-
湖泊的富营养化问题是全世界面临的主要水环境问题之一[1],富营养化进程加快易引起水华暴发[2-3],透明度下降[4],生物多样性下降[5]等一系列生态系统变化,甚至影响到工农业生产和居民生活,故富营养化问题值得密切关注[6]。关于富营养化现状、发生机制和控制措施等方面,国内外已有一些研究报道[7-10]。中国著名的太湖、巢湖、滇池(简称“三湖”)水华程度分别以“轻度水华”、“轻微水华”、“中度水华”为主[11]。一直以来国家将“三湖”治理纳入国家计划的重点环境治理工程[12]。鄱阳湖整体处于中营养状态,有向富营养化发展的趋势[13]。目前洞庭湖水体富营养化整体程度较轻,但局部水域(大小西湖)富营养化突出,已引起社会各界广泛的关注。有关洞庭湖富营养化研究报道也较多,熊剑等[14-15]利用水质单因子评价和综合营养状态指数对洞庭湖近30年的水质营养状况进行趋势分析,王婷等[16]系统分析了三峡工程运行导致的江湖关系变化对洞庭湖水环境和富营养风险的影响。吴可方等[17]于2016年对东洞庭湖环境因子和浮游植物进行调查,探讨了秋季东洞庭湖蓝藻水华发生的风险水平。然而鲜有在综合营养状态指数评价和洞庭湖浮游植物长期群落演变特征基础上,采用主成分分析对洞庭湖的富营养化影响因素进行研究。
本研究基于1988—2020年对洞庭湖全湖水质和浮游植物的数据跟踪,对洞庭湖的富营养现状及变化趋势作出了全面评价,并结合浮游植物长期的演变特征,采用主成分分析探讨了影响洞庭湖富营养化的主要水质因子,并运用RDA分析揭示了浮游植物与环境因子的关系,以期为洞庭湖水环境保护提供技术支撑。
-
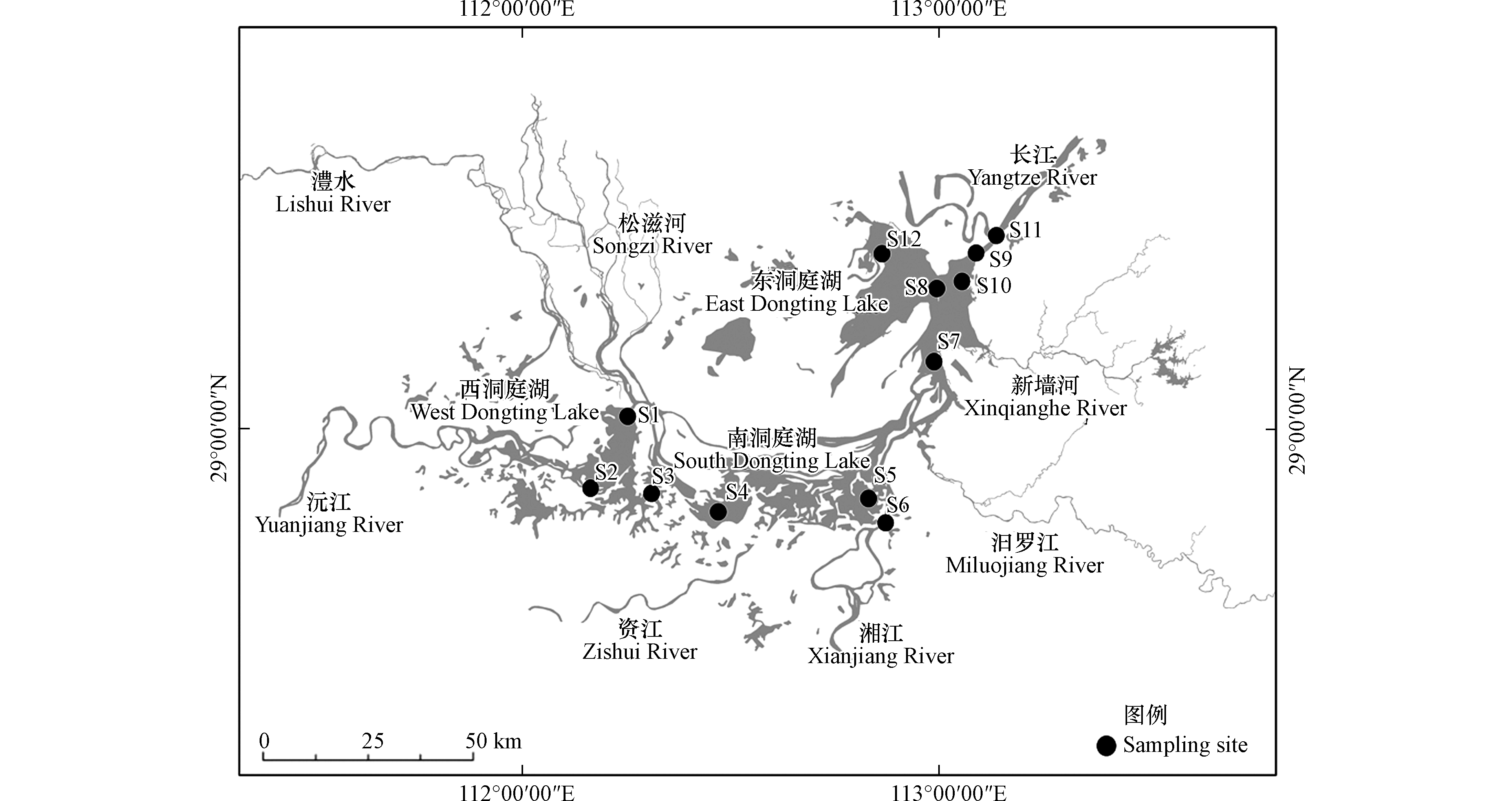
洞庭湖(111°53′E—113°05′E、28°44′N—29°35′N)位于湖南省东北部,长江中游荆江段南岸,由西洞庭湖、南洞庭湖和东洞庭湖组成,是我国第二大淡水湖,同时也是全球重要生态区和国际重要湿地。洞庭湖来水复杂,南纳湘、资、沅、澧(简称四水),北接长江松滋、太平、藕池(简称三口),经湖泊调蓄后,由城陵矶注入长江,有枯水一线、丰水一片的水文特征。洞庭湖共设置12个湖体监测断面,具体包括西洞庭湖区的南嘴(S1)、蒋家嘴(S2)和小河嘴(S3)断面;南洞庭湖区的万子湖(S4)、横岭湖(S5)和虞公庙(S6)断面;东洞庭湖区的鹿角(S7)、东洞庭湖(S8)、岳阳楼(S9)、扁山(S10)、洞庭湖出口(S11)和大小西湖(S12)断面,详见图1。
-
所有水质和浮游植物数据均来自于湖南省洞庭湖生态环境监测中心,各监测指标的年际变化趋势分别以年度算术平均值进行分析处理。采用《湖泊(水库)富营养化评价方法及分级技术规定》中的综合营养状态指数法对水体营养状态进行评价(缺少2002年监测数据)[18],评价指标包括叶绿素a(Chla)、总磷(TP)、总氮(TN)、透明度(SD)和高锰酸盐指数(CODMn)。使用SPASS软件对水质监测数据进行主成分分析,使用Canoco for Windows 4.5软件对浮游植物群落密度数据与水质因子数据进行RDA分析。
-
水质样品采集表层(0.5 m)水样,水样采集后现场自然沉降30 min,取上层非沉降部分分析。浮游植物样品分定量和定性采集。浮游植物定量样根据采样点位的水深设置采样层次。定性样品的采集在定量样品采集结束后进行。使用 25 号浮游生物网,于水面下 0.5 m 深处以每秒 20—30 cm 的速度作“∞”形循环缓慢拖动,拖动时间至少 1—3 min。水质指标在2004年之前每年监测3次(1月、5月和9月),2005年起每月监测1次,浮游植物指标每季度监测1次。
-
水质监测项目包含水温、pH、溶解氧(DO)、TP、TN、CODMn、化学需氧量(CODCr)、五日生化需氧量(BOD5)、氨氮(NH3-N)、Chla、SD等11项。水温、pH和DO采用YSI现场水质多参数仪直接测定;TP采用钼酸铵分光光度法(GB 11893—1989)测定;TN采用碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法(HJ 636—2012)测定;CODMn采用酸性滴定法(GB 11892—1989)测定;CODCr采用重铬酸钾法(HJ 828—2017)测定;BOD5采用稀释与接种法(HJ 505—2009)测定;NH3-N采用纳氏试剂分光光度法(HJ 535—2009)测定;Chla采用分光光度法(HJ 897—2017)测定;透明度采用塞氏盘法现场测定。浮游植物样品用鲁哥氏液固定沉淀48 h后进行显微镜分类计数,种类鉴定参照《中国淡水藻志》[19]。
-
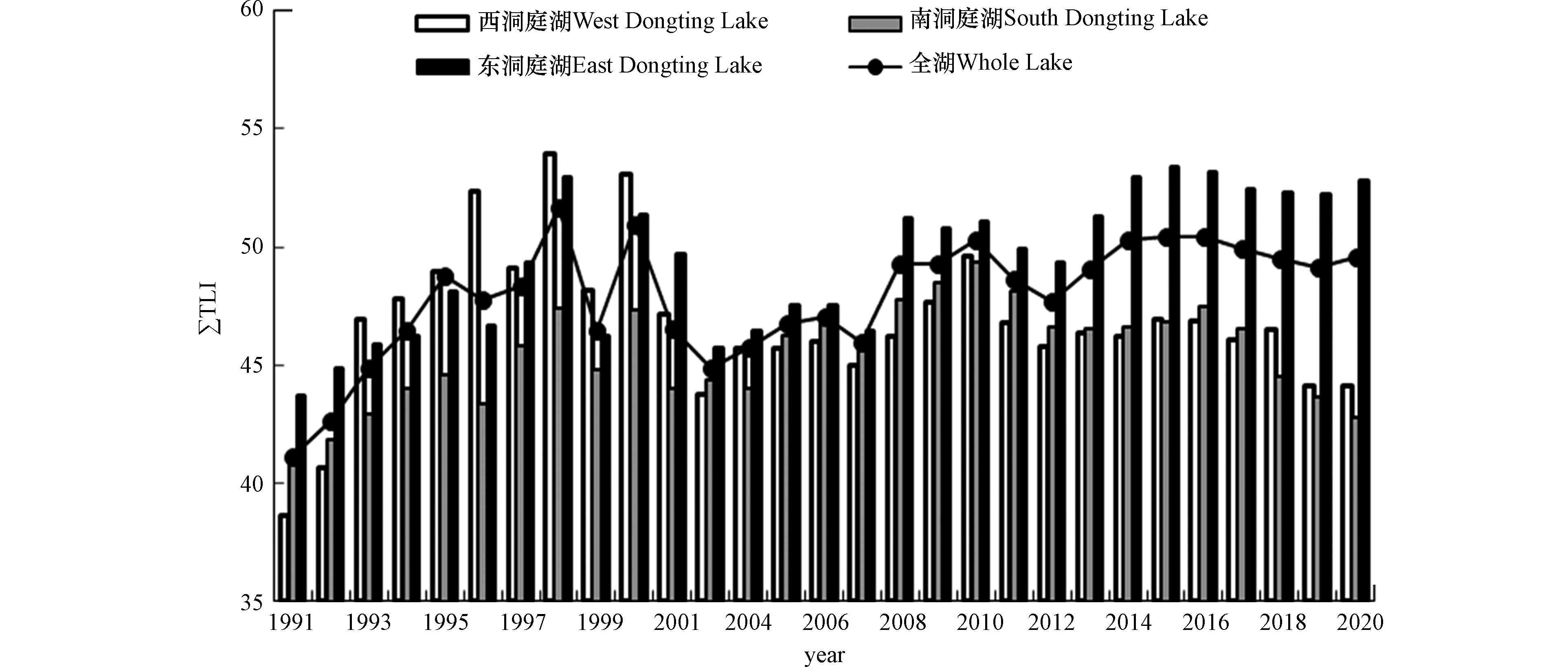
2020年洞庭湖全湖综合营养状态指数(ΣTLI)为49.60,属中营养;12个监测断面ΣTLI在43.24—59.05之间,西、南洞庭湖区域ΣTLI均低于50,处于中营养水平;东洞庭湖区域ΣTLI为52.86,处于轻度富营养状态,其中大小西湖断面的ΣTLI最大,为59.05。2020年1月、4—7月、12月,洞庭湖全湖ΣTLI均超过50,达到轻度富营养,其他月份ΣTLI均小于50,属于中营养。下半年营养状况稍好于上半年。
-
从时间上看,1991—2020年,洞庭湖全湖ΣTLI在41.09 — 51.68之间,总体呈上升趋势(图2),其中1998、2000、2010、2014—2016年的ΣTLI均超过50,处于轻度富营养状态,其余年份均处于中营养状态。可分为3个时间段分析:1991—2000年为第一阶段,这一时期ΣTLI明显上升,尤其是1998年和2000年达到轻度富营养水平,这可能与这一时期洞庭湖暴发洪水有关[20-21],洪水期间地表径流携带的大量悬浮物会使湖泊水体中氮磷等污染物浓度升高[22-23],另外强烈的风暴也会破坏水生植物群落,底泥悬浮易导致沉积物中营养物质得以释放[24]。2001—2007年为第二阶段,这一时期ΣTLI均低于50,水体富营养化趋势减缓,主要受低浓度叶绿素a的影响。2008—2020年为第三阶段,ΣTLI上升趋势明显,水体富营养化加剧。该时段洞庭湖流域工业和生活污染、农业面源污染增加,且湖区内水产养殖破坏水生植被,湖体自净能力减弱等加剧了湖泊富营养化进程[25]。另外,三峡工程运行也可能使洞庭湖水体透明度增大,水环境容量减少,水华暴发风险相对较大[16]。
-
洞庭湖富营养的空间分布按西、南、东的3个湖区进行比较,总体表现为东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>南洞庭湖,与熊剑等[14]的统计分析结果一致,也与汪星等[26]研究的藻类功能群的分布状况相符。近30年来,南洞庭湖区ΣTLI一直低于50,长期稳定在中营养水平。西洞庭湖区在1996、1998和2000年ΣTLI高于50,属轻度富营养,其他年份ΣTLI低于50,属中营养。东洞庭湖区ΣTLI呈上升趋势,与其他湖区差异性显著,在1996、1998、2008—2010年和2013—2020年都超过50,属轻度富营养,主要受大小西湖的影响。大小西湖断面位于东洞庭湖国家级自然保护区的核心区,其附近连通水域水流缓慢,营养盐浓度较高,在2008年首次出现水华,在2013年9月水华面积达400 km2,优势种为微囊藻[27]。“十三五”期间,大小西湖断面平均ΣTLI高于59,将接近中度富营养水平,应引起高度重视。
-
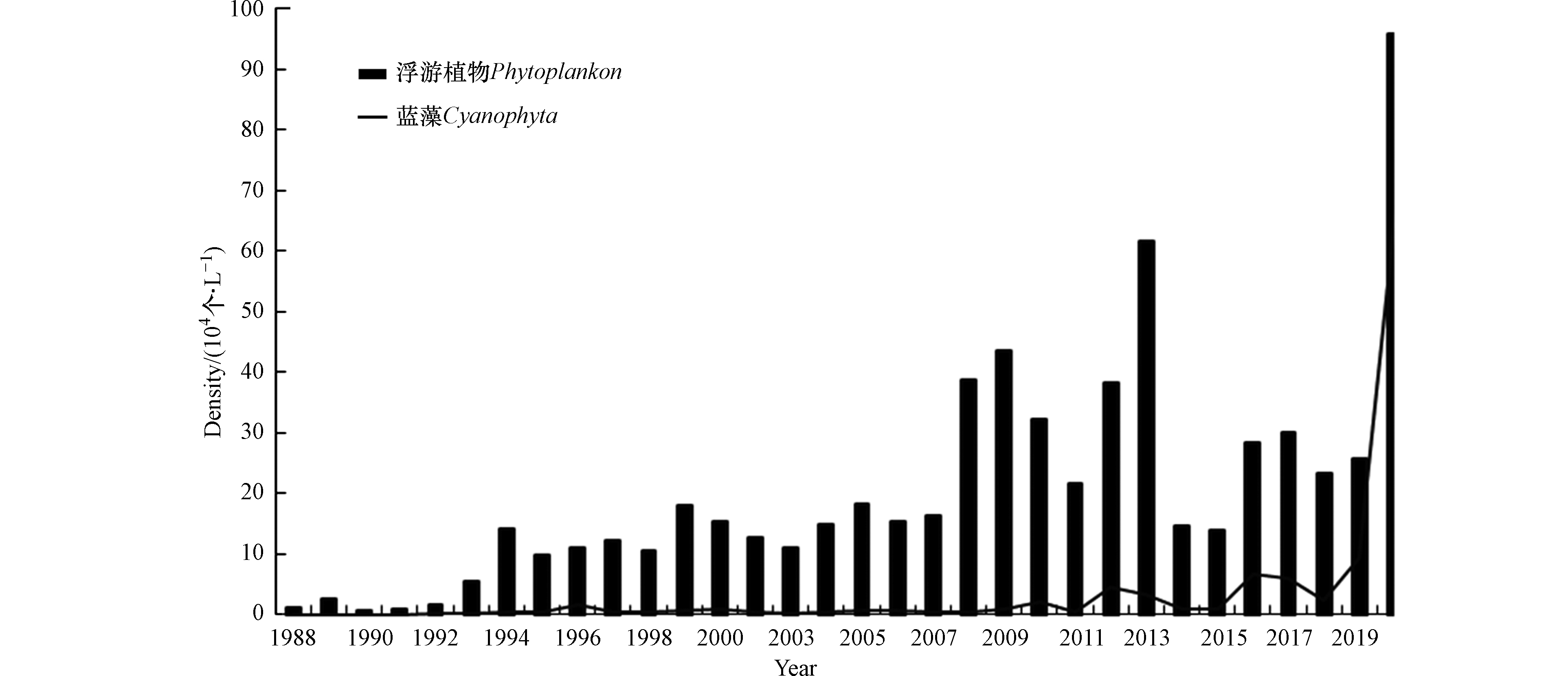
除了ΣTLI可以表征湖体富营养状态外,浮游植物也可以作为湖泊富营养化的指示性生物[28]。自1988年以来,洞庭湖共记录浮游植物8门118属,其中蓝藻门17属、绿藻门48属、硅藻门28属、裸藻门8属、甲藻门4属、隐藻门5属、金藻门5属、黄藻门3属。绿藻门、硅藻门和蓝藻门是洞庭湖的主要物种,分别占洞庭湖总物种属的40.7%、23.7%和14.4%。如图3所示,1988—2020年洞庭湖浮游植物密度呈波动上升趋势。
1993年之前,各年平均密度均小于10.0×104 个·L−1;1994—2007年,各年平均密度均小于20.0×104 个·L−1;2008年后洞庭湖浮游植物密度迅速上升,2020年达最大密度为95.7×104 个 ·L−1,远高于20世纪90年代初的水平,主要与东洞庭湖自然保护区大小西湖及附近区域出现水华有关[27,29]。近30年来,洞庭湖浮游植物优势种群由隐藻(贫-中营养代表种)和硅藻(中-富营养型代表种)[30]转变为硅藻和绿藻。值得注意的是,近30年来,洞庭湖的蓝藻门(富营养型代表种)[30]密度有显著上升趋势,由1988年的200个·L−1上升到2020年的6.75×105 个·L−1,且2008年后上升明显,这表明洞庭湖呈现出由中营养过渡到轻度富营养的趋势[29]。
-
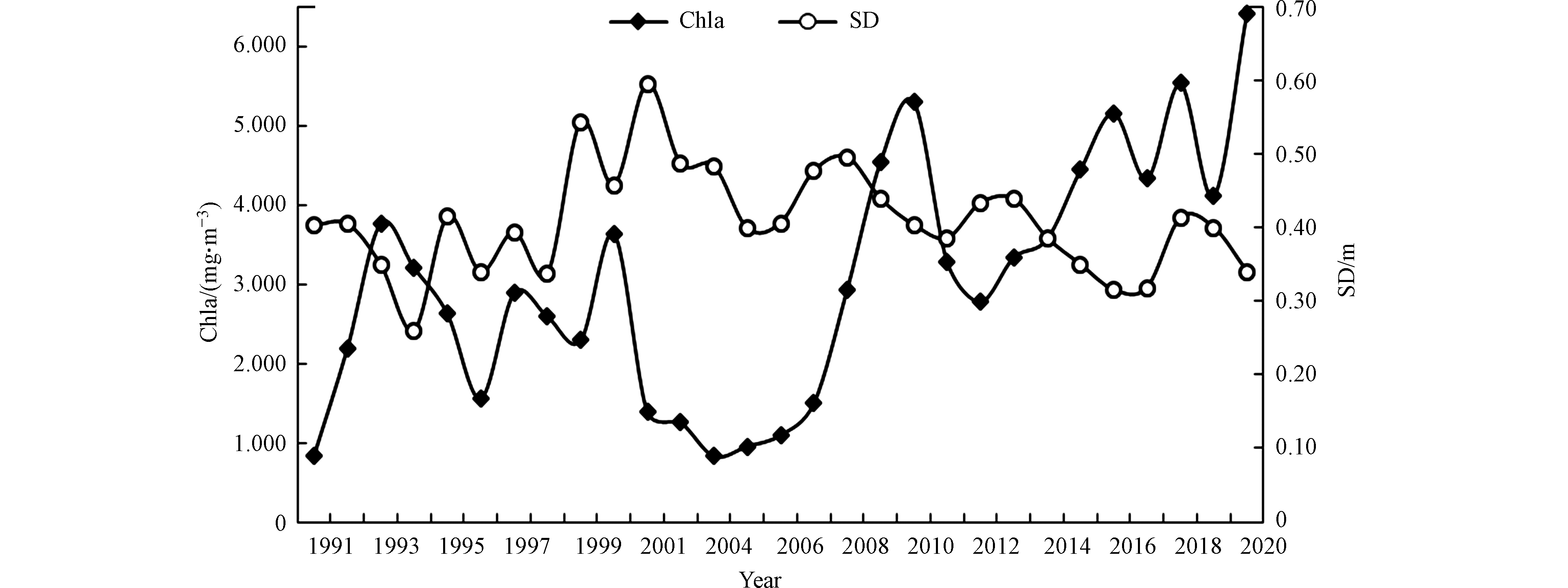
湖泊营养状态评价指标为TN、TP、CODMn、Chla和透明度5项指标。洞庭湖表层水中CODMn、TN和TP浓度的年变化趋势见图4,Chla和透明度的年变化趋势见图5。
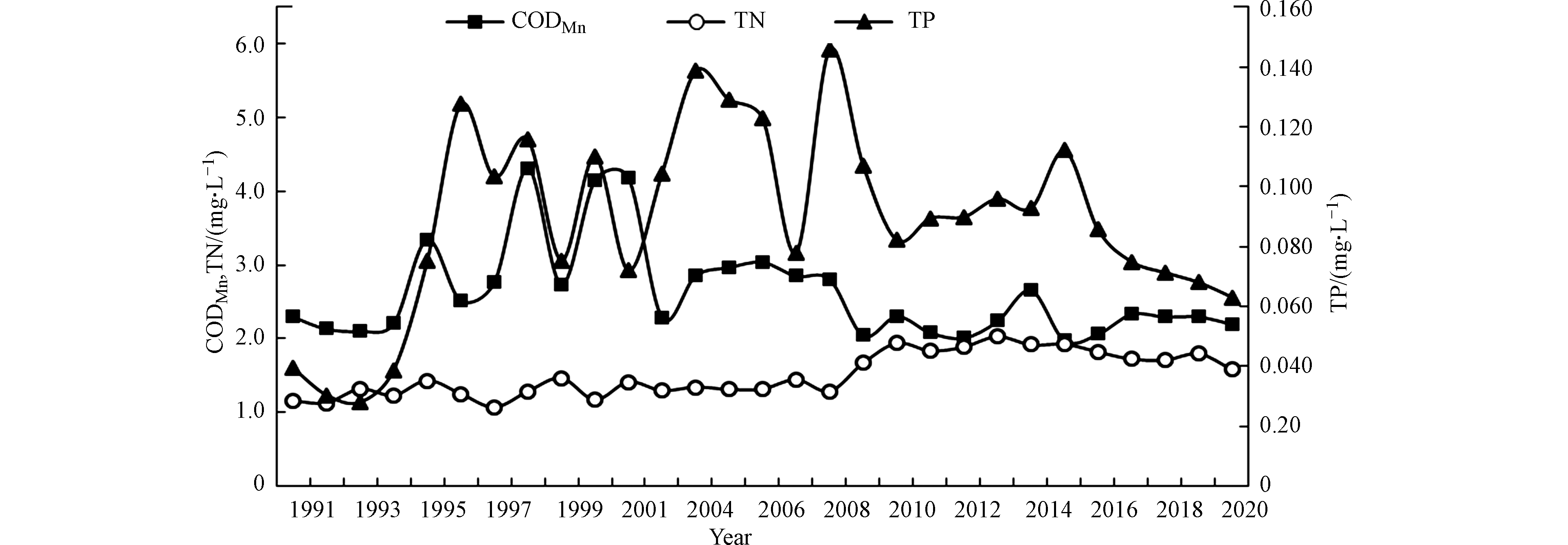
由图4可知,洞庭湖表层水中TN、TP浓度总体呈上升趋势,20世纪90年代中期后湖体TN、TP浓度超标,成为洞庭湖水质恶化和水体营养化程度加剧的重要因子。1991—2020年,TN年均浓度变化范围在1.06—2.04 mg·L−1之间,均高于地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838—2002)Ⅲ类标准限值(1.0 mg·L−1)。1991—2008年TN浓度一直在1.30 mg·L−1上下波动,无明显变化趋势;2009— 2020年TN浓度较前期明显上升,均超过1.60 mg·L−1,2013年达到峰值(2.04 mg·L−1),近7年有下降趋势。
1991—2020年,TP浓度波动较大,TP年均浓度变化范围在0.03—0.15 mg·L−1之间。1991—1994年,洞庭湖TP浓度较低,均低于地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838—2002)Ⅲ类标准限值(0.05 mg·L−1),1995年后TP浓度均高于Ⅲ类标准限值,有些年份甚至高于Ⅳ类标准限值(0.1 mg·L−1)。1995—2009年TP浓度波动较大,2010—2020年,TP浓度变化趋于平缓,近5年有下降趋势。
1991—2020年,洞庭湖CODMn浓度呈现先上升后下降的趋势。CODMn年均浓度变化范围在1.98—4.31 mg·L−1之间,CODMn浓度仅在1998、2000和2001年超过4 mg·L−1,其他年份都低于地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838—2002)Ⅱ类标准限值(4 mg·L−1)。
-
叶绿素a是所有浮游植物门类都含有的叶绿素类型,不仅是水体营养状态划分的重要指标,还可表征浮游植物的现存量。由图5可知,洞庭湖表层水中Chla浓度的年变化可分为3个阶段:第一个阶段为1991—2000年,此阶段叶绿素a浓度波动较大,平均浓度为2.56 mg·m−3;第二个阶段为2001—2007年,此阶段叶绿素a浓度较低且波动不大,叶绿素a浓度均不超过1.5 mg·m−3,平均浓度仅为1.17 mg·m−3;第三个阶段为2008—2020年,此阶段叶绿素a浓度显著高于前两个阶段,平均浓度为4.11 mg·m−3,2010年、2016年、2018年和2020年叶绿素a浓度甚至超过5 mg·m−3。历年来洞庭湖透明度一直较低,2001年峰值仅为0.60 m,呈现先上升后下降的趋势。
-
为分析各水质因子之间的相关性,并摸清洞庭湖水体富营养化的主导因子,运用主成分分析法[26,31-32]对监测结果进行统计分析(表1)。首先将环境质量监测数据进行标准化处理,后根据主成分选取标准(特征值γ大于1,特征值累积贡献率大于85%),提取F1、F2、F3三个主成分进行评价。从表中信息可知,第一主成分F1反应的信息量最大,贡献率为54.00%,与其关联的主要因子是CODCr、CODMn、NH3-N、Chla、TP,因子载荷量均超过0.85;第二主成分F2的贡献率为20.79%,关联较大的因子是TN和水温,因子载荷量分别为0.942和0.835;第三主成分F3的贡献率为12.75%,关联较大的因子是SD,因子载荷量为0.833;这也进一步证实了洞庭湖水体富营养化的主导因子是水体中的Chla、TP和TN含量。
从洞庭湖ΣTLI和藻密度与水体各环境因子之间的相关性分析结果(表2)可见,藻密度仅与Chla浓度呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与其他环境因子相关性不显著。ΣTLI与TN和Chla浓度两个指标均极显著正相关(P<0.01),其中与Chla浓度的相关系数最高(0.574),与CODMn和SD的相关性不显著。因此,洞庭湖ΣTLI的年变化趋势与Chla浓度的年变化趋势相似。Chla浓度与ΣTLI、藻密度、TN呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);与透明度、pH、CODMn、NH3-N呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。李利强等[33]的藻类增长生物学实验结果也证实了氮对洞庭湖浮游植物生长有明显的促进作用,而磷对浮游植物的生长影响不大,有时出现抑制作用。Chla浓度的高低不仅受营养盐的影响[34],还与洞庭湖特殊的水文和水动力条件有关[35]。钟成华[36]研究表明,利于藻类生长的水体流速为0.05—0.10 m·s−1,较大的流速导致的低透明度及低透光率限制了藻类的生长。三峡工程运行后,洞庭湖来水来沙相对较少,换水周期相对延长,平均水位下降[37],这些变化都利于藻类的生长,这可能也是2010—2020年叶绿素a呈上升态势的原因。SD是描述湖泊光学的一个重要参数,而光照直接影响到浮游植物的生长和繁殖,其与NH3-N和TP呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。
-
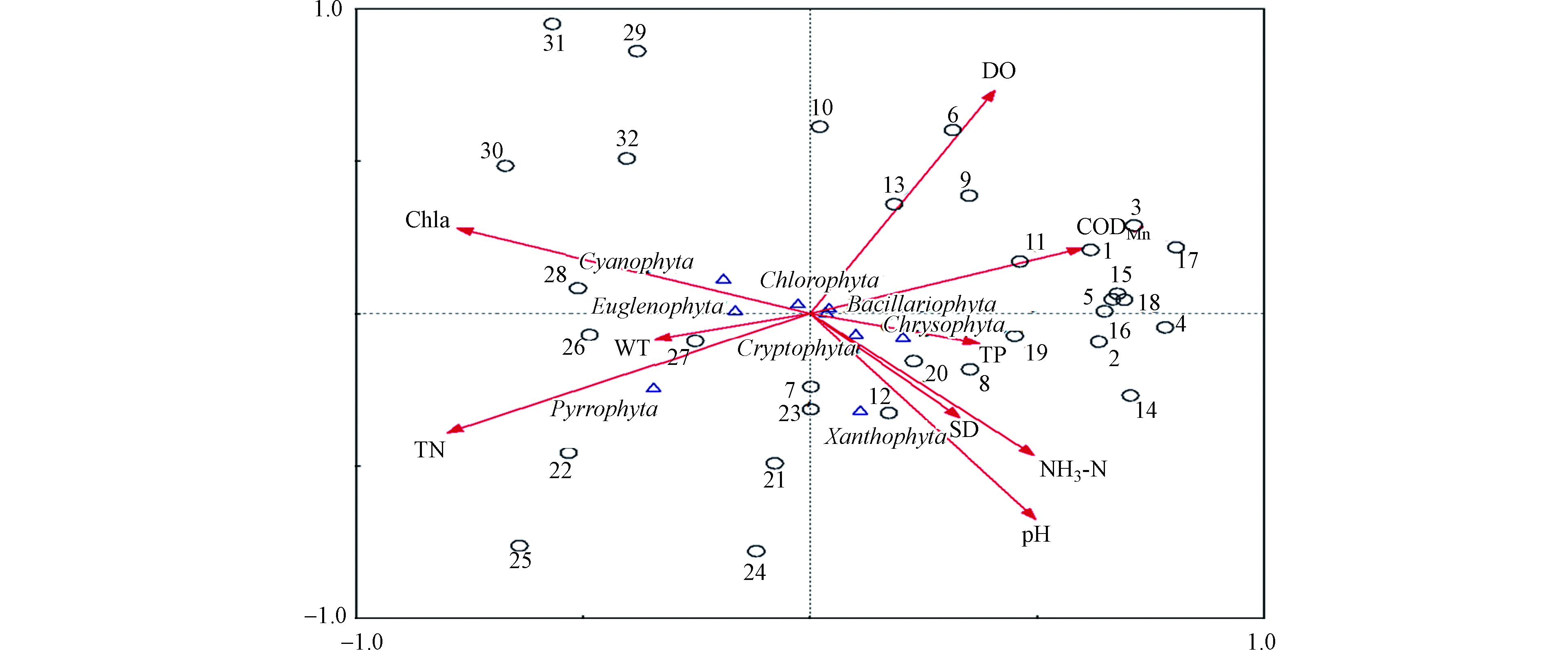
DCA分析结果中的4个排序轴的梯度长度最大值为1.17,因此采用RDA分析。RDA分析方法通过大量的分析数据进行直接梯度排序,从而反映洞庭湖浮游植物对环境因子的响应[38]。图6反映了浮游植物组成与9种环境因子间的关系。水质因子第一、二轴间的相关系数为0,表明分析结果可信[39]。前两个轴共解释了70.3%的物种数据的方差,95.5%的物种与环境关系的方差累计百分比。浮游植物种群密度与环境因子的RDA分析结果较好地反映了浮游植物与环境特征的相关性。
蓝藻(Cyanophyta)、绿藻(Chlorophyta)、硅藻(Bacillariophyta)与Chla和TN呈现显著正相关,蓝藻与pH显著负相关,绿藻、硅藻则与DO显著负相关。甲藻(Pyrrophyta)、隐藻(Cryptophyta)与TN显著正相关,而与DO显著负相关。蓝藻、绿藻和硅藻是洞庭湖绝大多数断面的优势种群,近些年来这些藻类的密度明显上升,因此洞庭湖chla含量也显著升高。总体来说,TN、Chla、pH和DO是影响洞庭湖浮游植物群落分布格局的主要因素。
-
一般地,湖泊水体出现富营养化的条件TN浓度大于0.20 mg·L−1、TP浓度大于0.02 mg·L−1 [35]。洞庭湖这两项指标浓度均已超出富营养化的阈值,但洞庭湖并未出现明显的富营养化及水华暴发现象,主要得益于洞庭湖属于过水性湖泊,水流较快,水体更新、交换频繁[40]。洞庭湖独特的水文和水动力条件(比如水位、水流流速)等都可能影响富营养发展进程。廖平安等[41-42]研究了水体流速与水华之间的关系,得出较快的流速可抑制藻类的生长,降低水华发生风险。故可以推断,洞庭湖没有发生大面积水华主要原因是洞庭湖水流速度较快,抑制了藻类的生长。而东洞庭湖的大小西湖水流流速较小,基本不受三口和四水洪水的动力影响,故水华发生几率很大。同样水位是调节自然湖泊生态系统结构和功能的重要参数,水位上升也可降低富营养化程度。杜冰雪等人[13]研究了鄱阳湖富营养与水位的关系,得出在年内季节变化上富营养化程度与水位呈负相关。至于洞庭湖水体富营养与水位的关系,有待下一步继续研究。
-
(1)2020年洞庭湖全湖ΣTLI为49.60,属中营养。1991—2020年,洞庭湖全湖ΣTLI在41.09 —51.68之间,总体呈上升趋势,表现为东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>南洞庭湖。“十三五”期间,大小断面平均ΣTLI高于59,将接近中度富营养水平,应引起高度重视。
(2)自1988年以来,洞庭湖共记录浮游植物8门118属,绿藻门、硅藻门和蓝藻门是洞庭湖的主要物种。值得注意的是,洞庭湖的蓝藻门(富营养型代表种)密度由1988年的200个·L−1上升到2020年的6.75×105 个·L−1,且2008年后上升明显,洞庭湖呈现出由中营养过渡到轻度富营养的趋势。
(3)洞庭湖水体富营养化的主导因子是水体中的Chla、TP和TN含量,其他环境因子也有一定影响。影响洞庭湖浮游植物群落分布格局的主要因素是TN、Chla、pH和DO。水位和水流流速也是影响洞庭湖富营养的重要因素。
洞庭湖的富营养演变特征及影响因素
The evolution and influencing factors of eutrophication in Dongting Lake
-
摘要: 基于近30年洞庭湖水环境质量调查数据,从综合营养状态指数和浮游植物密度两方面探讨了洞庭湖富营养演变特征,运用主成分分析法筛选主导因子,并进行了环境因子与浮游植物的冗余分析(RDA)。结果表明,2020年洞庭湖全湖综合营养状态指数为49.60,属中营养,近30年,洞庭湖全湖综合营养状态指数在41.09—51.68之间,总体呈上升趋势,表现为东洞庭湖>西洞庭湖>南洞庭湖。自1988年以来,洞庭湖共记录浮游植物8门118属,绿藻门、硅藻门和蓝藻门是洞庭湖的主要物种,洞庭湖呈现出由中营养过渡到轻度富营养的趋势,且蓝藻门上升速度最快。洞庭湖水体富营养化的主导因子是水体中的Chla、TP和TN含量,水位和水流流速也是影响洞庭湖富营养的重要因素。影响洞庭湖浮游植物群落分布格局的主要因素是TN、Chla、pH和DO。Abstract: Based on the investigation of water environmental quality in Dongting Lake in recent 30 years, the characteristics of eutrophication evolution in Dongting Lake were studied from the perspectives of comprehensive nutritional state index and phytoplankton density. The dominant factors were chosen by principal component analysis. The redundancy analyses (RDA) between the environmental factors and the phytoplankton were carried out. The results showed that the comprehensive nutritional state index of Dongting Lake was 49.60 in 2020, which belonged to middle nutrition. In the past 30 years, the comprehensive nutritional state index of Dongting Lake has remained from 41.09 to 51.68, which showed an upward trend, namely East Dongting Lake > West Dongting Lake > South Dongting Lake. Since 1988, a total of 8 phyla and 118 genera of phytoplankton species have been recorded in Dongting Lake. Chlorophyta, diatom and Cyanophyta were the main species in Dongting Lake, and Cyanophyta was growing the fastest. The trend in Dongting Lake was from moderate nutrition to mild nutrition. The dominant factors affecting the eutrophication in Dongting Lake were chlorophyll a (Chla), total phosphorous (TP) and total nitrogen (TN). The water level and flow velocity were also important factors. TN, Chla, pH and Dissolved Oxygen (DO) were the main factors affecting the distribution pattern of phytoplankton community in Dongting Lake.
-
随着工农业生产的迅速发展,汞在生产和使用的过程中被大量排放到环境中,并随着大气沉降、污水灌溉等途径进入到土壤[1]。对于农用地,土壤中汞含量升高主要原因是含汞污水灌溉,含汞农药的使用,随着灌溉水或降水渗入土壤;对于工业用地,主要是企业在生产过程中排放含汞废水、含汞固体废物等对土壤造成了污染。另外,场地所在区域土壤汞背景含量高或其他企业的高点源排放造成的含汞大气沉降也可能对土壤造成影响[2]。
土壤中的汞,尤其是对于有机汞来说,具有很强的生物富集性,一旦通过土壤或食物链途径进入到生物体,会对人类健康和整个生态环境造成极大危害[3]。随着工业化发展浪潮的到来,汞在土壤系统中的排放量呈现显著增加的趋势,已经威胁到了土壤环境的安全[4]。近年来,人们对于汞污染土壤的修复技术进行了很多探索,具有代表性的包括热解析法、固化法、淋洗法、电动力修复法和植物修复方法等,其中应用较多的为热处理法和电动修复法。本文在对工业场地土壤中汞的主要来源、汞在土壤中的主要赋存形态和土壤中汞的危害进行分析的基础上,对目前国内外应用较为广泛的汞污染土壤处理技术进行了概述,并对不同处理技术的适用环境和条件进行了分析,希望能为后续研究提供一定的参考和借鉴。
1. 土壤中汞的来源
1.1 土壤背景
汞是地壳中自然形成的一种元素,在岩石中主要以硫化物的形式存在,岩石经过漫长的自然风化或地壳活动,所形成的土壤母质中,有一部分汞残留下来,而残留下来的汞就成为天然背景下土壤中汞的主要来源,称之为汞的自然排放。XU et al[5]对全球不同类型土壤中的汞背景含量进行了研究,结果表明,不同类型的土壤中汞含量有所差异,总体介于0.58~1.8 mg/kg之间,其中有机质含量高的土壤中,汞的背景含量相对较高。需要指出的是,由于自然条件所形成的土壤母质多种多样,且形成的周期很长,不同时期也要受到自然环境的影响,因此难以通过土壤母质类型判断汞的释放量。王杰等[6-12]对不同湿地土壤中汞和甲基汞的含量进行了研究,结果表明,自然条件下,不同国家和地区湿地土壤中汞的含量从0.01~66.0 mg/kg不等,存在着较大的差异,见表1。
表 1 不同湿地土壤中总汞和甲基汞的含量1.2 工业生产
汞在自然界的矿物中分布极为广泛,几乎每一种矿物中都含汞,随着近代以来人们对矿山的大规模开发,使得大量赋存于矿物中的汞被排放到环境中,造成大面积农田和其他用地土壤汞超标,例如贵州部分地区的矿山开发,已经导致矿区土壤和周边耕地土壤的汞污染[13]。
除大规模的矿山开采以外,金属冶炼过程中也必然会产生大量的含汞废水和废渣。由于早期工业生产过程中对于环保的管理并不规范,因此,大量废水和废渣的随意排放也给企业周边的土壤造成了严重污染,导致土壤环境不断恶化。例如贵州万山特区作为我国主要的汞冶炼地区,已经对当地土壤造成了严重的汞污染问题,并且已经威胁到了水环境和农产品的安全[14]。根据2011年的一项调查,在万山区布设的26个耕地土壤调查点位中,超标率达到96%(对应当时国家有效标准《土壤环境质量标准(GB 15618—1995)》[15]中的二级标准0.5 mg/kg),超标十分严重。
另外,城市化进程的不断加快,也产生了越来越多的含汞固体废弃物,例如温度计、荧光灯泡,电石法生产聚氯乙烯过程中的汞触媒生产、废汞触媒堆放等,这些含汞废物大多都进入到垃圾填埋场进行填埋,从而也会导致填埋场周围的土壤受到影响。CHENG et al[16]就对我国部分城市进入垃圾填埋场的废弃物中汞浓度进行了研究,结果表明,废弃物中汞的浓度在0.17~46.2 mg/kg之间。其中,东部和东南沿海城市中废弃物和土壤中汞的含量明显高于北部和西北部城市,这也进一步说明工业生产活动对土壤中汞的含量有明显的影响。
1.3 大气沉降
大气沉降作用包括干沉降和湿沉降,干沉降是大气粒子在没有降水过程时的自身沉降作用,湿沉降是大气粒子由于降水冲刷而产生沉降的过程。工业革命以来,人类活动不断加剧,已经导致大气中的汞含量急剧增加[17],由于人类活动向空气中排放的汞每年达到1 960 t,通过干湿沉降作用,赋存于大气中的汞大多都会进入到土壤中,并在土壤中不断富集,造成土壤中汞含量超标。LYNAM et al[18]的研究表明,大气中汞的湿沉降作用更加明显,是汞从大气进入土壤中的主要形式,他们的研究发现大气汞湿沉降量是干沉降量的3.4倍。沉降的主要来源为燃煤发电、企业燃煤锅炉的使用,电石法生产聚氯乙烯过程中的含汞蒸汽等,不同地区的工业生产方式不同,导致大气汞的干湿沉降量也存在一定差异见表2。
表 2 不同地区大气汞的干湿沉降量μg·(m2·a)−1 地区 研究时段 干沉降 湿沉降 多伦多 2003~2008 7.66~26.06 18.60 伊利诺伊 2011 0.70~1.60 3.10~5.40 日本 2002~2003 5.30~10.70 8.90~16.70 重庆 2010~2011 / 23.60~33.80 台湾 2009~2012 / 10.18 注:“/”表示未进行相关研究。 由于湿沉降作用主要是在降雨过程中发生,因此大气中汞的沉降在夏季多雨时期会表现的更加明显,而且由于夏季温度较高,空气中的汞也更容易被氧化,更易进入土壤,这一点在SHEU et al[19]的研究中也得到了验证。朱佳雷等[20]也对中国地区大气汞沉降的速度进行了研究,结果表明,气候和季节差异也会导致大气汞沉降存在明显变化。
2. 土壤中汞的赋存形态和毒性
2.1 赋存形态
环境中汞存在的物理形态或化学形态不同,其对环境的毒性和生物有效性也随之不同,对于不同土壤修复技术的适用性也不同,因此,在选择汞污染土壤的修复技术时,首先需要了解汞在土壤中的赋存形态。不同修复技术对于不同形态汞的作用机理不同,其目标都是通过将土壤中汞的形态进行转化,使得留在土壤中的汞毒性大大降低,从而达到土壤安全利用的目的。
土壤环境中的汞主要是根据其物理和化学性质进行分类,包括金属汞、无机汞和有机汞[21-22],按照其化学形式来分,汞在自然环境存在形式主要以Hg0、Hg22+、Hg2+和有机汞等4种形式存在。土壤环境中汞的存在形态主要受两方面的影响,一是土壤性质的影响,如土壤pH值、Eh值、有机质和有机配体等指标,另外一方面是受环境微生物的影响[23]。
2.2 各形态间的转化
土壤中原始存在的汞,如果遇到一定的环境条件,或者在微生物的作用下,可能会发生各个不同形态之间的转化作用,总体的转化趋势为不同形态的汞会向惰性形态的汞转化[24],其转化规律包括:
1)汞在具有还原性环境的土壤中,一般是以单质的形式存在;
2)二价汞如果遇到了土壤中含有硫化氢的还原环境时,通常会生成极难溶的硫化汞,并且以硫化汞残渣的形式长期存在于土壤当中;
3)如果土壤中含氧量较高,此时硫化汞便可在氧化环境中形成硫酸亚汞和硫酸汞;
4)表层土壤当中的汞大多数情况下都会以一价的形态存在,比如说氢氧化汞、氯化汞等[25],如果土壤中的氯离子含量比较高,汞大多会以二价汞(尤其是HgCl42−)的形态存在;
5)大气中的汞通过各种途径进入到土壤后,首先会与土壤环境中的化学物质或微生物进行反应,一段时间后达到较为稳定的状态并逐渐老化。根据相关研究测定[26],约有25%的汞仍然会以原来的单质形式继续存留在土壤中,只有0.11%的汞会通过化学转化的形式变为有效态汞,有17%的汞会转化为无机态汞,4%会转化为有机态汞,其余54%的汞转化为残留态汞。
2.3 土壤中汞的毒性
2.3.1 汞的毒性机制
如果土壤中赋存的是单纯的金属汞,一般是不具有毒性作用的,土壤中的汞之所以会表现出一定的毒性作用,主要的原因有两点:第一,土壤中的汞具有一定的挥发性,当金属汞挥发到空气中以后,就会具有较强的扩散性,而且金属汞还具有很好的脂溶性特征,当挥发到空气中的汞随着生物体的呼吸作用进入到肺泡当中,就会随着血液循环作用很快扩散到全身,金属汞在生物体内会与血液结合,并会将零价的金属汞氧化,从而生成一价汞或二价汞,生成的一价汞和二价汞就会和细胞膜或者酶蛋白发生一定的反应,并形成不易分离的物质,比如硫化汞等,这些物质会破坏细胞的结构,严重情况下还会使得细胞发生变性或死亡。第二,土壤中的汞在一系列化学或微生物条件下转化为一价汞或二价汞,并随着食物链或生物体直接接触进入到体内,从而引发一系列生物反应,对生物体的健康造成危害。
2.3.2 汞的毒性表现
土壤中的汞对于植物体和动物体都具有一定的毒性,对于植物体来说,如果体内累积的汞含量达到或超过一定程度,汞元素会和植物酶活性中心的氢硫基结合,从而抑制酶的活性,此时对于植物生长细胞来说,其整个生理生化过程就会受到严重干扰,从而使得新陈代谢发生紊乱,并导致植物体的生长发育受到抑制,严重时可导致其枯萎、死亡。对于动物或人类来说,土壤中的汞主要是通过食物链或直接接触发生作用,其毒性表现主要为急性腹湾、血尿,同时还会引发慢性口腔发炎、精神失常等。
3. 工业场地汞污染土壤修复技术
工业场地汞污染土壤修复技术主要包括3类:物理修复技术、化学修复技术和生物修复技术。其中物理修复技术包括客土法、热处理法和阻隔修复等,化学修复技术包括固化稳定化技术、淋洗技术和电动修复技术等,生物修复技术主要包括微生物修复技术和植物修复技术。
3.1 物理修复技术
对于工业场地中的重金属污染土壤,实际上其总量削减的难度大且成本较高,在浸出含量能够达标,且汞总量浓度不高的情况下,采用物理稀释技术,不仅可以有效的控制土壤污染风险,同时也可以节省大量修复成本。
3.1.1 客土法
客土法指的是将一部分无污染土壤与工业场地上的汞污染土壤进行物理混合,从而减少土壤中汞含量的方法[27],在汞污染不是特别严重的场地上,采用客土法有以下几个优点:①客土法施工简单,无需在土壤中加入药剂,是一种天然的处理方法,不会产生二次污染问题;②客土法的成本主要在于客土购买,机械施工等环节,相对于其他修复技术成本更低;③在客土方量和污染土壤方量得到很好控制的情况下,该方法能够取得很好的修复效果。但在应用的过程中也要注意,对于高浓度的汞污染土壤,该方法并不适用,因为高浓度汞污染土壤需要的客土量较大,混合之后的土壤汞总量浓度难以得到有效降低,且增加的大量土方去向问题也难以解决,此时可以采用换土法或去土法代替。
3.1.2 热处理技术
重金属汞具有一定的挥发性,对于土壤中的汞可以采用热处理技术使其挥发为气相,从而与土壤分离,目前普遍采用的是热解析或热脱附方法,其本质都是通过高温手段将汞及其化合物从土壤中分离。在温度<200 ℃时,土壤中元素汞和甲基汞基本都能从土壤中脱离,当温度继续升高,其他形态的汞也能够分离[28]。但是在高温环境下,土壤中的易分解物质和土壤结构也会造成不可逆的破坏,营养成分会大量流失,因此这种处理技术只适合在工业场地中使用,不适合在农用地中使用。从成本上来看,这种修复技术在应用的过程中需要消耗大量的能量,相对来说投资会比较大,设施运行成本高。
为了解决这些问题,MA et al[29]开始探索一些新型热处理技术,例如可以在土壤中加入一定量的酸性物质,然后再对土壤进行加热,酸性环境不仅能有利于汞的挥发,还可以使土壤保持原有的生化特性,同时还可以节省约35%的能量。热处理技术适用于汞污染较为严重的场地,其一次性降低土壤中汞含量的效果好,修复周期短。
3.1.3 阻隔修复技术
阻隔修复技术是通过使用各种防渗材料,将汞污染土壤区域与未污染区域隔离开,从而有效减少或阻止污染区域的汞向未污染区域扩散的技术[30],实际上该方法并没有削减污染土壤中的汞总量浓度,是一种风险管控技术,只适合在中轻度汞污染,且暂时没有开发计划的场地中使用。从成本方面来看,如果需要阻隔的面积较大,涉及的工程量也越大,投资费用较高,且容易造成土体结构的破坏。
3.2 化学修复技术
3.2.1 土壤淋洗技术
淋洗技术就是我们通常所说的洗土法,它的原理就是通过在汞污染土壤中添加化学药剂,使其与土壤中的汞离子反应,从而将汞离子转移到淋洗液中,不仅可以去除土壤中的汞,还可以定向回收汞离子。对于土壤中汞浓度较低的情况,也可以采用清水灌溉稀释和去除汞离子,但这样的效果通常不明显。目前常用的淋洗剂包括碘化物、EDTA和硫代硫酸钠等,近年来人们也在不断研究一些新型的淋洗剂,但大都是处于实验阶段,例如林凯[31]在对几种不同的淋洗剂进行测试时发现,对于汞污染严重的土壤,氢氧化钠、乳化剂等物质对汞离子的去除能力较好,同时影响去除效率的因素还包括淋洗剂的浓度、反应时间和酸碱度等。
土壤淋洗技术的优点在于能够去除土壤中的汞,对污染土壤修复较为彻底,且修复周期较短,成本较低。缺点是淋滤液需要进行一定的后续处理之后才能够安全排放,淋滤过程也可能破坏土壤结构,使土壤中的营养成分流失。
3.2.2 电动力修复技术
进行电动修复时,需要将电极放置在汞污染土壤中,然后通低压直流电,使土壤中的电极形成电场梯度,此时汞离子会随着电极的驱动作用而迁移至电极室中,对其进行收集后统一处理。在进行电动力修复过程中,影响修复效果的因素也有很多,包括酸碱环境、络合剂的选择等,目前常用的络合剂包括乙二胺四乙酸二钠、碘化钾和氯化钠等,络合剂的浓度不同,修复效果也有较大差异[32]。
电动力修复的主要特点在于可实施原位修复,修复过程中保持土壤肥力,无二次污染,成本较低,能够实现金属汞与土壤的完全分离,并对金属汞进行再回收利用,适合于浓度较高的汞污染土壤。缺点在于修复的耗时较长,且修复效果受到多个因素的控制,主要适合低渗透性的粘性土壤修复。
3.2.3 固化稳定化技术
固化稳定化是采用不同材料将重金属汞钝化在土壤中,并且长时间的保持在土体中,防止由于浸出而产生对周围土壤和地表及地下水体的影响。钝化材料可分为无机材料、有机材料和氧化还原材料,达到了一定的修复效果。近几年也有很多学者进行了相关方面的研究工作,如袁俊 [33]对不同形态的硫吸收汞与甲基汞的影响进行了研究;谢园艳等[34]以汞矿区污染农田为试验田,研究了添加膨润土、磷酸氢二铵、膨润土+磷酸氢二铵混施3种方式对土壤中汞的形态分布的影响。总之,稳定化技术针对不同的污染物选择不同的材料尤为重要。不足之处是需要长时间的观察,并且材料使用量较大。
3.3 生物修复技术
3.3.1 植物修复技术
植物修复技术起源于“超级累积植物”的概念,这种技术主要是利用植物对土壤中的微量元素的吸收和富集作用。通过天然的或人工选育的一些植物对土壤中的汞进行固定、挥发和提取[35],在这方面国内外已经开展了很多研究工作,并在很多项目中有了成功应用的案例。20世纪80年代,CHANEY et al[36]首先提出,可以利用植物及其根系的微生物环境,对某些土壤重金属进行选择性地消除回收,后来人们通过大量的研究找到了几种可以富集重金属汞的植物,例如苎麻和小叶黄杨等。影响植物修复效果的因素包括土壤中汞的含量、酸碱度和土壤有机质等,为了能够提高植物对土壤中汞的吸收,也可以加入一定量的活化剂帮助植物根系对汞的吸收,这也是植物修复技术一个新的研究方向,WANG et al[37]发现(NH4)2S2O3可以协助植物对土壤中汞的吸收。
植物修复的主要特点在于不会破坏土壤性质,成本低廉,环境友好,在选择了合适的植物种类后,可取得较好的修复效果,主要缺点在于这种修复方法的修复周期很长,通常种植量较大,容易受到汞浓度、植物年龄等因素的影响。
3.3.2 微生物修复技术
微生物修复的原理是通过微生物的新陈代谢,对土壤中汞的亲和吸附能力进行削弱,并将其逐渐降解成低毒化合物。近年来的很多研究发现,汞在特定微生物的作用下可以实现烷基化和还原挥发,而且人们也发现了某些耐汞微生物,使得微生物法修复汞污染土壤成为可能。例如SINHA et al[38]的研究发现,利用藻酸钠和藻酸钙对肠杆菌属细胞进行处理之后,可以有效去除污水中的汞。研究表明,微生物在土壤中也具有一定的去毒作用,日本科学家通过将富汞细菌收集之后,再利用吸附和蒸发技术将土壤中的汞去除,李梅等[39]也对土壤中的汞对微生物的毒害效应进行了研究,以探索微生物修复汞污染土壤的可能性。
目前,微生物技术在汞污染土壤的修复中应用的案例还较少,但其应用前景较为广阔,其优点在于通过微生物作用可有效降低土壤毒性,且能够与植物修复等有效结合,修复成本较低。缺点在于土壤中的汞并不能完全去除,微生物对于土壤环境的变化比较敏感,相关的理论基础研究还比较薄弱。
4. 结语
土壤中汞的来源复杂,赋存形式多样,已经成为全球性的污染问题,关系到土壤环境安全和人类身体健康,汞污染土壤治理刻不容缓。目前人们已经探索出很多不同的汞污染土壤修复技术,不同的技术有着各自的优缺点,适用的土壤类型、环境不尽相同。物理稀释方法的施工工艺相对简单,但不能有效去除土壤中的汞,且需要修复后的长期监管措施。热处理技术可以有效去除污染物,但耗费资金较大,难以大面积使用,一般只适用于汞含量较高的土壤。生物修复技术成本低但周期长,对于面积较大且场地不急于开发的情况下较为适用。
未来对于汞污染土壤的修复应着重开发新材料和新技术,例如通过纳米Fe做催化剂能够显著的提高电动力修复的效率,通过基因工程技术的发展可以提高生物修复的效率,通过性质温和的淋洗剂开发可提升土壤淋洗的效果等。
-
表 1 因子载荷量
Table 1. Component matrix
F1 F2 F3 水温 0.336 0.835 0.345 pH 0.401 0.328 0.284 DO 0.695 -0.393 0.509 CODMn 0.987 -0.094 0.020 CODCr 0.991 -0.086 0.018 BOD5 0.828 -0.492 -0.235 NH3-N 0.935 0.297 -0.117 TP 0.861 0.209 0.380 TN -0.196 0.942 0.019 Chla 0.898 -0.056 -0.185 SD -0.279 0.216 -0.833 特征值 5.940 2.287 1.402 方差百分百/% 54.003 20.790 12.749 累积方差百分比 /% 54.003 74.794 87.543 表 2 洞庭湖各环境因子的相关分析
Table 2. Pearson Correlation coefficients of environmental factors in Dongting Lake
水温Temperature pH DO CODMn NH3−N TN TP Chla SD ΣTLI pH −0.023 DO −0.246 0.042 CODMn −0.300 0.166 0.319 NH3−N −0.227 0.407* −0.228 0.141 TN 0.029 −0.245 −0.568** −0.517** 0.044 TP −0.19 0.264 −0.032 0.351* 0.578** 0.01 Chla 0.068 −0.435* −0.173 −0.400* −0.449* 0.474** −0.276 SD −0.393* 0.331 0.164 0.3 0.559** −0.05 0.555** −0.350* ΣTLI −0.054 −0.324 −0.330 0.025 −0.107 0.510** 0.263 0.574** −0.066 藻密度 0.002 −0.149 0.107 −0.173 −0.347 0.158 −0.153 0.513** −0.256 0.195 注:**为极显著相关,P<0.01. *为显著相关,P<0.05. Note:**shows a very significant correlation, P<0.01. * shows a significant correlation, . -
[1] TONG T L, LI R L, WU S J, et al. The distribution of sediment bacterial community in mangroves across China was governed by geographic location and eutrophication [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 140: 198-203. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.01.046 [2] CHEN Y W, QIN B Q, TEUBNER K, et al. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China [J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2003, 25(4): 445-453. doi: 10.1093/plankt/25.4.445 [3] PAERL H W, XU H, MCCARTHY M J, et al. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy [J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(5): 1973-1983. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.018 [4] SHI K, ZHANG Y L, ZHU G W, et al. Deteriorating water clarity in shallow waters: Evidence from long term MODIS and in situ observations [J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2018, 68: 287-297. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2017.12.015 [5] CAI Y J, JIANG J H, ZHANG L, et al. Simplification of macrozoobenthic assemblages related to anthropogenic eutrophication and cyanobacterial blooms in two large shallow subtropical lakes in China [J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 2012, 15(1): 81-91. [6] JOHN V, JAIN P, RAHATE M, et al. Assessment of deterioration in water quality from source to household storage in semi-urban settings of developing countries [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2014, 186(2): 725-734. doi: 10.1007/s10661-013-3412-z [7] QIN B Q. Lake eutrophication: Control countermeasures and recycling exploitation [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2009, 35(11): 1569-1573. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.04.003 [8] 朱广伟, 许海, 朱梦圆, 等. 三十年来长江中下游湖泊富营养化状况变迁及其影响因素 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(6): 1510-1524. doi: 10.18307/2019.0622 ZHU G W, XU H, ZHU M Y, et al. Changing characteristics and driving factors of trophic state of lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River in the past 30 years [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(6): 1510-1524(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2019.0622
[9] 刘永, 蒋青松, 梁中耀, 等. 湖泊富营养化响应与流域优化调控决策的模型研究进展 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2021, 33(1): 49-63. doi: 10.18307/2021.0103 LIU Y, JIANG Q S, LIANG Z Y, et al. Lake eutrophication responses modeling and watershed management optimization algorithm: A review [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2021, 33(1): 49-63(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2021.0103
[10] 秦伯强. 浅水湖泊湖沼学与太湖富营养化控制研究 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(5): 1229-1243. doi: 10.18307/2020.0501 QIN B Q. Shallow lake limnology and control of eutrophication in Lake Taihu [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(5): 1229-1243(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0501
[11] 于洋, 彭福利, 孙聪, 等. 典型湖泊水华特征及相关影响因素分析 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2017, 33(2): 88-94. YU Y, PENG F L, SUN C, et al. Analysis on the characteristics and impact factors of water bloom in the lake [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2017, 33(2): 88-94(in Chinese).
[12] 国家环境保护总局. 三河三湖水污染防治计划及规划[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2000. Ministry of Environmental. Protection of the People’s Republic of China[M]. Water pollution prevention plan and planning of “three rivers” and “three lakes” [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2000(in Chinese).
[13] 杜冰雪, 徐力刚, 张杰, 等. 鄱阳湖富营养化时空变化特征及其与水位的关系 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(5): 795-801. DU B X, XU L G, ZHANG J, et al. The spatial-temporal characteristics of eutrophication in Poyang Lake and its relationship with the water level [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(5): 795-801(in Chinese).
[14] 熊剑, 喻方琴, 田琪, 等. 近30年来洞庭湖水质营养状况演变特征分析 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2016, 28(6): 1217-1225. doi: 10.18307/2016.0607 XIONG J, YU F Q, TIAN Q, et al. The evolution of water quality and nutrient condition in Lake Dongting in recent 30 years [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2016, 28(6): 1217-1225(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2016.0607
[15] 黄代中, 万群, 李利强, 等. 洞庭湖近20年水质与富营养化状态变化 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(1): 27-33. HUANG D Z, WAN Q, LI L Q, et al. Changes of water quality and eutrophic state in recent 20 years of Dongting Lake [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 26(1): 27-33(in Chinese).
[16] 王婷, 王坤, 王丽婧, 等. 三峡工程运行对洞庭湖水环境及富营养化风险影响评述 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2018, 31(1): 15-24. WANG T, WANG K, WANG L J, et al. Impacts of the Three Gorges dam operation on water environment and eutrophication of Dongting Lake: A review [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(1): 15-24(in Chinese).
[17] 吴可方, 欧伏平, 王丑明. 东洞庭湖秋季氮磷营养盐结构及水华风险分析 [J]. 人民长江, 2018, 49(23): 21-26,73. WU K F, OU F P, WANG C M. Nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient structure characteristic and risk analysis of cyanobacterial bloom in East Dongting lake in autumn [J]. Yangtze River, 2018, 49(23): 21-26,73(in Chinese).
[18] 中国环境监测总站. 湖泊(水库)富营养化评价方法及分级技术规定[S]. 北京: 中国环境监测总站, 2001. China Environmental Monitoring Station. Assessment method and classification technical regulation of lake (reservoir) eutrophication[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Monitoring Station, 2001(in Chinese).
[19] 齐雨藻, 李家英. 中国淡水藻志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. QI Y Z, LI J Y. Freshwater Algal Flora of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2004(in Chinese).
[20] 李景保, 朱翔, 周国华, 等. 洞庭湖区灾害性洪水对生态灾害群发的复合效应 [J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(3): 334-340. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.03.007 LI J B, ZHU X, ZHOU G H, et al. The compound effect of disastrous floods in Dongting Lake on concurrence of ecological disasters [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(3): 334-340(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2002.03.007
[21] 申锐莉, 鲍征宇, 周旻, 等. 洞庭湖湖区水质时空演化(1983—2004年) [J]. 湖泊科学, 2007, 19(6): 677-682. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.06.009 SHEN R L, BAO Z Y, ZHOU M, et al. Temporal-spatial evolution of water quality in Lake Dongting, China [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2007, 19(6): 677-682(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2007.06.009
[22] HAVENS K E, JIN K R, RODUSKY A J, et al. Hurricane effects on a shallow lake ecosystem and its response to a controlled manipulation of water level [J]. The Scientific World Journal, 2001, 1: 44-70. [23] 秦伯强, 杨柳燕, 陈非洲, 等. 湖泊富营养化发生机制与控制技术及其应用 [J]. 科学通报, 2006, 51(16): 1857-1866. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.16.001 QIN B Q, YANG L Y, CHEN F Z, et al. Mechanism and control technology of lake eutrophication and its application [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51(16): 1857-1866(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.16.001
[24] BACHMANN R W, HOYER M V, CANFIELD D E. Internal heterotrophy following the switch from macrophytes to algae in Lake Apopka, Florida [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2000, 418(1): 217-227. doi: 10.1023/A:1003997832707 [25] 秦伯强. 长江中下游浅水湖泊富营养化发生机制与控制途径初探 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2002, 14(3): 193-202. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2002.03.001 QIN B Q. Approaches to mechanisms and control of eutrophication of shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangze River [J]. Journal of Lake Science, 2002, 14(3): 193-202(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-5427.2002.03.001
[26] 汪星, 李利强, 郑丙辉, 等. 洞庭湖浮游藻类功能群的组成特征及其影响因素研究 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(12): 3766-3776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.12.031 WANG X, LI L Q, ZHENG B H, et al. Composition and influential factors of algal function groups in Dongting Lake [J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(12): 3766-3776(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.12.031
[27] 王丽婧, 田泽斌, 李莹杰, 等. 洞庭湖近30年水环境演变态势及影响因素研究 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(5): 1140-1149. WANG L J, TIAN Z B, LI Y J, et al. Trend and driving factors of water environment change in Dongting Lake in the last 30 years [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(5): 1140-1149(in Chinese).
[28] 邹伟, 朱广伟, 蔡永久, 等. 综合营养状态指数(TLI)在夏季长江中下游湖库评价中的局限及改进意见 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32(1): 36-47. doi: 10.18307/2020.0104 ZOU W, ZHU G W, CAI Y J, et al. The limitations of comprehensive trophic level index (TLI) in the eutrophication assessment of lakes along the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during summer season and recommendation for its improvement [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2020, 32(1): 36-47(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2020.0104
[29] 王丑明, 郭晶, 张屹, 等. 1988—2017年洞庭湖浮游植物的群落演变 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2018, 34(6): 19-25. WANG C M, GUO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Phytoplankton community succession trends of the Dongting Lake from 1988 to 2017 [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2018, 34(6): 19-25(in Chinese).
[30] 国家环保局. 水生生物监测手册[M]. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 1993. Ministry of Environmental. Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Aquatic monitoring manual[M]. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 1993 (in Chinese) .
[31] 陈焰, 黄宏, 彭文启, 等. 基于探索性数据分析的汉丰湖富营养化驱动因子研究 [J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018, 27(5): 1104-1113. doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201805017 CHEN Y, HUANG H, PENG W Q, et al. Research on eutrophication driven factors of Hanfeng Lake based on exploratory data analysis [J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018, 27(5): 1104-1113(in Chinese). doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201805017
[32] 廖宁, 李洪, 李嘉, 等. 基于主成分分析的西南山区典型河道型水库富营养化评价讨论 [J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2019(11): 104-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2019.11.021 LIAO N, LI H, LI J, et al. Eutrophication evaluation of typical river reservoirs in southwest mountainous areas based on principal component analysis [J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2019(11): 104-109(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2019.11.021
[33] 李利强, 黄代中, 熊剑, 等. 洞庭湖浮游植物增长的限制性营养元素研究 [J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(2): 283-288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.02.016 LI L Q, HUANG D Z, XIONG J, et al. Nutrient limiting phytoplankton growth in Dongting Lake [J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2014, 23(2): 283-288(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2014.02.016
[34] 张光贵. 洞庭湖水体叶绿素a时空分布及与环境因子的相关性 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2016, 32(4): 84-90. ZHANG G G. Spatial-temporal distribution of chlorophyll-a and its correlation with environment factors in Dongting Lake [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2016, 32(4): 84-90(in Chinese).
[35] 王岩, 姜霞, 李永峰, 等. 洞庭湖氮磷时空分布与水体营养状态特征 [J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(5): 484-491. WANG Y, JIANG X, LI Y F, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus and nutritional characteristics of water in Dongting Lake [J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(5): 484-491(in Chinese).
[36] 钟成华. 三峡库区水体富营养化研究[D]. 成都: 四川大学, 2004: 86-87. ZHONG C H. A study on the eutrophication of the Three Gorges reservoir[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2004: 86-87. (in Chinese)
[37] 张光贵, 卢少勇, 田琪. 近20年洞庭湖总氮和总磷浓度时空变化及其影响因素分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(11): 2377-2385. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016040501 ZHANG G G, LU S Y, TIAN Q. Analysis of spatial-temporal variations of total nitrogen and total phosphorus concentrations and their influencing factors in Dongting Lake in the past two decades [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(11): 2377-2385(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.11.2016040501
[38] 汪星, 郑丙辉, 刘录三, 等. 洞庭湖典型断面底栖动物组成及其与环境因子的相关分析 [J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(12): 2237-2244. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.12.019 WANG X, ZHENG B H, LIU L S, et al. Correlation analysis of macroinvertebrate composition and environmental factors of typical sections in Dongting Lake [J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(12): 2237-2244(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2012.12.019
[39] 王小毛, 欧伏平, 王丑明, 等. 洞庭湖底栖动物长期演变特征及影响因素分析 [J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(2): 336-345. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.02.018 WANG X M, OU F P, WANG C M, et al. Long-term evolution and influencing factors of macrozoobenthos in Dongting Lake [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(2): 336-345(in Chinese). doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016.02.018
[40] 赵运林, 肖正军, 戴梅斌, 等. 洞庭湖区湿地资源及生态系统现状的研究 [J]. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 16(4): 1-5. ZHAO Y L, XIAO Z J, DAI M B, et al. Research on the wetland resources and ecosystems in Dongting Lake area [J]. Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science), 2007, 16(4): 1-5(in Chinese).
[41] 廖平安, 胡秀琳. 流速对藻类生长影响的试验研究 [J]. 北京水利, 2005(2): 12-14,60. LIAO P A, HU X L. Experimental study on the effect of flow velocity on algal growth [J]. Beijing Water Resources, 2005(2): 12-14,60(in Chinese).
[42] ZHU W, WAN L, ZHAO L F. Effect of nutrient level on phytoplankton community structure in different water bodies [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences (China), 2010, 22(1): 32-39. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60071-1 -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: