-
细微粉尘是指空气动力学直径小于5 μm的颗粒物,包括细颗粒物(PM2.5)和亚微米粉尘[1]。细微粉尘能够直接进入人体肺泡,易使井下作业人员患上尘肺、硅肺等职业病,对人体危害巨大[2]。传统的除尘技术难以有效去除细微粉尘,电凝并技术可以使细微粉尘颗粒荷电、凝聚增大,然后通过收尘装置进行除尘[3]。因此,对细微粉尘电凝并效率影响因素展开实验研究并找出凝并效果最优的实验参数,提高细微粉尘电凝并效率,以进一步减小粉尘对人体的危害具有重要的现实意义。
凝并技术主要包括声凝并[4]、磁凝并[5]、湍流凝并[6]、化学凝并[7]、电凝并[8]和光凝并[9]等。电凝并是指通过外加电场增强细微颗粒的荷电能力,荷电后的细微颗粒在凝并区通过惯性碰撞、空间电荷力、离子风等作用力不断凝并变大的过程。向晓东等[10]研究发现,电凝并除尘装置主要用于收集细微粉尘,且双区式电凝并除尘装置的结构与性能优于三区式电凝并除尘装置。白敏菂等[11]通过将预荷电装置安装于模拟烟道中,发现离子浓度比除尘电场中高约1个数量级,粒子粒径增大了21%左右,带电粒子凝并作用增强。陈旺生等[12]设计了一种静电凝并除尘装置并对其性能进行研究,结果表明,该除尘装置对细微颗粒物的凝并效果较好,除尘效率明显高于普通除尘器。KILDES等[13]通过改变交变电场中预荷电粉尘的荷电极性,计算了异极性荷电粉尘凝并速率与粉尘荷电量、粒径及外加电压的关系。CHANG等[14]设计了一种在放电区有穿孔板的双极性预充器,以研究离子风辅助电荷诱导的凝聚收集作用。与无预充器的实验结果相比,具有一定板孔率的预充器可以优化颗粒凝并,提高12%左右的粉尘收集效率。GUAN等[15]研究了电袋复合式除尘器中风速对电场内气流分布和均匀性的影响,发现速度为0.8 m·s−1时不均匀性波动最小,进而更有利于除尘。张向荣等[16]利用Fortran程序模拟测算双极电流体场中某粒径的荷电分布,发现外电场与荷电粉尘的凝并系数呈正相关,通过增大外加电场强度可以有效提高凝并速率。
电凝并影响因素主要存在于放电、荷电和凝并过程中,放电过程的影响因素主要有电源大小、电极材质、形状、放电特性等,荷电过程的影响因素主要有粉尘性质、风速等,荷电凝并过程的影响因素主要是电场设置、极配间距等[17-18]。结合实验室现有条件,选取双极芒刺预荷电装置、外加直流电压和极配间距3个主要影响因素进行实验研究,由实验得出双区式电凝并的工况参数,可为电凝并技术在工业粉尘领域的应用提供参考。
全文HTML
-
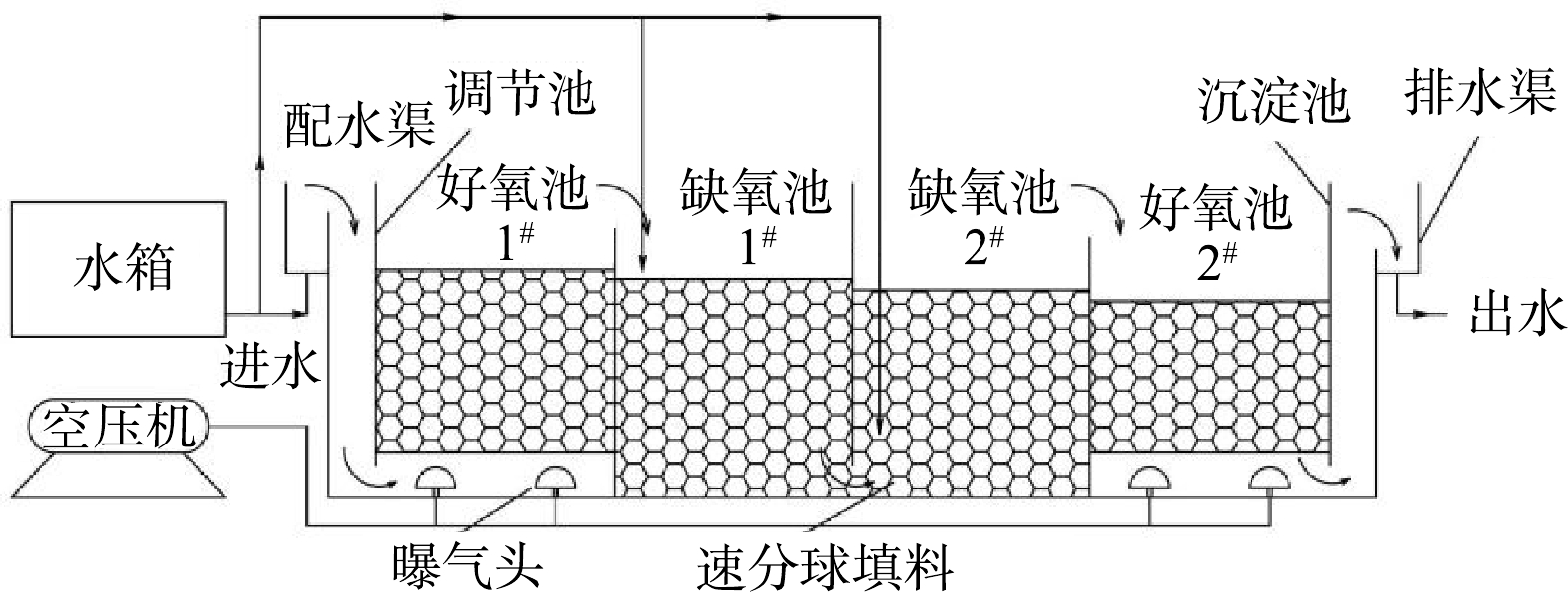
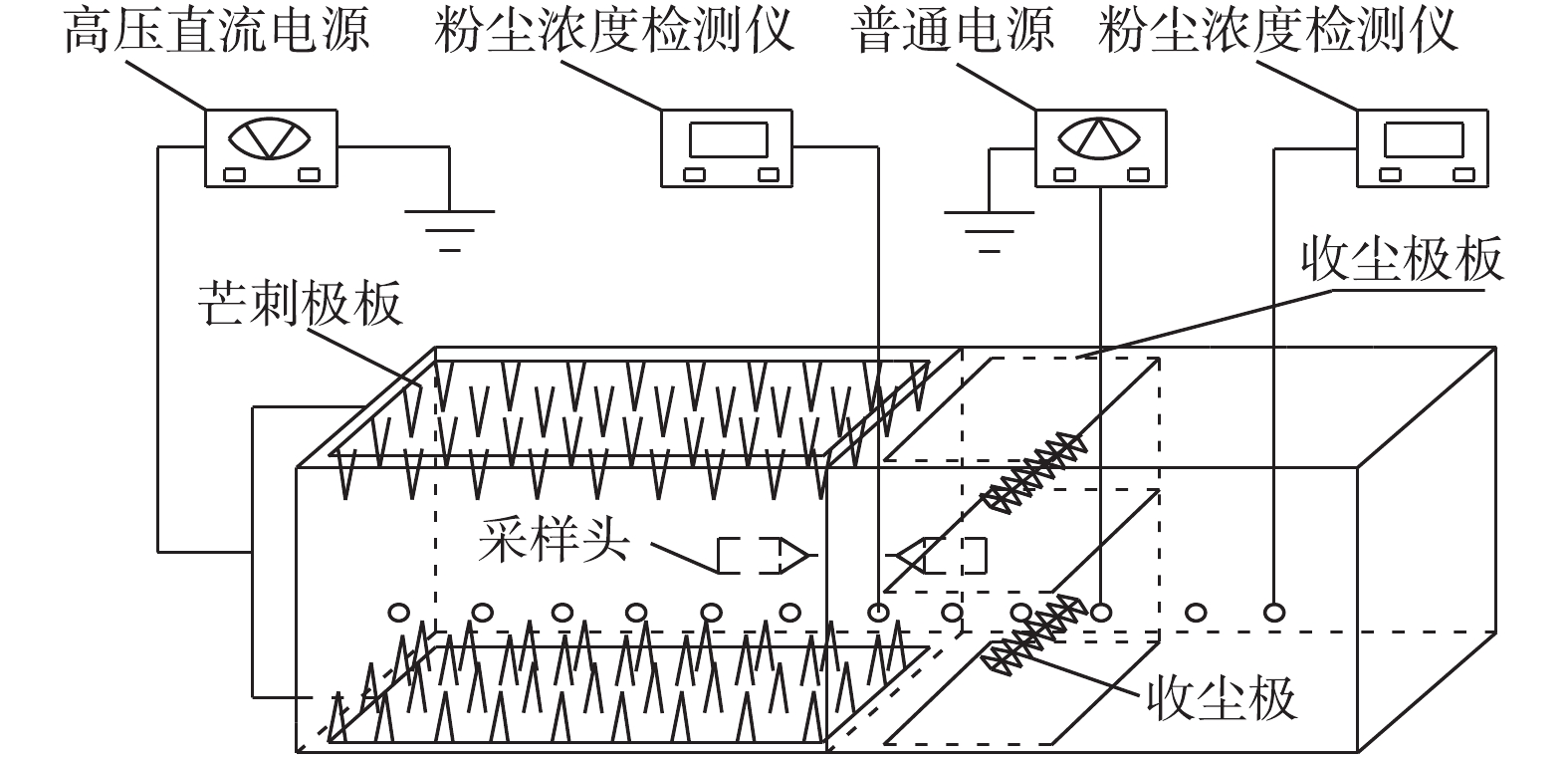
实验采用双极芒刺预荷电装置来实现荷电凝并收尘,电晕极板和反电晕极板均安装有相互交错的芒刺[19],双芒刺预荷电凝并实验装置系统如图1所示。双芒刺荷电区上下极板分别与高压电源的正负极相连,并使荷电区芒刺极板接地。收尘区极配形式为线-板式,收尘极板为长200 mm、宽200 mm的金属板,异极间距为200 mm,收尘区由平行交错放置的平行极板和收尘极组成,平行极板和收尘极的平面平行于粉尘气体流动的方向,输入电压为220 V。收尘极为鱼骨刺状,为刺间距30 mm,长度10 mm的芒刺,2个收尘极分别平行布置在距收尘极板20 mm处。参考双极荷电伏安特性和芒刺电晕极的间距对收尘的影响进行实验,对电凝并后的粉尘进行粉尘粒度分布测定,然后利用显微镜进行观察。实验装置系统主要由以下几部分组成:空气压缩机和气溶胶发生器组成的粉尘发生装置;橡胶绝缘塑料板外壳和金属电极平板组成的荷电凝并装置;外加直流高压电源装置、直流微安表和DusTrak DRX8533粉尘浓度测定仪组成的分析检测装置;实验模拟管道和风机。凝并区后的采样头从模拟巷道外部插入,测量时将采样头向左延伸至收尘区内部靠前的位置,模拟管道的尺寸为1.5 m×0.24 m×0.24 m。
-
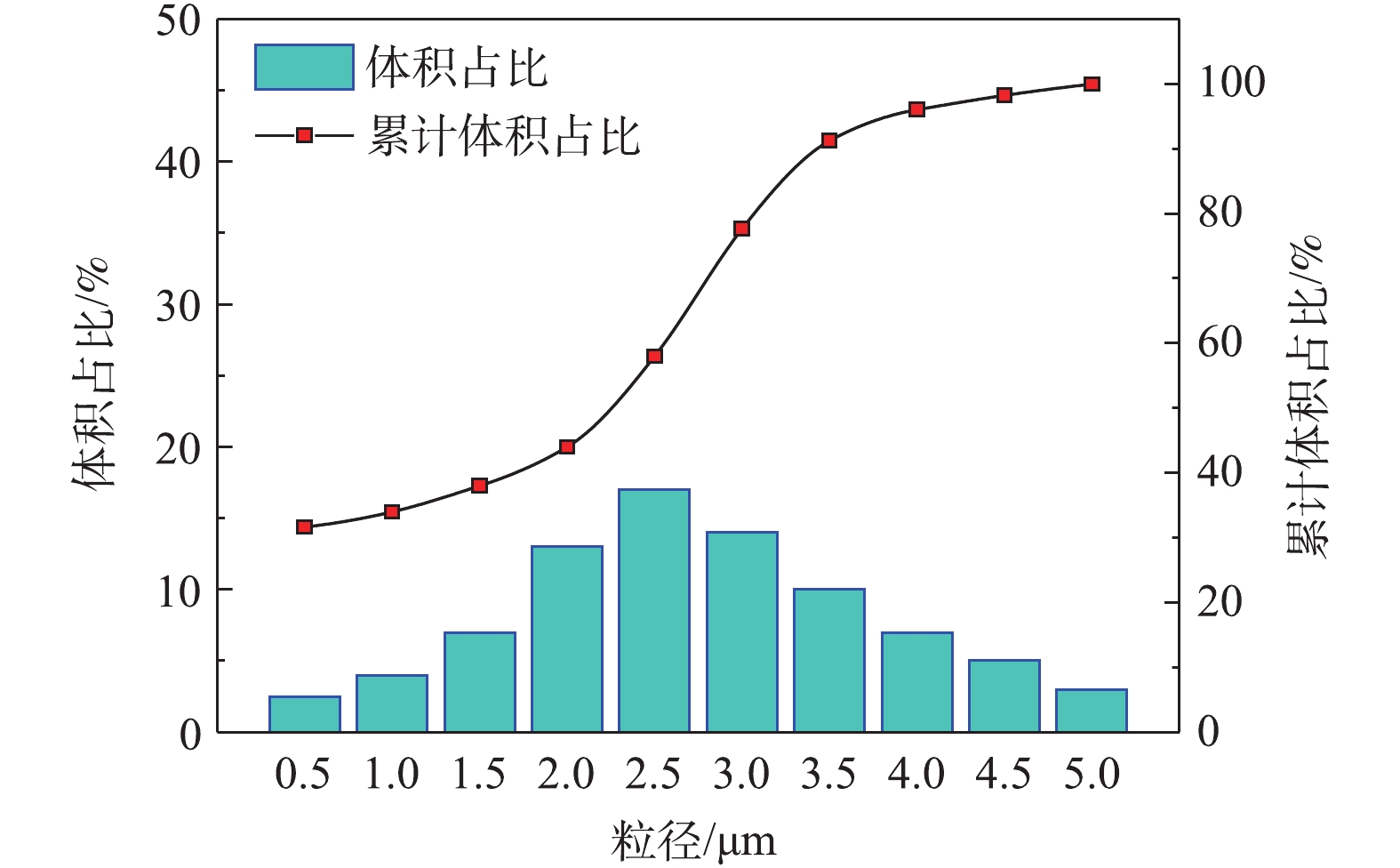
本研究采用Mastersizer 3000激光粒度分析仪,干法测量样本粉尘(Nominal ATD粉尘)的粒径分布,结果如表1所示,粒径分布累计百分比如图2所示。可以看出,实验粉尘的粒径分布为0~5 μm,中粒径为2.6 μm。由表1可知,小于3 μm的粉尘颗粒占比为77.66%,满足实验要求的细微粉尘即粒径小于5 μm的颗粒占比为99.97%。实验研究对象是细微粉尘(粒径<5 μm),粒径大小满足实验要求。
-
实验粉尘选用美国PTI厂家生产的无可燃性、无爆炸性的Nominal ATD粉尘。该粉尘性质稳定,主要成分为SiO2,粒径分布均匀,中粒径D50为2.1 μm,粒径范围为0~5 μm,比电阻为5×10−9 Ω·m。在使用实验粉尘前,先用干燥箱进行干燥处理,干燥箱温度设定为120 ℃,恒定后,将实验粉尘平铺于铁圆盘上,置于干燥箱内,定时30 min加热处理。粉尘浓度大小通过改变气溶胶发生器给料速率来进行调节,设定空气压缩机初始的工作压力为0.4 MPa,相对应的压缩空气流量为1.2 m3·h−1,含尘气体的流速为0.5 m·s−1。在实验过程中,通过调节空气压缩机工作风量及出风口阀门大小来实现风量调节,使用风速仪对风速进行测定,最后使用DusTrak DRX8533粉尘浓度测定仪测量凝并前后的粉尘浓度。
1.1. 实验装置设计
1.2. 实验样品粉尘粒径分析
1.3. 实验过程
-
由于细微粉尘粒径小、质量轻且初始浓度较小,采用计重法进行称量计算误差较大,所以采用计数法对不同粒径大小的粉尘分别计数。细微粉尘的凝并效率通过粒子数浓度来计算,针对不同粒径大小的细微粉尘,采用粉尘浓度测定仪对凝并前后的粒子数浓度进行测量,计算各粒径细微粉尘的凝并效率[20],凝并效率的计算方法见式(1)。
式中:
ηi 为粒径i的粉尘的凝并效率;ηt 为凝并后粒径i的粒子数浓度,个·mL−1;η0 为凝并前粒径i的粒子数浓度,个·mL−1。 -
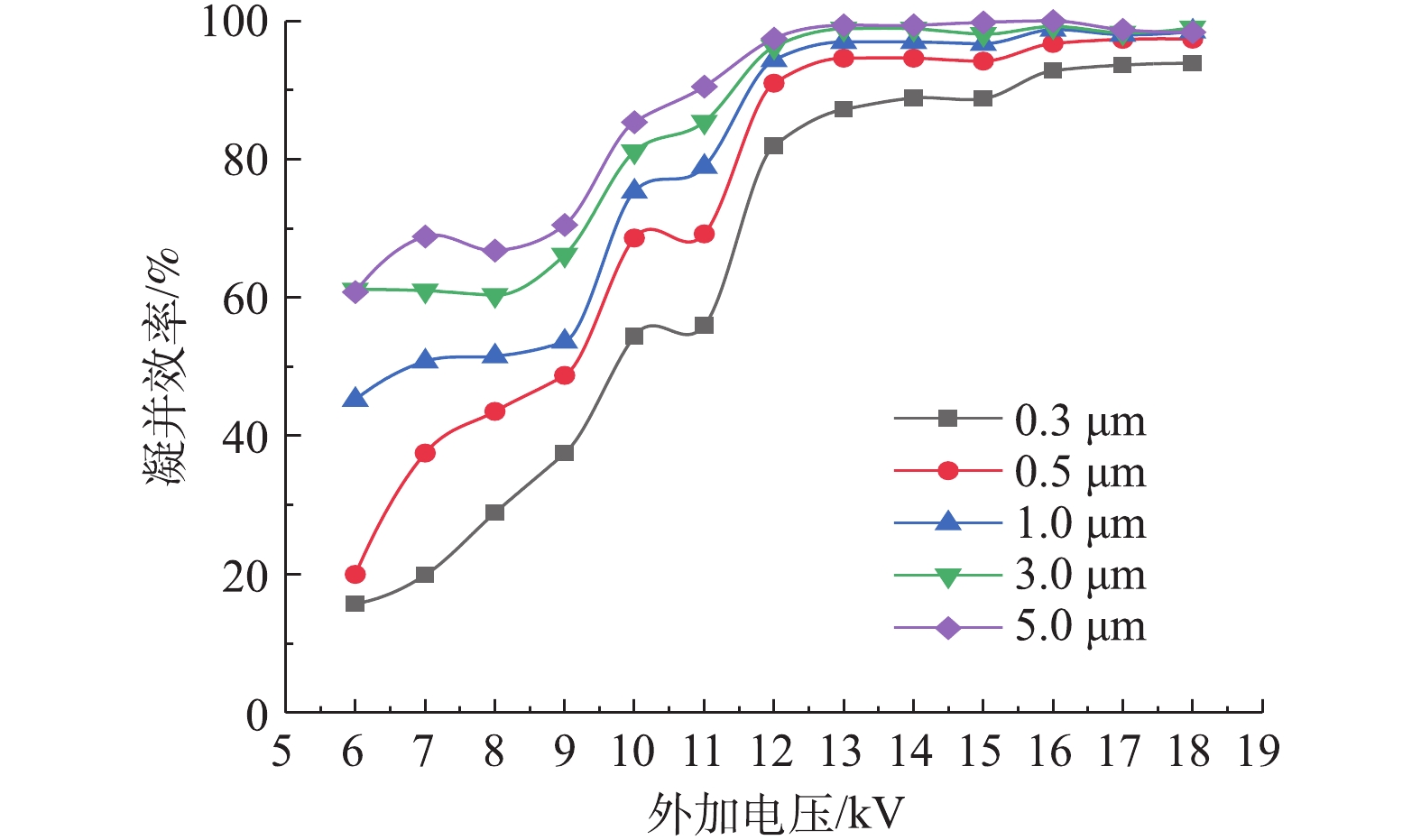
在实验过程中,当未安装双极芒刺预荷电装置和极配间距为0.025 m时,巷道风速设定为0.5 m·s−1。向粉尘发生器中加入干燥粉尘,连接各设备和电源,调节粉尘发生口阀门来控制粉尘量大小,测定粉尘发生器的最小发尘量并稳定在1 g·m−3。分析外加电压为6、7、8、9、10、11、12,13、14、15、16、17、18 kV时对凝并效果的影响。每种对应条件测量5次来计算凝并效率,不同外加电压条件下各种粒径的粉尘凝并效率见图3。由此可知,相同外加电压下粉尘凝并效率随粉尘粒径的增大而升高,即粉尘粒径越小,同一外加电压下的凝并效率越低。外加电压由6 kV增加到12 kV时,不同粒径粉尘的凝并效率显著提高。当外加电压为6 kV时,实验测得粒径为0.3、0.5、1、3、5 μm粉尘的凝并效率分别为15.74%、19.97%、45.26%、61.15%、60.82%。当外加电压升高至12 kV时,各粒径粉尘的凝并效率均达到80%以上。外加电压由13 kV增加到18 kV时,各粒径粉尘的凝并效率基本不再上升。
综上所述,随着外加电压的升高,电晕极板间的场强不断增加,空气电离的离子增多使得细微粉尘粒子的荷电量增大,荷电粉尘粒子之间的库仑凝并作用随之增强。电压上升的同时,芒刺尖端产生的离子风也增大,微细颗粒不仅能在离子风的作用下向极板运动,而且提高了电场区域的湍流强度,使微细颗粒间的碰撞频率大大增加。因此,正负离子风对电凝并具有很好的促进作用,大部分凝并后的粒子在强离子风以及外加强电场的作用下运移到收尘极板被捕集。当外加电压达到13 kV以后,细微颗粒的荷电量已基本饱和,故继续提高外加电压,粉尘的凝并效率不再增大。当电压相对较低时,在相同风速和浓度下,粉尘荷电量增强,粉尘凝并效果增加,所以增大凝并室电压有利于粉尘的凝并。因此,外加直流电压为13 kV时,对细微粉尘的凝并效果最好。
-
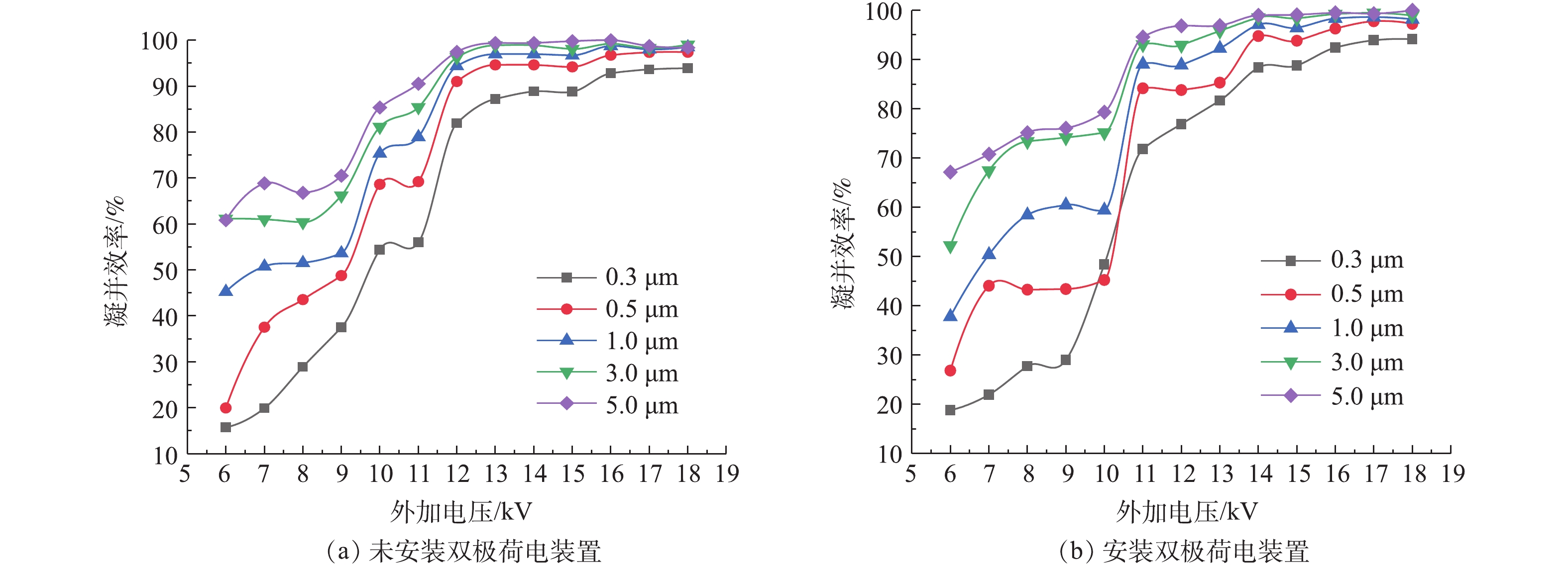
在实验过程中,选取巷道风速为0.5 m·s−1,粉尘发生器的发尘量稳定在1 g·m−3,在外加电压分别为6、7、8、9、10、11、12,13、14、15、16、17、18 kV时,分析有无双极芒刺预荷电装置对凝并效果的影响。不同粒径粉尘的凝并效果见图4,可以看出,安装双极芒刺预荷电装置后,在外加电压增大初期,粒径为1、3、5 μm粉尘的凝并效率快速增大;但是粒径为0.3、0.5 μm粉尘相比未安装双极荷电装置,其凝并效率增加不明显。实验测得粒径为1、3、5 μm粉尘在外加电压6 kV增大至9 kV的过程中,安装双极芒刺预荷电装置后,凝并效率分别提升24.45%、23.72%和12.11%,平均提升20.09%,比未安装双极芒刺预荷电装置的凝并效率高10%以上。当外加电压达到14 kV时,安装双极芒刺预荷电装置比未安装预荷电装置的粉尘凝并效率无明显差异。相比未安装双极芒刺预荷电装置时,安装后不同粒径粉尘的凝并效率先提升,后渐缓,最后趋于无影响。分析原因为,双极芒刺预荷电装置极板上的芒刺尖端放电产生大量的电子并在电场力的作用下获得一定的能量,大量电子射入到荷电凝并区,撞击空气中的分子而变为离子,粒子与空气中的离子结合可以使荷电更充分,因此,能在一定程度上提高凝并效率。
-
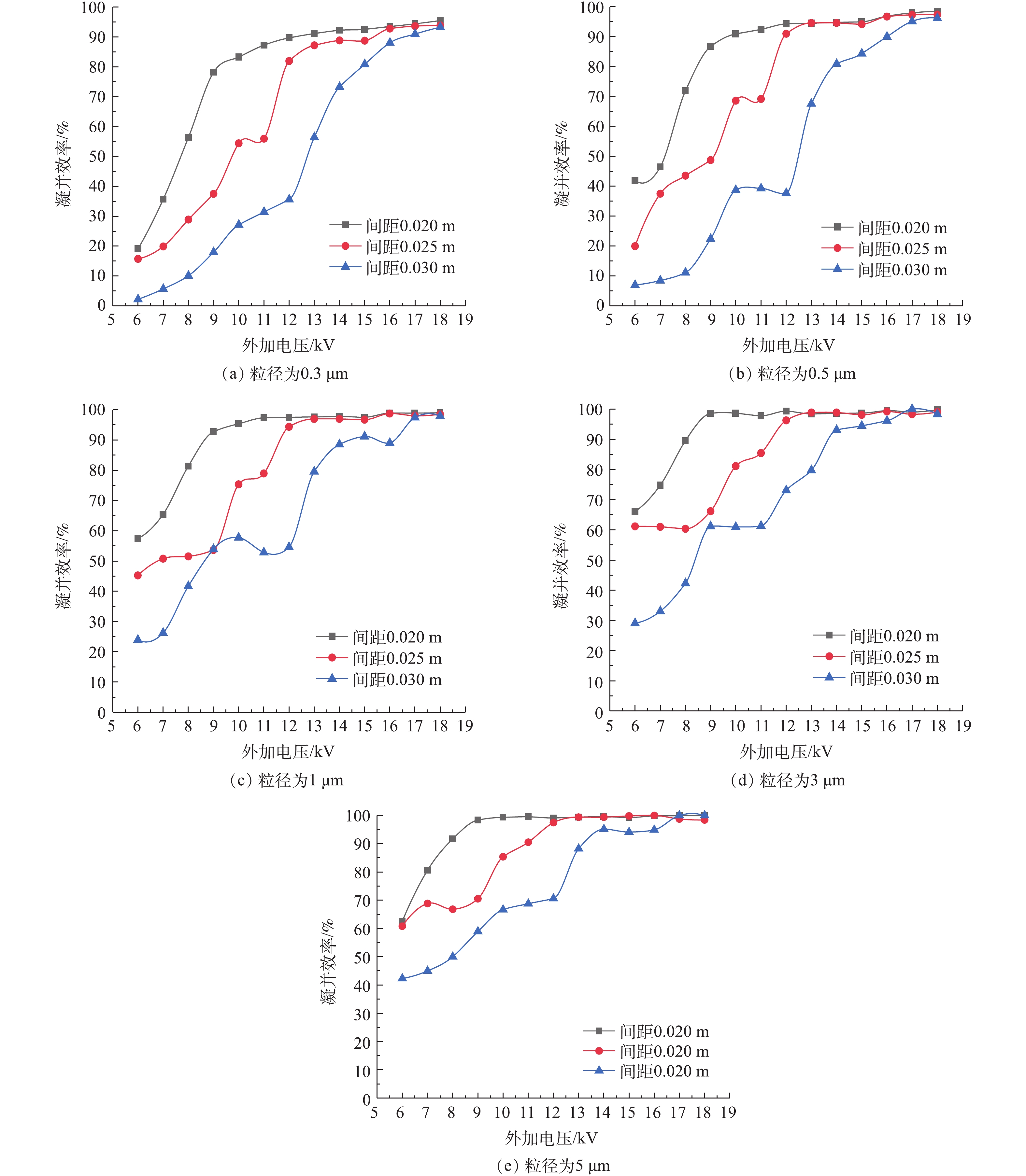
实验设定巷道风速为0.5 m·s−1,粉尘初始质量浓度为1 g·m−3,外加电压分别为6、7、8、9、10、11、12,13、14、15、16、17、18 kV时,研究极配间距为0.02、0.025、0.03 m时的粉尘的凝并效果。在不同极配间距条件下,各粒径粉尘的凝并效果见图5。由此可知,针对同一粒径粉尘,在相同外加电压下,缩短极配间距可以显著提升粉尘的凝并效率。当外加电压为6 kV时,极配间距由0.03 m缩短至0.025 m,各粒径粉尘的凝并效率均有10%以上的提高。缩短极配间距至0.02 m,当外加电压达到9 kV时,0.3 μm和0.5 μm粒径粉尘的凝并效率超过80%,1、3、5 μm粒径粉尘的凝并效率均超过90%;但是当外加电压达到14 kV时,缩短极配间距对增加各粒径粉尘凝并效率的作用不明显。
综上所述,在外加直流电压相对较低时,缩短极配间距,电晕放电明显,荷电凝并区内的离子数量增多,粉尘粒子荷电充分,粒子间的库仑凝并作用力较强,在外加电场力、离子风作用力下,凝并后的粒子快速驱进到收尘极板后被捕集,所以凝并效率更高。当芒刺列间距由0.02 m增至0.03 m后,凝并效率明显下降。这是因为芒刺列间距过大,相邻芒刺电晕放电时几乎不受影响,电晕放电区域之间形成了空白区域,在空白区域内产生的离子较少,粉尘粒子荷电不充分,粒子间的凝并作用较小;此外,当列间距较大时,离子风的收尘区域无法完全覆盖2列芒刺间的极板,粉尘粒子主要受到了电场力的作用,不能到达收尘极板;另外,芒刺列间距过大,使电晕放电过于集中,也不利于粉尘的均匀荷电,从而使粉尘的凝并效率降低。
2.1. 凝并效果的评价方法
2.2. 外加电压对凝并效果的影响
2.3. 双极荷电装置对凝并效果的影响
2.4. 极配间距对凝并效果的影响
-
1)当外加电压在一定范围内(不大于13 kV),细微粉尘的凝并效率随外加电压的增大而升高;相同外加电压下,粉尘粒径越大,凝并效率越高;当外加电压大于13 kV时,电压的升高对粉尘的凝并效率无明显影响,证明了外加电压过高或过低都不利于粉尘的凝并。
2)安装双极芒刺预荷电装置可以提高不同粒径粉尘的凝并效果,当外加电压达到14 kV时,安装双极芒刺预荷电装置比未安装预荷电装置的粉尘凝并效率无明显差异。
3)缩短极配间距可以显著提高各粒径粉尘凝并效率,极配间距为0.02 m时凝并效果最佳,0.025 m时次之,0.03 m时凝并效果最差。根据实验数据分析得出,细微粉尘电凝并最佳实验参数为安装双极芒刺预荷电装置、极配间距0.020 m和外加电压13 kV。
4)对比传统的三区式电凝并装置,该双区芒刺式电凝并装置结构简单,能进一步提高细微粉尘的凝并效率,除尘性能优于三区式电凝并装置,可为柴油机尾气颗粒及工业粉尘的去除提供参考。





 下载:
下载:

 本站查看
本站查看


