-
矿物的浮选过程会产生大量的选矿废水,其中含有重金属离子、残留的有机浮选药剂等有毒有害物质。这些选矿废水中的重金属离子由于毒性强、不能降解,直接排入水体中会毒害水生生物和破坏环境[1]。目前,针对含重金属选矿废水的处理技术主要为向选矿废水中投入过量的碱性物质,使重金属离子转化为相应的氢氧化物沉淀,再通过混凝沉淀法去除废水中的重金属离子。李香兰等[2]利用石灰乳调节pH,使选矿废水中重金属离子形成难溶的氢氧化物沉淀。张同胜[3]采用2段石灰乳中和法处理废水中的重金属。由以上研究可知,化学混凝沉淀法能有效地处理高浓度的含重金属废水,但是该技术也具有出水pH偏高[4]、药剂消耗大[5]、重金属回收难[6],处理低浓度重金属废水效果差[7]等不足。另外,浮选药剂需要在适宜的pH条件下使用,而铅锌矿的浮选过程通常在碱性条件下进行,导致选矿废水多数呈碱性[8]。因此,开发一种低成本、易回收且能够有效处理中低浓度重金属废水的处理工艺势在必行。
生物吸附法是利用具有活性或非活性生物作为生物吸附剂将环境或水溶液中的金属离子或非金属化合物通过吸附分离出来的方法[9]。由于其具有处理成本低、重金属易回收、能有效处理低浓度的重金属废水等优势,近年来逐渐被应用于含重金属废水的处理研究中[10]。生物吸附法的研究主要集中在生物吸附剂的制备、生物吸附的工艺参数和吸附机理[11]。如何降低生物吸附剂的制备成本、优化生物吸附的工艺参数和明确其吸附机理,成为生物吸附法工业推广应用的重要影响因素。
近年来,农林废弃物[12]和剩余污泥[13]来源广、价格低廉,且具有良好的潜在吸附能力,已成为制备生物吸附剂的重要原料。本研究利用自制的活性污泥基生物吸附剂对广东省某铅锌矿的含铅选矿废水进行了生物吸附处理。分别考察了吸附剂投加量、吸附时间、pH和温度4个因素对活性污泥基生物吸附剂对Pb2+吸附的影响,利用响应曲面法(response surface methodology, RSM),对自制生物吸附剂吸附选矿废水中的重金属离子进行工艺参数优化,并对各影响因素之间的交互影响作用进行评价,同时通过红外光谱对吸附前后的自制生物吸附剂官能团进行了分析,初步探讨了其对Pb2+的吸附机理,研究结果可为生物吸附法处理含铅选矿废水提供参考。
全文HTML
-
实验使用的吸附剂为氧化钙改性污泥基吸附剂(CaO-SA)。按氧化钙/污泥固体含量为1∶0.05的比例投加,在25 ℃下,以130 r·min−1搅拌2 min,再以60 r·min−1搅拌2 min,重复搅拌至均匀,敞开放置4 h后,于60 ℃烘干,并研磨成0.45~0.85 mm的颗粒。NaOH与HNO3等试剂均为分析纯。实验水样为广东省某铅锌矿含铅选矿废水(pH=11.38,Pb2+为25 mg·L−1)。
所用仪器包括RADWAG AS220.R3分析电子天平、ZQTY-70S恒温振荡器、JJ-4B六联电动搅拌器、DHC-9123A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱、Ohuas ST2100pH计、感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Agilent 713)、高新超高分辨场发射扫描电子显微镜(日立高新SU8000系列)、全自动快速比表面积及中孔/微孔分析仪(ASAP 2020系列)、X-射线衍射光谱 (Rigaku UItima IV) 分析仪、傅里叶红外光谱仪(Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS5)。
-
考察CaO-SA的投加量(2、3、4、5、6 g·L−1)、pH(3、5、7、9、11)、温度(20、25、30、35、40 ℃)和吸附时间(30、45、60、75、90 min)对CaO-SA处理实际含铅选矿废水的影响。每个参数各设3个平行实验,利用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(Agilent 713)测定吸附后Pb2+的浓度,以平均值作为实验结果。以Pb2+的去除率作为评价指标,其去除率按式(1)进行计算。
式中:η为Pb2+的去除率;C0 为溶液的初始浓度,mg·L−1;Ce为溶液平衡浓度,mg·L−1。
运用响应曲面法预测最优工艺条件的优势在于设计的实验次数少、能建立高精度的回归方程、预测准确性高。因此,利用响应曲面优化分析法研究吸附时间、投加量、pH、温度等4个因素对CaO-SA吸附Pb2+影响的主效应和交互作用,在实验范围内对吸附条件进行优化。本实验采用Box-Behnken响应面优化实验设计,分别在低(−1)、中(0)、高(1) 3个水平上对吸附实验进行中心复合设计,共有29组实验,中心点实验重复5组,且每组实验重复3次,取其平均值作为对应的响应值,4因素3水平编码和实验值见表1。
对CaO-SA的表面特征、物质组成和结晶状况进行分析,同时对最优吸附条件下吸附前后的CaO-SA进行红外光谱分析,探讨CaO-SA处理含铅选矿废水的吸附机理。利用高新超高分辨场发射扫描电子显微镜对CaO-SA的表面进行扫描,观测其表面特征;采用X-射线衍射光谱分析仪对CaO-SA的物质组成及结晶状况进行表征分析;采用傅里叶红外光谱仪对吸附前后的CaO-SA进行分析。
1.1. 实验材料与仪器
1.2. 实验方法
-
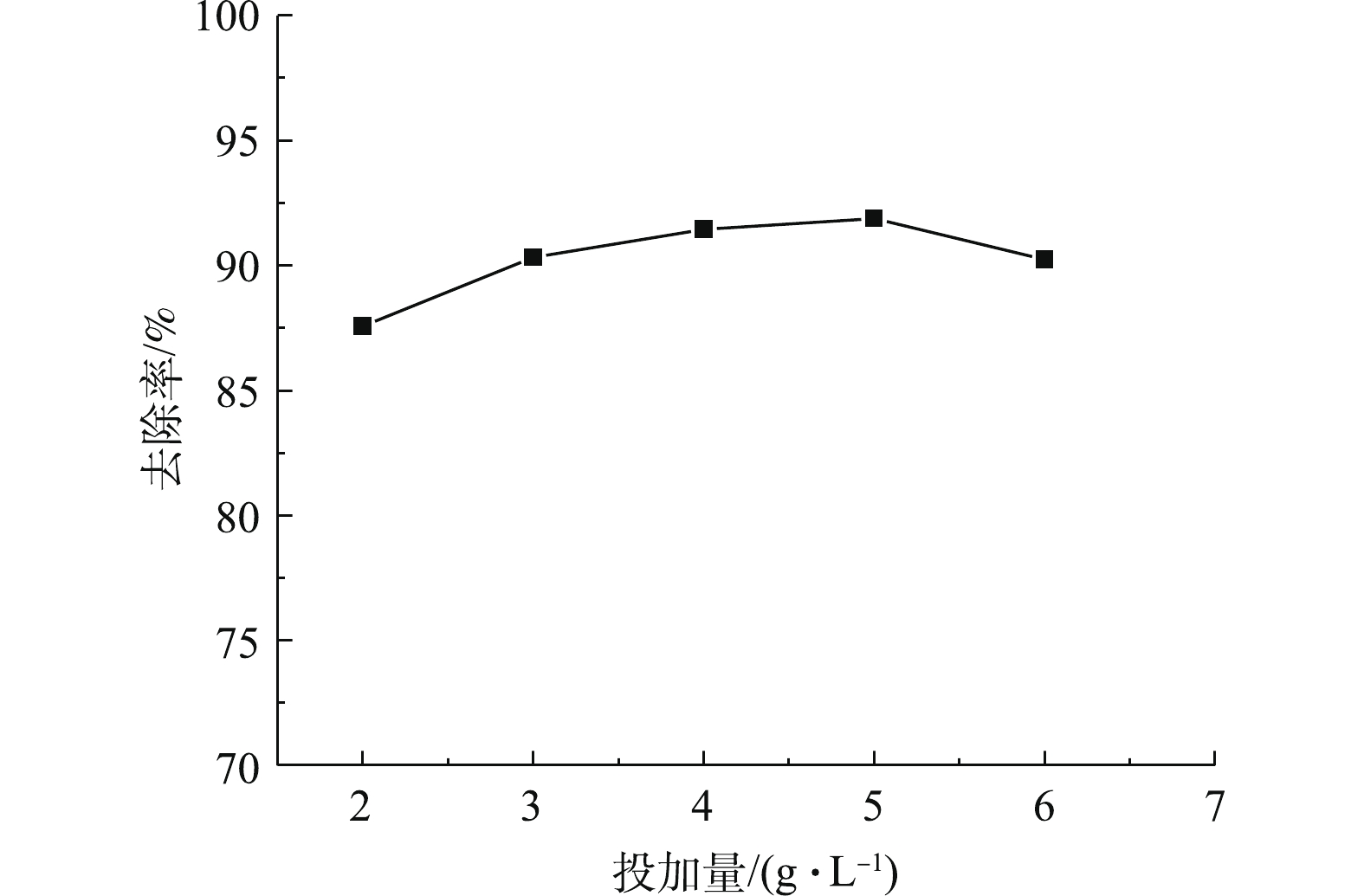
在温度为25 ℃、pH=11、吸附时间为30 min的条件下,改变CaO-SA的投加量,探讨其对Pb2+去除率的影响,结果如图1所示。可以看出,在投加量为5 g·L−1时,CaO-SA对Pb2+的去除率达到最高,此后,去除率不随吸附剂投加量的增加而改变。其原因可能归为以下3点:当 CaO-SA吸附Pb2+的去除率达到最大时,溶液中的 Pb2+浓度相对降低,造成Pb2+扩散至吸附剂表面并被吸附的驱动力减小,而解吸的趋势增大;过量的吸附剂聚集使吸附剂的有效表面积增加有限[14];过量吸附剂间参与吸附的相邻活性基团彼此干扰对方的吸附[15]。因此,为更准确地预测CaO-SA的投加量,响应曲面法中的投加量水平取值应为2、4和6 g·L−1。
在温度为25 ℃、投加量为5 g·L−1、吸附时间为30 min的条件下,通过改变pH来探讨pH对Pb2+去除率的影响,结果如图2所示。可以看出:当pH<7时,CaO-SA对Pb2+的吸附效果较差,去除率仅为70%~86%,这可能是由于体系中的H+与Pb2+争夺CaO-SA中的吸附位点,从而导致部分Pb2+无法被吸附,导致去除率有所下降[16];在pH≥7时,Pb2+去除率均在88%以上,这是由于在中性或碱性条件下,H+含量较低,CaO-SA能更好地与Pb2+结合。此外,颜游子等[17]的研究表明,Pb2+可在碱性条件下生成可溶性的
HPbO−2 与[Pb(OH)4]2− ,从而抑制了Pb(OH)2的生成,导致在碱性条件下铅以溶解态分散在水中,且可被检测。因此,在pH=11.38时,所处理的实际选矿废水中Pb2+含量约为25 mg·L−1,这说明在pH≥7时,大量OH−的存在对此体系中Pb2+的去除效果影响不大,在实验结果中,Pb2+的去除应是CaO-SA的吸附作用[18]。为了在较高的去除率中进行最优条件的预测,响应曲面法中pH设定为6、9、12。在温度为25 ℃、投加量为5 g·L−1、pH=11的条件下,考察了吸附时间对Pb2+去除率的影响,结果如图3所示。可以看出,在30~90 min内,Pb2+的去除率均在90%以上,且结果相差不大;在吸附时间为60 min后,吸附基本达到平衡。为节省时间,响应曲面法中吸附时间应为30、45、60 min。
在吸附时间为30 min、投加量为5 g·L−1、pH=11的条件下,考察了温度对Pb2+去除率的影响,结果如图4所示。可以看出,随着温度的上升,Pb2+的去除率不断提高。CaO-SA吸附Pb2+的反应可能为吸热反应,因此,温度上升给体系提供了能量,可促进吸附剂中的吸附位点与Pb2+相结合,属于化学吸附。为了与处理选矿废水的环境温度相近,响应曲面法中温度设定为20、30、40 ℃。
-
基于以上实验的结果,采用Box-Behnken进行实验设计,以含铅选矿废水的去除率作为响应值,进行了曲面优化模型的预测与分析。实验设计和结果如表2 所示。
根据Design-Experts8,对表2的实验结果进行分析。以 Pb2+ 去除率为响应值,以吸附剂投加量、吸附时间、温度、pH为自变量,建立响应面编码形式的二次多项式,计算方法如式(2)所示。
式中:η为去除率;A为吸附时间;B为温度;C为投加量;D为pH。
利用Design-Experts8,对表2中的实验结果进行了方差分析,结果见表3。利用F值进行统计显著性检测,利用P值检测每个回归系数的显著性。若P<0.05,表示回归模型所对应项目的相关性显著;若P>0.05,表示回归模型所对应项目的相关性不显著[19]。由表3可知,模型F为14.84,模型的P< 0.000 1< 0.05,这表示回归方程描述各因素与响应值之间的拟合曲线的相关性显著。该模型可代替实验真实点对实验结果进行分析;预测模型的R2=0.936 9,校正判定系数
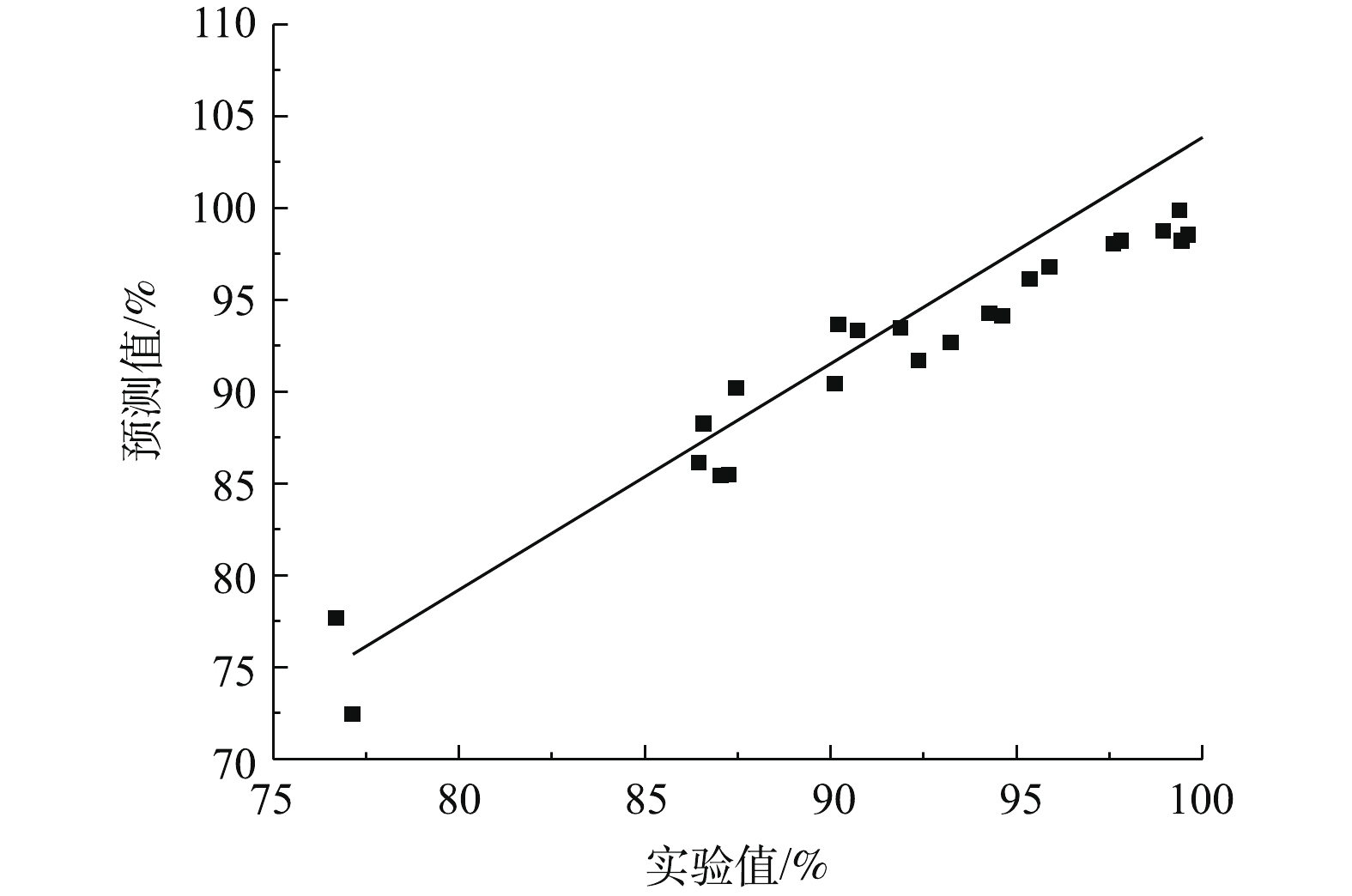
R2Adj=0.8737 ,仅有13.63%不能用模型解释,说明该模型与实验结果拟合良好,准确度高。去除率的实验值和模型预测值对比结果如图5所示,R2接近于1,表明 Pb2+去除率的模型预测结果与实验结果高度吻合。残差正态概率可用于判断吸附模型是否服从正态分布,如图6所示,数据点比较接近直线,拟合程度较高,说明构建的响应曲面模型符合正态分布。变异系数CV=2.47%<10%,信噪比为15.043,远大于4,这表明该模型具有比较高的可信度和精密度。通过上述分析可知,模型可用于预测。由表 3可知,在单因素条件下,吸附时间、温度和吸附剂投加量对 Pb2+ 去除率的影响显著(P<0.05)。同时,由 F可知,各因素对Pb2+去除率的影响顺序为温度>吸附时间>投加量>pH,pH对Pb2+去除率的影响不显著。铅可在强碱性条件下生成可溶性的
HPbO−2 与[Pb(OH)4]2− ,从而抑制了Pb(OH)2沉淀的生成。因为铅锌矿的选矿过程是在碱性条件下进行的,须投入大量的碱性试剂,因此,选矿废水中碱性试剂过量,导致存在大量的OH−。颜游子 [17]的研究表明,铅会在强碱条件下生成可溶性的HPbO−2 与[Pb(OH)4]2− ,从而抑制了Pb(OH)2沉淀的生成,故在碱性条件下可检测到铅。这说明,在CaO-SA吸附Pb2+的过程中,选矿废水中大量的OH−没有与Pb2+形成相对应的氢氧化物沉淀,Pb2+的去除过程应是CaO-SA的吸附起主导作用。因此,相对其他3个因素而言,pH对Pb2+去除率的影响较小。在交互作用中,CaO-SA对Pb2+的去除效果显著的是:投加量与吸附时间、吸附时间与温度。Design Expert 8.0 以两两自变量为坐标的3D图像可以更加直观地说明各因素之间的交互作用关系及其对去除率的影响,投加量、吸附时间、温度和pH 4个单因素对去除率的影响以及表征响应曲面函数的性状结果如图7和图8所示。
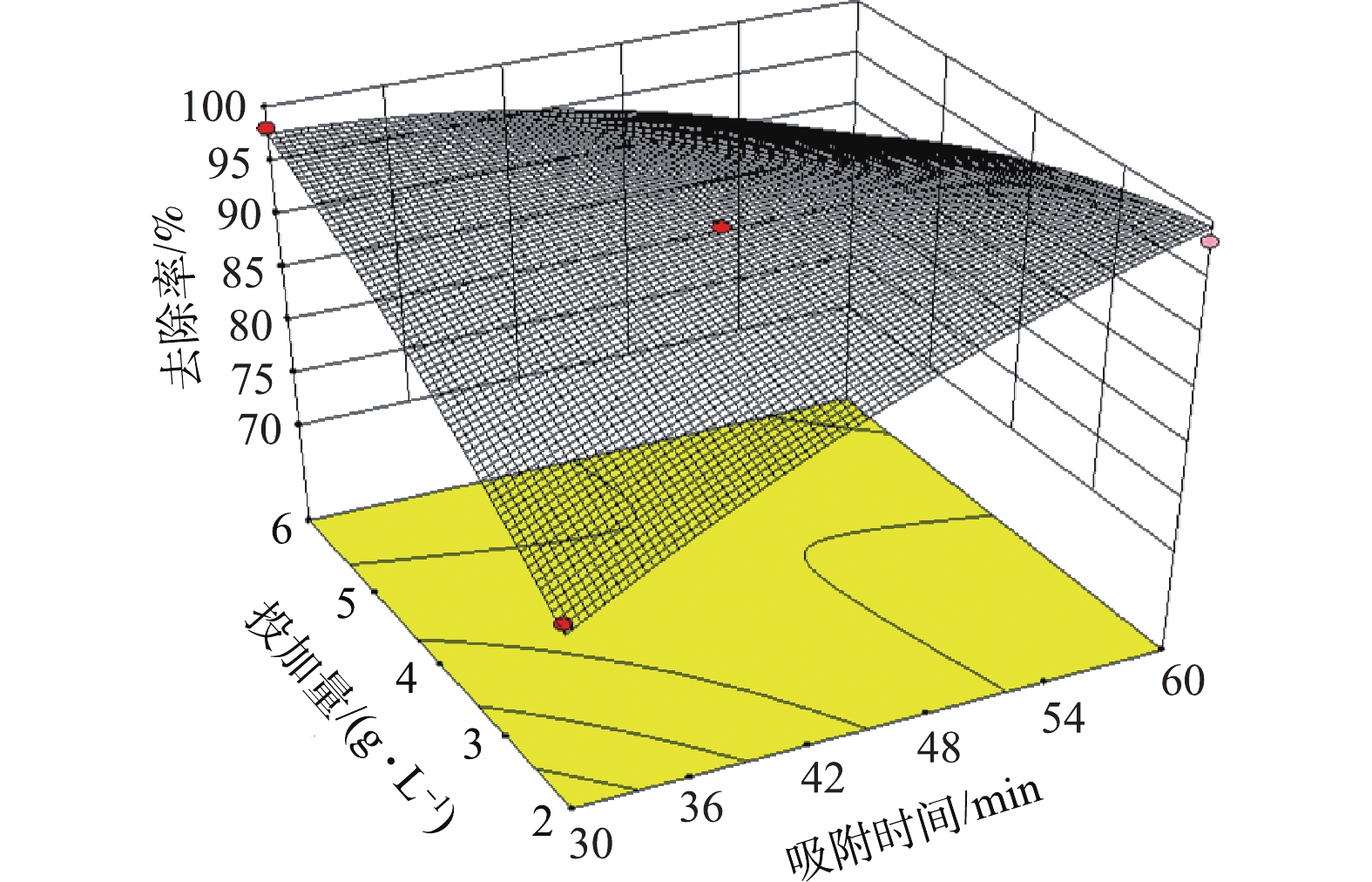
在投加量为4 g·L−1、pH=9的条件下,吸附时间与温度对Pb2+去除率的影响如图7所示。可以看出,在温度较低时,去除率随吸附时间的增大而升高;当温度较高时,去除率随着吸附时间的增加略有降低。这是由于:在温度较低时,离子混乱程度较低,随着吸附时间的延长,可提供足够多的接触时间,使Pb2+与CaO-SA中的吸附位点充分接触,进而导致去除率升高;而在温度较高时,由于温度较高时使离子自由能增加,随着吸附时间的延长,离子自由能积聚到一定程度后,导致部分Pb2+释放出来[20-21],从而导致去除率降低。由于物理吸附是放热反应,因此,当反应达到了吸附平衡,升高温度会使吸附量下降,这说明此体系中存在物理吸附。活性污泥具有羟基、羧基等官能团,在吸附过程中,这些基团容易与Pb2+发生反应,其为吸热反应[22-23],升高温度有利于吸热反应的进行。由图7可见,在相同时间内,温度的升高会导致Pb2+去除率有明显的提高,说明吸附反应往正反应方向进行,进而说明了该吸附过程应存在自发的吸热反应,这与以往的研究结果[21-22]相符。综上所述,自制生物吸附剂吸附Pb2+可能是物理吸附与化学吸附共存的结果,并以化学吸附为主。
图8反映了pH与温度在中心条件下(温度为30 ℃、pH=9),吸附时间与投加量对Pb2+去除率的影响。可以看出,在吸附时间较短时,去除率随着投加量的增大而升高。这是因为Pb2+与CaO-SA中的吸附位点接触时间较短,导致部分Pb2+来不及与CaO-SA中的吸附位点相结合,而投加量的增加提供了大量的吸附位点数目,更多的Pb2+可以与CaO-SA中的吸附位点结合,从而提高去除率。而在吸附时间较长时,去除率随着投加量的增大而降低。由于吸附剂达到饱和时,溶液中的 Pb2+浓度会相对降低,造成Pb2+扩散至吸附剂表面,被吸附的驱动力减小[14],此时若增加吸附剂,便会增大吸附剂之间相互摩擦的概率,而相互摩擦产生的剪切力可能使某些吸附结合力较弱的位点中的Pb2+被释放出来,从而降低去除率。此现象又说明该体系里存在着一定的物理吸附作用。同时,也可以看出:在一定投加量的条件下,随着吸附时间的延长,去除率开始时迅速增加,随后则开始降低。这说明吸附达到某个时间点时,吸附已达到饱和的状态。此时,延长吸附时间会使饱和吸附的吸附剂互相摩擦的概率增大,使得某些吸附结合力较弱的位点中的Pb2+由于摩擦的剪切力作用被释放出来,导致去除率有一定的波动。因此,在较短的吸附时间内,适当增加吸附剂投加量和提高温度有助于提高Pb2+的去除率。
应用 Design-Expert 8.0 软件对最佳实验条件进行了预测,得到CaO-SA吸附Pb2+最佳吸附条件为:CaO-SA投加量为6 g·L−1、温度为40 ℃、pH=12、吸附时间为30 min,此时Pb2+去除率可达100%。为验证响应曲面模型的准确性,在预测的最佳条件下,进行3组平行实验,测得去除率的平均值为 99.63%,与预测值仅相差0.37%,这说明该计算模型具有较好的预测效果。然而pH对CaO-SA吸附Pb2+的影响较低,为了更接近本研究处理对象的实际pH,调整优化条件为:CaO-SA投加量为6 g·L−1、温度为40 ℃、pH=11、吸附时间为30 min。在此条件下,模型预测值为100%,取3次平行实验的平均值,得吸附率实验值为99.54%,与最优条件下的吸附效果很接近。
-
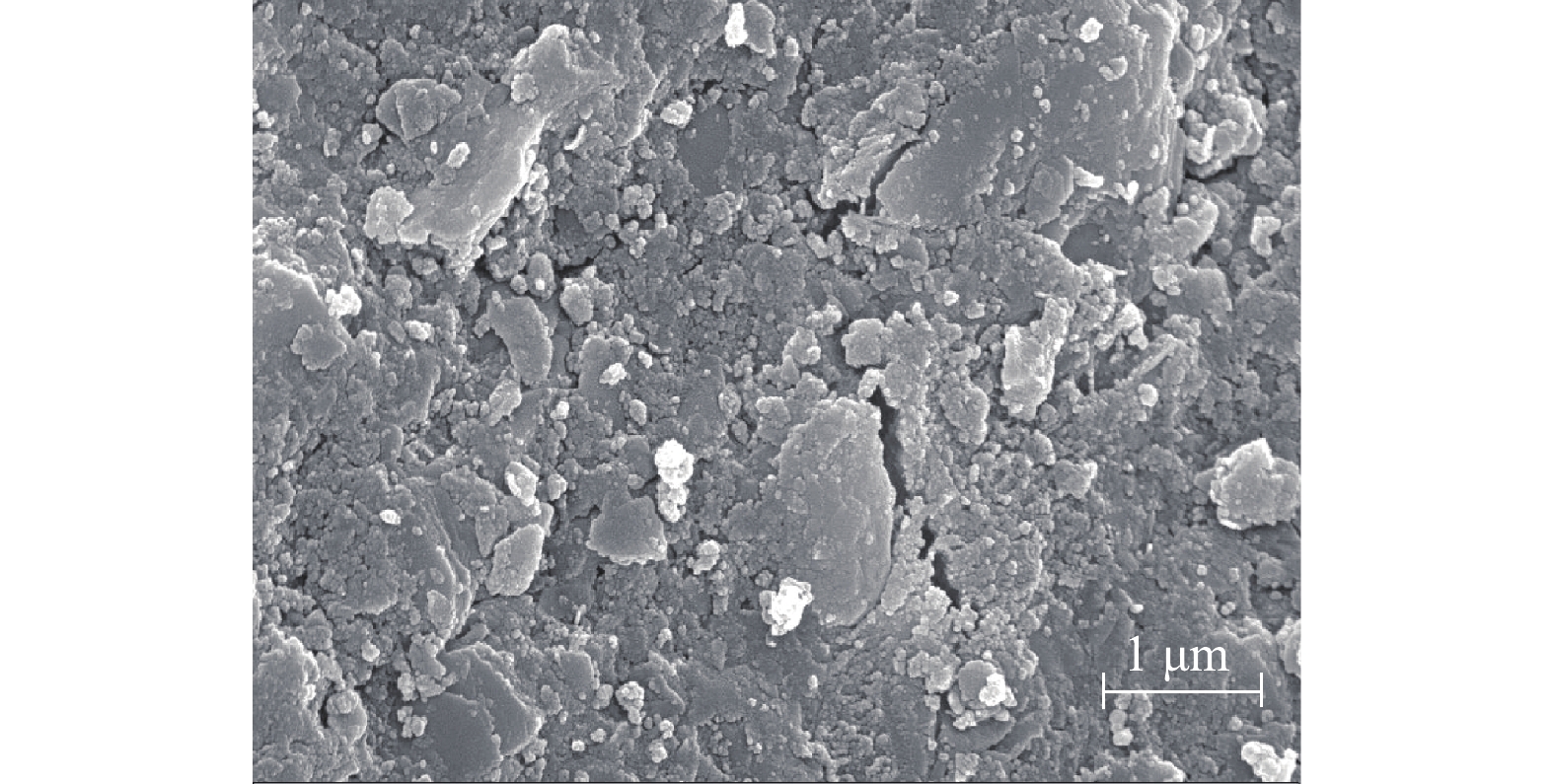
为了解CaO-SA的表面结构,利用电子显微镜将CaO-SA放大30 000倍后进行观察,结果如图9所示。可以看出,该吸附剂表面凹凸不平,附有大量的层状结构,排列松散,空隙较多且孔道明显。由于结构疏松,比表面积大,提供的吸附位点增多,在吸附剂吸附Pb2+时,具有较强的去除能力。
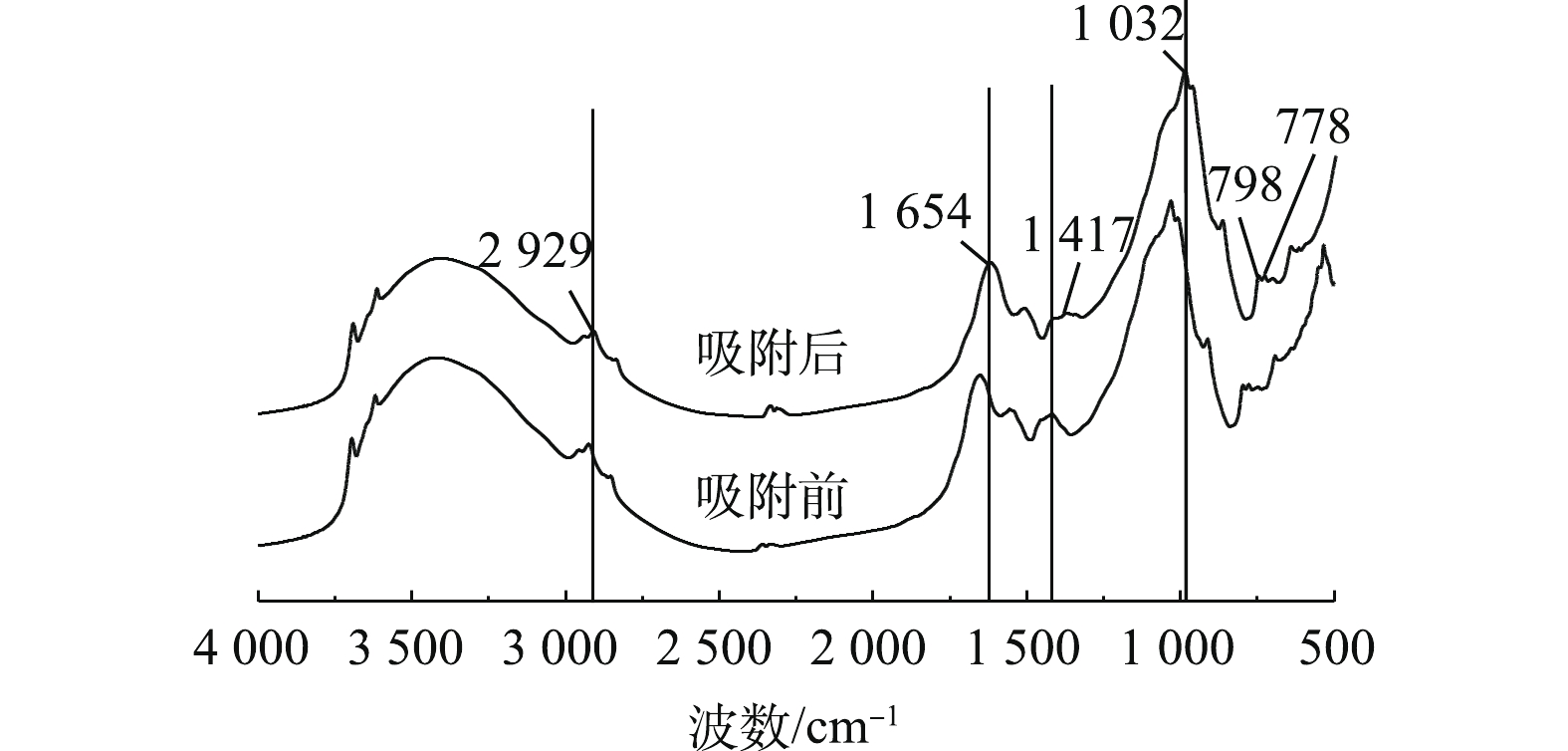
为分析CaO-SA吸附Pb2+的行为,利用红外光谱对CaO-SA处理含铅选矿废水前后吸附剂的官能基团进行了分析,结果如图10所示。可以看出,在CaO-SA吸附Pb2+前,在1 417 cm−1和1 654 cm−1处的吸收峰归属为羧酸盐中C—O和C=O的对称伸缩振动;1 032、778、798 cm−1处的吸收峰归属为SiO4四面体中的Si—O—Si伸缩振动和 Si—O 伸缩振动、石英族矿物产生的 Si—O—Si 对称伸缩振动;2 929 cm−1处的吸收峰归属为烷烃类中亚甲基的反对称伸缩振动[24]。由此可见,CaO-SA中主要组分是硅酸盐、烷烃类有机物和羧酸盐。
对比图10中CaO-SA吸附Pb2+前后的红外光谱图,可以看出,CaO-SA的主要吸收峰的种类没有变化,也未发生位移,这说明CaO-SA吸附Pb2+后没有新的官能团产生。生物吸附剂中的羧基基团易与重金属离子结合[25],而图10显示,羧基在1 417 cm−1处的吸收峰强度有大幅度降低,说明在CaO-SA吸附选矿废水的过程中,Pb2+与羧基基团发生反应并占据此处官能团,导致其吸收峰强度大幅降低。因此,CaO-SA中含有的羧酸盐在吸附选矿废水Pb2+的过程中起主要的作用,这与ZHOU等[26]的研究结果一致。由于Pb2+与羧酸盐是通过化学反应相结合,说明在该吸附过程中存在化学吸附,与上述曲面分析结果互为一致。此外,在1 032 cm−1处的吸收峰强度有所降低,说明CaO-SA吸附Pb2+的过程中硅酸盐起到一定的作用。吴宏海等[27]的研究表明,主要成分为硅酸盐的石英类物质对Pb2+有一定的吸附作用。
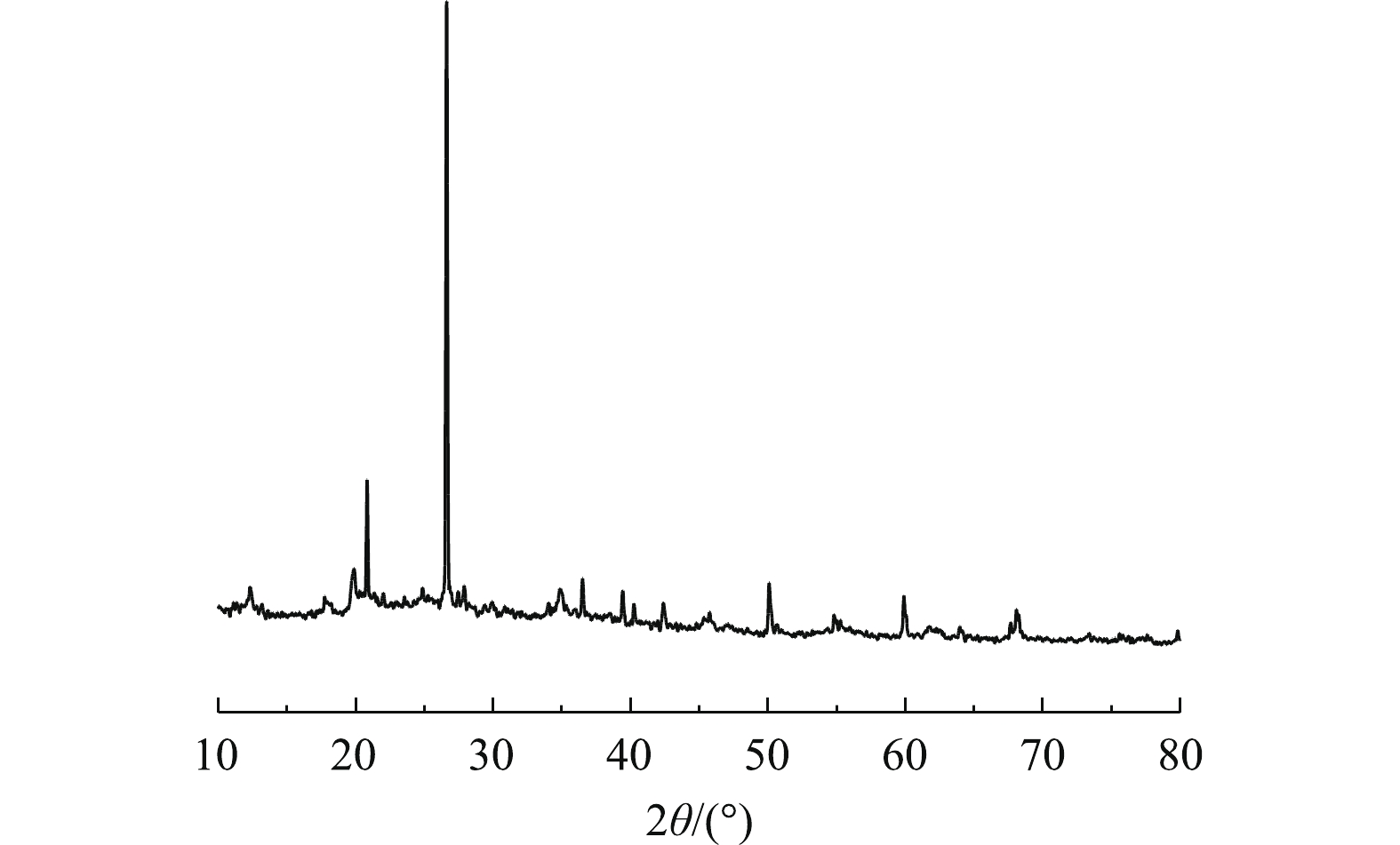
图11为CaO-SA的X射线衍射图谱。可以看出,CaO-SA在2θ = 20.82°、26.58°、36.50°、50.11°、59.92°、68.11°处存在明显的特征衍射峰。已有的研究[28-30]表明,主要成分为SiO2的吸附材料对重金属都具有一定的吸附能力。通过以对照标准卡片为参照与图11进行比对,确定图11出现的特征衍射峰为SiO2。此结果与红外谱图分析结果相吻合,这说明制备CaO-SA的脱水污泥中存在大量的SiO2,因此,其对Pb2+具有一定的吸附效果。
2.1. 吸附影响因素
2.2. 响应曲面法优化CaO-SA处理含铅选矿废水的实验条件
2.3. CaO-SA处理含铅选矿废水的吸附机理
-
1)单因素结果表明:吸附饱和时间为60 min;最优吸附剂投加量为5 g·L−1;提高温度有利于吸附的进行。在碱性条件下,投加量为5 g·L−1,适当增加温度有利于提高Pb2+的去除率。
2) Box-Behnken 实验设计可以较好地拟合CaO-SA对含铅碱性选矿废水中Pb2+的吸附过程。单因素对吸附效果的影响顺序为温度>吸附时间>投加量>pH;交互作用中投加量与吸附时间、吸附时间与温度对吸附效果的影响程度一样,在较短吸附时间内,适当地增加投加量并提高温度,可有助于提高Pb2+的去除率;根据曲面优化法的预测模型,结合实际操作,确定最佳吸附条件为:投加量为6 g·L−1、温度为40 ℃、pH=11、吸附时间为30 min,在此条件下Pb2+的去除率为99.63%,与预测值基本吻合。
3)由SEM的表征结果可知,CaO-SA表面结构疏松、比表面积较大,可提供较多的吸附位点。红外光谱与XRD的表征结果说明,在CaO-SA吸附Pb2+时,以吸附剂含有的羧酸盐与Pb2+结合的化学吸附为主导,其次是吸附剂中大量存在的硅酸盐与Pb2+结合的物理吸附。



 下载:
下载: