珠江八大入海口门可溶态铜的时空变化及其影响因素
Spatio-temporal Variability and the Influencing Factors of Dissolved Copperin Riverine Runoff at Eight Outlets in the Pearl River Estuary
-
摘要: 以1987年至2011年的月测数据为基础,分析了珠江八大人海口可溶态铜的时空变化,并探讨了工业发展、铜矿厂分布、水产养殖及铜消费量等因素对它们的影响。研究结果表明:与国内外其它人海口相比,珠江口可溶态铜的含量处于较高水平,其中,虎门水道(A1)可溶态铜的含量显著高于除鸡啼门水道(A6)外的其它人海口(p<0.1),可能是受工业废水排放及铜矿厂分布的影响。在时间变化趋势上,8个采样点之间,除了A1与A4外,其它采样点间均呈显著的正相关性(p<0.1),其中A5和A6的变化趋势还与我国的铜消费量具有显著相关性(p<0.1),表明人海口之间铜污染可能具有相似的影响因素,且工业生产活动对水体铜污染的波动具有一定的影响。Abstract: On the basis of monthly measurement data from 1987 to 2011,the spatio-temporal variability of dissolved copper in riverine runoff at the eight outlets of the Pearl River Estuary were examined and associated influencing factors,such as industrial effluents,distribution of copper factories and aquaculture,were discussed.The results indicated that the dissolved copper in this study showed high levels compared to those in other estuaries in the world.The levels of the dissolved copper in Humen outlet(Al) were significantly higher than others except for Jitimen outlet(A6)(p<0.1),which may be affected by the industrial discharges and copper mining factories.The temporal tends of copper concentration shad significant correlations among the eight sampling points,except for Al and A4.In addition,the temporal tends at A5 and A6 significantly correlated with the copper consumptionrates in China(p<0.1).This finding suggested that the copper pollution atthe eight riverine runoff outlets may be influenced by similar factors,and that the industrial activities may be an important factor in influencing the temporal tends of copper pollution in the Pearl River Delta.
-
Key words:
- dissolved copper /
- Pearl River /
- runoff outlet /
- spatio-temporal variability
-
近年来,可吸入颗粒物(PM10)和细颗粒物(PM2.5)是我国大气环境的主要污染物,PM10和PM2.5会影响人体健康、降低大气能见度[1-2]。北京市2018年PM2.5源解析结果表明,扬尘源对本地源的贡献率高达16%[3],施工扬尘和道路扬尘并重,施工工地是造成道路扬尘的来源之一,因此,施工扬尘污染防治显得尤为重要。近年来,国内施工扬尘排放特征[4-5]、排放因子[6-7]、排放清单[8]、防治技术[9-12]和排放标准(含征求意见稿)[13-18]的研究越来越多。我国一些地方施工扬尘排放标准(含征求意见稿)[17-18]以PM10作为控制指标,因为施工扬尘以粗颗粒物为主,其粒径分布为总悬浮颗粒物(TSP)∶PM10∶PM2.5为1.00∶0.49∶0.10[19],加之《环境空气质量标准》(GB 3095-2012)对PM10的关注程度高于TSP,因此,以PM10监测仪作为施工扬尘监测工具较为合适。
环境空气PM10连续自动监测系统是我国环境空气监测领域应用较早和国产化技术较成熟的连续自动监测仪,按监测原理可分为微量振荡天平法和β射线法[20-21]。我国地方施工扬尘排放标准将环境空气PM10连续自动监测仪应用于施工扬尘PM10监测,并且将“光散射法”作为第3种监测原理的仪器[13]。我国《环境空气颗粒物(PM10和PM2.5)连续自动监测技术要求及检测方法》(HJ 653-2013)提出了自动监测仪参比方法比对测试技术要求[22],并规定采用重量法作为参比方法[23]。虽然已有研究对PM10和PM2.5的手工和自动监测仪进行了比对[24-26],但在施工扬尘PM10领域的监测应用还属于较新的课题,国内外尚缺乏施工扬尘PM10监测仪的准确性和适用性评价数据。鉴于国内在这方面的迫切需求,2019年6月中国环境监测总站发布了《扬尘颗粒物监测仪(光散射法)》适用性检测作业指导书。
为了解不同原理多种型号监测仪对施工扬尘PM10的适用性,本研究选取国内外10种光散射法和4种β射线法监测仪,开展施工扬尘PM10自动监测仪参比方法比对测试,分析自动监测仪与手工采样器监测结果的相关关系,确定符合我国环境质量现状和监测需求的施工扬尘PM10监测仪“参比方法比对测试”技术要求和检测方法,为我国仪器认证和施工扬尘污染防治提供依据,亦为国家或地方制定施工扬尘排放标准提供参考。
1. 仪器和方法
1.1 自动监测仪
本次比对测试选取了10种光散射法和4种β射线法共14种型号的施工扬尘PM10监测仪,每种型号监测仪器提供3台。对14种型号仪器进行编号,施工扬尘PM10自动监测仪信息见表1。
表 1 施工扬尘PM10自动监测仪信息Table 1. Information of PM10 automate monitor for construction fugitive dust序号 仪器编号 分析原理 1 A 光散射 2 B 光散射 3 C 光散射 4 D 光散射 5 E 光散射 6 F 光散射 7 G 光散射 8 H 光散射 9 I 光散射 10 J 光散射 11 K β射线 12 L β射线 13 M β射线 14 N β射线 1.2 手工参比采样测量仪器
选取3台德国康姆德润达PNS 16T-3.1型自动换膜颗粒物采样器作为比对测试使用的手工参比采样(以下简称:参比采样)测量仪器,采样流量为16.7 L∙min−3。采用美国TSI 4146型流量校准仪对参比采样器进行流量校准。采用瑞典梅特勒电子天平称量滤膜,电子天平精度为1/100 000 g,保证滤膜称量所需的恒温恒湿要求。
1.3 比对测试方法
2018年9月中旬,在北京市通州区北京环球影城施工工地内开展施工扬尘PM10监测仪参比方法比对测试,测试场地如图1所示。测试场地相对施工工地的位置见图2。图2中红色多边形区域为施工工地,蓝色圆形区域为测试场地。测试场地位于工地西侧办公区,施工工地面积为4 km2,测试场地面积约为100 m2,测试场地与施工工地面积相比非常小,测试场地内扬尘PM10浓度相对均匀,每种监测仪在场地中的分布位置不影响仪器评价效果。比对测试方法参照HJ 653-2013执行,同型号PM10监测仪3台,参比采样器3台,共计45台仪器。同种型号的仪器安放位置相距1 m,仪器采样头高度统一为3 m。实验开始前,由各仪器厂家对自动监测仪的进气管道和PM10切割器进行清洗。实验周期为5 d,自动监测仪和参比采样器同步进行监测或采样,实验期间不得对仪器进行维护。首先,应符合HJ 653-2013规定的同型号3台(套)仪器平行性P≤10%的要求;其次,参照美国加州《法规403 扬尘》[27],每个样品采样时间为(5±0.2) h,这是因为施工现场PM10相比一般大气环境浓度高,共测试15组样品。采样时间和样品数量有别于HJ 653-2013的(24±1) h和10个样品,减少了采样时间,同时增加了样品数量。在比对测试期间,主导风向为西南风和东北风,风频分别为36%和26%,平均风速分别为1.7 m∙s−1和1.4 m∙s−1,比对测试场地既不在施工工地主导风向的上风向也不在下风向,比对测试场地扬尘PM10浓度代表了该施工工地平均水平。
取相同时间段内的自动监测数据Cij和参比采样数据Rj作为一个数据对,i是仪器的序号(i=1~14),j是有效样品的个数(j=1~15)。分析过程包括4个步骤:1)计算3台手工采样器测试每组样品PM10浓度的平均值,平均值应尽量选择在15~300 μg∙m−3,分别计算每组采样器测试结果的标准偏差(≤15 μg∙m−3)或相对标准偏差(≤7%),则该组参比测试数据有效,平均值≤100 μg∙m−3和平均值>100 μg∙m−3的有效数据对数均应≥3;2)计算每种型号自动监测仪测试结果的平行性;3)计算相同时间段内同型号自动监测仪和参比采样器测试的样品PM10浓度的平均值;4)将每组对应的参比测试数据均值分别与各型号自动监测数据均值组成一个有效数据对,进行线性回归分析,以参比测试数据为横轴,以自动监测仪数据为纵轴,计算线性回归方程的斜率(k)、截距(b)和可决系数(R2),判断是否满足HJ 653-2013的要求(0.85≤k≤1.15,−10 μg∙m−3≤b≤10 μg∙m−3,R2≥0.85)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 施工扬尘PM10监测仪的平行性
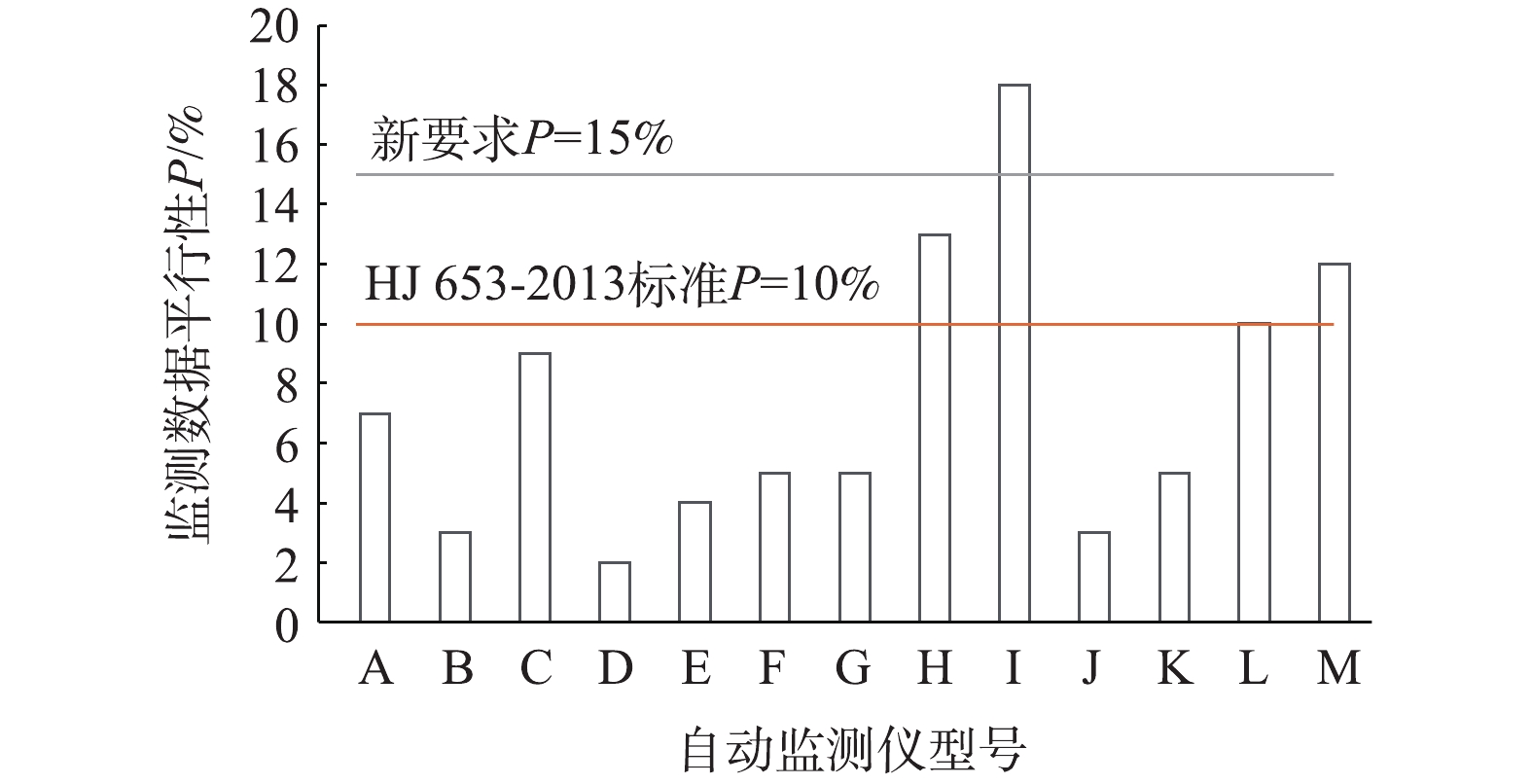
3台参比采样器监测结果的平行性是开展PM10参比采样比对测试的基础。图3显示了参比采样器和自动监测仪的监测结果。另外,经计算可得出A-N型号的14种自动监测仪的平行性(见图4)。由图3和图4可看出,参比采样器测试结果的平行性很好,3条线几乎重合。光散射法和β射线法2种类型的监测仪自身的平行性均有好有坏,其中2种光散射法(I型、J型)和1种β射线法(N型)自动监测仪监测结果平行性相对较差,分别为13%、18%和12%,不符合HJ 653-2013中规定的PM10连续监测系统平行性P≤10%的要求,如果将要求降低为平行性P≤15%,那么只有一种光散射法监测仪(J型)不符合新要求。
2.2 自动监测仪和参比采样器的相关性
由于有一种光散射法(J型)监测仪的平行性不符合新要求(P≤15%),故对其他13种型号监测仪和参比采样器的相关性做评价。将自动监测仪与参比采样器在同时间段内得到的15组比对测试有效数据进行线性回归方程(见图5),各个回归曲线的斜率(k)、截距(b)和可决系数(R2)的结果见表2。
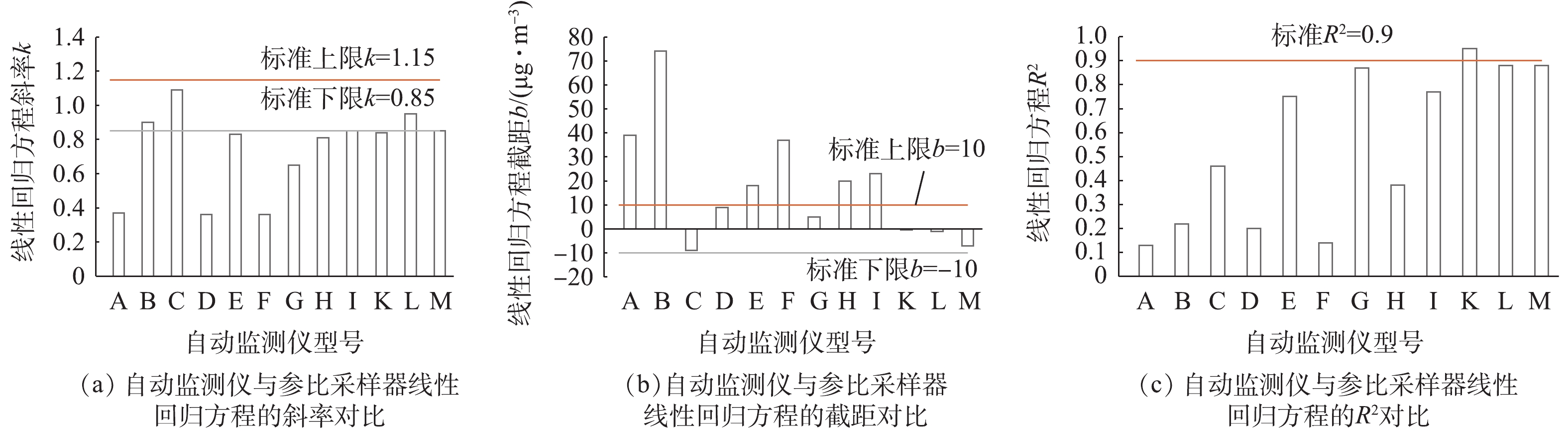
表 2 自动监测仪与参比采样器的线性分析结果Table 2. Linear analysis results between automated monitor and reference sampler分析方法 仪器编号 斜率k 截距b 可决系数R2 光散射法 A 0.92 8 0.88 B 0.37 39 0.13 C 0.90 74 0.22 D 1.09 -9 0.46 E 0.36 9 0.20 F 0.83 18 0.75 G 0.36 37 0.14 H 0.65 5 0.87 I 0.81 20 0.38 β射线法 K 0.85 23 0.77 L 0.84 -0.4 0.95 M 0.95 -1 0.88 N 0.85 -7 0.88 将13种型号监测仪与参比采样器得到线性回归方程的k、b和R2数值进行对比分析。由图6可以看出,A~I型9种光散射法监测仪各自线性回归方程的同一类参数值差别较大,其中k为0.36~1.09,A型、C型和D型监测仪符合HJ 653-2013中的要求;b为−9~74 μg∙m−3,A型、D型、E型和H型监测仪符合要求;R2为0.13~0.88,A型和H型监测仪接近符合要求。K~N型4种β射线法监测仪的检测结果整体优于光散射法监测仪,4个线性回归方程的同一类参数数值差别较小,其中k为0.84~0.95,K型、M型和N型监测仪符合HJ 653-2013的要求;b为−7~23 μg∙m−3,L型、M型和N型监测仪符合要求;R2为0.77~0.95,L型监测仪符合要求。
综上所述,在施工扬尘PM10环境条件下,参与本研究的光散射法和β射线法监测仪都不符合HJ 653-2013的要求,主要原因是施工现场扬尘PM10浓度空间均匀性远不如一般大气环境,次要原因是参与本研究的光散射法监测仪不属于法规仪器,β射线法监测仪是小型仪器。但是,β射线法监测仪相比光散射法更接近标准要求,这是因为光散射法的监测结果受颗粒物粒径分布、颜色、密度及环境温湿度等因素影响,而β射线法不受影响。
2.3 施工扬尘自动监测仪技术要求
鉴于参与秋季施工扬尘PM10参比方法比对测试的14种自动监测仪都不符合HJ 653-2013的要求,而目前国内已经颁布的地方施工扬尘排放标准和《大气PM2.5网格化监测技术要求和检测方法技术指南(试行)》[28]对颗粒物自动监测仪的技术要求相比HJ 653-2013都略有放松,结合本研究所得到的比对结果以及施工扬尘PM10监测的特殊性,现提出一种适用于施工扬尘自动监测仪的技术要求。技术要求如下,自动监测仪P≤15%,线性回归方程的k为(1±0.20),b为(0±20) μg∙m−3,R2≥0.72。以新要求重新对本研究的比对测试结果进行评价,发现有2种光散射法和3种β射线法监测仪符合新要求,另外有一种β射线法监测仪接近符合新要求。表明采用光散射法监测仪开展施工扬尘PM10监测并支撑施工扬尘排放标准具有可行性,当然β射线法监测仪性能更优越,但价格是限制β射线法广泛应用的制约因素。
3. 结论
1)除2种光散射法和1种β射线法监测仪之外,80%的监测仪各自的平行性都符合HJ 653-2013的要求(P≤10%),调整P≤15%之后,除了1种光散射法监测仪之外,93%的监测仪符合新要求。
2)去掉1种平行性不达标的光散射法监测仪,β射线法监测仪与参比方法线性回归方程的斜率k、截距b和可决系数R2整体优于光散射法监测仪,但都不符合HJ 653-2013的要求(0.85≤k≤1.15,−10 μg∙m−3≤b≤10 μg∙m−3,R2≥0.85)。
3)对HJ 653-2013的要求略做放松(P≤15%,0.80≤k≤1.20,-20 μg∙m−3≤b≤20 μg∙m−3,R2≥0.72)之后,有2种光散射法和3种β射线法监测仪符合新要求,还有1种β射线法监测仪接近符合新要求,新要求符合率仅为36%,监测仪的性能亟待提升。
4)采用光散射法监测仪开展施工扬尘PM10监测并支撑施工扬尘排放标准具有可行性,建议继续在其他季节开展施工扬尘PM10监测仪参比方法比对测试,为施工扬尘污染监测与防治提供技术支撑。
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 1000
- HTML全文浏览数: 1000
- PDF下载数: 26
- 施引文献: 0



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: