全球新型冠状病毒爆发以来,消毒剂已经成为了人们生产生活的必需品。 据报道,2020年2月武汉市消毒剂的居民使用量高达1 900 多t,此外,污水处理厂的消毒剂投放量高达1 700 多t[1]。 至今,国外疫情依旧没有得到全面控制。 可想而知,全球消毒剂的使用量将是一个极为庞大的数字。 大量消毒剂的使用导致生态环境面临较大的潜在危险。Tong 等[2]研究发现含氯消毒剂的大量使用会造成菌的耐药性。 此外,在消毒剂使用的过程中会伴随有消毒副产物的生成[3],对生态环境造成了更为严重的影响。 有调查甚至发现,新冠疫情后有98.6%的人在使用消毒剂的时候会将多余的消毒剂遗弃到环境中,这势必会导致水生生态环境被直接或是间接的污染[4]。 消毒剂的过量使用会使水生生态系统遭遇极大的破坏,影响水质进而增加动物和人类的间接风险[5-6]。 相比于一般重金属、抗生素和离子液体等污染物而言,消毒剂易挥发,更易对人体健康产生危害。 Park 等[7]发现加湿器消毒剂的主要成分(聚六亚甲基胍)会造成孕妇和儿童肺部发生病变。Herron 等[8]研究发现苯扎氯铵消毒剂会对胆固醇生物合成产生影响从而破坏神经发育。 在众多消毒剂中,季铵盐类消毒剂(quaternary ammonium salt disinfectant, QASD)是在卫生、养殖业和工业等各个领域中广泛被使用的一种消毒剂[9],目前,对消毒剂毒性风险评估的研究较少,对QASD 的毒性风险评估则更少,因此有必要对QASD 进行毒性研究。
在自然环境中,污染物常以混合物形式存在[10-12],这就势必会造成污染物的复合污染。 混合物可能会产生比单个污染物风险更大、更复杂的毒性相互作用,采用适当的模型客观和准确地评估混合物对环境的危害和风险是非常关键的。 浓度加和(concentration addition, CA)模型[11-14]是目前众多评估模型中应用最为广泛的一种,然而,CA 模型只能定性评估混合物毒性相互作用。 在环境风险评估时,需要关注到混合污染物对环境产生最大风险的程度[15],因此,需要对混合物毒性相互作用的强度进行定量评估。 基于CA 模型的拟合归零法[16]将拟合的浓度剂量效应曲线(concentration-response curves,CRCs)上的各个效应归一化到同一尺度,并对CA 模型预测线和CRCs 做偏差分析,可对毒性相互作用进行定量表征。
综上所述,本文拟以蛋白核小球藻(Chlorella pyrenoidosa)为受试生物,以生活中常用的3 种季铵盐类消毒剂双十二烷基二甲基溴化铵(didodecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide, DAB)、 苯 扎 溴 铵(benzalkonium bromide, BKB)和度米芬(domiphen bromide, DOM)为研究对象,采用均匀设计射线法(uniform design ray, UD-ray)设计消毒剂的三元混合物体系。 应用时间依赖微板毒性分析法(time-dependent microplate toxicity analysis, t-MTA)考察消毒剂及其三元混合体系对C. pyrenoidosa 的毒性效应。分别应用CA 模型和拟合归零法对三元消毒剂混合物的毒性相互作用进行定性和定量评估,以此为其环境风险评估提供数据和方法参考。
1 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 试剂
选取3 种常用的季铵盐类消毒剂(QASD)作为实验对象,其中双十二烷基二甲基溴化铵(DAB)为分析纯,购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司,苯扎溴铵(BKB)和度米芬(DOM)为分析纯,购自上海麦克林生化科技有限公司,它们的理化性质如表1所示。 为避免消毒剂浓度在储存过程中发生变化,3种消毒剂的溶液均是当天现配现用,且采用Milli-Q水配制,并储存于棕色瓶中,放置于4 oC 的冰箱内。
表1 3 种消毒剂的理化性质和储备液浓度
Table 1 Physical and chemical properties of the three disinfectants and concentration of stocks
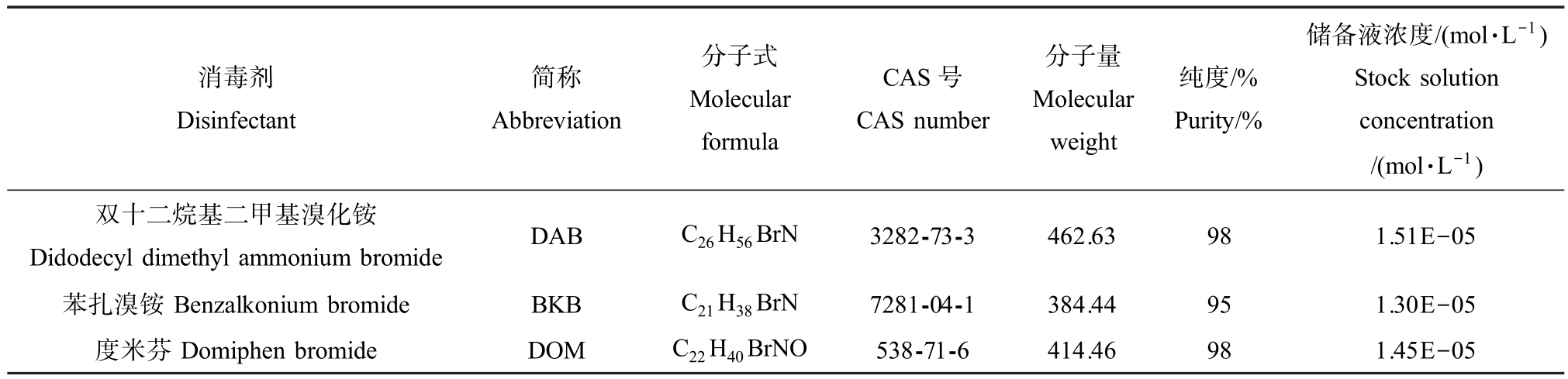
消毒剂Disinfectant简称Abbreviation分子式Molecular formula CAS 号CAS number分子量Molecular weight纯度/%Purity/%储备液浓度/(mol·L-1)Stock solution concentration/(mol·L-1)双十二烷基二甲基溴化铵Didodecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide DAB C26H56BrN 3282-73-3 462.63 98 1.51E-05苯扎溴铵Benzalkonium bromide BKB C21H38BrN 7281-04-1 384.44 95 1.30E-05度米芬Domiphen bromide DOM C22H40BrNO 538-71-6 414.46 98 1.45E-05
1.2 藻种与培养方法
蛋白核小球藻(C. pyrenoidosa)购自中国科学院典型培养物保藏委员会淡水藻种库(FACHB),编号为FACHB-5,采用BG11 培养基[17]进行培养,藻液按1 ∶5 的比例进行转接,为防止C. pyrenoidosa 聚于瓶底,也为了藻液受光均匀,需要每天定时摇晃锥形瓶,藻的详细培养过程参考文献[18]。
1.3 混合物设计
均匀设计射线法(UD-Ray)是一种可用于全面表征三元及以上多元混合物的方法[12,19],在此,采用UD-Ray 设计QASD 的三元混合物体系,其中包括5条射线 U1、U2、U3、U4 和 U5,每条射线中各组分的浓度比例(pi)如表2 所示。
表2 三元混合体系中季铵盐类消毒剂(QASD)的浓度比(pi)
Table 2 Concentration ratio (pi) of quaternary ammonium salt disinfectant (QASD) of the ternary mixture system
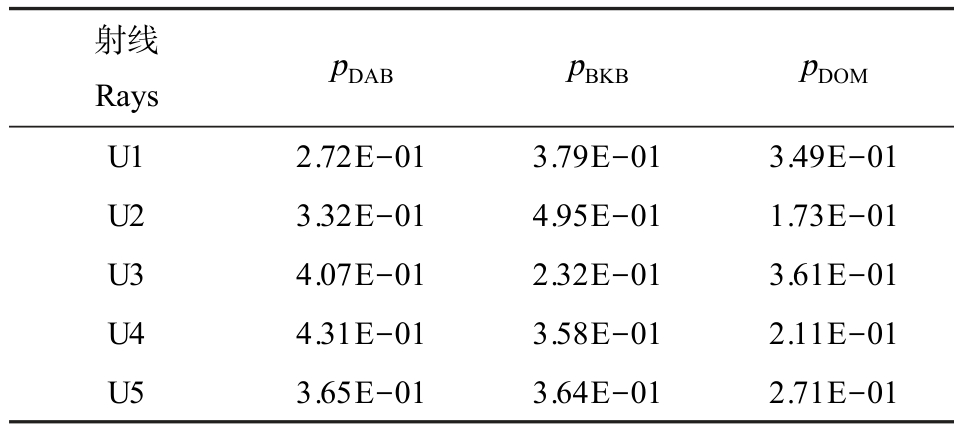
射线Rays pDAB pBKB pDOM U1 2.72E-01 3.79E-01 3.49E-01 U2 3.32E-01 4.95E-01 1.73E-01 U3 4.07E-01 2.32E-01 3.61E-01 U4 4.31E-01 3.58E-01 2.11E-01 U5 3.65E-01 3.64E-01 2.71E-01
1.4 时间依赖微板毒性分析法
通过时间依赖微板毒性分析法(t-MTA)[20-21]获得单个消毒剂及其三元混合物的浓度-效应数据。选择透明的96 孔板为实验载体,在其四周共36个微孔中加入200 μL 超纯水以避免边缘效应。 在第6、7 列剩余的 12 孔中加入 100 μL 超纯水作为空白对照组,其余列按预实验的稀释因子设置12个浓度梯度,最终在每个微孔中加入100 μL 处于对数生长期(0.2<OD690 <0.3)的藻液使得每个孔的总体积为200 μL。 为减少实验误差,每个实验组均设置3个平行样。 此外,为了避免蒸发,每个透明的96 孔板都加盖,并放置在(25±1)℃、光暗比14 h ∶10 h、光照强度为5 000 lx 的光照培养箱中培养,每天定时交换板的位置以确保受光均匀,在12、24、48、72 和96 h 时取出,放置于酶标仪中读取OD690 值。 毒性效应(E)计算公式如下:
1.5 数据拟合
毒性数据采用两参数非线性模型 Logit 函数[22-23]来进行拟合,数据拟合通过APTox 软件[24]来实现。 Logit 函数公式如下:
式中:E 表示效应(0≤E≤1),α 和 β 是模型参数,c是污染物的浓度。
为了描述实验数据的精密程度,采用观测值置信区间(confidence interval based on the observation,OCI)[25-26]来表征数据的不确定度。
1.6 混合物毒性相互作用分析
常采用CA 模型[13-14]来评估混合物的毒性相互作用,其公式如下:
式中:n 表示组分的个数;ci 表示当混合体系表现出效应x 时所对应的第i个组分的浓度;ECx,i 表示第i个组分所对应的等效应浓度。 当CA 模型拟合线与95% OCI 的相对位置不同时,代表了不同的相互作用规律,详细见判别示意图1(a)。
为了进一步对混合物毒性相互作用进行定量评估,采用基于浓度加和偏离指数(deviation from CA model, dCA)[15,27]和95% OCI 的拟合归零法对毒性相互作用实现动态定量表征,其公式如下:
式中:dOCI 表示置信区间的偏差程度,ECAx 表示CA 模型预测的效应,Ex 表示Logit 函数拟合的效应。 毒性相互作用见判别示意图1(b)。
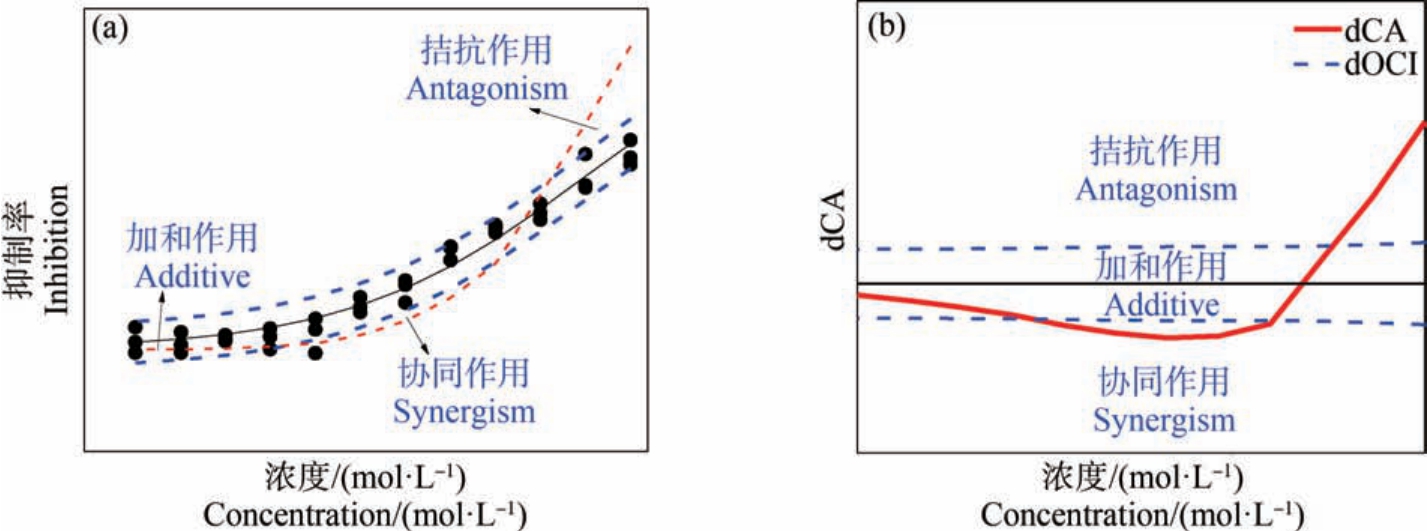
图1 毒性相互作用判别示意图
注:dCA 表示浓度加和偏离指数,dOCI 表示置信区间的偏差程度。
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of toxicity interaction identification
Note: dCA represents deviation from concentration addition model, and dOCI represents the degree of deviation of confidence interval based on the observation.
2 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 3 种 QASD 对 C. pyrenoidosa 的单元毒性
采用两参数非线性函数(Logit 函数)对由t-MTA法测得的3 种QASD 的单元毒性数据进行拟合,拟合的参数(α 和 β)和统计学参数(RMSE 和 R)如表 3所示。 此外,将不同时间点下的CRCs 绘制于图2。
由表 3 可知,3 种 QASD 对 C. pyrenoidosa 的单元毒性数据可以较好地被Logit 函数拟合(RMSE<0.070, R>0.8700)。 其中,初始时间(12 h)的拟合情况比后面时间点(24 ~96 h)的拟合情况稍差,这可能是藻在初始时间下存在适应性差异的原因[28]。 半数效应浓度(median effect concentration, EC50)由 Logit 函数(公式 2)的反函数计算而来。 3 种 QASD 对C. pyrenoidosa 的EC50 值比离子液体对发光菌[29]、农药对发光菌[30]和重金属对C. pyrenoidosa[31]的EC50 值分别小3个、2个和 2个数量级。 已有研究表明,发光菌比C. pyrenoidosa 对毒性响应更加敏感[32],如以pEC50 值(EC50 的负对数)为毒性大小指标[33-34],可知,3 种QASD 的毒性远大于文献中所报道的离子液体、农药和重金属的毒性。 这也表明在自然环境下对消毒剂进行风险评估尤为重要。 一般藻类的测试终点是96 h,此时的毒性顺序是:DOM>BKB>DAB。 但是越来越多的研究表明,时间是毒性研究中的一个重要因素[20,35]。 由表3 和图2 可知,3种消毒剂对C.pyrenoidosa 呈显著的时间依赖毒性效应,但在48 h 后毒性不再明显增加。 这也说明,在对污染物的毒性进行研究时,需要关注时间这一因素,不同污染物随时间变化的毒性效应规律有所不同。
表3 Logit 函数对3 种 QASD 在不同暴露时间下毒性数据的拟合参数(α 和 β)、统计学参数(RMSE 和R)、EC50 和 pEC50 值
Table 3 The fitting parameters (α and β), statistical parameters (RMSE and R), EC50, and pEC50 values of the three QASD toxicity data of the Logit function at different exposure times
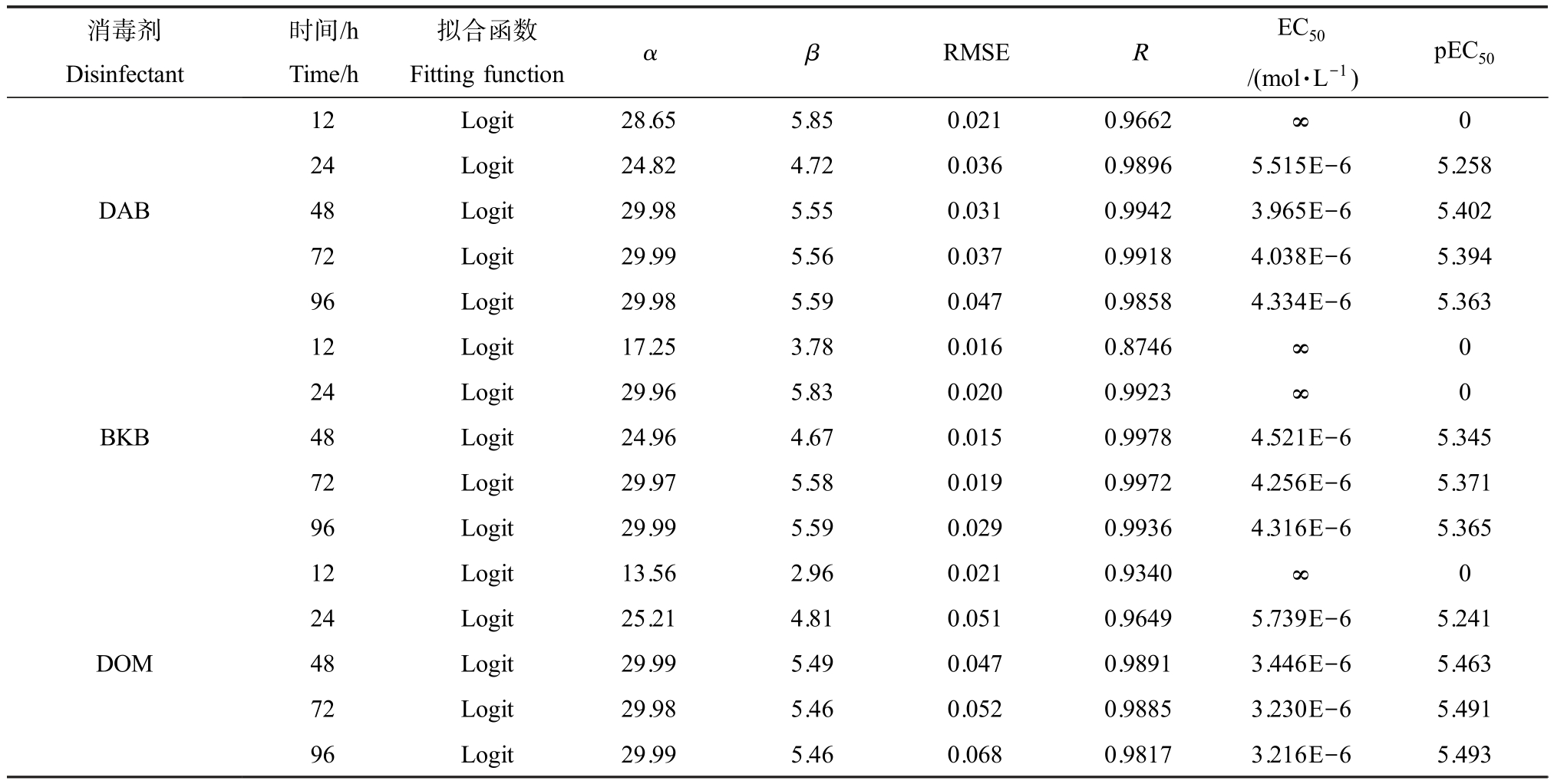
注:α 和β 是函数拟合参数;RMSE 和R 是统计学参数,分别表示均方根误差和确定系数;EC50 是半数效应浓度;pEC50 是EC50 的负对数。
Note: α and β are the function-fitting parameters;RMSE and R are the statistical parameters,representing root mean square error and the correlation coefficient, respectively; EC50 is the median effect concentration; pEC50 is the negative log value of the EC50.
消毒剂Disinfectant时间/h Time/h Fitting functionα β RMSE R EC50/(mol·L-1)拟合函数pEC50 12Logit28.655.850.0210.9662∞ 0 DAB BKB 24 Logit 24.82 4.72 0.036 0.9896 5.515E-6 5.258 48 Logit 29.98 5.55 0.031 0.9942 3.965E-6 5.402 72 Logit 29.99 5.56 0.037 0.9918 4.038E-6 5.394 96 Logit 29.98 5.59 0.047 0.9858 4.334E-6 5.363 12Logit17.253.780.0160.8746∞ 0 24Logit29.965.830.0200.9923∞ 0 48 Logit 24.96 4.67 0.015 0.9978 4.521E-6 5.345 72 Logit 29.97 5.58 0.019 0.9972 4.256E-6 5.371 96 Logit 29.99 5.59 0.029 0.9936 4.316E-6 5.365 DOM 12Logit13.562.960.0210.9340∞ 0 24 Logit 25.21 4.81 0.051 0.9649 5.739E-6 5.241 48 Logit 29.99 5.49 0.047 0.9891 3.446E-6 5.463 72 Logit 29.98 5.46 0.052 0.9885 3.230E-6 5.491 96 Logit 29.99 5.46 0.068 0.9817 3.216E-6 5.493
2.2 3 种QASD 对C. pyrenoidosa 的三元混合毒性效应
5 条三元混合射线的毒性效应数据可以较好地被 Logit 函数拟合(RMSE<0.050, R>0.8600)。 拟合的参数(α 和 β)和统计学参数(RMSE 和 R)如表 4 所示。 因三元混合物的时间-毒性-效应数据在效应0~1 范围内分布比单个消毒剂的均匀,为了更好地分析消毒剂毒性随暴露浓度和时间的变化规律,在三维曲线图(图2)的基础上绘制了浓度时间效应三维曲面图,如图3 所示。
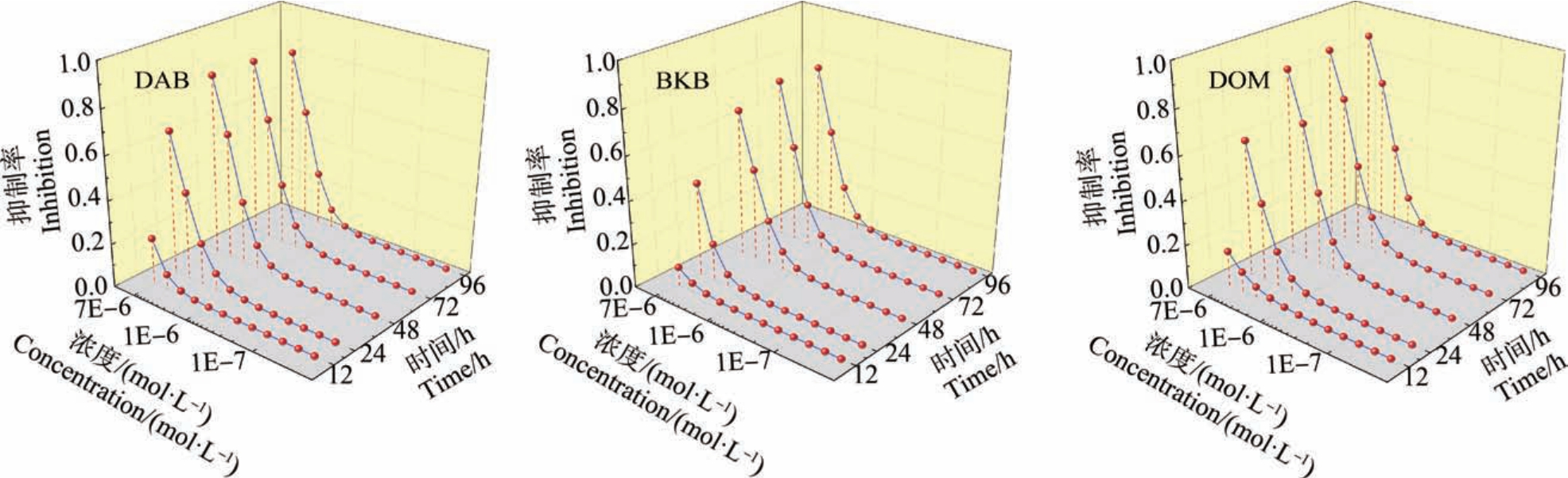
图2 不同暴露时间下3 种QASD 对C. pyrenoidosa 的拟合浓度剂量效应曲线(CRCs)
Fig.2 Fitted concentration-response curves (CRCs) of three QASD to C. pyrenoidosa at different exposure times
由图3 可知,三维曲面图的颜色映射情况可以很好地呈现出污染物毒性与浓度和时间因素的变化规律。 同一暴露时间下,5 条QASD 三元混合射线对C. pyrenoidosa 的抑制率随混合浓度增加而逐渐变大,即具有浓度依赖毒性效应。 张瑾等[33]在研究氨基甲酸酯类农药对青海弧菌毒性特点时也发现了该规律。 同一浓度下,5 条QASD 三元混合射线对C. pyrenoidosa 的抑制率随时间的延长而逐渐变大,即具有时间依赖毒性效应,丁婷婷等[32]发现氨基糖苷类抗生素对发光菌和C. pyrenoidosa 也具有时间依赖毒性效应。 将0.1 ~0.9 的效应用红色实线在三维曲面上标注出来,可知不同的效应浓度随时间的变化规律有所不同。 12 ~48 h 时,EC10、EC20、EC30和EC40 在逐渐减小,而在48 ~96 h 时则逐渐变大,但每个效应浓度随时间的变化程度有所不同。 由红色实线的弯曲程度可知,48 ~96 h 的效应浓度变化的程度在逐渐变小。 图3 中5 条射线的 EC50 值在12 ~48 h 快速减小,在48 ~72 h 缓慢减小,而在72~96 h 则缓慢增大,这和表4 中EC50 值的变化规律一致。
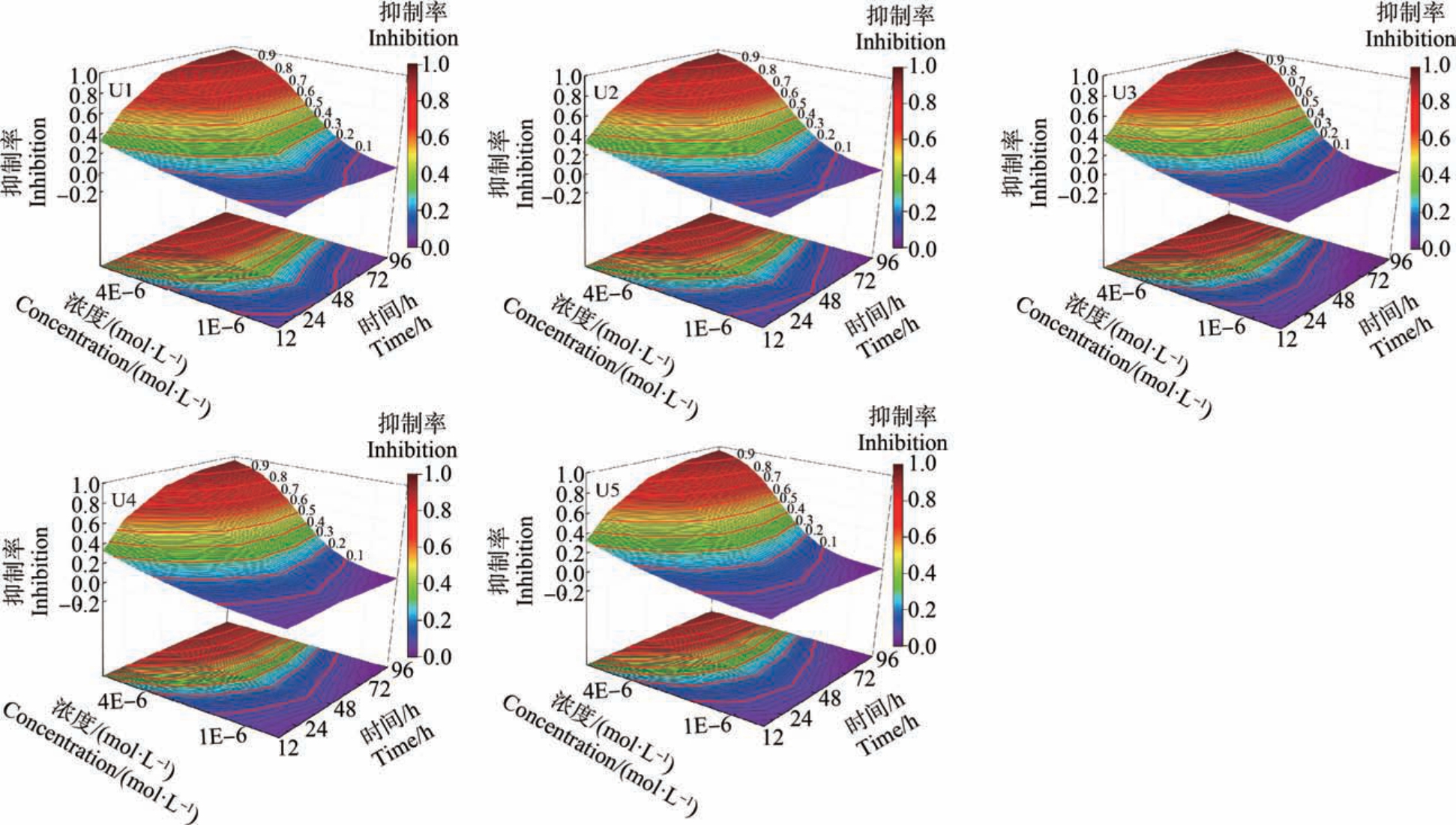
图3 3 种QASD 对C. pyrenoidosa 的浓度-时间-效应三维曲面图
Fig.3 Three dimensional surface diagram of concentration-time-effect of three QASD on C. pyrenoidosa
表4 Logit 函数对三元混合物的5 条射线在不同暴露时间下毒性数据的拟合参数(α 和β)、统计学参数(RMSE 和 R)、EC50 和 pEC50 值
Table 4 The fitting parameters (α and β), statistical parameters (RMSE and R), EC50, and pEC50 values of the ternary mixture toxicity data of the Logit function at different exposure times
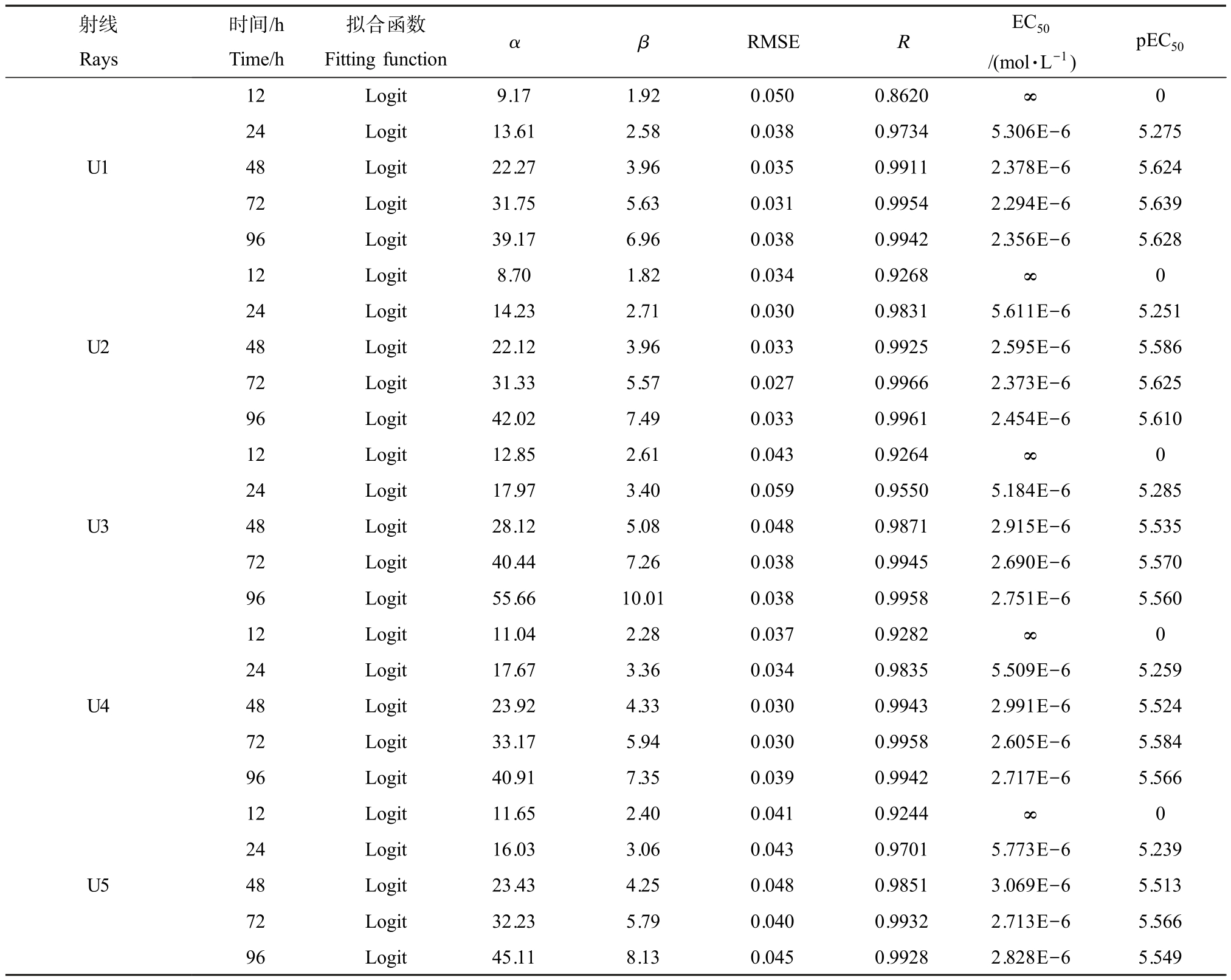
射线Rays时间/h Time/h拟合函数Fitting functionα β RMSE R EC50/(mol·L-1)pEC50 12Logit9.171.920.0500.8620∞ 0 U1 24 Logit 13.61 2.58 0.038 0.9734 5.306E-6 5.275 48 Logit 22.27 3.96 0.035 0.9911 2.378E-6 5.624 72 Logit 31.75 5.63 0.031 0.9954 2.294E-6 5.639 96 Logit 39.17 6.96 0.038 0.9942 2.356E-6 5.628 U2 U3 U4 12Logit8.701.820.0340.9268∞ 0 24 Logit 14.23 2.71 0.030 0.9831 5.611E-6 5.251 48 Logit 22.12 3.96 0.033 0.9925 2.595E-6 5.586 72 Logit 31.33 5.57 0.027 0.9966 2.373E-6 5.625 96 Logit 42.02 7.49 0.033 0.9961 2.454E-6 5.610 12Logit12.852.610.0430.9264∞ 0 24 Logit 17.97 3.40 0.059 0.9550 5.184E-6 5.285 48 Logit 28.12 5.08 0.048 0.9871 2.915E-6 5.535 72 Logit 40.44 7.26 0.038 0.9945 2.690E-6 5.570 96 Logit 55.66 10.01 0.038 0.9958 2.751E-6 5.560 12Logit11.042.280.0370.9282∞ 0 24 Logit 17.67 3.36 0.034 0.9835 5.509E-6 5.259 48 Logit 23.92 4.33 0.030 0.9943 2.991E-6 5.524 72 Logit 33.17 5.94 0.030 0.9958 2.605E-6 5.584 96 Logit 40.91 7.35 0.039 0.9942 2.717E-6 5.566 U5 12Logit11.652.400.0410.9244∞ 0 24 Logit 16.03 3.06 0.043 0.9701 5.773E-6 5.239 48 Logit 23.43 4.25 0.048 0.9851 3.069E-6 5.513 72 Logit 32.23 5.79 0.040 0.9932 2.713E-6 5.566 96 Logit 45.11 8.13 0.045 0.9928 2.828E-6 5.549
2.3 QASD 三元混合体系的时间依赖协同作用
5 条QASD 三元混合射线的实验数据点、拟合的CRCs、95% OCI 和 CA 模型预测线如图4 所示。由图4 可知,在12 h 时,5 条射线在低浓度区间的CA 模型预测线落于95% OCI 内,呈加和作用,但随暴露浓度的加大CA 模型预测线逐渐低于95%OCI 下限,呈协同作用。 在 24 h 时,U1 和 U2 在中浓度区间的CA 模型预测线低于95% OCI 下限,呈协同作用,而低浓度和高浓度区却呈加和作用,U3、U4 和U5 在整个浓度区间的CA 模型预测线几乎都在 95% OCI 内,呈加和作用。 在 48 h 时,U1 和 U2中浓度区的CA 模型预测线和95% OCI 下限的偏离程度加大,即协同作用变强,而 U3、U4 和 U5 在中浓度区也逐渐表现出弱协同作用。 在72 h 和96 h 时,低浓度下5 条射线都呈加和作用,随暴露浓度的增加,CA 模型预测线逐渐低于95% OCI 下限,呈协同作用。 当暴露时间从24 h 到96 h 的过程中,5 条射线的协同作用都在逐渐变强,呈现时间依赖协同作用规律。

尽管CA 模型可以很好地评估混合毒性相互作用,但在不同浓度水平下,协同作用(图4)强度无法由CA 模型进行定量表征。 结合置信区间的拟合归零法将各个浓度水平的效应归一化到同一尺度,可以对毒性相互作用进行定量表征,拟合归零指数如图5 所示。
与CA(图4)相比,拟合归零指数图(图5)可以很清晰地看出协同作用随浓度的变化存在有非常明显的差异。 在12 h 时,随浓度变大,5 条射线的协同作用强度逐渐变强。 虽然浓度会改变混合物毒性相互作用的强度,但并不是浓度越大毒性相互作用强度就越强。 在24 ~96 h 时,随浓度变大,每条射线的协同作用强度在逐渐变强,当到达最大协同作用强度后,浓度继续变大,协同作用强度则在不断减弱(除U3-24 h 在整个浓度水平下都是加和作用外)。Zhang 等[15]在研究氨基糖苷类抗生素对青海弧菌毒性相互作用规律时,也发现混合物体系的协同作用强度随浓度呈先变强后变弱的现象。 此外,随暴露时间的延长,5 条射线具有最大协同作用强度所对应的浓度都逐渐变大。 值得注意的是,在24 ~96 h的过程中,5 条射线的最大协同作用强度都在逐渐变强。 在96 h,最大协同作用强度达到最大,此时,U1、U2、U3、U4 和 U5 的最大协同作用强度分别为0.3227、0.3507、0.3105、0.2804 和 0.2626。 陈敏等[36]在研究抗生素与重金属混合物对C. pyrenoidosa 的毒性效应时也发现了部分混合射线具有时间依赖协同作用。 上述研究结果表明,疫情后大量使用的消毒剂可能会导致自然水体环境受到严重污染,而消毒剂之间所产生的协同毒性作用,且随时间的延长而增强,这很可能会对环境健康产生更大的威胁,值得我们密切关注消毒剂的潜在生态环境风险。
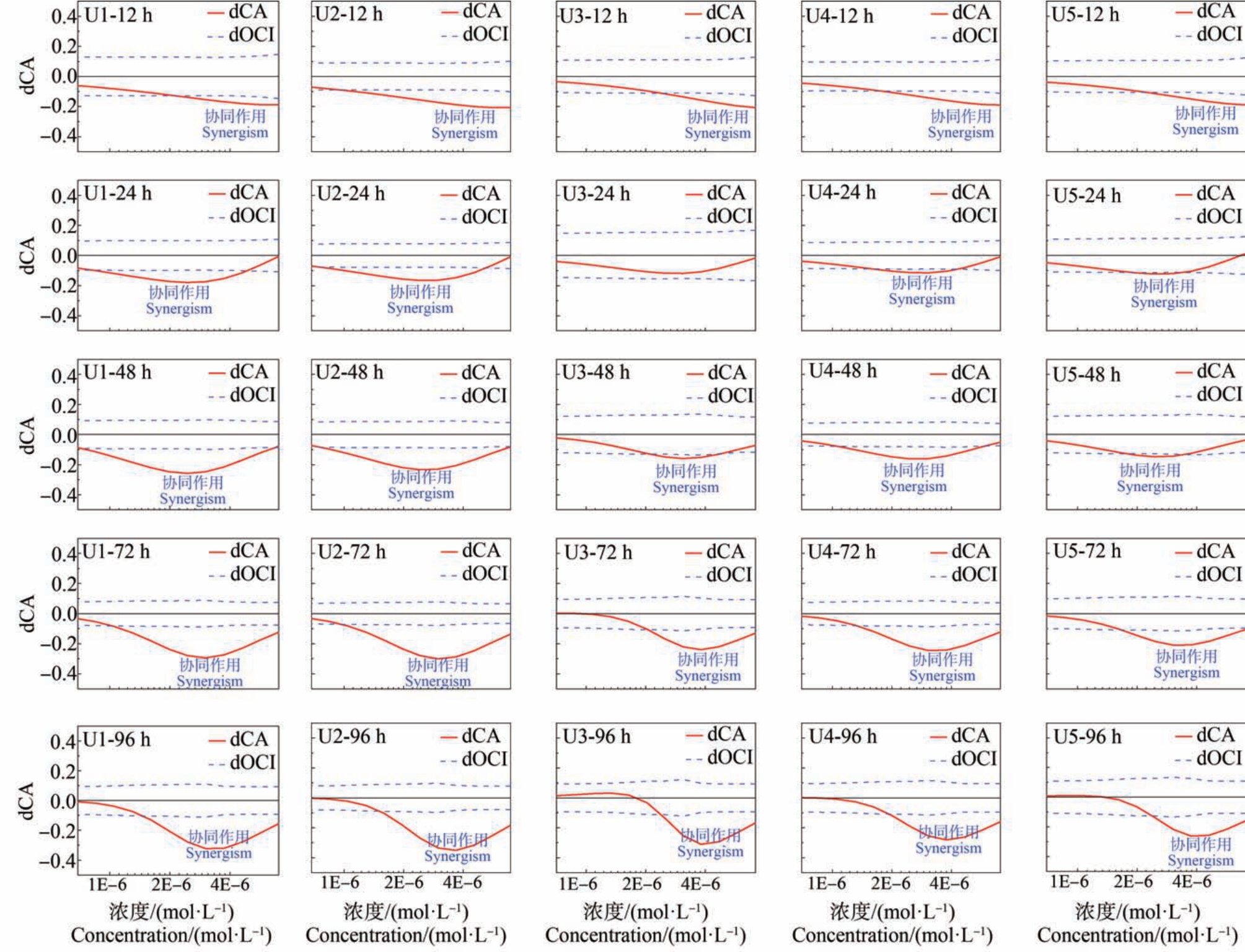
图5 不同暴露时间下QASD 三元混合体系的5 条射线的拟合归零指数图
注:dCA 表示浓度加和偏离指数,dOCI 表示置信区间的偏差程度。
Fig.5 Fitting zero index diagram of five mixture rays of QASD ternary mixture systems at different exposure times
Note: dCA represents deviation from concentration addition model, and dOCI represents the degree of deviation of confidence interval based on the observation.
综上所述:
(1) Logit 函数可以较好地对 DAB、BKB、DOM及其三元混合射线进行拟合。
(2)3 种消毒剂对C. pyrenoidosa 呈显著的时间依赖毒性效应,即随暴露时间的延长,毒性逐渐增强,但在48 h 后毒性不再明显增加。
(3) 时间-浓度-效应三维曲面图适合描述效应在空间浓度分布较为均匀的毒性随时间变化规律,在同一暴露时间,QASD 三元混合物对C. pyrenoidosa 的抑制率随混合浓度增加而逐渐变大,同一暴露浓度,QASD 三元混合物对C. pyrenoidosa 的抑制率随时间的延长而逐渐变大。
(4) 依据 CA 模型,QASD 三元混合体系的5 条射线对C. pyrenoidosa 的毒性相互作用几乎都是协同作用,且在24 ~96 h 具有时间依赖协同作用。
(5) 基于拟合归零法,可以实现协同作用强度的定量表征。 随暴露浓度增加,协同作用强度先变强后变弱,随暴露时间的延长,5 条射线具有最大协同作用,强度都逐渐变大。
[1]叶利兰, 甘春娟, 陈垚, 等. 疫情防控期间含氯消毒剂大量使用对水生生物的影响综述 [J]. 环境污染与防治,2021,43(5):644-648
Ye L L, Gan C J, Chen Y, et al. Effect of chlorinated disinfectants usage on aquatic organism during the epidemic control: A review [J].Environmental Pollution & Control,2021,43(5):644-648 (in Chinese)
[2]Tong C Y, Hu H, Chen G, et al. Chlorine disinfectants promote microbial resistance in Pseudomonas sp. [J]. Environmental Research,2021,199:111296
[3]Watson K, Shaw G, Leusch F D, et al. Chlorine disinfection by-products in wastewater effluent: Bioassay-based assessment of toxicological impact [J]. Water Research,2012,46(18):6069-6083
[4]Guo J, Liao M F,He B S,et al.Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on household disinfectant consumption behaviors and related environmental concerns: A questionnairebased survey in China [J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2021,9(5):106168
[5]Panseri S, Chiesa L, Ghisleni G, et al. Persistent organic pollutants in fish: Biomonitoring and cocktail effect with implications for food safety [J]. Food Additives & Contaminants Part A, Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure& Risk Assessment,2019,36(4):601-611
[6]El-Nahhal I Y, El-Nahhal Y. Ecological consequences of COVID-19 outbreak [J]. Journal of Water Science and Engineering,2020,1(5):1-5
[7]Park S, Kim H, Ji K. Developmental toxicity and thyroid endocrine disruption of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride and humidifier disinfectant in zebrafish larvae [J]. Applied Sciences,2021,11(11):4884
[8]Herron J M, Tomita H, White C C, et al. Benzalkonium chloride disinfectants induce apoptosis, inhibit proliferation, and activate the integrated stress response in a 3-D in vitro model of neurodevelopment [J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology,2021,34(5):1265-1274
[9]陈血建, 郭正洋, 黄建飞, 等. 季铵盐类消毒剂的研究现状[J]. 广东化工,2019,46(16):240-241
Chen X J, Guo Z Y, Huang J F, et al. Research progress on quaternary ammonium salt disinfectant [J].Guangdong Chemical Industry,2019,46(16):240-241 (in Chinese)
[10]Zhang J,Liu S S,Liu H L,et al.A novel method dependent only on the mixture information (MIM) for evaluating the toxicity of mixture [J].Environmental Pollution,2011,159(7):1941-1947
[11]Mo L Y, Liu S S, Zhu Y N, et al. Combined toxicity of the mixtures of phenol and aniline derivatives to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology,2011,87(4):473-479
[12]王元, 方开泰.关于均匀分布与试验设计(数论方法)[J].科学通报,1981,26(2):65-70
[13]Huang W Y,Liu F,Liu S S,et al.Predicting mixture toxicity of seven phenolic compounds with similar and dissimilar action mechanisms to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. nov.Q67 [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2011,74(6):1600-1606
[14]Ge H L, Liu S S, Zhu X W, et al. Predicting hormetic effects of ionic liquid mixtures on luciferase activity using the concentration addition model [J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2011,45(4):1623-1629
[15]Zhang J, Tao M T, Song C C, et al. Time-dependent synergism of five-component mixture systems of aminoglycoside antibiotics to Vibrio qinghaiensis-Q67 induced by a key component [J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10 (21):12365-12372
[16]刘树深. 化学混合物毒性评估与预测方法[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2017:104-107
[17]胡小贞, 马祖友, 易文利, 等.4 种不同培养基下铜绿微囊藻和四尾栅藻生长比较[J]. 环境科学研究, 2004, 17(S1):55-57
Hu X Z, Ma Z Y, Yi W L, et al. Growth of Microcystis aeruginosa and Scendesmus quadricauda in four different mediums [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2004,17(S1):55-57 (in Chinese)
[18]Wang L J, Liu S S, Yuan J, et al. Remarkable hormesis induced by 1-ethyl-3-methyl imidazolium tetrafluoroborate on Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Chemosphere,2011,84(10):1440-1445
[19]Liu S S,Song X Q,Liu H L,et al.Combined photobacterium toxicity of herbicide mixtures containing one insecticide [J]. Chemosphere,2009,75(3):381-388
[20]Zhang J, Liu S S, Dong X Q, et al. Predictability of the time-dependent toxicities of aminoglycoside antibiotic mixtures to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(129):107076-107082
[21]陈琼, 张瑾, 李小猛, 等. 几种抗生素对蛋白核小球藻的时间毒性微板分析法[J]. 生态毒理学报,2015,10(2):190-197
Chen Q, Zhang J, Li X M, et al. Time-dependent microplate toxicity analysis (T-MTA) of several antibiotics to Chlorella pyrenoidosa[J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2015,10(2):190-197 (in Chinese)
[22]Zhang Y H, Liu S S, Liu H L, et al. Evaluation of the combined toxicity of 15 pesticides by uniform design [J].Pest Management Science,2010,66(8):879-887
[23]Zhou X F,Sang W J,Liu S S,et al.Modeling and prediction for the acute toxicity of pesticide mixtures to the freshwater luminescent bacterium Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 22(3):433-440
[24]刘树深, 张瑾, 张亚辉, 等. APTox: 化学混合物毒性评估与预测[J]. 化学学报,2012,70(14):1511-1517
Liu S S, Zhang J, Zhang Y H, et al. APTox: Assessment and prediction on toxicity of chemical mixtures [J]. Acta Chimica Sinica,2012,70(14):1511-1517 (in Chinese)
[25]朱祥伟, 刘树深, 葛会林, 等. 剂量-效应关系两种置信区间的比较[J]. 中国环境科学,2009,29(2):113-117
Zhu X W, Liu S S, Ge H L, et al. Comparison between two confidence intervals of dose-response relationships[J]. China Environmental Science, 2009, 29(2): 113-117(in Chinese)
[26]Liu L, Liu S S, Yu M, et al. Application of the combination index integrated with confidence intervals to study the toxicological interactions of antibiotics and pesticides in Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology,2015,39(1):447-456
[27]黄子晏, 陶梦婷, 张瑾, 等. 重金属与农药污染物对青海弧菌Q67 拮抗作用的定量评估[J]. 环境化学, 2020,39(9):2441-2449
Huang Z Y, Tao M T, Zhang J, et al. Quantitative evaluation on the antagonism between heavy mental and pesticide pollutants to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2441-2449 (in Chinese)
[28]卞志强, 张瑾, 王滔, 等. 氨基甲酸酯类农药对蛋白核小球藻联合毒性作用特点及机制[J]. 生态毒理学报,2019,14(4):150-162
Bian Z Q, Zhang J, Wang T, et al. Time-dependent joint toxicity characteristics and mechanisms of five carbamate pesticides towards Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2019,14(4):150-162 (in Chinese)
[29]Zhang J,Liu S S,Dou R N,et al.Evaluation on the toxicity of ionic liquid mixture with antagonism and synergism to Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Chemosphere, 2011,82(7):1024-1029
[30]Wang L J, Liu S S, Zhang J, et al. A new effect residual ratio (ERR) method for the validation of the concentration addition and independent action models [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2010,17(5):1080-1089
[31]宋崇崇, 陶梦婷, 张瑾, 等.3 种重金属对蛋白核小球藻的联合毒性及机理[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(2):88-95
Song C C, Tao M T, Zhang J, et al. Combined toxicity and the mechanisms of three heavy metals to Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,43(2):88-95 (in Chinese)
[32]丁婷婷, 董欣琪, 张瑾, 等.3 种氨基糖苷类抗生素对水生生物的时间依赖联合毒性作用比较[J]. 生态毒理学报,2018,13(1):126-137
Ding T T,Dong X Q,Zhang J,et al.Comparison of timedependent joint toxicity interaction of three aminoglyco-sides antibiotics between two aquatic organisms [J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2018, 13(1): 126-137 (in Chinese)
[33]张瑾, 董欣琪, 陈敏, 等. 五元氨基甲酸酯类农药混合物体系对青海弧菌的毒性特点[J]. 生态毒理学报,2017,12(4):138-145
Zhang J, Dong X Q, Chen M, et al. Toxicity characteristics of five-carbamate pesticide mixture system towards Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.Q67 [J].Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology,2017,12(4):138-145 (in Chinese)
[34]Zhang Y H, Liu S S, Song X Q, et al. Prediction for the mixture toxicity of six organophosphorus pesticides to the luminescent bacterium Q67 [J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2008,71(3):880-888
[35]Zhang J,Liu S S.Time-dependent stimulations of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride on redox reactants and antioxidases in Vibrio qinghaiensis sp.-Q67 [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,283:568-573
[36]陈敏, 张瑾, 董欣琪, 等. 多元抗生素与重金属混合物对蛋白核小球藻的时间依赖性协同与拮抗作用[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2018,37(5):850-859
Chen M, Zhang J, Dong X Q, et al. Time-dependent synergism and antagonism within multi-component mixtures of heavy metals and antibiotics towards Chlorella pyrenoidosa [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018,37(5):850-859 (in Chinese)