南淝河沉积物可转化态氮赋存形态及其对上覆水水质的影响
Transferable nitrogen forms in sediment from Nanfei River and its impacts on overlaying water quality
-
摘要: 为了探讨黑臭河道沉积物可转化态氮(TF-N)的赋存对上覆水的影响,以典型黑臭水体——南淝河为研究对象,采用连续提取的方法将沉积物中可转化态氮分为离子交换态氮(IEF-N)、弱酸浸提态氮(WAEF-N)、强碱浸提态氮(SAEF-N)和强氧化剂浸提态氮(SOEF-N),研究南淝河沉积物中可转化态氮形态受排口类型和沉积物理化性质的影响规律,及其与上覆水氮素含量之间的关系。结果表明:南淝河沉积物可转化态氮以TF-NO3--N为主,占TF-N的88.57%±6.13%,而TF-NH4+-N仅占TF-N的11.43%±6.13%;从赋存形态的角度看,南淝河沉积物中SOEF-N相对含量最高(57.48%±3.67%),WAEF-N次之(26.16%±3.10%),SAEF-N和IEF-N较少,其相对含量分别为10.30%±4.85%和6.05%±1.73%;沉积物中TF-NH4+-N含量受排口类型的影响较为敏感,且4种赋存形态氮含量受排口类型影响的规律各不相同。另外,pH值和有机质含量对IEF-N影响较大,而CEC影响着WAEF-N含量。上覆水中溶解有机氮(dissolved organic nitrogen,DON)含量与沉积物IEF-N含量之间的显著相关(P4+-N赋存含量越多,释放到上覆水体的可能性越大。研究结果表明黑臭水体是一个复杂的生态系统,调控沉积物可转化态氮形态给黑臭水体内源污染控制提供新思路。Abstract: To pursue the effects of transferable nitrogen in sediment on overlying water quality, nitrogen in sediment from Nanfei River, a typical malodorous-black water body, were fractioned into ion exchangeable form nitrogen (IEF-N), weak acid extractable form nitrogen(WAEF-N), strong alkaline extractable form nitrogen (SAEF-N) and strong oxidant extractable form nitrogen(SOEF-N) using sequential extraction method. Meanwhile, the impacts of different outfall and physicochemical properties on the forms of transferable nitrogen in sediment as well as the releasing risks of transferable nitrogen from sediment into overlying water body were discussed. It was found that TF-NO3--N contributed 88.57%±6.13% to TF-N while only 11.43%±6.13% for TF-NH4+-N/TF-N, which suggested that TF-NO3--N was the dominant chemical form in sediment from Nanfei River. In addition, SOEF-N had the highest concentration (57.48%±3.67%)followed by WAEF-N(26.16%±3.10%), SAEF-N (10.30%±4.85%) and IEF-N (6.05%±1.73%) in sediment from Nanfei River. Significant influence of outfall types on (P4+-N in sediment was detected, though the 4 kinds of TF-NH4+-N forms displayed different variation trends in different outfall types. Moreover, IEF-N was greatly affected by pH and organic matters content while WAEF-N by CEC in sediment. There was significant correlation between DON concentration in overlying water and IEF-N contents in sediment (P4+-N content in sediment, the greater possibility for releasing into overlying water would arise. As a result, it can be figured out that the malodorous-black river was a complex ecosystem, and it was a novelty idea to transform the exchangeable nitrogen into stabile forms in sediment for the control of internal source pollution.
-
Key words:
- Nanfei River /
- outfall types /
- nitrogen forms /
- overlying water
-
目前全球染料年产量超过700×104 t,染料品种已经超过10×104余种,常用染料有2 000种以上,而且每年人工合成的新型染料也层出不穷,各地的江河湖泊都受到不同程度的污染[1-2]。而且这些染料大多为酚类化合物、苯类化合物[3],其结构复杂、难以生物降解、对生态环境危害极大[4-5]。因此,处理有机废水中的染料大分子是当前必须解决的热点问题。目前常用于有机废水治理的方法主要有物理吸附法、化学法、生物处理法、膜分离技术等[6-7]。但是这些方法往往对系统条件要求苛刻,成本和能耗高,需要二次维护[8-9]。与上述处理方法相比,光催化技术具有操作简单、成本低廉、循环性好等优点[10-11]。
g-C3N4作为一种通过π-π共轭形成的可见光响应型催化剂,通过范德华力作用堆砌形成二维层状结构,与石墨烯的层状结构类似,其具有优异的光稳定性和热稳定性[12]、良好的生物相容性、合适的能带结构以及优异的光电转化性能,常用于光催化分解水制氢[13-15]、二氧化碳还原[16-17]、有机污染物降解[18-19]等。然而,g-C3N4也有不可避免的缺陷,如比表面积小导致对有机污染物的吸附性能差[20];光生电子-空穴对复合率高导致催化活性差等,严重限制了其对有机污染物的降解性能[21-22]。目前,有研究者通过制备三维多孔氮化碳改善了上述问题。LIU等[23]以三聚氰酸-三聚氰胺超分子和离子液体分别做为前体和模板,合成了三维多孔超薄g-C3N4纳米片。其中,3D多孔结构增大了g-C3N4的比表面积,暴露了更多的活性位点,超薄结构的纳米片降低了载流子传输距离,抑制了载流子的复合率。WANG等[24]在软模板P-123存在下对超分子前驱体进行水热处理,制备出由空心气泡组成的三维g-C3N4催化剂。硬模板法[25]在控制造孔孔径大小和孔径分布上具有明显优势,但脱除模板的过程中要用到强酸或强碱进行处理,容易使氮化碳的—N—、═NH和—NH2官能团发生质子化作用,最终破坏其缩聚结构,且模板脱除过程产生的废酸、废碱过多[26-27]。软模板法可选择大多数表面活性剂以及低沸点分子充当模板,但是实验过程中需要调控的因素很多,生成的孔不如硬模板法整齐,并且表面活性剂可能不随高温完全分解从而残留于样品表面[28]。与上述方法相比,NH4Cl作为气体模板辅助造孔,无需在后续过程中去除模板,实验操作步骤更加简便,且不容易改变g-C3N4的基本结构。此外,以NH4Cl为模板辅助制备多孔g-C3N4不仅有利于对污染物的吸附[29],还可在煅烧前驱体的过程中促进CN−的生成,进而抑制光生电子空穴对的复合,提高对有机污染物的降解性能。
本研究采用气体模板NH4Cl辅助制备出多孔g-C3N4,通过XRD、FT-IR、UV-vis和XPS等表征研究样品的化学结构和晶相结构,通过SEM和TEM表征样品的表面形貌和微观结构,通过光催化降解水中RhB评价样品的光催化性能和循环性能,利用荧光光谱仪、瞬态荧光光谱仪和电化学工作站研究光生电子与空穴的复合和迁移状况,最后通过自由基捕获实验和高分辨质谱仪测试分析其光催化降解机理,旨在为开发新型光催化剂和建立RhB的降解方法提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验原料
实验所用的药品均为分析级试剂,使用前无需纯化。三聚氰胺和RhB购自天津科密欧科技有限公司,NH4Cl购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司,对苯醌购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司,三乙醇胺购自天津市大茂化学试剂公司,无水乙醇和异丙醇购自天津富宇精细化工有限公司,去离子水由超纯水仪处理所得。
1.2 实验仪器
马弗炉(KSL-1400X-A1,合肥科晶材料技术有限公司),X射线衍射仪(D2 PHASER,德国Bruker公司),X射线光电子衍射仪(ESCALAB 250XI,美国Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc公司),场发射扫描电镜(SU5000,日本Hitachi公司),透射电子显微镜(FEI Tecnai G2 F20 S-TWIN,美国FEI公司),紫外-可见分光光度计(UV-2600,日本岛津公司),傅里叶红外光谱仪(INVENIO,德国Bruker公司),BET比表面积测试仪(Autosorb-IQ-II,陕西盖卓电子科技有限公司),荧光光谱仪(FS5,英国爱丁堡公司),电化学工作站(CHI600E,上海辰华仪器有限公司),氙灯光源(CEL-HXF300-T3,北京中教金源有限公司),总有机碳分析仪(vario TOC cube,Elemental仪器公司),高分辨质谱仪(Thermo Scientific Q Exactive,美国Thermo Scientific公司)。
1.3 实验方法
1) g-C3N4的制备。以三聚氰胺为前驱体,通过高温煅烧法制备g-C3N4。取1.5 g三聚氰胺,用锡箔纸包裹后,置于有盖坩埚中,在马弗炉以550 ℃煅烧3 h。自然冷却所得黄色即为g-C3N4,研磨后进行光催化性能测试。
2) 多孔g-C3N4的制备。采用高温煅烧三聚氰胺和NH4Cl混合物的方法制备多孔g-C3N4。将1.5 g三聚氰胺分别与相应质量(0.675、0.75、0.825、0.9、0.975 g)的NH4Cl溶于50 mL去离子水中,磁力搅拌4 h,放入70 ℃烘箱中,蒸干水分。随后用锡箔纸包裹后,放入有盖的坩埚内,在马弗炉以550 ℃煅烧3 h,自然冷却所得黄色固体即为x%-PCN(x%表示前驱体中NH4Cl的质量分数),研磨后进行光催化性能测试。
1.4 表征和性能测试
1) 各项表征和测试。XRD测试:以Cu Kα为辐射源,扫描范围为2θ=5°~80°,扫描速度为2(°)·min−1。FT-IR测试:样品与KBr以1:100质量比混合研磨,压成半透明薄片测样,波数为400~4 000 cm−1。SEM测试:取少量样品贴于黑色导电胶上,真空喷金后测样。TEM测试:将样品溶于无水乙醇,超声混匀后滴在铜网上,装样测试。BET测试:样品以150 ℃脱气6 h。UV-vis测试:采用紫外-可见分光光度计,扫描波长为200~800 nm。PL测试:以波长为385 nm的激发光测量样品波长为390~640 nm的发射光谱。光电流-阻抗测试:采用三电极体系,0.1 g催化剂溶于10 mL溶剂(V水∶V无水乙醇=9∶1),超声后取上清液涂膜于FTO玻璃上,以此作为工作电极,参比电极为饱和甘汞电极,铂片电极为对电极,电解液为0.5 mol·L−1的Na2SO4溶液。高分辨质谱:取1.5 mL降解后RhB液体,甲醇为溶剂,EIS为离子源。
2) 催化剂降解性能测试。取0.1 g催化剂,加入100 mL质量浓度为30 mg·L−1的RhB溶液中,在黒暗环境下磁力搅拌20 min,以达到吸附-脱附平衡。随后用300 W氙灯模拟太阳光照射,每隔10 min取5 mL溶液,离心后取上清液,用UV-vis分光光度计测试吸光度。将使用过后的催化剂用水和乙醇洗至中性,烘干后按照上述步骤重复4次,以考察催化剂的稳定性。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 催化剂表征
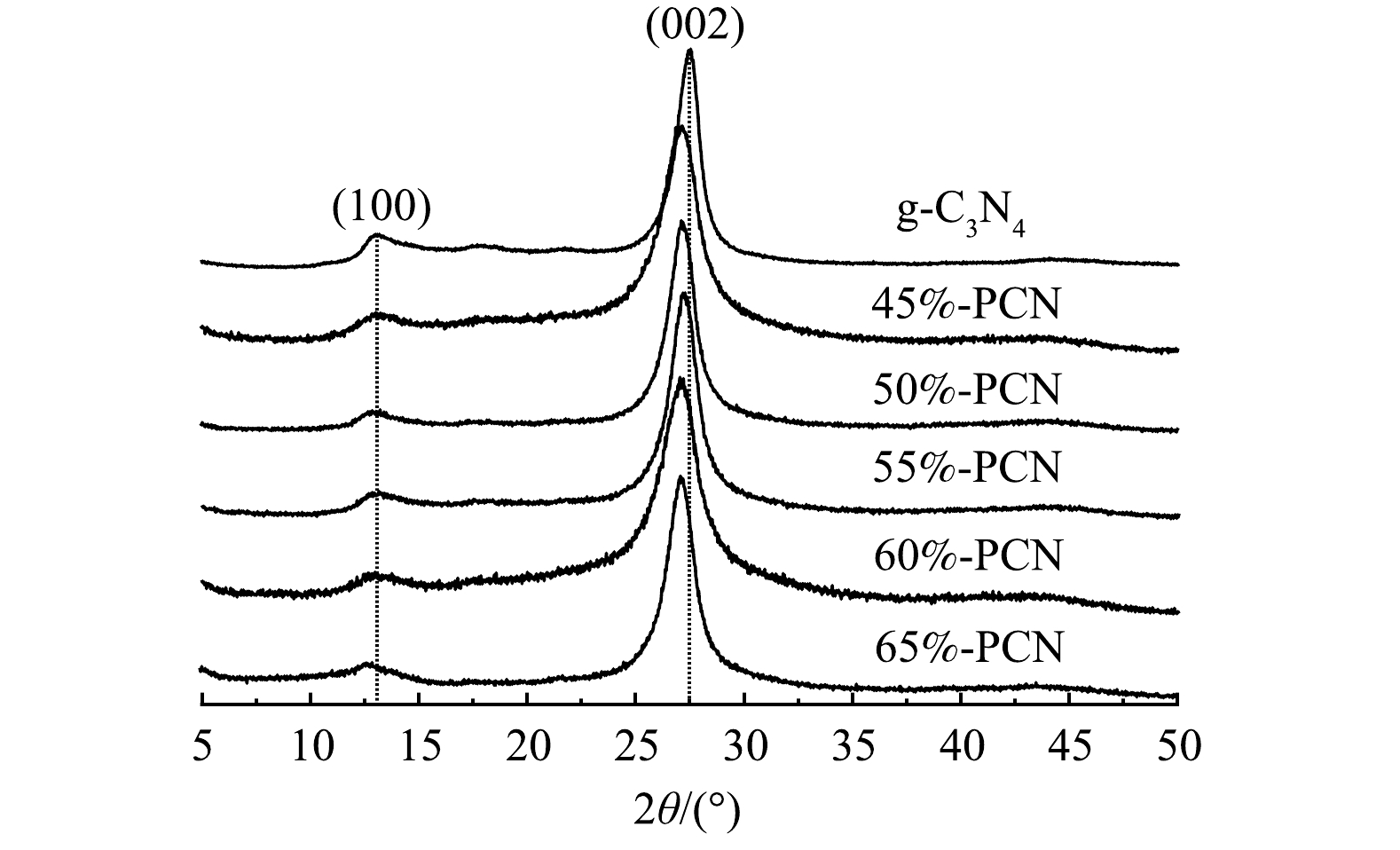
1) XRD分析。由图1可以看出,g-C3N4在13.5°和27.5°处有2个特征衍射峰,13.5°处的峰是面内三嗪环之间相互连接的特征峰,对应g-C3N4的(100)晶面,27.5°处的峰是环状芳香物层与层之间的堆积特征峰,对应g-C3N4的(002)晶面。与g-C3N4相比,PCN的2个特征峰均未发生明显改变,说明以气体模板法辅助制备PCN没有改变g-C3N4的晶相结构。此外,55%-PCN与g-C3N4相比,27.5°处的峰向左偏移至27.16°,根据布拉格公式(2dsinθ=nλ)[30]计算g-C3N4和55%-PCN的晶面层间距,分别为0.324 nm和0.329 nm,说明层间距变大。这可能是由于,三聚氰胺在高温下团聚脱氨的过程中,NH4Cl同时受热分解为NH3和HCl气体,导致生成的g-C3N4层与层之间的堆积作用变弱[31]。以上分析表明,气体模板的加入可以使g-C3N4片层与片层之间分离开来,从而进一步影响样品的性能。
2) 形貌分析。由图2(a)和图2(b)可以观察到g-C3N4整齐的片层堆叠,由图2(e)也可以观察到其表面光滑完整的大块结构。由图2(c)可以看出,55%-PCN的形貌与g-C3N4相比发生很大的改变,大片层破裂为小碎片,并且由图2(d)也可以看到样品表面产生很多孔径为50~100 nm的介孔。由图2(f)也可以看出孔的生成。
3) FT-IR分析。如图3所示,在g-C3N4的FT-IR光谱中,3 000~3 500 cm−1的宽峰为前驱体中未聚合的氨基(—NH2或═NH)的伸缩振动峰,1 200~1 640 cm−1对应于三嗪环间C—N和C═N键的特征峰,位于810 cm−1附近的吸收峰对应三嗪环的伸缩振动。与g-C3N4相比,PCN在1 200~1 600 cm−1和810 cm−1处的特征峰没有发生明显的变化,表明以NH4Cl为模板并未破坏g-C3N4的主体结构,在3 000~3 500 cm−1处的吸收峰变宽,可能是NH4Cl分解时的氨基与g-C3N4边缘位置未聚合的氨基或羟基结合,导致吸收范围变宽。值得注意的是,PCN在2 173 cm−1处出现1个明显的吸收峰,此为—C≡N的特征吸收峰[32]。并且随着前驱体中NH4Cl添加量的增多,峰强度越强,说明改性后的多孔结构有利于氰基的形成,使g-C3N4的面内形成更多的孔道结构。
4) UV-vis表征。如图4(a)所示,g-C3N4在波长小于470 nm处的蓝紫光和紫外光区吸收较强,可见光区的吸收较弱。55%-PCN在紫外光区和可见光区的吸收明显增强。此外,禁带宽度可利用UV-vis光谱数据、按照Kubelka-Munk函数由式(1)计算获得。
αhν=A(hν−Eg)1/2 (1) 式中:α为吸光度;h代表普朗克常数;ν为频率;Eg为禁带宽度;A为常数。以(αhν)2为纵坐标,hν为横坐标作图,对所得曲线取切线,切线与横坐标的交点即为Eg,即所对应的样品的禁带宽度[33]。由图4(b)可以看出,55%-PCN的禁带宽度为2.73 eV,与g-C3N4禁带宽度(2.78 eV)相似。这说明改性后的PCN具有较强光吸收性能且带隙宽度变化不大。
5) XPS分析。由图5(a)可以看出,g-C3N4和55%-PCN的C1s、N1s、O1s峰均出现在285、400、520 eV左右,表明二者的元素组成一致。在图5(b)中,284.8、286.6、288.3 eV的3个峰分别是g-C3N4的C—C键、C—O键和N═C—N键的特征峰。这表明,以NH4Cl为模板,只在g-C3N4中产生了较多的孔道结构,没有影响到C的键合状态。在图5(c)中,g-C3N4和55%-PCN在398.7、399.5、401.1 eV处的3个峰,分别对应三嗪环内C═N—C键、环与环之间的H—N—(C)3键和末端氨基上的C—N—H键,表明N的键合状态也未受到气体模板的影响。由图5(d)可以看出,g-C3N4和55%-PCN的价带电位分别为+1.14 eV和+0.88 eV。采用文献中的方法[34]计算出g-C3N4和55%-PCN的导带电位,分别为−1.64 eV和−1.85 eV。这表明多孔结构不仅有利于提高g-C3N4的光吸收性能,还使导带上电子的还原电势更负。
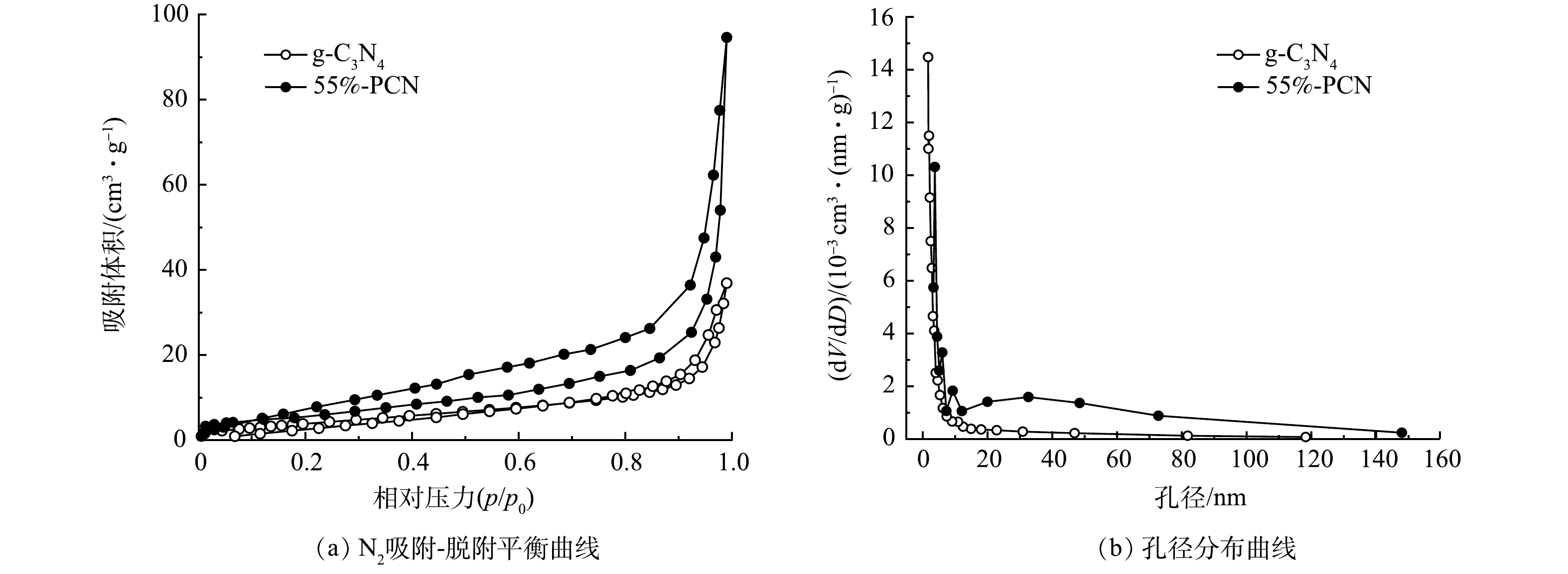
6) BET分析。如图6(a)所示,二者的曲线趋势为Ⅳ型等温曲线,表明g-C3N4和55%-PCN均为中孔材料。另外,测试结果显示,55%-PCN的比表面积(28.548 m2·g−1)与g-C3N4(13.878 m2·g−1)相比有所提高,55%-PCN的孔体积(0.143 cm3·g−1)与g-C3N4(0.046 cm3·g−1)相比也有所提高。这表明PCN的表面性能得到了改善。由图6(b)可以看出:g-C3N4的孔径集中分布于5 nm左右;55%-PCN的孔径分布比较宽泛,增加了10 nm左右和10~80 nm孔道结构。这表明以NH4Cl为模板可增加g-C3N4的孔道结构,有利于提高催化剂对有机污染物的吸附性能。
2.2 性能分析
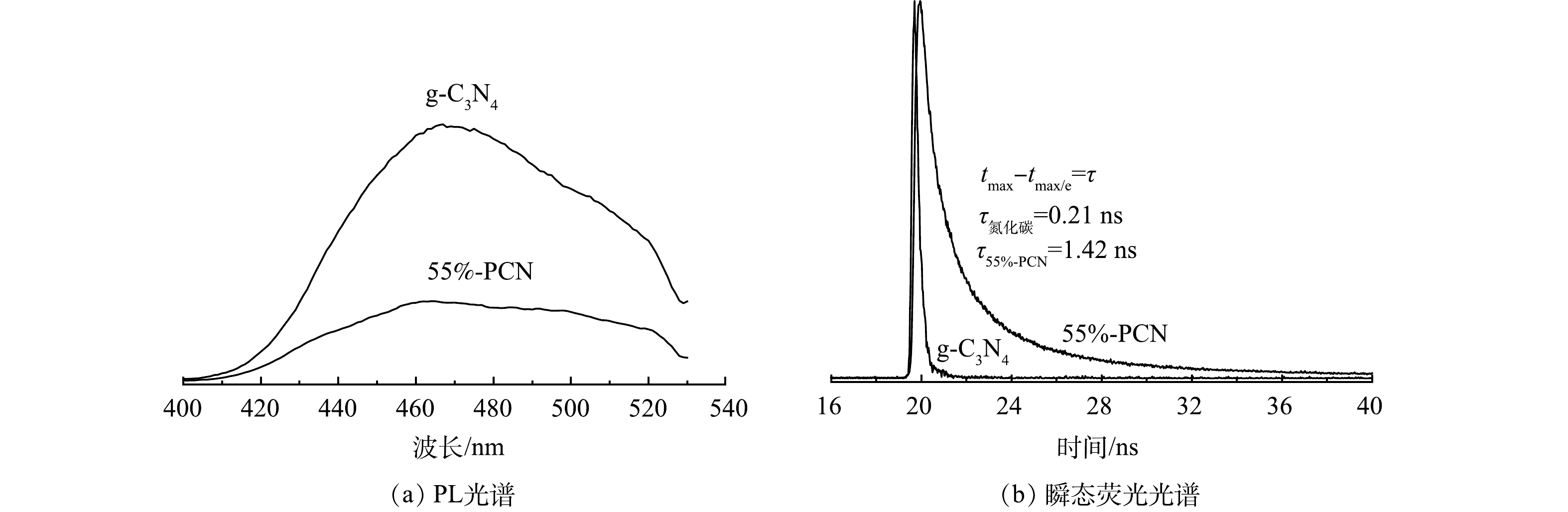
1) 光致发光(PL)光谱和瞬态荧光光谱分析。PL峰强度越强表明光生电子空穴对的复合率越高。由图7(a)可以看出,55%-PCN的发射峰强度较g-C3N4明显降低,表明光生电子空穴对的复合率受到一定程度的限制,有利于光催化性能的提升。图7(b)是g-C3N4和55%-PCN的瞬态荧光光谱图。当荧光强度衰减到最大值的1/e时所用的时间为荧光寿命,即光生电子的平均寿命,其寿命越长,越有利于光催化性能的提升。可以看出,55%-PCN的平均寿命为1.42 ns,接近g-C3N4的7倍(0.21 ns),表明55%-PCN中载流子具有较长的寿命来参与光催化反应。氰基是一种常见的吸电子基团,可以更好地使55%-PCN表面的光生电子和空穴分离[32],提升载流子的寿命,最终影响其光催化性能。
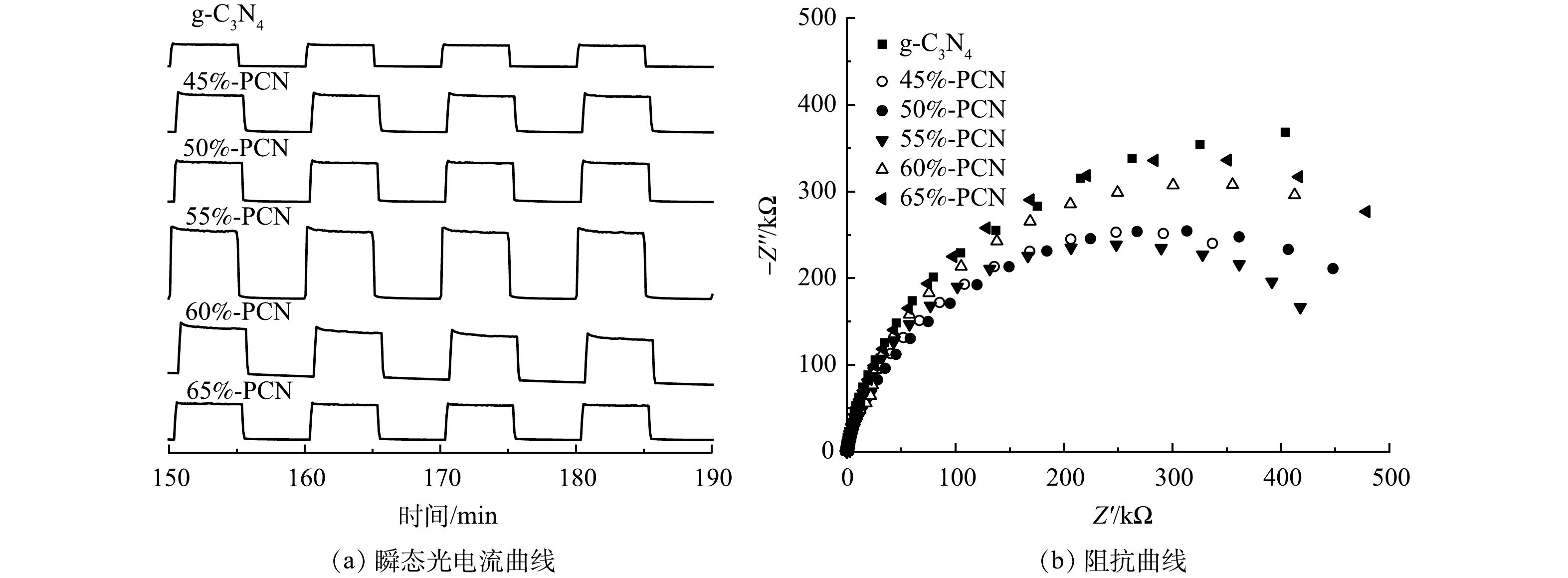
2) 光电性能。虽然通过PCN的制备可以抑制光生电子空穴对的复合,但光生电子-空穴对参与到光催化反应的数量尚不清楚。采用瞬态光电流强度和电化学阻抗谱研究光生电子的迁移效率和迁移阻力,结果如图8所示。在图8(a)中,光电流强度越大,表示催化剂中的激发电子向导电玻璃表面的迁移效率越高,越有利于光催化性能的提升,PCN-55%的光电流强度最大,是g-C3N4的2.5倍,表明其电子迁移效率最高。电化学阻抗谱的圆弧半径越小,电阻越小,电荷转移效率更高效。由图8(b)同样可以看出,55%-PCN的电子迁移阻力最小,可提高光生电子向催化剂表面的迁移效率。综合以上分析,55%-PCN样品中的电子迁移阻力较小,有利于激发电子的迁移。
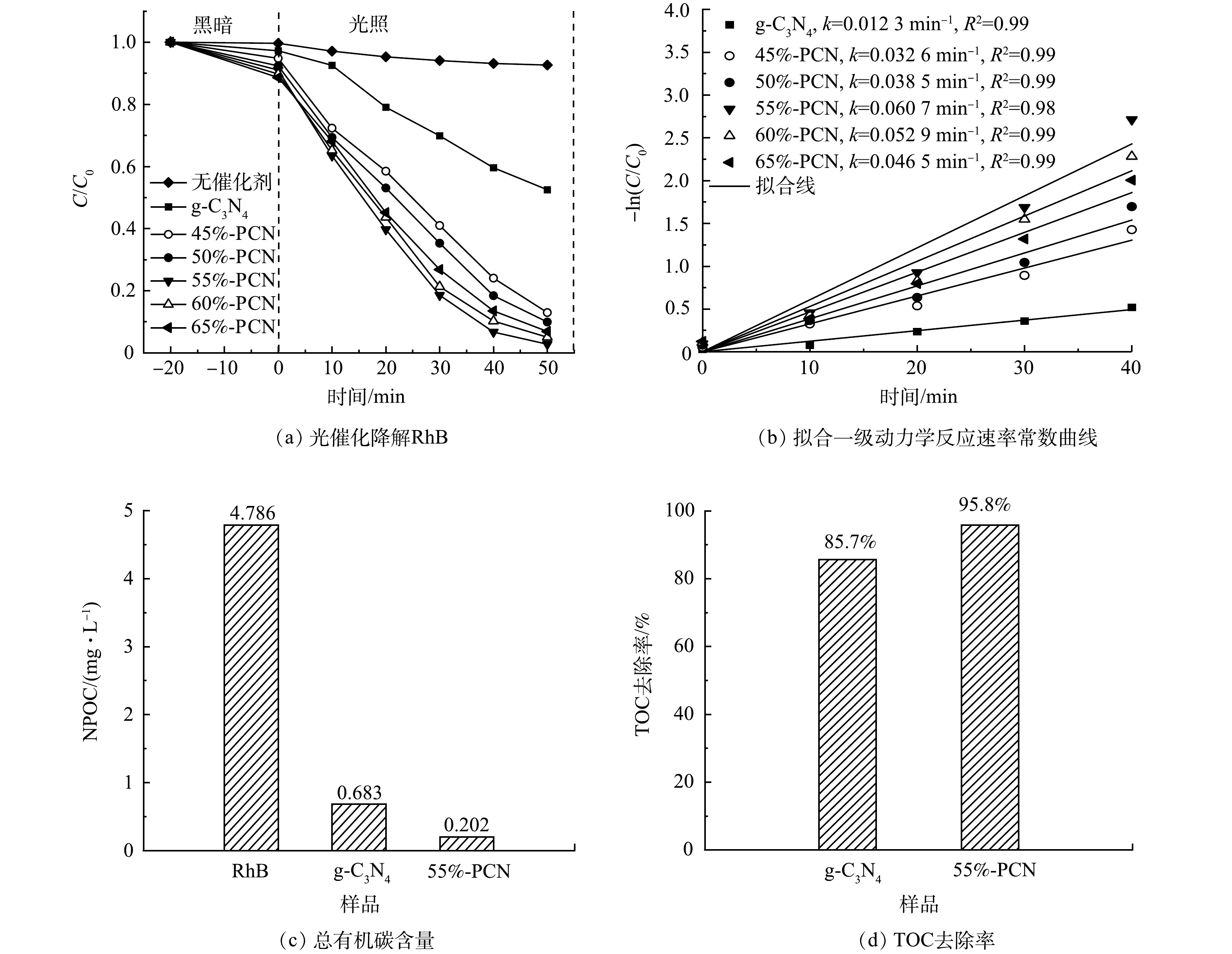
3) 光催化降解罗丹明B性能。在图9(a)中,−20~0 min表示催化剂在黑暗环境下对RhB的吸附过程,0~50 min表示光照下光催化降解RhB的过程。可以看出,不加催化剂时,RhB在光照50 min后的自去除率只有7.4%,g-C3N4的暗吸附率为2.8%,而45%-PCN、50%-PCN、55%-PCN、60%-PCN和65%-PCN的暗吸附率分别为5.2%、7.7%、8.9%、10.3%、11.5%。这表明,PCN中的孔道随气体模板NH4Cl的增加而增多,同时对RhB的吸附性能也越强。55%-PCN在50 min内即可将RhB完全降解,而在相同时间内g-C3N4的降解率只有50%左右。
为了更直观地比较样品在光照下降解RhB溶液的光催化性能,可根据拟合伪一级动力模型[35]计算反应的表观速率常数。光催化降解RhB的伪一级动力学速率常数和降解率关系如式(2)所示。
lnCC0=−kt (2) 式中:k为表观速率常数,min−1;C0和C分别为RhB的初始质量浓度和光照时间t时的质量浓度,mg·L−1。由于0~40 min的降解数据更符合伪一级动力学方程,故选择此范围数据,根据文献中的方法[32]作图。以ln(C0/C)为纵坐标,t为横坐标做图,斜率为k,计算所得的k值标记于图9(b)中。g-C3N4的k值为1.23×10−2 min−1,55%-PCN的k值最大(6.07×10−2 min−1),是g-C3N4的5倍。
根据有机碳含量计算g-C3N4和55%-PCN降解RhB的TOC去除率,g-C3N4为85.7%,55%-PCN为95.8%(图9(c)和图9(d)),所以RhB有机物大分子基本被全部分解为无机物小分子。55%-PCN与g-C3N4相比,去除率升高,说明其可以更好地将RhB大分子吸附并降解。
2.3 催化剂稳定性分析
以上研究表明,55%-PCN具有对RhB优异的吸附性能和降解性能,但催化剂的稳定性是限制其能否工业化应用的又一关键指标。由图10(a)可以看出,55%-PCN在相同循环时间内重复使用4次的降解率分别为97.4%、95.4%、93.6%、92.7%,对水中RhB的降解率未发生明显变化。由图10(b)可以看出,55%-PCN使用前后的XRD图谱出峰位置不变,说明反应前后样品的结构和化学组成也没有发生改变。以上均表明55%-PCN具有稳定的光催化活性。
2.4 光催化机理分析
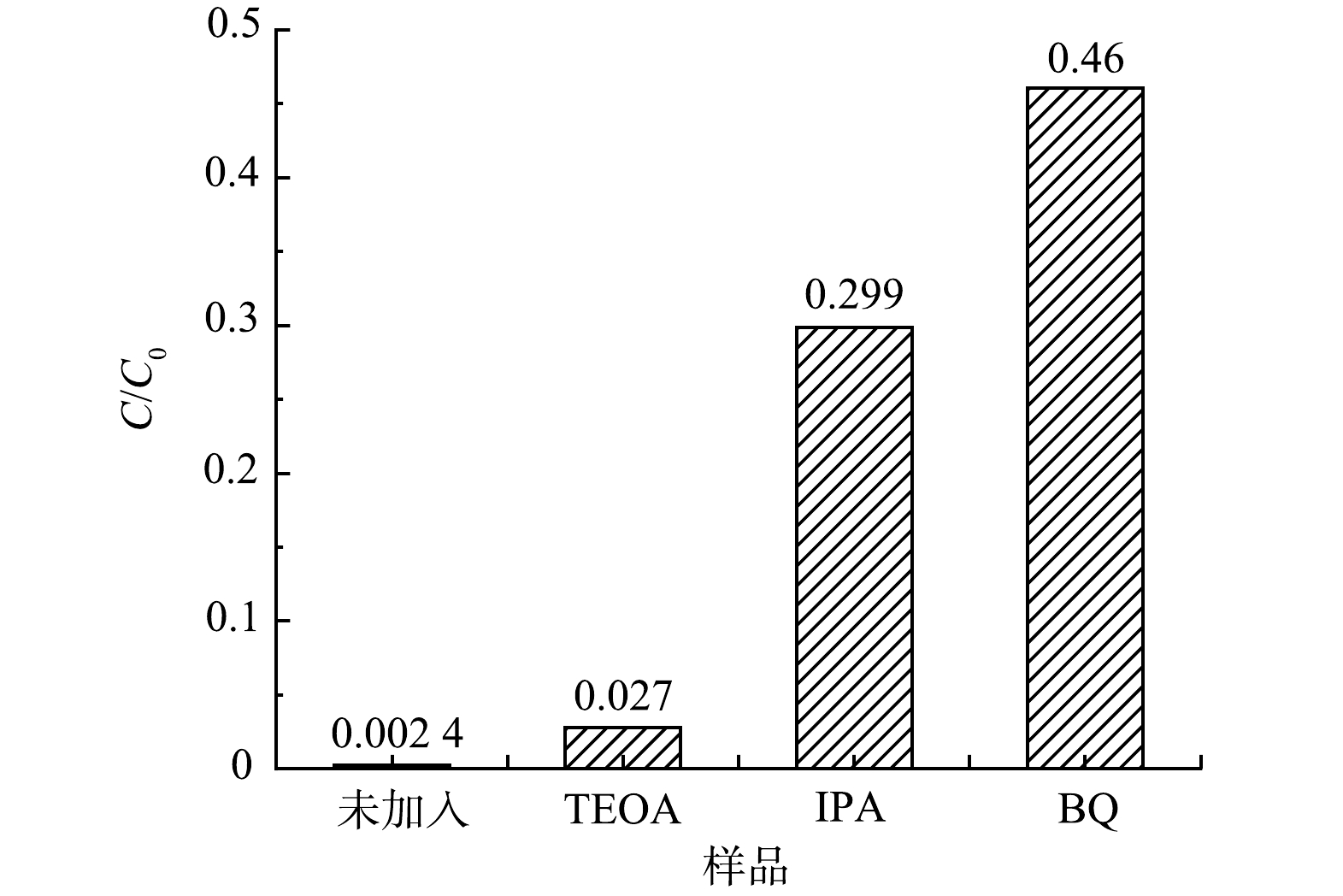
为了研究55%-PCN光催化降解RhB过程中的主要物种,分别用三乙醇胺(TEOA)、苯醌(BQ)和异丙醇(IPA)作为光催化降解体系中空穴(h+)、超氧自由基(·O2−)、羟基自由基(·OH)的捕获剂[36]来进行实验,结果如图11所示。当加入TEOA后,降解率未发生明显变化,即h+被捕获后催化活性变化不大,表明h+不是RhB降解的主要活性物种;在降解体系中加入IPA后,降解率下降明显,说明·OH对RhB的降解具有一定的促进作用;当加入BQ后,光降解效率明显下降,光催化活性被抑制的最明显,表明·O2−是RhB降解时最主要的活性物种。基于以上分析,在RhB降解时,最主要的活性物种是·O2−,其次是·OH,h+的活性可忽略不计。
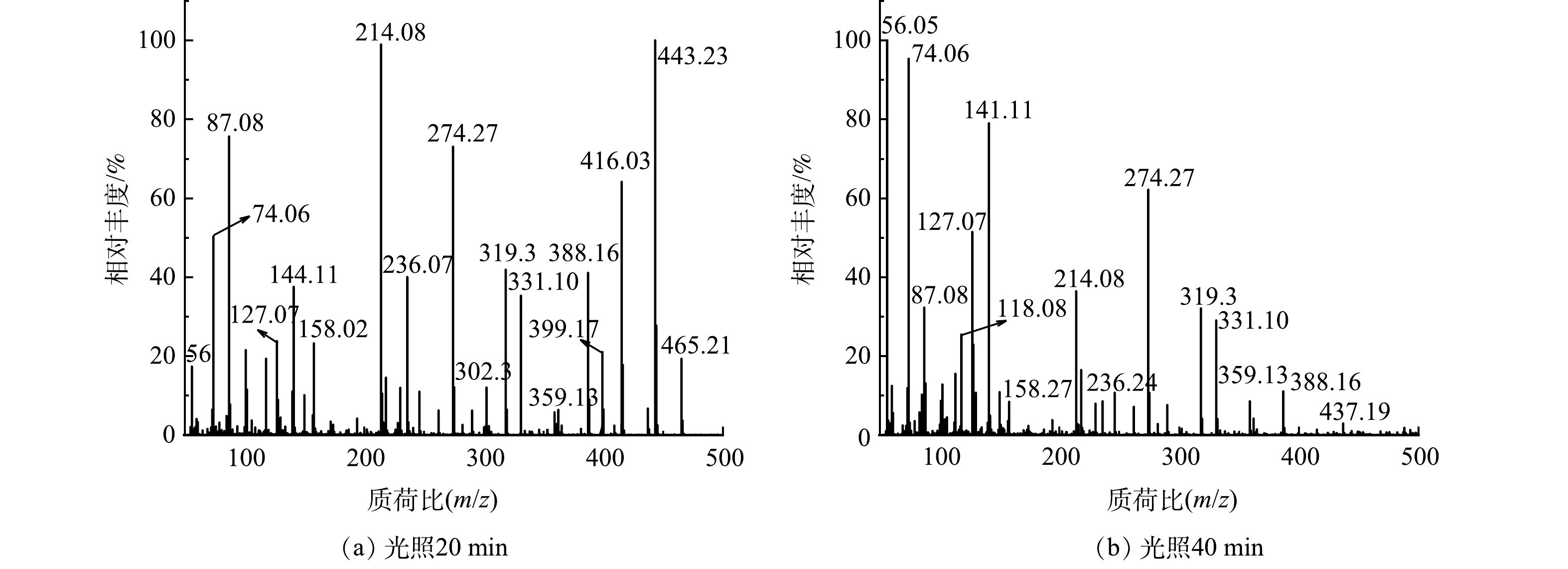
本研究对降解后RhB溶液进行高分辨质谱测试,以探究55%-PCN光催化降解RhB的具体过程。在图12(a)中,m/z=444表示RhB的阳离子峰;m/z=416、388、359、331表示RhB脱去1、2、3、4个乙基的分子离子峰;m/z=399表示RhB脱去1个羧基的离子峰;m/z=302可能是脱去4个乙基和1个羧基后被1个·OH羟基化所得产物的离子峰;m/z=319可能是脱去4个乙基和1个羧基后被2个·OH羟基化获得产物的离子峰[37];推测其余离子峰也是各个大分子不断被·OH多次氧化后的产物。由图12(b)可以看出,m/z>150的各处离子峰强度都有一定程度上的降低,而m/z<150的各个离子峰强度明显升高。这说明55%-PCN光催化降解RhB的过程是一个随着光照时间的升高,RhB开始脱乙基和羧基,同时·OH不断进攻苯环使其断裂、氧化,最终经过多次氧化反应生成各个小分子的过程。
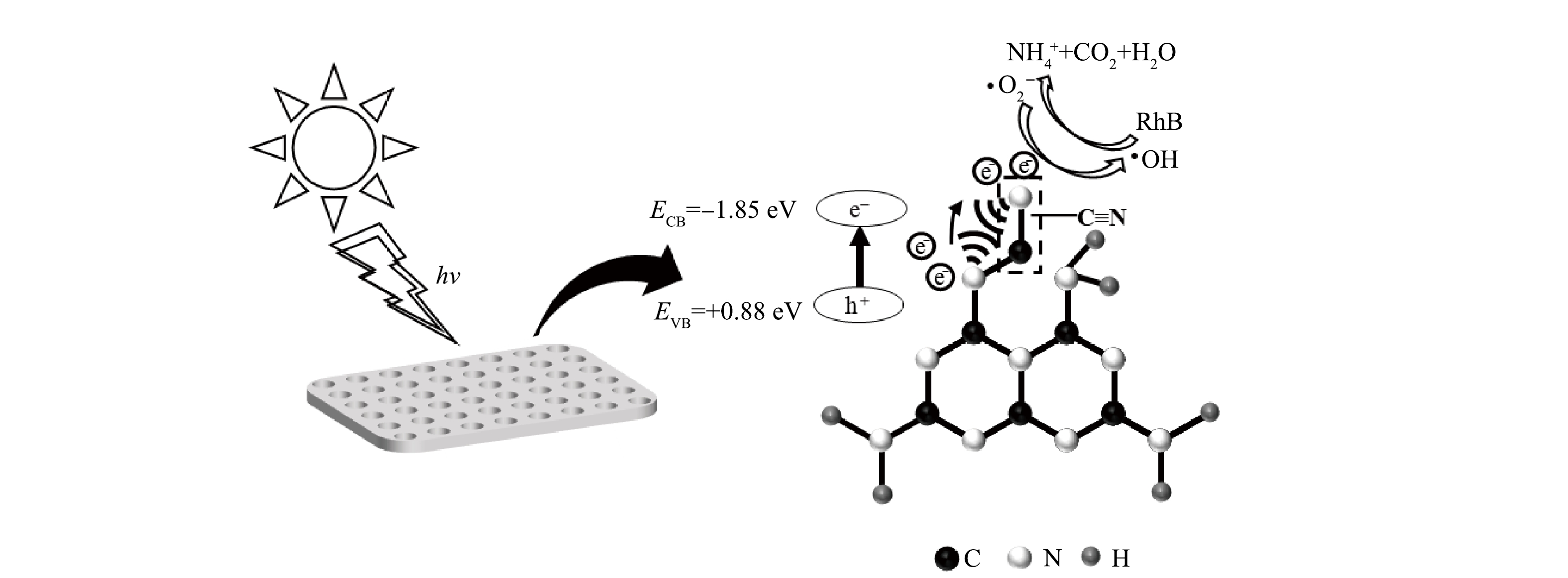
基于以上结果,推测55%-PCN光催化降解RhB的机理如图13所示。可以看出55%-PCN的价带主要由N原子的N2p轨道构成[32,38]。在光照射下,N原子上的电子充当电子供体被激发到导带生成光生e−,价带上留下大量h+(式(3))。导带上e−的还原电势较E(O2/·O2−)=−0.046 eV更负,与水中溶解的O2反应生成·O2−(式(4)),超氧自由基进一步反应生成过氧氢根(HOO·)和过氧化氢(H2O2)(式(5)和式(6)),接下来继续又被还原成具有强氧化性的·OH[32](式(7))。55%-PCN的孔结构给RhB的降解反应提供了更多边缘反应位点,RhB在脱乙基和脱羧基过程中不断与·OH接触,发生羟基化氧化反应。另外,氰基是常见的吸电子基团,常被用作电子受体[39]。当g-C3N4的结构中存在氰基时,氰基与相邻的N原子之间会形成局部分子内供体-受体(D-A)体系。D-A体系可以有效转移分子内的电荷,使光生e−和h+分离开来,从而降低载流子重组率[40]。故55%-PCN中的氰基的引入进一步给光催化降解RhB提供更多的活性位点,最终使RhB被氧化为NH4+、CO2、H2O等小分子。
PCN+hν→h++e− (3) e−+O2→·O−2 (4) ·O−2+H+→HOO⋅ (5) e−+HOO⋅→H2O2 (6) e−+H2O2→⋅OH (7) 3. 结论
1) 气体模板NH4Cl的引入可以在不破坏g-C3N4基本结构的基础上制备PCN,表面介孔数量增多,大大增加其比表面积和孔体积,给后续反应提供更多的活性位点。同时有利于提高吸光性能,经过测试其可见光吸收范围相比g-C3N4变宽。
2) 当前驱体中NH4Cl添加量为55%时所制备样品降解性能最佳。55%-PCN在50 min内对RhB的降解率为98%,伪一级动力学速率常数为6.07×10−2 min−1,是g-C3N4的5倍;并且其对RhB的TOC去除率比g-C3N4高,说明其可以更好地将RhB大分子吸附并降解。
3) 自由基捕获实验表明,在RhB降解时,·O2−和·OH参与了反应,在反应中,·O2−为最主要的活性物种。吸电子基团氰基与相邻的N原子之间会形成局部分子内D-A体系,使光生电子和空穴更好地分离,增加载流子寿命。55%-PCN的孔结构以及氰基的引入,均给RhB的降解反应提供了更多反应活性位点,在脱乙基和羧基过程中不断与·OH发生氧化反应,最终产物为NH4+、CO2、H2O等小分子。
-
[1] 王旭,王永刚,孙长虹,等. 城市黑臭水体形成机理与评价方法研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报,2016,27(4):1331-1340 [2] 胡洪营,孙艳,席劲瑛,等. 城市黑臭水体治理与水质长效改善保持技术分析[J]. 环境保护,2015,43(13):24-26 [3] 马红波,宋金明,吕晓霞,等. 渤海沉积物中氮的形态及其在循环中的作用[J]. 地球化学,2003,32(1):48-54 [4] 王圣瑞,金相灿,焦立新. 不同污染程度湖泊沉积物中不同粒级可转化态氮分布[J]. 环境科学研究,2007,20(3):52-57 [5] 王健,张靖天, 昝逢宇,等. 中国东部浅水湖泊沉积物总氮总磷基准阈值研究[J]. 生态环境学报,2014,23(6):992-999 [6] PURKAMO L,BOMBERG M L,NYYSSÖNEN M,et al. Response of deep subsurface microbial community to different carbon sources and electron acceptors during 2 months incubation in microcosms[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2017,8(2):232-245 [7] YANG Z,KAPPLER A, JIANG J. Reducing capacities and distribution of redox-active functional groups in low molecular weight fractions of humic acids[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2016, 50(22):12105-12113 [8] 吴峰. 关于控源截污工程的后思考[J]. 中国给水排水,2015,31(6):22-25 [9] 秦伯强,张运林,高光,等. 湖泊生态恢复的关键因子分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2014,33(7):918-924 [10] 王功芹,朱珠,张硕.海州湾表层沉积物中氮的赋存形态及其生态意义[J]. 环境科学学报,2016,36(2):450-457 [11] GU L, HUANG B,XU Z,et al. Dissolved organic matter as a terminal electron acceptor in the microbial oxidation of steroid estrogen[J]. Environmental Pollution,2016,218:26-33 [12] LI Y, ZHANG L,WANG S, et al. Composition, structural characteristics and indication of water quality of dissolved organic matter in Dongting Lake sediments[J]. Ecological Engineering,2016,97:370-380 [13] HASSETT J P. Dissolved natural organic matter as a microreactor[J]. Science,2006,311(5768):1723-1724 [14] 王娟. 稻田土壤碳氮转化与微生物群落结构及活性之间的联系机制[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2015 [15] ZHANG Y,XU W,DUAN P,et al. Evaluation and simulation of nitrogen mineralization of paddy soils in Mollisols area of Northeast China under waterlogged incubation[J]. Plos One,2017,12(2):e0171022 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2660
- HTML全文浏览数: 2350
- PDF下载数: 436
- 施引文献: 0





 下载:
下载: