-
活性污泥法于20世纪初在英国发展起来,因其经济以及高效的处理效果,迅速在全球的污水厂得到广泛的应用和发展。在正确的运行工艺及运行条件下保证微生物在曝气过程中有效除去水中有机物、以及二沉池中良好的泥水分离是活性污泥法出水水质达标的关键[1]。污泥的沉降性能决定了泥水分离的效果,表征污泥沉降性能的主要指标为沉降比(Settled Volume,SV30)和污泥体积指数(Sludge Volume Index,SVI,mL/g),一般SVI<70 mL/g,则认为污泥缺乏活性;SVI>200 mL/g认为发生污泥膨胀,污泥膨胀一旦发生将导致二沉池泥水分离受阻,污泥处理系统的污泥流失,出水水质恶化、处理能力下降等,影响市政工程的正常运行。尽管经过无数的小试、中试甚至污水厂的实验研究,污泥膨胀的处理仍然是一大难题,堪称污水处理界的“癌症”。本文综述了污泥膨胀的研究现状,对大多数污泥膨胀的解决方案做了总结及归纳,并对未来研究方向及重点难点进行展望。
-
污泥膨胀可分为丝状菌膨胀及非丝状菌膨胀,丝状菌膨胀指丝状菌的过度繁殖生长,导致泥水分离时沉降速率下降而引起泥水分离受阻;非丝状菌膨胀又叫粘性膨胀,主要为微生物吸附大量有机物无法代谢,大量高粘性多糖积聚在细胞外导致细胞表面附着物大量增加,难以压缩,从而发生污泥膨胀。非丝状菌膨胀的发生概率远远不及丝状菌膨胀,一般仅占污泥膨胀总数的10%以下[2]。
-
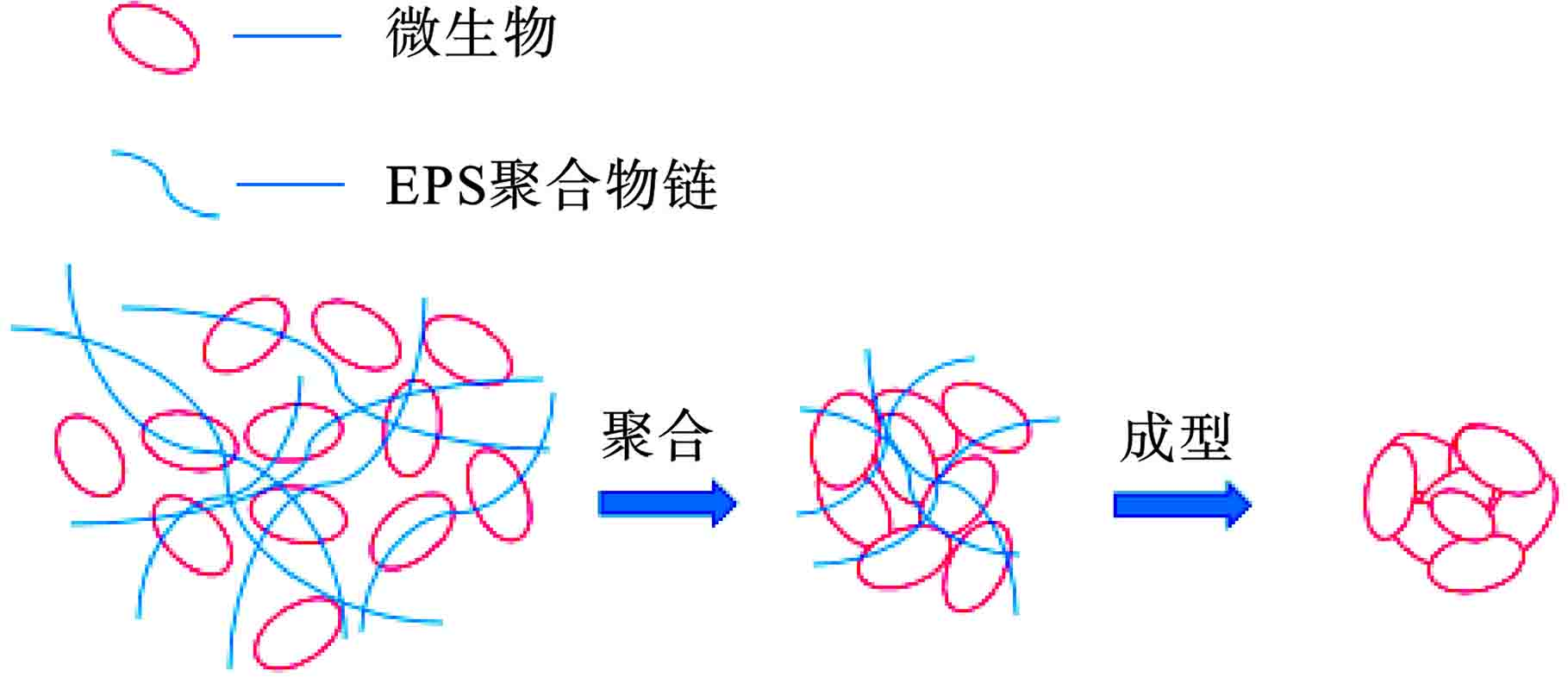
活性污泥絮体是菌胶团细菌通过分泌胞外聚合物(EPS)粘附在以丝状菌作为骨架的结构上形成的,丝状菌胞外多糖(Extracellular polysaccharides,PS)和胞外蛋白(Extracellular polysaccharides,PN)是EPS的主要成分[3],两者约占70%~80%,多糖是污泥絮凝体的支柱[4]在污泥絮凝体的形成中起着重要作用[5],蛋白促进絮凝体聚集和颗粒污泥形成[6],维持絮凝体的稳定性,EPS源于微生物自身产生的有机物,CHRYSI et al [7]发现EPS中非活性有机物的合成需要消耗基质,而微生物的生长也需要消耗基质,因此EPS含量过高会对微生物生长产生抑制作用,SEZGIN et al[8]通过研究对比将污泥絮体根据丝状菌和菌胶团的比例分为3类:1)针状絮凝体污泥:絮凝体内部无丝状菌,结构较为松散,荧光显微镜下为散落颗粒状,沉降性能好,但出水较为浑浊,悬浮物过多;2)理想型絮凝体污泥:絮凝体内部含有少量丝状菌,污泥絮体大块且结构稳定,沉降性能好,反应器出水较为清澈;3)丝状菌膨胀污泥:絮体外被丝状菌包裹,丝状菌互相联接,絮体体积大,结构松散,沉降性能差,泥水难分离,经常发生泡泥现象。EPS促进细胞聚合作用,见图1[9]。
JIN et al [10]发现含有丝状菌的絮凝体沉降性能远高于不含丝状菌的絮凝体,控制丝状菌与菌胶团细菌之间的比例是维持絮体结构紧密性、保持污泥沉降性良好的重要因素,改变外界环境进而刺激絮体间微生物,破坏丝状菌与菌胶团比例的平衡,引起丝状菌大量繁殖或微生物分泌的EPS增多,将导致活性污泥絮体解体,相对质量的变轻及体积的膨胀,致使污泥的沉降性能恶化,不能进行正常的泥水分离,发生污泥膨胀。
LI et al [11]推测丝状菌的不断生长可能是由絮凝体表面的性质变化造成的,使得微生物难以附着在丝状菌上,最后无法形成结合紧密的絮体结构。
IC et al [12]从形态或丝状菌和絮状微生物之间的竞争角度来解释丝状菌污泥膨胀这一现象。丝状菌相比非丝状菌的竞争优势在于丝状菌的表面体积比(A/V)更大,丝状菌优先向1个或2个方向生长,这种形态特征在底物浓度限制下给予丝状菌竞争优势[13];在低底物浓度时,营养物质更容易转移到高A/V比的细胞。丝状菌将比其他微生物更易吸收有机物,这将导致相对较高的生长速率。
高春娣等[14]在研究低温对污泥膨胀的影响时发现,尽管膨胀后SVI恶化到663.99 mL/g,但COD、TN去除率仍可维持90%左右,说明丝状菌相比功能菌同样具有较好的污水处理能力,且丝状菌较大的比表面积使其相互联接形成网状絮凝体,网状的絮凝体更易捕捉悬浮物,出水水质将更加清澈。近年来有不少研究[15-17],试图通过控制丝状菌的量提高出水水质,通过在不同条件下培养丝状菌,利用其良好的捕捉能力和水处理能力来处理污水,将污泥SVI控制在200 mL/g左右,形成污泥微膨胀状态,研究结果显示污泥微膨胀状态将更有利于水处理,但实际运行中长期保持微膨胀状态较为困难,还需要继续进行大量研究。
-
能引起污泥膨胀的核心菌群主要有腐败螺旋菌科、黄杆菌属、丝硫细属、微丝菌属和束缚杆菌属等,核心膨胀菌群主要为变形菌门和拟杆菌门,电子显微镜观察下丝状菌形态上主要呈现直形、弯曲、链状、盘旋或发射状[18],STROM et al[19]根据环境条件和基质的不同,将引起膨胀的丝状菌分为5类:低DO型、低底物浓度型、高硫化物型、营养缺失型和低pH型,见表1。
这些丝状菌在丝状菌膨胀污泥中出现的概率高达70%,其中Type0041型、Type0092型、Type1851型和Microthrix parvicella等类型丝状菌能在好氧厌氧交替环境中生存,是水厂处理系统发生污泥膨胀的主要原因。
-
通过分析和研究污泥膨胀的机理,可更好的从根源上可持续性地控制污泥膨胀发生的频率,并及时采取应对不同类型污泥膨胀的措施。
-
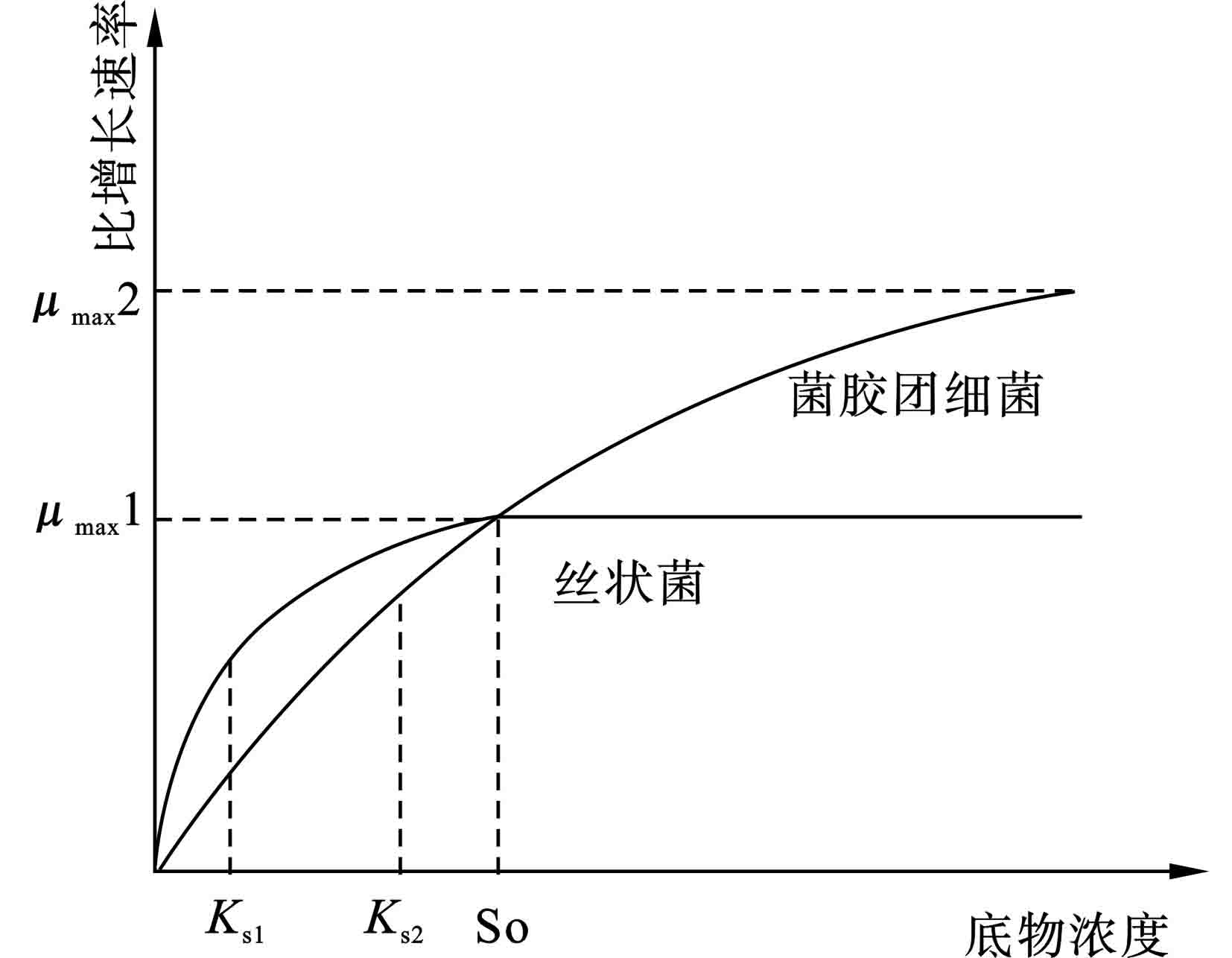
上节丝状菌形态结构特性中提到,有研究表明丝状细菌较大的比表面积有助于在低营养物质或低氧浓度环境条件下底物的吸收,在较低的底物浓度下,由于扩散阻力,污泥絮体内底物会形成一定的浓度梯度,丝状菌可轻易生长穿透到相对更高浓度的絮体外部。CHUDOBA et al [20]在1973年根据Monod方程及不同类型微生物具有的不同最大生长速率μmax值及饱和常数Ks,将具有低Ks和μmax的丝状菌分为A类,菌胶团具有高Ks及μmax为B类,丝状菌在低底物浓度下具有生长优势,而菌胶团在高底物浓度下则为优势菌种,该理论解释了低DO、低底物浓度情况下丝状菌污泥膨胀的现象,并成为污泥膨胀研究领域的主要理论,见图2[21]。
-
STEVEN et al [22]根据不同底物浓度下微生物的耐饥饿程度将其分为菌胶团中细菌、对饥饿敏感的快速生长丝状菌以及生长缓慢耐饥饿的丝状菌。低底物浓度下,耐饥饿的丝状菌占据生长优势;营养物质均衡DO充足情况下,菌胶团生长成为优势;高底物浓度下,快速生长的丝状菌成为优势菌种,这种假说不仅解释了低DO、低底物浓度情况下丝状菌污泥膨胀的现象,还适用于高底物浓度下的丝状菌污泥膨胀现象[23]。
-
传统观念认为非丝状菌在底物丰富的状态下能将多余的营养物质转化成内聚物贮存起来,底物缺乏时可将其利用合成蛋白质提供能量,在底物浓度高浓度梯度的环境中,如SBR系统、选择器等,非丝状菌的生长将占据额外的优势,但目前已研究发现,部分丝状菌在任何环境下都具有较强的贮存能力,如丝状菌Microthrix parvicella,因此丝状菌较低的贮存能力不能作为非丝状菌选择机制中的绝对规律,但这种假说在选择器方面可发挥重要作用。
-
假说认为丝状菌在反硝化过程中只能将NO3−反硝化至NO2−,而反硝化细菌可将NO3−反硝化成N2。KAPPELER et al [25]通过实验比较丝状菌和反硝化细菌在不同反硝化机制下对底物营养物质的竞争时发现,底物浓度不足时,反硝化细菌反硝化不充分,会产生中间产物、亚硝酸盐等,而丝状菌不会产生,好氧条件下,亚硝酸盐、NO会与细胞色素氧化酶作用对反硝化细菌产生抑制作用,长期运行,则会引起丝状菌膨胀。
-
通过改变外界环境刺激絮体间微生物,破坏丝状菌与菌胶团比例的平衡则会引发污泥膨胀,经过总结发现污泥膨胀的外部成因可主要分为3个方面:进水水质[26]、处理环境和运行条件。
-
进水有机物量过高过低、pH过低、C/N/P的比例过大过小及重金属、有毒物质硫化物等均会导致污泥发生膨胀,可类比于新陈代谢,过量或低量的食入或营养的缺失、食物有毒均会导致身体的不健康。
实验表明,进水小分子有机物如葡萄糖、乳糖及乙酸等较易被丝状菌直接利用而引起污泥膨胀,大分子淀粉则需分解后才可利用,不易发生污泥膨胀[27],所以当进水中溶解性小分子有机物过多时,容易引发污泥膨胀。进水负荷过高时,微生物利用有机物产生大量高粘性物质附着在菌胶团表面,易引发非丝状菌膨胀。C/N/P的大小影响着微生物的吸收,研究表明当进水中缺乏氮和磷中的一种元素时,会引发非丝状菌膨胀[28-30],较低的碳氮比情况下,丝状菌依靠比表面积大的优势比一般微生物更易吸收。陈滢等[31]通过在几个相同运行条件的SBR反应器内投加11组不同的C/N/P的进水形成对照实验,通过检测污泥的SVI、MLSS、出水COD、TN、TP和DO等,得出调整C/N/P的大小为100/5/1时较适宜反应器的运行,SVI稳定在100 mL/g以内,且出水指标均稳定达标。另外,停留时间过久的污泥会水解酸化形成大量小分子有机酸、硫化氢等物质,引起丝状菌膨胀。工业废水中通常含有有毒物质,对功能菌有毒性作用,而对丝状菌的影响较小,同样会引起丝状菌膨胀。
进水pH的改变极大程度的影响着反应器运行,pH超过11时,微生物绝大多数将失去活性,污泥菌胶团絮体将受到破坏,当pH低于4.5,真菌完全占据生长优势,菌胶团微生物生长受到限制,出水水质严重下降,pH在6.7~8.0左右有利于微生物的生长,在活性污泥法处理过程中氨化硝化过程均会导致水体pH的下降,一般进水pH可控制调控至7.4~8.3[32]。张安龙等[33]通过小试对反应器调控不同pH,得出进水pH<4.5时开始出现膨胀;pH调节控制在6.5~8.5时,SVI从375 mL/g降至128 mL/g,COD去除率也从32.88%提升至88.89%,丝状菌膨胀基本得以控制。
-
环境温度影响着反应器的运行,每种微生物都有适合自己生长的温度范围,当环境温度适宜某类丝状菌大量生长时,则会产生污泥膨胀,污水生物处理过程中的大多数微生物都适宜在20~32 ℃进行培养,<15 ℃时Microthrix parvicella丝状菌开始大量繁殖[34],调查发现我国北方污水厂相比南方更易发生污泥膨胀现象,高温也易引发丝状菌膨胀,贝氏硫菌、丝硫菌的适宜生长温度为30~36 ℃。高春娣等通过低温下实验研究得出,系统温度在(14±1)℃时可成功诱发丝状菌污泥膨胀,SVI恶化至663.99 mL/g,通过分析高通量观察到低温下功能菌群的丰度极度下降,脱氮菌群由21%降至14%,除磷菌群由4%降至1%,而丝状菌群丰度大幅度上升,由0.49%上升至26%。
低温环境还易引发非丝状菌膨胀,水温过低而污泥负荷过高时,微生物吸附了大量的有机物而来不及代谢,在细胞外壁聚集了大量的高粘性多糖。MOURA et al [35]研究发现温度降低,活性污泥EPS含量降低,而EPS中多糖含量上升,多糖较为粘稠吸附大量结合水,改变污泥活性,使污泥沉降性能变差,从而引起污泥膨胀;同时EPS可以降低细胞表面的负电荷,使相邻的2个细胞相互连接,电斥力是影响污泥膨胀过程中细菌聚集和絮凝能力的关键因素,因此EPS的降低会导致絮体之间电斥力的增加,导致絮团结构疏松,沉降性能差。
-
反应器运行过程中,通过改变实验参数经常会影响污泥的生长,如:曝气量、污泥负荷、水力停留时间和运行流态等。曝气量不变的情况下,较高的负荷会形成低DO环境,不利于菌胶团繁殖,有利于部分适合在低DO状态下的丝状菌的繁殖,而较低负荷情况下,丝状菌的特殊形态相比菌胶团微生物更有利于吸收营养物质,同样会引起丝状菌的大量繁殖[36]。曝气量的大小影响了DO的高低,过低的DO会抑制微生物的生长,丝状菌则可借助其表面积较大的优势吸收DO,占据生长优势。污泥龄是控制活性污泥絮体稳定性的一个重要因素,停滞过久的污泥会变成惰性污泥,失去活性并消耗反应器内的DO[37],促进丝状菌的生长,引起污泥膨胀。反应器的类型直接决定了泥水混合物的流态,完全混合式因底物浓度和底物浓度梯度都较低,因此最易发生污泥膨胀,而间歇式反应器具有高底物浓度和梯度的优势,不易发生膨胀。
-
目前控制活性污泥膨胀一般分为药剂投加法和条件控制法,条件控制法主要通过改变或增加反应器运行外在条件、控制反应器运行参数等物理方式来控制污泥膨胀;药剂投加法通过投加药剂的化学方式杀死丝状菌或加强污泥的絮凝能力来提高污泥的沉降性能。
-
相比条件控制法,投加药物通常是污水厂面对污泥膨胀及时修复补救的常规措施,也是应对污泥膨胀最为急速控制的方式,主要投加药物能改善污泥的沉降性能、絮凝能力、杀死丝状菌,药剂可分为物理药剂及化学氧化剂。
-
(1)增重剂。增重剂会与活性污泥絮体相结合,增加絮体比重,从而改善污泥的沉降性,一般增重剂有:高岭土、碳酸钙、氢氧化钙和硅藻土等。SEKA et al [38]研究发现投加滑石粉对重度丝状菌膨胀的处理效果极佳,并对硝化菌和聚磷菌活性不会造成影响;缺点是改善效果不会太持久,2 d后会慢慢消失。如Bodegraven污水处理厂发生严重膨胀时,通过投加PE8414粉末(滑石粉和亚氯酸盐按比例混合)至已膨胀的污泥中,SVI由850 mL/g快速降至250 mL/g,之后2 d又进一步降低至100~125 mL/g,期间通过测试观察,菌种数量基本没有大的变化,且COD等去除率也无影响,实验证明PE8414粉末可有效控制污泥膨胀,但其会增加污泥产量,进而增加后续处理费用[39]。
(2)絮凝剂。絮凝剂加强污泥絮凝能力,提高密度,改善污泥的沉降性能,常用絮凝剂有石灰、铁盐和铝盐。铝盐不仅可增加絮体的絮凝性,而且对丝状菌Microthrix parvicella的生长有抑制作用[40]。铁盐可除去部分丝状菌且促进菌胶团的生长,但会对出水的色度有所影响,MATSCHET et al [41]在进水过程中投加10~14 mg/L硫酸亚铁,发现SVI从455 mL/g降至60 mL/g,且使引起膨胀的021N型丝状菌消失。
混凝絮凝剂等作用原理是促进形成体积大且结构紧密的污泥絮体,从而改善污泥的沉降性,但药剂持续时间过短,想要长期保持沉降性能,必须持续投加药剂,重复投加药剂会增加污泥量。投加絮凝剂等会对活性污泥的功能菌有影响,影响反应器的稳定运行。
-
(1)氯。氯是最早用来控制污泥膨胀的氧化剂,由于绝大多数污水处理厂出水前都需经过加氯消毒才可排入自然水体,因此可利用现有设备通过投加氯控制污泥膨胀。JENKINS et al[42]发现,加氯对绝大多数丝状菌都有很好的控制作用,其对污泥中的功能菌也有一定的损害作用,投加量越高,对聚磷菌硝化菌伤害越大。
(2)过氧化氢。投加H2O2不会像加氯那样带来负面影响,并且投加H2O2可提升反应器内DO浓度,提高脱氮除磷效率,但因为其价格昂贵,实际工程应用并不广泛。
(3)臭氧。O3对污泥膨胀有明显的控制效果,且可分解大分子难降解有机物为小分子为微生物所利用,如淀粉等。 NILSSON et al [43]通过实验发现投加臭氧不仅能改善反应器污泥膨胀的现象,而且能去除难降解有机物并提高硝化效率。吕永涛等[44]通过研究得出低浓度投加臭氧(0.085 g/g,以O3/MLSS计)有利于打断丝状菌,且SVI由300 mL/g降至80~90 mL/g恢复了活性污泥的沉降性,但高浓度投加臭氧,污泥沉降性能反而开始恶化,脱氮除磷效率降至60%。
投加氧化剂对污泥膨胀有较好的控制作用,其作用原理是杀死阻碍沉淀的丝状菌,丝状菌膨胀的污泥中丝状菌大多都在菌胶团外部,相比其他细菌更易受到氧化剂影响,但还需控制投加的量,大多数氧化剂是没有选择性的,过量投加会对功能菌造成损害,甚至造成污泥絮体的解体,处理能力下降,出水恶化。化学氧化剂普遍存在的问题为成本昂贵,并且难以精准的控制投加的量,实际工程应用较广的为投加氯。
-
SBR工艺为最不易发生污泥膨胀的运行工艺,主要原因可分为:1)好氧环境与缺氧环境的交替有效抑制丝状菌;2)较高的底物浓度以及较大的底物浓度梯度有利于菌胶团的生长;3)污泥龄短,一般丝状菌的比增长速率比其他微生物小,污泥龄的倒数数值等于污泥比增长速率,较长污泥龄的完全混合式易于繁殖丝状菌,SBR较短的泥龄使得剩余污泥的排放速度大于丝状菌增长速率,丝状菌无法大量繁殖。
-
根据选择性理论,通过设置生物选择器在污水进入反应器之前提前筛去部分丝状菌,促进反应器内菌胶团微生物的生长,历史上对选择器的应用可推演至20世纪70年代,LINNE et al [47]成功开发了选择反应器,并成为控制污泥膨胀的最广泛的工程工具,减少了很多活性污泥系统中的膨胀问题,但并未根本性解决膨胀问题,实际运行中经常有失败的报告[47-48]。美国的Hamilton完全混合式污水处理厂在发生丝状菌污泥膨胀后,SVI升至300~500 mL/g,仅仅通过在处理系统前增设了一个停留时间为4 min的生物选择器,SVI就降到50~100 mL/g[46];无独有偶,美国的VOSO污水处理厂冬季经常发生污泥膨胀,SVI常常可达到400 mL/g以上,在增设一个反应时间为15 min的生物选择器后,就可控制10 ℃时产生的污泥膨胀,SVI降至100 mL/g以下[46]。常用的生物选择器可按运行条件分为3类:好氧、厌氧和缺氧。
(1)好氧选择器。好氧选择器主要利用扩散选择理论,根据丝状菌和其他细菌的不同动力学竞争速率来进行筛选菌种,即底物浓度较大时,菌胶团中其他细菌比生长速率大于丝状菌,菌胶团中细菌占据生长优势;相对的,底物基质浓度较小时,丝状菌占据生长优势。好氧选择器的水力停留时间(反应器容积)对污泥的沉降性有很大的影响,停留时间不足会导致可溶性基质在接触区未被消耗完全,随进水进入反应器,引起丝状菌的生长;而停留时间过长导致底物浓度过低,变相成为完全混合模式,有利于丝状菌的生长。
(2)缺氧选择器。缺氧选择器利用了一氧化氮假说。缺氧条件下,反硝化菌降解有机物作为电子供体,利用硝酸盐(NO3−)作为电子受体,快速增殖;而丝状菌无法利用硝酸盐(NO3−)作为电子受体生长受到抑制,从而控制污泥膨胀。缺氧选择器的选择效果与进入选择器的硝酸盐浓度有关,外界条件一定情况下,硝酸盐浓度越高,反硝化作用越强烈,进入反应器易降解有机物含量越少(丝状菌难以利用大分子难降解有机物),从而改善污泥沉降性。
(3)厌氧选择器。吴凡松等[49]发现厌氧处理后,聚磷菌释磷,后续好氧段吸磷,污泥含磷量增加,P/C比值上升,SVI降低,聚磷菌在厌氧过程中迅速吸收COD,转化成PHAs,好氧时PHAs分解获取能量,厌氧下丝状菌生长缓慢,具有较低的多聚磷酸盐释放速率,从而控制膨胀。厌氧区重在释磷阶段,需要通过大量吸收COD的聚磷菌快速占据生长优势,成为优势菌群。
-
污泥龄(SRT)是控制活性污泥絮体稳定性的一个重要因素,停滞过久的污泥会变成惰性污泥,失去活性并消耗反应器内DO,促进丝状菌的生长,导致污泥膨胀[50]。因此一般采取缩短SRT的方式来防止丝状菌膨胀,但这种方法同时抑制了硝化细菌的培养[50],硝化菌生长速度较慢,需较长时间培养。彭赵旭等[51]通过改变SRT来研究对丝状菌微膨胀系统的影响,发现厌氧/好氧运行时,适当减小SRT可提高污泥的比硝化速率,同步硝化反硝化率和剩余污泥的含磷量与SRT成正比,SRT由小变大时,污泥絮体的结构由紧密向疏松转化。
对于负荷较低的反应器,可提高负荷满足菌胶团微生物对营养物质的需求,使其成为优势菌种,从而控制污泥膨胀,但提高负荷会使污染物处理效率会受到影响,且增加了实际运行费用,简耀先[52]在研究SBR处理工业水的过程中发现严重的污泥膨胀,SV30升至100%,经分析研究为进水水质C/N比失衡,且反应运行周期不稳定,后期经过调控,将C/N比稳定在4.5左右,活性污泥沉降性逐渐恢复正常值为30%~40%。
曝气量是控制反应器良好运行的重要因素,应着重考虑,反应器DO>1 mg/L时,好氧菌占据优势进行硝化作用;DO<0.5 mg/L,厌氧菌占据优势进行反硝化作用。不少研究通过长期调低DO,形成短程硝化及同步硝化反硝化来节约水处理能耗,提高处理效率,但低DO同时也是丝状菌大量增长的主要原因。丝状菌的比表面积较大,在低DO环境中更容易获取氧气,成为优势菌种,一般可通过加大曝气量[53],以避免因供养不足而导致的丝状菌污泥膨胀。陆秋萍等[54]通过调控DO,控制硝化菌、反硝化菌的生长,将SVI由220 mL/g降至110 mL/g;过大的曝气量同样会导致污泥絮体结构的松散,曝气产生的剪切力会破坏菌胶之间的粘结力,李军等[55]发现过大的曝气量会使胞外聚合物中多糖的含量上升,吸附大量结合水,使细胞间结合性变差,絮体结构松散,沉降性大幅下降。
一些硫代谢丝状菌在较高硫化物存在的条件下更易生长,硫化物质量浓度>1 mg/L,有机酸质量浓度>100 mg/L时,更容易发生污泥膨胀[56],对于高硫化物引起的污泥膨胀,一般采取预曝气、化学氧化和化学沉淀等方法控制。
-
ZAIDI et al [57]通过对比施加88 mT的磁场强度,研究得出在较长污泥龄的不利影响下,磁场能够增强污泥的聚集能力和相对疏水性,并保持显著的表面负电荷,从而使絮凝体更加稳定,极大的减小了污泥膨胀的发生率,且磁场对生物量的增长有促进作用,在较长的污泥龄条件下,磁场仍能增强好氧菌的生物降解能力[58]。
-
刘波等[59]通过利用超声波(0.035 W/cm2,15 min)穿透性和均匀的特点作用于膨胀的污泥将SVI由475 mL/g降至183 mL/g,将超声过的冻干污泥进行扫描电镜显示,丝状菌有明显的断裂萎缩现象,可见超声对丝状菌具有机械折断作用和显著的抑制作用。
条件控制法是基于对污泥膨胀机理的深入研究得出的方法,主要通过调节工艺运行条件创造出有利于功能菌生长不利于丝状菌生长的环境,从根本上抑制了丝状菌的生长,达到良好的沉降性,因此是一种可持续的方法。
此外,还可通过利用生物法治疗污泥膨胀,AGNIESZKA et al [60]研究发现轮虫可对丝状菌进行捕食,FILKOWSKA et al [61]将丝状菌膨胀的污泥放入2个实验反应器内,并在其中一个反应器内加入轮虫进行对比实验,结果表明,相同时间内装有轮虫的反应器内污泥体积为14 mL,而没有轮虫的反应器中污泥体积为44 mL,可见轮虫对丝状菌有较好的去除作用。
-
丝状菌、菌胶团本为一体,活性污泥中定量的丝状菌有利于出水水质的提升,防止丝状菌污泥膨胀在于控制两者良好比例。目前,通过控制丝状菌的量,达到微膨胀状态的研究已广泛开展,改善出水水质,提高处理效率。非特异性方法例如投加絮凝剂、氧化剂等可短时间内改善污泥的沉降性,但这类方法无法根除丝状菌过度的生长,通过分析污泥膨胀产生的机理并加以运用,通过调控运行条件参数、添加选择器,可持续性的改善污泥膨胀现象是长久之计。近年来,对于控制污泥膨胀有不少新颖的研究发现,类似于通过超声、磁场等。目前对丝状菌及其他微生物互相影响的研究并未深入,未来可从此角度分析膨胀的机理,寻找更多微生物之间的联系;此外对污泥膨胀的防治研究主要基于改变外加条件及运行参数,对于未知微生物的研究较少,可能仍有引起膨胀的微生物未被发现,对于未知微生物的鉴别和研究有待发展。
污泥膨胀特性及控制研究现状
Research status of characteristics and control of sludge bulking
-
摘要: 文章通过总结大量研究成果,重点阐述了污泥膨胀的特性研究现状,并根据特性研究,分析污泥膨胀主要产生因素和控制措施。其次,结合丝状菌膨胀机理及形态结构特征,阐述了3种选择器控制污泥膨胀的原理和其他可持续性控制措施。最后从微生物方向对未来污泥膨胀控制及研究进行了展望。Abstract: This paper summarizes a lot of research results, focuses on the characteristics and research status of the sludge bulking, and analyzes main factors and control measures of it. Based on the mechanism and morphology of filamentous bacteria bulking, the principle of controlling sludge bulking by three kinds of selectors and other sustainable control measures are described. Finally, prospects for the future control and research of sludge bulking from the microbiological direction are prospected.
-
Key words:
- sludge bulking /
- sewage treatment /
- activated sludge process /
- filamentous bacteria /
- morphology
-

-
表 1 不同环境条件下引起膨胀的丝状菌
水质条件 丝状菌种类 低DO Type1701、浮游球衣细菌、软发菌 低底物浓度 Type021N、Type0041、Type0092、Type0581、Type0961、Type0803、微丝菌、软发菌、诺卡式菌 高硫化物 发硫菌、Type021N、贝氏硫菌 营养缺失 发硫菌、浮游球衣细菌、Type021N、软发菌、Type0041、Type0657 低pH 真菌 -
[1] TARPY D, DAVID R, MATTILA, et al. Development of the Honey Bee Gut Microbiome throughout the Queen-Rearing Process[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 81(9): 3182 − 3191. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00307-15 [2] 郝晓地, 朱景义, 曹秀芹. 污泥膨胀形成机理及控制措施研究现状和进展[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2006, 7(5): 1 − 9. [3] LIU Y, FANG H. Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on flocculation, settling, and dewatering of activated sludge[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2003, 33(3): 237 − 273. doi: 10.1080/10643380390814479 [4] ADAV S S, LEE D, TAY J. Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule[J]. Water Research, 2008, 42(6-7). [5] SEVIOUR T. Gel-forming exopolysaccharides explain basic differences between structures of aerobic sludge granules and floccular sludges[J]. Water Research: A Journal of the International Water Association, 2009, 43(18): 4469 − 4478. [6] JUNPING L, YAQIN W, CHEN Z, et al. The effect of quorum sensing and extracellular proteins on the microbial attachment of aerobic granular activated sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology: Biomass, Bioenergy, Biowastes, Conversion Technologies, Biotransformations, Production Technologies, 2014: 152, 53 − 58. [7] CHRYSI S, BRUCE E. A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass[J]. Water Research:A Journal of the International Water Association, 2002, 36(11): 2711 − 2720. [8] SEZGIN, MESUTA, DAVID L, et al. A unified theory of filamentous activated sludge bulking[J]. Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation), 1978, 50(2): 362 − 381. [9] LIU Y, LIU Y, TAY J. The effects of extracellular polymeric substances on the formation and stability of biogranules[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2004, 65(2): 143 − 148. [10] JIN B, MARIE B, LANT P. A comprehensive insight into floc characteristics and their impact on compressibility and settleability of activated sludge[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2003, 95(1-3): 221-234 . [11] LI W M, LIAO X W, GUO J S, et al. New insights into filamentous sludge bulking: The potential role of extracellular polymeric substances in sludge bulking in the activated sludge process[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 248: 126012. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126012 [12] IC L, REYES F. Clarifying the roles of kinetics and diffusion in activated sludge filamentous bulking[J]. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2008, 101(2): 327 − 336. doi: 10.1002/bit.21886 [13] MARTINS A M P, HEIJNEN J J, LOOSDRECHT M. Effect of feeding pattern and storage on the sludge settleability under aerobic conditions[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(11): 2555 − 2570. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00070-8 [14] 高春娣, 张娜, 彭永臻, 等. 低温下丝状菌膨胀污泥的微生物多样性[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(7): 396 − 406. [15] 王中玮, 彭永臻, 王淑莹, 等. 不同运行方式下低溶解氧污泥微膨胀的可行性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(8): 173 − 178. [16] 彭赵旭, 彭永臻, 桂丽娟, 等. 低溶解氧丝状菌污泥微膨胀在SBR中的可行性[J]. 化工学报, 2010, 61(6): 200 − 1539. [17] 彭赵旭, 彭永臻, 左金龙, 等. 污泥微膨胀状态下短程硝化的实现[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(8): 127 − 131. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2009.08.022 [18] EIKELBOOM D, GEURKINK B. Filamentous micro-organisms observed in industrial activated sludge plants[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2002, 46(1/2): 535 − 542. [19] STROM P F, JENKINS D. Identification and significance of filamentous microorganisms in activated sludge[J]. Water Pollution Control Federation. 1984, 56(5): 449-459. [20] CHUDOBA J, GRAU P, OTTOVA V. Control of activated-sludge filamentous bulking II, selection of microorganisms by means of a selector[J]. Water Research. 1973, 7(10): 1389-1398. [21] 彭赵旭. 低溶解氧丝状菌污泥微膨胀的控制策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2012. [22] STEVEN C C, ROBERT L. Growth and control of filamentous microbes in activated sludge: an integrated hypothesis[J]. Water Research. 1985, 19(4): 471-479. [23] CHAO L, WWEIHUA H, DANDAN L, et al. The anaerobic and starving treatment eliminates filamentous bulking and recovers biocathode biocatalytic activity with residual organic loading in microbial electrochemical system. [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal. 2021: 127072. [24] CGGN A S, KARAHAN O, ORHON D. Effect of feeding pattern on biochemical storage by activated sludge under anoxic conditions[J]. Water Research. 2007, 41(4): 924-934. [25] KAPPELER J, GUJER W. Development of a mathematical model for “aerobic bulking”[J]. Water Research. 1994, 28(2): 303-310. [26] MARTINS A M, PAGILLA K, HEIJNEN J, et al. Filamentous bulking sludge-a critical review[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(4): 793 − 817. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2003.11.005 [27] MARTIN W, SCHAUER M. ‘Candidatus aquirestis calciphila' and 'candidatus haliscomenobacter calcifugiens', filamentous, planktonic bacteria inhabiting natural lakes. [J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 2007, 57(5): 936-940. [28] 高春娣, 彭永臻, 王淑莹, 等. 氮缺乏引起的非丝状菌活性污泥膨胀[J]. 环境科学, 2001(6): 61 − 65. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2001.06.013 [29] 田园. SBR反应器中氮和磷含量对污泥膨胀现象影响研究[D]. 长春: 吉林建筑大学, 2013. [30] 杨雄, 彭永臻, 郭建华, 等. 氮/磷缺乏对污泥沉降性能及丝状菌生长的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(3): 284 − 292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2014.03.038 [31] 陈滢, 彭永臻, 刘敏, 等. 营养物质对污泥沉降性能的影响及污泥膨胀的控制[J]. 环境科学, 2004(6): 54 − 58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2004.06.011 [32] 杨庆, 丁峰, 王淑莹, 等. 缺氮和不同pH值对活性污泥膨胀的影响[J]. 环境污染治理技术与设备, 2006(4): 35 − 37. [33] 张安龙, 张雪, 王森, 等. 低pH值对活性污泥膨胀及废水处理效果的影响[J]. 纸和造纸, 2013, 32(10): 41 − 45. [34] KNOOP S, KUNST S. Influence of temperature and sludge loading on activated sludge settling, especially on Microthrix parvicella[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 37(4): 27 − 35. [35] MOURA L L, DYRTE K L S, SANTIAGO E P, et al. Bassin . Strategies to re-establish stable granulation after filamentous outgrowth: Insights from lab-scale experiments[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection. 2018, 117(0): 606-615. [36] PALM J, JENKINS E, DAVID L, et al. Relationship between organic loading, dissolved oxygen concentration and sludge settleability in the completely-mixed activated sludge process[J]. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation. 1980, 52(10): 2484-2506. [37] JENKINS D, RICHARD M G, DAIGGER G T, et al. Manual on the causes and control of activated sludge bulking, foaming, and other solids separation problems [M]. CRC Press: 2003. [38] SEKA M A, DEWIELE T V, VERSTRAETE W. Full-scale evaluation of a multi-component additive for efficient control of activated sludge filamentous bulking[J]. Environmental Technology. 2002, 23(1): 67-72. [39] EIKELBOOM D. H, GROVENSTEIN J. Control of bulkingin a full scale plant by addition of talc(PE 8418)[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1998, 37(45): 297 − 301. [40] 李鹏, 周利, 赵永柱, 等. 药剂法在控制丝状菌污泥膨胀中的应用[J]. 工业水处理, 2008(7): 4 − 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-829X.2008.07.002 [41] MATSCHET N F. Control of bulking sludgepractical experiences in Austria[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1982, 1(14): 311. [42] JENKINS D, MICHAEL, GLEN T, et al. Manual on the causes and control of activated sludge bulking, foaming, and other solids separation problems [M]. CRC Press: 2004. [43] NILSSON, FILIN, MARINETTE H, et al. Application of ozone in full-scale to reduce filamentous bulking sludge at resundsverket WWTP. [J]. Ozone: Science & Engineering. 2014, 36(3): 238-243. [44] 吕永涛, 朱传首, 张旭阳, 等. 臭氧投量对SBR系统污泥沉降性能及脱氮除磷的影响[J]. 环境科学. 2021, 42(7): 312-316. [45] 李清位, 段付岗. SBR工艺抑制活性污泥膨胀的技术优势和防范措施[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2014(12): 43 − 47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8397.2014.12.013 [46] 张永吉. 控制完全混合式曝气池污泥膨胀的生物选择器[J]. 中国给水排水, 1990(2): 39 − 42. [47] LINNE L, STEPHEN R, STEVEN C, et al. Operational variables affecting performance of the selector-complete mix activated sludge process[J]. Water Pollution Control Federation. 1987, 59(7): 716-721. [48] GABB D M D, STILL D A, EKAMA G, et al. The selector effect on filamentous bulking in long sludge age activated sludge systems[J]. Water Science and Technology, 1991, 23(4-6). [49] 吴凡松, 彭永臻, 王维斌. 生物选择器与除磷脱氮[J]. 给水排水, 2003(12): 32 − 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2003.12.011 [50] DAVID J, MICHAEL G, GLEN T. Manual on the causes and control of activated sludge bulking, foaming, and other solids separation problems [M]. CRC Press: 2004. [51] 彭赵旭, 彭澄瑶, 何争光, 等. 污泥龄对低氧丝状菌活性污泥微膨胀系统的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35(1): 245 − 251. [52] 简耀先. SBR工艺活性污泥膨胀原因分析及调控措施[J]. 中氮肥, 2021(1): 77 − 80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9932.2021.01.022 [53] PALM J, JENKINS, DAVID L, et al. Relationship between organic loading, dissolved oxygen concentration and sludge settleability in the completely-mixed activated sludge process[J]. Journal of Water Pollution Control Federation. 1980, 52(10): 2484-2506. [54] 陆秋萍, 李海勤, 刘华, 等. 污泥膨胀的原因分析及调整实例[J]. 工业用水与废水, 2019, 50(6): 43 − 46. [55] 李军, 商卫纯, 蔡娟, 等. 不同曝气强度下活性污泥中松散束缚型胞外聚合物组分含量及其对污泥沉降性能的影响[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2014, 36(4): 6 − 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2014.04.002 [56] 于德洋, 程显好, 罗毅, 等. 大型真菌重金属富集的研究进展[J]. 中国食用菌, 2011, 30(1): 10 − 13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8310.2011.01.003 [57] ZAIDI N S, SOHILI J, HUSSEIN S. Enhanced biomass properties in sludge bulking: impact of static magnetic field[C]// IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 2020. [58] ZAIDI N S, MUDA K, SOHAILI J, et al. Enhancement of nitrification efficiency during sludge bulking by magnetic field under long sludge retention time[J]. 3 Biotech. 2020, 10(9): 408. [59] 刘波, 丁新春, 张建朱, 等. 超声强制作用下的污泥膨胀控制研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(3): 283 − 287. [60] AGNIESZKA P S, EDYTAL F. The Influence of temperature on the effectiveness of filamentous bacteria removal from activated sludge by rotifers[J]. Water Environment Research. 2012, 84(8): 619-625. [61] FILKOWSKA E. PAJDAK-STOS A. The role of Lecane rotifers in activated sludge bulking control[J]. Water Research. 2008, 42(10): 2483-2490. -



 下载:
下载: