湘江衡阳段沉积物中铊等重金属的污染特征及其生态风险评估
Distribution and Risk Assessment of Thallium and Other Metals in Sediments from Hengyang Section of Xiangjiang River
-
摘要: 湘江是我国重金属污染最重的河流之一。为了更全面了解湘江衡阳段表层沉积物重金属污染现状及其潜在生态风险,在前期相关研究基础上,分析了重金属Tl及其他4种重金属(Mn、Co、Ni和V)的含量水平和分布特征,并采用地累积指数法和潜在生态风险指数法对沉积物中重金属污染现状和潜在生态风险进行了评价。结果表明,湘江衡阳段表层沉积物中Tl和Mn有一定程度的累积和污染,其含量分别为0.12~2.09 mg·kg-1和234~4 580 mg·kg-1。由于Tl具有较强的毒性响应,其潜在生态风险不容忽视。综合前期相关研究结果,研究区域中10种重金属总潜在生态风险指数(RI)为27.8~6 266,约70%采样点具有重度生态风险,其主要风险来源于Cd和Tl。Abstract: Xiangjiang River is one of the highly heavy-metal polluted rivers in China. To obtain comprehensive evaluation about the pollution status of heavy metals and their potential ecological risks, the levels and distribution of thallium (Tl) and four other heavy metals (Mn, Co, Ni and V) in surface sediments from Hengyang section of Xiangjiang River were analyzed based on our previous study. The potential ecological risks of these heavy metals were calculated using index of geoaccumulation (Igeo) as well as Hakanson potential ecological risk index (RI). Results indicated that surface sediments from Hengyang Section of Xiangjiang River were polluted by Tl and Mn to some extent, with concentrations ranging from 0.12~2.09 mg·kg-1 and 234~4 580 mg·kg-1, respectively. Much more attention should be paid to the ecological risk from Tl due to its high toxicity. Combined with our previous study, the total RI values of 10 heavy metals in the studied area varied from 27.8~6 266, among which about 70% sampling sites exhibited high ecological risk. The ecological risk was mainly caused by Cd and Tl.
-
热脱附修复技术对于多环芳烃、石油烃等有机污染物的去除具有良好的效果。异位热脱附技术更是具有修复周期短、普适性强的显著优势,在目前有机污染场地修复中应用较为广泛[1]。然而,由于异位热脱附修复工程涉及污染土壤的清挖和转运,施工过程中极易产生有机污染物挥发,造成二次污染,对施工区域及运输路线周边环境产生不良的影响。因此,为了保障修复效果、尽可能地避免二次污染,对污染场地异位热脱附修复工程的全过程环境监理尤为重要。
污染场地修复工程的处理处置对象多为可能危害人体健康的污染物,修复过程具有专业性强、技术复杂及风险高等特点,由此对相应的环境监理工作提出了更高的要求[2]。2014年2月19日,国家环境保护主管部门批准了《场地环境调查技术导则》,并于7月1日起正式实施,首次将环境监理纳入我国污染场地修复工作范畴,标志着污染场地修复工程环境监理开始规范化、系统化和法律化。一些开展污染场地修复相关工作较早的省市(如北京、上海和广东等)积累了若干项目经验,参考国际相关程序和方法,编制了污染场地修复工程环境监理地方性规范。但目前关于环境污染修复工程环境监理方面的研究和案例仍相对匮乏[3]。
本研究以北京某污染场地异位热脱附修复工程为例,结合实际情况对其环境监理工作要点进行了研究,并分析了本案例的典型意义,对环境监理过程中存在的问题进行梳理,提出了若干建议,为污染场地修复工程环境监理研究与实践、为相关管理制度制定都提供了案例参考。
1. 场地与修复工程概况
场地原为钢铁企业辅助设施(如运输、料仓、旧货场等)所在地,已有30年生产经营历史。根据场地环境调查与风险评估结果,场内零散分布29个多环芳烃污染地块,最大污染深度4.5 m,污染面积3.1万m2,污染土方量3.9万m3。土壤中16种多环芳烃均超标,超标率范围0.43%~34.89%,超标率最大的是苯并(a)芘。根据《北京城市总体规划(2004年−2020年)》[4],场地所在区域规划为生态友好型产业集聚地,该场地未来为居住用地、商业用地及公共设施用地。
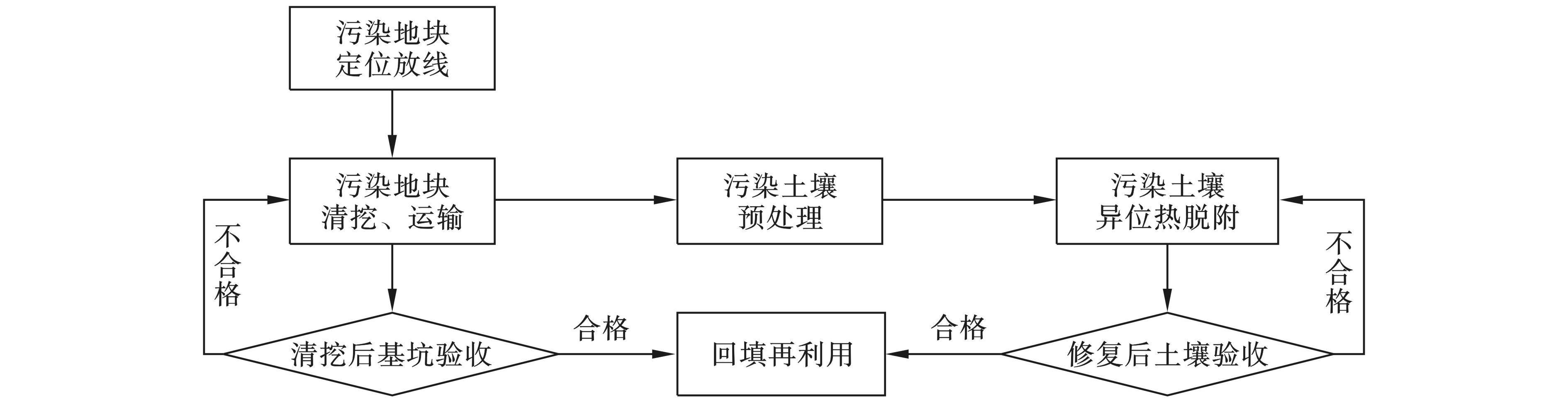
根据项目实施方案及相关批复文件,该场地采用异位热脱附技术修复。对场地内污染土壤进行清挖后,用密闭式专用运输车运往热脱附设施,经筛分、破碎等预处理后,送入回转窑加热至500 ℃并停留20 min。污染土壤热脱附处理后达到《污染场地修复后土壤再利用环境评估导则:DB11/T 1281—2015》[5]的一级再利用筛选值,达标后的土壤可用于原址回填。污染地块清挖后基坑内各目标污染物的检测结果须满足场地管控值方为合格。总体修复技术路线见图1。
修复过程涉及污染土壤的清挖、运输及热脱附处理等阶段,极易产生废气、噪声、废水和固体废物,对场地及其周边环境造成不良影响。因此,需开展严格的环境监理工作,对可能产生二次污染的各环节进行监管,尽可能地降低施工对周边环境带来的负面影响。
2. 本工程环境监理工作要点
污染场地修复工程环境监理工作一般包括3个阶段:修复工程设计阶段环境监理、修复设施建设阶段环境监理和修复工程实施阶段环境监理[5]。本工程环境监理工作除了上述3个阶段外,还包括在修复工程验收阶段的协助工作。
2.1 工程设计阶段环境监理工作要点
工程设计阶段环境监理工作的目的在于“事前控制”和“主动控制”[6],需熟悉修复工程环评报告与设计文件,审查施工单位的施工方案并提出审查意见和修改要求,同时编写环境监理方案等用于指导本工程环境监理工作的技术文件。
2.1.1 文件审核
通过资料梳理、现场踏勘和人员访谈等方式,在熟悉本项目场地污染调查评估状况、场地及周边环境状况、环保主管部门相关批复情况、场地修复工程施工条件等的基础上,对修复技术方案和施工方案进行审核。
核查施工方案是否满足污染场地修复技术方案的要求,如污染场地清挖位置、运输路线、暂存场地、热脱附场所和回填去向等。核查修复方案、施工方案及其中的污染防治措施是否符合相关法律法规与技术规范、环保主管部门批复文件的要求,如产尘点抑尘、污染土遗撒处理和施工期雨废水收集等。经核查,本工程施工方案中缺少针对装载污染土车辆的清洁措施,向建设单位反馈后,要求施工方补充完善,并在后续施工阶段督促该措施的落实。
2.1.2 环境监理方案编制
编制环境监理方案的目的在于指导环境监理工作。根据场地污染情况、场地环境调查与评估报告、修复技术方案和施工方案及修复目标,结合现场踏勘情况编制环境监理方案。在环境监理方案中明确工作目标与范围、工作程序与方法以及各施工环节注意事项,并针对工程实际情况提出可能出现的问题,做好预防措施。
2.2 设施建设阶段环境监理工作要点
规范环境监理工作是设施建设阶段环境监理的主要目的。在本工程环境监理工作中,该阶段工作要点如下:一是建立环境监理体系和制度,督促建设单位针对修复工程产生的废水、废气、噪声、固废等污染物建立相应的污染防治措施和操作规程;督促建设单位落实各类环保协议、相关环保手续的办理工作;督促建设单位建立完善有效的环保责任体系,明确分工、责任到人。二是核查污染防治措施落实情况:核实配套环保设施是否与主体修复设施同时建设,其主要技术指标是否满足修复工程实施方案的要求;核查试运行期间的排放指标是否符合相关标准要求;未达到相关要求的,及时反馈建设单位并监督其整改。
2.3 工程实施阶段环境监理工作要点
工程实施阶段环境监理工作是对修复工程的“事中控制”,其重点工作是监督施工全过程、督促污染防治措施落实,并记录日常工作事项与编制环境监理报告。具体体现在检查施工情况是否符合修复方案要求、环境保护措施是否落实到位,对施工过程进行监督性环境监测,同时参与修复工程管理,对不符合环保要求及修复方案的环节提出整改要求[6]。
2.3.1 监督施工全过程
监督施工全过程是环境监理工作的重点之一。对于异位热脱附修复工程而言,主要包括挖掘、运输、暂存、处理、回填/外运等环节,需按照修复方案和施工方案核实工程位置、挖掘工程量、运输路线、运输量、暂存场地、修复设施以及修复后土壤去向等的达标性。本工程各施工环节环境监理工作要点见表1。
表 1 本工程各施工环节环境监理工作要点施工环节 环境监理工作要点 施工准备 参加环境监理工作交底会,向建设单位、施工单位明确环境监理要求,建立沟通机制。督促施工单位设置必要的施工安全措施及安全标志,如围挡和项目信息告知牌等 挖掘 根据修复方案确认清挖位置,监督测量放线工作。清挖时旁站,核查清挖范围与深度,监督二次污染防治措施落实情况,如洒水抑尘、裸土苫盖等。基坑清挖完成后协助验收取样,并跟踪检测结果,将超标点位告知建设单位和施工单位,督促开展扩挖工作。直至基坑取样检测合格 运输 向装载污染土壤的运输车辆签发运输五联单,沿途确保运输车辆将污染土壤运至修复方案指定的暂存与处理区域。核查运输车次和运输量。运输过程中检查是否有污染土壤遗撒或扬尘,如有则通知施工单位及时清理 暂存 检查污染土壤暂存区的密闭情况及地面防渗情况,防止污染物挥发至空气中或下渗至土壤中 热脱附处理 检查热脱附及尾气处理设备是否符合修复方案要求,监督处理过程,督促施工单位及时对处置后土壤进行取样检测,并对检测合格的土壤进行抽检,发现超标则通知施工单位对该样品代表的土壤批次进行再次处理,直至检测合格 原址回填 督促施工单位对验收合格的修复后土壤及时原址回填,检查回填过程的二次污染防治措施,如洒水抑尘和密闭运输等。检查回填土壤是否满足修复方案的相关要求 2.3.2 督促污染防治措施落实
与一般建设项目相比,污染场地修复工程的施工对象为污染土壤,施工过程中现场及周边环境易受到污染,因此施工期废气、废水、固废和噪声的二次污染防治是环境监理工作的重中之重[7]。本工程针对二次污染防治的环境监理工作要点见表2。
表 2 本工程二次污染防治工作要点施工环节 环境影响 污染源 环境监理工作要点 清挖 大气环境影响 开挖时产生扬尘、重金属及VOCs/SVOCs等污染物挥发,挖掘机、铲车和运输车辆等运行产生尾气,表土临时堆放产生扬尘 核查施工时是否尽可能减小开挖面,是否洒水抑尘,是否有刺鼻气味,裸土是否及时苫盖 水环境影响 污染土壤堆存期间的雨水淋滤,污染土壤清挖后遇雨天坑内积水,工作人员生活污水 核查是否尽量避免污染土壤堆存,基坑是否有排水沟,生活污水是否统一排放 土壤环境影响 污染土壤及废物堆存期间经雨水淋滤产生下渗 核查是否尽量避免污染土壤堆存,如有堆存,是否有防渗措施 固体废弃物 污油及废油,报废的一般设施、设备、工具及器具,一般生活及餐厨垃圾 核查是否将固废统一收集处理 噪声 清挖过程中挖掘机、铲车、运输车辆等运行产生噪声 核查机械车辆是否状况良好,是否严格控制作业范围,是否避免夜间施工,是否采取其他降噪措施 运输 大气环境影响 土方运输产生扬尘,车辆运输时排放尾气 车辆是否密闭运输,是否满载超载,运输道路是否及时洒水抑尘 水环境影响 污染土壤运输过程中发生遗撒经雨水冲刷,设施、设备、工具及器具清洗产生废水 核查运输过程是否有遗撒,如有是否立即采取清洁措施,机械设备清洗废水是否统一收集处理 土壤环境影响 污染土壤运输过程中遗撒 污染土壤装车后是否对车轮及车身进行清扫,运输车轮是否密闭,是否满载超载,是否减速慢行 噪声 车辆运输时产生噪声 运输时是否避开环境敏感区,是否尽可能减少鸣笛,是否减速慢行 热脱附处理 大气环境影响 热脱附尾气,污染土壤临时堆存产生扬尘 核查热脱附设备的尾气处理装置是否运行良好,活性炭是否及时更换,污染土壤临时堆存区域是否密闭 水环境影响 热脱附产生的冷却水、含酸废水 是否统一收集处理后达标排放 土壤环境影响 污染土壤临时堆存期间雨水淋滤,污染治理所用化学品渗漏遗洒 污染土壤临时堆存区域是否有防渗措施, 固体废弃物 热脱附过程收集的除尘灰,尾气处理装置更换下来的活性炭,经过处理后的土壤或废物 是否统一收集后送有资质的单位处理 噪声 施工过程机械噪声 是否尽量选用低噪声设备,是否采取有效的降噪措施 原址回填 大气环境影响 扬尘,推土机、铲车、车辆等运行时排放尾气 是否洒水抑尘,裸土是否及时苫盖,回填后是否及时压实 水环境影响 设施、设备、工具及器具清洗排放废水,工作人员生活污水 废水是否统一收集处理后达标排放 固体废弃物 污油及废油,报废的一般设施、设备、工具及器具,一般生活及餐厨垃圾 核查是否将固废统一收集处理 噪声 推土机、运输车辆等运行产生噪声 核查机械车辆是否状况良好,是否严格控制作业范围,是否避免夜间施工,是否采取其他降噪措施 2.3.3 开展施工期环境监测
对修复工程污染物排放和环境影响进行监督性监测是修复工程环境监理工作的重要组成部分,主要包括大气环境监测、水污染排放监测以及场界环境噪声监测等。通过监测判断修复工程污染物排放是否满足修复方案及其他相关规定的要求,如有不达标情况,督促施工单位整改。
本工程环境监理在污染土壤清挖及热脱附处理环节针对大气环境与场界噪声均开展了监督性监测(无废水排放),及时掌握工程的污染物排放情况,尽可能确保对周边环境的不良影响最小化。具体监测情况见表3。
表 3 本工程环境监理监督性监测施工环节 监测对象 监测位置 监测方式 监测频次 清挖 现场VOCs/SVOCs 清挖作业现场 手持PID 每天2次 环境空气 根据修复方案在场地四周环境敏感点及场界布设监测点位 大气综合采样仪器 每2周1次,每次1天 场界噪声 根据修复方案在场地四周环境敏感点及场界布设监测点位 积分平均声级计 每天2次 热脱附处理 现场VOCs/SVOCs 清挖作业现场 手持PID 每天2次 热脱附尾气 / 烟气在线监测系统 每天检查汇总自动监测数据 环境空气 根据修复方案在场地四周环境敏感点布设监测点位 大气综合采样仪器 每2周1次,每次1天 场界噪声 根据修复方案在场地四周环境敏感点及场界布设监测点位 积分平均声级计 每天2次 2.3.4 记录日常工作事项与编制报告
在修复工程启动后,环境监理员对每天的工作情况进行记录,包括:环境监理日志、现场巡视和旁站记录、监理会议记录和监测记录等,记录方法采用文字、数据、图表和影像等多种方式。
当修复工程出现实施与设计不符、环保措施落实不到位或其他重大环保问题时,环境监理员根据问题的严重程度,及时下达一般联系单、整改通知单或停/复工指令单,将问题反馈至建设单位,督促施工单位及时处理。
当修复工程进行到一定阶段时,环境监理根据现场工作日常记录编写总结材料,包括环境监理定期报告(月报、季报、年报)、阶段报告和总结报告,作为修复工程竣工验收与效果评估的技术材料之一。
2.4 工程验收阶段环境监理要点
工程验收阶段环境监理工作主要集中在2个方面:一是在开展工程效果评估前,环境监理对施工单位提交的施工过程资料进行完整性和准确性检查,如工程量出错或资料中出现与实际施工不符的内容,及时查清原因,督促施工单位修改完善。二是在开展效果评估期间,协助效果评估单位进行基坑土壤样品采集和热脱附后土壤样品采集,跟踪样品检测结果,如有不合格情况,督促施工单位及时采取处理措施,直至样品检测结果满足修复方案中的相关要求。同时,要协助开展效果评估阶段的其他相关工作。
3. 本案例的典型意义
3.1 修复技术代表性
异位热脱附是一种较为成熟的土壤修复技术,目前已广泛应用于国内外有机污染场地修复实践中。我国自2009年首次引进异位热脱附设备[1],异位热脱附修复技术更是在国内得到快速发展,截至2017年已开展23例污染场地异位热脱附修复项目,同时以其修复工期短、修复效率高的显著优势在现阶段土壤修复中逐渐占据更大比例[8]。保障异位热脱附技术的修复效果对于有机污染土壤修复意义重大。本研究通过案例分析,明确了在异位热脱附修复工程环境监理实际工作中应重点关注的事项,对于开展类似工程的环境监理工作、加强异位热脱附修复工程的环境监管具有一定的指导意义。
3.2 参与过程全面性
环境监理工作的重点在于对修复工程过程的把控,只有对工程全过程进行有效监管,确保施工质量与二次污染防治措施落实到位,才能保障最终的修复效果。本案例的环境监理工作涵盖了污染土壤异位热脱附修复工程的全过程,即:自施工前的文件审核至污染土壤修复后的原址回填,在工作内容方面具有全面性,在工作流程上具有较好的衔接性,基本覆盖了此类工程环境监理工作的关键环节,可对类似工程提供良好的借鉴与参考。
3.3 存在问题普遍性
本工程环境监理工作中存在的主要问题如下:一是环境监理地位不明确,工作范围模糊,在实际工作中易与工程监理产生职责混淆或推诿等问题,造成工作不畅。二是缺乏专业的环境监理人员,环境监理人员应兼备工程管理与环境保护相关专业知识技能,任何一方面的缺失即有可能造成修复工程中的偏差,对修复效果产生负面影响。三是修复工程组织方式协调不足,修复工程一般由建设单位、施工单位、工程监理单位、验收单位等多家参与,在实际工作中由于缺乏有效的协调机制,导致施工受阻或沟通断层,从而降低了工作效率。
上述问题也存在于多个案例中[9-11],通过案例分析,梳理问题、探索解决途径,对于改进污染场地异位热脱附修复环境监理工作具有一定的普适性。
4. 讨论与建议
4.1 讨论
目前,有关污染场地修复工程环境监理的研究日益增多。从研究对象上看,主要涉及焦化厂[3]、蓄电池厂[12]、尾矿库[13]、公路项目[14]和石化项目[11, 15-16]等。然而,鲜有针对钢铁企业污染场地修复工程的案例研究。钢铁企业多为重污染企业,随着全国各地有关钢铁企业退城搬迁政策的出台,城市建成区内遗留大量钢铁企业污染场地。在对其实施污染修复时,须密切关注修复工程中的环保措施落实和二次污染防治情况,尽可能地削弱修复工程对周边人居环境的不良影响。本研究可为钢铁企业污染场地修复工程环境监理提供案例参考。
从研究内容上看,主要集中在环境监理工作方式方法[17-18]和问题对策[10, 19]这2个方面。类似研究并未根据修复工程所采用的技术而进一步对环境监理内容加以区分。然而,目前污染场地修复常用技术种类较多,不同修复技术对应的环境监理工作要点存在一定差异。如“3.1修复技术代表性”中所述,异位热脱附修复技术在国内污染场地修复中应用普遍且发展迅速,但在目前能够检索到的中文文献中鲜有关于异位热脱附修复工程环境监理的研究。本研究则专门针对异位热脱附修复工程的各个环节,进行全过程的环境监理要点分析,对于实践工作有着较强的指导意义。
4.2 建议
根据本案例研究情况,针对目前环境监理工作存在的问题,提出以下建议:
1)出台权威的环境监理工作指南。目前污染场地环境监理工作缺乏较为统一的标准,导致实际工作中工作范围不清晰等问题。因此,亟需根据实际情况建立一套科学合理的标准以指导实践;同时还需与地方环境政策相结合,最大限度地做到因地制宜。
2)优化环境监理工作模式。在工程准备期做好组织体系构建工作,细化工作内容,明确各方职责,建立良好的沟通协调机制,保障污染场地修复工作的过程完整性和结果有效性。与工程监理充分合作,在施工期临时组建共同的领导部门,在统一领导下开展工作,权责分明,沟通顺畅,全方位保障修复工程质量[18, 20]。
3)组建环境监理人才队伍。环境监理人员需对相关环保的法律法规等相关规定要有较为全面的认知,掌握必要的环保知识,有针对性地将工程建设项目中的环境污染和生态保护的特点进行归类总结,准确分析施工环境影响、环保措施实施效果及环境监测结果。同时,需熟悉项目施工流程及其特点,尽可能全面地预防和控制可能造成的环境问题。
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2002
- HTML全文浏览数: 2002
- PDF下载数: 31
- 施引文献: 0





 下载:
下载:
