-
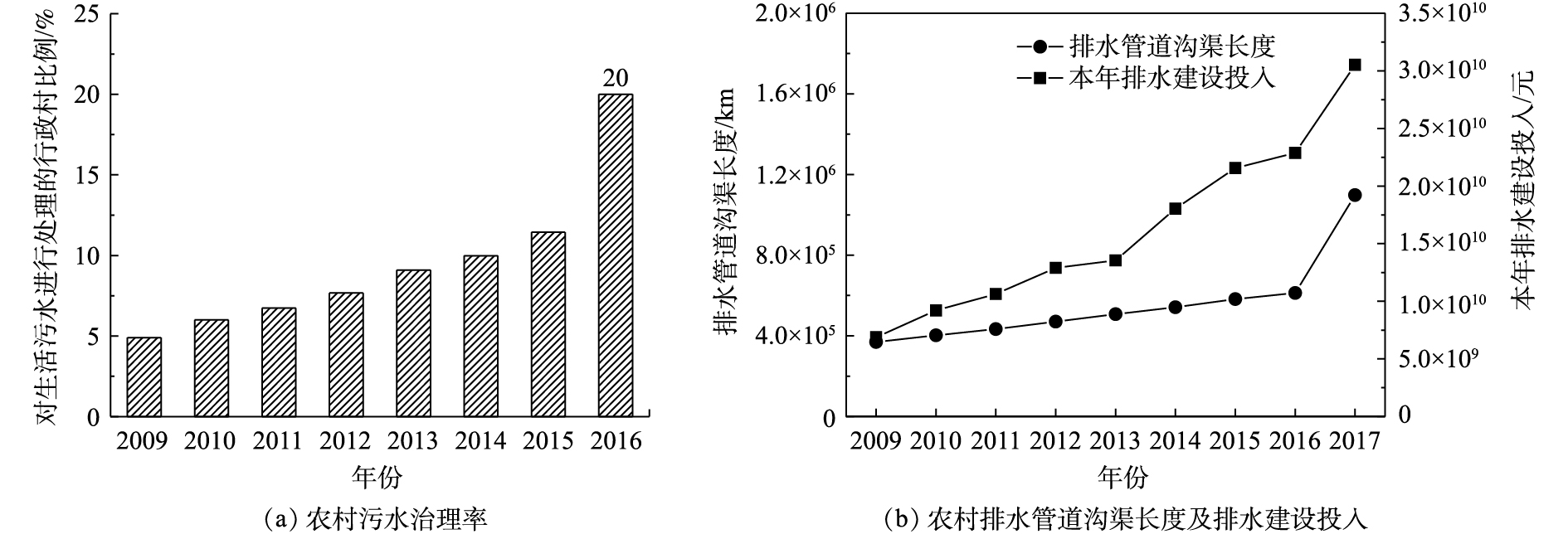
近年来,随着我国农村社会经济的发展和农村居民生活水平的提高,农村环境保护工作取得了长足的发展,很多农村地区相继建设了农村生活污水收集和处理系统。根据住房和城乡建设部的相关统计数据,建设有农村生活污水处理设施的行政村数量逐年上升,截至2016年,全国约有20%的行政村对农村污水进行了处理(图1)。从污水治理模式的角度来看,农村生活污水收集处理模式主要可以分为3种:纳入城镇污水管网处理、村落集中处理和分散处理[1]。除分散处理以外,纳入城镇污水管网处理和村落集中处理均需建设农村污水管网。随着农村污水治理工作的推进,我国农村地区的排水管道沟渠长度和排水建设投入逐年增加,2017年,我国农村排水管道沟渠总长达到近1.1×106 km,年度排水建设投入约3.05×1010元(图1)。由于污水管网建设成本很高(约占整个污水处理系统建设成本的70%)[2],而我国农村地区经济仍不发达,基础设施建设相对滞后,因此,许多农村排水主要采用渠道进行。农村污水治理工作在许多经济欠发达的农村地区推进缓慢,个别农村地区甚至出现了建有农村污水处理设施,但是没有配套管网的尴尬局面。另外,由于农村地区在污水管道特点和居民生活方式等方面与城市地区有一些客观差异,农村污水管道问题较为复杂,已建成污水处理系统的农村地区对于污水管道的运维工作普遍不足,带来了很多问题。
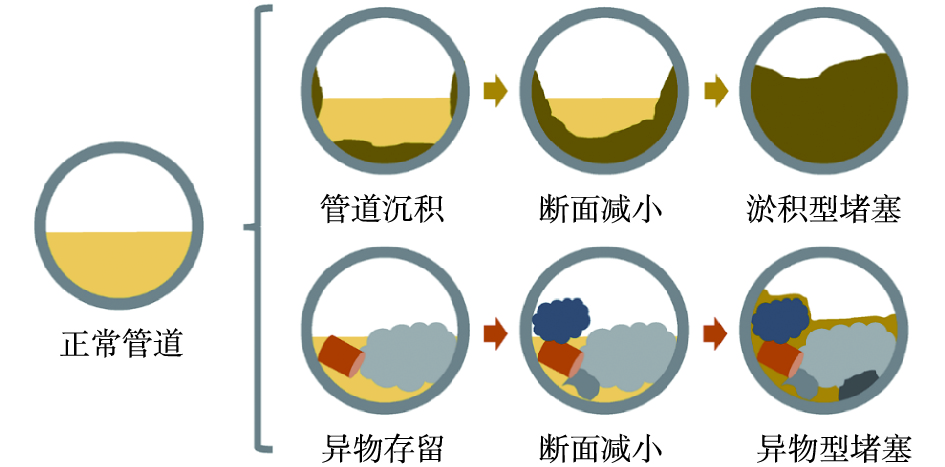
农村污水管道在运行过程中,管道堵塞问题时有发生。一般而言,农村污水管道堵塞可以大致分为淤积型堵塞和异物型堵塞2类(图2)。淤积型堵塞是指污水在管道流动过程中泥沙、有机颗粒物等悬浮物逐渐在管道底部沉积,在减小管道有效截面积的同时,增大了管壁粗糙系数,致使管道过水能力下降,最终逐渐形成的管道堵塞。异物型堵塞是指在污水管道中由于不正常的工况引入了较大的异物(湿巾、菜叶、塑料包装袋等),这些异物直接滞留在管道内,形成管道的堵塞。一般异物型堵塞会造成污水流动受阻,如果管内异物没有及时得到清理,会进一步诱发淤积型堵塞。农村污水管道在堵塞后会造成上游污水外溢、农户污水无法有效排放等问题,严重影响村民日常生活和村容村貌。另外,污水管道堵塞还会造成污水处理终端水量不足,终端实际水量明显低于设计水量,影响污水处理效果。为有效降低农村污水管道堵塞发生率,提升农村污水收集系统的效率和稳定性,本研究结合农村污水管道工程实践和理论研究,系统地分析了农村污水管道堵塞成因,并结合农村发展的实际情况,提出了相应的解决方案。本研究对于保证农村污水收集处理设施的有效运转,解决污水散排这一基本民生问题和发挥污水处理系统应有的生态环境效益具有积极的意义。
-
首先,存在管径-水量不匹配的问题。目前,我国尚没有针对农村污水管道设计的国家标准。许多农村地区直接参照《室外排水设计规范》(GB 50014-2006)进行污水管道设计。根据规范,室外污水管道设计的最小管径为200 mm,这一管径在城市污水管网设计中相对合理,但用于人口密度相对较低、居住较为分散的广大农村地区,存在诸多问题。基于该规范的最小管径要求,许多农村地区往往不经过水量核算,直接采用接户管为110 mm或160 mm,排水支管为200 mm 或225 mm,干管为 300 mm的管道设计方案。该设计方案虽然在管道建设初期,可以保证农村生活污水的有效收集,降低了污水管道发生异物型堵塞的概率,但管道内径过大,而实际污水量较小,日间管道充满度长期低于0.3,在夜间管道基本无水,在排水较少的时段,污水流速低于自冲刷流速0.6 m·s−1,管道沉积现象严重,容易导致管道淤积型堵塞。另外,由于农村用水量相对较低,一般为70~160 L·(人·d)−1[3],同时排水习惯与城市地区有一定的差异,农村污水悬浮颗粒物浓度相对于城市污水一般较高,悬浮颗粒物在低流速管道内逐渐沉积,形成管道堵塞。
即使在进行水量核算的农村地区,大部分的水量设计采用的水量总变化系数KZ均参考城市污水变化系数,一般取2.3~2.5。根据部分地区的实践,实测的农村污水总变化系数KZ大致为2.5~4.5,明显高于城市最小流量下的总变化系数2.3。这也就意味着农村污水的水量变化更为显著,采用城市系数设计的管道,在干管段如果设计不合理,可能导致水量高峰期时管道过流量不足,无法及时排出的污水短期暂存在检查井中,会造成污水外溢。另外,在农村污水管道设计阶段,一般将包括洗涤污水在内的所有生活污水全部纳入水量核算范围,而部分农村地区存在洗涤废水不纳管而直接泼洒的客观现状,管道实际水量低于设计水量,长此以往,管道污水流速不足,容易产生淤积型堵塞。
第二,存在配套设施不合理的问题。主要表现在以下几个方面。
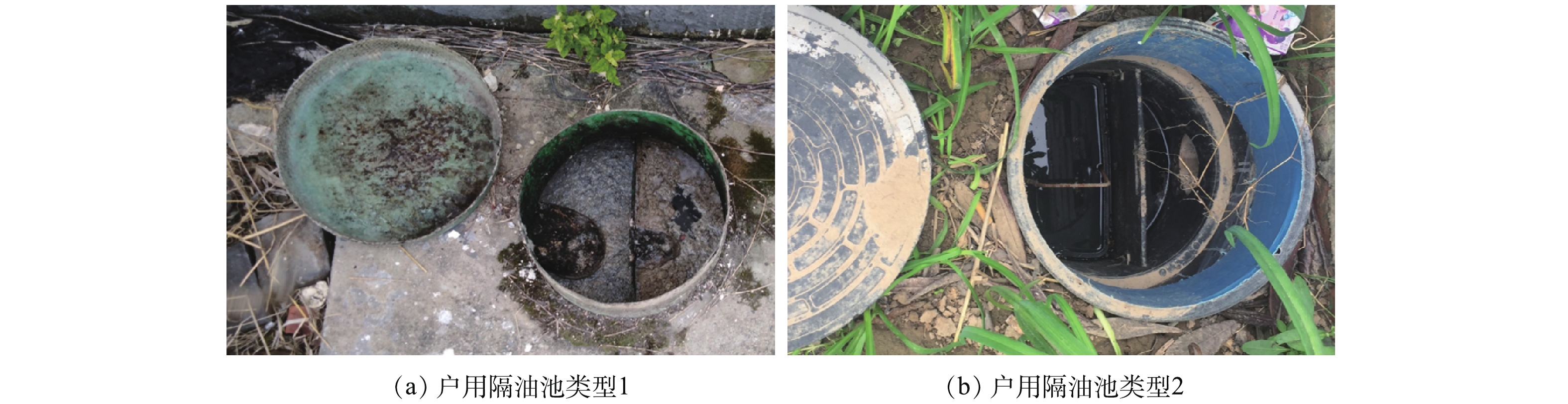
1) 隔油池建设不足。在农村污水收集处理系统中,隔油池一般用于降低厨房污水含油量[4],以减少餐厨污水中的油脂对于污水管道和处理终端的不良影响(图3)。在当前的农村污水管道建设中,隔油池不是强制安装的配套设施,很多地区为了降低管道建设成本,取消了户用隔油池,村民生活产生的餐厨污水直接排放进入管道,餐厨污水含有大量的油脂,这些油脂进入管道后,会逐渐粘附在污水管道内壁,显著增加管道堵塞风险[5-6]。
2) 接户井筛网配置不足。在当前的农村污水管道系统的建设中,一般在农户内的下水口均会设置滤网,但随着时间的推移,这些滤网逐渐堵塞,一些村民为了方便,直接将滤网拆除并将湿巾、菜叶等杂物直接冲入下水道,这些杂物未经筛网过滤,直接进入污水管道,会直接堵塞接户管或排水支管,从而造成异物型堵塞。由于农户私自拆除户内滤网的行为较为常见并且不易管理,目前,部分农村地区已经在接户井处另设置一层筛网,以防止未经下水口滤网过滤的大块杂物进入下游管道,进而造成异物型堵塞。但是,目前大部分农村地区对于接户井筛网的设置不重视,没有进行安装。
3) 老旧化粪池直接接入管道。化粪池在预处理农村污水的同时,还对管道防堵具有重要的作用。通过在化粪池内的沉淀和厌氧发酵,污水中的悬浮颗粒物可以得到部分去除,有效避免了接户管以及排水支管的堵塞。但是,在农村污水管网设计和建设的过程中,许多农村地区直接将已经老旧破损的化粪池出水接入管道,没有及时修复或更换化粪池,导致进入管道的污水中悬浮颗粒物含量高,容易引发管道堵塞。
4) 检查井井孔引入泥沙。一般而言,为了方便污水管道检修,我国的污水检查井大多设有开启孔。根据相关研究,污水检查井的井孔除了具有方便开启的作用,还具有重要的管道通风功能[7],对于降低管道内有害气体的浓度具有一定的积极作用。但是,检查井井孔在雨季会被动的接受地表径流,地表径流中携带的泥沙因此进入污水管道[8]。泥沙是造成污水管道堵塞的重要因素,检查井引入的泥沙会加剧管道堵塞风险。根据农村污水管道建设经验,和城市市政污水管道相比,大部分农村污水管道长度较短、水量较小,污水停留时间较短并且一般不需要人工进入管道进行检修,H2S和CH4等有害气体产生量相对较低,农村污水检查井的井孔通风作用意义相对不是很高,而井孔引入的雨季泥沙反而对于管道运行有一定的威胁。因此,一些农村地区的污水检查井已经开始采用不开孔的塑料检查井盖或双层式检查井盖以防止井孔引入泥沙(图4)。根据实际的运行效果,农村污水检查井不开孔的利大于弊,值得推广。
第三,存在施工水平不足的问题。由于很多农村地区缺乏专业的污水管道施工团队,污水管道施工工程主要由当地临时聘用的工人完成,但其在农村污水治理设施施工方面的专业性不足,甚至个别地区的施工队连设计图纸都无法准确理解,随意施工的现象时有发生。污水管道作为一项地下设施,其施工质量受路面和地下土层的影响很大。大部分农村地区的路面尚未完全硬化,土路、石子路等路面广泛存在。一些施工队在管道施工过程中,没有按照设计要求开挖沟槽并敷设垫层,或者没有按照管道施工要求进行沟槽回填,直接采用原土回填管道支撑面和管底腋角,导致管道在长期使用后发生沉降,甚至形成局部管道倒坡,造成管道沉积物或泥沙淤积甚至堵塞。在行驶大型载重车辆的路面下的污水管道施工水平不足,容易形成管道受外压变形甚至破裂,直接造成管道过水断面减小和管周泥沙进入管道,形成管道堵塞。
另外,作为最常见的管道异味控制部件,存水弯基本在每个户内下水管入口处均有设计,但是有些农村地区在污水管道接户的位置又额外安装了一个存水弯,在控制管道异味的同时,兼具落水井的功能,用于找齐管道高程。存水弯会显著改变污水的动力学参数,不利于污水的重力流动,在存水弯处的管道堵塞风险显著高于直管道,因此在施工过程中存水弯的安装不宜过多。
第四,存在雨污分流不彻底的问题。目前,新建排水管网的农村地区的排水体制主要为雨污分流,雨污分流可以有效降低因雨季地表径流引入泥沙造成管道堵塞的发生率。但是,在部分已经完成排水管网建设的农村地区,仍然存在一些合流制管道,在长期运行中,这些合流制管道的泥沙堵塞风险相对较大。另外,在很多雨污分流的农村地区,虽然排水管道在设计和建设时为分流制管道,但在实际使用中,因雨季庭院和街道排水较慢,个别农户为了个人利益自行打开污水井盖排水,形成了临时性的合流制排水,造成了潜在的管道泥沙堵塞隐患。
-
1)排水习惯有待提高。部分村民排水习惯有待提高。在农村污水管道实际运行过程中,部分村民为了提高排水速度,私自拆除下水管滤网,使得大量的菜叶、泥沙、头发等异物进入管道,造成了很大的异物型堵塞隐患。另外,由于一些农村地区刚由旱厕改为水厕,部分村民的不良冲厕习惯,导致湿巾、尿布、卫生巾等直接冲入管道,造成了很多管道堵塞事故的发生。由于部分因为不良排水习惯造成的堵塞并没有在接户管内部发生,而是发生在支管等户外管段,村民对于排水习惯造成的管道堵塞认识并不到位,也很难明确堵塞责任。
2)维护管理工作滞后。维护管理工作明显不足。由于我国农村污水治理工作正处于起步阶段,农村污水收集处理设施的维护管理工作尚未得到很好的落实,一些地区的农村污水处理设施尚处于“建而不管”的无运维阶段,地下的污水管道的维护管理工作更是没有得到足够的重视。大部分农村地区的维护管理重点放在污水处理终端,没有定期检查污水管道,只有在管道发生堵塞,收到村民投诉之后才派人疏通管道。污水管道虽然结构相对简单,但是位于地下,一旦发生严重的堵塞事故,其不良影响和疏通成本也很高,不完善的维护管理工作明显增大了管道堵塞发生的概率。另外,由于农村生产生活方式的转变和化肥的普及,化粪池粪渣的农田利用逐渐减少,带来了农户化粪池清掏周期延长甚至不清掏的现象。而目前大部分农村地区对于户用化粪池的运维工作落实不到位,化粪池长期不清掏,过量储存的粪渣会随污水进入排水管道,加大排水管道的堵塞机率。
-
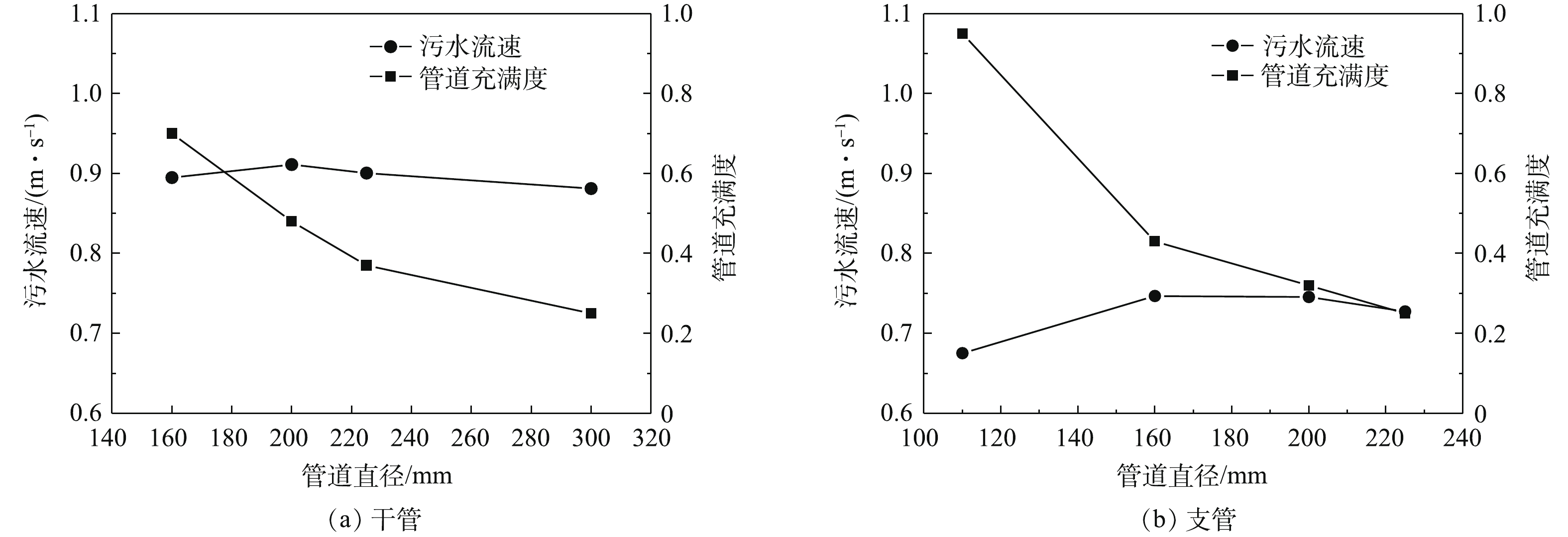
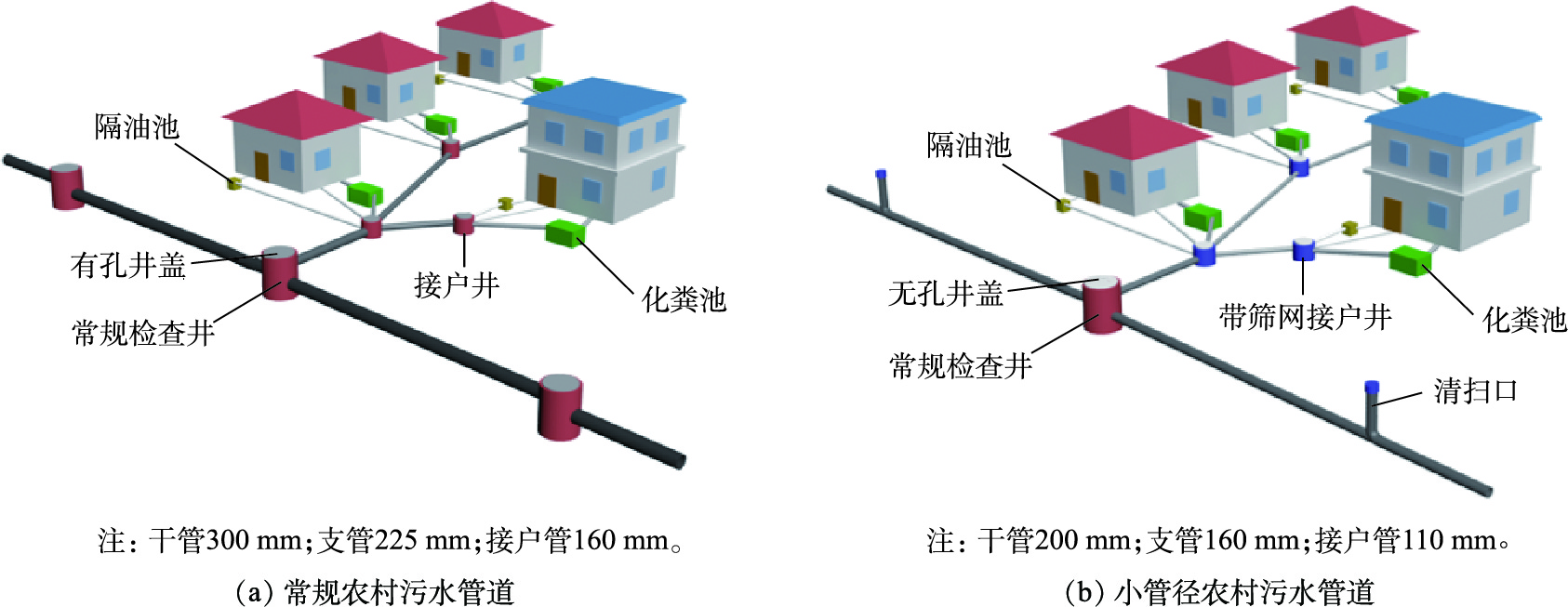
1)优化管径设计。在农村污水管道设计过程中,应摒弃过去重视处理终端,轻视污水管网的落后观念,做到管-站同步设计。具体到实际设计时,应实地考察,避免盲目采用室外排水建设规范和城市污水管道建设经验,结合村庄地形并通过管道水力学计算管道管径、坡度等相关参数,必要时可以采用计算流体力学(CFD)等手段优化管道设计细节[9-10],降低管道堵塞发生概率。根据管道水力学计算[11-14]和部分地区的应用实践,小管径管道系统(干管管径不大于200 mm)在农村地区具有一定的可行性。农村污水管道一般采用UPVC管和HDPE双壁波纹管。UPVC管的管径主要为75、110、160和200 mm;HDPE双壁波纹管的管径主要选用的是225 mm和300 mm。如图5所示,利用谢才-曼宁公式[15-16]推算,在人口相对稀疏的农村地区,在同样的污水流量(12 L·s−1)和管道坡度(5‰)的前提下,干管管径由300 mm缩小为200 mm,管道充满度由0.25提升到0.48,理论污水流速由0.88 m·s−1提升到0.91 m·s−1,在降低管道成本的同时,有效降低了淤积型堵塞的发生率。同理,若支管污水流量为6 L·s−1,坡度为5‰,支管管径由200 mm缩小为160 mm,管道充满度由0.32提升到0.43,理论污水流速变化不大,均为0.75 m·s−1左右,管道充满度的适当增加可以帮助控制管道沉积[17],进而降低淤积型堵塞的发生率。在污水流量相对较低时,可以采用接户管为110 mm,支管为160 mm,干管为200 mm的管道设计方案以提升管道充满度,避免淤积。相关研究也证实,采用小管径的排水管道,污水对于管道内颗粒物的冲刷作用更强,有助于防止管道的堵塞[18]。小管径管道的主要缺点是对于异物型堵塞的适应性较差,相对较小的异物进入管道系统,就可能引起异物型堵塞。因此,采用小管径管道的前提是接户井设有筛网,避免大块异物进入管道,小管径农村污水管道系统和常规农村污水管道系统对比见图6。
2)补齐配套设施。基于当前很多农村地区在污水管道设计时为降低建设成本而大幅削减配套设施的现状,应该在控制总体建设成本的同时配全设施。建议设计户用小型隔油池,减少餐厨污水的油脂进入管道,同时在接户井设置筛网,拦截出户管异物。这些成本的增加可以通过减少检查井的方式得到削减。农村污水管道的支管段,管径一般为160~225 mm,没有必要全程都设置为全尺寸的检查井,可以采用清扫口或配备无孔井盖的简易检查井,以替代部分直管段上的全尺寸检查井,在减少雨季泥沙汇入的同时,可降低管道建设成本。应尽量采用无孔的检查井井盖,避免农户自行开启检查井。在接户管和支管转弯的位置设置清扫口以方便检修,同时取消不必要的存水弯。为保证施工质量和便于后期运维,应尽量采用统一规格的预制设施。
3)提升施工质量。高水平的施工是农村污水管道正常运行的重要保证。为避免不专业的管道施工,应结合农村污水治理县域整体打包建设的思路,通过整县域的统一招标,聘用具有相应资质的专业农村污水管道施工团队。在施工过程中,对于材料、人工、运输等进行登记,并委派专人进行施工监督,确保施工队使用符合标准的管材、严格按照图纸施工。对于管道接口、管-井连接、管道基础平整、沟槽回填等工序进行监控,保证施工质量。对于很多农村地区为了降低成本,不使用中粗砂回填管道支撑面和管底腋角而直接使用原土回填的违规作法,要严格管控。施工完成后的管道必须进行闭水试验,确保水密性达标。另外,由于树根侵入管道也是一种导致管道堵塞的原因,在设计和施工过程中,开挖的沟槽应尽量避开大型树木的根系,使污水管道尽量远离树根[5]。
-
1)排水习惯宣教。农村污水管道堵塞很大程度上是由于不良的排水习惯造成的。因此,应以村、镇为单位,开展排水习惯宣传教育工作,向村民介绍正确的排水习惯,提升村民素质,减少私自拆除下水道滤网的发生。同时,对于刚由旱厕转变为水厕的农村,开展相应的水厕使用教学宣传,教育村民不要将大块的杂物,特别是湿巾、卫生巾等杂物直接冲入水厕。可以将排水习惯的宣传工作融入农村综合整治和美丽乡村建设的宣传工作中,政府、第三方运维公司以及村民3方共同发力,引导村民形成正确的排水习惯,从源头上减少污水管道异物型堵塞的发生。
2)强化维护管理。根据当前农村污水治理的运维趋势,大部分农村地区已经逐渐由村民自管的方式转变为以第3方运维公司为主体,政府、村民协同监督的维护管理模式。农村污水管道中户内管段由专业人员入户维护管理的可行性不高,可以采用维护管理责任区的方式统筹农村污水管道维护管理工作。由镇政府、村委会牵头,划分维护管理责任区,农户至接户井入口段为农户自行维护,接户井入口以外的管段(含接户井)由第3方运维公司负责维护管理。在经济较为发达的农村地区,农户自行维护的部分发生堵塞的情况应自行解决,自行解决不了的情况由农户自行出资购买疏通服务;在经济水平一般的地区,农户对于管道疏通收费较为敏感,可以先由村集体出资疏通户内管道,之后再逐步过渡到上述运维方式。第3方运维公司负责的管段应派专人定期巡查,特别是对于排水干管和排水支管,须通过开井探查的方式进行管道状况评估。平均每2个月将单个行政村内所有污水干、支管全部巡查一遍。同时,第3方运维公司还应对接户井情况进行巡视。另外,当污水处理终端进水量显著降低时,应全面排查排水管网情况。
-
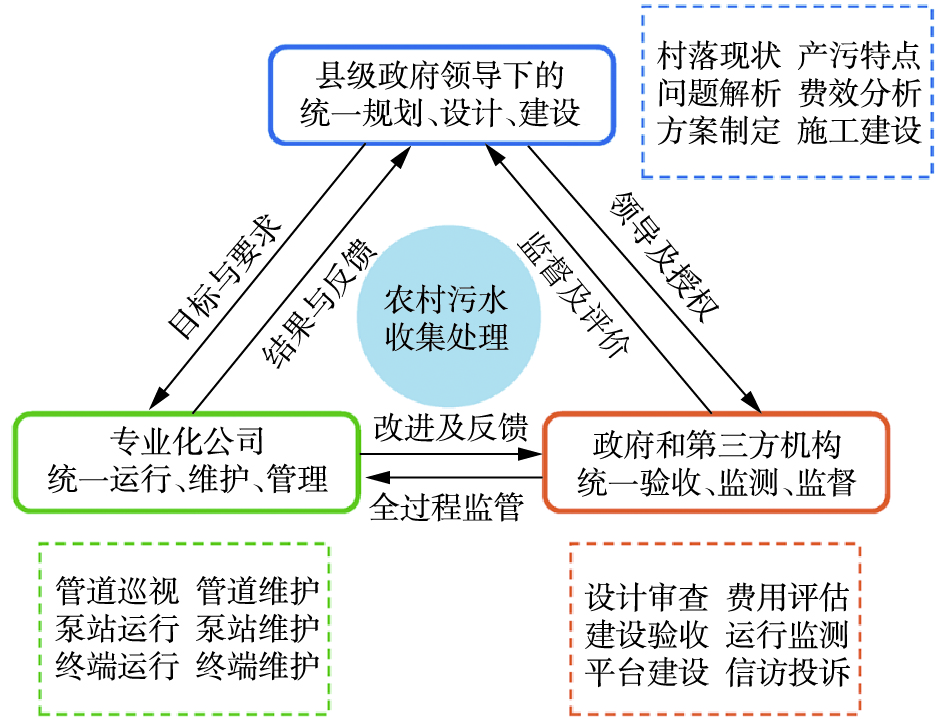
针对农村污水治理问题,不论是农村污水管网堵塞控制,还是农村污水处理设施运行维护,均需要从体制机制建设方面发力,建设良好的农村污水收集处理全过程管控体制,形成县级政府领导下的统一规划、设计和建设,专业化公司具体实施的统一运行、维护、管理以及政府和第3方机构配合形成的统一验收、监测、监督为主要层面的“三位一体”农村污水治理县域统筹模式(图7)。通过该模式可以有效集成政府规划建设,专业队伍运行维护及第三方机构验收监管3个主要层面的优势,发挥合力,共同提升县域农村污水治理工作的时效性和长效性。同时,应重视村民对于农村污水治理工作的参与和监督。具体到农村污水管道问题上,采用该“三位一体”的县域统筹模式,可以更好的集中优势技术力量、合理调度分配资金、强化运行维护实效、明确权利责任归属,实现建成管网设计更科学、管网质量更可靠、运行维护更有效、监督管理更有力、综合效益更明显的现代化农村污水管道系统。
-
1)农村污水管道堵塞可以分为淤积型堵塞和异物型堵塞,农村污水管道在设计、建设、运行、维护以及管理方面存在的问题可能导致农村污水管道的堵塞。
2)应根据农村的客观自然地理条件和社会经济现状,避免盲目套用城市排水管道设计参数,科学设计农村污水管道,保证施工质量,完善运行维护工作,降低农村污水管道堵塞发生率。
3)宣传正确的排水习惯并采用“三位一体”的县域统筹模式可以促进农村污水收集处理设施的稳定长效运行,提升农村卫生水平和生态环境质量。
农村污水管道堵塞成因分析与解决对策
Analysis and solutions of sewer blockage in rural areas
-
摘要: 农村污水管道系统是农村污水收集处理设施的重要组成部分,在采用纳入城镇污水管网处理和村落集中处理模式的农村地区发挥了重要作用。由于农村污水管道在设计、建设、运行、维护等环节存在一些问题,农村污水管道堵塞的现象时有发生。为有效降低农村污水管道堵塞发生率,保证农村污水收集系统的稳定运行,分析了农村污水管道堵塞的成因,提出了农村污水管道防堵和长效运行的建议和对策,包括优化农村污水管道管径设计、补齐管道系统配套设施、提升施工质量、强化正确的排水习惯宣传、加强科学维护管理工作和采用“三位一体”的县域统筹模式等。这些建议和对策可以有效降低农村污水管道堵塞的发生率,为提升农村卫生水平和生态环境质量提供参考。Abstract: Rural sewer system is an essential part of rural sewage collection and treatment facilities, which plays an important role in rural areas, especially in the fields of rural wastewater into urban sewers and rural centralized wastewater treatment systems. The blockage phenomenon of rural sewer occurs frequently since the potential issues during the process of design, construction, operation and maintenance of rural sewers. Therefore, in order to reduce the blockage incidence of rural sewer and ensure the stable operation of rural sewage collection system, the causes of the rural sewer blockage and corresponding suggestions was put forward in the current study, which could provide the efficient measures for the blockage prevention and long-term operation of rural sewers. In detail, optimizing the design of rural sewer diameter, complementing the supporting facilities of sewer system, improving the practical construction quality, strengthening the publicity of benign drainage habits, intensifying the scientific maintenance and management of rural sewer system, and adopting the “trinity” county mode would effectively will effectively reduce the blockage incidence of rural sewer system and take references for improving hygiene level and eco-environmental quality.
-
Key words:
- rural /
- sewer /
- blockage /
- small diameter /
- supporting facility
-
近年来,随着我国农村社会经济的发展和农村居民生活水平的提高,农村环境保护工作取得到了长足的发展,很多农村地区相继建设了农村生活污水收集和处理系统。根据住房和城乡建设部的相关统计数据,建设有农村生活污水处理设施的行政村数量逐年上升,截至2016年,全国约有20%的行政村对农村污水进行了处理(图1)。从污水治理模式的角度来看,农村生活污水收集处理模式主要可以分为3种:纳入城镇污水管网处理、村落集中处理和分散处理[1]。除分散处理以外,纳入城镇污水管网处理和村落集中处理均需建设农村污水管网。随着农村污水治理工作的推进,我国农村地区的排水管道沟渠长度和排水建设投入逐年增加,2017年,我国农村排水管道沟渠总长达到近1.1×106 km,年度排水建设投入约3.05×1010元(图1)。由于污水管网建设成本很高(约占整个污水处理系统建设成本的70%)[2],而我国农村地区经济仍不发达,基础设施建设相对滞后,因此,许多农村排水主要采用渠道进行。农村污水治理工作在许多经济欠发达的农村地区推进缓慢,个别农村地区甚至出现了建有农村污水处理设施,但是没有配套管网的尴尬局面。另外,由于农村地区在污水管道特点和居民生活方式等方面与城市地区有一些客观差异,农村污水管道问题较为复杂,已建成污水处理系统的农村地区对于污水管道的运维工作普遍不足,带来了很多问题。
农村污水管道在运行过程中,管道堵塞问题时有发生。一般而言,农村污水管道堵塞可以大致分为淤积型堵塞和异物型堵塞2类(图2)。淤积型堵塞是指污水在管道流动过程中泥沙、有机颗粒物等悬浮物逐渐在管道底部沉积,在减小管道有效截面积的同时,增大了管壁粗糙系数,致使管道过水能力下降,最终逐渐形成的管道堵塞。异物型堵塞是指在污水管道中由于不正常的工况引入了较大的异物(湿巾、菜叶、塑料包装袋等),这些异物直接滞留在管道内,形成管道的堵塞。一般异物型堵塞会造成污水流动受阻,如果管内异物没有及时得到清理,会进一步诱发淤积型堵塞。农村污水管道在堵塞后会造成上游污水外溢、农户污水无法有效排放等问题,严重影响村民日常生活和村容村貌。另外,污水管道堵塞还会造成污水处理终端水量不足,终端实际水量明显低于设计水量,影响污水处理效果。为有效降低农村污水管道堵塞发生率,提升农村污水收集系统的效率和稳定性,本研究结合农村污水管道工程实践和理论研究,系统地分析了农村污水管道堵塞成因,并结合农村发展的实际情况,提出了相应的解决方案。本研究对于保证农村污水收集处理设施的有效运转,解决污水散排这一基本民生问题和发挥污水处理系统应有的生态环境效益具有积极的意义。
1. 堵塞成因分析
1.1 设计建设问题
首先,存在管径-水量不匹配的问题。目前,我国尚没有针对农村污水管道设计的国家标准。许多农村地区直接参照《室外排水设计规范》(GB 50014-2006)进行污水管道设计。根据规范,室外污水管道设计的最小管径为200 mm,这一管径在城市污水管网设计中相对合理,但用于人口密度相对较低、居住较为分散的广大农村地区,存在诸多问题。基于该规范的最小管径要求,许多农村地区往往不经过水量核算,直接采用接户管为110 mm或160 mm,排水支管为200 mm 或225 mm,干管为 300 mm的管道设计方案。该设计方案虽然在管道建设初期,可以保证农村生活污水的有效收集,降低了污水管道发生异物型堵塞的概率,但管道内径过大,而实际污水量较小,日间管道充满度长期低于0.3,在夜间管道基本无水,在排水较少的时段,污水流速低于自冲刷流速0.6 m·s−1,管道沉积现象严重,容易导致管道淤积型堵塞。另外,由于农村用水量相对较低,一般为70~160 L·(人·d)−1[3],同时排水习惯与城市地区有一定的差异,农村污水悬浮颗粒物浓度相对于城市污水一般较高,悬浮颗粒物在低流速管道内逐渐沉积,形成管道堵塞。
即使在进行水量核算的农村地区,大部分的水量设计采用的水量总变化系数KZ均参考城市污水变化系数,一般取2.3~2.5。根据部分地区的实践,实测的农村污水总变化系数KZ大致为2.5~4.5,明显高于城市最小流量下的总变化系数2.3。这也就意味着农村污水的水量变化更为显著,采用城市系数设计的管道,在干管段如果设计不合理,可能导致水量高峰期时管道过流量不足,无法及时排出的污水短期暂存在检查井中,会造成污水外溢。另外,在农村污水管道设计阶段,一般将包括洗涤污水在内的所有生活污水全部纳入水量核算范围,而部分农村地区存在洗涤废水不纳管而直接泼洒的客观现状,管道实际水量低于设计水量,长此以往,管道污水流速不足,容易产生淤积型堵塞。
第二,存在配套设施不合理的问题。主要表现在几个方面。
1) 隔油池建设不足。在农村污水收集处理系统中,隔油池一般用于降低厨房污水含油量[4],以减少餐厨污水中的油脂对于污水管道和处理终端的不良影响(图3)。在当前的农村污水管道建设中,隔油池不是强制安装的配套设施,很多地区为了降低管道建设成本,取消了户用隔油池,村民生活产生的餐厨污水直接排放进入管道,餐厨污水含有大量的油脂,这些油脂进入管道后,会逐渐粘附在污水管道内壁,显著增加管道堵塞风险[5-6]。
2) 接户井筛网配置不足。在当前的农村污水管道系统的建设中,一般在农户内的下水口均会设置滤网,但随着时间的推移,这些滤网逐渐堵塞,一些村民为了方便,直接将滤网拆除并将湿巾、菜叶等杂物直接冲入下水道,这些杂物未经筛网过滤,直接进入污水管道,会直接堵塞接户管或排水支管,从而造成异物型堵塞。由于农户私自拆除户内滤网的行为较为常见并且不易管理,目前,部分农村地区已经在接户井处另设置一层筛网,以防止未经下水口滤网过滤的大块杂物进入下游管道,进而造成异物型堵塞。但是,目前大部分农村地区对于接户井筛网的设置不重视,没有进行安装。
3) 老旧化粪池直接接入管道。化粪池在预处理农村污水的同时,还对管道防堵具有重要的作用。通过在化粪池内的沉淀和厌氧发酵,污水中的悬浮颗粒物可以得到部分去除,有效避免了接户管以及排水支管的堵塞。但是,在农村污水管网设计和建设的过程中,许多农村地区直接将已经老旧破损的化粪池出水接入管道,没有及时修复或更换化粪池,导致进入管道的污水中悬浮颗粒物含量高,容易引发管道堵塞。
4) 检查井井孔引入泥沙。一般而言,为了方便污水管道检修,我国的污水检查井大多设有开启孔。根据相关研究,污水检查井的井孔除了具有方便开启的作用,还具有重要的管道通风功能[7],对于降低管道内有害气体的浓度具有一定的积极作用。但是,检查井井孔在雨季会被动的接受地表径流,地表径流中携带的泥沙因此进入污水管道[8]。泥沙是造成污水管道堵塞的重要因素,检查井引入的泥沙会加剧管道堵塞风险。根据农村污水管道建设经验,和城市市政污水管道相比,大部分农村污水管道长度较短、水量较小,污水停留时间较短并且一般不需要人工进入管道进行检修,H2S和CH4等有害气体产生量相对较低,农村污水检查井的井孔通风作用意义相对不是很高,而井孔引入的雨季泥沙反而对于管道运行有一定的威胁。因此,一些农村地区的污水检查井已经开始采用不开孔的塑料检查井盖或双层式检查井盖以防止井孔引入泥沙(图4)。根据实际的运行效果,农村污水检查井不开孔的利大于弊,值得推广。
第三,存在施工水平不足的问题。由于很多农村地区缺乏专业的污水管道施工团队,污水管道施工工程主要由当地临时聘用的工人完成,但其在农村污水治理设施施工方面的专业性不足,甚至个别地区的施工队连设计图纸都无法准确理解,随意施工的现象时有发生。污水管道作为一项地下设施,其施工质量受路面和地下土层的影响很大。大部分农村地区的路面尚未完全硬化,土路、石子路等路面广泛存在。一些施工队在管道施工过程中,没有按照设计要求开挖沟槽并敷设垫层,或者没有按照管道施工要求进行沟槽回填,直接采用原土回填管道支撑面和管底腋角,导致管道在长期使用后发生沉降,甚至形成局部管道倒坡,造成管道沉积物或泥沙淤积甚至堵塞。在行驶大型载重车辆的路面下的污水管道施工水平不足,容易形成管道受外压变形甚至破裂,直接造成管道过水断面减小和管周泥沙进入管道,形成管道堵塞。
另外,作为最常见的管道异味控制部件,存水弯基本在每个户内下水管入口处均有设计,但是有些农村地区在污水管道接户的位置又额外安装了一个存水弯,在控制管道异味的同时,兼具落水井的功能,用于找齐管道高程。存水弯会显著改变污水的动力学参数,不利于污水的重力流动,在存水弯处的管道堵塞风险显著高于直管道,因此在施工过程中存水弯的安装不宜过多。
第四,存在雨污分流不彻底的问题。目前,新建排水管网的农村地区的排水体制主要为雨污分流,雨污分流可以有效降低因雨季地表径流引入泥沙造成管道堵塞的发生率。但是,在部分已经完成排水管网建设的农村地区,仍然存在一些合流制管道,在长期运行中,这些合流制管道的泥沙堵塞风险相对较大。另外,在很多雨污分流的农村地区,虽然排水管道在设计和建设时为分流制管道,但在实际使用中,因雨季庭院和街道排水较慢,个别农户为了个人利益自行打开污水井盖排水,形成了临时性的合流制排水,造成了潜在的管道泥沙堵塞隐患。
1.2 运行维护问题
1)排水习惯有待提高。部分村民排水习惯有待提高。在农村污水管道实际运行过程中,部分村民为了提高排水速度,私自拆除下水管滤网,使得大量的菜叶、泥沙、头发等异物进入管道,造成了很大的异物型堵塞隐患。另外,由于一些农村地区刚由旱厕改为水厕,部分村民的不良冲厕习惯,导致湿巾、尿布、卫生巾等直接冲入管道,造成了很多管道堵塞事故的发生。由于部分因为不良排水习惯造成的堵塞并没有在接户管内部发生,而是发生在支管等户外管段,村民对于排水习惯造成的管道堵塞认识并不到位,也很难明确堵塞责任。
2)维护管理工作滞后。维护管理工作明显不足。由于我国农村污水治理工作正处于起步阶段,农村污水收集处理设施的维护管理工作尚未得到很好的落实,一些地区的农村污水处理设施尚处于“建而不管”的无运维阶段,地下的污水管道的维护管理工作更是没有得到足够的重视。大部分农村地区的维护管理重点放在污水处理终端,没有定期检查污水管道,只有在管道发生堵塞,收到村民投诉之后才派人疏通管道。污水管道虽然结构相对简单,但是位于地下,一旦发生严重的堵塞事故,其不良影响和疏通成本也很高,不完善的维护管理工作明显增大了管道堵塞发生的概率。另外,由于农村生产生活方式的转变和化肥的普及,化粪池粪渣的农田利用逐渐减少,带来了农户化粪池清掏周期延长甚至不清掏的现象。而目前大部分农村地区对于户用化粪池的运维工作落实不到位,化粪池长期不清掏,过量储存的粪渣会随污水进入排水管道,加大排水管道的堵塞机率。
2. 建议和对策
2.1 设计建设
1)优化管径设计。在农村污水管道设计过程中,应摒弃过去重视处理终端,轻视污水管网的落后观念,做到管-站同步设计。具体到实际设计时,应实地考察,避免盲目采用室外排水建设规范和城市污水管道建设经验,结合村庄地形并通过管道水力学计算管道管径、坡度等相关参数,必要时可以采用计算流体力学(CFD)等手段优化管道设计细节[9-10],降低管道堵塞发生概率。根据管道水力学计算[11-14]和部分地区的应用实践,小管径管道系统(干管管径不大于200 mm)在农村地区具有一定的可行性。农村污水管道一般采用UPVC管和HDPE双壁波纹管。UPVC管的管径主要为75、110、160和200 mm;HDPE双壁波纹管的管径主要选用的是225 mm和300 mm。如图5所示,利用谢才-曼宁公式[15-16]推算,在人口相对稀疏的农村地区,在同样的污水流量(12 L·s−1)和管道坡度(5‰)的前提下,干管管径由300 mm缩小为200 mm,管道充满度由0.25提升到0.48,理论污水流速由0.88 m·s−1提升到0.91 m·s−1,在降低管道成本的同时,有效降低了淤积型堵塞的发生率。同理,若支管污水流量为6 L·s−1,坡度为5‰,支管管径由200 mm缩小为160 mm,管道充满度由0.32提升到0.43,理论污水流速变化不大,均为0.75 m·s−1左右,管道充满度的适当增加可以帮助控制管道沉积[17],进而降低淤积型堵塞的发生率。在污水流量相对较低时,可以采用接户管为110 mm,支管为160 mm,干管为200 mm的管道设计方案以提升管道充满度,避免淤积。相关研究也证实,采用小管径的排水管道,污水对于管道内颗粒物的冲刷作用更强,有助于防止管道的堵塞[18]。小管径管道的主要缺点是对于异物型堵塞的适应性较差,相对较小的异物进入管道系统,就可能引起异物型堵塞。因此,采用小管径管道的前提是接户井设有筛网,避免大块异物进入管道,小管径农村污水管道系统和常规农村污水管道系统对比见图6。
2)补齐配套设施。基于当前很多农村地区在污水管道设计时为降低建设成本而大幅削减配套设施的现状,应该在控制总体建设成本的同时配全设施。建议设计户用小型隔油池,减少餐厨污水的油脂进入管道,同时在接户井设置筛网,拦截出户管异物。这些成本的增加可以通过减少检查井的方式得到削减。农村污水管道的支管段,管径一般为160~225 mm,没有必要全程都设置为全尺寸的检查井,可以采用清扫口或配备无孔井盖的简易检查井,以替代部分直管段上的全尺寸检查井,在减少雨季泥沙汇入的同时,可降低管道建设成本。应尽量采用无孔的检查井井盖,避免农户自行开启检查井。在接户管和支管转弯的位置设置清扫口以方便检修,同时取消不必要的存水弯。为保证施工质量和便于后期运维,应尽量采用统一规格的预制设施。
3)提升施工质量。高水平的施工是农村污水管道正常运行的重要保证。为避免不专业的管道施工,应结合农村污水治理县域整体打包建设的思路,通过整县域的统一招标,聘用具有相应资质的专业农村污水管道施工团队。在施工过程中,对于材料、人工、运输等进行登记,并委派专人进行施工监督,确保施工队使用符合标准的管材、严格按照图纸施工。对于管道接口、管-井连接、管道基础平整、沟槽回填等工序进行监控,保证施工质量。对于很多农村地区为了降低成本,不使用中粗砂回填管道支撑面和管底腋角而直接使用原土回填的违规作法,要严格管控。施工完成后的管道必须进行闭水试验,确保水密性达标。另外,由于树根侵入管道也是一种导致管道堵塞的原因,在设计和施工过程中,开挖的沟槽应尽量避开大型树木的根系,使污水管道尽量远离树根[5]。
2.2 运行维护
1)排水习惯宣教。农村污水管道堵塞很大程度上是由于不良的排水习惯造成的。因此,应以村、镇为单位,开展排水习惯宣传教育工作,向村民介绍正确的排水习惯,提升村民素质,减少私自拆除下水道滤网的发生。同时,对于刚由旱厕转变为水厕的农村,开展相应的水厕使用教学宣传,教育村民不要将大块的杂物,特别是湿巾、卫生巾等杂物直接冲入水厕。可以将排水习惯的宣传工作融入农村综合整治和美丽乡村建设的宣传工作中,政府、第三方运维公司以及村民3方共同发力,引导村民形成正确的排水习惯,从源头上减少污水管道异物型堵塞的发生。
2)强化维护管理。根据当前农村污水治理的运维趋势,大部分农村地区已经逐渐由村民自管的方式转变为以第3方运维公司为主体,政府、村民协同监督的维护管理模式。农村污水管道中户内管段由专业人员入户维护管理的可行性不高,可以采用维护管理责任区的方式统筹农村污水管道维护管理工作。由镇政府、村委会牵头,划分维护管理责任区,农户至接户井入口段为农户自行维护,接户井入口以外的管段(含接户井)由第3方运维公司负责维护管理。在经济较为发达的农村地区,农户自行维护的部分发生堵塞的情况应自行解决,自行解决不了的情况由农户自行出资购买疏通服务;在经济水平一般的地区,农户对于管道疏通收费较为敏感,可以先由村集体出资疏通户内管道,之后再逐步过渡到上述运维方式。第3方运维公司负责的管段应派专人定期巡查,特别是对于排水干管和排水支管,须通过开井探查的方式进行管道状况评估。平均每2个月将单个行政村内所有污水干、支管全部巡查一遍。同时,第3方运维公司还应对接户井情况进行巡视。另外,当污水处理终端进水量显著降低时,应全面排查排水管网情况。
2.3 体制机制
针对农村污水治理问题,不论是农村污水管网堵塞控制,还是农村污水处理设施运行维护,均需要从体制机制建设方面发力,建设良好的农村污水收集处理全过程管控体制,形成县级政府领导下的统一规划、设计和建设,专业化公司具体实施的统一运行、维护、管理以及政府和第3方机构配合形成的统一验收、监测、监督为主要层面的“三位一体”农村污水治理县域统筹模式(图7)。通过该模式可以有效集成政府规划建设,专业队伍运行维护及第三方机构验收监管3个主要层面的优势,发挥合力,共同提升县域农村污水治理工作的时效性和长效性。同时,应重视村民对于农村污水治理工作的参与和监督。具体到农村污水管道问题上,采用该“三位一体”的县域统筹模式,可以更好的集中优势技术力量、合理调度分配资金、强化运行维护实效、明确权利责任归属,实现建成管网设计更科学、管网质量更可靠、运行维护更有效、监督管理更有力、综合效益更明显的现代化农村污水管道系统。
3. 结语
1)农村污水管道堵塞可以分为淤积型堵塞和异物型堵塞,农村污水管道在设计、建设、运行、维护以及管理方面存在的问题可能导致农村污水管道的堵塞。
2)应根据农村的客观自然地理条件和社会经济现状,避免盲目套用城市排水管道设计参数,科学设计农村污水管道,保证施工质量,完善运行维护工作,降低农村污水管道堵塞发生率。
3)宣传正确的排水习惯并采用“三位一体”的县域统筹模式可以促进农村污水收集处理设施的稳定长效运行,提升农村卫生水平和生态环境质量。
-
-
[1] 刘俊新. 因地制宜, 构建适宜的农村污水治理体系[J]. 给水排水, 2017, 43(6): 1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2017.06.001 [2] 范彬, 胡明, 顾俊, 等. 不同农村污水收集处理方式的经济性比较[J]. 中国给水排水, 2015, 31(14): 20-25. [3] 李新艳, 李恒鹏, 杨桂山, 等. 江浙沪地区农村生活污水污染调查[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2016, 32(6): 923-932. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2016.06.009 [4] PAULO P L, AZEVEDO C, BEGOSSO L, et al. Natural systems treating greywater and blackwater on-site: Integrating treatment, reuse and landscaping[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2013, 50: 95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.03.022 [5] MARLOW D R, BOULAIRE F, BEALE D J, et al. Sewer performance reporting: Factors that influence blockages[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 2011, 17(1): 42-51. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)IS.1943-555X.0000041 [6] DESILVA D, MARLOW D, BEALE D, et al. Sewer blockage management: Australian perspective[J]. Journal of Pipeline Systems Engineering and Practice, 2011, 2(4): 139-145. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)PS.1949-1204.0000084 [7] 刘艳涛, 卢金锁, 闫帅军. 污水检查井盖调研及其预留孔对井内气体组分影响[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(3): 97-101. [8] HASS J L. The evolution of the small diameter variable gradient sanitary collection system into the small bore sewer™[J]. Water Practice, 2007, 1(6): 1-9. [9] HUSAIN I A F, ALKHATIB M F, JAMI M S, et al. The application of multiphase DEM for the prediction of fat, oil and grease (FOG) deposition in sewer pipe lines[J]. Journal of Advanced Research in Fluid Mechanics and Thermal Sciences, 2017, 39(1): 9-16. [10] MOHSIN M, KAUSHAL D R. 3D CFD validation of invert trap efficiency for sewer solid management using VOF model[J]. Water Science and Engineering, 2016, 9(2): 106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.wse.2016.06.006 [11] 茅泽育, 相鹏, 赵璇, 等. 圆形断面排水管道水力特性探讨[J]. 给水排水, 2006, 32(7): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2006.07.013 [12] POMEROY R D. Flow velocities in small sewers[J]. Water Pollution Control Federation, 1967, 39(9): 1525-1548. [13] YAO K M. Functional design of sanitary sewers[J]. Water Pollution Control Federation, 1976, 48(7): 1772-1778. [14] DIAS S P, MATOS J S. Small diameter gravity sewers: Self-cleansing conditions and aspects of wastewater quality[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2001, 43(5): 111-118. [15] GUZM N K, MOTTA E J L, MCCORQUODALE J A, et al. Effect of biofilm formation on roughness coefficient and solids deposition in small-diameter PVC sewer pipes[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007, 133(4): 364-371. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(2007)133:4(364) [16] 严煦世, 刘遂庆. 给水排水管网系统[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2014. [17] 周玉文, 赵洪宾. 排水管网理论与计算[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2000. [18] MEMON F A, FIDAR A, LITTLEWOOD K, et al. A performance investigation of small-bore sewers[J]. Water Science & Technology, 2007, 55(4): 85-91. -




 下载:
下载: