搅拌速率和时间对强化混凝去除微污染水中镍(Ⅱ)及有机物的影响
Effect of stirring speed and time on removal of nickel(Ⅱ) and organic matter in micro-polluted water by enhanced coagulation
-
摘要: 采用静态实验考察了投加高铁酸钾强化混凝的效果,通过控制不同的絮凝搅拌速率、絮凝时间及原水浊度来强化镍(Ⅱ)和有机物的去除。结果表明,絮凝搅拌速度和时间、原水浊度是影响镍(Ⅱ)和有机物的去除效果的重要因素。原水镍(Ⅱ)质量浓度为1 mg·L-1、TOC为10 mg·L-1,在一级絮凝搅拌速率为200 r·min-1、时间为2 min,二级絮凝搅拌速率为40 r·min-1、时间为10 min,原水浊度为36.7 NTU时,出水剩余镍为0.018 mg·L-1,去除率达到98.2%,TOC去除率为58.8%,浊度去除率为73.8%。出水可满足《生活饮用水卫生标准》的要求。高铁酸钾强化混凝可作为给水厂应对镍污染的一种有效处理措施。Abstract: A static trial was performed to study the effect of enhanced coagulation though the addition of potassium ferrate,with flocculation stirring speed,flocculation time,and raw water turbidity controlled to strengthen the nickel (Ⅱ) and organics removal.The results showed that flocculation stirring speed,flocculation time,and raw water turbidity were key influences on nickel (Ⅱ) and organics removal efficiency.The first level of flocculation stirring speed was 200 r·min-1,flocculation time was 2 min;the second level of flocculation stirring speed was 40 r·min-1,flocculation time was 10 min;and raw water turbidity was 36.7 NTU.The nickel concentration in the effluent was 0.018 mg·L-1,and the removal rate of the nickel (Ⅱ),TOC,and turbidity were 98.2%,58.8%,and 73.8%,respectively,when the nickel (Ⅱ) and TOC concentrations were 1 mg·L-1 and 10 mg·L-1,respectively,in the raw water.These levels satisfied the demand of the Hygienic Standard for Drinking Water.Potassium-ferrate-enhanced coagulation can be used as an effective treatment for nickel pollution in water supply plants.
-
Key words:
- enhanced coagulation /
- nickel /
- stirring speed /
- flocculation time /
- raw water turbidity
-
随着国家对环境保护的不断重视以及人民群众对碧水蓝天、美好环境热切需求的不断增长,以流域治理、湿地建设、“碧水绕城” “美丽乡村”等为代表的水环境治理项目越来越多[1]。城市化水平较高的地区,人们的生产生活活动对城市湖泊水体的影响更为突出,尤其是作为河流蓄泄的枢纽湖泊(如嘉兴南湖),其水环境治理一直是生态环境领域的难点。
国内外比较成熟的湖泊生态修复理论主要包括多稳态理论、营养盐浓度限制理论和生物操纵理论[2]。多稳态理论指在相同的外部环境条件下,浅水型湖泊可能处在“草型清水态”和“藻型浊水态”2种完全不同的状态[3],2种状态之间存在着临界阈值[4-5];营养盐浓度限制理论强调营养盐对生物群落的限制与驱动,是湖泊多稳态保持和转化的动力[2];生物操纵理论通过生物调控治理藻类水华[6]而应用在富营养化湖泊的治理中[7]。柯杰等[8]认为湖泊湿地修复技术主要包括物理技术、生物技术和化学技术。物理技术中的环保疏浚是采取人工、机械的措施适当去除水体中的污染底泥,以降低底泥中污染物的释放通量和生态风险,并对疏浚后的污染底泥进行安全处理处置的技术,是河流、湖泊(水库) 水污染治理的重要技术之一[9]。南京玄武湖采用的围堰分区干式法[10-11],西安兴庆湖采用的高压水枪水力冲挖方式[12],杭州西湖采用的环保绞吸式挖泥船疏浚方式[13]等均属于比较常见的环保疏浚技术。但环保疏浚缺乏与生态修复技术之间的衔接,如疏浚底泥的二次利用、无害化处置通常缺乏考虑[14]。其他物理技术包括通过机械、设备对城市湖泊湿地进行换水、补水,实现水量稀释,可以快速降低营养盐浓度[8],比如常用的混凝-沉淀、磁混凝技术、超磁分离一体化工艺等。其中超磁分离一体化工艺已在巢湖塘西河[15]生态补水、吴江同里古镇[16]景观补水、北京总装航天城人工湖[17]活水循环等水环境项目中进行广泛应用。在生物技术方面,以沉水植物为主或结合其他修复技术的原位生态修复已十分普遍,在太湖[18-19]、上海临港滴水湖[20]、杭州西湖[21]、昆明滇池草海[22]等均有广泛应用。化学技术主要是指利用药剂、化学工艺对湖泊进行治理,在城市湖泊水体生态修复方面应用较少。
与传统城市湖泊相比,浙江嘉兴南湖作为嘉兴主要河流的交汇处,其水体库容小、水力停留时间短,形式上更接近“河流型湖泊”。南湖作为5A级景区,往来游客众多,游船航次频繁,关注度极高,生态修复对水体的扰动相对更为受限。本研究以嘉兴南湖生态环境修复工程(一期)项目为例,基于南湖水环境调查的已有成果[23-26],对南湖水质问题和水体浑浊原因进行分析,提出嘉兴南湖生态系统构建的整理思路和关键技术,并对工程实施后的效果进行评价,以期为平原河网水系、开放性水域、高浊度水体的城市湖泊治理提供借鉴和参考。
1. 南湖水体概况与生态修复难点
1.1 南湖水体概况
南湖位于浙江省嘉兴市区,湖体南北长、东西狭,常年水面面积为0.52 km2,是嘉兴市各主要河流蓄泄的枢纽,是海盐塘、平湖塘、嘉善塘等多条河流的起点、终点交汇处[27]。南湖水体悬浮物(SS)含量较高,透明度较低(基本维持在25 cm左右),总磷(TP)远远高于水环境功能区考核的Ⅲ类标准(湖泊标准)[28-29]。而南湖水体由于透明度低,光线条件差,湖区水底基本上无沉水植物覆盖。换水周期是湖泊水环境的一个重要参数,影响着水体中污染物与营养物的质量浓度与停留时间,同时也影响着水体中发生的生物与化学反应过程时间的长短[30]。南湖换水周期仅为1.59 d[31],水力停留时间短,每天的水体交换量大,导致上游来水所带来的悬浮性颗粒物很难沉降。
南湖水体中TP质量浓度为0.121~0.388 mg·L−1,平均为0.246 mg·L−1,超过地表水Ⅴ类水质标准(湖泊标准)[29]。空间分布显示,水体中TP的空间分布差异性显著,质量浓度较高的区域主要集中在西南部及东南部的南湖入湖河道,而低值区主要分布在南部堤岸及周围区域[23]。南湖水体中TN质量浓度为3.81~4.99 mg·L−1,平均为4.32 mg·L−1,超过地表水Ⅴ类水质标准(湖泊标准)[29]。空间分布显示,TN质量浓度从南湖西南角和东南角向北部出口逐渐递减,而在湖心岛的南部堤岸周围的TN质量浓度明显低于其他区域[24]。NH3-N的质量浓度相对较低(0.67~1.67 mg·L−1),在地表水Ⅲ~Ⅴ类水质标准(湖泊标准)[29]之间波动,均值为1.22 mg·L−1,NH3-N的空间分布与TN较为相似[24]。近年来,南湖水质持续好转,NH3-N指标年均可达到Ⅲ类水标准(湖泊标准)[29],但TN和TP含量依然很高,大部分月份的TP仍在0.20 mg·L−1以上,颗粒形态磷占比达到60%以上。总体来看,水质仍处于地表水劣Ⅴ类水平(湖泊标准)[29]。
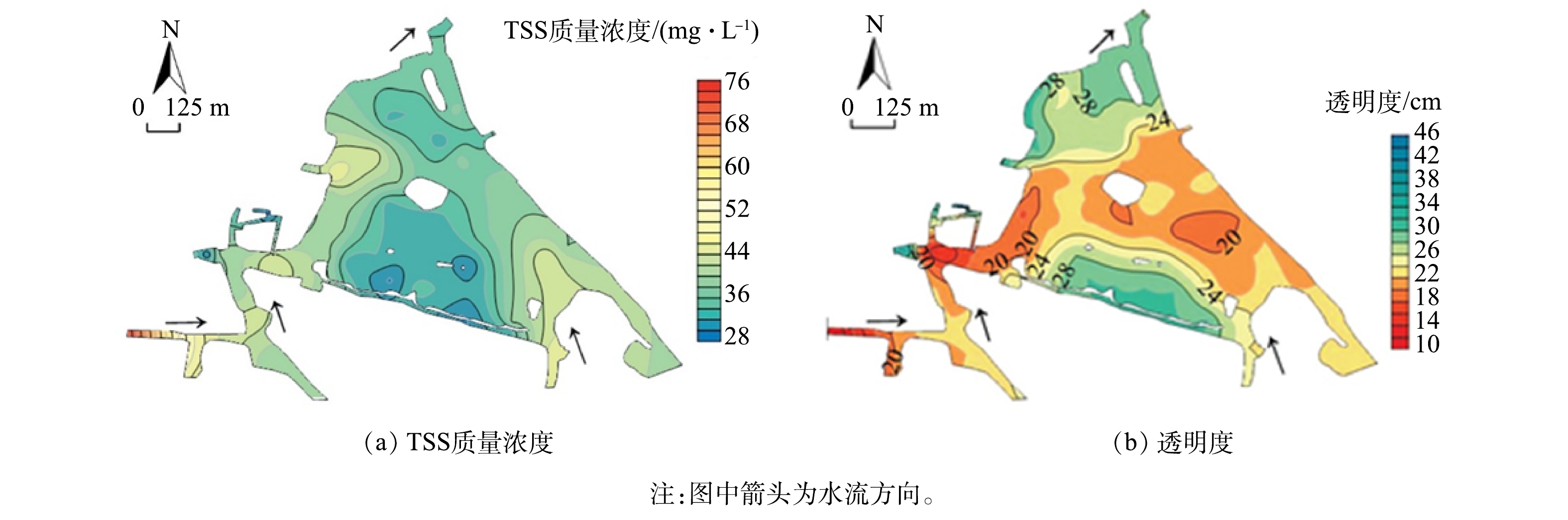
南湖水体悬浮物质量浓度为29.2~75.2 mg·L−1,均值为39.0 mg·L−1。与国内其他主要湖泊相比,南湖水体悬浮物质量浓度均值略低于巢湖,高于其他湖泊[25](表1)。入河道悬浮物中粒径为10~50 μm的颗粒占比较大,而湖区水体中悬浮物粒径以4~10 μm为主,湖区底泥最上层颗粒粒径多以10~50 μm 为主。这说明河道携带的悬浮物粒径为10~50 μm的颗粒可沉降下来,但粒径为10 μm 以下的悬浮物很难通过重力沉降下来。南湖水体悬浮物质量浓度大小主要受上游来水及湖区船舶活动的影响,航道区域悬浮物质量浓度明显高于周边水体[25]。南湖水系中的水体悬浮物分布[25]如图1所示。
表 1 南湖与国内其他湖泊水体中的TSS质量浓度及其均值Table 1. TSS mass concentration and its mean value in Nanhu Lake and other domestic lakes湖泊名称 质量浓度/( mg·L−1) 均值/( mg·L−1) 东湖 13. 80~23. 76 18. 72 蠡湖 1. 00~78. 00 17. 35 鄱阳湖 5. 00~72. 00 23. 87 梁子湖 2. 83~26. 85 12. 41 洪湖 2. 24~25. 66 10. 98 太湖 11. 08~85. 40 34. 31 巢湖 17. 80~67. 53 42. 76 南湖 29. 20~75. 20 38. 95 南湖水体透明度为10~46 cm,均值为25 cm,南湖湖区水体透明度的空间分布差异性较为显著,水体透明度较低的地方主要集中在西南水域以及湖体航道[26]。河流、湖泊中船舶的航行对于水体底部的沉积物具有很大的扰动作用[32],特别是船舶尾部的螺旋桨对于浅水河流及湖泊底泥扰动的作用更为巨大。南湖游船、巡逻艇、执法船、保洁船等船舶扰动引起底泥再悬浮是航道区域透明度低的主要原因。南湖水系中的水体透明度分布情况[26]如图1所示。
1.2 南湖水体生态修复的难点
南湖周边多为景观块石护岸和直立式岸坡,上游河道多为浆砌块石或钢筋混凝土直立式岸坡。该类型岸坡生态型差,近岸侧几乎无挺水植物。受水体浑浊、透明度低、氮磷超标等影响,南湖湖区水下几乎无沉水植物。南湖生态环境恢复的困难主要有以下几点。
1)水体透明度低,水深条件差。光线是沉水植物生存的最基本条件,这是因为沉水植物需要通过光合作用进行代谢活动,因此水下光照条件是影响沉水植物生长存活的最主要因素。影响水下光照条件的主要指标包括水深、透明度、悬浮物浓度、藻类等。在常水位为1.16 m时,南湖平均水深为2.8 m,而南湖水体透明度均值只有25 cm。沉水植物生长所需的光补偿深度一般应为水体透明度的1.5倍[33],按照南湖目前的水深条件,其水体透明度远远不能满足沉水植物生长的基本条件,这也是南湖生态系统构建面临的最大困难。
2)景区内施工,沉水植物种植方式受限。沉水植物的常见种植方式主要包括扦插法、抛投法等。扦插法根据种植水深的不同又分为浅水扦插(水深一般小于0.5 m)和船上扦插(水深为0.5~2.0 m)。浅水扦插的前提是需对拟种植区域进行抽水,形成干地作业环境,再根据植物的生长习性逐渐蓄水,直至达到设计常水位。沉水植物“扦插”种植具有生产效率高、苗木成活率高、定位造型易控制等优点。抛投法则分为配重抛投和带土抛投。抛投法虽然施工效率快、无需降水,但是水草成型不规则、容易飘草,且成活率低。嘉兴南湖为5A级景区,且处于城市核心区,邻近红船保护区域,严禁抽水作业,故只能采用水上抛投的施工方法。
3)湖区船舶多,船行波扰动大。在沉水植物生长初期,由于幼苗尚未扎根,船舶引起的船行波作用会影响沉水植物幼苗的正常扎根,直接威胁沉水植物的成活。南湖湖心岛与会景园之间有固定的红船游览航线,嘉兴水上巴士也从小瀛洲入南湖。此外,南湖管理单位众多,海事、港航、水上派出所、名胜公司、旅发公司等均有执法或巡逻船舶,湖区船舶密度大、航线分散,影响沉水植物的成活率。
2. 南湖水体生态修复系统的构建
2.1 生态系统构建的整体思路
水体透明度的主要影响因子包括光学衰减系数、悬浮物及叶绿素a等[34]。南湖透明度低的关键原因是悬浮物质量浓度高。沉水植物生长的基本条件是光照强度,此外,水深条件、污染物浓度、波浪条件等也能影响沉水植物的正常生长。综合来看,嘉兴南湖生态修复的核心就是要提升水体透明度和恢复湖区水下生态系统。
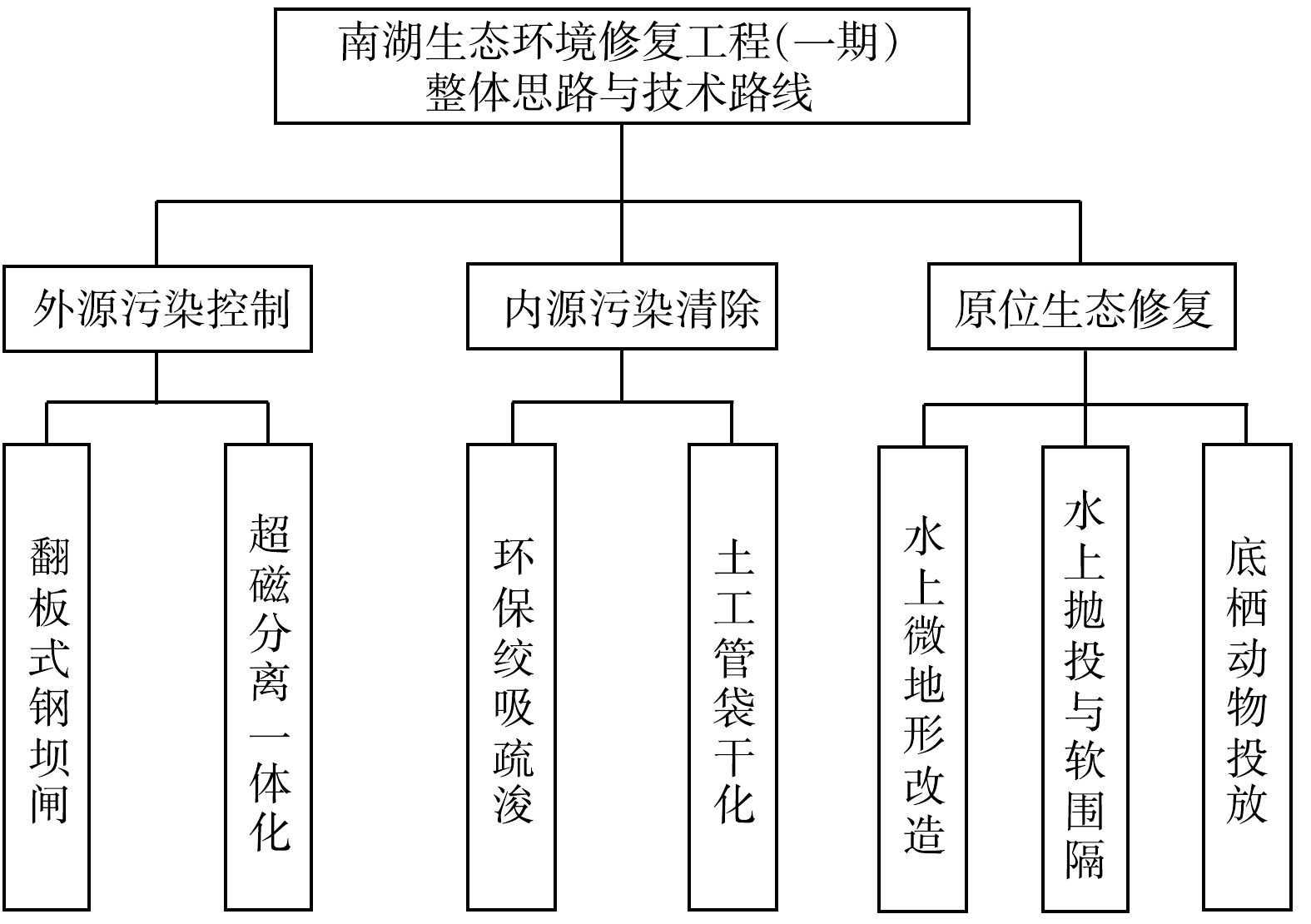
嘉兴南湖生态环境修复工程(一期)项目实施的主要目的是改善南湖水体质量,恢复湖区生态系统,实现南湖水质、生态及景观的全面提升。本项目的质量目标是使湖区水体透明度达到80 cm,沉水植物覆盖率达到25%。以沉水植物为主导,与水生动物相结合构建的水下生态系统作为一种新兴的河湖水体治理技术,已被许多工程采用,以实现湖泊氮磷污染、维持清水态湖泊的目标[35]。为实现工程治理目标,项目团队创新性地采用了前期“水养草”、后期“草养水”的治理理念。前期通过一系列工程措施提升水体透明度等指标,以便为沉水植物创造生长条件。后期待沉水植物恢复良好、“水下森林”生态系统构建成功后,再通过沉水植物生态系统的自净能力提升水体透明度等指标。南湖生态系统构建的整体思路如图2所示。
2.2 外源污染控制
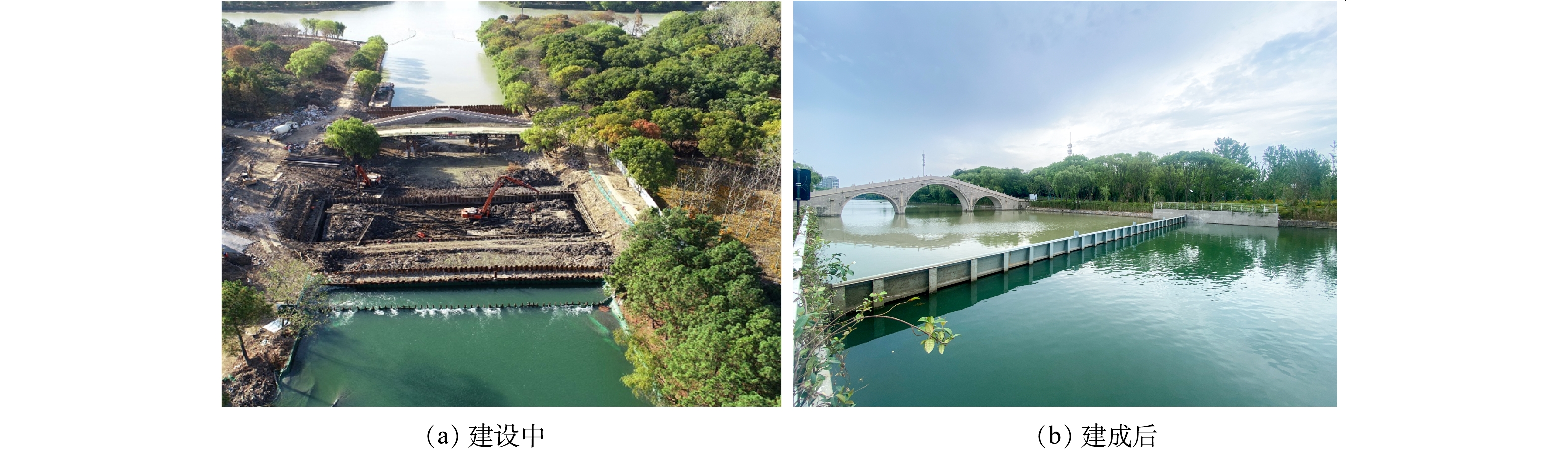
1)翻板式钢坝闸——水量调控。上游来水悬浮物质量浓度高[25]、TP污染物高[23],为防止上游浊水持续进入南湖,在南湖上游河道(青龙港、采菱桥港、宝莲桥港、长盐塘、张家门港)修建水量调控的闸坝措施。拦河闸坝的结构形式通常有直升式钢闸门、上翻式液压门、倒卧式液压门、钢坝、橡胶坝等。直升式闸门上部结构较大,整体景观效果差;上翻式液压门闸门开启时,影响通航且景观效果差;倒卧式液压门闸门开启以后河道易产生淤积。本工程的水量调控措施主要采用了5座带船舶自动识别的自动化控制翻板式钢坝闸,既能满足设计对外源污染的拦截及水体交换的控制,又不影响正常通航秩序,同时钢坝启闭机室为地下结构,建成后美观大方,最大程度地保证了节能、环保、人居和谐。上游长盐塘钢坝建设实施和建成后现场照片如图3所示。
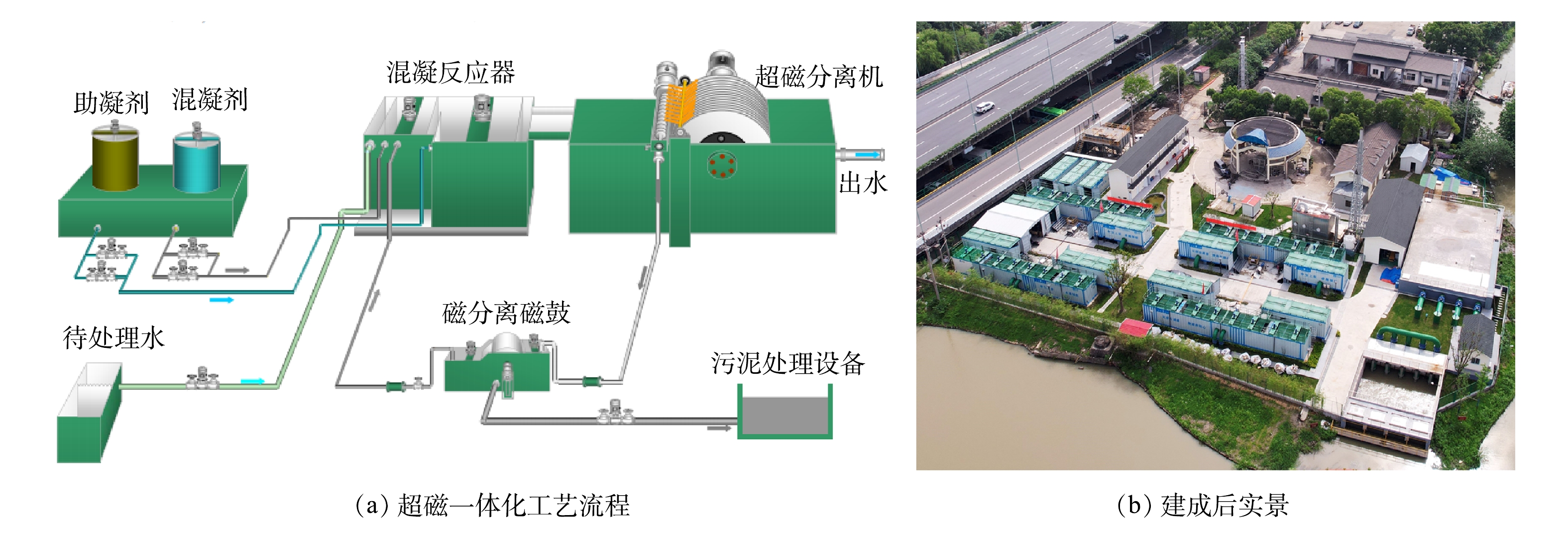
2)超磁分离一体化工艺——净水降浊。悬浮物的去除通常可采用混凝-沉淀、磁粉-混凝工艺等措施。混凝-沉淀工艺在我国大中型水厂中应用较为普遍,但是工艺所需占地面积较大,而南湖位于嘉兴核心城区,无法满足工艺所需的占地需求。超磁分离一体化工艺作为磁粉-混凝工艺的典型代表,通过磁盘吸附进行固液分离,实现水体快速净化,具有占地面积小、处理速度快、自动化程度高、模块化快速安装的优点[17],特别适合嘉兴南湖等城市核心区用地面积紧张的水环境治理项目。超磁设备部分主要由16个标准集装箱组成,土建部分由取水池、调蓄池、加药间、磁粉仓库等组成,全部的设备和土建集中在嘉兴大桥南侧大约3 000 m2场地内,整个超磁设备的补水规模达到20×104 t·d−1。超磁分离一体化工艺流程[17]和建成后实景如图4所示。
2.3 内源污染清除
环保绞吸疏浚与土工管袋干化技术——去除底泥污染物。环保疏浚的目的主要是为了清除污染底泥,一般以清淤厚度作为控制标准,而非传统疏浚的增加通航水深。内河或湖泊、湿地的环保清淤常用船机包括抓斗式挖泥船、反铲式挖泥船、链斗式挖泥船、绞吸式挖泥船等。前3种挖泥船的挖泥工艺均为“挖-运-抛”,泥驳靠泊、抛泥均需要作业时间,导致工艺不能连续作业,影响施工效率;而绞吸式挖泥船的最大优点就是可以连续作业,施工效率较高。嘉兴南湖湖区的清淤采用了加装整流罩的环保绞吸挖泥船,减小了因绞刀切削疏浚土导致的污染物再悬浮,疏浚土通过排泥管线输送至处理场地,利用土工管袋干化的方式,实现了疏浚土减量化、无害化的处理。同时,干化后的疏浚土可以作为绿化种植土回收利用,干化尾水再次通过超磁分离一体化设备处理,实现达标排放,疏浚工艺全程环保化处理[36]。
2.4 原位生态修复
1)水上微地形改造技术——重塑水下地形。微地形改造的目的是改变近岸侧沉水植物种植区域的水深条件,重塑水下地形,为沉水植物种植建立良好的下部基础。南湖南岸成功堤一侧为景观块石护岸,其他位置多为直立式护岸结构,基本无自然岸坡,近岸侧水深接近湖区平均水深,无梯级过渡。南湖的近岸侧微地形改造采用松木桩护脚,松木桩内侧为土工袋装土,防止内侧土方冲刷渗漏,微地形改造区域主体采用种植土散装回填。松木桩施打、袋装土填筑和散装土回填均采用平板驳船配合反铲挖机施工。微地形改造后,近岸侧沉水植物种植区域水深由2.5 m左右恢复至1.5 m左右,为沉水植物种植创造了良好的水深、地形和土质条件。
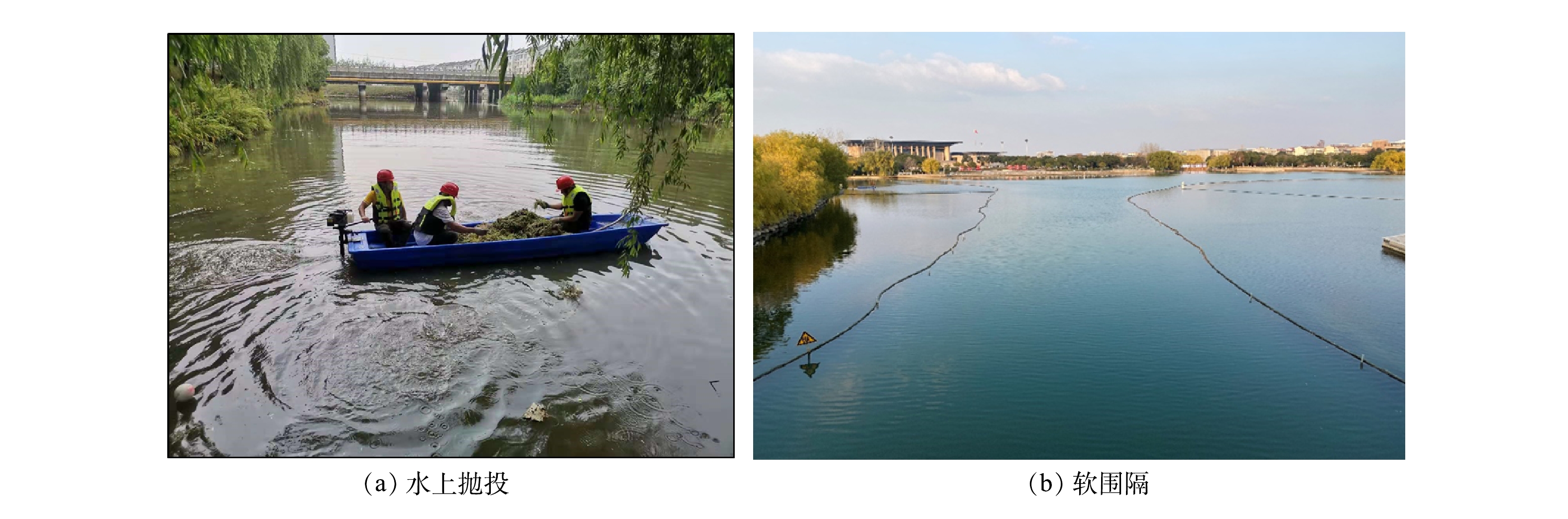
2)水上抛投与软围隔技术——带水栽植沉水植物。嘉兴南湖由于不具备抽水干地作业施工的条件,故沉水植物不能采用常规的扦插种植方式。本次沉水植物种植采用了水上小型作业辅助船舶、沉水植物带土或配重抛投的带水栽植方式。带土抛投是直接将植物基地的苦草连土带苗铲起,装入周转箱中并运输至项目现场。抛投时将土块分成小丛,直接投放至湖底,这种方式仅限于种植根系发达的苦草。配重抛投是将沉水植物包裹在切割好的网片上,并放入石子后用橡皮筋扎牢,做成球状,将加工好的单个个体放入泡沫箱或周转箱中并运输至项目现场,按照密度直接投放至水底。虽然水上抛投施工效率和幼苗成活率低,但受限于南湖苛刻的施工条件,也取得了良好的施工效果。另一方面,为了减少南湖湖区频繁的船舶航行所带来的船行波影响,在沉水植物种植区域外围布置软围隔,用以削减船行波、风成浪等对沉水植物幼苗扎根的不良影响。此外,在沉水植物种植前期,通过拉网赶鱼、软围隔隔断等措施,防止食草性鱼类在沉水植物生长初期啃食幼苗,确保沉水植物的成活率。沉水植物水上抛投和软围隔如图5所示。
3) 底栖动物投放——构建完整的生态系统。完整的“水下森林”生态系统是以沉水植物为主体,并辅以螺类、蚌类等底栖动物,以及水中的草食性、肉食性鱼类等生物群落共同组成。嘉兴南湖除恢复了湖区25%面积、约14.8×104 m2的沉水植物外,还配套投放了约5.6 t的螺类、蚌类和虾类,如铜锈环齿螺、背角无齿蚌、三角帆蚌、日本沼虾,重新构建了南湖的“水下森林”生态系统。
3. 工程实施效果评价
3.1 整体效果
通过南湖生态环境修复工程(一期)项目的实施,南湖水体感官明显好转,水体污染物指标显著改善,水体透明度基本达到设计要求,沉水植物恢复良好。翻板式钢坝闸、超磁分离一体化工艺、环保绞吸疏浚与土工管袋干化、水上抛投与软围隔等关键技术在南湖水体生态修复过程中发挥了重要作用。
1)翻板式钢坝闸兼具美观、通航、挡水、船舶自动识别的作用,克服了传统挡水建筑物影响通航或者占用水域面积影响景观效果的缺点,尤其适用于城市核心区域、通航河道挡水或拦河建筑物的建设。
2)超磁分离一体化工艺设备具有占地面积小、噪音低、自动化程度高、安装速度快等优点,特别适合嘉兴南湖此类治理工期紧张、用地限制、环保要求高的项目。
3)湖区环保疏浚采用环保绞吸疏浚和土工管袋干化结合的技术,土工管袋干化后的尾水创新性地采用超磁分离一体化设备进行二次处理。南湖所采用的环保疏浚技术减小了疏浚过程中的底泥再悬浮,实现了疏浚土的减量化、无害化处置。
4)沉水植物水上抛投与软围隔技术解决了南湖不能抽水作业的难题,配合水生动物的投放,南湖水下森林生态系统恢复良好,为南湖水体生态修复奠定了基础。
3.2 南湖水质监测效果
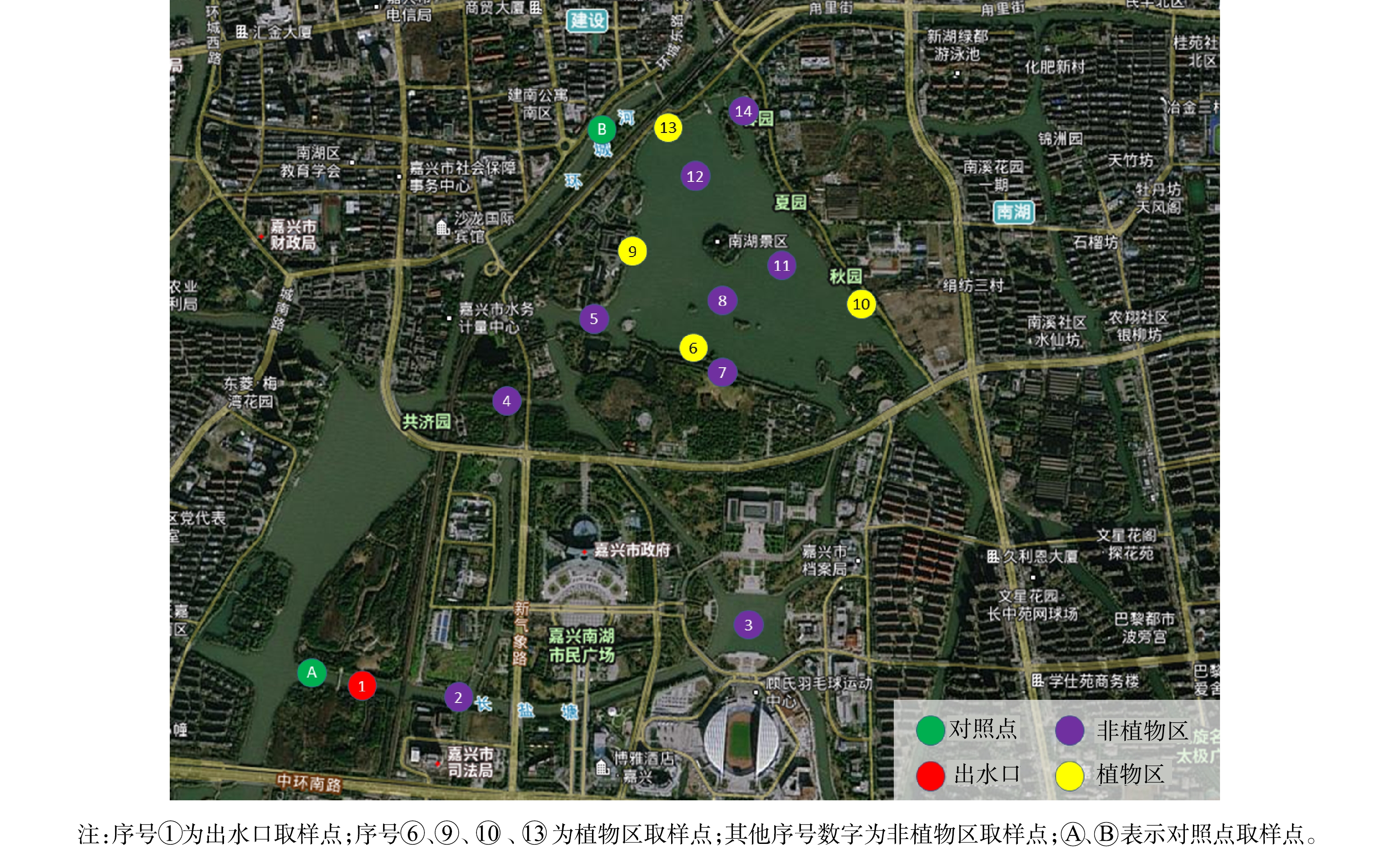
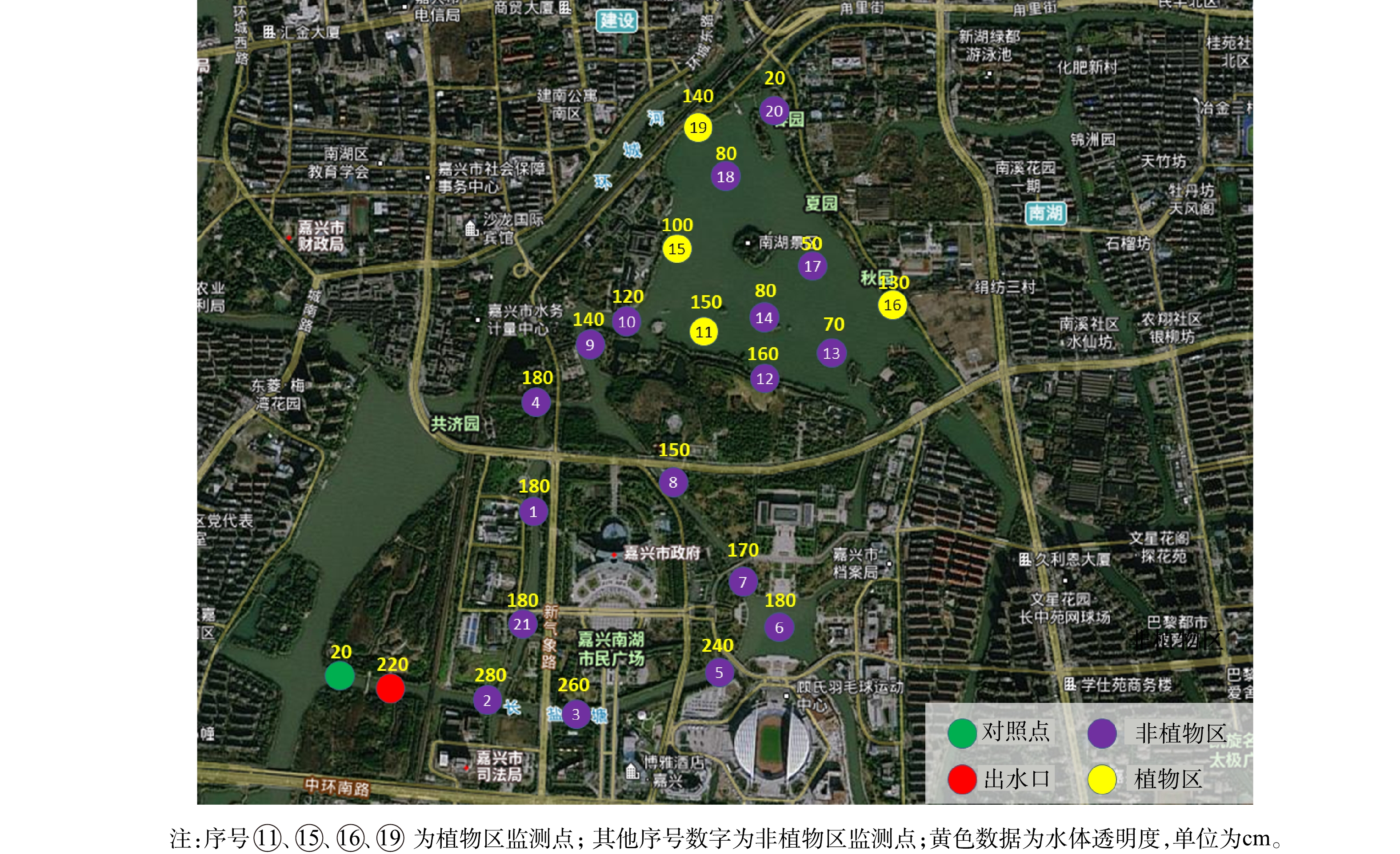
该工程完工后,项目组开展了多次水质监测,NH3-N稳定达到地表Ⅱ类水标准(湖泊标准)[29],COD稳定达到地表Ⅲ类水标准(湖泊标准)[29],南湖(除下游海盐塘出口外)大部分区域TP指标基本达到了地表Ⅱ类水标准(湖泊标准)[29]。为进一步验证工程实施效果,选取工程完工后2021年6月1日至2021年6月24日的6次水质监测数据,汇总后取平均值,进行分析讨论。各监测点、对照点位置分布及具体水质监测数据如图6、表2所示。为了验证超磁分离一体化设备对土工管袋干化后的尾水处理效果,对尾水水质进行了监测,监测数据如表3所示。
表 2 南湖水质监测数据平均值Table 2. Average value of water quality monitoring data of Nanhu lake取样点位 浊度/NTU COD/(mg·L−1) NH3-N/(mg·L−1) TP/(mg·L−1) 叶绿素a/(μg·L−1) SS/(mg·L−1) TN/(mg·L−1) 1号点 3 14 0.301 0.011 8 13 2.69 2号点 3 13 0.337 0.012 8 13 2.74 3号点 3 16 0.318 0.011 12 12 2.55 4号点 3 17 0.271 0.018 9 16 2.71 5号点 4 18 0.197 0.016 11 13 2.47 6号点 4 13 0.082 0.017 16 14 1.84 7号点 4 14 0.056 0.017 11 14 1.75 8号点 7 18 0.126 0.022 18 24 2.43 9号点 3 15 0.060 0.016 16 14 2.12 10号点 3 13 0.097 0.014 15 14 2.20 11号点 10 16 0.110 0.038 20 26 2.54 12号点 11 16 0.110 0.039 21 29 2.54 13号点 8 13 0.111 0.026 32 19 2.44 14号点 14 18 0.141 0.060 13 32 2.59 对照点A 16 14 0.485 0.149 17 28 2.48 对照点B 22 17 0.292 0.161 10 42 2.98 表 3 疏浚土干化尾水水质监测数据Table 3. Monitoring indicators of tail water quality from dredged soil drying日期 COD/(mg·L−1) NH3-N /(mg·L−1) SS/(mg·L−1) pH 磷酸盐/(mg·L−1) 2021-01-01 21 1.93 <4 7.56 0.02 2021-01-07 17 1.84 <4 7.47 0.04 2021-01-14 14 1.92 <4 7.39 0.05 2021-01-21 20 1.84 <4 7.44 0.04 由表2可以看出,河道1号点为超磁分离一体化设备出水口(最终入水系位置),对照点A靠近超磁分离一体化设备取水口,对照点A和河道1号点分别位于长盐塘钢坝的上/下游,通过水量调控措施(长盐塘钢坝)分隔开。2处位置的水质数据分析结果表明:1)超磁分离一体化设备出水浊度可以维持在3 NTU左右,与项目组对超磁设备直接出水的浊度每日监测数据基本一致;2)超磁分离一体化设备可以显著去除水体中的TP(去除率为92.61%),对NH3-N(去除率为37.94%)也有一定的去除作用,但是对TN、COD等的去除不明显。
通过对沉水植物种植区域悬浮物质量浓度进行对比分析可以看出,湖区沉水植物种植区(6、9、10、13号点)的悬浮物平均质量浓度15.25 mg·L−1明显低于湖区其他区域(8、11、12号点)的平均质量浓度26.33 mg·L−1,沉水植物种植区域悬浮物下降比值为42.09%。这表明沉水植物对水体中悬浮物具有明显的吸附作用。项目组利用水下摄像机对沉水植物进行观察也发现,植物叶片上附着了大量的悬浮性颗粒物。因此,通过沉水植物吸附、收割打捞、生长、吸附这一循环过程,能够实现水中悬浮物的转移去除。
由表2可以看出,南湖下游平湖塘出口位置(14号点)TP指标明显优于平湖塘位置(对照点B)。这表明现有工程治理措施及沉水植物系统已发挥一定的作用,但是悬浮物质量浓度和浊度改善效果不明显。因此,项目团队在南湖下游小瀛洲出口位置布置了流量计,对出入湖流量进行了监测。监测数据表明每天仍有大量的浊水通过下游出口进入南湖。这可能是由于嘉兴南湖水系仍受到不规则半日潮每天2次涨潮所带来的水流顶托的影响,对南湖正常的清水补给、置换产生了一定的削弱。
由表3可以看出,土工管袋干化后的尾水经4次检测,悬浮物SS均不超过4 mg·L−1,优于《污水综合排放标准》(GB 8978-1996)一级A标准10 mg·L−1的要求,实现了疏浚土尾水的达标排放。
3.3 南湖水体感官效果
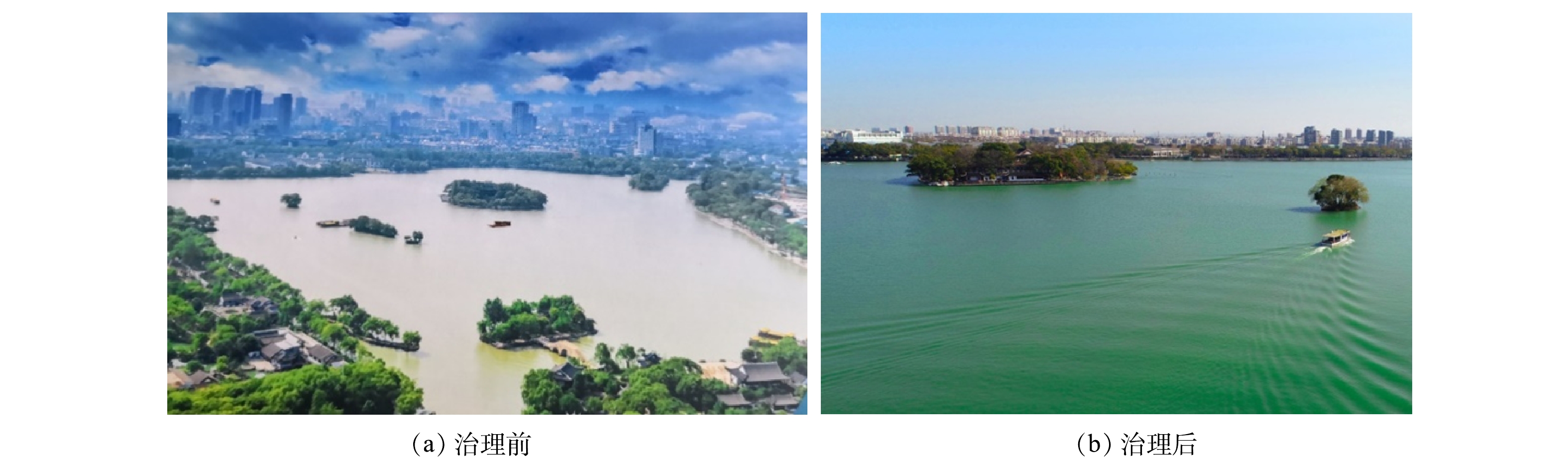
南湖生态环境修复工程(一期)项目完工后,湖区大部分水体透明度已达到80 cm以上(图7),湖区水体颜色由黄色变为浅绿色,重现了嘉兴南湖“秀水泱泱”的美丽画卷(图8和图9)。由南湖水体透明度的监测数据和湖区感官效果改善情况可以看出: 1)南湖水系水体透明度沿两条清水入湖路线“长盐塘→蒋水港→壕股塔→平湖塘出口”和“长盐塘→七一广场→金谷桥港→壕股塔→平湖塘出口”呈下降趋势,表明在项目治理前期(水养草阶段),超磁分离一体化设备的清水补给是南湖水系透明度提升的关键; 2)南湖平湖塘出口区域的透明度仅有20 cm,表明每天涨潮流潮汐顶托进入南湖的浊水对靠近出口区域的水体透明度影响很大。
3.4 建议
1)在现有工程措施的基础之上,如果能在南湖出口位置修建水量调控措施(如翻板式钢坝闸或橡胶坝),将南湖水系完全封闭,并通过水量和水位的精细化调控,可能会进一步提升南湖水体透明度,且可以减少超磁分离一体化设备处理量并大幅缩减设备的运维成本。
2)超磁一体化设备购置费用和运维成本偏高,仍需针对不同水环境项目选择性价比更优的处理设备。
3)南湖由于不能降水作业,沉水植物种植方式受限,故只能采用水上抛投方式,这导致沉水植物成活率偏低。在沉水植物种植条件允许的情况下,利用抽水作业进行浅水扦插种植仍是施工综合效率高、成活率高、造型美观的最佳种植方式。
4)通过无人机航拍视频发现,游船航经区域呈现明显的“浑浊带”,表明船行波对底泥扰动造成的底泥再悬浮作用非常明显。如果能对南湖游船进行“电动化改造”、减小吃水深度,或者通过管理手段控制航行频次和航行速度,可能会更加有利于湖区水体透明度的改善。
4. 结论
1)嘉兴南湖生态环境修复工程(一期)项目完工后,水质监测结果表明,南湖主要水质指标(COD、NH3-N、TP)基本达到地表水Ⅲ类(湖泊标准),湖区大部分区域水体透明度达到80 cm以上,水体颜色由黄色变为浅绿色。由此可以看出,南湖生态环境修复的整理思路和技术路线是可行的。
2)超磁分离一体化设备适合在城市核心区处理高浊度水体,可以显著去除水体中的TP(去除率为92.61%),对NH3-N(去除率为37.94%)也有一定的去除作用,但是对TN、COD等的去除不明显。
3)以“沉水植物”为主体的水下森林生态系统对悬浮型颗粒物具有明显的去除作用,沉水植物种植区域悬浮物下降了42.09%。同时,在沉水植物养护阶段,应及时进行补种、收割、打捞,并通过沉水植物品种的搭配保证四季常绿,以确保沉水植物的长效净化作用。
4)湖区疏浚采用环保绞吸疏浚与土工管袋干化相结合的技术,减少了疏浚过程中的底泥再悬浮,土工管袋干化后的尾水采用超磁分离一体化设备二次处理,悬浮物SS指标均不超过4 mg·L−1,实现了疏浚土尾水的达标排放。
-
[1] 马培培.强化混凝去除微污染源水中重金属砷(Ⅲ)、汞(Ⅱ)的研究.广州:暨南大学硕士学位论文,2010MA Peipei.Studies on removal of heavy metals As(Ⅲ)、Hg(Ⅱ) from micro-polluted waters by enhanced coagulation.Guangzhou:Master Dissertation of Jinan University,2010(in Chinese) [2] 吴舜泽,夏青,刘鸿亮.中国流域水污染分析.环境科学与技术,2000,23(2):1-6WU Shunze,XIA Qing,LIU Hongliang.Analysis of river basin water pollution in China.Environmental Science & Technology,2000,23(2):1-6(in Chinese) [3] 许保玖.论水质科学与工程兼论21世纪的水处理科技.工业水处理,2000,20(1):1-4XU Baojiu.On water quality science and engineering and the water treatment technology of the 21st century.Industrial Water Treatment,2000,20(1):1-4(in Chinese) [4] 孟紫强.环境毒理学.2版.北京:中国环境科学出版社,2003:110-113 [5] 魏智宽,蒋世云,李德洁,等.饮用水源水突发性镍污染应急处理试验研究.工业水处理,2014,34(8):47-50WEI Zhikuan,JIANG Shiyun,LI Dejie,et al.Experimental study on the emergency treatment of drinking water source accidents caused by sudden nickel pollution.Industrial Water Treatment,2014,34(8):47-50(in Chinese) [6] 曹翠萍,王雪莉.重金属-镍对人体健康的危害及预防.中国现代药物应用,2013,7(9):78-79CAO Cuiping,WANG Xueli.The harm to human health and prevention of heavy metal nickel.Chinese Journal of Modern Drug Application,2013,7(9):78-79(in Chinese) [7] 皮嵩云,王艳,张玉莲.低浓度镍对人体健康影响的探讨.实用预防医学,2006,13(4):969-970PI Songyun,WANG Yan,ZHANG Yulian.On the impact of low concentration of nickel for human health.Practical Preventive Medicine,2006,13(4):969-970(in Chinese) [8] 赵越,韩雪,崔崇威.强化混凝沉淀去除水中三种二价重金属离子的试验研究.化学工程师,2011,25(6):51-53ZHAO Yue,HAN Xue,CUI Chongwei.Experimental studies of removal of three divalent heavy metal ions with enhanced coagulation.Chemical Engineer,2011,25(6):51-53(in Chinese) [9] 张晓健.松花江和北江水污染事件中的城市供水应急处理技术.给水排水,2006,32(6):6-12ZHANG Xiaojian.Emergent drinking water treatment in water pollution accidents in Songhuajiang River and Beijiang River.Water & Wastewater Engineering,2006,32(6):6-12(in Chinese) [10] 杨立成,王春,邱燕.吸附法处理有机物:金属复合污染体系的研究进展.中国资源综合利用,2008,26(2):29-31 YANG Licheng,WANG Chun,QIU Yan.Advance in treatment of combined pollution of heavy metals and organics by adsorption.China Resources Comprehensive Utilization,2008,26(2):29-31(in Chinese) [11] VRTOCH L.,PIPÍŠKA M.,HORNÍK M.,et al.Sorption of cesium from water solutions on potassium nickel hexacyano ferrate-modified Agaricus bisporus mushroom biomass.Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry,2011,287(3):853-862 [12] AUDERSON R.W.,NEFF W.A.Electroless nickel bath recovery by cation change and precipitation.Plating and Surface Finishing,1992,79(3):22-26 [13] 施周,贺维鹏.饮用水水源中重金属污染防控技术与对策.给水排水,2012,38(8):1-3 SHI Zhou,HE Weipeng.Prevention and control technology and the countermeasures drinking water sources in the heavy metal pollution.Water & Wastewater Engineering,2012,38(8):1-3(in Chinese) [14] 石华前,黄孟,李娟,等.高铁酸钾处理含油污水的应用研究.山东化工,2014,43(6):187-188 SHI Huaqian,HUANG Meng,LI Juan,et al.Treatment of oily wastewater of Hui Zhou oil field using Ferrate (Ⅵ).Shandong Chemical Industry,2014,43(6):187-188(in Chinese) [15] 刘旭东,林雪,薄文晴,等.高铁酸盐去除炼油废水中COD的研究.沈阳建筑大学学报,2014,5(2):12-14 LIU Xudong,LIN Xue,BO Wenqing,et al.Study on removing of COD in refinery wastewater by ferrate.Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science),2014,5(2):12-14(in Chinese) [16] 谢鸿芳,郑淑英,陈巧平,等.高铁酸盐/Al(OH)3 对偶氮类染料的降解脱色研究.福建师范大学学报(自然科学版),2011,27(4):112-116 XIE Hongfang,ZHENG Shuying,CHEN Qiaoping,et al.Study on treating azo dyes waste water by FeO2-4/Al(OH)3 coagulant.Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2011,27(4):112-116(in Chinese) [17] 金鹏康,王晓昌.腐殖酸混凝过程FI曲线的特征参数分析.环境科学学报,2002,22(4):423-427 JIN Pengkang,WANG Xiaochang.An analysis of characteristic parameters of FI curve for coagulation of humic acid.Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2002,22(4):423-427(in Chinese) [18] 程方,秦涛,赵现勇,等.加药量和水力搅拌速度对雨水混凝效果的影响.环境工程学报,2012,6(11):3905-3909 CHENG Fang,QIN Tao,ZHAO Xianyong,et al.Effect of coagulant dosage and hydraulic strirring speed on rainwater coagulation.Chinese journal of Environmental Engineering,2012,6(11):3905-3909(in Chinese) [19] 马艳,高乃云,楚文海,等.高铁酸钾及其联用技术在水处理中的应用.水处理技术,2010,36(1):10-14 MA Yan,GAO Naiyun,CHU Wenhai,et al.Application of potassium ferrate and hyphenated techniques in water treatment.Technology of Water Treatment,2010,36(1):10-14(in Chinese) [20] 马军,梁咏梅,刘伟,等.预投加高铁酸盐强化混凝去除原水中的铅、镉.中国给水排水,2007,23(7):48-50 MA Jun,LIANG Yongmei,LIU Wei,et al.Ferrate pretreatment for enhancing removal of lead and cadmium from water.China Water & Wastewater,2007,23(7):48-50(in Chinese) -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2478
- HTML全文浏览数: 2015
- PDF下载数: 452
- 施引文献: 0



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: