云南曲靖地区铜的暴露与肺癌相关性研究
Study on the Relationship between Copper Exposure and Lung Cancer in Qujing Area,Yunnan Province
-
摘要: 我国云南省曲靖的宣威和富源等地是全世界肺癌高发区,为了研究环境介质中铜(Cu)等重金属的暴露与体内分布特征,探讨Cu与肺癌的相关性,在当地开展肺癌环境流行病学调查,采集宣威和富源高发区人群饮食、饮水以及人体血浆和肺组织样品,微波消解ICP-MS法测定样品中Cu等元素。结果显示,当地居民使用燃料类型是影响肺癌高发的重要因素。高发区人群Cu的日摄入总量低于我国推荐的每日膳食中营养素供给量(RDA)。肺癌组血液中Cu含量显著高于对照组,肺癌组织中Cu含量显著高于癌旁组织和正常组织,且肺癌患者的血浆和肺组织中Cu/Zn比值均升高。Pearson相关性分析结果表明,Cu和Ni、Cu和Pb呈显著正相关,提示在致癌作用上具有协同效应;Cu和Fe、Cu和Zn呈显著负相关,提示具有抑制或拮抗作用。多因素Logistic回归结果表明,Cu是肺癌发生的重要影响因素,人体中Cu含量和Cu/Zn比值可为肺癌的早期预防和诊断提供科学依据。Abstract: Xuanwei and Fuyuan,located in Qujing,Yunnan province,were found as areas with the highest lung cancer incidence worldwide.The relationships of the copper distribution and lung cancer incidence were investigated in the areas with high lung cancer communes.Water,food,human plasma and lung tissue samples were collected and analyzed for the copper contents using microwave digestion-ICP-MS.The results showed that fuel type is the most important factor influencing lung cancer occurrence.The total daily intake of copper was lower than Recommended Dietary Allowance(RDA) in high lung cancer incidence areas.Copper concentrations in plasma samples from lung cancer patients were significantly higher than those in the control samples.The concentrations of copper in lung cancer tissues were also higher than those in paracancerous lung tissues and benign lung tissues.Ratio of Cu/Zn increased in both plasma and lung cancer tissue.The results of Pearson multiple correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between Cu and Ni,Cu and Pb respectively,which indicated that these elements had synergism of anticarcinogenic effects or carcinogenesis.Cu and Fe,Cu and Zn were negatively correlated to each other.It indicated that the elements had some effects of antagonism.The results of logistic regression showed that copper might be the important factor for lung cancer occurrence.
-
Key words:
- copper /
- exposure /
- lung cancer /
- relationship
-
近年来,汽车工业飞速发展,汽车保有量持续增加,这给人们出行带来了极大便利但同时也产生了大量的废轮胎。据统计,2015年我国产生废轮胎3.3×108条,超过1.2×106 t,已成为世界上产生废轮胎最多的国家[1]。废橡胶不易降解,堆积、填埋、焚烧都会对大气、土壤、水源造成污染,如何处理日益增加的废橡胶已经成为一个严重的环境问题。20世纪70年代以来,美国、瑞典、英国、法国等先后开展了橡胶沥青和橡胶粉沥青混合料的应用研究和铺路实验,极大地促进了废轮胎在道路工程中的利用[2]。我国自20世纪80年代,开始对胶粉沥青进行研究应用。将废轮胎胶粉用于制备胶粉改性沥青,能够大量消耗废轮胎,同时也能够显著改善路面的耐磨、抗老化、抗开裂等性能,对于满足飞速发展的公路建设需求具有重要的意义[3-5]。
胶粉改性沥青性能的改善来源于胶粉与沥青之间的相互作用,但两者之间的作用十分复杂。关于胶粉改性沥青中胶粉与沥青相互作用机理至今仍存在争议,目前主要有物理共混机理、网络填充机理、化学共混机理和溶胀降解机理等几种不同观点[5-6]。其中获得较多人支持的观点[7]认为,废胶粉和沥青混合后,胶粉发生溶胀和部分溶解而在沥青中扩散,这些高分子链和沥青轻质组分在胶粉表面形成界面层。同时,界面层的外围吸附沥青中的胶质形成界面过渡层。界面层与沥青中胶团(沥青质和胶质)的外层胶质有亲和作用,使沥青中的胶团与废胎胶粉表面的界面层通过界面过渡层紧紧地结合为一体,形成了废胎胶粉和沥青连续或相互交错的三维空间网络结构。但这个三维网状结构多是通过范德华力缔结的,因此,这种结构较不稳定,对长时间和高温下的存储较为不利[8]。同时也有部分研究[7]表明,胶粉表面特征官能团与沥青中特征基团的化学作用,能够显著影响胶粉改性沥青的性能。
通过对废轮胎胶粉进行表面化学改性[9-11]、脱硫改性[12-14]、微波改性[15]、共混改性[16-21]等,能够显著改善胶粉表面的物理化学结构,增强胶粉界面层与沥青胶团的相互作用,改善胶粉改性沥青的性能。于凯等[9-10]采用H2O2和次氯酸钠等为氧化剂改性废轮胎胶粉,在胶粉表面形成羟基、环氧基等有机官能团,能够与沥青中的羧基等基团发生化学反应,形成强相互作用,使改性沥青的软化点显著提高。而脱硫改性能够部分切断交联橡胶中的S—S键和C—S键,使废轮胎胶粉中的交联网状结构部分破坏,在沥青中溶胀更加充分,界面结合层厚度显著提高,使脱硫胶粉改性沥青延度提高,黏度降低,低温性能和加工性能明显改善[12-14]。通过以上研究不难发现,在废轮胎胶粉表面修饰特定有机官能团或者增加胶粉-沥青界面结合层的厚度,能够显著提高胶粉改性沥青的界面相容性和界面结合强度,改善胶粉改性沥青的高/低温性能。
由于橡胶的主要成分是聚烯烃,其表面存在着丰富的不饱和键。通过接枝聚合改性的方法能够在橡胶表面接枝不同的聚合物链段,可以对橡胶的物理化学性质起到明显的改善作用。目前常见的橡胶接枝聚合改性方法包括乳液聚合[22-24]、溶液聚合[25-26]、本体聚合[27-28]和辐射接枝[29]等,常见的接枝单体包括苯乙烯、甲基丙烯酸甲酯、甲壳素、马来酸酐等。其中乳液聚合以水为分散介质,条件较为温和,更适于在橡胶粉表面的接枝聚合改性。通过接枝聚合改性的方法将特定的聚合物链段接枝到废轮胎胶粉的表面,可以显著增加胶粉-沥青界面层的厚度,从而增强胶粉-沥青界面相容性与结合强度。但到目前为止,采用接枝聚合改性胶粉制备胶粉改性沥青的研究还未见报道。
本研究尝试在废轮胎胶粉表面接枝聚苯乙烯链段,并将其用于制备湿法胶粉改性沥青。利用废轮胎胶粉表面的接枝聚苯乙烯链段,提高胶粉/沥青界面层与沥青中胶质的相互作用,增强胶粉与沥青的界面结合强度。系统研究废轮胎胶粉表面聚苯乙烯链段的接枝率对胶粉改性沥青25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度和软化点等主要性能指标的影响规律,探讨废轮胎胶粉的接枝改性对胶粉改性沥青性能的影响机理。
1. 实验部分
1.1 试剂与仪器
基质沥青采用市售滨阳70号沥青。40目废轮胎胶粉由天津海泰环保科技发展有限公司提供,接枝改性前用环己烷洗涤并干燥后使用。苯乙烯、过氧化二苯甲酰、环己烷等均为市售分析纯试剂。苯乙烯通过预处理去除阻聚剂,其余试剂未经预处理。
主要实验仪器有英国Kratos Analytical Ltd生产的Axis Ultra DLD型X射线光电子能谱仪,美国瓦里安公司生产的Infinityplus-300固体核磁共振谱仪,中国上海昌吉地质仪器有限公司生产的SYD-2810D型针入度检测仪,中国无锡市石油仪器设备有限公司生产的LYY-9A型沥青延伸度测定仪,以及中国北京兰航测控技术研究所生产的RH-2型沥青软化点测定仪。
基质沥青及改性沥青的25 ℃针入度按照GB/T 4509—2010测定、软化点按照GB/T 4507—2014测定,5 ℃延度按照GB/T 4508—2010测定,在延度仪上对样品以5 cm·min−1的速度进行拉伸,直至断裂,指针指示的标尺读数即为所测沥青的延度。其中25 ℃针入度和软化点结果取2次测试平均值,5 ℃延度结果取3次测试平均值。
1.2 实验过程
1.2.1 废轮胎胶粉的苯乙烯接枝改性
将废轮胎胶粉2 g置于100 mL圆底烧瓶中,加入0.1~0.2 g过氧化苯甲酰,并在圆底烧瓶中分别加入2、4、6 mL苯乙烯和8 mL去离子水,搅拌使之均匀分散混合,油浴加热至120 ℃,恒温反应2~12 h。对反应后的胶粉用环己烷进行多次抽滤清洗,至无明显白色物质,以除去样品中未接枝的聚苯乙烯。将清洗好的胶粉样品置于60 ℃烘箱干燥2 h,称取胶粉质量。则可初步计算胶粉的质量接枝率见式(1)。
R=mt−m0m0×100% (1) 式中:R为胶粉的质量接枝率;m0为初始胶粉质量,即反应前胶粉质量,g;mt为反应前胶粉质量,g。
1.2.2 湿法制备胶粉改性沥青
将400 g的基质沥青搅拌加热,待温度升高到185~190 ℃,缓慢加入质量百分比为21%的改性废轮胎胶粉,在1 400 r·min−1的转速下搅拌30 min,过胶体磨研磨,在180~185 ℃下搅拌发育4 h,得到胶粉改性沥青。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 苯乙烯用量及反应时间对接枝率的影响
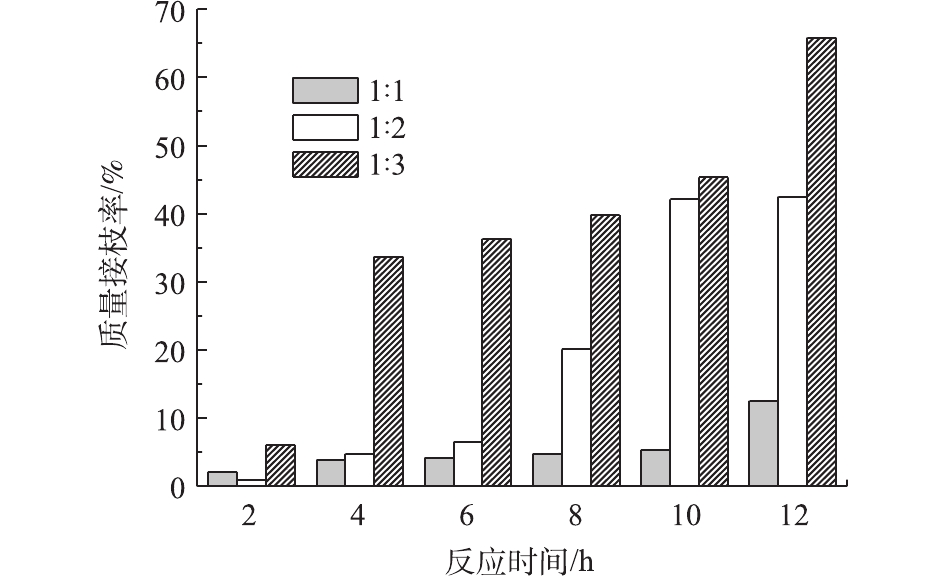
在引发剂用量、反应时间相同的条件下,改变苯乙烯用量,计算胶粉的质量接枝率,结果如图1所示。过氧化苯甲酰用量为0.1 g,分别取1、2和3份的苯乙烯,在120 ℃条件下,分别反应2、4、6、8、10、12 h。由图1可知,在相同苯乙烯用量的条件下,反应时间越长,胶粉的质量接枝率越大。反应时间大于8 h后的胶粉质量接枝率显著高于反应时间小于8 h的胶粉样品。而在反应时间相同的条件下,苯乙烯用量越大,胶粉的质量接枝率越大,当胶粉与苯乙烯的质量比为1∶1时,胶粉的接枝率均低于10%,当苯乙烯与胶粉用量为1∶2时,胶粉的接枝率均低于20%,当苯乙烯与胶粉用量为1∶3时,胶粉的质量接枝率显著高于前2种情况。苯乙烯用量对于胶粉接枝率的影响总体上看要高于反应时间对接枝率的影响。
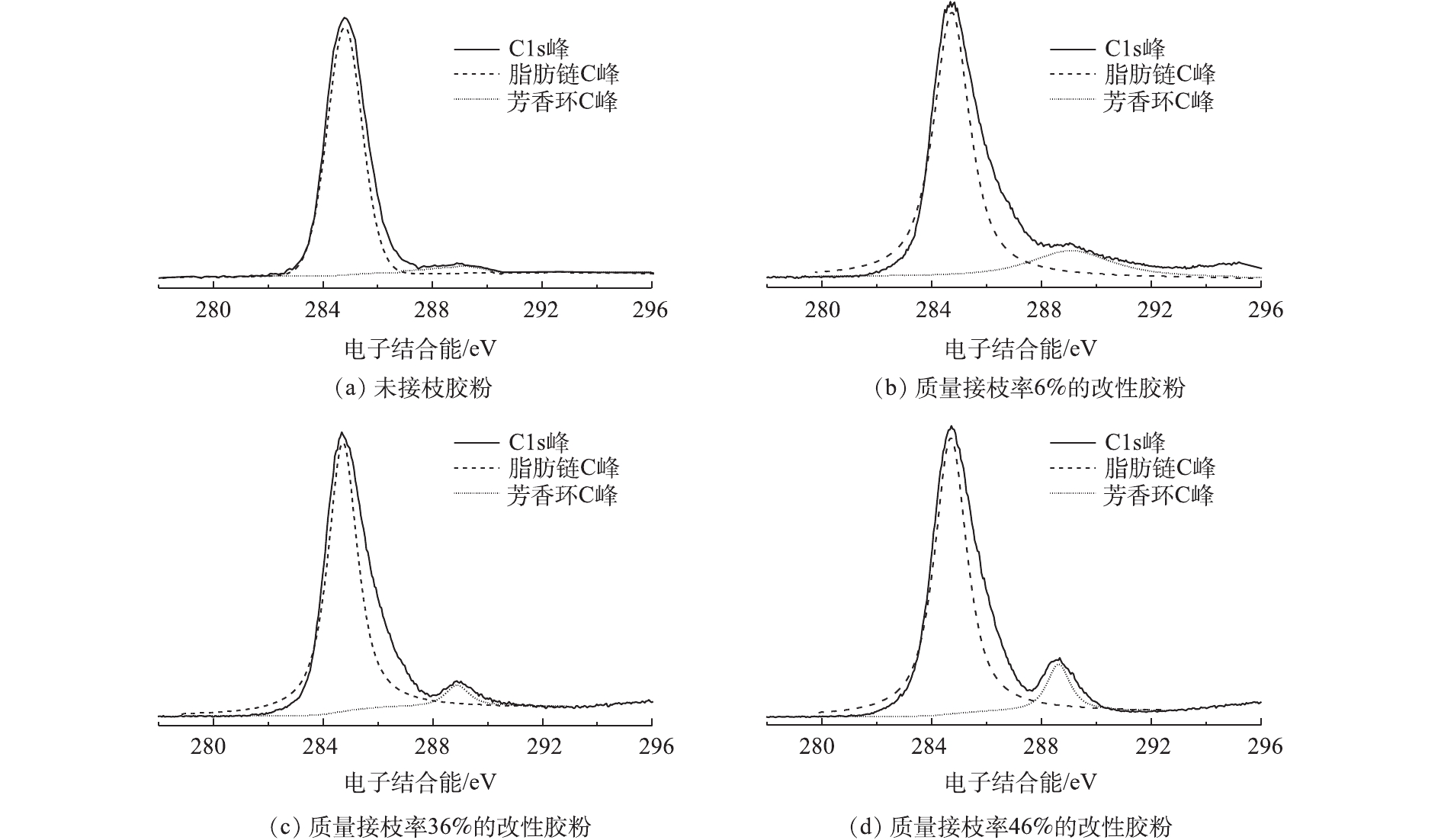
2.2 X射线光电子能谱表征(XPS)
图2中XPS分析了废轮胎胶粉表面元素及元素含量的变化情况。由图2(a)看出,未改性胶粉XPS谱图显示出C1s峰、O1s峰和Zn2p3/2峰,表明胶粉表面含有较多碳元素、氧元素和锌元素,且碳元素为胶粉表面最主要的元素,但接枝反应后,由于在胶粉表面引入聚苯乙烯链段,使得其表面碳元素含量及价态发生了相应变化,因此,对接枝胶粉的C1s峰进行分峰拟合,以进一步研究改性胶粉的接枝率变化情况。选取质量接枝率为6%、36%、46%的改性胶粉,利用XPS表征其C1s峰,并通过XPS谱图中C1s峰的分峰拟合,分析接枝胶粉中碳元素的化学键类型以及含量。图2(b)、图2(c)和图2(d)为不同接枝率的改性胶粉C1s峰分峰拟合结果。通过图2可以分析胶粉表面碳元素化学键的连接情况。表1为接枝前后胶粉表面碳元素的化学键种类及其所占比例。
表 1 胶粉表面碳元素的化学键存在形式Table 1. Chemical bonds on the surface of three crumb tire rubbers碳原子种类 结合能/eV 未接枝胶粉/% 接枝改性胶粉中碳元素含量/% 6% 36% 46% 脂肪链碳 284.8 98.5 92.8 91.1 87.5 芳香环碳 289.0 1.5 7.2 8.9 12.5 在未接枝胶粉中,脂肪链碳的含量是98.5%,芳香环碳的含量为1.5%。随着聚苯乙烯接枝率提高,胶粉中芳香环碳的含量逐步上升,脂肪链碳的含量下降。当聚苯乙烯接枝率为46%时,芳香环碳的含量达到12.5%。这表明聚苯乙烯链段成功接枝到胶粉表面。
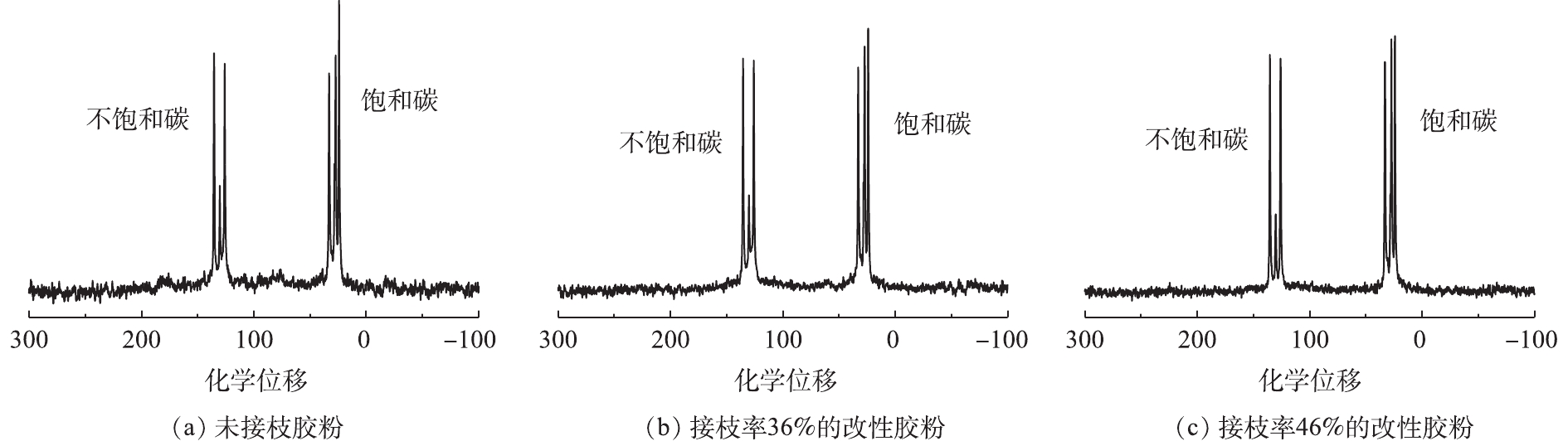
2.3 固体核磁共振谱图表征
对不同接枝率的改性胶粉进行固体核磁13C NMR表征,如图3所示,化学位移在10~45的峰可归属为饱和碳核磁共振峰,不饱和碳的核磁共振峰化学位移在120~145。谱峰的强度与相应碳原子的摩尔含量成正比,通过对比接枝改性废轮胎胶粉中饱和碳与不饱和碳的峰面积比值,可以判断聚苯乙烯的接枝情况。
由计算可以得出不同接枝率的改性胶粉样品中不饱和碳与饱和碳的峰面积比值。未接枝胶粉的不饱和碳与饱和碳的比值为0.70,质量接枝率为36%的改性胶粉的比值增大到0.83,而质量接枝率为46%的改性胶粉的比值则增大到0.88。可见,随着质量接枝率的提高,废轮胎胶粉中不饱和碳与饱和碳的比值明显提高,进一步证明了聚苯乙烯链段成功接枝到了胶粉表面。
2.4 接枝胶粉对改性沥青的影响
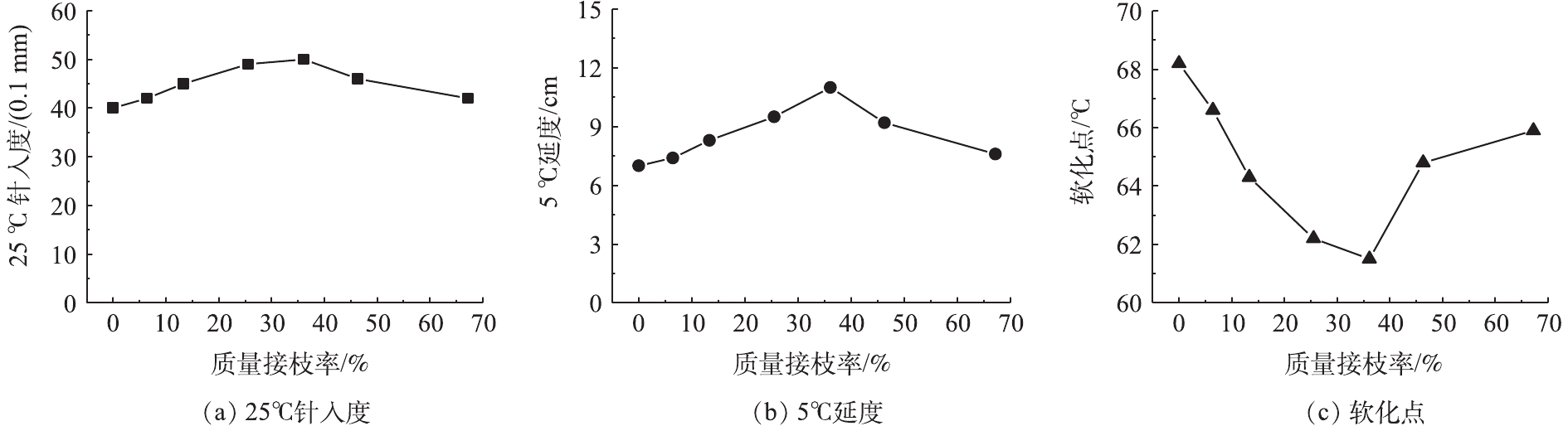
根据聚苯乙烯接枝率的变化规律,依次选取接枝率为6%、13%、26%、36%、46%和67%的接枝改性胶粉以及未接枝胶粉制备胶粉改性沥青,并检测25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度和软化点等改性沥青主要性能指标。根据胶粉改性沥青的性能指标结果,得到其与胶粉表面聚苯乙烯接枝率的变化规律,如图4所示。
由图4可知,随着胶粉表面聚苯乙烯接枝率的增加,胶粉改性沥青的25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度均呈先上升后下降的变化趋势;软化点则呈先下降后上升的变化趋势。同时,25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度、软化点均在接枝率为36%时出现极值。其中,接枝率为36%的接枝胶粉改性沥青的5 ℃延度达到了11.0 cm,相比于原样胶粉改性沥青(5 ℃延度为7.0 cm)提高了57%。
分析上述结果,其原因可能为,随着接枝率的提高,胶粉表面聚苯乙烯链段比例增加。聚苯乙烯链段中的苯环结构与沥青中的芳香类化合物具有良好的相容性,使得胶粉与沥青的界面结合强度加强,改性沥青的延展性能提高,因此,5 ℃延度和25 ℃针入度增加,黏度和软化点降低。但进一步增加胶粉中聚苯乙烯链段的接枝比例,胶粉-沥青界面层的延展性降低,因而改性沥青5 ℃延度和25 ℃针入度降低,软化点上升。
2.5 聚苯乙烯与胶粉共混对改性沥青性能的影响
为进一步探究胶粉表面接枝聚苯乙烯链段对改性沥青性能的作用,设置对照实验:将一定量的聚苯乙烯颗粒与未接枝胶粉混合,制备改性沥青,测定改性沥青主要性能指标。其中聚苯乙烯颗粒参照文献中的方法[30]采用悬浮聚合的方式制备,粒径约为3 mm。
如表2所示,聚苯乙烯颗粒占胶粉和聚苯乙烯总量的质量分数分别为0%、18%、36%和100%时,测得的改性沥青主要性能指标。当胶粉中混有少量聚苯乙烯颗粒时(<36%),改性沥青的性能变化与表面接枝聚苯乙烯链段的胶粉改性沥青类似,25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度上升,软化点下降。由此可见,一定量的聚苯乙烯共混改性也能够改善胶粉改性沥青的界面相容性。但是,当聚苯乙烯加入量为36%时,所得胶粉改性沥青的5 ℃延度为8.3 cm,低于接枝率为36%的接枝改性胶粉所制备的胶粉改性沥青(11.0 cm)。这表明,废轮胎胶粉表面接枝聚苯乙烯链段,相比共混改性,能够更加显著的提高胶粉改性沥青的界面结合强度。当采用100%的聚苯乙烯对沥青进行改性,制备沥青的25 ℃针入度提高、5 ℃延度和软化点明显降低,表明改性沥青的性能明显降低。
表 2 胶粉与聚苯乙烯共混制备改性沥青的性能指标Table 2. Main properties of bitumen prepared through mixing crumb tire rubber with polystyrene聚苯乙烯含量/% 25 ℃针入度/(0.1 mm) 5 ℃延度/cm 软化点/℃ 0 40 7.0 68.2 18 45 8.2 64.1 36 48 8.3 62.5 100 55 4.4 57.4 基于以上研究,对废轮胎胶粉的苯乙烯接枝改性对所制备胶粉改性沥青性能的影响机理进行初步探讨。将改性后的胶粉加入沥青中后,在高温及机械力的作用下,吸收沥青中的轻质组分,胶粉本身致密的高分子网状结构发生溶胀,一些交联点和分子链发生断裂。废胎胶粉在沥青中不断溶胀的过程中,其表面的高分子链段可以扩散到沥青中,而一些沥青中的轻质组分则进入到胶粉的高分子网络中。这样,这些高分子链和沥青轻质组分在胶粉表面形成界面层。同时,界面层的外围吸附沥青中的胶质形成界面过渡层。界面层与沥青中胶团(沥青质和胶质)的外层胶质有亲和作用,从而形成废胎胶粉和沥青连续或相互交错的三维空间网络结构。在胶粉表面聚合接枝聚苯乙烯链段,可以使胶粉表面的界面层和界面过渡层增厚,由于芳香基团的相似相容原理,界面层与沥青胶团的相互作用增强,从而增大了三维空间网络结构的结合强度,进而提高改性沥青的界面稳定性和性能。
3. 结论
1)采用乳液聚合的方式对废轮胎胶粉进行聚苯乙烯接枝改性,通过XPS、13C NMR等表征手段,证明了聚苯乙烯链段的成功接枝。
2)通过研究不同接枝率的胶粉改性沥青25 ℃针入度、软化点和5 ℃延度3个主要性能指标的影响规律发现:随着胶粉表面聚苯乙烯接枝率的增加,胶粉改性沥青的25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度均呈先上升后下降的变化趋势;软化点则呈先下降后上升的变化趋势。同时25 ℃针入度、5 ℃延度、软化点均在接枝率为36%附近出现极值。此时,接枝胶粉改性沥青的5 ℃延度达到11.0 cm,显著高于未接枝胶粉改性沥青和胶粉苯乙烯共混改性沥青。
3)由于在废轮胎胶粉表面接枝适量的聚苯乙烯链段,能够显著提高胶粉/沥青界面层和界面过渡层的厚度。同时由于聚苯乙烯与沥青中胶质基团的亲和作用,使胶粉改性沥青的界面层结合强度显著提高,显著改善胶粉改性沥青的低温延展性。
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 1033
- HTML全文浏览数: 1033
- PDF下载数: 25
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: