-
石油是一种由饱和烃、芳香烃、胶质及沥青质等组成的复合体,故石油污染具有环境体系复杂、波及范围广、治理困难、修复周期长、产生危害大的特征。石油烃污染物进入土壤后会改变土壤的理化性质,威胁地下水安全,致使动植物死亡,甚至危害人类健康[1-3]。石油在加工和运输过程中产生的三泥、罐底泥、船舱底泥等油泥污染物中主要成分都是石油污染土壤和泥沙[4-6],我国每年因石油造成的污染土壤近1×105 t,所以石油烃污染土壤的修复治理已迫在眉睫。
目前,污染土壤的修复方法主要分为物理修复、化学修复和生物修复。常见的修复方法有土壤洗涤法[7-8]、化学氧化法[9-10]、电动修复法[11]、生物强化法[12-13]、机械洗脱法等。其中,机械洗脱法以其修复周期短、修复彻底而被广泛应用于土壤修复中。机械洗脱法的前期研究主要集中在超声、微波、喷射反应[14-17]等方面,这些技术均通过外加场强的方法进行污染物的脱附,故普遍存在高能耗的弊端[18]。目前,有研究[19]表明颗粒运动可以提高其中污染物的脱附效果。因此,在低能耗下,依靠特殊物理结构调控土壤颗粒自身运动状态强化污染物脱附,对于石油烃污染土壤的修复具有重要意义。
本研究将使用CFD软件Fluent(UDF)对石油烃污染土壤颗粒的不同运动状态进行模拟,得到颗粒运动状态与脱附效果之间的关系,并基于此结果,设计一种管式涡流结构,满足颗粒的运动状态,探究在不同结构参数下,颗粒运动状态的变化及石油烃脱附效果。
-
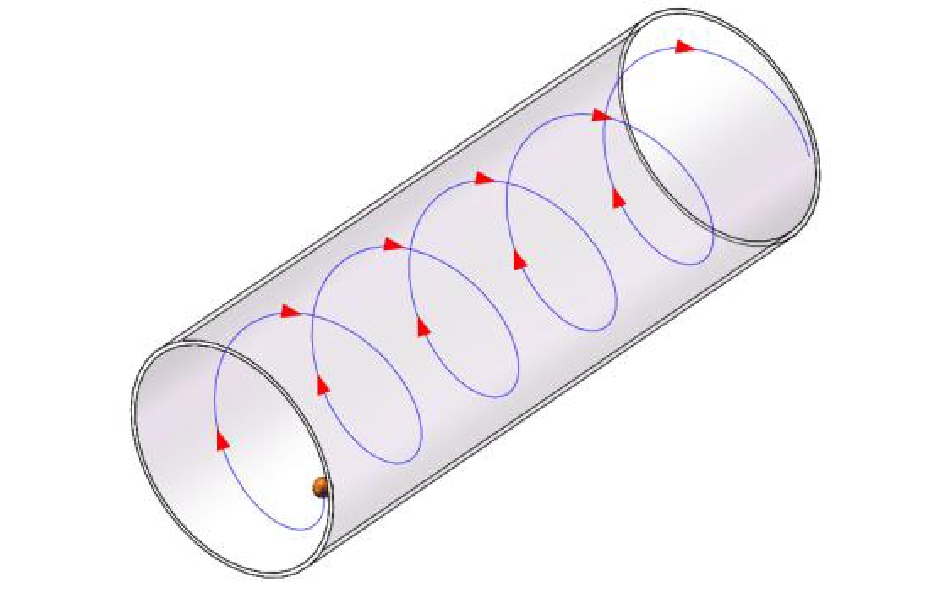
以流体仿真的方法研究颗粒运动状态与脱附效果之间的关系,利用SW软件建立三维几何模型(如图1所示)。其中,直径为2 mm的小球代表土壤颗粒,内径为25 mm且长度为75 mm的圆柱代表管路。
利用ICEM对几何模型进行网格划分,设置小球与圆柱之间的封闭区域为SUR,小球所在的封闭区域为SUR2,球面为interior。采用四面体网格,设置网格密度为8.6×109 m−3并保证网格质量均在0.45以上,这样才符合计算要求。划分后的网格如图2所示。为消除网格数目对计算结果的影响,对网格进行无关性检测。进一步增大网格密度,以脱附后土壤颗粒含油量为特征参数,通过比较发现,增大网格密度后,误差始终保持在1%以内。综合考虑计算精度及计算成本,选取网格密度为8.6×109 m−3。
-
使用Fluent中的组分输送模型,通过计算每种物质的扩散、对流以及反应热源守恒方程来模拟混合和组分的输运。污染土壤颗粒的洗脱过程就是将污染物由颗粒转移到洗涤液中的过程,故选用组分输送模型来模拟这一过程。选择混合组分为柴油-丙酮,选择密度为体积-质量混合定律,选择质量扩散率为2.88×10−20 m2·s−1。由于不涉及传热过程,比热、热导率等其余参数均保持默认值。
土壤颗粒是一种典型的多孔介质,故需要开启多孔介质模型对小球封闭区域SUR2进行定义。多孔介质模型的本质是在标准动量方程的基础上,添加了一个动量方程源项。动量源项又由黏性损失项和惯性损失项组成,计算方法如式(1)所示。
式中:Si为i(x,y,z)动量方程的源项;|v|为速度;D、C为矩阵。
Fluent中动量源项表现形式分为2种:一种为一元二次方程形式;另一种为幂函数形式。本研究多孔介质模型采用一元二次方程形式,计算方法如式(2)和式(3)所示。
式中:α为渗透系数;C2为惯性阻力系数;vi为表观速度;A为黏性阻力系数。
根据经验,设置黏性阻力系数为2×1012 m−2,惯性阻力系数为2×1012 m−1。由于模拟过程不涉及传热,故传热设置保持为默认值。
湍流模型中常用的方程模型如表1所示。模拟过程中,只有颗粒的运动,流体无旋转运动。综合考虑计算精度及成本,湍流模型选择标准k-ε模型。
-
动网格用于解决流场形状因边界的运动而随时间变化的问题。动网格的设置首先要确定网格的更新过程。动网格的网格更新方式有弹簧光顺、扩散光顺、局部网格重构等多种方法。弹簧光顺相对于扩散光顺计算量小,且适用于四面体网格,但其无法改变网格拓扑结构,边界发生大幅运动时,易产生负体积,常与局部网格重构方法结合使用以模拟旋转运动过程,故选择弹簧光顺及局部网格重构的方法进行网格更新。更新后动网格质量的好坏主要由模型的参数设置决定。经过多次调整,最终确定弹簧常数为0.6,Laplace节点松弛因子为0.4,其余采用默认值。重构方法选择局部单元重构,重构参数采用默认值。其次是设置动网格运动区域,设置SUR2及球面为运动区域,形式为刚体。利用UDF中的Deffine_CG_MOTION宏设置颗粒的运动形态,分别为静止、直线运动、1圈顺时针螺旋运动、2圈顺时针螺旋运动、2圈逆时针螺旋运动、4圈瞬时针螺旋运动,并保持土壤颗粒在管路中运动的位移及停留时间相同。
求解器采用三维双精度解算器,压力速度耦合项采用SIMPLE算法。由于模拟为瞬态模拟,故离散格式采用精度更高的二阶迎风格式。设置完成并进行初始化后,利用Patch功能,将柴油组分赋予到SUR2上,柴油初始含量设置为20%。
-
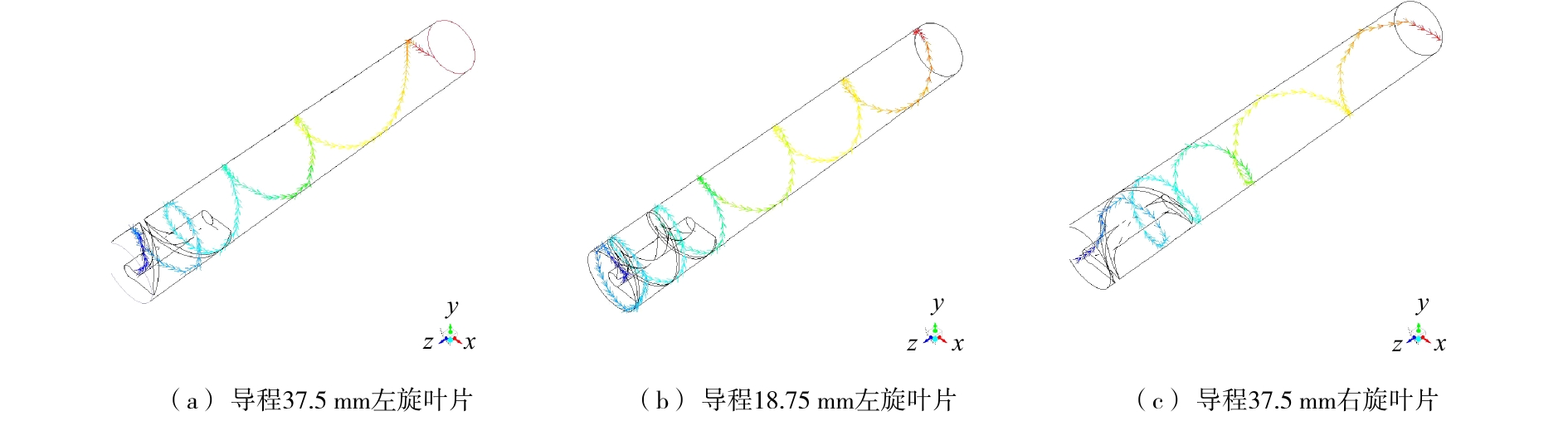
管式涡流结构由圆柱形直管和螺旋叶片2部分组成,如图3所示。根据螺旋叶片的导程及旋向不同可分为3种形式,如表2所示。对模型进行网格划分并进行无关性检测,最终确定网格密度为4.43×108 m−3,网格质量保持在0.4以上。
-
Fluent中离散相模型(DPM)可以通过对拉格朗日坐标系下颗粒作用力微分方程进行积分,进而得出连续相湍流涡旋作用对颗粒运动轨迹的影响。故本研究利用DPM,研究在管式涡流结构的作用下土壤颗粒的运动轨迹。设置颗粒形式为惰性颗粒,射流源类型选择点源注射,其余保持默认值。其中,颗粒初始速度绝对值为0.57 m·s−1,颗粒的密度为2 200 kg·m−3,颗粒直径为2 mm。
由于模拟流体存在旋转运动,而相比于标准k-ε模型,可实现型k-ε模型可以更好地解决旋转剪切流动和漩涡问题[20]。考虑到计算精度,故湍流模型选择可实现型k-ε模型。
-
入口边界条件为速度入口,液相流速为0.57 m·s−1。根据计算,设置水力直径为2.5 mm,湍动强度为5%。出口边界条件为压力出口,压力为标准大气压。出口水力直径为2.5 mm,湍动强度为5%。入口及出口的离散相边界条件为逃逸,壁面的离散相边界条件为反射。
求解器采用三维双精度解算器,压力速度耦合项采用SIMPLE算法。离散格式采用二阶迎风格式。设置完成后进行初始化,通过迭代计算得到管式涡流结构作用下的流场及颗粒运动轨迹。
-
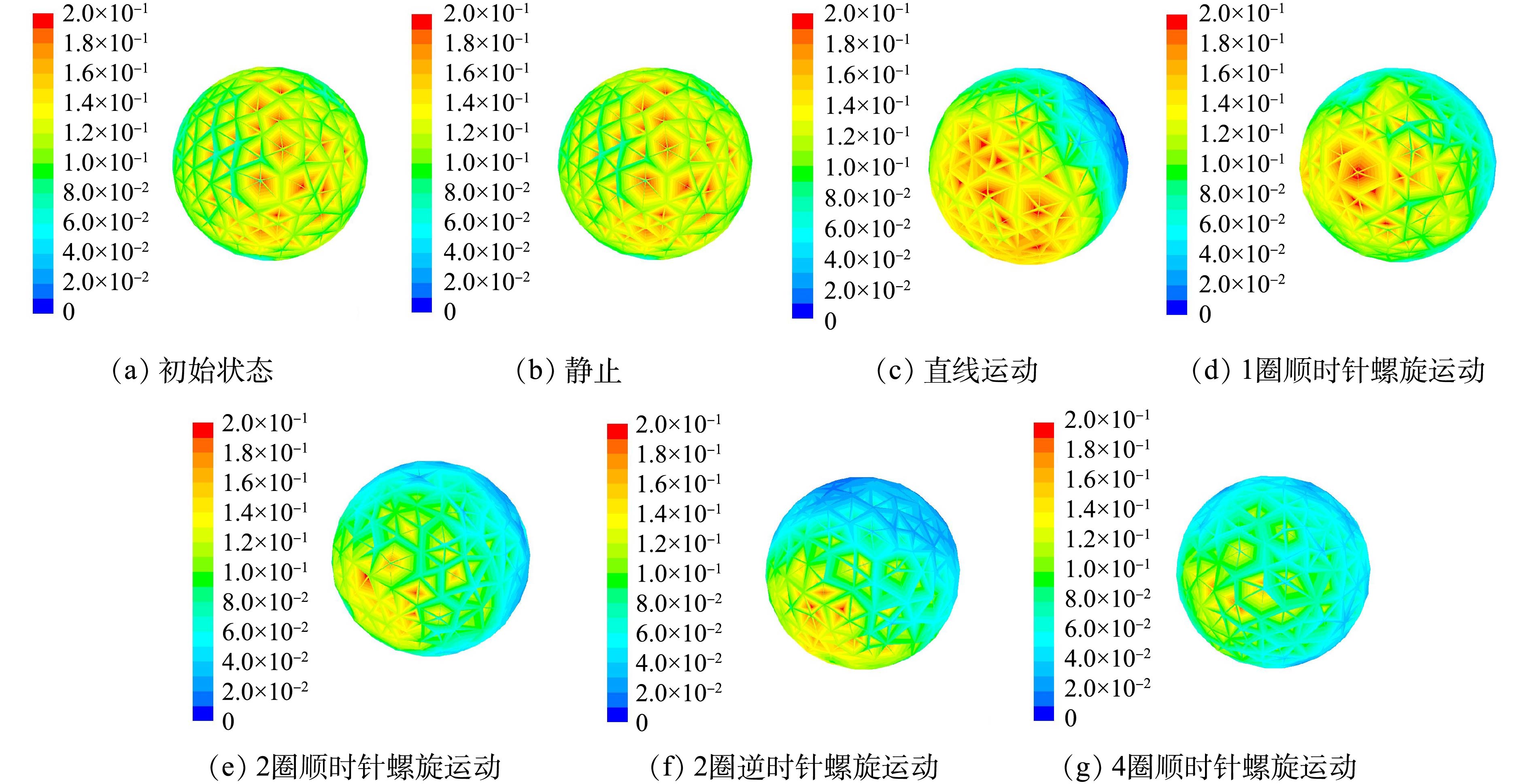
土壤颗粒初始含油量三维云图如图4(a)所示。图4(b)~(g)反映了土壤颗粒经不同状态的运动后颗粒内部最终含油量情况。分析图4(a)和图4(b)可知,对于静止的颗粒,初始状态与最终状态相差不大,含油量的变化并不明显。这表明单独依靠浸泡的方法,石油烃污染土壤的脱附效果较差。分析图4(b)和图4(c)可知,相对于静止状态,运动颗粒的除油率更高,脱附效果更好。推测这是由于相比静止状态,运动的颗粒会受到液相冲刷或剪切等力的作用,导致石油烃污染物从颗粒上脱附。且随着颗粒的运动,颗粒表面液相不断更新,增强了传质效果。分析图4(c)~(e)可知,运动颗粒的脱附效果与颗粒的运动状态有关,螺旋运动颗粒的脱附效果要优于直线运动。推测这是由于相比直线运动,螺旋运动除了受到冲刷及剪切力外,还受到离心力的作用,强化了石油烃污染物的脱附。且螺旋运动颗粒表面的液相更新速率更快,传质更为剧烈。分析图4(d)、图4(e)和图4(g)可知,螺旋运动颗粒的脱附效果与相同时间下颗粒做螺旋运动的圈数有关。相同时间下做螺旋运动的圈数越多,颗粒的脱附效果越好。推测这是由于相同时间下,颗粒做螺旋运动的圈数越多,颗粒表面的液相更新速率越快,传质越剧烈。相应地,颗粒的脱附效果越好。分析图4(e)和图4(f)可知,相同圈数下,顺时针螺旋运动颗粒与逆时针螺旋运动颗粒的脱附效果相差不大。这表明颗粒的脱附效果与螺旋运动的旋向无关。
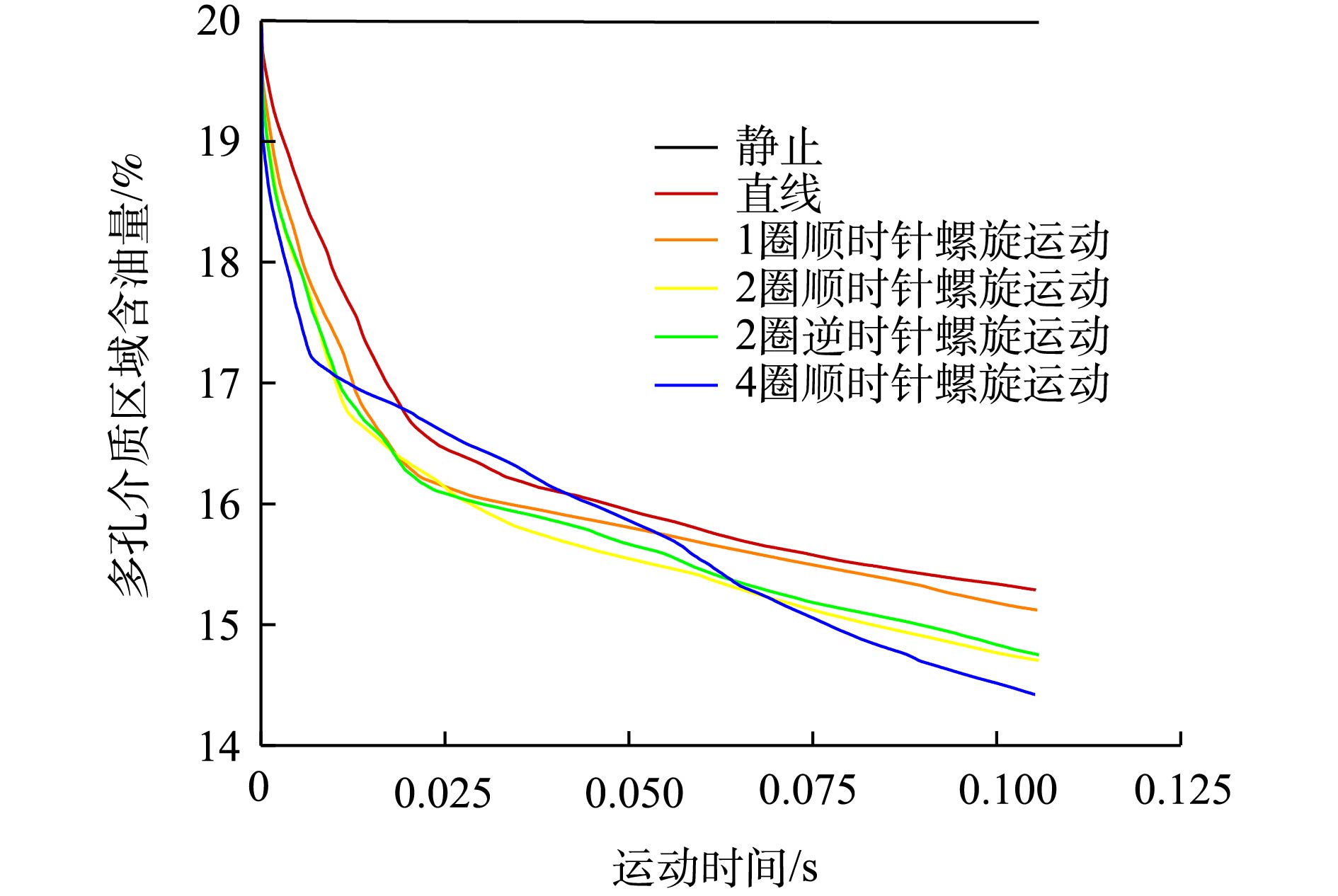
三维云图只对土壤颗粒含油量的始末状态进行了分析。为研究土壤颗粒含油量随时间的详细变化情况,将Fluent中的监测数据导出,利用Origin2017进行数据整理,整理后数据如图5所示。由图5可知,运动颗粒含油量-时间曲线斜率的绝对值随着时间的增长而逐渐减小。这表明随着时间的增长,颗粒的脱附效率逐渐降低。推测这是因为随着脱附时间的增长,颗粒含油量逐渐减小,颗粒与液相中石油烃污染物的浓度梯度减小,扩散过程减弱进而降低了脱附效率。
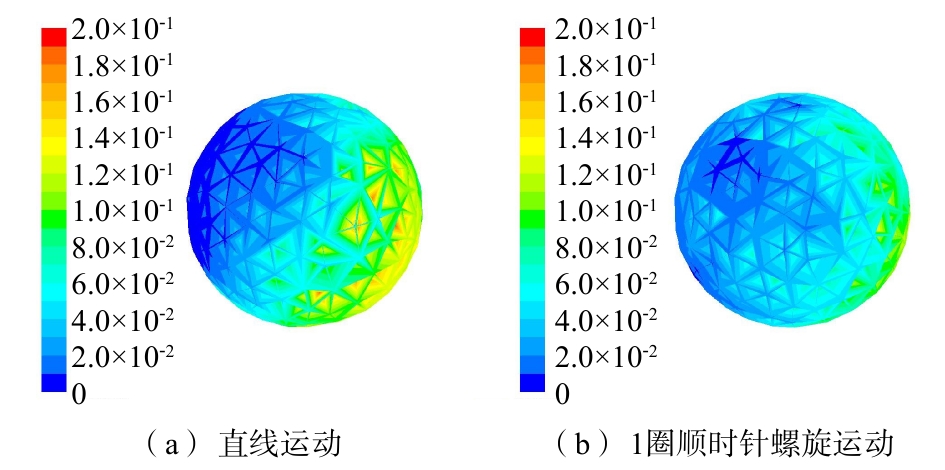
分析图5还可以发现,对于直线运动和做1圈顺时针螺旋运动的颗粒,脱后含油量相差不大。但分析脱后颗粒的正面(以x、y、z坐标轴正方向围成的颗粒表面)含油量云图(图4(c)和图4(d))及反面(以x、y、z坐标轴负方向围成的颗粒表面)含油量云图(图6)后可知,无论颗粒是做直线运动还是螺旋运动,脱后颗粒中石油烃污染物均存在浓度梯度。但螺旋运动颗粒的脱附相对于直线运动更为均匀。
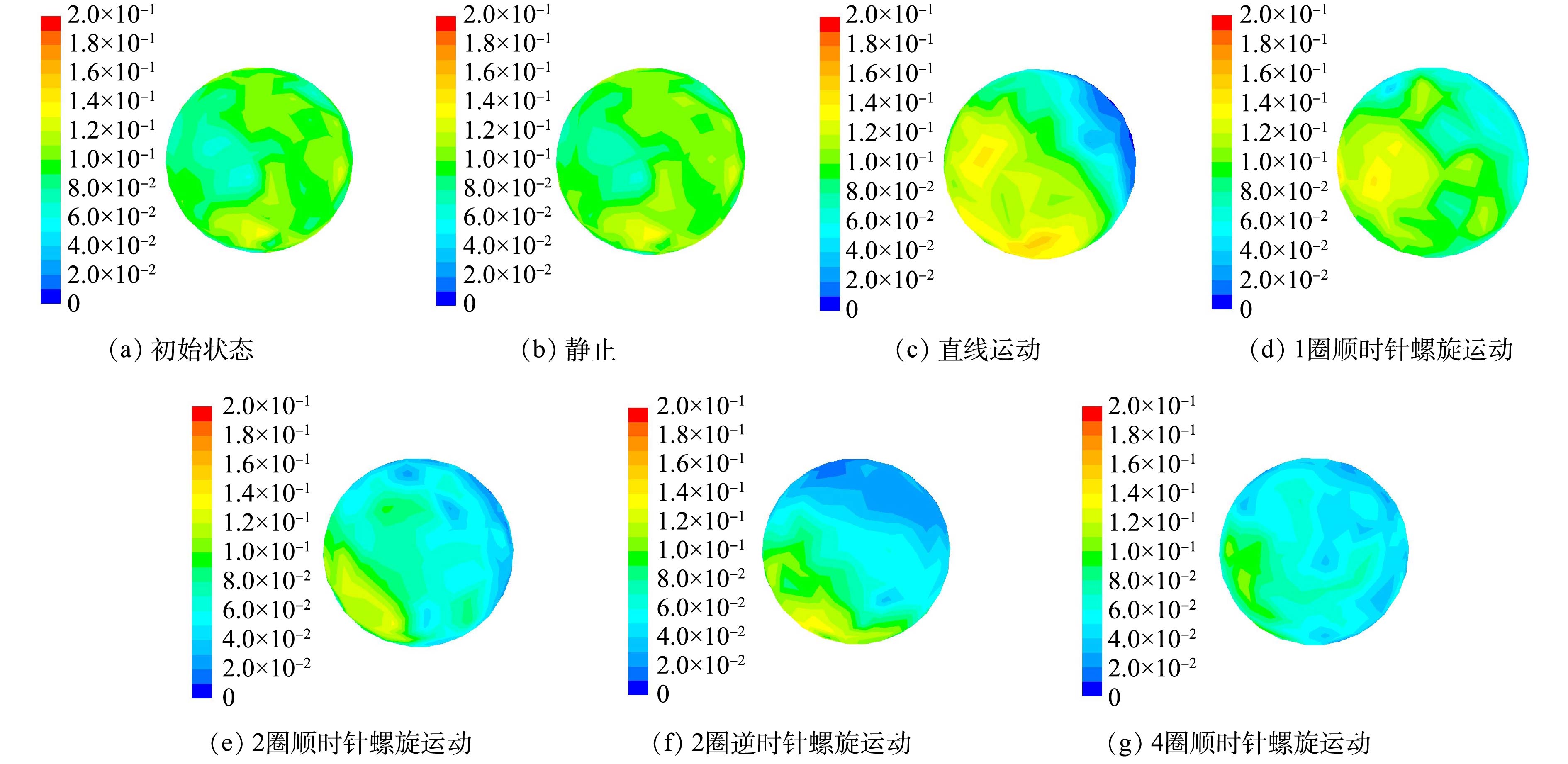
图7反映了土壤颗粒初始状态以及经不同状态的运动后,颗粒表面最终含油量情况。对比图4与图7发现,对于被石油烃完全浸透的单一土壤颗粒而言,颗粒内部油含量要高于表面油含量。且内部油的脱附较表面油更为困难,表面油含量很低时,内部油可能仍然保持较高浓度。
-
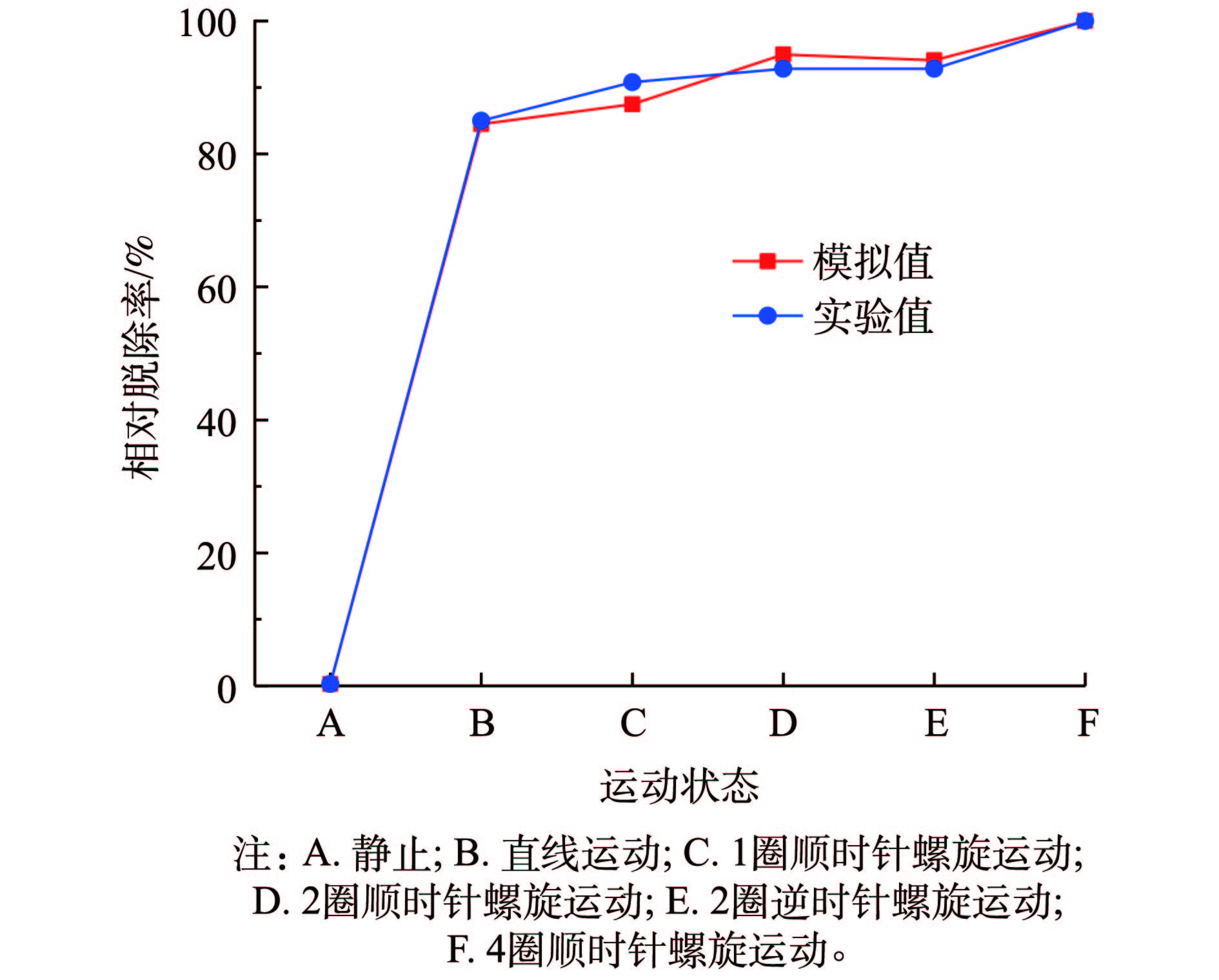
为了验证模型的可靠性,本研究单独做了运动状态与脱除率关系实验。为便于颗粒运动形态的控制,防止其以小颗粒的形式分散在洗涤液中,实验以强度大、孔隙发达、对污染物吸附效果好的麦饭石作为实验材料,经过除杂、筛分后,将麦饭石加入过量的柴油中,并不断搅拌,使麦饭石表面及内部孔道被柴油充分浸润至饱和。经充分搅拌后,在常温避光条件下保存备用。实验时,将污染后的麦饭石颗粒置于金属筛网上沥干不能被吸收的柴油,然后将制备好的颗粒分别加入到不同结构的管式涡流洗涤器中,并以相对脱除率作为研究对象,将模拟结果与实验结果进行了比较,结果如图8所示。其中相对脱除率的计算如式(4)所示。
式中:E代表相对脱除率;En代表该运动状态下的脱除率;Emax代表所有运动状态中最大脱除率。
由图8可知,模拟值与实验值有着相似的趋势且吻合程度较好。由此说明,本研究模拟在颗粒运动状态与脱附关系的趋势上具有很强的可靠性。
-
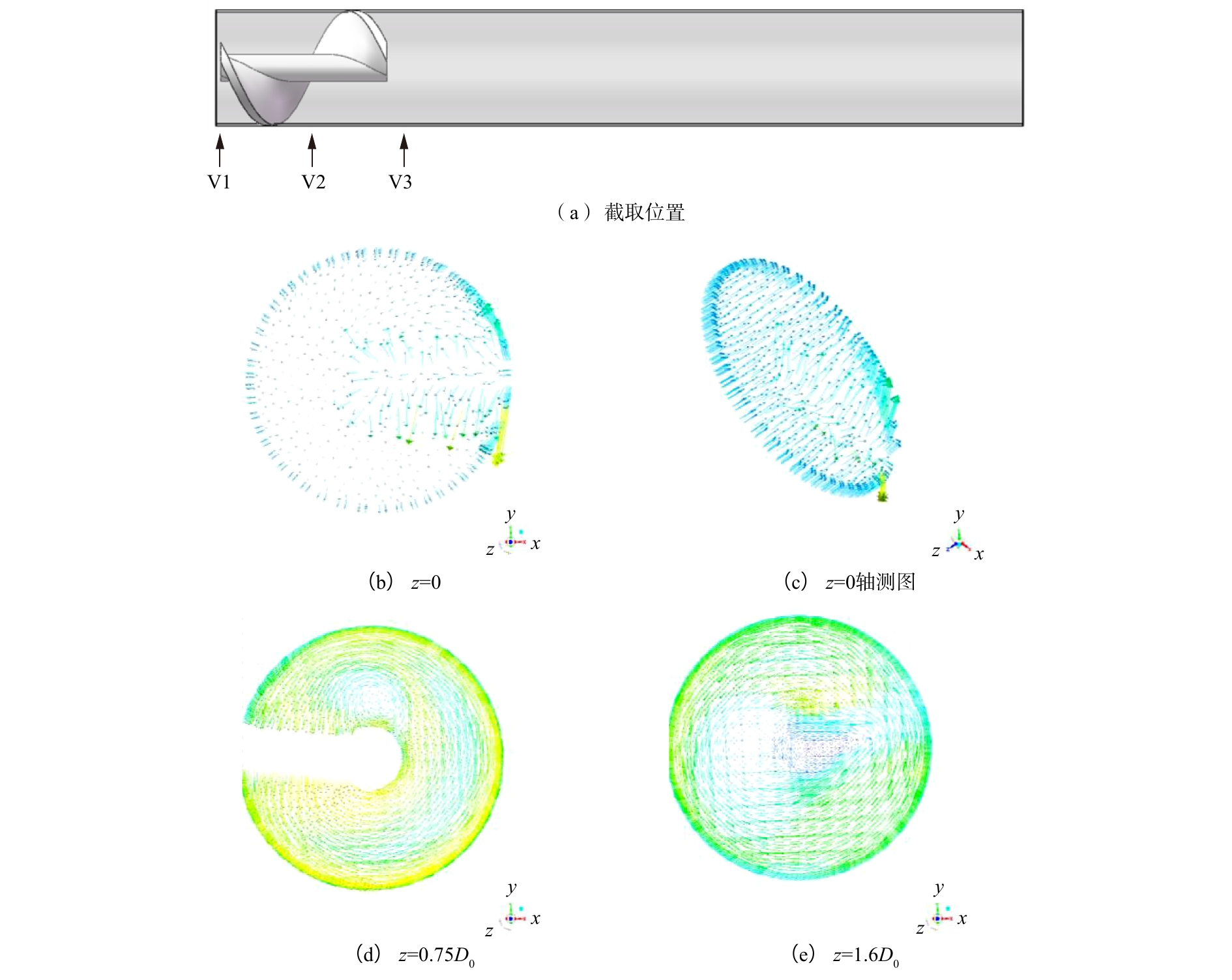
分别截取直径为D0的直管V1(z=0)、V2(z=0.75D0)和V3(z=1.6D0)处的截面,获取截面上的速度矢量图,如图9所示。由图9(b)和图9(c)可知,当流体刚进入直管时,速度方向与轴线方向平行,流体呈水平流动。由图9(d)可知,在管式涡流结构的调控下,流体由水平运动变为旋转运动,且旋转方向与螺旋叶片的旋向一致。并且在接近螺旋叶片处湍动加剧,产生漩涡。由图9(e)可知,流体流过螺旋段后,仍保持旋转运动且伴随着涡的产生,但强度相对于螺旋段有所减弱。由图9综合分析可知,螺旋叶片可以通过自身特殊的几何结构,调控流体运动状态,使流体由水平流动变为螺旋转动。
-
图10反映了颗粒在不同管式涡流结构调控下的运动轨迹。由此可知,3种结构参数不同的管式涡流结构都能调控颗粒做螺旋运动。但不同的结构参数会产生不同的颗粒运动轨迹。螺旋叶片的旋向会调控颗粒螺旋运动的旋向,螺旋叶片的导程会调控颗粒在单位位移下螺旋运动的圈数。推测这是由于螺旋叶片可以调控管内流体的流动形态,产生涡流。颗粒在涡流的作用下,进而也做螺旋运动。不同结构参数的管式涡流结构会产生不同的流体运动状态,进而会导致不同的颗粒运动轨迹。
-
1)不同运动状态的土壤颗粒脱附效果不同,脱附效果由低至高排序为静止<直线运动<螺旋运动。螺旋运动的脱附效果与旋向无关但与运动圈数有关。相同时间下做螺旋运动的圈数越多,颗粒的脱附效果越好。但无论何种运动方式,随着时间的增长,颗粒的脱附效率都会逐渐降低。
2)无论颗粒是做直线运动还是螺旋运动,脱附后颗粒中石油烃污染物均存在浓度梯度。但相对于直线运动,螺旋运动脱附后颗粒中污染物的浓度梯度较小,脱附更为均匀。
3)对于被石油烃完全浸透的单一土壤颗粒而言,颗粒内部油含量要高于表面油含量。且内部油的脱附较表面油更为困难,表面油含量很低时,内部油可能仍然保持较高浓度。
4)通过添加螺旋叶片,可以改变流体的流动形态,产生涡流,进而调控颗粒做螺旋运动。不同结构的螺旋叶片会产生不同的颗粒运动轨迹。螺旋叶片的旋向能够调控颗粒的运动旋向,螺旋叶片的导程能够调控颗粒的运动圈数。
5)通过设置管式涡流结构,能够调控颗粒做螺旋运动。通过运动状态的改变,能够增强土壤颗粒中污染物的脱附。这为今后低耗、高效修复石油烃污染土壤提供了新思路。但仿真模型只考虑到流体与颗粒间的传质作用,未考虑到流体对颗粒的剪切力以及颗粒转动产生的离心力等力的作用影响。后续工作将继续针对模型进行优化,使模拟结果更为精确。
石油烃污染土壤颗粒运动状态与脱附关系数值模拟
CFD numerical simulation of the relationship between particle movement and desorption of petroleum hydro-carbon contaminated soil
-
摘要: 针对土壤中石油烃污染的脱附,采用计算模拟方法对污染土壤颗粒的运动状态与脱附关系进行了研究。结果表明,颗粒中污染物的脱附效果与其运动状态有关,脱附效果由低至高排序为颗粒静止<直线运动<螺旋运动,且颗粒做螺旋运动对污染物的脱附较其他运动状态更为均匀;螺旋运动的脱附效果与旋向无关,但与运动圈数有关,单位时间内螺旋运动的圈数越多,颗粒的脱附效果越好。基于上述结果,设计了一种管式涡流结构以期实现颗粒的螺旋运动,实现了土壤颗粒中石油烃污染物的强化脱附。利用Fluent模拟了不同管式涡流结构的流体流动形态及颗粒运动轨迹,发现螺旋叶片的旋向能够调控颗粒的运动旋向,螺旋叶片的导程能够调控颗粒的运动圈数。Abstract: In this study, the CFD software Fluent was used to study the relationship between the motion status and desorption efficiency of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil particles. The results showed that the pollutant desorption efficiency was related to particle motion status, and the desorption efficiency ranked in ascending order as stationary<linear motion<spiral motion. The desorption effect created by spiral motion status was more evenly around the particle than that by other motions. The desorption effect of particles in spiral motion was independent of the direction of rotation but related to the number of revolving circles. The more the number of turns of spiral motion, the better the desorption effect of particles. Based on these findings, a tube with spiral fans was designed to create the spiral motion of particles to achieve the enhanced desorption of pollutants. Fluent was used to simulate the fluid flow patterns and particle motions trajectory of different spiral structures. It was found that the rotating direction and the lead of the spiral fans could regulate the direction and number of revolving circle of particles, respectively.
-
Key words:
- petroleum hydrocarbons /
- soil particles /
- motion state /
- desorption /
- numerical simulation
-
如果大量含重金属的废水、固废等未经妥善处理直接排入环境,会造成地表水重金属污染[1]。同时,多种重金属复合污染的问题也越来越普遍[2]。重金属进入环境后,会随食物链不断富集,最后通过直接或间接摄入的方式进入人体,引起多种疾病,因而一直受到环保学者的广泛关注[3-4]。重金属不能被降解,只能通过改变其形态或价态的方式来降低其迁移能力和生物有效性。通常,重金属污染水体的治理方法主要有化学沉淀法、氧化还原、生物处理和吸附法[5-7]。随着环保标准越来越严,急切需要更有效的方法来处理重金属复合污染。锌(Zn)、镍(Ni)和铬(Cr)是水体中很常见的重金属污染物。其中,Zn和Ni主要以阳离子的形式存在于水体中,而Cr主要以Cr2O72−、CrO42−等阴离子的形式存在于水体中。对于这些以不同离子形态共存的重金属复合污染水体,其处理难度更大。
零价铁(Fe0或ZVI)具有来源广泛、价格低廉、生态风险小和中等还原性(E0= -0.44V)的特点,已成为环境污染控制和修复的重要材料之一[8-10]。通过还原反应,Fe0可以处理标准电位比其高的重金属,例如Cr(Ⅵ)、Cu(Ⅱ)、Hg(Ⅱ)、Ag(Ⅰ)、As(Ⅴ)和Se(Ⅵ)等[11-14],但对于标准电位与其非常接近的重金属元素(Ni(Ⅱ)或Zn(Ⅱ)),则主要依靠铁腐蚀产物的吸附和共沉淀作用,处理效果都不够理想[9,15]。不管是通过Fe0的直接还原,还是通过铁腐蚀产物的吸附和共沉淀,都必须保证Fe0腐蚀反应的持续进行,从而不断释放电子并且产生新的腐蚀产物。常规的Fe0体系,由于产生的三价铁腐蚀产物覆盖在Fe0表面,抑制了Fe0腐蚀反应的持续进行,从而容易导致Fe0表面钝化,这是限制Fe0技术被广泛应用的关键瓶颈[16]。为了延缓Fe0表面钝化,很多学者提出了不同的方法,如酸洗[17]、超声处理[18]、弱磁场[19]、双金属体系[20]等。TANG等[21-22]通过直接加入或反应生成Fe3O4,形成复合体系Fe0/Fe3O4,可显著提高Fe0对Se(Ⅵ)的还原速率。由于Fe3O4是半导体,不会阻碍电子传递,从而可以持续保持Fe0的活性。同时,利用Fe3O4的磁性,能实现固-液的快速分离。目前,大多数的研究是直接加入Fe3O4或利用化学反应生成Fe3O4。这样做操作比较麻烦,且难以保证只生成Fe3O4,往往是不同铁氧化物/氢氧化物的混合物。如果能通过简单的方法,在Fe0表面只生成Fe3O4,则在实际应用中将更方便。基于上述研究,本研究通过简便方法,原位制备了Fe0/Fe3O4复合体系,并且考察了该体系同时去除Zn2+、Ni2+和Cr(Ⅵ) 3种重金属的效果和机理;通过批处理实验和连续进出水的流化床反应器考察了不同反应条件对复合体系去除这3种重金属的影响;并借助XRD、SEM和XPS,探讨了对不同金属的去除机理。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验试剂
还原铁粉(98%)(100目和400目)、锌标样、镍标样、铬标样、乙酸铵、乙酸、氯化锌(ZnCl2)、氯化镍、重铬酸钾、氯化亚铁、盐酸、硝酸、邻菲罗啉等试剂均为分析纯;溶液配制及材料制备均采用去离子水。
1.2 实验方法
1)批处理实验。称取0.15 g和0.25 g的铁粉置于20 mL血清瓶中,再加入14 mL去离子水和1 mL FeCl2储备液,此时反应瓶内顶部还有一定体积的空气,再密封后将反应瓶置于360°旋转的木箱中,以30 r·min−1的转速开始反应一定时间。预处理完成后,再用微量注射器加入300 μL的Zn2+、Ni2+和Cr(Ⅵ)的混合储备液,得到10 mg·L−1的Ni2+和Zn2+以及不同浓度的Cr(Ⅵ),再将反应瓶放入旋转箱中反应并开始计时,在预定时间每次取出2个反应瓶作为重复,打开塞子后先测定溶液pH,再经0.45 μm滤膜过滤,收集滤液测定Fe2+和重金属离子的浓度。在Fe2+的样品中加入2滴3 mol·L−1的HCl酸化保存待测。其余滤液加入1滴3 mol·L−1HNO3保存,待测金属离子。采用准一级(式(1))、准二级(式(2))动力学方程拟合各重金属去除情况。
ln(qe−qt)=lnqe−k1t (1) tqt=1k2qe2+1qet (2) 式中:
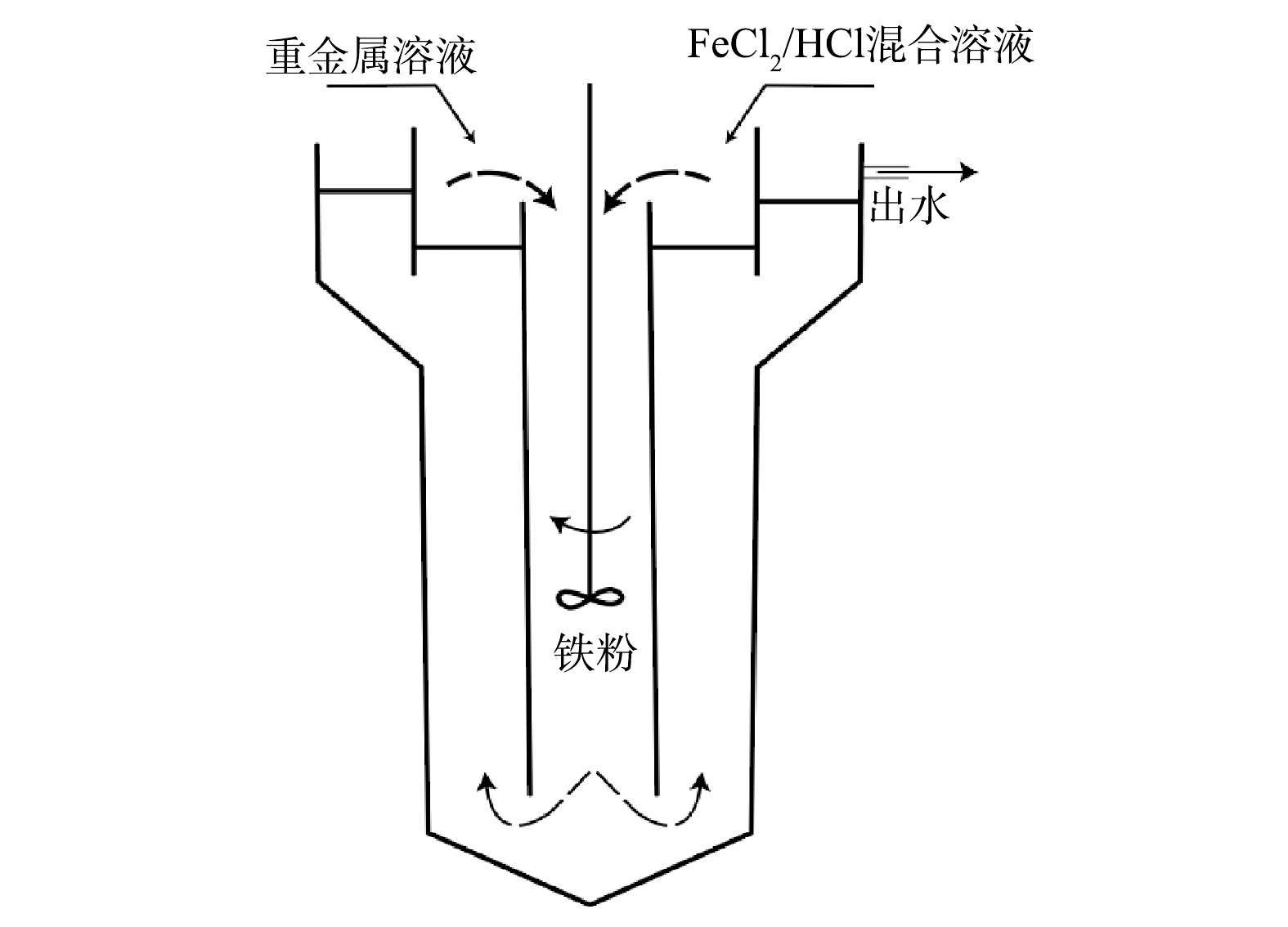
qe qt k1 k2 2)流化床反应器实验。使用纯水配制50 mmol·L−1FeCl2和30 mmol·L−1HCl混合液,进水中Zn、Ni和Cr的质量浓度均为10 mg·L−1。4个流化床反应器的操作条件见表1,流化床反应器的示意图见图1。通过可调式电子机械搅拌器搅动溶液,使铁粉悬浮于溶液中,防止铁粉沉积到反应器底部。反应器的有效体积为11.5 L。与批处理实验类似,流化床反应器也需经过预处理,先制备Fe0/Fe3O4复合体系。预处理过程中,只添加不同的氧化剂,反应2~3 d完成预处理,后再通入重金属模拟废水。模拟废水用自来水配置,为防止重金属沉淀,先用HCl将溶液pH调为7.0,再加入重金属试剂,采用连续进出水的方式运行。在反应区反应后,通过溢流口排出,固体会自动下沉流入反应区,从而保证出水所含悬浮物少,减少铁粉的流失。
表 1 不同流化床反应器的操作参数Table 1. Operation parameters of different fluidized bed reactors条件反应器 铁粉粒径/目 铁粉浓度/(g·L−1) 预处理氧化剂 预处理氧化剂浓度/(mg·L−1) 水力停留时间/h 搅拌器转速/(r·min−1) A 400 50 K2Cr2O7 20 5 700 B 400 70 K2Cr2O7 20 5 700 C 400 50 DO(曝气) / 5 700 D 400 50 KNO3 20 5 700 1.3 分析方法
采用原子吸收光谱(PerkinElmer 900T)测定滤液中的Zn2+、Ni2+和总Cr;采用二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法测定Cr(Ⅵ);采用邻菲啰啉分光光度法(紫外可见光度计,TU-1810,北京普析)在波长510 nm测定Fe2+浓度。文中的结果均为2个平行样。
在制备SEM样品时,按照批处理实验的条件,反应后分离固液,将固体在高纯氮气保护下干燥,再用SEM(日本电子,JSM-7500F)分析。在制备XPS样品时,为了增大待测元素的含量,所加入的各重金属浓度比实验高1倍,其它反应物均相应提高1倍。反应一定时间后,通过超声处理将铁腐蚀物从铁粉表面剥落下来,再过滤分离腐蚀物,通过连续吹入高纯氮气风干样品用于XPS(日本岛津,AXIS Supra)分析。XPS采用单色铝Kα X射线(hv=1 486.6 eV),管电压15 kV,管电流12 mA,功率180 W,步长为0.05 eV,分析Ni和Cr反应前后的价态变化,以C1s 284.5 eV校正结合能,采用XPSPEAK4.1软件分析结果。在制备XRD样品时,与批处理反应条件完全一样,而且反应后,无需任何处理,直接将铁粉分离,然后在高纯氮气气流下干燥,用于XRD分析(日本理学,Ultima IV)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 材料表征
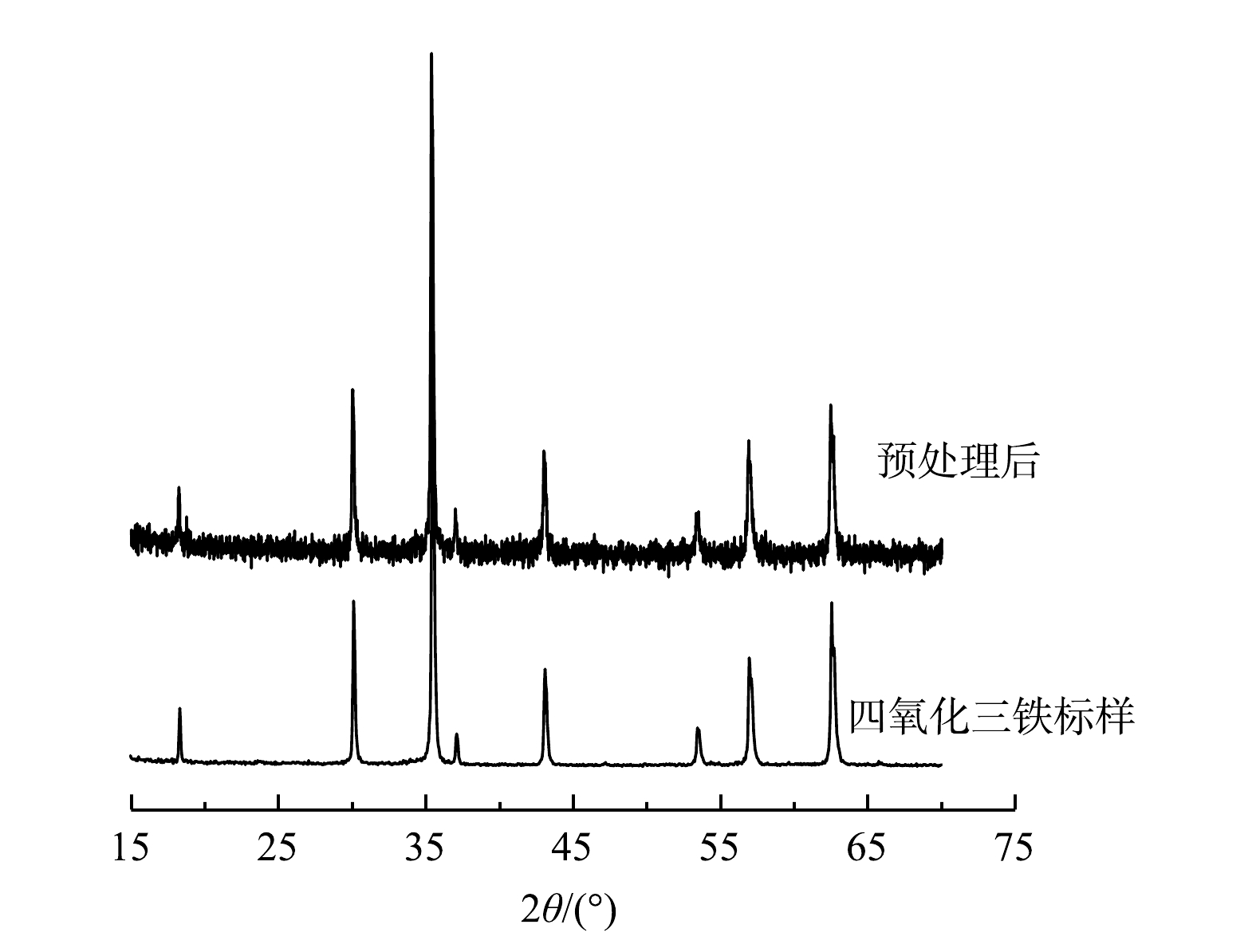
由图2可看出,复合体系的谱图与Fe3O4标样完全一致。这与SU等[23]制成的纳米Fe3O4峰形一致,表明预处理后,在铁表面形成了晶型完好且纯度很高的Fe3O4,没有其它晶态铁氧化物或氢氧化物峰。这说明,该预处理方法可以在Fe0表面生成了一层晶相单一的Fe3O4,形成了Fe0/Fe3O4复合体系。由图3可看出,反应前的铁粉表面光滑,铁粉颗粒不规则(图3(a))。这与前人的研究观察现象一致[24]。在厌氧条件下反应后,铁表面由于发生反应而变得粗糙,而且有一些白色的小点,可能是沉淀的重金属离子。由于没有强氧化剂的参与,铁腐蚀反应很慢,产生的腐蚀产物也很少(图3(b))。如图3(c)所示,在预处理后复合体系中铁腐蚀产物的表面有很多颗粒状和片状的晶体。这些晶体的形貌与Fe3O4(图3(d))的晶体形态非常相似[21]。WU等[25]经过酸预处理,反应后的铁腐蚀物主要是棒状和片状。这也再次证明腐蚀产物主要是Fe3O4,与图2中的XRD的结果吻合。由此可见,通过预处理可在Fe0表面形成一层晶型完好的Fe3O4。
2.2 Fe0/Fe3O4去除复合重金属的批处理实验
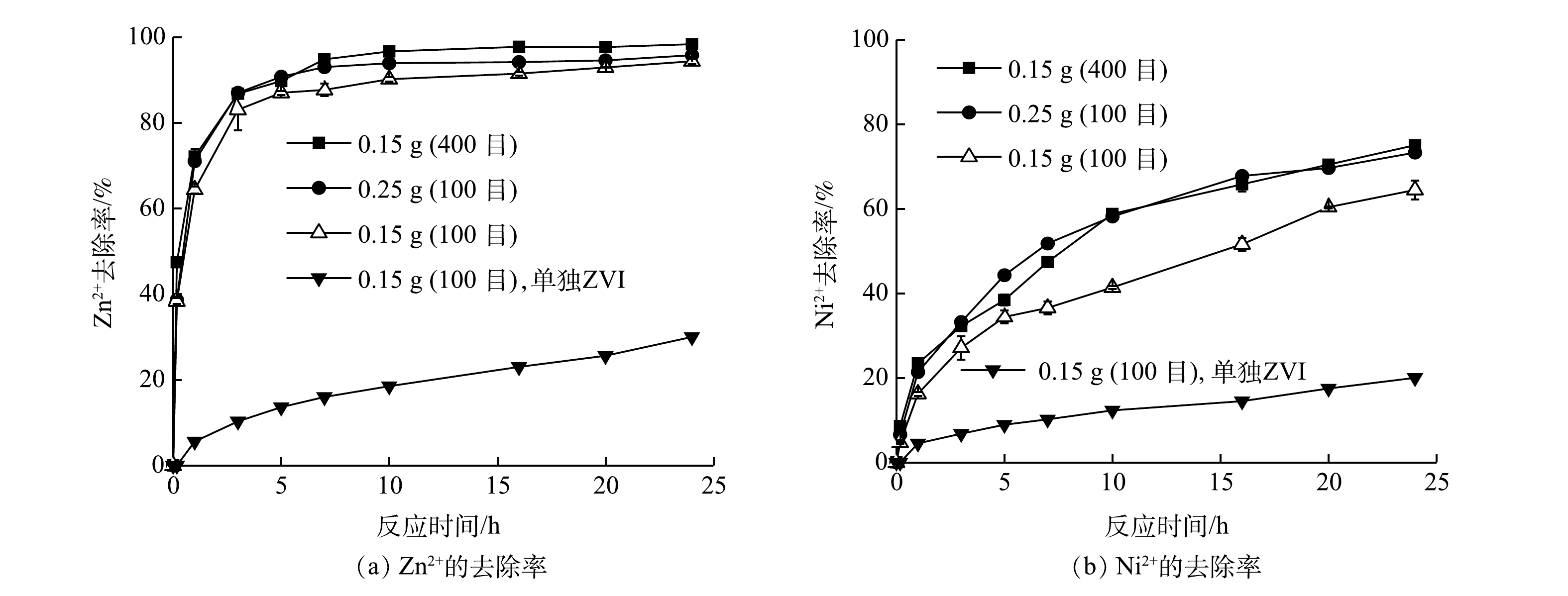
1)不同铁粉用量和不同铁粉粒径的影响。为了评估Fe0/Fe3O4的活性,对Fe0/Fe3O4与Fe0处理Zn2+和Ni2+的效果进行了比较,结果见图4。显然,Fe0/Fe3O4的活性远高于Fe0。在相同铁粉用量下,反应24 h后,Fe0对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除率分别只有31%和20%;而Fe0/Fe3O4对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除率分别为93%和62%。因此,后续的实验只考察Fe0/Fe3O4在不同条件下对复合重金属离子的去除效果。
通常,铁粉粒径越小或铁粉用量越大,均会促进Fe0对污染物的去除[26]。由图4可以看出,随着铁粉粒径减小或铁粉用量的增加,Fe0/Fe3O4去除Ni2+和Zn2+的效率均升高。当加入0.15 g 100目的铁粉时,反应24 h以后,Zn2+的去除率为93%,而Ni2+去除率为62%。当铁粉用量增加到0.25 g或铁粉用量不变而粒径减小为400目时,Zn2+的去除率分别提高到95%和98%,而Ni2+去除率均约为70%。增加铁粉用量或减小铁粉粒径均可增加铁粉表面活性位点[24],从而提高反应速率。在相同条件下,Zn2+的去除率明显高于Ni2+,说明Zn2+更容易被吸附。由于Zn的标准电位(-0.76 V)比Fe(-0.44 V)低,Fe0不可能将Zn2+还原,只能通过铁腐蚀产物的吸附和共沉淀来去除。前人在研究微米或纳米Fe0处理Zn2+的过程中,也认为吸附和共沉淀是其去除机理[27-28]。由于Fe3O4的导电性,不会钝化铁表面,从而使铁腐蚀反应能够持续进行,不断产生新的铁腐蚀产物,从而能够持续地去除Ni2+和Zn2+。
2)预处理时,不同Fe2+浓度对重金属去除的影响。在Fe0预处理的时候,利用反应瓶溶液中的溶解氧(来自瓶中顶部空气中的氧气)作为氧化剂,借助溶液中的Fe2+,通过一系列化学反应在铁表面形成一层Fe3O4膜,从而得到Fe0/Fe3O4复合体系。因此,在预处理的时候,氧气和Fe2+的量都可能改变复合体系中Fe3O4的量,从而改变后续的反应速率。同时,Fe2+与Zn2+和Ni2+的价态一样、离子半径也相似,可能会对其吸附产生抑制作用。因此,预处理的时候,分别加入0.5、1.0和2.0 mmol·L−1Fe2+,考察其对不同重金属去除的影响。由图5(a)可知,预处理以后,溶液中还保留了大量的溶解态Fe2+。起始加入0.5、1.0和2.0 mmol·L−1 Fe2+,预处理后,分别检测到0.37、0.71和1.8 mmol·L−1溶解态的Fe2+。这表明在预处理阶段,只要少量的Fe2+就可以完成预处理。与重金属混合液反应后,Fe2+浓度逐渐升高,在前2 h内增加最快,随后逐渐减慢并趋于稳定。这说明,在反应过程中,伴随重金属的去除,可以释放出Fe2+。其中,Zn2+不可能与Fe0发生置换反应,只有Ni2+有可能被Fe0还原,释放等量的Fe2+[29-30]。但也有研究认为,当Zn2+吸附到铁腐蚀产物表面后,会通过水解过程释放等量的H+,这些H+再与Fe0反应,释放出与Zn2+等量的Fe2+[31]。由图5(b)、图5(c)可知,体系中过多的Fe2+会抑制Fe0/Fe3O4对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除,尤其对Ni2+的去除抑制作用更明显。当Fe2+起始浓度为0.5 mmol·L−1和1.0 mmol·L−1时,对Zn2+的去除影响不大,反应24 h以后,去除率均在90%左右;但当Fe2+起始浓度增加到2.0 mmol·L−1,在反应前8 h内,Zn2+去除速率最慢,但在24 h以后,去除率与其它Fe2+浓度的相当。这说明Fe2+对Zn2+去除的影响比较小,对于低浓度的Fe2+(≤2.0 mmol·L−1),可以忽略其影响。但对于Ni2+的去除,Fe2+的抑制作用非常明显,随着其浓度的增加,其抑制作用则增强。当预处理Fe2+为0.5 mmol·L−1时,Ni2+的去除效果最高,可以达到77%;但当Fe2+初始浓度分别为1.0 mmol·L−1和2.0 mmol·L−1时,Ni2+去除率分别只有65.48%和48.85%。这可能归因于以下2点:一是由于过多的Fe2+会抑制Fe0与Ni2+的置换反应(Fe0 + Ni2+→ Fe2+ + Ni0),从而不利于Ni2+的去除;二是由于Ni2+在铁氧化物表面的吸附能力比Zn2+和Fe2+差。
3)不同Cr(Ⅵ)浓度对Zn2+和Ni2+去除的影响。Cr(Ⅵ)是环境中很常见的重金属污染物,常与Zn2+和Ni2+等重金属共存于污染水体中。Cr(Ⅵ)的水溶性好,迁移能力很强,容易被生物利用。图6是不同浓度的Cr(Ⅵ)对Zn2+和Ni2+去除的影响。相比于不加Cr(Ⅵ)的体系,低浓度(10 mg·L−1)的Cr(Ⅵ)会显著促进Ni2+和Zn2+的去除,反应24 h后,Zn2+的去除率达到92%,Ni2+的去除率达到67.5%。但随Cr(Ⅵ)浓度的升高,其促进作用不明显,甚至在反应开始后的最初几个小时,反而抑制了Ni2+和Zn2+的去除,直到24 h后,Cr(Ⅵ)对Ni2+和Zn2+的去除最终表现为促进作用,且促进作用较小。Cr(Ⅵ)影响Zn2+和Ni2+去除的原因主要有2点:一是由于Cr(Ⅵ)的还原也会消耗Fe2+,从而减少了Fe2+的竞争吸附作用,有助于Zn2+和Ni2+的去除;二是由于Cr(Ⅵ)被还原为Cr(Ⅲ)后,与Fe(Ⅲ)形成共沉淀FexCr1-x(OH)3,附在Fe0表面,抑制了电子传递和Fe0的腐蚀反应,从而不利于Ni2+和Zn2+的去除[32-33]。相比于Zn2+和Ni2+,Cr(Ⅵ)在很短的时间内就被快速去除(图6(c))。这说明Fe0/Fe3O4可以快速去除Cr(Ⅵ)。对于相对低浓度的Cr(Ⅵ)与Zn2+和Ni2+共存时,Fe0/Fe3O4可以同时快速地去除3种重金属,但当Cr(Ⅵ)浓度过高时,只能有效地去除Cr(Ⅵ),而对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除效果并不理想。
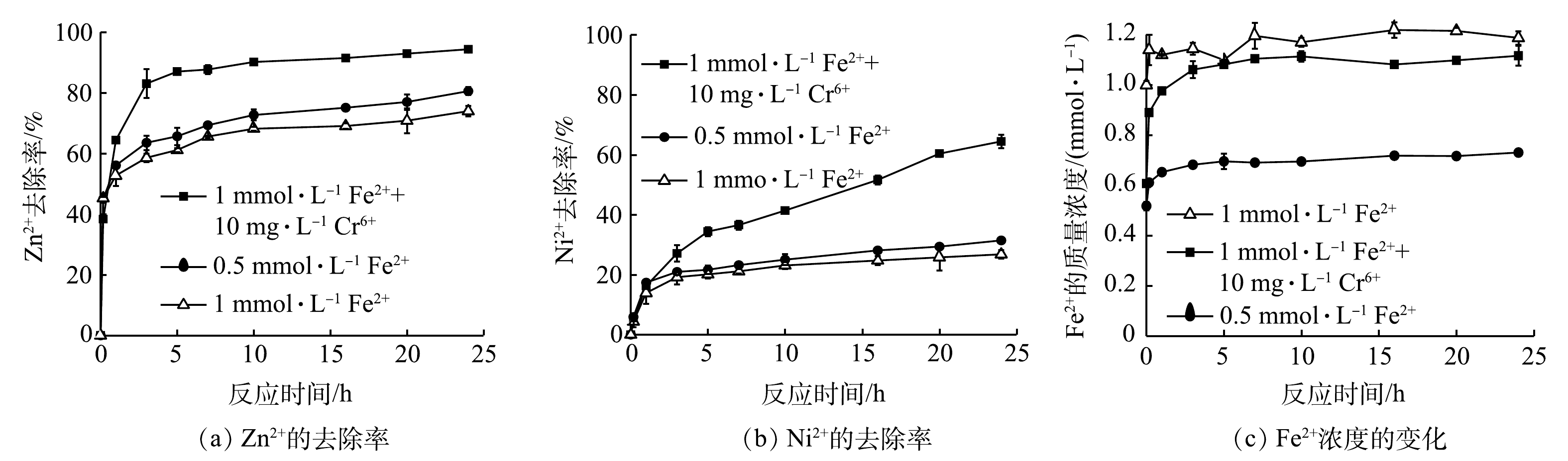
4)不同Fe2+预处理及其与Cr(Ⅵ)共存时对重金属去除的影响。根据以上结果,在预处理中,过高浓度的Fe2+不利于后续对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除。而低浓度的Cr(Ⅵ)会显著促进对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除。因此,单独考察了在预处理过程中加入不同初始浓度的Fe2+以及同时加入Fe2+和Cr(Ⅵ)对Fe0/Fe3O4去除Zn2+和Ni2+的影响。如图7所示,不加Cr(Ⅵ)时,预处理Fe2+浓度升高,不利于后续Zn2+和Ni2+的去除。这与前面的结果一致。在相同条件下,加入10 mg·L−1Cr(Ⅵ)后, Zn2+的去除率由74%提高到94%。Fe2+增加不利于Ni2+的去除,但在加入Cr(Ⅵ)后,Ni2+的去除率由26%提高到65%。加入Cr(Ⅵ)会消耗部分Fe2+,这也是其促进作用的原因之一。此外,有研究[34]表明,Fe(Ⅲ)与Cr(Ⅵ)还原产生的Cr(Ⅲ)形成CrxFe1-x(OH)3,该产物具有很好的混凝沉淀效果,能够吸附去除重金属离子。但是,产生的CrxFe1-x(OH)3覆盖在铁表面,由于其导电性差,不利于后续铁腐蚀反应的进行,因而对Ni2+和Zn2+的去除产生不利的影响。因此,Cr(Ⅵ)对Ni2+和Zn2+去除会受到Cr(Ⅵ)浓度变化的影响。
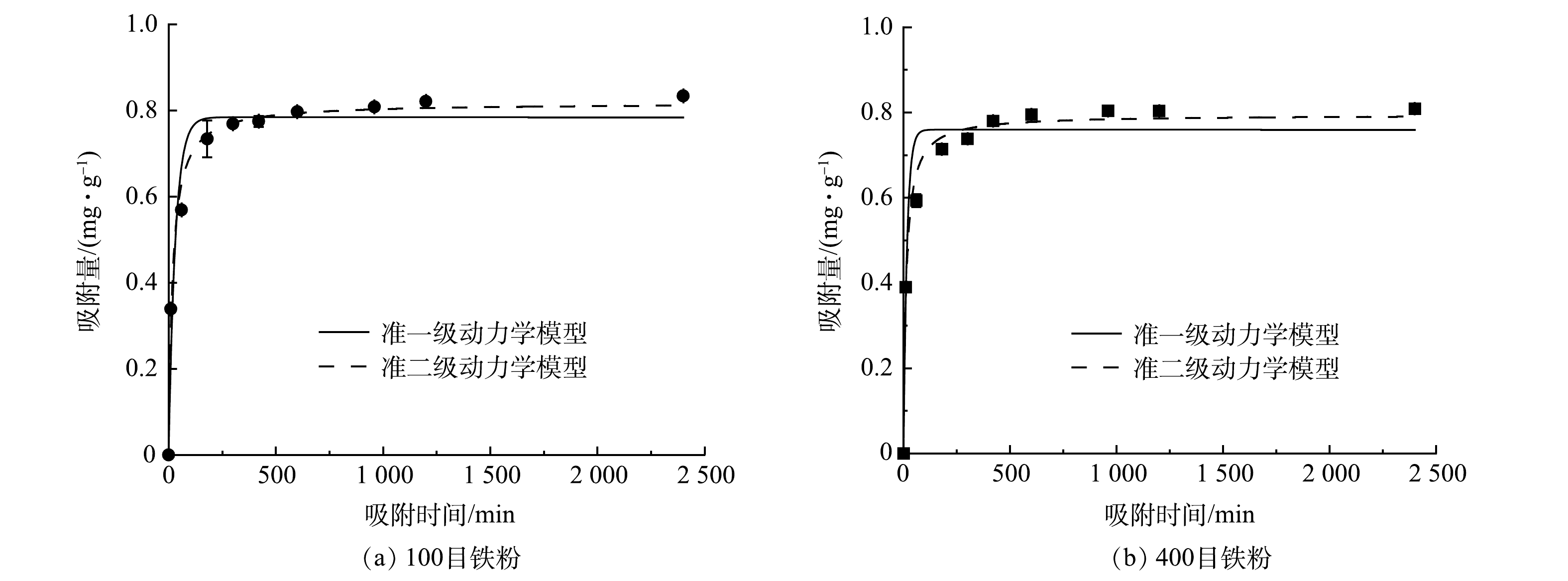
2.3 吸附动力学
对所获得的实验结果分别用准一级动力学和准二级动力学模型进行了拟合。由图8可看出,不论哪种粒径的铁粉,对于Zn2+的去除,反应前10 min均非常迅速,很快就达到平衡。如图9所示,Ni2+的去除速率在反应初期慢很多,平衡吸附量也比Zn2+低。这说明Fe0对Zn2+的吸附性能要明显优于Ni2+。由表2可见,准二级动力学模型的可决系数R2要稍微优于准一级动力学模型,说明Fe0/Fe3O4对Zn2+和Ni2+的吸附更符合准二级动力学模型。这也表明在整个吸附过程中,化学吸附占主导地位。这与Fe0去除Zn2+和Ni2+的结论一致[35- 36]。
表 2 吸附动力学拟合参数Table 2. Adsorption kinetics fitting parameters重金属 铁粉粒径/目 准一级动力学 准二级动力学 qe/(mg·g−1) K1/(min−1) R2 qe/(mg·g−1) K2/(mg·(g·min)−1) R2 Zn 100 0.784 0.031 0.951 0.817 0.067 0.989 400 0.759 0.061 0.944 0.794 0.098 0.986 Ni 100 0.570 0.002 0.959 0.673 0.004 0.978 400 0.694 0.002 0.962 0.807 0.004 0.975 2.4 Fe0/Fe3O4流化床反应器去除复合重金属
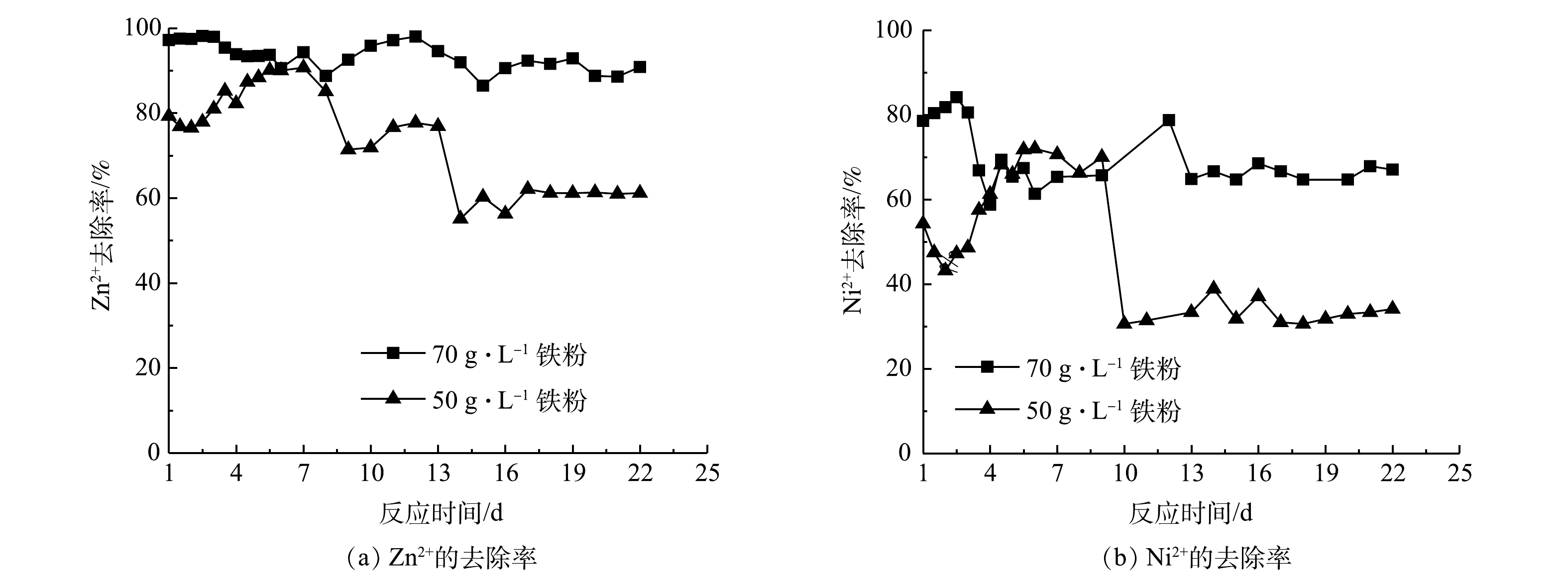
1)不同铁粉浓度对复合重金属去除的影响。从前面的批处理实验结果可知,Fe0/Fe3O4是一个高活性的系统,可以持续有效地去除Zn2+、Ni2+。由图10可见,以K2Cr2O7作为预处理剂,当铁粉质量浓度从50 g·L−1提升到70 g·L−1时,Zn2+和Ni2+的去除率随之升高。当铁粉质量浓度70 g·L−1时,在22 d的运行时间内,Zn2+的去除率基本维持在90%左右,而Ni2+的去除率虽然波动较大,仍可维持在68%左右。但当铁粉质量浓度降到50 g·L−1时,在前7 d,Zn2+的去除率在80%~90%,然后逐渐降低,15 d以后,维持在62%;在第6~9天,Ni2+的去除率保持在70%左右,随后快速降低到30%左右,并一直保持到第22天。增加铁粉用量,单位体积内有更多的铁表面活性点位吸附Ni2+和Zn2+,其去除效果更好。这也与前面的批处理实验结果一致。对于50 g·L−1的铁粉用量,在起始阶段,其去除率就比70 g·L−1的铁粉用量下低,虽然随后差距缩小,但十几天以后,去除率远低于70 g·L−1。这可能是由于:在初始阶段,铁粉腐蚀产物的不断增加,减小了低浓度铁粉带来的影响;但是随着铁粉的不断消耗,产生的腐蚀产物越来越少,其处理效率也很快降低,但由于Zn2+和Ni2+的浓度不高(10 mg·L−1),因而依然可以保持相对稳定的去除效果。这说明50 g·L−1的铁粉用量过少,难以维持持续、有效的处理效果,最好要保持70 g·L−1或更高的铁粉质量浓度。对于Cr(Ⅵ)的处理效果,与前面批处理的结果一致,很快就被去除完全,因此,这里没有给出其结果。
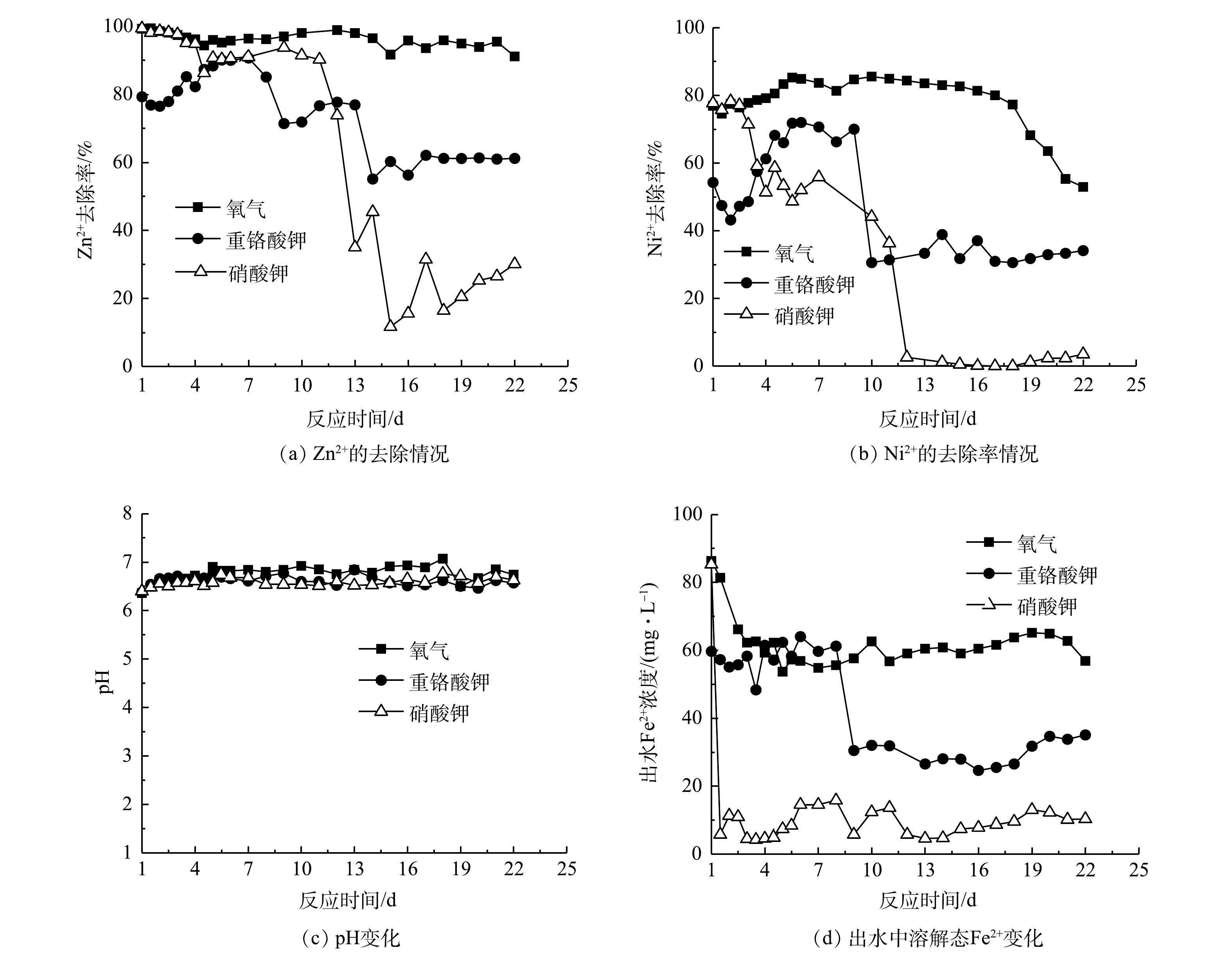
2)不同氧化剂对复合重金属去除的影响。在预处理阶段,加入氧化剂才能生成复合体系。因此,比较了不同氧化剂(氧气、硝酸盐和重铬酸钾)对复合体系活性的影响,结果如图11所示。以氧气(空气)预处理制备的复合体系对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除率最高。连续运行22 d,Zn2+的去除效果一直可以保持在90%以上,而Ni2+的去除率在前18 d可稳定在在80%左右,随后去除率逐渐降低,到第22天的时候,只有50%。以重铬酸钾预处理时,在第一周内,Zn2+和Ni2+的去除效果持续升高,最高分别达到91%和72%,但随后又不断下降,尤其是Ni2+,在第10天的时候,去除率快速下降到~30%。以硝酸钾作为预处理剂,Ni2+和Zn2+的处理效果最差。在前10 d,对Zn2+的去除效果保持在90%左右,随后去除效果快速降低,而且不稳定。而对于Ni2+的去除,从一开始就持续下降,12 d以后,几乎没有去除。从3种体系中的pH来看,并没有明显差别(图11(c))。在3种氧化剂预处理体系中,Fe2+的浓度差别较大(图11(d))。在氧气体系中,Ni2+和Zn2+的去除效果最好,所以Fe2+的浓度一直最高;而另外2个反应器中的Fe2+最低,尤其是硝酸钾预处理的反应器,出水中的Fe2+仅有5 mg·L−1左右。与批处理实验的结果相似,出水中都没有检测到溶解态的Cr(Ⅵ)。这说明复合体系对Cr(Ⅵ)的处理效果有保障。总体而言,以氧气作为预处理剂的效果最好,其次是用重铬酸钾和硝酸钾的预处理。
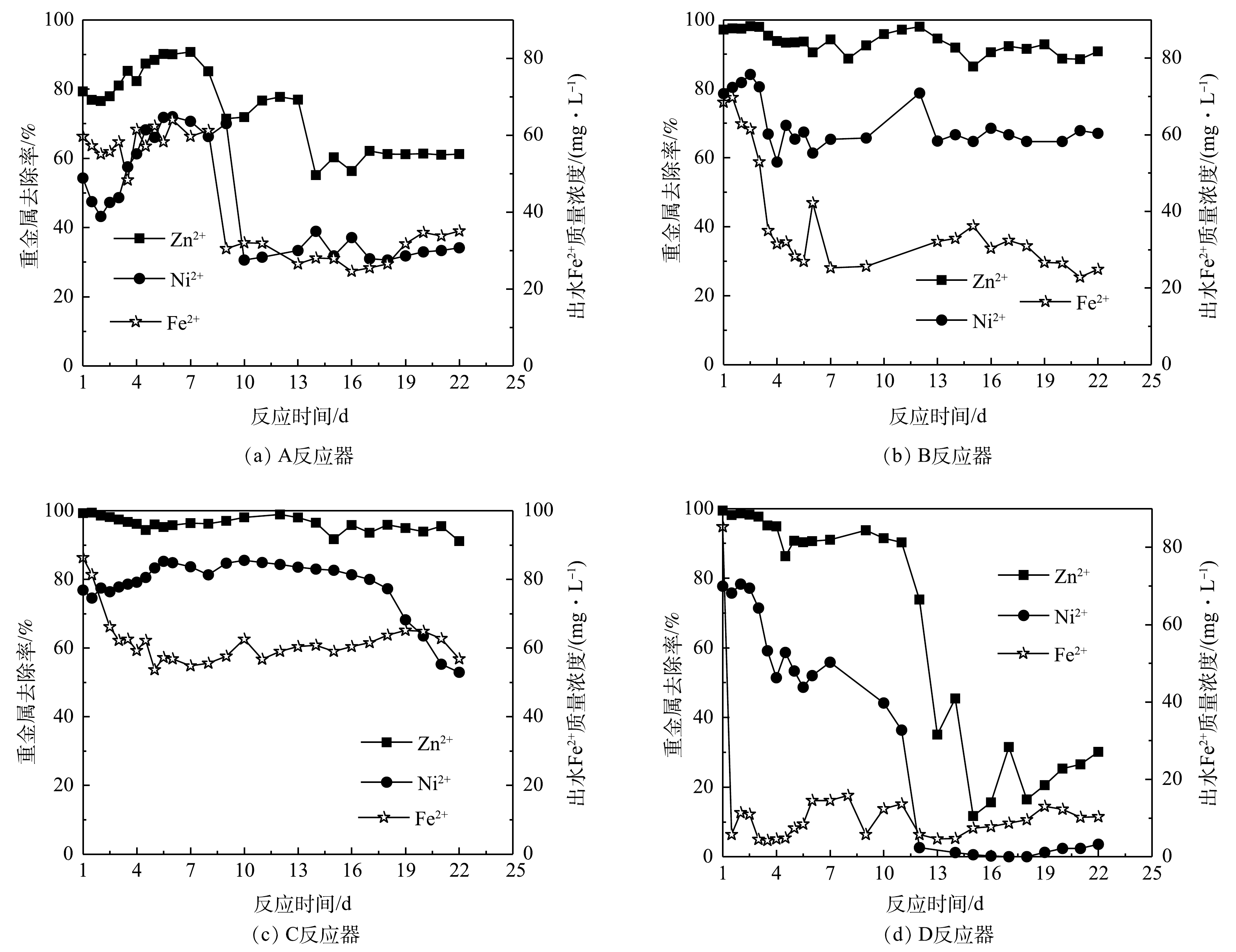
3)4个反应器去除复合重金属的效果比较。图12展示了4个流化床反应器对Zn2+和Ni2+的处理效果。各流化床反应器的操作条件见表1。其中,由于4个反应器的出水中都未检测到溶解态的Cr(Ⅵ),故未提供其数据。由图12可看出,反应器C对Zn2+和Ni2+的处理效果最好,Zn2+的去除率都维持在90%以上;Ni2+在前17 d的去除率一直保持在80%左右,随后不断下降,到第22天,去除率降到50%。其次是反应器B,对Zn2+的去除效果基本保持在90%左右,尽管Ni2+的去除率在开始阶段波动很大,但运行7 d后也可稳定在68%左右。C反应器出水中的Fe2+浓度最高,这说明在Zn2+和Ni2+去除的同时释放出Fe2+,与前文的实验结果一致。尽管C反应器(50 g·L−1)的铁粉质量浓度比B反应器(70 g·L−1)低,但C反应器的处理效果最好,这说明以氧气作为预处理剂制备的复合体系活性最强。A反应器在前9 d对Ni2+和Zn2+的去除率较高,但随后快速下降,Fe2+浓度的变化趋势类似。D反应器的处理效果最差,不管是Zn2+还是Ni2+,去除率很快下降。综上所述,复合体系对Zn2+的去除效果要远远好于Ni2+,这与批处理实验的结果一致。4个反应器的Fe2+出水浓度与Ni2+和Zn2+的变化趋势一致。出水中的Fe2+浓度越高,Ni2+和Zn2+的去除效果也越好。这说明Ni2+和Zn2+的去除过程中,会直接或间接影响产生Fe2+。
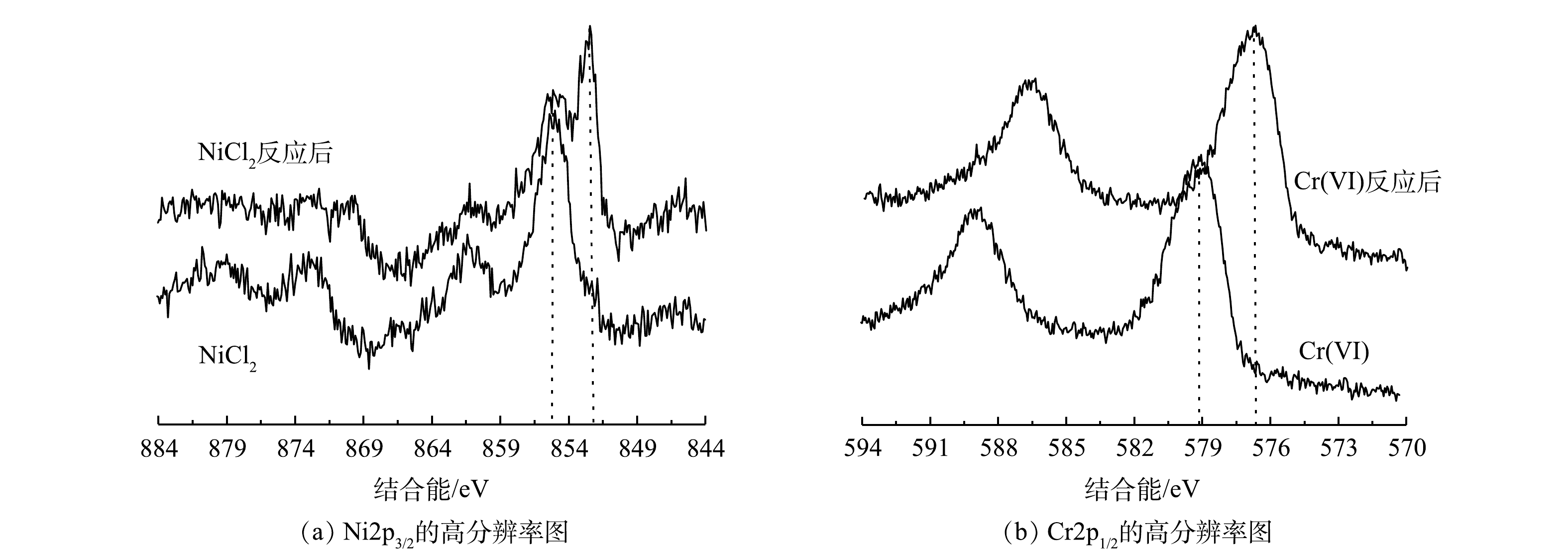
4)重金属去除机理分析。批处理和流化床实验的结果均说明Fe0/Fe3O4具有很强的活性,可以持续地去除Cr(Ⅵ)、Zn2+和Ni2+。对三者的处理速率为Cr(Ⅵ)>Zn2+>Ni2+。在很短的时间内Cr(Ⅵ)就可以被快速去除。根据3种重金属和Fe0的标准电位,可以从理论上判断不同重金属的去除机理。根据Zn和Ni的标准电位,Fe0不可能还原Zn2+,只能通过铁腐蚀产物的吸附和共沉淀去除。Ni2+的标准电位稍微高于Fe0,其氧化还原反应的驱动力很小,还原反应的速率很慢,也可能不会发生氧化还原反应。Cr(Ⅵ)的标准电位为1.33V,远高于Fe0,因此,很容易被Fe2+和Fe0还原。为确定Cr(Ⅵ)和Ni2+的去除机理,通过XPS对反应前后Cr和Ni的价态进行了分析,结果如图13所示。反应前,Ni2+的2p3/2结合能在856.5 eV(图13(a)),反应后在852.6 eV处出现1个尖峰,归属于单质镍,856.5 eV处的峰变弱。这说明部分Ni2+被还原为Ni0,部分Ni(Ⅱ)可能是被吸附或共沉淀。在纳米Fe0去除Ni2+的过程中,也存在部分还原和部分吸附的现象[37-38]。由图13(b)可见,反应后Cr(Ⅵ)的2p1/2峰(579.2 eV)消失,而在577.1 eV处出现1个几乎相同的峰,可归于Cr(Ⅲ),说明Cr(Ⅵ)全部被还原为Cr(Ⅲ)。已有的研究[39-40]也表明Fe0可以有效地还原Cr(Ⅵ)为Cr(Ⅲ)。
3. 结论
1)经过预处理后,在Fe0表面生成一层晶型完好、晶相单一的Fe3O4。复合体系的活性远高于单独的Fe0,显著提高其对Zn2+、Ni2+和Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率。
2)增加铁粉用量或减小铁粉粒径均可提高对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除效果。Fe2+浓度升高对Fe0/Fe3O4去除Zn2+的影响不大,但会明显抑制对Ni2+的去除。10 mg·L−1Cr(Ⅵ)会促进Fe0/Fe3O4对Zn2+和Ni2+的去除,但过多的Cr(Ⅵ)由于与Fe(Ⅲ)共沉淀覆盖在Fe0表面,不利于铁腐蚀反应的进行,从而大大降低其促进作用。无论是改变铁粉用量、铁粉粒径、Fe2+或Cr(Ⅵ)浓度,还是预处理氧化剂的不同,对Cr(Ⅵ)的处理效果最好,其次是Zn2+和Ni2+。
3)在流化床反应器中,Fe0/Fe3O4可有效去除Zn2+、Ni2+和Cr(Ⅵ),增加铁粉用量可提高Zn2+和Ni2+的去除效果。相比于重铬酸钾和硝酸钾,以空气作为预处理辅助剂,制备的复合体系活性最强,能持续、有效地去除Zn2+和Ni2+。
4)在Fe0/Fe3O4中,Ni2+的去除机理为部分还原为单质镍、部分吸附或共沉淀,而Cr(Ⅵ)全部被还原为Cr(Ⅲ)。
-
表 1 湍流模型比较
Table 1. Comparison of turbulence models
湍流模型 适用范围 标准k-ε模型 完全湍流的流动过程模拟,计算量小 重整化群k-ε两方程模型 强流线弯曲、漩涡和旋转等,计算量大 可实现型k-ε模型 旋转均匀剪切流,自由流(射流和混合层),腔道流动和边界层流动等,计算量大 表 2 管式涡流结构形式
Table 2. Tube vortex structure
序号 叶片旋向 叶片导程/mm 1 左旋 37.5 2 右旋 37.5 3 左旋 18.75 -
[1] BUZMAKOV S, EGOROVA D, GATINA E. Effects of crude oil contamination on soils of the Ural region[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2019, 19(1): 38-48. doi: 10.1007/s11368-018-2025-0 [2] KHODARY S M, NEGM A M, TAWFIK A. Geotechnical properties of the soils contaminated with oils, landfill leachate, and fertilizers[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 11(2): 13-29. doi: 10.1007/s12517-017-3372-7 [3] ZHU H, GAO Y, LI D. Germination of grass species in soil affected by crude oil contamination[J]. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 2018, 20(6): 567-573. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2017.1405376 [4] MULLAKAEV M S, VEXLER G B, MULLAKAEV R M. Sonochemical technology for separating oil sludge and oil-contaminated soil[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2018, 36(8): 604-608. doi: 10.1080/10916466.2018.1440297 [5] EGAZAR'YANTS S, VINOKUROV V, VUTOLKINA A, et al. Oil sludge treatment processes[J]. Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, 2015, 51(5): 506-515. doi: 10.1007/s10553-015-0632-7 [6] LIU C, ZHANG Y, SUN S, et al. Oil recovery from tank bottom sludge using rhamnolipids[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 170: 14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.031 [7] GITIPOUR S, HEDAYATI M, MADADIAN E. Soil washing for reduction of aromatic and aliphatic contaminants in soil[J]. Clean-Soil Air Water, 2015, 43(10): 1419-1425. doi: 10.1002/clen.v43.10 [8] LI G, GUO S, HU J. The influence of clay minerals and surfactants on hydrocarbon removal during the washing of petroleum-contaminated soil[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 286: 191-197. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.006 [9] WU H, SUN L, WANG H, et al. Persulfate oxidation for the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 2016, 25(2): 851-857. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/60857 [10] CHEN K, CHANG Y, CHIOU W. Remediation of diesel-contaminated soil using in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) and the effects of common oxidants on the indigenous microbial community: A comparison study[J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2016, 91(6): 1877-1888. doi: 10.1002/jctb.2016.91.issue-6 [11] 李婷婷, 郭书海, 王加宁, 等. 周期切换电极极性对电动-微生物修复石油污染土壤的影响[J]. 环境工程, 2016, 34(1): 159-163. [12] LOMZA P, POSZYTEK K, SKLODOWSKA A, et al. Evaluation of bioremediation of soil highly contaminated by petroleum hydrocarbons[J]. New Biotechnology, 2016, 33: 141. [13] 张秀霞, 滕芝, 吴佳东. 生物强化修复石油污染土壤[J]. 环境工程学报, 2013, 7(4): 1573-1577. [14] FENG D, LORENZEN L, ALDRICH C, et al. Ex situ diesel contaminated soil washing with mechanical methods[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2001, 14(9): 1093-1100. doi: 10.1016/S0892-6875(01)00114-5 [15] SON Y, CHA J, LIM M, et al. Comparison of ultrasonic and conventional mechanical soil-washing processes for diesel-contaminated sand[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(4): 2400-2407. doi: 10.1021/ie1016688 [16] 刘珑, 王殿生, 曾秋孙, 等. 微波修复石油污染土壤升温特性影响因素的实验研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2011, 5(4): 898-902. [17] GAO Y, DING R, WU S, et al. Influence of ultrasonic waves on the removal of different oil components from oily sludge[J]. Environmental Technology, 2015, 36(14): 1771-1775. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2015.1010594 [18] 孙荣江, 侯峰, 丁焱梁, 等. 重金属污染土壤旋流洗脱设备的设计及性能评估[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(4): 1208-1217. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201710036 [19] HUANG Y, LI J, ZHANG Y, et al. High-speed particle rotation for coating oil removal by hydrocyclone[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 177: 263-271. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2016.12.001 [20] 竺嘉斌. 变径式微混器结构参数的优化研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2018. -










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: