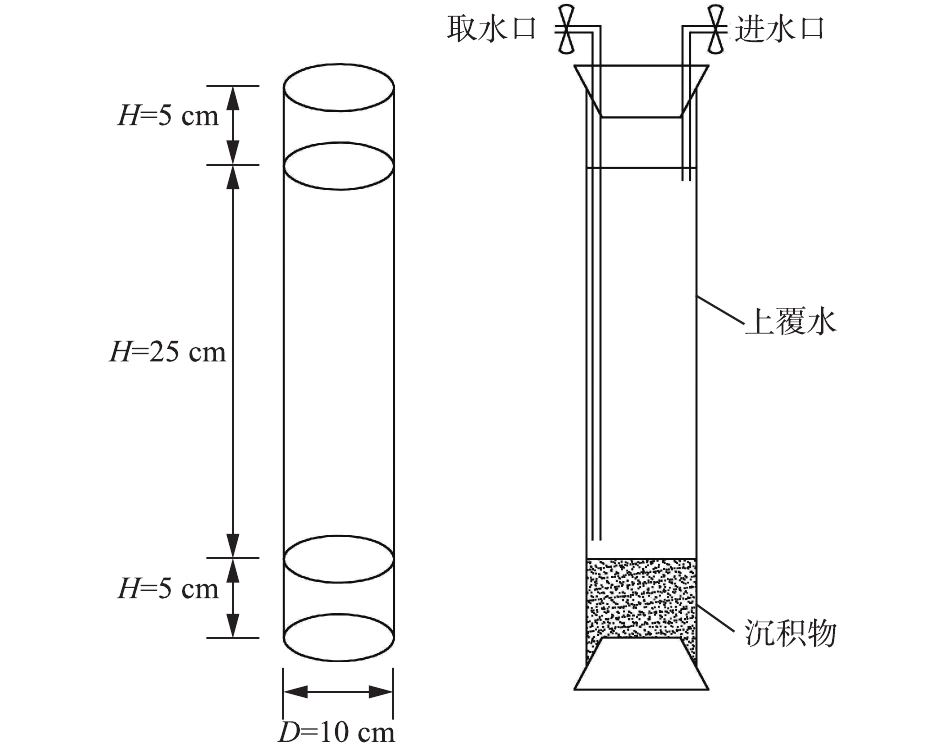
在实验室将采回来的泥样平铺于有机玻璃柱底部,将上覆水缓缓加入底泥上部进行实验,培养装置如图2所示。选取的环境因子有温度、溶解氧、pH(X1、X2、X3)。上覆水温度的调节通过恒温培养箱控制;溶解氧的调节通过向水中充氮气或氧气实现;pH的调节通过向原水中加盐酸或氢氧化钠来调控。
在单因子实验中,环境因子水平值的设置参考湖泊历史实测值。每个因子设置5个水平值:温度分别为5、10、17.5、25、30 ℃;溶解氧分别为3、4.5、6、7.5、9 mg·L−1;pH分别为 5、6、7、8、9,共15个培养柱。每隔12 h取一次上覆水,检测其中TN、TP、
NH+4 -N、PO3−4 -P的含量,每个指标测定3个平行样,整个实验周期共持续7 d。每次取完水样补充相同体积的上覆水。响应面实验根据Box-Behnken模型设计要求设有17个培养柱,为估计实验误差,其中有5组中心点重复实验。所测营养盐种类同单因子实验,每个指标测定3个平行样。因子水平数的设置根据单因子的设置及Box-Behnken模型设计要求决定,最终设置的变量水平及对应编码如表1所示。
-
上覆水中TN、TP、
NH+4 -N、PO3−4 -P,参照文献中的方法[21]测定,温度、pH、溶解氧用便携式多参数测定仪测定。本研究采用实验室培养法进行交换通量的估算,具体计算方法[22]如式(1)所示。
式中:F为交换通量,mg·(m2·h)−1,F>0表示污染物从沉积物向上覆水扩散,否则,从上覆水向沉积物扩散;A为沉积物与水界面营养盐交换面积,m2;t为培养时间,h;Mt为t时间段内营养盐的质量变化量,mg,计算方法如式(2)所示。
式中:V为培养柱中上覆水的总体积,L;Ct为t时刻测得的上覆水中营养盐浓度,mg·L−1;Dt−1为t−1时刻上覆水中实际的营养盐浓度,mg·L−1,计算方法如式(3)所示。
式中:V0为每次所取的上覆水体积,L;C0和Ct−1分别为原始时刻和t−1时刻上覆水中营养盐的浓度,mg·L−1。
-
图3为氮磷通量随温度变化的趋势。氨氮和总氮、正磷酸盐和总磷表现出一致性的变化规律,通量均随温度增加呈现明显的上升趋势。30 ℃下的氨氮和总氮通量分别为5 ℃时的1.8倍和2.2倍。一方面是由于温度较高时微生物活性有所增强,直接加速有机氮的矿化作用[23];另一方面是由于微生物代谢和运动强度的增加,会消耗环境中氧气,使沉积物-上覆水界面处于厌氧环境,从而增强反硝化作用,进而加速界面间氮扩散。由图3可知,温度为5 ℃时的磷通量最小,正磷酸盐和总磷通量仅为0.166 mg·(m2·h)−1和0.315 mg·(m2·h)−1,随着温度逐渐升高,磷通量也逐渐增大,在30 ℃时正磷酸盐、总磷通量分别增加至0.243 mg·(m2·h)−1和0.566 mg·(m2·h)−1。这是因为升温会增加体系中离子的活性,促进离子交换反应的进行,加快磷酸盐的溶解及扩散作用;同时由于生物活动增强导致界面间耗氧增强,厌氧条件加速了Fe3+还原成Fe2+、Mn4+还原成Mn2+的速率[24],使铁锰结合态磷得到释放。
在不同溶解氧浓度的条件下,底泥的氮磷释放规律呈现一定的差异性。图4为氮磷通量随溶解氧浓度的变化趋势。氨氮通量为2.102~3.109 mg·(m2·h)−1,总氮通量为3.342~5.942 mg·(m2·h)−1,即溶解氧从最高水平(9 mg·L−1)减小到最低水平(3 mg·L−1)时,氨氮和总氮通量分别增加了1.5倍和1.8倍,在厌氧条件下的氮通量显著有所增加,低溶解氧水平下会促进底泥中有机氮的矿化[25],同时反硝化作用剧烈,无机氮主要以氨氮的形式释放,使得氮通量有明显的增加。对于磷的释放,在高溶解氧(9 mg·L−1)水平下,正磷酸盐通量为实验范围内最小,为0.183 mg·(m2·h)−1;而在厌氧条件下(3 mg·L−1),其通量达到0.333 mg·(m2·h)−1,为好氧条件下的1.8倍,总磷通量也由好氧条件下的0.456 mg·(m2·h)−1增加到0.566 mg·(m2·h)−1。这是因为厌氧条件促使Fe3+还原成Fe2+,使得原本被氢氧化铁胶体吸附的磷释放出来;而在高溶解氧条件下,体系处于氧化状态,Fe2+会被氧化成Fe3+,形成的氢氧化铁胶体会吸附部分磷沉积在底部[26];同时,Fe3+也会直接与部分磷酸盐结合成沉淀吸附在沉积物表层,从而降低磷的交换通量。
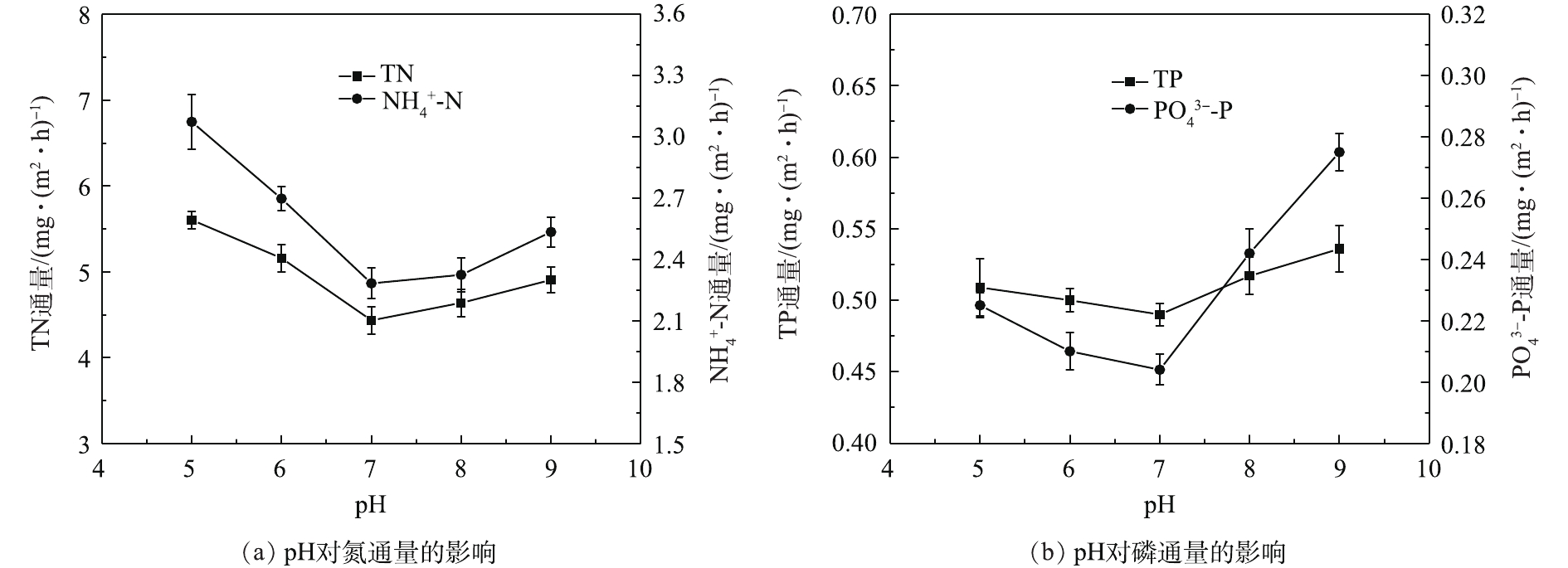
pH对沉积物中氮磷释放的影响如图5所示。可以看出,在偏酸或碱性条件下的氮通量显著大于中性条件下。在pH=7时,氨氮和总氮通量最低;在pH=5时,氨氮和总氮通量达到最大值,均为最小值的1.3倍。在酸性条件下,存在较多H+,会和体系中
NH+4 竞争吸附在胶体上[27],pH越低,竞争作用越强,氮释放越强;在碱性条件下,上覆水中存在的OH−会和NH+4 反应生成气态NH3,其可从上覆水中逸出,上覆水中氨氮减少,使得两相间浓度差变大,促进了底泥中氮向上覆水的释放。pH对底泥磷的影响主要通过吸附-解吸和离子交换2种作用得以实现。由图5可知:在中性条件下,正磷酸盐通量最小,在pH=9时达到最大,为中性条件下的1.4倍;随着pH增加,总磷通量也由最小值0.490 mg·(m2·h)−1 (pH=7时)增加到最大值0.536 mg·(m2·h)−1 (pH=9时)。在碱性条件下,磷释放主要以离子交换为主[28],体系中OH−会与磷酸根发生离子交换,碱性愈强,交换作用愈强,导致磷通量增加;在酸性条件下,难溶性磷酸盐及吸附了磷的氢氧化物胶体会溶解,使磷脱离底泥进入上覆水,酸性愈强趋势越明显,磷通量越大;而在pH=7时,磷酸盐主要以HPO2−4 及H2PO−4 的形式存在,此时离子易与体系中的金属离子结合被底泥吸附,使得底泥中的磷不容易释放。 -
1) BBD设计方案及测定结果。根据Box-Behnken模型设计要求,以温度、溶解氧、pH为自变量,以各营养盐交换通量为响应值进行实验设计。设有3组平行样,实测结果如表2所示,实验工况设计及通量平均值如表3所示。
2)模型的建立和方差分析。利用BBD模型,对表3中的结果进行数据回归拟合,温度(X1)、溶解氧(X2)、pH(X3)与TN通量(FTN)、TP通量(FTP)、
NH+4 -N通量(FNH+4−N) 、PO3−4 -P通量(FPO3−4−P) 4个响应值的二次多项式回归模型分别如式(4)~式(7)所示。对4个模型方程分别进行了方差分析和显著性分析,结果如表4所示。4个模型的P值均<0.01,说明显著性高,失拟项也均大于0.5,即所得方程和实际拟合中非正常误差所占比例小,这说明所得模型可信度高,模拟精确。TN、TP、
NH+4 -N及PO3−4 -P模型的变异系数分别为0.077、0.044 4、0.075 4、0.032 7,即数据离散程度较小,表明各方程拟合度好,模型回归性较好。4个模型的校正决定系数R2Adj 分别为0.907 5、0.922 8、0.914 5、0.958 2,即4个模型分别能解释90.75%、92.28%、91.45%、95.82%各自响应值的变化,总变异度分别有9.25%、7.72%、8.55%、4.18%不能用模型解释;且R2Adj 和R2值接近。在此基础上,用回归方程进行模拟,图6为氮磷交换通量的实际值和预测值的对比,过原点的斜率为1的直线代表实际值和预测值完全吻合的情况[29]。可以看出,部分点落在直线上,其余点基本均匀地分布在直线两侧且偏离较小,这进一步说明4个模型与实验结果吻合度较高。由此可知,所建立的4个模型稳定性较高,拟合度良好,能够用来分析各环境因子对底泥氮磷交换通量的影响效果。由表4可知,单因子温度(X1)和溶解氧(X2)对各营养盐通量的影响显著(P<0.01),pH(X3)无显著影响。交互项X1X2对
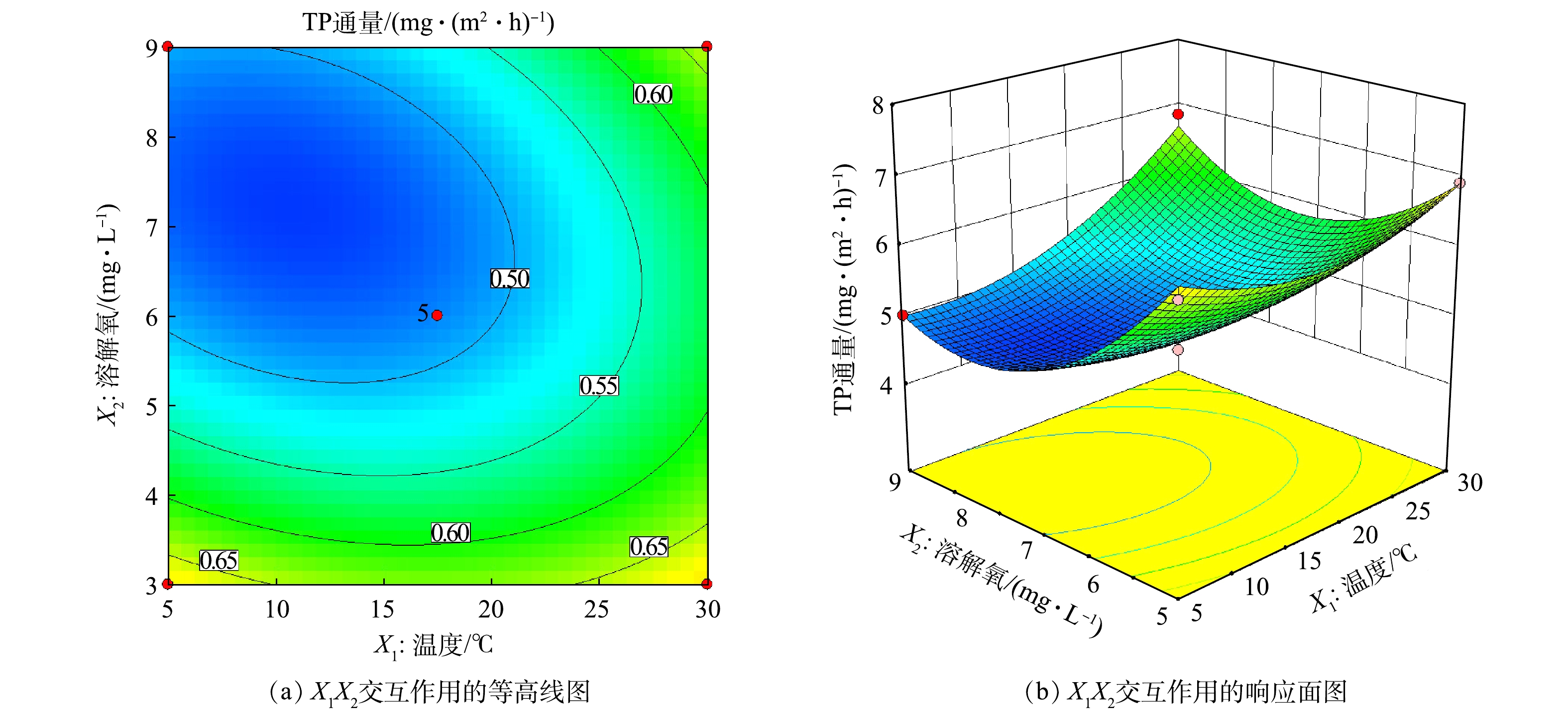
PO3−4 -P通量影响显著(P<0.01),对TP和NH+4 -N通量影响显著(P<0.05),对TN无显著影响;X1X3对TN和NH+4 -N通量影响显著(P<0.05),对TP和PO3−4 -P通量无显著影响;X2X3对4种营养盐通量均无显著影响。模型X11 、X22 和X33 对各响应值的均有显著影响(P<0.01),说明环境因子与响应值之间不是简单的线性关系,二次项对响应值有着较大的影响。从整体显著性来看,与TN和TP相比,环境因子对离子态的NH+4 -N及PO3−4 -P的交换通量影响作用更大。3)响应面交互作用分析。为直观反映温度、溶解氧、pH 3个环境因子及其交互作用对各营养盐交换通量的影响,利用回归方程建立对应的等值线和响应面图。一般来说,等高线越接近于椭圆状,响应面坡度越大,说明交互作用越明显[30-31]。根据回归模型,本研究中选取交互作用效果较好的等高线图和曲面图。
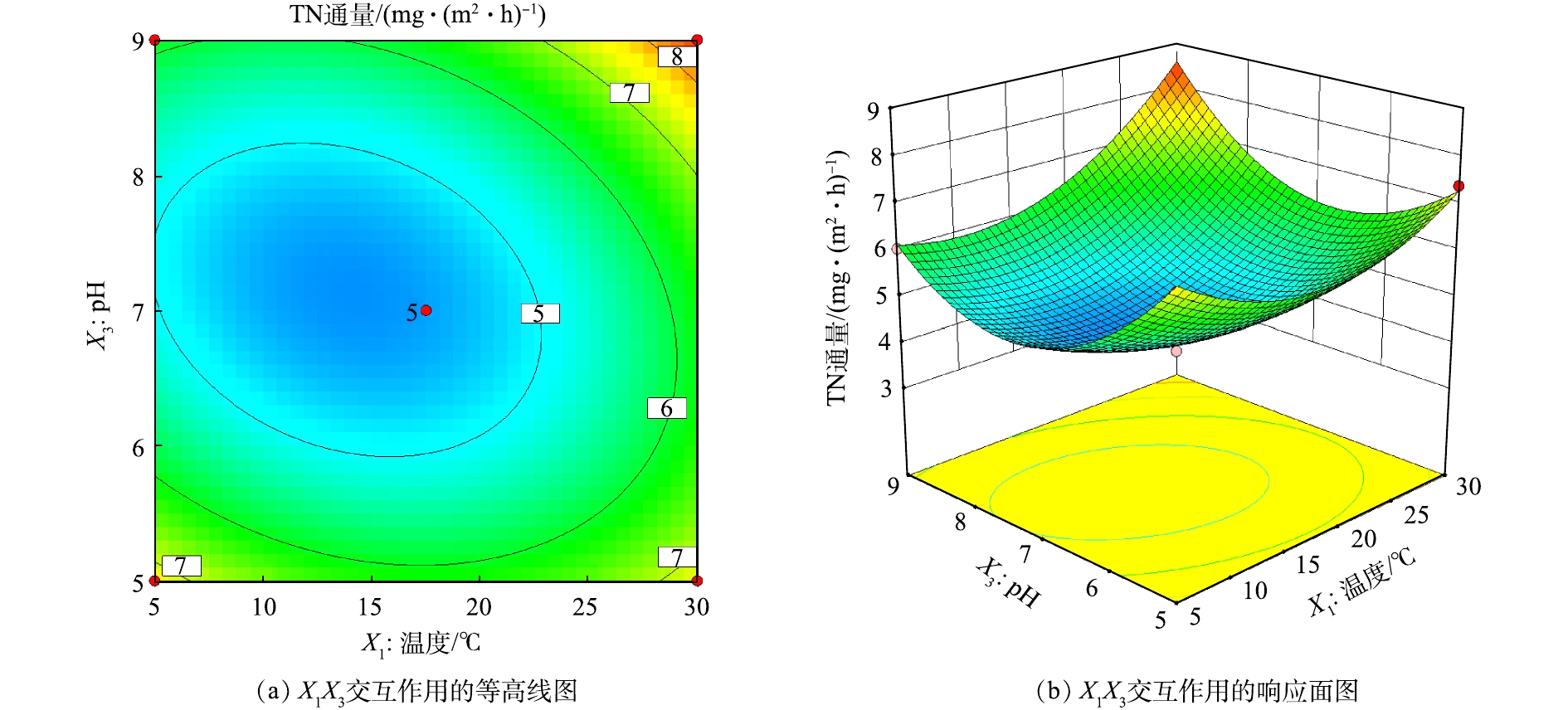
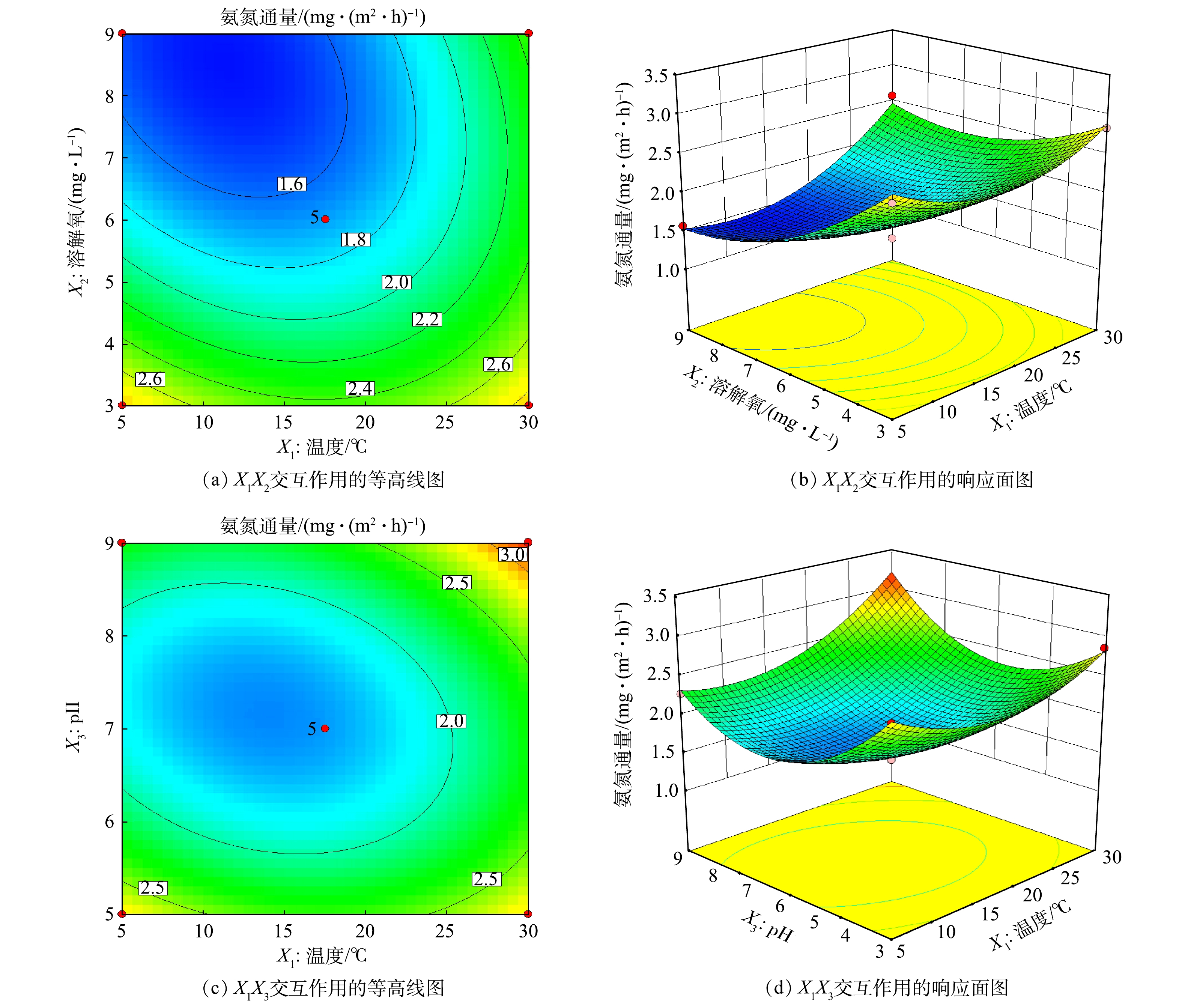
图7反映了温度和pH对TN通量交互作用的影响。可以看出,等高线图呈现明显的椭圆形状,且由图7(b)可以看出,最小响应值在曲面上,与沿着单一因子坐标轴走向的最小值不重合,表明温度和pH对TN通量有交互作用。图8为温度和溶解氧对TP通量交互作用的影响,等高线接近椭圆,响应面存在一定弯曲,表明温度和溶解氧交互作用对TP通量有一定的影响。由等高线图8(a)可知,沿溶解氧轴方向上的等高线比沿温度轴方向上的密集且陡峭,表明相对于温度,溶解氧对TP通量影响更为显著,这与方差分析结果一致(表4)。由图9可知,温度和溶解氧、温度和pH的交互作用均对
NH+4 -N通量的等高线呈椭圆,且响应面有一定坡度,表明温度和溶解氧交互作用、温度和pH交互作用均对NH+4 -N通量影响显著。由图9(a)和图9(c)可知,在实验范围内,当温度一定时,NH+4 -N通量随pH变化波动很小,而随溶解氧变化很大,表明溶解氧对响应值的贡献更大,即溶解氧对NH+4 -N通量的影响作用比pH更显著,这与方差分析结果一致。由图10可知,等高线及响应面形状表明了温度和溶解氧之间存在交互作用。由图10(a)可知,当溶解氧一定时,PO3−4 -P通量随温度变化很小;当温度一定时,PO3−4 -P通量却随溶解氧的增大而减小,这说明相比于温度,溶解氧对PO3−4 -P通量影响更显著。4)最不利释放条件的预测与结果验证。在对内源污染进行防控时,可通过对环境因子的控制使得底泥释放量较小,所以对雁鸣湖底泥最不利释放(即释放量最小)条件进行了预测。图7~图10也显示响应面开口向上,即响应值有极小值。以响应面优化得到条件组合,通过响应面分析得出氮磷释放量最小时自变量的数值分别为X1=10 ℃、X2=7.87 mg·L−1、X3=7.13。温度为10 ℃、溶解氧为7.87 mg·L−1、pH为7.13时,各响应值取最小值,TN交换通量为3.956 mg·(m2·h)−1,TP交换通量为0.471 mg·(m2·h)−1,
NH+4 -N交换通量为1.469 mg·(m2·h)−1,PO3−4 -P交换通量为0.146 mg·(m2·h)−1。为了检验响应面法所得的实验结果,通过实验加以验证,结合实验情况将条件修正为:X1=10 ℃、X2=8.0 mg·L−1、X3=7.0,即在温度为10 ℃、溶解氧为8.0 mg·L−1、pH为7.0的条件下,进行了3次平行实验,实验结果如下:TN交换通量为3.779 mg·(m2·h)−1,TP交换通量为0.488 mg·(m2·h)−1,
NH+4 -N交换通量为1.409 mg·(m2·h)−1,PO3−4 -P交换通量为0.141 mg·(m2·h)−1,与预测值很接近,误差均在5%以内,表明预测结果是可靠的,进一步说明所得模型能较好地预测雁鸣湖界面间营养盐的交换通量。因此,园区应注意对温度、溶解氧及pH进行控制,以防止内源释放对雁鸣湖环境造成更严重的污染。 -
1)控制单因子变化条件下,雁鸣湖沉积物-上覆水界面间氮磷通量随着温度的升高而增加,30 ℃时达到最大;随溶解氧浓度的增加而减小,在缺氧条件下(DO=3 mg·L−1),氮磷通量取得最大值;pH为中性条件下最小,氮通量在酸性条件下(pH=5)达到最大,磷通量在碱性条件下(pH=9)达到最大。
2)对环境因子与雁鸣湖沉积物-上覆水界面间营养盐通量的关系进行拟合,结果表明4种营养盐通量与环境因子间均符合二次多项式回归模型。
3) 方差分析及响应面结果表明,温度和pH交互作用对TN通量影响显著;温度和溶解氧交互作用对TP通量影响显著;温度和溶解氧交互作用、温度和pH交互作用对
NH+4 -N通量影响显著;温度和溶解氧交互作用对PO3−4 -P通量影响极显著。4)响应面优化结果表明,温度为10 ℃、溶解氧为7.87 mg·L−1、pH为7.13是雁鸣湖底泥释放的最不利条件,此时TN交换通量为3.956 mg·(m2·h)−1,TP交换通量为0.471 mg·(m2·h)−1,
NH+4 -N交换通量为1.469 mg·(m2·h)−1,PO3−4 -P交换通量为0.146 mg·(m2·h)−1,各响应值取最小值。
环境因子对雁鸣湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响
Effects of environmental factors on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from the sediment of the Yanming Lake, China
-
摘要: 为探明环境因子对雁鸣湖沉积物-上覆水界面间氮磷释放的影响,通过单因子实验和响应面实验分析探究了温度、溶解氧及pH对氮磷释放通量的影响。单因子实验结果表明:雁鸣湖沉积物-上覆水界面间氮磷通量随着温度的升高而增加;随溶解氧浓度的升高而减小;当pH为中性时,氮磷通量最小,氮通量在pH=5时达到最大值,磷通量在pH=9时达到最大值。BBD模型拟合结果显示,各环境因子与氮磷通量间拟合关系均为二次多项式。响应面实验结果表明:温度和pH交互作用对TN通量影响显著;温度和溶解氧交互作用对TP通量影响显著;温度和溶解氧交互作用、温度和pH交互作用对
NH+4 -N通量影响均为显著;温度和溶解氧交互作用对PO3−4 -P通量影响极显著;雁鸣湖底泥释放的最不利条件为T=10 ℃、DO=7.87 mg·L−1、pH=7.13,此时的TN交换通量为3.956 mg·(m2·h)−1,TP交换通量为0.471 mg·(m2·h)−1,NH+4 -N交换通量为1.469 mg·(m2·h)−1,PO3−4 -P交换通量为0.146 mg·(m2·h)−1。以上研究结果可为雁鸣湖富营养化防治提供参考。Abstract: To investigate the effect of environmental factors on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus between the sediment-overlying water interface of the Yanming Lake, the effects of temperature, dissolved oxygen and pH on the release flux of nitrogen and phosphorus were investigated by single factor test and response surface analysis. The results of single factor experiment showed that the nitrogen and phosphorus fluxes between the sediment-overlying water interface of the Yanming Lake increased with the increase of temperature, and decreased with the increase of dissolved oxygen concentration. At neutral pHs, the lowest nitrogen and phosphorus fluxes occurred. The nitrogen flux reached its maximum value at pH=5 and the phosphorus flux reached its maximum value at pH=9. The fitting results of the BBD model showed that the fitting relationships between environmental factors and the fluxes of nitrogen and phosphorus were quadratic polynomial equations. The results of response surface test showed that the interaction between temperature and pH had a significant effect on TN flux. The interaction between temperature and dissolved oxygen had a significant effect on TP flux. The interactions between temperature and dissolved oxygen, temperature and pH had a significant effect onNH+4 -N flux. The interaction between temperature and dissolved oxygen had a very significant effect on the flux ofPO3−4 -P; the most unfavorable conditions for the release from the Yanming Lake sediment were temperature of 10 ℃, dissolved oxygen of 7.87 mg·L−1, pH 7.13, at which the exchange flux of TN was 3.956 mg·(m2·h)−1, the exchange flux of TP was 0.471 mg·(m2·h)−1, and the exchange flux ofNH+4 -N was 1.469 mg·(m2·h)−1, the exchange flux ofPO3−4 -P was 0.146 mg·(m2·h)−1. The research results can provide a reference for the eutrophication prevention of the Yanming Lake. -
重金属因其在环境中的持久性、高毒性以及生物蓄积性等特性,广泛的分布于全球各环境介质中,成为全球性的环境公害。重金属可由大气沉降、地表径流、污水直排等途径进入海洋环境[1-4]。海水中的重金属易吸附于颗粒物中,通过络合、沉淀等过程转移并富集于沉积物中[5-6]。当水环境改变时,富集于沉积物中的重金属可再次释放至水环境中,形成“二次污染”[7-8],这种“源”与“汇”之间的转化,对海洋生态系统造成严重危害。因此,海洋沉积物环境中重金属可作为海域重金属污染程度的“指示剂”,蕴含着丰富的环境信息和海洋地质过程,对评价环境生态风险具有重要的意义[6, 9]。
北部湾位于南海西北部,该海域生产力高,生物多样性丰富,是沿海地区重要的渔场及渔业产品的主要来源[10-11]。但由于北部湾是一个半封闭海湾,水动力条件弱,污染物不容易扩散而易富集于海湾内。近年来,随着广西沿海工业化、城市化的快速发展,北部湾近海生态也正面临着日益严重的重金属污染压力[3, 12]。例如,北部湾部分近海港口、潮间带、油田等区域也发现了不同程度的重金属污染[11-13]。此外,北部湾入海河流中,部分河流(如大风江和南流江)污染物含量在雨季处于较高水平,该时期大量的污染物排入北部湾近岸[14]。研究显示,北部湾沉积物芯中重金属含量从1985年至2008年呈显著上升趋势[15],这很可能与陆源污染物输入增加有关。但对于广西北部湾整体海域重金属的相关研究仍相对较少,对海域重金属来源及影响因素的认识仍相对较弱。因此,对北部湾重金属研究及生态风险评价具有重要的意义。
本研究以广西北部湾采集的表层沉积物为对象,分析沉积物中6种重金属(As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn)的污染特征、潜在来源以及生态风险评价,揭示人类活动对北部湾海洋生态的影响,对维护北部湾生态环境提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法 (Material and mathods)
1.1 研究区域及样品采集
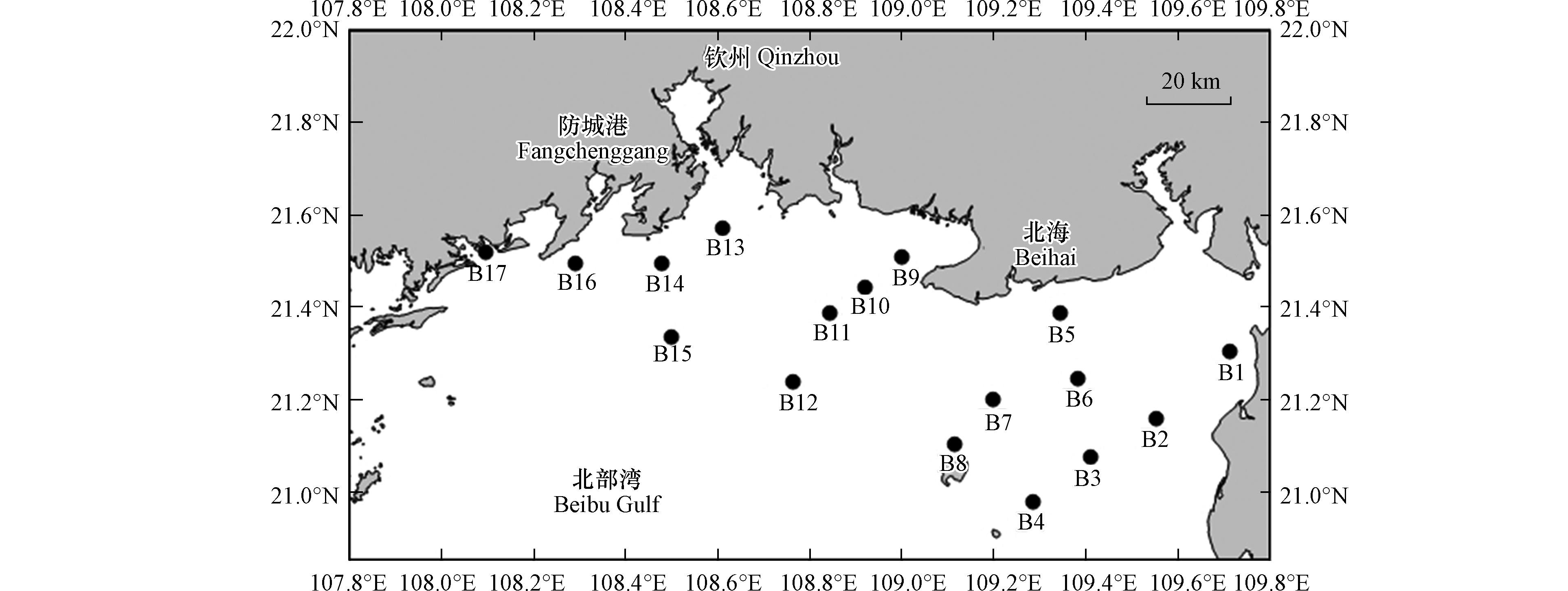
本研究位于广西北海、钦州和防城港沿海的北部湾近海区域(图1),该海湾属于半封闭海湾,水动力条件较弱,易受到人类活动的影响,污染物质难以扩散,使得海湾生态系统极易受到破坏。
于2018年8月(夏季)使用抓斗式采样器在该区域共采集17个表层沉积物样品(0—5 cm),并将采集好的沉积物样品置于聚乙烯密封袋中,密封冷藏(4℃)保存,用以分析重金属和总有机碳(TOC)。
1.2 样品的处理及分析检测
沉积物样品的处理及分析检测方法按照《海洋监测规范第5部分:沉积物分析》(GB 17378.5-2007)进行。一部分沉积物样品在105℃条件下的烘箱干燥,用于检测Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As,检测Hg的样品在自然室温条件下烘干。烘干并除去石头等大颗粒物后,用玛瑙研磨样品,通过160目筛网筛出Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd和As样品,通过80目的筛网筛出Hg样品,待测。另一部分沉积物样品进行冷冻干燥,用以测定TOC含量。在整个实验分析过程中均使用超纯水,实验所用的玻璃器皿均在1:3的硝酸溶液中浸泡至少7 d,然后使用超纯水清洗。
处理后的沉积物样品,取0.5 g,用硝酸和盐酸混合溶液在95℃条件下消解1 h,然后用超纯水稀释至50 mL,待分析。Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn采用原子吸收光谱法(ZEENH700P, Jena, German)测定,As和Hg采用原子荧光光谱法(AFS-9530,北京海光仪器,中国)测定。Cu、Pb、Zn、Cd、Hg和As的检出限分别为2.0、1.0、6.0 、0.04、0.002、0.06 μg·g−1。TOC含量采用重铬酸钾氧化硫酸亚铁滴定法测定,检出限为0.01%。
1.3 重金属污染评价
1.3.1 单因子污染指数法
根据《海洋沉积物质量标准》(GB 18668-2002)中Ⅰ类沉积物标准值,对As、Cd、Cu、Hg、Pb和Zn进行单因子污染评价,计算如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 其中,
Cif Ci Cin Cif Cif Cif Cif Cif 表 1 国家海洋沉积物重金属含量标准值Table 1. National standard values of heavy metals in marine sediments指标Index 海洋沉积物质量标准值/(μg·g−1)Standard value of marine sediment Cu Hg Pb Zn Cd As Ⅰ类Class I 35 0.2 60 150 0.5 20 Ⅱ类Class Ⅱ 100 0.5 130 350 1.5 65 1.3.2 生态风险指数法
根据沉积物中重金属浓度及毒性响应特征和污染物类型,针对不同地域环境背景差异,Hakanson于20世纪80年代提出了生态风险指数评价法[16],该方法被广泛应用于海洋环境重金属危害程度及潜在生态风险评价[6, 17-18]。方法如下:
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) 其中,
Pi Cif Ci Cin Tir Eir Eir 表 2 重金属污染程度及潜在生态风险等级Table 2. Contaminant grades and potential ecological risk levels of heavy metalsPi 重金属总体污染程度Overall pollution level Eir 单个重金属潜在生态危害程度Potential ecological hazard of single metal RI 重金属总体潜在生态危害程度Overall potential ecological hazard of metals <8 低度污染 <40 低危害 <150 低危害 8—16 中等污染 40—80 中等危害 150—300 中等危害 16—32 重污染 80—160 较重危害 300—600 重危害 ≥32 严重污染 160—320 重危害 ≥600 严重危害 — — >320 严重危害 — — 2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 沉积物中重金属分布特征
北部湾沉积物中重金属含量及分布特征见表3和图2。Hg的浓度范围为0.023—0.037 μg·g−1,平均为0.030 μg·g−1,Hg浓度的高值主要分布在钦州和涠洲岛近岸区域。Cd的浓度范围为0.04—0.09 μg·g−1,平均为0.06 μg·g−1,其浓度的分布特征表现为涠洲岛近岸区域、大风江口和南流江口外海域较高,而钦州和北海近岸区域较低。Pb的浓度范围为12.1—26.7 μg·g−1,平均为18.9 μg·g−1,其浓度的分布表现为外海区域高于近岸区域。As、Cu和Zn浓度的分布趋势相似,As的浓度范围为0.39—9.21 μg·g−1,平均为3.73 μg·g−1;Cu的浓度范围为3.59—16.90 μg·g−1,平均为11.16 μg·g−1;Zn的浓度范围为ND—62.3 μg·g−1,平均为27.8 μg·g−1。As、Cu和Zn浓度的分布呈现北部湾西部(钦州、防城港近岸区域)和涠洲岛近岸区域较高,而东部海域(北海近岸区域)的浓度较低。北部湾重金属分布特征的差异,表明不同重金属间的来源可能不同。
表 3 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属的监测结果及与其他区域对比(μg·g-1)Table 3. The results of measured metals values in the surface sediments of Beibu Gulf and comparison with other regins数据统计Data statistics Hg As Cu Zn Pb Cd 参考文献 Reference 最小值 Minimum value 0.023 0.39 3.59 ND 12.1 0.04 本研究This study 最大值 Maximum value 0.037 9.21 16.90 62.3 26.7 0.09 平均值 Mean value 0.030 3.73 11.16 27.8 18.9 0.06 标准偏差 Standard deviation 0.005 3.40 4.74 25.4 4.6 0.02 Ⅰ类沉积物/个Class I 17 17 17 17 17 17 湛江湾 Zhanjiang Bay 18.7 73.60 43.89 0.15 [10] 厦门湾 Xiamen Bay 44.0 139.0 54.0 0.33 [19] 广东近岸 Coast of Guangdong Province 0.13 20.83 43.83 139.93 44.29 0.38 [20] 珠江口 Pearl River Estuary 348.0 383.4 102.6 1.72 [21] 北部湾 Beibu Gulf(1998年) 0.03 1.74 1.7 19.9 1.26 0.05 [22] 海南岛北部 Northern Hainan Island 0.02 8.40 8.32 35.87 18.77 0.06 [6] 注:ND为未检出. 与其他区域对比(表3),北部湾重金属含量明显低于厦门湾[19]、广东近岸[20]和珠江口[21]区域,与海南岛近岸浓度相当[6],但明显高于20世纪90年代时期北部湾沉积物的浓度[22],表明近些年来,北部湾沉积物重金属呈现一定程度富集。
2.2 重金属的来源与主控因素分析
沉积物中重金属含量受环境背景、生物过程、海洋物理过程以及人类活动等多方面的影响。此外,TOC主要为沉积物中有机质,其对重金属具有极强的吸附和络合作用[23-24]。因此,在讨论沉积物中重金属潜在来源时,常用利用TOC含量通过与重金属浓度的相关性分析,可对它们的来源进行初步判断[3,18,23]。沉积物中Cu和Zn的含量与TOC含量呈显著正相关性(表4),表明Cu和Zn在沉积物中的富集受到TOC含量的影响。Cu和As、Cu和Zn、Pb和Zn、Pb和Cd之间呈显著正相关性(表4),表明这些元素之间具有同源性;而Hg与其他元素均无相关性,说明Hg与其他重金属的来源方式可能不同。
表 4 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属和TOC 相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis of heavy metals and TOC in surface sediments of Beibu GulfTOC Hg As Cu Zn Pb Cd TOC 1 Hg −0.255 1 As 0.159 0.394 1 Cu 0.706** 0.183 0.532* 1 Zn 0.574* 0.086 0.327 0.792** 1 Pb 0.445 −0.018 0.000 0.397 0.573* 1 Cd −0.081 0.104 −0.019 0.222 0.367 0.547* 1 注:*在0.05水平上显著相关;**在0.01水平上显著相关. 为进一步了解重金属的潜在来源及主控因素,对沉积物中重金属含量进行主成份分析,结果如表5所示,当特征值大于1时,可提取3个成份,可分别解释总因子的43.54%、21.23%和18.66%,累积贡献率为83.43%。在成份1中,TOC、Zn、Cu和Pb具有很高载荷,这些重金属元素组合的高值区主要分布在钦州、防城港和涠洲岛近岸区域,表明这些金属元素在沉积物中的富集受到沉积物中有机质含量的影响。Zn、Cu和Pb主要来源于交通运输和工业生产[9]。钦州和防城港是北部湾沿海主要的工业活动区域,表明这些元素来源可能受到近海工业活动的影响。成份2中,Hg和As具有较高的载荷。As的富集受到低温热液成矿的影响,主要来源于农药残留、网箱养殖和工业生产[6,9]。Hg主要来源于石化产品、金属冶炼和煤炭燃烧[9]。As含量的高值主要分布于钦州和防城港近岸区域,其来源仍为近海人类活动为主;而外海较远区域As浓度的高值可能受控于自然地质背景因素,或于外海物质来源有关[9]。成份3仅Cd具有高载荷,其主要用于杀虫剂、化工业、电镀业等,通过河流排污入海并富集于沉积物中[6]。Cd浓度的高值主要分布在大风江口和南流江口外海域,反映了北部湾城市发展进程导致的区域污染差异性影响。
表 5 北部湾表层沉积物中重金属和TOC 主成份分析Table 5. Principal component analysis of heavy metals and TOC in surface sediments of Beibu Gulf元素Element 因子载荷 Factor load 成分1 成分2 成分3 TOC 0.720 −0.272 −0.557 Hg 0.133 0.775 0.417 As 0.458 0.737 −0.140 Zn 0.902 −0.038 0.015 Cu 0.909 0.196 −0.204 Cd 0.421 −0.229 0.798 Pb 0.697 −0.420 0.353 特征值 3.047 1.486 1.306 贡献率/ % 43.54 21.23 18.66 累积贡献率/% 43.54 64.77 83.43 2.3 重金属污染评价
对北部湾沉积物中重金属含量进行单因子分析,结果显示,所有站位的重金属污染因子均小于1,其含量低于Ⅰ类沉积物标准,污染程度低。北部湾沉积物中重金属单因子污染影响程度如表6所示,依次为Cu>Pb>As>Zn>Hg>Cd。
表 6 北部湾沉积物中重金属污染指数和潜在生态风险评价Table 6. Contaminant index and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metal in the sediments of Beibu Gulf元素Element Cif Eir 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean 最小值Minimum 最大值Maximum 平均值Mean Hg 0.100 0.205 0.150 27.59 56.55 41.31 As 0.020 0.721 0.290 0.50 18.47 7.43 Zn 0.000 0.415 0.240 0 0.82 0.47 Cu 0.103 0.837 0.401 1.14 9.27 4.44 Cd 0.080 0.180 0.121 13.33 30.00 20.17 Pb 0.202 0.445 0.305 2.09 4.62 3.17 Cd 2.25 7.13 4.45 RI 54.71 105.12 76.99 各重金属潜在生态风险系数(
Eir 综上评价,尽管北部湾沉积物中重金属处于低程度污染和底潜在生态危害风险,但随着北部湾经济区城市化、工业化的不断发展,局部海域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度处于较高水平,仍需警惕。
3. 结论 (Conclusion)
(1)北部湾沉积物中不同重金属的分布特征差异明显,其中As、Cu、Hg和Zn的分布总体呈现西部和涠洲岛近岸海域高于东部海域,Cd浓度的高值主要分布在涠洲岛近岸区域、大风江口和南流江口外海域,Pb浓度的分布表现为外海区域高于近岸区域,表明北部湾重金属的来源可能存在差异。
(2)与其他区域相比,北部湾沉积物中重金属含量处于较低水平,但与历史数据相比呈现增长趋势,表现一定程度的富集。
(3)Zn、Cu、Pb、Hg和As的来源主要受到近海人类活动的影响,而Cd反映了北部湾城市发展进程导致的区域污染差异性影响。
(3)北部湾沉积物重金属的污染评价显示,局部海域污染程度和潜在生态风险程度处于较高水平,重金属的污染仍需警惕。
-
表 1 响应面实验的因子与水平编码
Table 1. Factors and level codes for response surface tests
编码 环境因子 水平 −1 0 1 X1 温度/℃ 5 17.5 30 X2 溶解氧/(mg·L−1) 3 6 9 X3 pH 5 7 9 表 2 BBD实验实测值
Table 2. Experimental results of BBD
实验组号 TN通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1) TP通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1) NH+4 -N通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1)PO3−4 -P通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1)平行样1 平行样2 平行样3 平行样1 平行样2 平行样3 平行样1 平行样2 平行样3 平行样1 平行样2 平行样3 1 8.445 7.754 8.559 0.756 0.764 0.673 3.375 3.115 2.974 0.236 0.234 0.217 2 5.012 5.689 5.541 0.623 0.645 0.651 2.045 1.997 2.289 0.186 0.215 0.195 3 7.415 7.525 7.894 0.574 0.701 0.681 2.852 2.682 2.962 0.203 0.211 0.225 4 7.551 7.045 7.541 0.676 0.678 0.636 2.942 2.964 2.675 0.195 0.221 0.215 5 4.604 5.197 4.141 0.468 0.451 0.431 1.589 1.576 1.786 0.137 0.151 0.139 6 5.212 4.634 4.791 0.473 0.475 0.504 1.841 1.846 1.619 0.149 0.142 0.155 7 8.111 8.697 8.119 0.664 0.727 0.671 3.047 3.202 3.105 0.229 0.221 0.197 8 5.789 5.865 6.436 0.612 0.627 0.589 2.412 2.276 2.248 0.197 0.189 0.190 9 4.789 5.327 5.214 0.523 0.554 0.475 1.825 2.241 1.965 0.161 0.169 0.151 10 5.589 6.549 6.989 0.678 0.697 0.679 2.758 2.388 2.587 0.216 0.197 0.214 11 4.707 4.784 4.314 0.467 0.504 0.441 1.772 1.590 1.810 0.142 0.145 0.162 12 6.417 6.124 5.585 0.650 0.617 0.563 2.357 2.412 2.057 0.178 0.192 0.196 13 4.321 4.012 4.338 0.463 0.525 0.518 1.669 1.559 1.496 0.166 0.145 0.154 14 8.807 7.981 8.913 0.711 0.789 0.765 3.321 3.197 3.124 0.224 0.245 0.232 15 3.974 3.954 3.515 0.524 0.503 0.531 1.416 1.482 1.329 0.171 0.160 0.146 16 7.258 7.569 7.841 0.607 0.547 0.643 2.791 2.760 3.060 0.196 0.174 0.200 17 7.305 7.394 7.211 0.678 0.697 0.611 2.804 2.649 2.717 0.196 0.221 0.213 表 3 BBD实验设计及通量平均值
Table 3. BBD experiment design and average flux
实验组号 环境因子 TN通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1) TP通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1) NH+4 -N通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1)PO3−4 -P通量/(mg·(m2·h)−1)温度/℃ 溶解氧/(mg·L−1) pH 1 17.5 3 5 8.253 0.731 3.155 0.229 2 17.5 9 5 5.414 0.640 2.110 0.199 3 30 3 7 7.611 0.691 2.832 0.213 4 30 6 5 7.379 0.663 2.860 0.210 5 17.5 6 7 4.373 0.450 1.650 0.142 6 17.5 6 7 4.879 0.484 1.769 0.149 7 30 6 9 8.309 0.687 3.118 0.216 8 17.5 9 9 6.030 0.609 2.312 0.192 9 17.5 6 7 5.110 0.517 1.895 0.160 10 30 9 7 6.769 0.685 2.578 0.209 11 17.5 6 7 4.602 0.471 1.724 0.150 12 5 6 9 6.042 0.610 2.275 0.189 13 5 9 7 4.224 0.502 1.575 0.155 14 17.5 3 9 8.567 0.755 3.214 0.234 15 17.5 6 7 3.814 0.519 1.409 0.159 16 5 6 5 7.556 0.599 2.870 0.190 17 5 3 7 7.303 0.662 2.723 0.210 表 4 底泥释放通量回归方程方差分析
Table 4. Analysis of variance for regression equation of the release flux from sediment
方差来源 TN通量回归分析 TP通量回归分析 NH+4 -N通量回归分析PO3−4 -P通量回归分析df F P>F 显著性 df F P>F 显著性 df F P>F 显著性 df F P>F 显著性 模型 9 18.45 0.000 4 ** 9 22.26 0.000 2 ** 9 20.02 0.000 3 ** 9 41.79 < 0.000 1 ** X1 1 13.19 0.008 4 ** 1 21.68 0.002 3 ** 1 14.95 0.006 2 ** 1 35.61 0.000 6 ** X2 1 46.65 0.000 2 ** 1 28.42 0.001 1 ** 1 44.41 0.000 3 ** 1 56.5 0.000 1 ** X3 1 0.065 0.806 7 1 0.14 0.717 1 1 0.022 0.885 2 1 0.03 0.868 2 X1X2 1 5.4 0.053 1 1 8.33 0.023 4 * 1 6.32 0.040 2 * 1 17.13 0.004 4 ** X1X3 1 6.45 0.038 7 * 1 0.054 0.822 5 1 5.76 0.047 5 * 1 0.32 0.587 8 X2X3 1 0.098 0.762 9 1 1.02 0.345 7 1 0.16 0.699 8 1 0.95 0.362 6 X21 1 21.53 0.002 4 ** 1 15.41 0.005 7 ** 1 22.46 0.002 1 ** 1 29.29 0.001 ** X22 1 12.61 0.009 3 ** 1 53.2 0.000 2 ** 1 14.26 0.006 9 ** 1 90.08 < 0.000 1 ** X23 1 51.16 0.000 2 ** 1 58.57 0.000 1 ** 1 61.8 0.000 1 ** 1 120.78 < 0.000 1 ** 残差 7 7 7 7 失拟项 3 0.83 0.541 3 0.55 0.672 9 3 0.94 0.500 1 3 0.23 0.868 4 纯误差 4 4 4 4 总值 16 16 16 16 变异系数 0.077 0.044 4 0.075 4 0.032 7 R2 0.959 5 0.966 2 0.962 6 0.981 7 R2Adj 0.907 5 0.922 8 0.914 5 0.958 2 注:**表示P <0.01下差异显著;*表示P<0.05下差异显著;df表示自由度。 -
[1] 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2018中国生态环境状况公报[EB/OL]. [2019-12-01]. http://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb. [2] RUSSEL J M, HOPMANS E C, LOOMIS S E, et al. Distributions of 5- and 6-methyl branched glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (brGDGTs) in East African lake sediment: Effects of temperature, pH, and new lacustrine paleotemperature calibrations[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2018, 117: 56-69. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2017.12.003 [3] BEUTEL M W, HORNE A J. Nutrient fluxes from profundal sediment of ultra-oligotrophic lake tahoe, california/nevada: Implications for water quality and management in a changing climate[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(3): 1549-1559. doi: 10.1002/2017WR020907 [4] 韩宝红, 宋蕾, 李浩, 等. 不同温度条件下稳定剂对沉积物中镉稳定化的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(8): 2610-2616. [5] 李鑫, 耿雪, 王洪伟, 等. 外源输入对底泥疏浚新生表层磷恢复及迁移的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8): 3539-3579. [6] OKOGBUE C O, OYESANYA O U, ANYIAM O A, et al. Evaluation of the extent of pollution of discharged oil field brine in the Bonny estuary, Niger Delta, Nigeria[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(10): 382-396. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7542-z [7] MAIERYEMU Y, MAMAT S, NIGELA T, et al. Distribution of heavy metal pollution and assessment of its potential ecological risks in Ugan-Kuqa River Delta of Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(20): 226-233. [8] 郭赟, 赵秀红, 黄晓峰, 等. 原位活性覆盖抑制河道底泥营养盐释放的效果研究及工程化应用[J]. 环境工程, 2018, 36(6): 6-11. [9] 雷晓玲, 韩亚鑫, 冉兵, 等. 环境因子对三峡库区底泥污染物释放的影响研究[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(1): 47-50. [10] KAISER D, UNGER D, QIU G, et al. Natural and human influences on nutrient transport through a small subtropical Chinese estuary[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 450-451: 92-107. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.01.096 [11] LIANG Z, LIU Z, ZHEN S, et al. Phosphorus speciation and effects of environmental factors on release of phosphorus from sediments obtained from Taihu Lake, Tien Lake, and East Lake[J]. Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry Reviews, 2015, 97(3/4): 335-348. [12] LI R F, FENG CH, WANG D X. Role of salinity in the multiphase redistribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediment suspension[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(2): 116-122. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5014-2 [13] 张文斌, 董昭皆, 徐书童, 等. 微生物和藻类分解对荣成天鹅湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(4): 561-567. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190412 [14] FERENCZ B, TOPOROWSKA M, JAROSLAW D, et al. Hydro-chemical conditions of shaping the water quality of shallow leczna-wlodawa lakes[J]. Clean-Soil Air Water, 2017, 45(5): 356-369. [15] DEVORE C L, RODRIGUEZ F L, MEHDI A, et al. Effect of bicarbonate and phosphate on arsenic release from mining-impacted sediments in the Cheyenne River watershed, South Dakota, USA[J]. Environmental Science: Processes and Impacts, 2019, 21(3): 456-468. doi: 10.1039/C8EM00461G [16] YAO C, HU X Z, LU S Y, et al. Repression of nitrogen and phosphorus release from lakeshore sediment by five littoral-zone plants[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(2): 589-599. [17] 张强, 曹秀芹, 胡明, 等. 扰动对城市河道底泥污染物释放影响[J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(9): 40-44. [18] 张茜. 漳泽水库沉积物和上覆水污染特征及氮磷释放规律研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019. [19] 张硕, 方鑫, 黄宏, 等. 基于正交试验的沉积物-水界面营养盐交换通量研究: 以海州湾海洋牧场为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(11): 4266-4276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.11.032 [20] 姜伟, 周川, 纪道斌, 等. 三峡库区澎溪河与磨刀溪电导率等水质特征与水华的关系比较[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(6): 2326-2335. [21] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002. [22] 王圣瑞. 湖泊沉积物-水界面过程: 基本理论与常用测定方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. [23] JEROEN J M, CISKA C O, CHRISTIAN J J, et al. Effect of temperature on oxygen profiles and denitrification rates in freshwater sediments[J]. Wetlands, 2017, 37(5): 975-983. doi: 10.1007/s13157-017-0933-1 [24] 张红, 陈敬安, 王敬富, 等. 贵州红枫湖底泥磷释放的模拟实验研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2015, 43(2): 243-251. [25] BAREHA Y, GIRAULT R, JIMENEZ J, et al. Characterization and prediction of organic nitrogen biodegradability during anaerobic digestion: A bioaccessibility approach[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 263: 425-436. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.085 [26] 郭念, 闫金龙, 魏世强, 等. 三峡库区消落带典型土壤厌氧呼吸对铁还原及磷释放的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(3): 271-276. [27] LI Z, WANG S R, WU Z H. Coupling effect of pH and dissolved oxygen in water column on nitrogen release at water-sediment interface of Erhai Lake, China[J]. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 2014, 149: 178-186. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.08.009 [28] 袁和忠, 沈吉, 刘恩峰, 等. 模拟水体pH控制条件下太湖梅梁湾沉积物中磷的释放特征[J]. 湖泊科学, 2015, 21(5): 663-668. [29] 王荣杰, 沈本贤, 刘纪昌, 等. 响应面分析法优化不溶性硫黄萃取提浓工艺[J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47(7): 1457-1461. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.07.035 [30] 闫晓涛, 李杰, 冯淑琪, 等. 响应面法优化混凝处理黄河兰州段低温低浊水[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(6): 68-74. [31] 杜凤龄, 王刚, 徐敏, 等. 新型高分子螯合-絮凝剂制备条件的响应面法优化[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(4): 158-164. -














 下载:
下载: