-
随着社会的不断发展,人们对于饮用水水质日益关注,饮用水水质标准也日益严格。传统的饮用水处理工艺已经不能完全达到标准。超滤膜作为一种新型水处理工艺,凭借其占地面积少、出水水质稳定等优点,逐渐被广泛运用于饮用水处理过程中[1-2]。原水中微生物、胶体物质、溶剂大分子可在膜表面和膜孔内沉积、吸附,从而造成膜通量下降的现象[3-6],即为膜污染。过滤一旦开始,膜污染就产生,因此膜污染是无法避免的。
已有研究[7-8]表明,膜污染成为了膜技术发展过程中最主要的制约因素。膜污染使得膜技术在实际运用中出水水质和产水率降低的同时,导致基建、操作、膜清洗等费用的增加[9]。常见的针对膜污染的预防和解决方式通常包含加强膜前预处理、优化操作工艺、对膜污染的清洗以及寻找并研发新型抗污染能力强的新型膜材料和膜组件等。
对污染膜进行清洗是使用较多且较便捷的方式。通过物理清洗和化学清洗可减轻膜污染问题,进而恢复膜的过滤性能[10]。LIANG等[11]在对含藻废水的超滤膜进行化学清洗后发现,与单一清洗剂相比,NaOH和NaClO混合液清洗剂清洗效果更好。MA等[12]将化学清洗与PVDF膜表面改性相结合,提高了膜通量的恢复效果。因此,研究膜污染的化学清洗对超滤工艺的实际运用具有重要意义。
本研究针对江苏某自来水厂的膜污染情况,利用HCl溶液、NaOH溶液对污染膜进行化学清洗。通过对洗脱液的有机化学指标、物质组分、金属离子浓度以及清洗前后膜表面特性的分析,分析膜污染状况并选择适合的清洗剂及其pH条件,以期能寻找出有效的清洗药剂和清洗方法,并应用到实际工程案例中,为解决水厂膜污染问题提供参考。
全文HTML
-
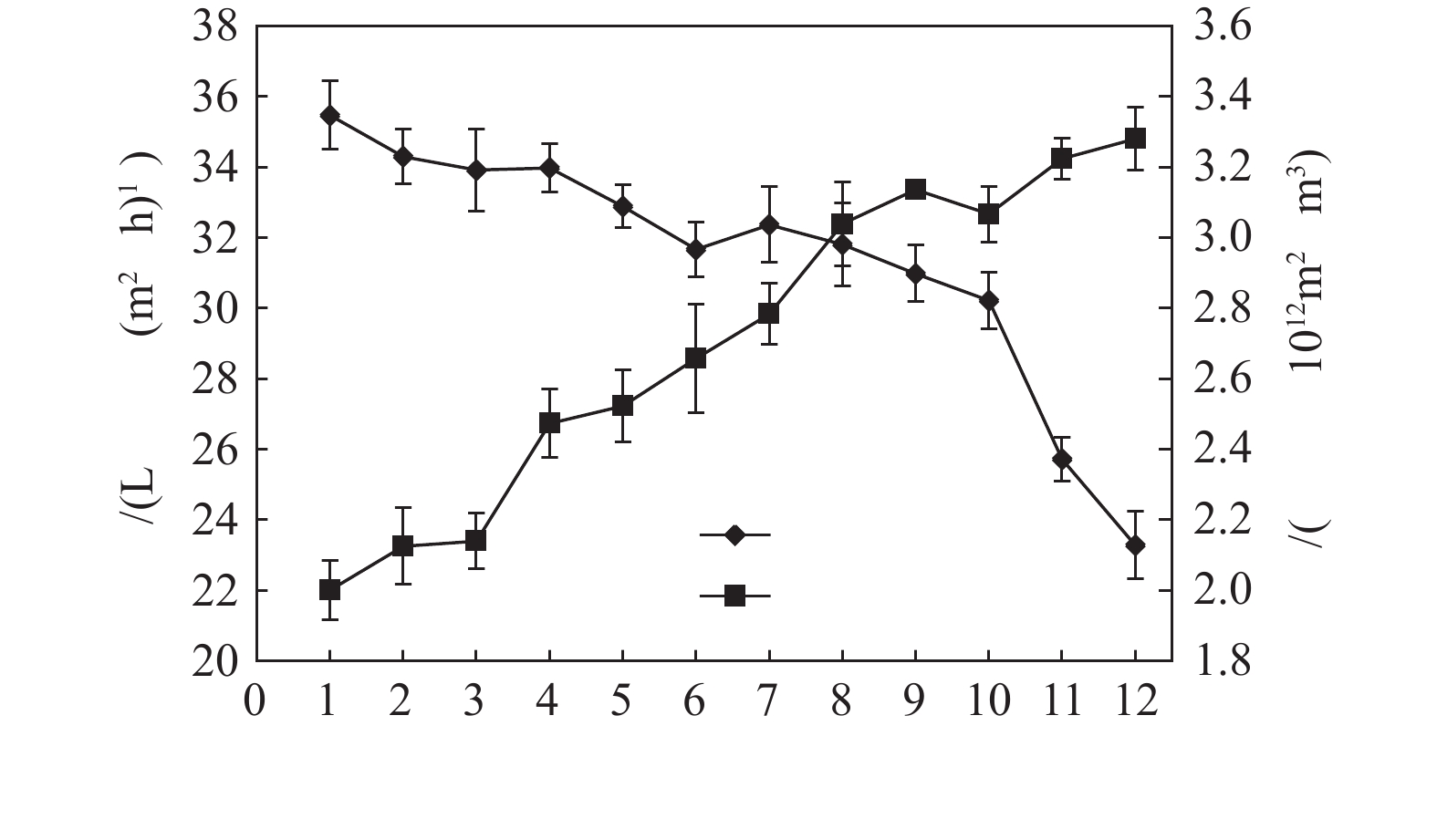
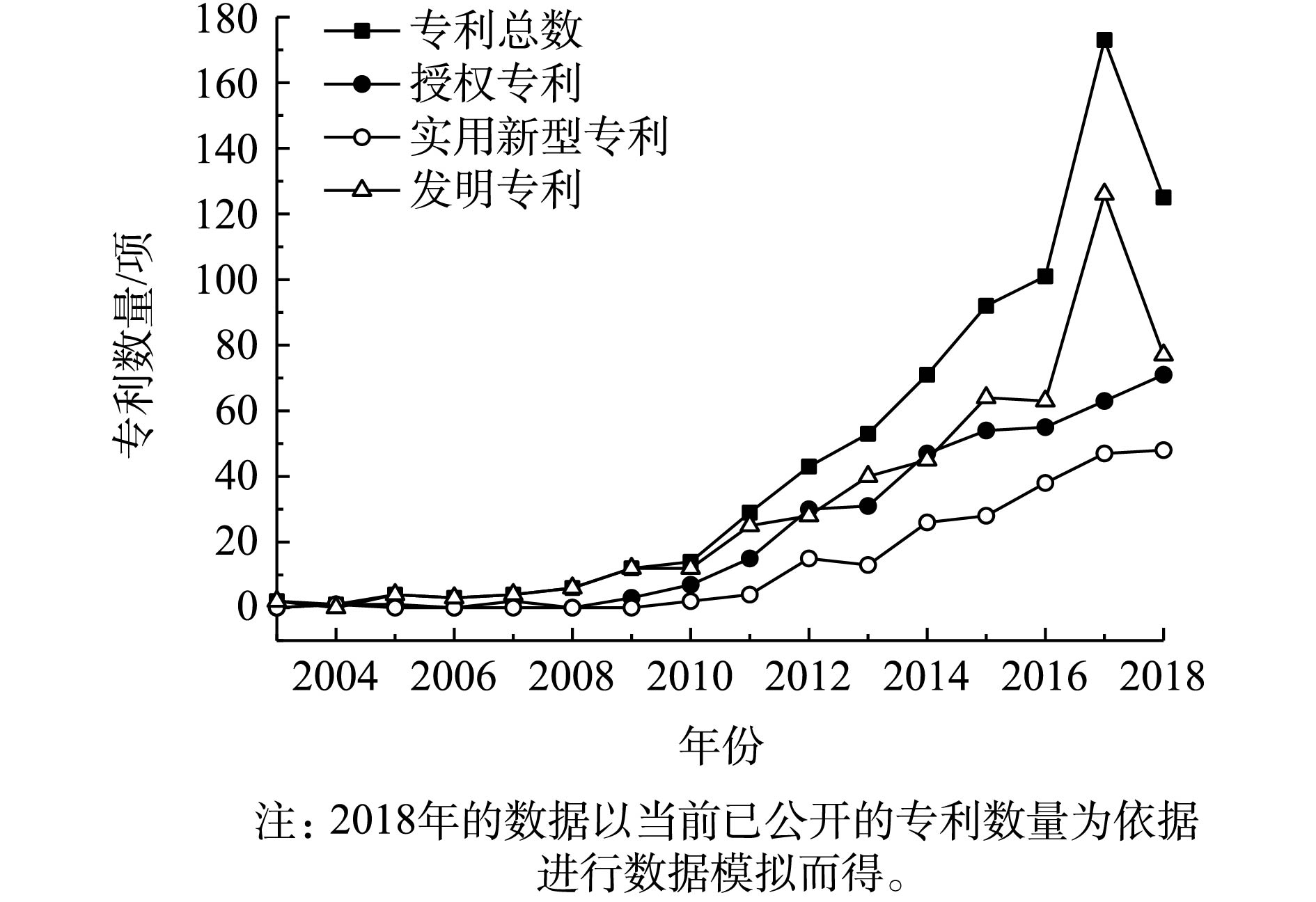
江苏某水厂是国内首家采用短程混凝和膜过滤组合工艺的自来水厂,使用PVC中空纤维超滤膜,超滤系统设计产水能力为25 000 m3·d−1,共10组膜。每组分为2个膜单元,每个膜单元由26个超滤膜组件组成。每个膜组件的有效过滤面积为35 m2,设计通量为32 L·(m2·h)−1。超滤系统运行中每小时进行30 s反冲洗,水力反洗强度为60 L·(m2·h)−1,曝气强度为90 m3·(m2·h)−1。水力停留时间和污泥停留时间分别为0.768 h和3 h。每2周进行1次维护性清洗,清洗剂为次氯酸钠(NaClO),浓度为200 mg·L−1。超滤膜运行初期,通过水力反冲洗和维护性清洗,能够有效地去除和控制膜污染。但是随着膜系统运行时间的不断增加,膜通量不同下降,膜阻力逐渐增加(图1),污染愈发严重,仅通过水力反冲洗和维护性清洗已经无法保证产水回收率。因此,须进行恢复性化学清洗。
-
膜丝样品来自江苏某自来水厂的PVC外压式中空纤维超滤膜(立升公司,海南),外径为1.45 mm,内径为0.85 mm,有效过滤面积为0.01 m2,截留分子质量为50 kDa。膜样品表面某些部位肉眼可见附着滤饼层,呈黄色。经湿态保存运输至实验室,使用海绵擦拭除去滤饼后,进行清洗实验。
化学试剂:氢氧化钠(北京化学试剂公司,优级纯),盐酸(上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司,分析纯)。
-
配制不同pH的化学清洗剂:HCl溶液(pH=1.5、2.0、2.5);NaOH溶液(pH=11.5、12.0、12.5)。将膜丝样品等长度分割,浸泡在200 mL不同种类的化学清洗剂中,静置24 h后取出,随后对浸泡液进行成分分析。使用超纯水将膜丝表面的浸泡液清洗去除,清洗过后的膜丝经过冷冻干燥后,对其膜表面特性进行分析。
-
三维荧光(EEM,F-7000, Hitachi,Japan)用于定性分析所测水样中溶解性有机物的特征。将待测水样通过0.45 μm滤膜,采用氘灯为激发光源,条件为:发射波长λem =220~550 nm,激发波长λex=200~400 nm[13]。发射和激发狭缝宽度为10 nm,扫描速度为12 000 nm·min−1,随后使用软件Origin 8.0进行光谱图绘制。电感耦合等离子体-原子发射光谱(ICP-OES OPTIMA-2000,PerkinEler,USA)用于分析清洗液中金属离子的浓度。
pH采用Meter型pH计(Mettler-Toledo, Switzerland)进行测定。水样通过0.45 μm滤膜后,使用TOC分析仪(TOC-VCPH,SHIMA-DZU,Japan)测定出的结果即为DOC。样品UV254使用紫外/可见光分光光度计(U-2900,Hitachi,Japan)进行测定。通过测定出的DOC和UV254,根据式(1)可以计算出SUVA值。SUVA值为有机物亲疏水性指标[14]。
式中:RSUVA为水中溶解性有机物中含有双键的有机物占总有机物的比例,L·(mg·m)−1;AUV254为水中含有碳碳双键的有机物,cm−1;CDOC代表溶解性有机物,mg·L−1。
-
扫描电子显微镜(SEM,LEO-1530, Germany)能够用于直观地观察膜表面的形貌特征,清洗后的膜丝经过24 h的冷冻干燥后,膜表面及膜孔内的水分得以去除,以便于观察。全反射傅里叶红外光谱仪(ATR-FT-IR,Magna-IR 750, Nicolet, USA)用于分析膜表面的官能团,测量波数为600~4 000 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1。通过比较新膜与污染膜表面官能团的差异,进行膜污染的分析。
2.1. 实验样品与试剂
2.2. 污染膜清洗实验
2.3. 水质分析
2.4. 膜表面特征分析
-
表1为使用不同化学清洗剂清洗污染膜后,所测得的洗脱液DOC、UV254以及经计算得出的SUVA值。由表1可以看出,相比于HCl溶液,NaOH溶液作清洗剂的洗脱液中DOC浓度更高。这表明NaOH溶液对有机物的清洗效果优于HCl溶液。对比同种清洗剂在不同pH条件下洗脱液的DOC,可以得出,pH=1.5时的HCl溶液的清洗效果要优于pH=2.0和2.5时的效果。这说明HCl溶液的酸性越强,对有机物的清洗效果越好。而采用NaOH溶液对污染膜进行清洗时,pH=12.5时洗脱液DOC大于pH=11.5、12.0时的洗脱液DOC,说明NaOH溶液的碱性越强,对有机物的清洗效果越好。而根据计算的SUVA值分析,相比于NaOH溶液,HCl溶液的洗脱液SUVA值更高,说明HCl溶液洗脱出的有机物以大分子以及疏水性有机物为主[15]。
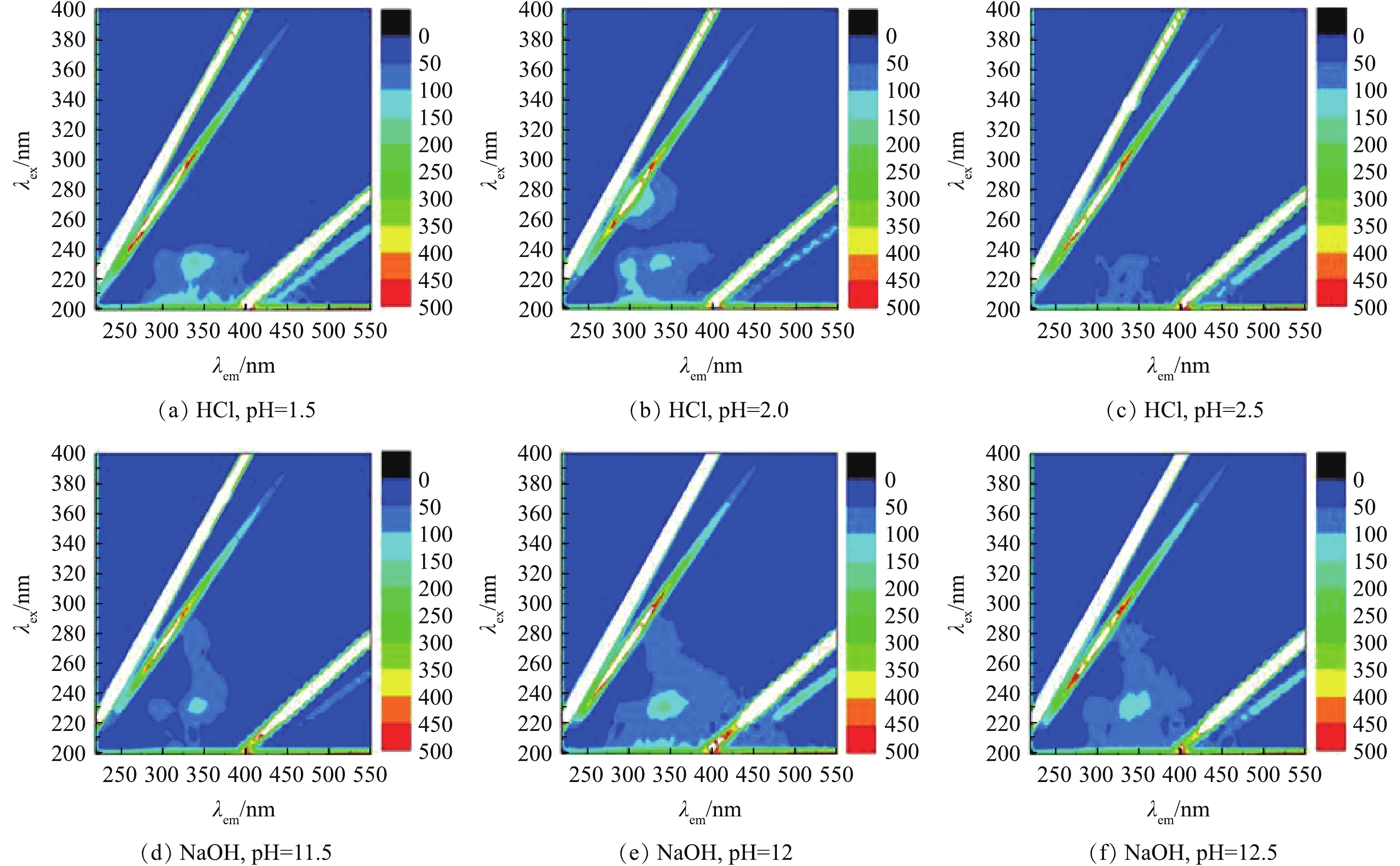
采用EEM对洗脱液进行物质组分分析,结果如图2所示。采用HCl溶液为洗脱液时,不同pH下特征峰显著不同。当pH=1.5时,仅有一个特征峰,位于λex< 250 nm处,λem为330~380 nm。这说明洗脱液中主要有机物为芳香类蛋白质。当pH=2.0时,特征峰位于λex > 250 nm,λem为280~330 nm;λex < 250 nm,λem为280 ~ 380 nm。这说明洗脱液中主要有机物为溶解性微生物代谢产物及芳香类蛋白质[12]。而当pH=2.5时,没有明显的特征峰。采用NaOH溶液为洗脱液时,无论洗脱液pH为多少(11.5、12.0、12.5),特征峰均在λex < 250 nm,λem在330~380 nm处有类似的特征峰。可以看出,NaOH洗脱液中主要的有机物为芳香类蛋白质[13]。对比这2种洗脱液的响应范围和响应强度,可知NaOH溶液对有机物的洗脱效果更好。这与前述洗脱液有机化学指标分析结果一致。通过对2种洗脱液成分的EEM分析,发现蛋白类有机物是造成PVC中空纤维超滤膜膜污染的有机物之一。
表2为PVC中空纤维超滤膜经清洗剂清洗后洗脱液中Ca、Mg、Al、Si、Fe、Mn的浓度。对于Ca、Mg这2种元素来说,HCl清洗效果较好。而Si元素更容易与NaOH反应形成可溶性硅酸盐,因此,NaOH清洗剂的清洗效果较好。HCl溶液能够与Fe、Mn发生络合,促进Fe、Mn化合物的溶解,因此,HCl对Fe、Mn的清洗效果相比于NaOH更好。针对无机金属污染,2种清洗剂的清洗效果各有利弊。总体而言,HCl的清洗效果优于NaOH溶液的清洗效果。实验结果表明,造成膜污染的无机金属元素主要有Ca、Mg、Si、Fe。
-
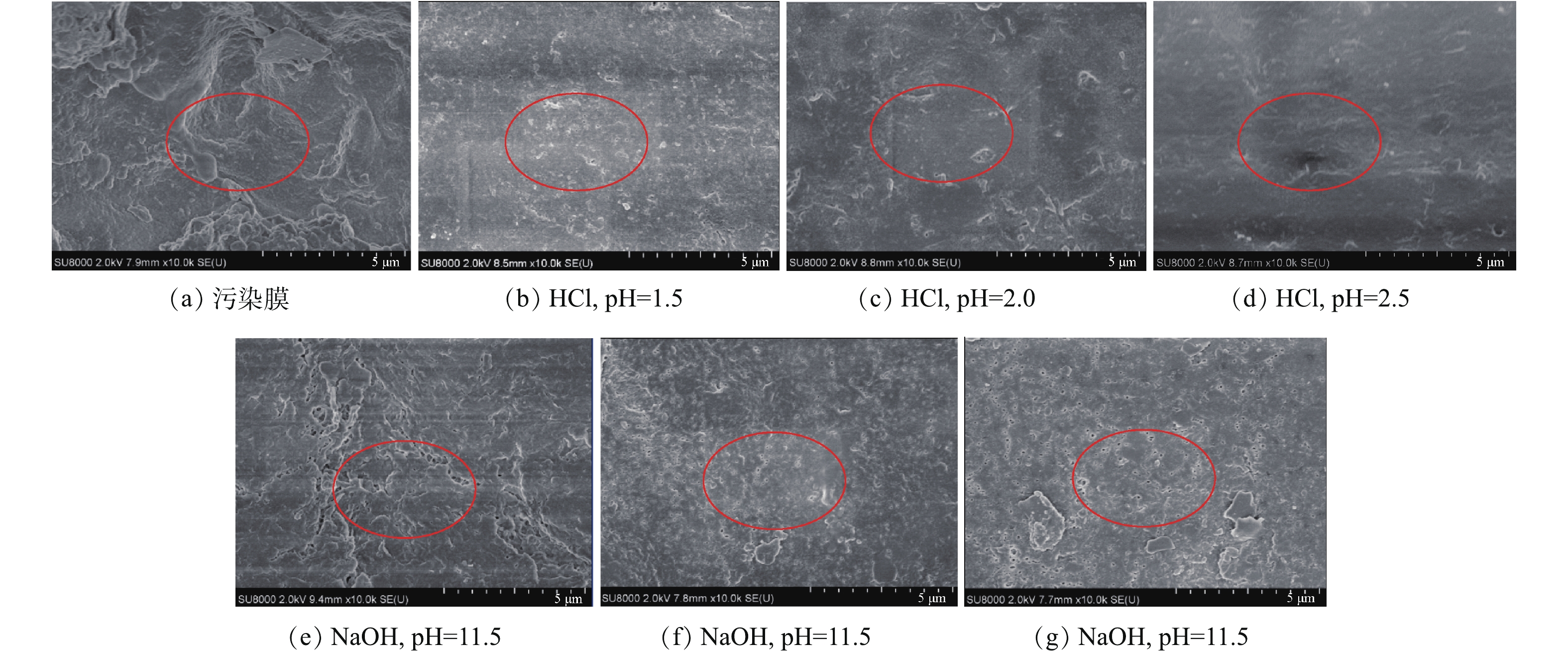
采用SEM观察膜丝表面形貌。图3为污染膜化学清洗前后PVC中空纤维超滤膜表面的形貌变化。由图3(a)可以看出,污染膜表面覆盖大量污染物,观察不到膜孔的分布。对比使用同种洗脱液在不同pH下的清洗效果发现,采用pH=1.5的HCl溶液清洗后,膜表面污染物最少,膜孔显露且表面纹路分布清晰,说明其清洗效果在3种不同pH的HCl中是最好的;而pH=2.5的HCl溶液清洗的效果相对较差。对于NaOH清洗液,pH=12.5的清洗效果最好。通过对不同清洗剂的最优pH条件下膜表面形貌的观察发现,污染膜经过pH=1.5的HCl或者pH=12.5的NaOH清洗后,膜孔显露较多且相对较为清晰可见。
-
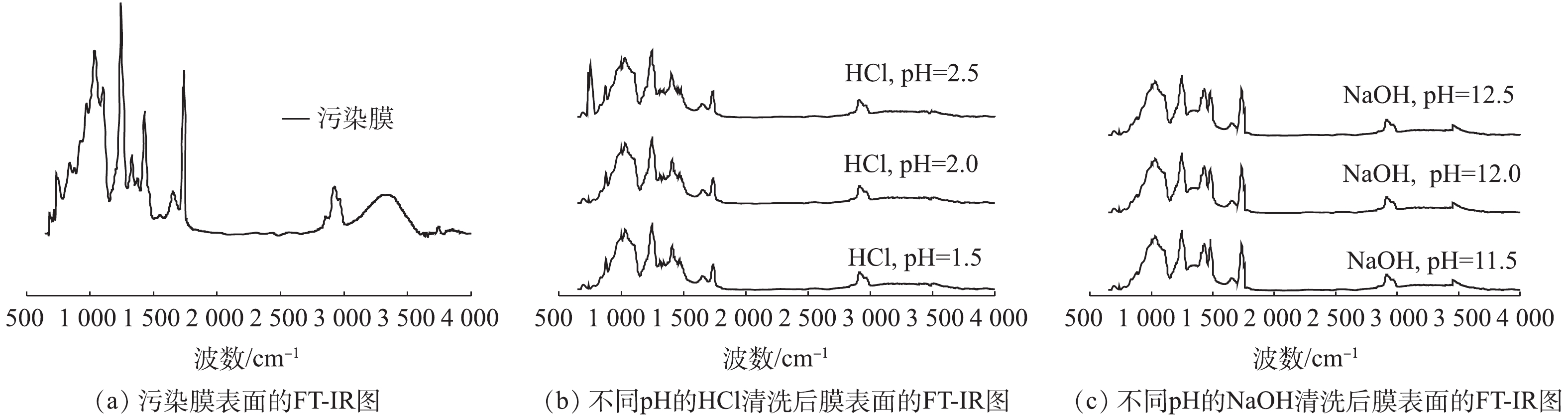
采用ATR-FT-IR对清洗前后PVC中空纤维超滤膜膜表面官能团进行表征,结果如图4所示。图4(a)为污染膜,该污染膜在波数1 000 cm−1处有强烈的吸收峰,表明污染膜表面存在多糖或多糖类物质[16-17]。在1 430 cm−1附近的吸收峰显示羧酸C—OH面内弯曲振动,表明存在羧酸类化合物,具体是何物质尚需进一步研究和证实。而在波数为1 737 cm−1处出现的特征峰表明羰基的存在[18-19]。同时,在1 200 ~ 1 300、2 940和3 300 cm−1附近出现特征峰,表明污染膜表面还存在腐殖酸类物质[15]。因此,总体而言,污染膜表面含有多种有机污染物,包含了蛋白类、多糖类和腐殖酸类。与污染膜相比,经清洗剂清洗后的污染膜官能团吸收峰位置变化不大(见图4(b)和图4(c)),而强度会有所减弱,说明污染物种类并没有因为膜清洗而发生大的变化,化学清洗只能去除膜表面部分有机污染物。
-
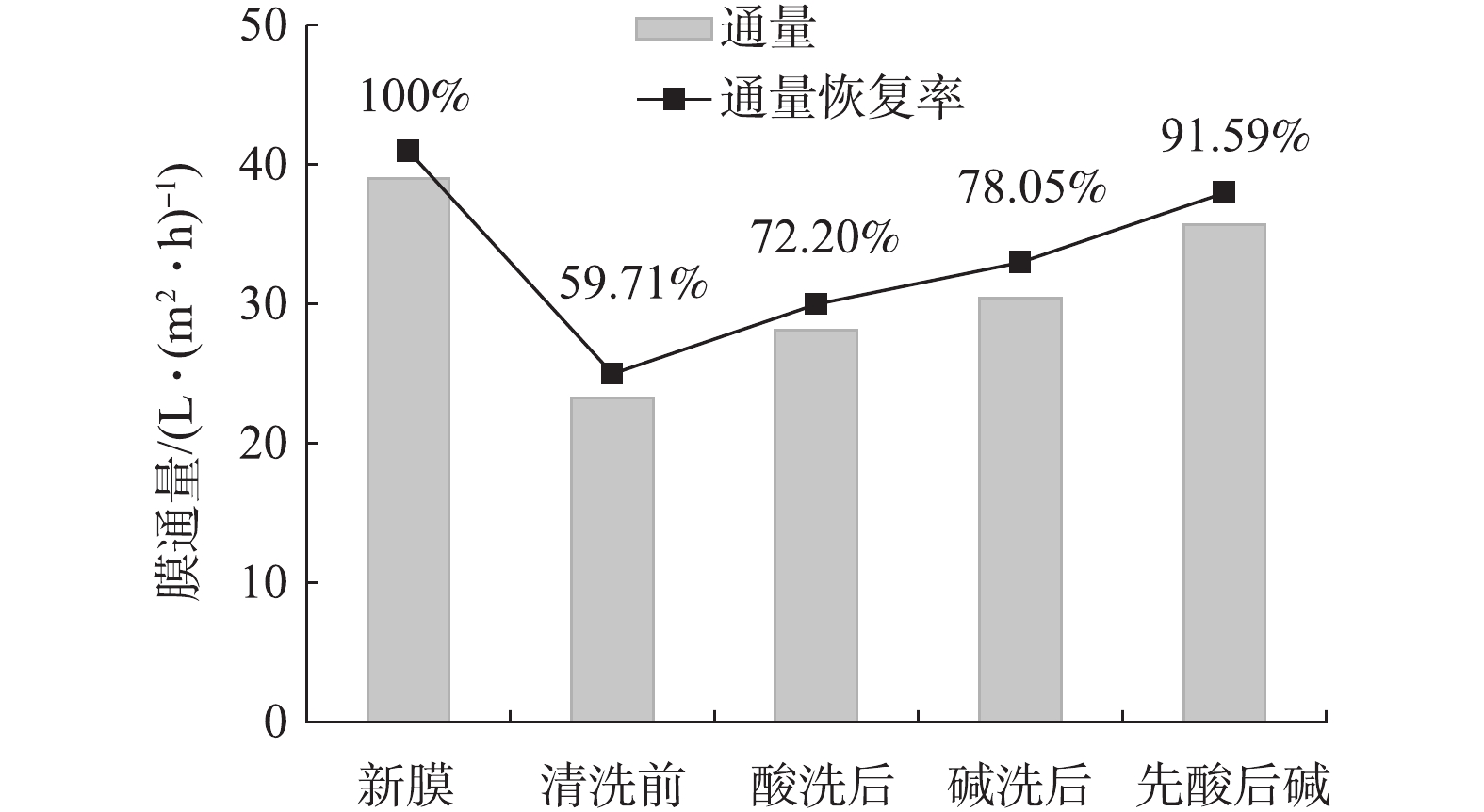
通过实验室污染膜的清洗实验可知,采用酸碱清洗能够有效地去除膜表面污染物。由于实验室仅仅是对洗脱液和清洗后膜表面形态变化的分析,并未考察膜通量的恢复情况,而膜通量是考察膜清洗效果最直接和重要的参数,因此,为了更好地评估酸碱对污染膜的清洗效果,在实际工程中分别采用pH=1.5的HCl溶液和pH=12的NaOH溶液对膜污染进行恢复性的化学清洗。同时考虑到酸碱各自清洗效果的不同,还采用先酸后碱的组合清洗方式。清洗后膜通量如图5所示。HCl清洗后膜通量的恢复率为72.2%,而碱洗后通量恢复率为78.05%。清洗结果表明,采用碱洗效果优于酸洗。而采用组合清洗方式,先酸洗后碱洗通量的恢复率高达91.59%,说明组合清洗方式效果更佳。而膜污染是多种污染物共同造成的,仅用一种清洗剂清洗效果并不能获得较高的通量恢复率。由前述结果可知,NaOH能够有效地去除有机污染物和硅离子,HCl则可以去除部分有机物(大分子和疏水性的有机物),同时对钙离子去除效果较好,因此,在实际污染膜清洗工程中,最佳的清洗方式为先酸洗后碱洗的组合清洗方式。
3.1. 污染物成分分析
3.2. 清洗前后超滤膜表观形貌分析
3.3. 清洗前后超滤膜表面官能团分析
3.4. 工程应用
-
1) 通过对江苏某水厂实际运行的PVC中空纤维超滤污染膜化学清洗后洗脱液的分析可知:蛋白类、多糖类以及腐殖酸类有机物均造成了超滤膜污染,其中以蛋白类和多糖类有机物为主;造成膜污染的无机金属元素主要为Ca、Mg、Si、Fe。
2) 污染膜经过化学清洗后,pH较高的NaOH溶液能够洗脱更多的有机物,且能够有效地去除硅离子。而HCl溶液可以去除部分有机物,同时能够去除钙、镁、铁离子。对于酸性清洗剂HCl,pH越低,清洗效果越好;对于碱性清洗剂NaOH,pH=12时清洗效果最好;两者结合能够有效地去除膜污染物。实际清洗案例表明,采用先酸后碱的组合清洗方式能够获得较高的通量恢复率。



 下载:
下载: