-
随着国民生活水平的日益提高,与人民生活密切相关的《生活饮用水卫生标准》也更加严苛。目前,生活饮用水面临的主要问题是输水管网带来的饮用水中生物安全隐患[1]。可同化生物有机碳(AOC)被普遍认为是饮用水生物稳定性的一个重要参数[2]。已有研究[3]发现,磷是控制管网中饮用水微生物生长的重要因素,当饮用水中磷酸盐浓度低于0.01 mg·L−1时,显示出明显的细菌生长抑制作用[4]。因此,控制饮用水中磷含量是有效的控制细菌生长的重要手段之一。
与其他的除磷技术相比,吸附法具有占地面积小、稳定性强等特点,故引起越来越广泛的关注[5]。在已有的研究中,以天然高分子材料[6]、碳基材料[7]、无机金属氧化物材料[8]、纤维材料[9]等作为改性材料来吸附水中的磷均具有良好的效果。与其他材料相比,镧基改性材料[10]对磷酸盐的吸附容量高,吸附选择性强,且具有较好的生物安全性,在水体除磷领域备受关注[11]。
本研究以熔融纺丝法制备纳米氧化镧负载的聚丙烯纤维复合材料,再经聚乙烯亚胺改性制备成PEI/La2O3/PP纤维吸附材料,研究了其对饮用水中微量磷的去除效果及对饮用水中细菌生长的抑制作用;考察了pH、共存离子等因素对磷吸附效果的影响;采用吸附等温模型、吸附动力模型对吸附机理进行了探讨;通过微生物实验,探究了饮用水中细菌生长与磷含量的关系。本研究可为控制饮用水中微生物的二次生长潜能提供参考。
-
试剂:氢氧化钠(AR,天津市风船化学试剂有限公司)、盐酸(AR,天津市风船化学试剂有限公司)、磷酸二氢钾(AR,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司)、抗坏血酸(AR,天津市天新精细化工开发中心)、钼酸铵(AR,天津市光复科技发展有限公司)、过硫酸钾(AR,天津市风船化学试剂有限公司)、H2SO4(AR,天津市风船化学试剂有限公司)、纳米氧化镧(50 nm,罗恩试剂)、聚丙烯(工业级,中国石化上海石油化工股份有限公司)、聚乙烯亚胺(M.W.600,上海麦瑞尔化学技术有限公司)、戊二醛(上海麦瑞尔化学技术有限公司)、异丙醇(AR,天津市津东天正精细化学试剂厂)、牛肉膏蛋白胨培养基(BR,北京奥博星生物技术有限公司)。
仪器:小型单丝纺丝试验机(无锡市兰华纺织机械有限公司)、真空干燥箱(恒幸仪器设备厂)、精密电子天平(奥豪斯国际上海贸易有限公司)、PH-3210PH计(德国WTW公司)、磁力加热搅拌器(C-MAG HS7)、蠕动泵BT100-2J(Longer Pump)、立式压力蒸汽灭菌器(上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂)、紫外可见分光光度计TU-1810(北京朴析通用仪器有限责任公司)、超净工作台(苏州金大净化工程有限公司)、光照培养箱SPX-300B-G型(上海博讯实业有限公司)。
-
氧化镧/聚丙烯(La2O3/PP)复合纤维材料的制备:将25、50、100、300 g纳米La2O3颗粒分别与10 kg聚丙烯颗粒手动混合约2 min,然后将混合物加入到熔融纺丝机的进样料斗中,将进样料斗调到振荡模式,保证混合均匀,随后进入高温熔融室(熔融温度约为210 ℃),经过高温熔融纺丝制得负载La2O3的聚丙烯纤维材料,La2O3的负载质量分数分别为0.25%、0.5%、1%、3%。
La2O3/PP复合纤维材料的亲水性改性:使用去离子水∶异丙醇=1∶1配制质量分数为0.25%、0.5%、1%、3%聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)溶液。将筛选出的最佳La2O3负载量的La2O3/PP复合材料分别溶于不同浓度的聚乙烯亚胺溶液中,浸渍24 h。然后将其浸渍于质量分数为0.1%的戊二醛溶液中,交联反应12 h,用大量蒸馏水洗涤,烘干。最终制得吸附材料,简称为PEI/La2O3/PP。采用X射线衍射分析仪(XRD)进行晶型结构分析。
-
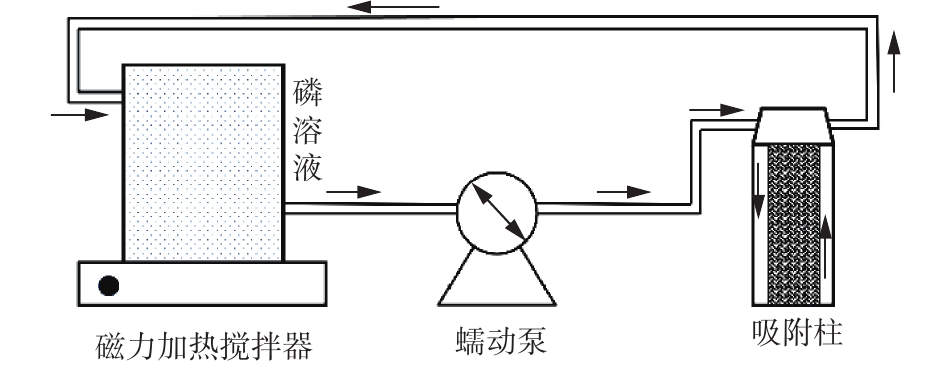
实验均取3 L不同浓度磷溶液,置于实验装置中,加入复合纤维材料,反应一定时间,测定溶液的磷含量。循环吸附实验装置如图1所示。
配置0.1 mg·L−1的磷溶液,加入氧化镧负载量分别为0.25%、0.5%、1%、3%的吸附材料,在实验装置中进行吸附反应,测定反应后磷溶液的浓度。使用磷钼蓝分光光度法(GB 11893-1989),此方法磷的检出限为0.01 mg·L−1。使用电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱(ICP-OES)测定镧元素的溶出率,此方法的镧检出限为1 μg·L−1。
配置0.1 mg·L−1的磷溶液,加入PEI浓度分别为0.25%、0.5%、1%、3%的吸附剂,其余步骤同上述实验。
配置0.1 mg·L−1的磷溶液,用NaOH/HCl调节pH为3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11,其余步骤同上述实验。
配置
CO2−3 、SO2−4 、Cl−、NO−3 离子浓度均为1 mmol·L−1,磷浓度为0.1 mg·L−1的溶液,其余步骤同上述实验。配置初始浓度为1~80 mg·L−1的磷溶液,置于实验装置中,控制温度在25、35、45 ℃,反应6 h后取样,测定溶液中磷含量。
Langmuir等温吸附理论的观点是:吸附剂表面吸附位点分布均匀,吸附质在固体表面上存在着吸附和解析2种过程,这2种过程通过相互作用最后达到吸附平衡[12]。其吸附等温线模型如式(1)所示。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qm为饱和吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为平衡吸附浓度,mg·L−1;KL为平衡吸附常数。
Freundlich吸附机理对表面不均匀、比表面积大的固体具有很好的适应性[12],其表达式如式(2)所示。
式中:qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;Ce为平衡吸附浓度,mg·L−1;KF为吸附相关系数;n为吸附相关系数。
根据Freundlich吸附理论,KF表征吸附剂的吸附能力,n值反映了吸附剂的不均匀吸附反应,当n<0.5时,吸附不易进行。
配置初始浓度为0.1 mg·L−1的磷溶液,置于吸附实验装置中,控制温度在25、35、45 ℃,在一定时间间隔中取样,测定溶液中磷含量。
准一级动力学方程认为,吸附速率与吸附剂上未被占据的吸附位点成正比,方程如式(3)所示。
式中:k1为准一级吸附速率常数,min−1;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qt为t时刻吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,h。
准二级动力学方程认为,吸附速率与吸附剂上未被占据的吸附位点的平方成正比,方程如式(4)所示。
式中:k2为准二级吸附速率常数,min−1;qe为平衡吸附量,mg·g−1;qt为t时刻吸附量,mg·g−1;t为吸附时间,h。
-
测定细菌浓度具体方法按照《生活饮用水标准检测方法》(GB/T 5750-2006)进行检测。取一定量超纯水,经过高温灭菌制成无菌水,用无菌水配置细菌浓度为1 000 CFU·mL−1的大肠杆菌溶液,取3 L大肠杆菌溶液于实验装置中,分别加入PEI/La2O3/PP纤维材料和PEI /PP纤维材料,在一定时间内取样,测定自来水中细菌浓度。饮用水在无菌的条件下放置3 d,以达到去除余氯的目的。取3 L自来水于实验装置中,加入复合纤维材料,在一定时间间隔内取样,测定自来水中细菌浓度。
-
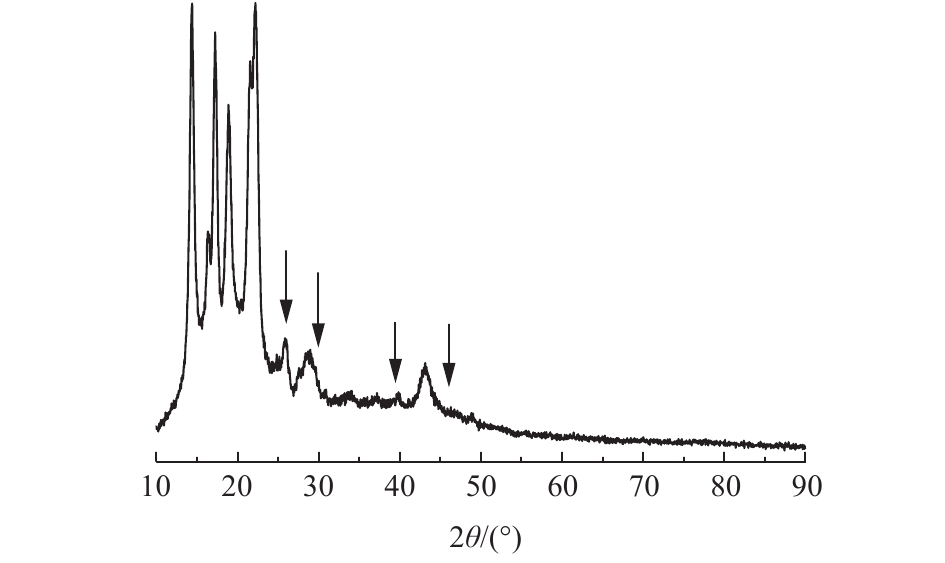
由图2可以看出,氧化镧负载聚丙烯纤维后衍射谱图中出现了较多新的峰,与PDF标准卡片进行比对,发现新出现的峰与氧化镧标准物的衍射峰相对应,说明氧化镧成功负载在聚丙烯纤维上。图2中衍射角26.106°、29.950°、39.474°、46.058°分别对应氧化镧的(100)、(012)、(012)、(110)晶面。
-
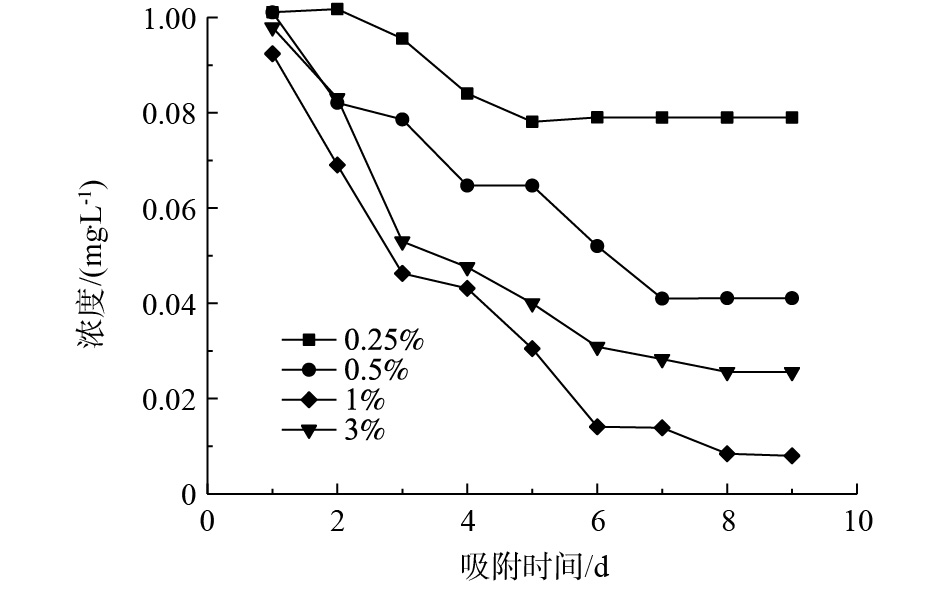
吸附剂对低浓度含磷溶液的吸附效果如图3所示。吸附8 d后,氧化镧负载量为1%的吸附剂将磷浓度吸附至0.01 mg·L−1以下。当氧化镧负载量为3%时,磷的吸附效果反而下降,这是因为较高负载量条件下,纳米氧化镧颗粒容易发生团聚现象,在聚丙烯纤维中的分散性较差,使有效的吸附位点减少,造成了吸附效果降低。而过低的氧化镧负载量会导致有效吸附位点的不足,因此,在制备La2O3/PP复合吸附材料过程中,氧化镧的最佳负载量为1%。
将最佳负载量的La2O3/PP复合材料氧化镧的溶出率进行检测,实验结果表明,吸附时间为9 d后,溶液中的镧浓度均小于10 μg·L−1,证明该复合材料具有很好的稳定性。
-
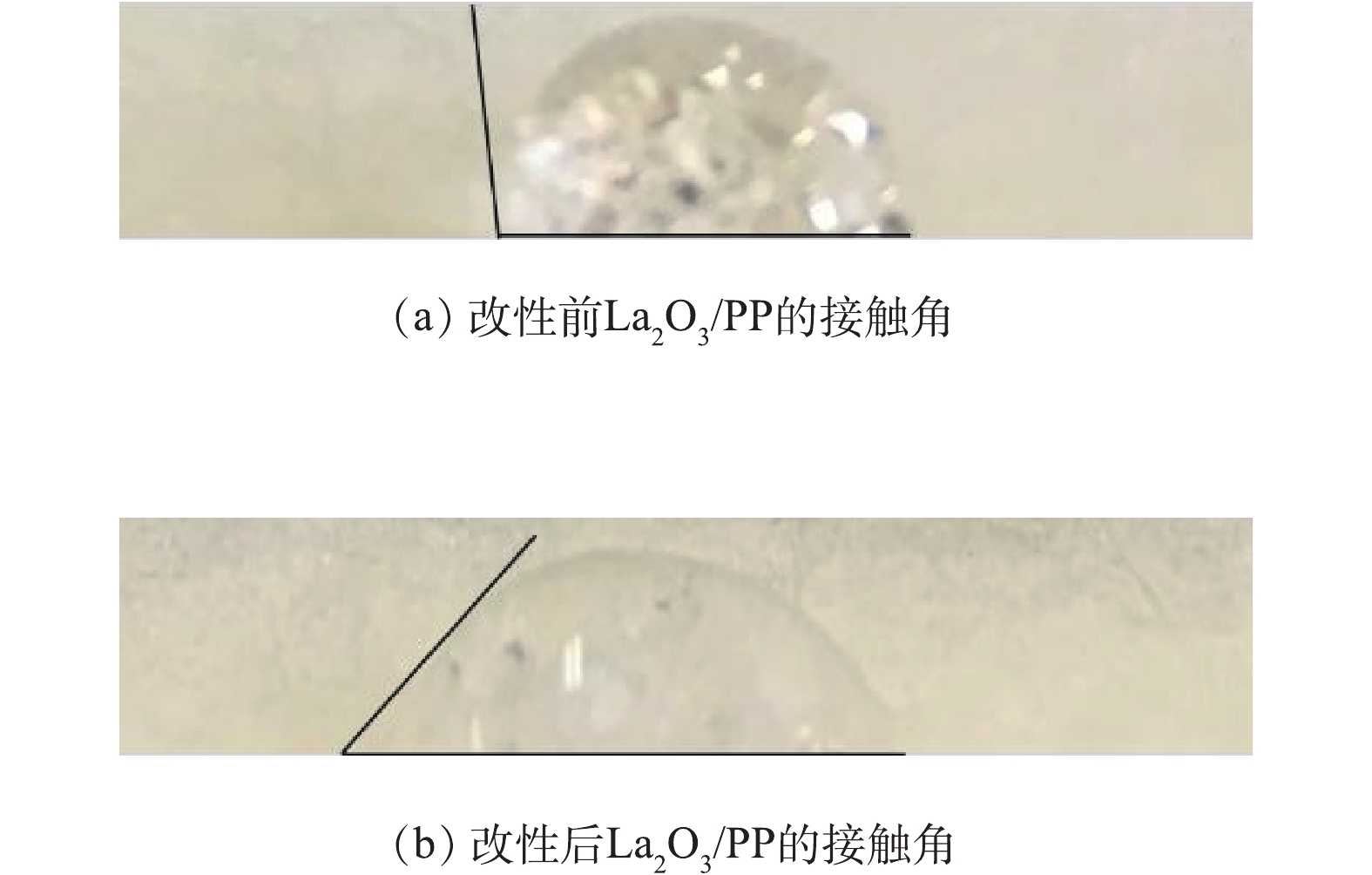
由于聚丙烯纤维表面的非极性特征,其本身亲水性能很差,并且容易带静电[13],降低了La2O3/PP材料与磷溶液的反应速率。本实验通过聚乙烯亚胺与戊二醛交联反应,在聚丙烯纤维表面交联氨基[14],使其具有良好的亲水性。改性前后La2O3/PP接触角的变化如图4所示。改性前La2O3/PP的接触角为98°,而经过PEI处理后的PEI/La2O3/PP的接触角发生明显变化,减小到50°,表现出较好的亲水性。这是由于PEI改性使纤维表面增加了一定数量的氨基亲水性基团,从而明显提高了聚丙烯材料的亲水性。材料表面亲水性的增强能够明显增加磷酸盐的吸附速率。
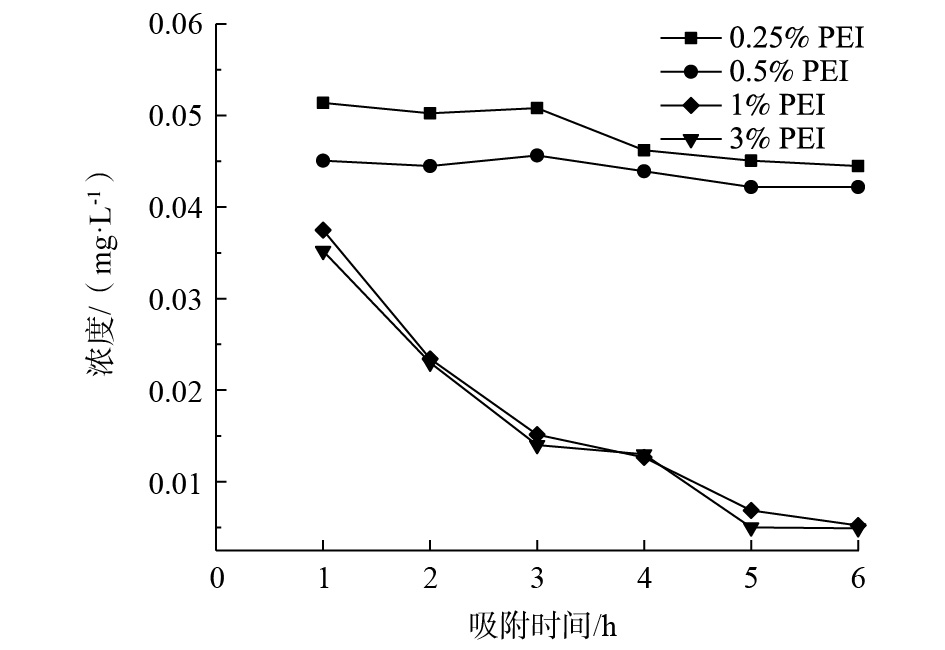
此外,氨基的质子化作用还可以与磷酸根发生静电引力作用,从而促进磷酸盐的吸附。不同PEI浓度对磷吸附效果的影响如图5所示。La2O3/PP复合材料经亲水改性后,对磷的吸附反应速率大大提高。当PEI浓度为1%和3%时,吸附速率的变化明显,吸附反应6 h后,磷浓度降至0.01 mg·L−1以下;当PEI浓度为3%时,吸附速率没有明显提高,这是由于较高浓度的PEI会导致溶液黏度增大,不利于PEI分子的扩散。因此,本实验选取PEI的最佳浓度为1%。
-
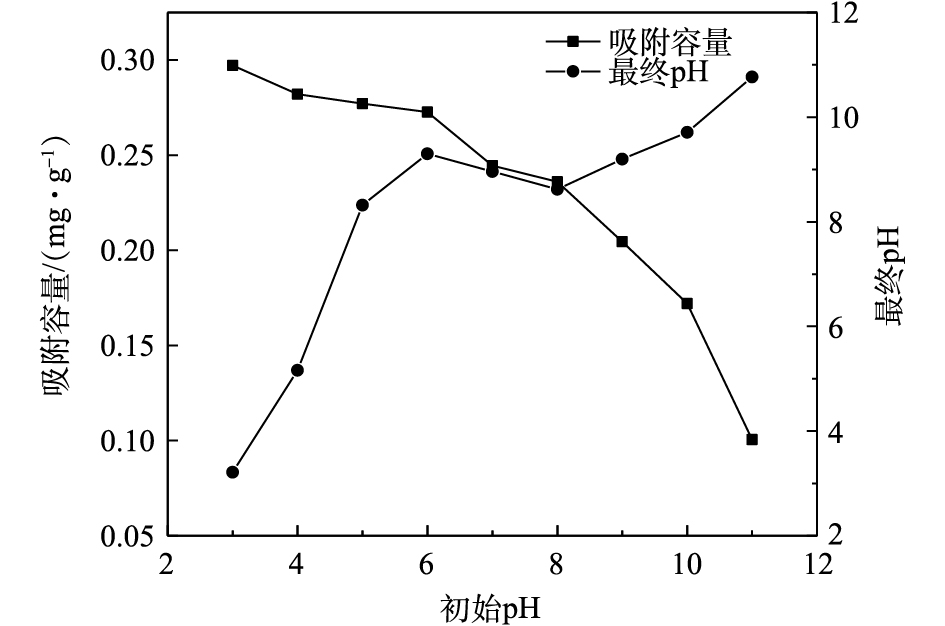
不同初始pH对磷吸附效果的影响如图6所示。随着溶液初始pH的升高,吸附容量呈现出下降趋势,吸附材料的吸附能力降低。当pH=3时,磷的最大吸附容量为0.30 mg·g−1;当pH在3~8时,磷的吸附容量保持在0.24 mg·g−1以上,这说明吸附剂具有较宽的pH适用范围。当溶液初始pH不断增大时,吸附容量快速下降,说明碱性条件不利于吸附剂对磷的吸附。吸附后溶液的pH都有所升高,这是氧化镧对磷的吸附是一个化学反应过程,且反应过程中有OH−的释放。
通过测量PEI/La2O3/PP表面的Zeta电位,测出PEI/La2O3/PP的等电点为8.2。这说明当溶液pH小于8.2时,吸附材料表面呈现正电性,可以与溶液中的带负电荷的磷酸根离子产生静电吸引作用。同时,大量质子化的磷酸根与材料表面氧化镧羟基化产生的氢氧根离子发生离子交换作用,这也进一步证实了吸附磷后溶液pH升高的现象。
-
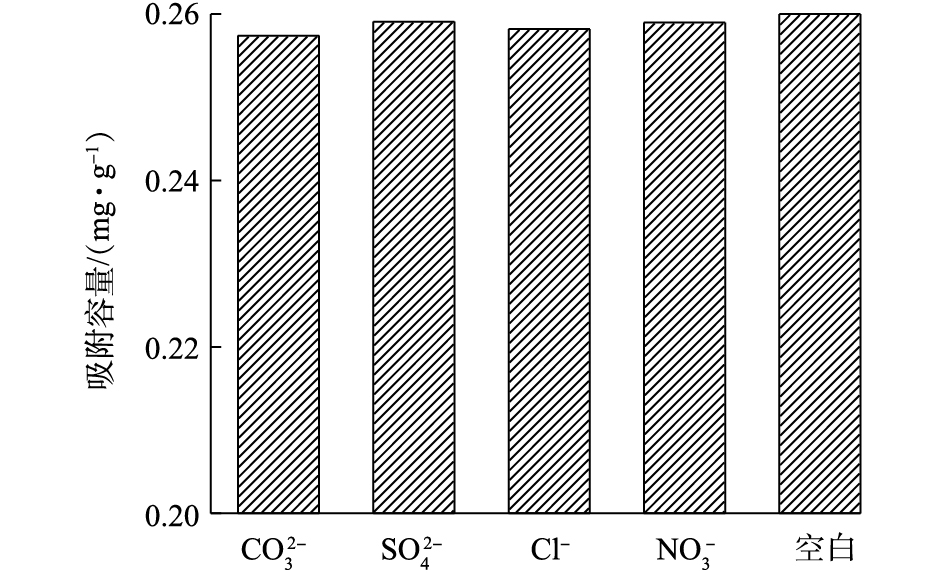
水体中与磷酸根共存的常见阴离子有
CO2−3 、SO2−4 、Cl−、NO−3 [15],这4种阴离子对PEI/La2O3/PP复合材料除磷的影响如图7所示。实验结果表明,这4种阴离子对PEI/La2O3/PP复合材料的磷吸附能力没有明显的影响,说明PEI/La2O3/PP对磷酸盐具有很强的吸附选择性。 -
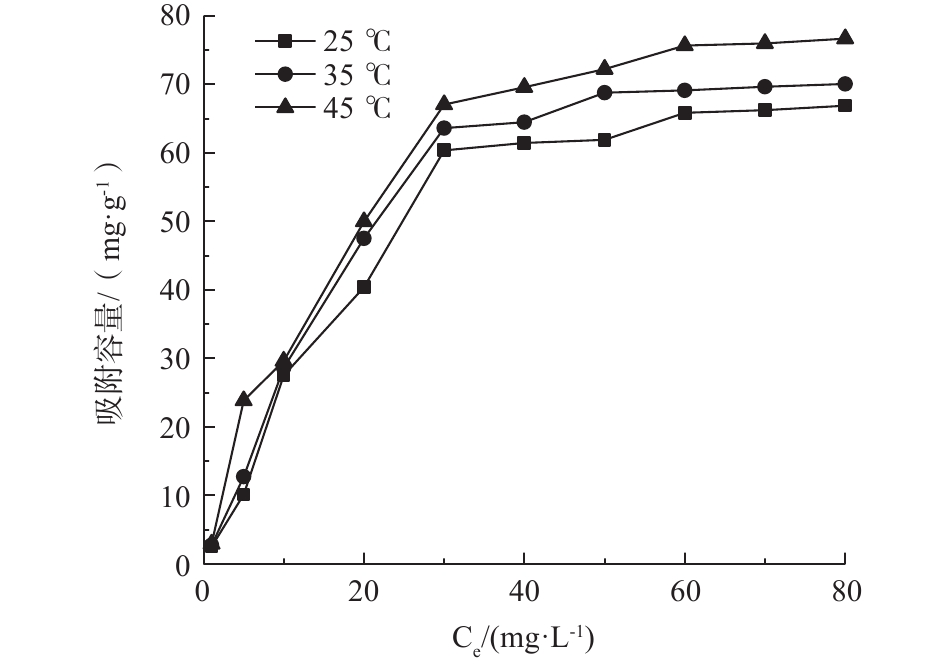
吸附等温线可以确定吸附平衡浓度与吸附容量的关系,通过模型拟合可以估算吸附剂的最大吸附容量。如图8所示,吸附剂的吸附容量随着磷初始浓度的升高而不断升高,当达到一定浓度时吸附容量趋于平稳。在不同温度条件下,磷吸附容量随着温度的升高而升高。当温度为45 ℃时,最大吸附容量达到76.67 mg·g−1。
采用Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型对吸附等温线进行拟合,拟合结果如表1所示。Langmuir模型和Freundlich模型均能较好地拟合PEI/La2O3/PP对磷酸盐的吸附,但Langmuir模型的拟合程度更好。KL是表示吸附剂对磷的吸附亲和力强弱的重要参数,随着温度从25 ℃逐渐提高到45 ℃,平衡吸附常数KL从0.032提高到0.045,表明PEI/La2O3/PP吸附磷的过程为吸热反应,在一定范围内,提高温度有利于反应的进行。Freundlich模型中的n值也能反映吸附剂对吸附质吸附能力的强弱,如表1所示,不同温度下的n值均大于0.5,表示吸附反应较容易进行。
-
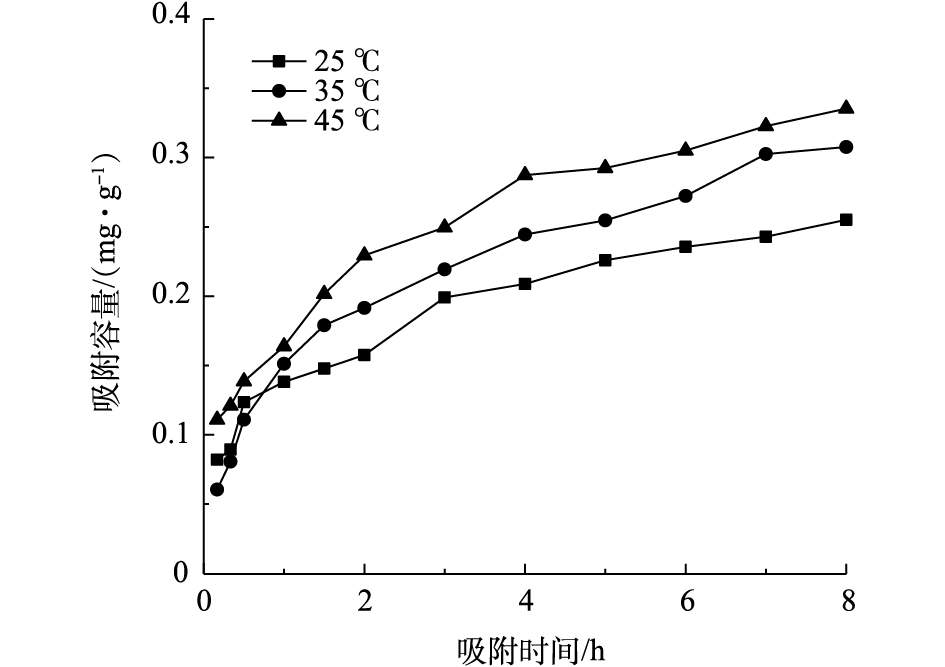
吸附动力学曲线主要用于描述吸附速率变化的特征,通过拟合动力学反应模型可以进一步分析吸附原理。不同温度条件下PEI/La2O3/PP吸附磷酸盐的动力学曲线如图9所示。当温度从25 ℃上升到45 ℃时,吸附反应速率明显加快,这进一步说明升温有利于吸附反应的进行。准一级和准二级动力学模型拟合结果如表2所示,可见,准二级动力学模型能更好地拟合PEI/La2O3/PP吸附磷的反应过程,模型的R2为0.93~0.98。
-
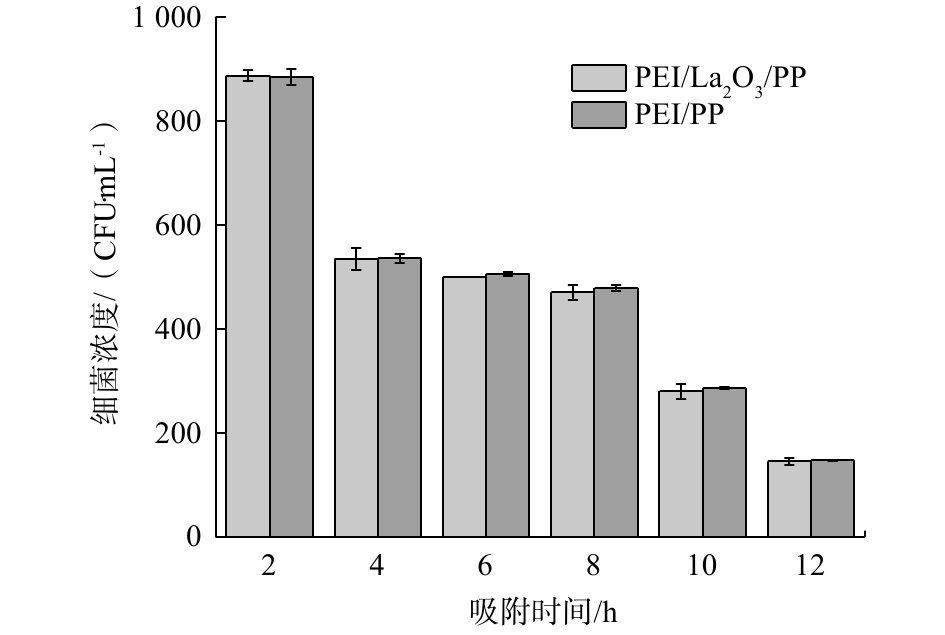
为了研究PEI/La2O3/PP纤维自身的杀菌能力,本实验对比了负载氧化镧颗粒的PP纤维与未负载氧化镧颗粒的PP纤维对大肠杆菌生长的作用。由图10可以看出,2种材料在不同的反应时间条件下大肠杆菌的数量基本相同,说明PEI/La2O3/PP纤维所负载的氧化镧颗粒自身对大肠杆菌生长没有明显的抑制作用,这可能是由于氧化镧颗粒的负载量较小的缘故。但是,在磷源极度缺乏的状态下,大肠杆菌浓度会迅速下降,证明控制磷营养源才是抑制细菌生长繁殖的关键因素。
-
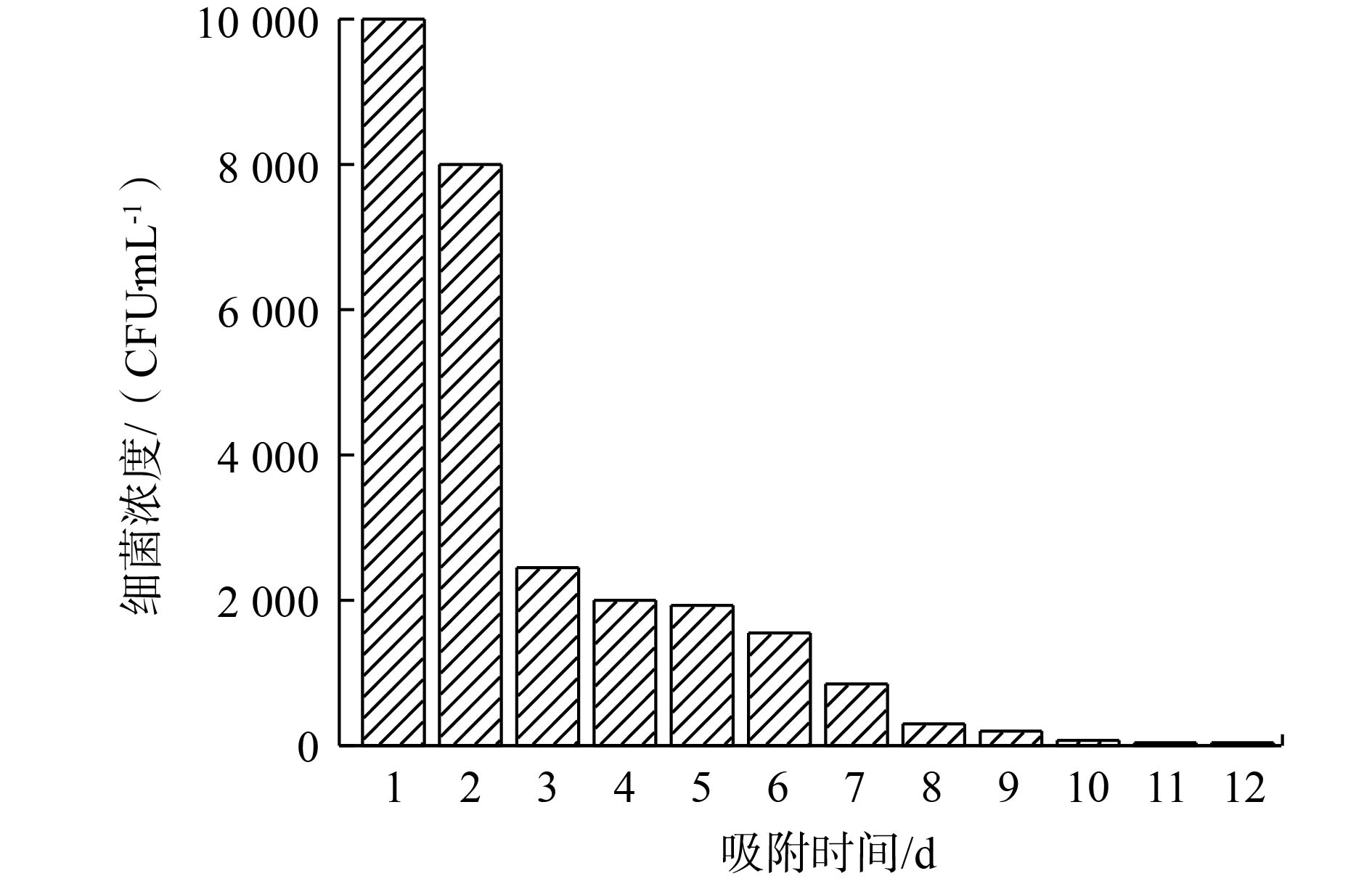
为了进一步研究本实验中制备的吸附材料对实际饮用水是否具有除磷控菌的效果,本研究以饮用水为研究对象,考察了磷浓度与细菌生长之间的关系,实验结果如图11所示。取饮用水并自然晾晒3 d,以去除余氯,之后使用平板计数法检测水中细菌浓度为10 000 CFU·mL−1,饮用水磷浓度的本底值为0.02 mg·L−1。通过PEI/La2O3/PP吸附2 h后,磷浓度降至0.01 mg·L−1以下。在磷源极度缺乏的条件下,细菌含量明显下降,除磷后的1~3 d细菌含量迅速下降,自来水中磷酸盐被去除,细菌由于失去了存活必备的磷源而迅速减少,随后是细菌缓慢凋亡的过程。到第10天,细菌含量降至100 CFU·mL−1以下;到第11天,细菌含量进一步降至10 CFU·mL−1左右。除磷控菌的微生物学实验表明,饮用水中细菌生长与磷浓度存在明显的正相关性,当水中磷浓度降低到0.01 mg·L−1以下时,细菌生长受到强烈抑制。因此,除磷控菌方法为控制饮用水中微生物的二次生长潜能提供了一种具有前瞻性的水质稳定技术。
-
1) PEI/La2O3/PP复合纤维材料的最佳制备条件:氧化镧的最佳负载量为1%,PEI的最佳浓度为1%。中性和偏酸性条件有利于磷的吸附,水中常见共存阴离子对磷的吸附效果影响不大。
2) PEI/La2O3/PP复合纤维材料对水中磷酸盐具有很好的吸附效果,最大吸附容量可达76.67 mg·g−1。在温度为25~45 ℃时,随着温度的升高,磷吸附容量和吸附速率均有明显提高。吸附模型拟合结果表明,PEI/La2O3/PP对磷的吸附过程主要以单分子层化学吸附为主。
3) PEI/La2O3/PP复合纤维材料对饮用水中的磷具有很好的吸附效果,可以将饮用水中磷浓度降至0.01 mg·L−1以下。饮用水中磷源的缺乏可以起到明显的控菌效果,吸附反应11 d后,细菌浓度从10 000 CFU·mL−1降至10 CFU·mL−1左右。
改性La2O3/聚丙烯纤维对饮用水中磷的吸附及控菌效果
Effect of phosphate adsorption and antibacteria in drinking water by modified La2O3/polypropylene fibers
-
摘要: 为了研究吸附剂在饮用水中除磷控菌效果,在聚丙烯(PP)纤维上负载氧化镧(La2O3)纳米颗粒,并用聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)对吸附剂表面进行亲水改性,制备出PEI/La2O3/PP纤维吸附材料,使用X射线衍射分析(XRD)对其进行了表征。实验结果表明:偏酸性条件有利于磷的吸附,溶液中共存离子对吸附效果的影响不大;当温度为45 ℃时,PEI/La2O3/PP对磷的饱和吸附容量达到76.67 mg·g−1,吸附过程能够较好地拟合Langmuir模型;吸附动力学过程能够较好地拟合准二级反应动力学方程。该吸附材料对饮用水中的微量磷具有良好的吸附去除效果,磷深度去除后能达到明显的抑菌效果。Abstract: In order to study the effect of adsorbent on phosphate removal and antibacteria in drinking water. Lanthanum oxide (La2O3) nanoparticles were loaded on polypropylene (PP) fibers and polyethyleneimine (PEI) was used to perform hydrophilic modification of the adsorbent surface, then PEI/La2O3/PP adsorbent was prepared. The materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The experimental results showed that the weak acidic conditions could facilitate its phosphate adsorption, and the coexistence ions had slight effect on the adsorption effect. When the temperature was 45 ℃, the saturated adsorption capacity of PEI/La2O3/PP towards phosphate reached 76.67 mg·g−1. The adsorption isotherm followed Langmuir model. The kinetic equation followed pseudo-second-order kinetics. The adsorbent had a good adsorption effect on trace phosphate in drinking water. Moreover, an excellent bacteriostatic effect could occur after phosphate removal.
-
Key words:
- La2O3 /
- polypropylene fibers /
- adsorption /
- phosphate /
- antibacteria
-
表 1 吸附等温线模型拟合参数
Table 1. Adsorption isotherm parameters for phosphate adsorption
温度/℃ Langmuir Freundlich qm/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·g−1) R2 n KF/(L·g−1) R2 25 99.305 0.031 67 0.934 08 1.317 1 3.297 0 0.947 57 35 99.701 0.037 29 0.951 96 1.348 0 3.789 2 0.943 01 45 102.56 0.044 52 0.964 86 1.428 9 3.609 2 0.915 82 表 2 吸附动力学模型拟合参数
Table 2. Kinetic parameters for phosphate adsorption
温度/℃ 准一级动力学 准二级动力学 k1/min−1 qe/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/(g·(mg·min)−1) qe/(mg·g−1) R2 25 0.505 16 0.263 70 0.873 42 1.649 71 0.326 50 0.930 91 35 0.570 99 0.289 43 0.893 24 1.802 26 0.352 28 0.953 54 45 0.631 57 0.318 02 0.949 80 1.891 19 0.382 24 0.986 28 -
[1] 姜登岭, 张晓健. 饮用水中磷与细菌再生长的关系[J]. 环境科学, 2004, 25(5): 57-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2004.05.012 [2] KOOIJ D V D, VISSER A, HIJNEN W A M. Determining the concentration of easily assimilable organic carbon in drinking water[J]. Journal American Works Association, 1982, 74(10): 540-545. doi: 10.1002/j.1551-8833.1982.tb05000.x [3] MIETTINEN I T, VARTIAINEN T, MARTIKAINEN P J. Contamination of drinking water[J]. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 1996, 29(6584): 19-20. [4] MIETTINEN I T, VARTIAINEN T, MARTIKAINEN P J. Phosphorus and bacterial growth in drinking water[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 1997, 63(8): 3242-3245. [5] 孟顺龙, 胡庚东, 宋超, 等. 镧改性吸附剂废水除磷技术研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(S2): 194-199. [6] 杨金梅, 吕建波, 李莞璐, 等. 壳聚糖载纳米羟基氧化铁对水中磷的吸附[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 14-22. [7] LIU T, CHEN X, WANG X, et al. Highly effective wastewater phosphorus removal by phosphorus accumulating organism combined with magnetic sorbent MFC@La(OH)3[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 335: 443-449. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.117 [8] 雷行, 杨雪, 刘婷, 等. 锆改性铝氧化物对水中磷的吸附特性[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 117-124. [9] HE J J, WANG W, SHI W X, et al. La2O3 nanoparticles polyacrylonitrile nanofibers for bacterial inactivation based on phosphate control[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6: 99353-99360. doi: 10.1039/C6RA22374E [10] HAGHSERESHT F, WANG S B, DO D D. A novel lanthanum-modified bentonite, phoslock, for phosphate removal from wastewaters[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2009, 46(4): 369-375. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2009.09.009 [11] COPETTI D, FINSTERLE K, MARZIALI L, et al. Eutrophication management in surface waters using lanthanum modified bentonite: A review[J]. Water Research, 2016, 97: 162-174. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.11.056 [12] 于岩. 新型水相吸附材料[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. [13] ZHU H T, QIU S S, JIANG W, et al. Evaluation of electrospun polyvinyl chloride/polystyrene fibers as sorbent materials for oil spill cleanup[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45(10): 4527-4531. [14] LIU C, WU L L, ZHANG C C, et al. Surface hydrophilic modification of PVDF membranes by trace amounts of tannin and polyethyleneimine[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 457: 695-704. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.131 [15] 杜涛, 王莹, 高超, 等. 离子色谱法测定饮用水中无机阴离子[J]. 沈阳师范大学学报 (自然科学版), 2011, 29(2): 260-263. -




 下载:
下载: