-
随着城市化水平的逐渐提高,大量生活污水和工业废水持续排入地表水体,但普通污水处理厂对污染物的处理效果有限,因此,亟需一种更为生态有效的氮、磷去除技术,来进一步提升污水处理厂尾水水质。
以“绿色生态系统”建设的人工湿地处理技术,与臭氧/活性炭[1-2]、生物滤池[3-4]和反渗透[5]等其他深度处理技术相对比,具有维护操作便捷、工程运转费用低和抗水力冲击能力强等显著优势[6-9],逐渐在尾水提标中得到更普遍的推广运用。现阶段我国大部分污水处理厂尾水已达到一级A的出水标准,但其作为生态补给水直接排入受纳水体,会导致地表水体水质恶化,甚至产生富营养化等问题,进而影响周边水环境质量。选取江心洲污水处理厂闲置用地,建设尾水人工湿地示范工程,研究湿地系统对污水处理厂尾水净化能力和效果。以该系统为研究目标,分析各处理单元的水质情况,进而确定湿地系统的适宜组合形式及运行工况,可为污水处理厂尾水水质提升和人工湿地的运用普及提供技术参数和工程示范。
-
本工程为南京江心洲污水处理厂,项目建于2020年6月,项目区面积为1 800 m2,设计规模为1 200 m3/d,水力负荷约为0.67 m3/(m2·d),湿地系统进水为江心洲污水厂的一级A标准出水,实际进水负荷与设计进水负荷相比偏高,设计出水水质符合《地表水环境质量标准GB3838—2002》近Ⅳ类水标准,见表1。
-
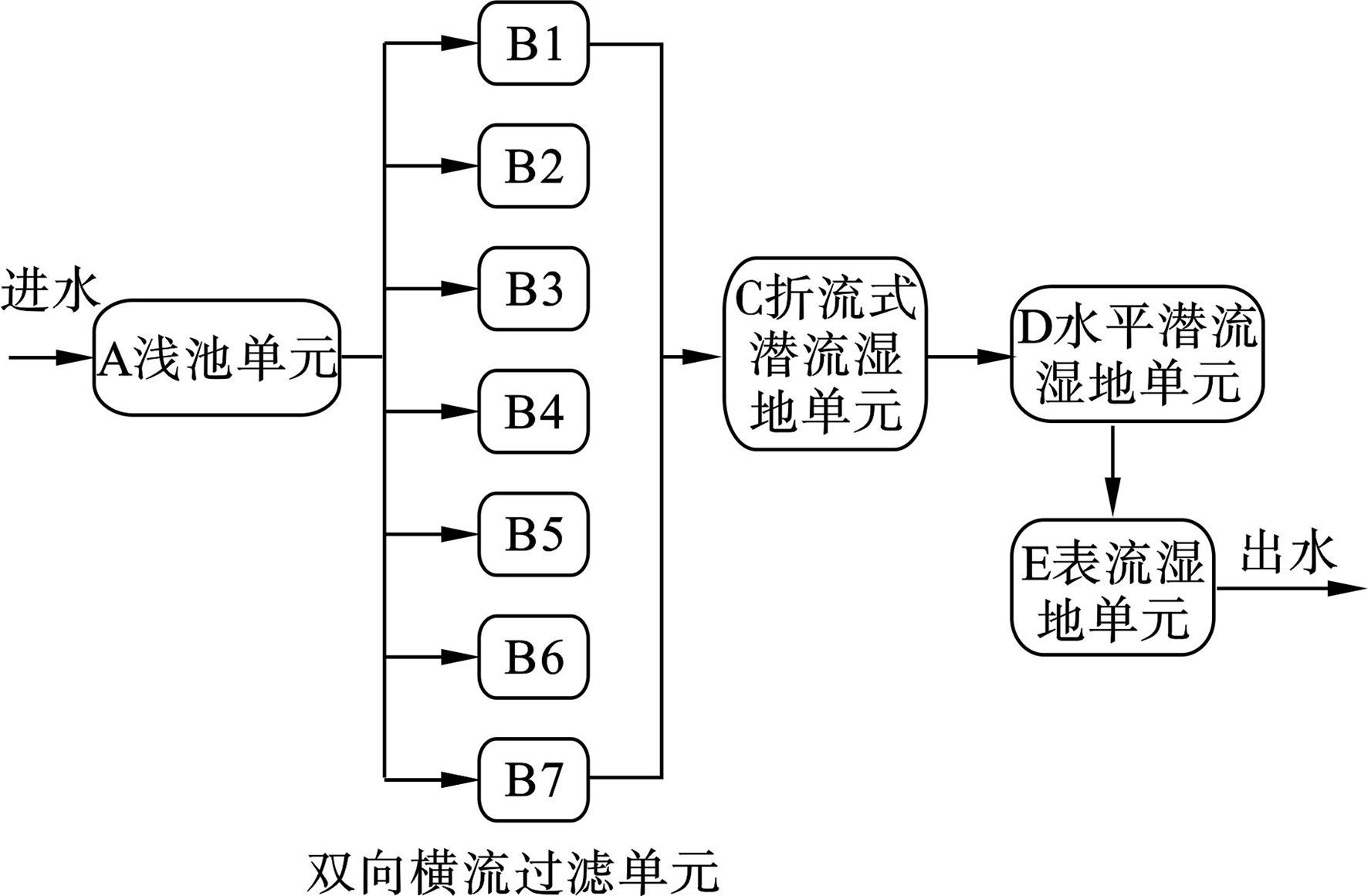
该人工湿地示范工程的设计流程,见图1。
待处理污水通过水泵一次提升后,进入高位水池即浅池单元A,完成水质与水量的调节与控制,同时可对悬浮物、颗粒物或泥沙等进行去除;预处理后的污水正向或反向地进入7 座并联的双向横流生态过滤单元B,实现污水中有机物氧化和反硝化脱氮;出水自流入折流式潜流单元C,污水均匀折流使湿地中的污染物质与内部基质进行充分接触,同时折流式潜流湿地单元中的缺氧环境,可促进反硝化脱氮;出水向下流入水平潜流单元D,污水在非饱和条件下,强化有机物去除、磷的吸附以及深度硝化,使水质得到稳定提升;出水流入表流湿地单元E,实现有机物和氮的去除,进一步保障水质和营造生态景观,最终出水依据相应水质标准进行再生水回用。
-
复合式人工湿地处理系统的主要构筑物设计参数,见表2。
-
研究阶段分为:1)启动期为2020年7月1日~2020年8月31日(61 d),采样频率为1周1次;2)过渡期为2020年9月1日~2020年11月30日(91 d),采样频率为1周1次;3)稳定期为2020年12月1日~2020年3月28日(121 d),采样频率为1周1次,分析了系统从启动到稳定运行9个月(270 d)内各单元进出水TN、NH4+-N、COD和TP的变化情况。相关水质指标的测定参照《水和废水监测分析方法(第4版)》 。
-
2020年7月湿地系统初步建设完成,随即开展湿地系统的启动调控。湿地启动过程中需保持工程基建设施与配水管路系统等稳定运转,待复合式人工湿地系统各个单元运行情况良好后(连续7~10 d对各污染物具有较为稳定的处理效果),即视为湿地启动调试工作完成。
-
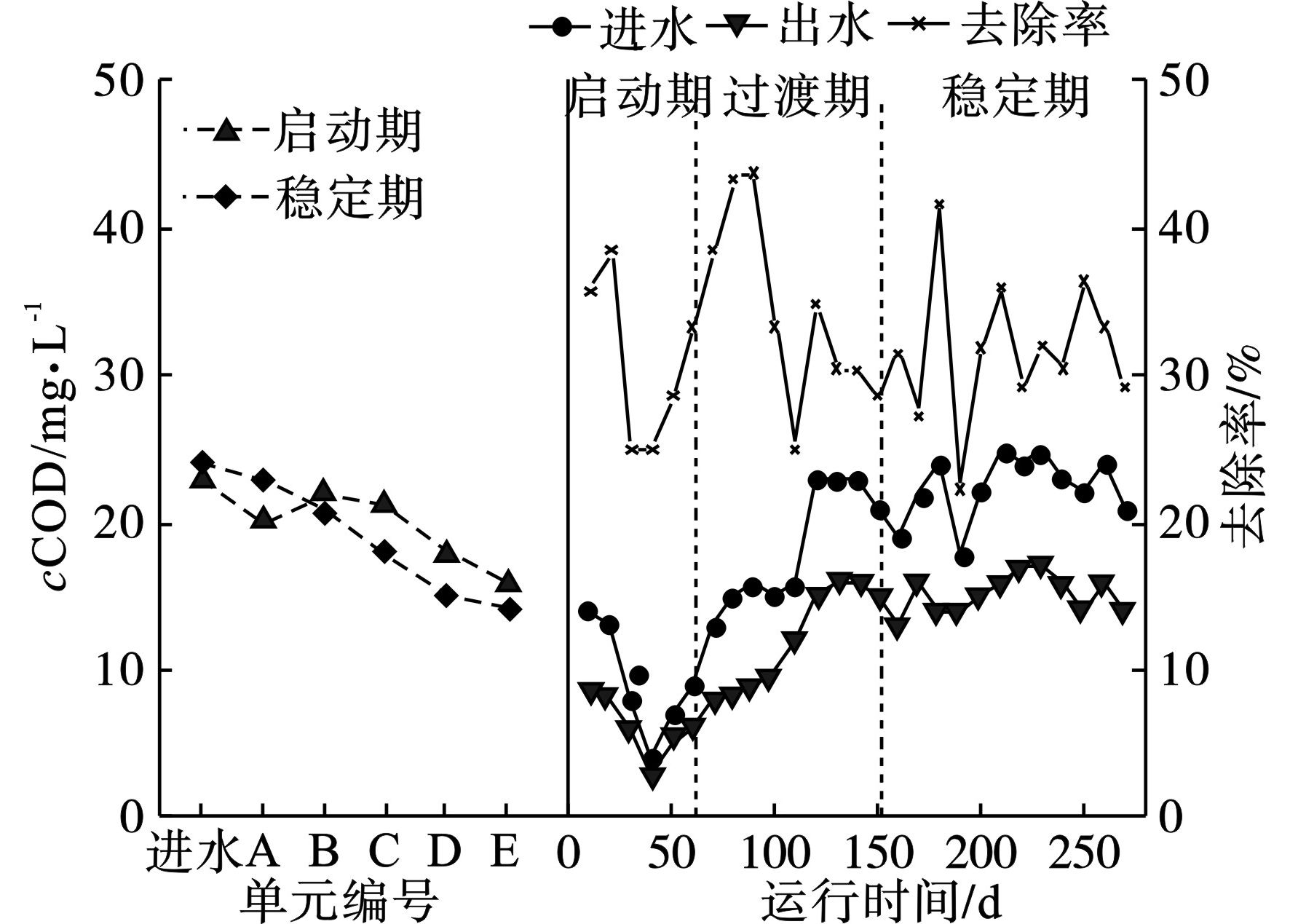
复合式人工湿地系统对COD的去除效果,见图2。
COD实际进水浓度为(19.11±6.59) mg/L,尾水经湿地系统处理后COD含量逐渐降低,在启动期,尾水中COD浓度在进水端有1个高速降低的阶段,这主要是因为尾水中COD含量相对不高,尾水流动的过程中大部分有机物借助填料吸附、湿地植物根系吸收和多种微生物的降解作用被有效去除。当污水从浅池单元流至其他单元时,有机物浓度已经较低且大部分为难降解有机物,因此系统其他单元对COD的去除效果减弱。启动期时系统对COD的去除能力具有较高的波动性,平均去除率为31.1%,最高去除率接近40.0%。随着系统的运行,过渡期和稳定期时对COD的去除效果逐渐趋于稳定,系统处于稳定期时对COD的平均去除率为32.2%,最高去除率接近50.0%,优于启动期与过渡期。整体来看,系统对COD的去除能力略弱,原因可能是由于实际进水中COD含量较低,并且冬季过渡期时,温度较低,造成微生物活性衰退;又由于对生态景观效果的提升,该系统在浅池单元处养殖锦鲤,其排泄物溶于水体使后续单元有机物浓度产生波动,导致系统对COD的总体去除效果不佳。虽然进水中COD水质变化较大,但COD出水水质较为平稳,出水COD均小于《地表水环境质量标准》中的Ⅳ类水标准。
-
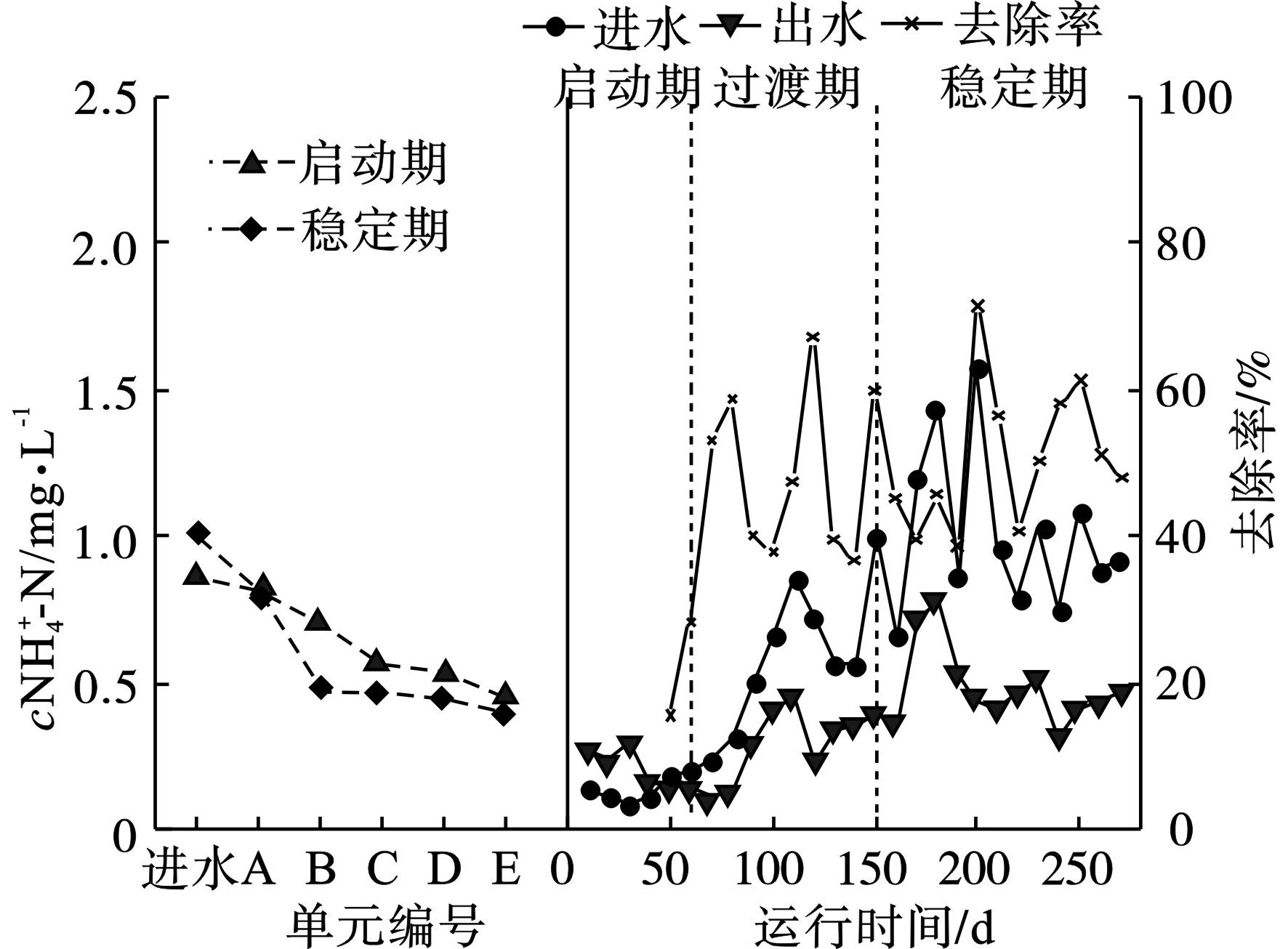
复合式人工湿地系统对NH4+-N的去除效果,见图3。
NH4+-N实际进水浓度为(0.87±0.51)mg/L,NH4+-N的处理单元主要为双向横流生态过滤单元,此单元水体横向流动,在填料上产生生物膜,前端将NH4+-N转化为NO3--N,末端DO浓度下降,形成缺氧环境,可进行初步反硝化,随着对该单元进水流向的调换,能够实现微生物的内源反硝化,有效增强NH4+-N处理效果。但在水平潜流湿地单元中偶尔出现NH4+-N含量增加的情况,王博等[10]研究表明,人工湿地中微生物的硝化过程对NH4+-N的去除起到显著作用,但氧含量的缺乏是导致潜流湿地不能进行硝化反应的重要原因。潜流湿地系统底部缺氧,抑制NH4+-N的硝化作用,使得潜流单元中NH4+-N的去除趋势相对平缓甚至出现反复。该系统初运行时对NH4+-N的处理效果不佳,但在过渡期时平均去除率上升至49.2%,稳定期NH4+-N的平均去除率为51.3%,最高去除率可达71.7%,且NH4+-N是所有水质指标中波动性最强的,显示出冬季时温度较低对NH4+-N处理效果的影响最大。出现该情况的原因可能是NH4+-N的去除以湿地填料的吸附作用和硝化-反硝化作用为主,而这2种途径受温度影响较大,在启动期时,系统刚刚运行,湿地基质的生物膜尚未形成且湿地内植物未进行种植,导致基质微生物的硝化与反硝化作用不佳,因此启动期处理效果差,随着时间的推移及植物生长,湿地基质生物膜逐渐产生,稳定期时NH4+-N的去除率明显上升。
-
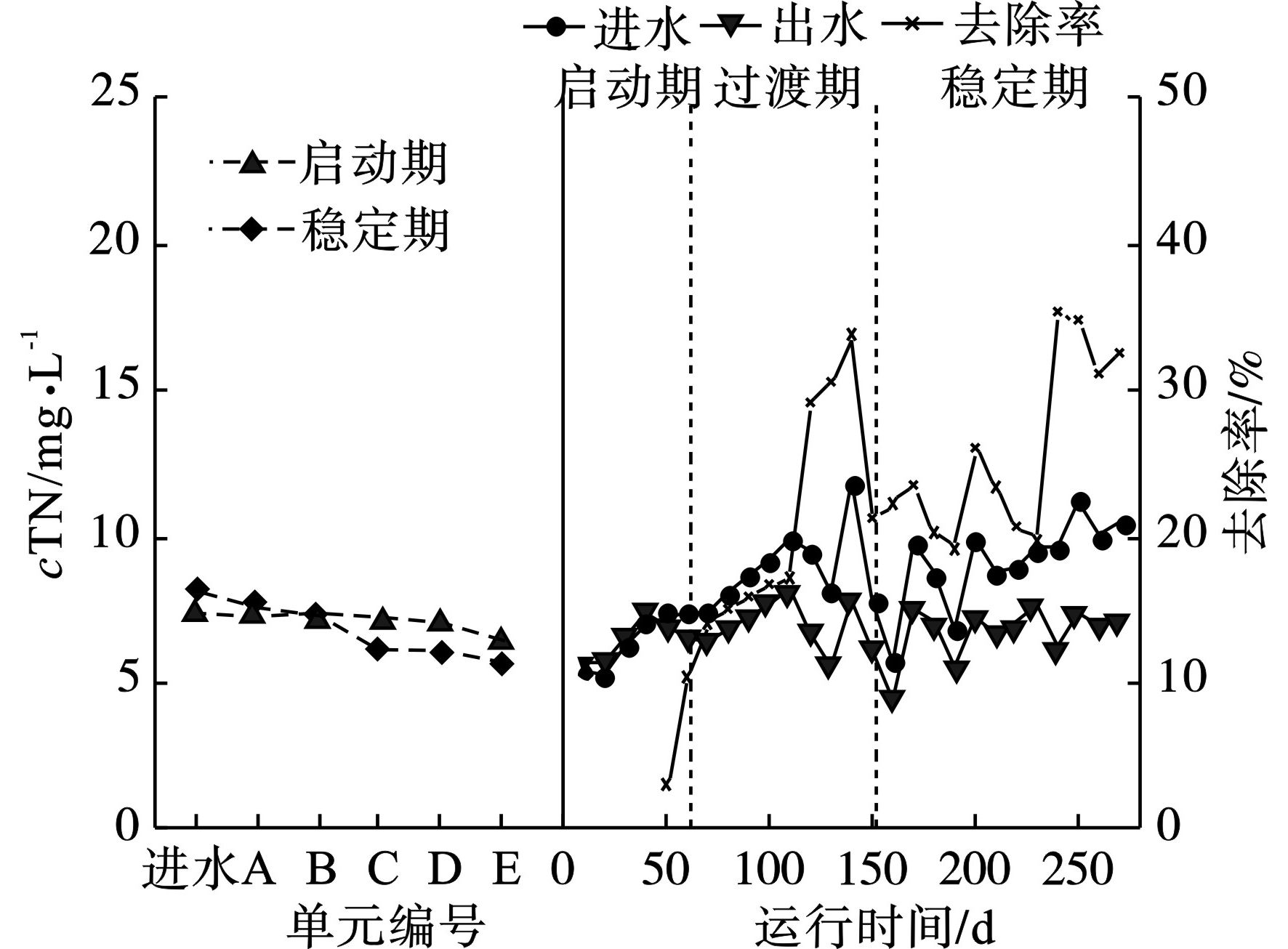
复合式人工湿地系统对TN的去除效果,见图4。
TN实际进水浓度为(8.63±2.71) mg/L,尾水经处理后TN浓度逐渐降低,湿地系统中折流式潜流湿地单元对TN的去除效果较强,这是由于折流式潜流湿地单元内部设有穿水挡墙,以控制水流路径并延长水体与基质的接触时间,实现尾水的高效脱氮,因此该单元对TN的处理效果较强。启动期的平均处理率仅为12.2%,系统运转40 d左右,出现出水TN高于进水的情况,这可能是由于进水TN浓度较低,且湿地系统生物膜尚未形成,系统停留时间较长,基质中的部分污染物溶于水体,使得出水TN浓度有所升高。随着系统逐渐运行,过渡期时系统去除率起伏较大,最高去除率可达33.9%,最低为14.2%,可能是运行前期湿地植物还处于环境适应阶段,且过渡期处于冬季,气温相对较低,微生物活性偏弱。当系统处于稳定期时TN的平均去除率为25.4%,最高接近40.0%.。此外,实际进水负荷偏高,且进水中COD较低,C /N不足,对人工湿地的反硝化过程产生影响,可能是造成系统对TN去除效果较差的重要原因。
-
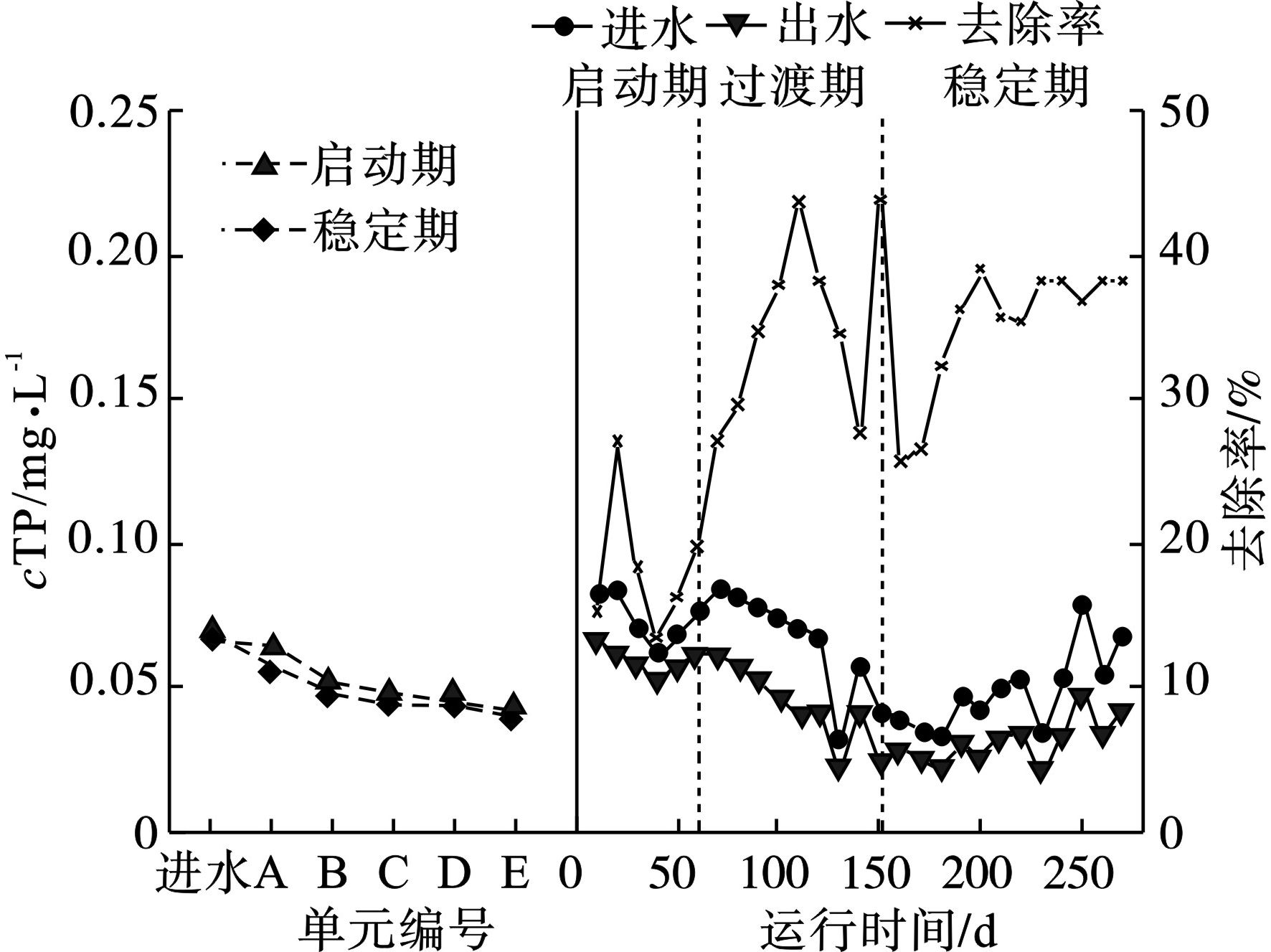
TP浓度的沿程变化,见图5。
TP实际进水浓度为(0.07±0.02) mg/L,尾水经系统后TP浓度逐渐降低,总体来看,双向横流生态过滤单元对TP的处理效果最佳,双向横流生态过滤单元的中层填料介质采用了火山石、碎石,有研究表明[11-12],该填料介质对湿地单元中的磷具有高效的吸附性,且湿地种植了再立花、花叶芦竹等植物,根系有较强的泌氧能力,因此好氧条件产生更有益于基质的吸附。该系统对总磷的去除效果较稳定,过渡期时TP平均去除率为35.3%,与启动期相比,稳定期时TP去除效果约提高1/4,平均去除率为35.2%,最高去除率接近50.0%。这是由于在启动期时期并未种植植物,而进入稳定期后,植物的生长以及微生物代谢作用使得去除率增高,而总体平均去除率不高是由于进水TP过低导致的,但出水TP仍满足地表水近Ⅳ类标准。
-
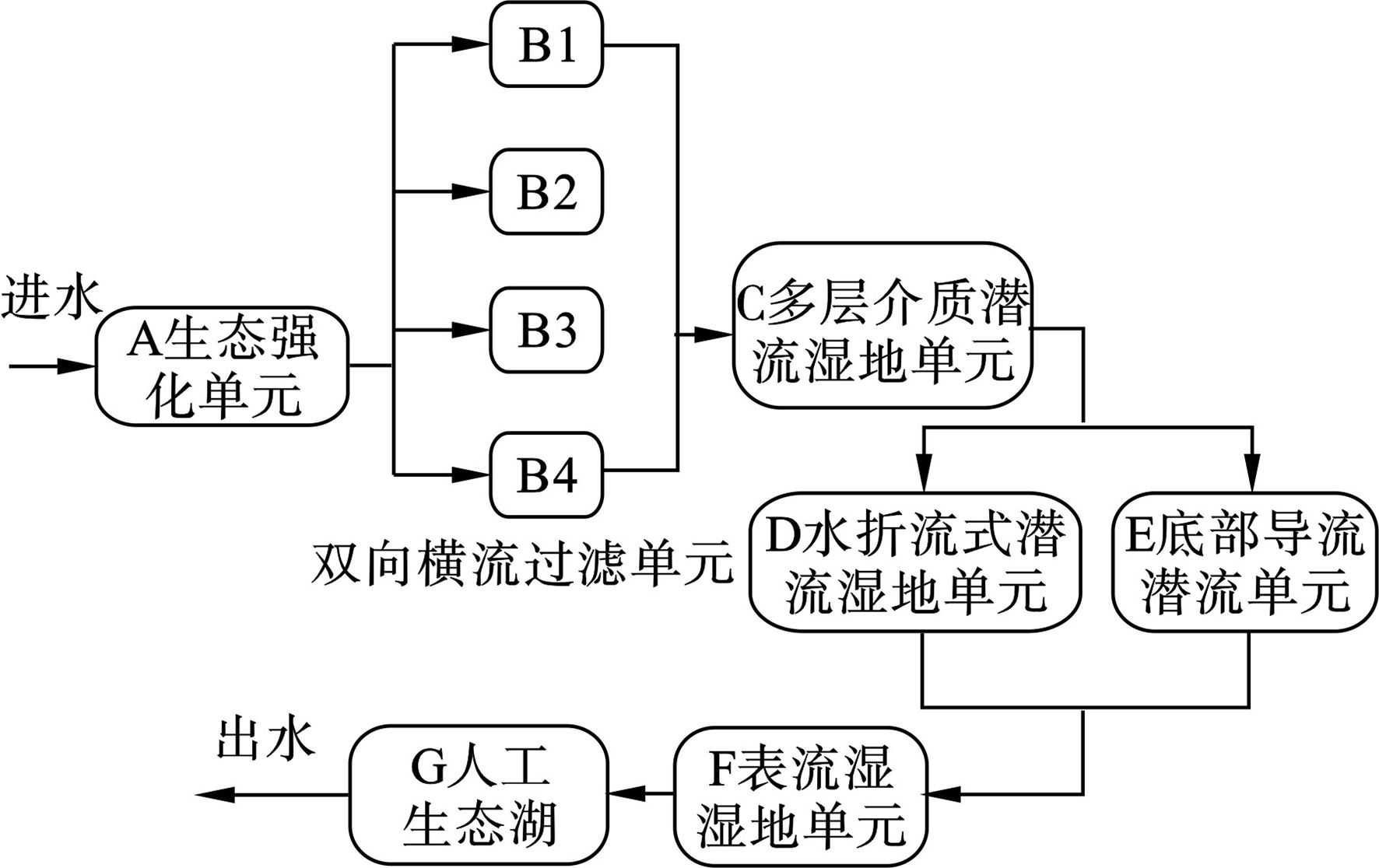
尾水首先进入生态强化单元A,再进入4座并联双向横流过滤单元B,出水自流进入多层介质潜流湿地单元C,然后通过生态配水渠同时进入折流式潜流湿地单元D和底部导流潜流单元E,出水流入表流湿地单元F,最后进入生态人工湖G。
-
与研究团队前期在宜兴城市污水处理厂设计建设的尾水净化复合式人工湿地处理系统的工艺流程相比较,两系统工艺流程的区别首先在于湿地处理单元的搭载方式不同,其中宜兴人工湿地面积较大,系统处理单元较多,相较于江心洲人工湿地,两系统都设置了双向横流生态过滤湿地单元、折流式潜流湿地单元、表流湿地单元,不同之处在于宜兴人工湿地设置了多层介质潜流湿地单元、底部导流潜流湿地单元,江心洲人工湿地设置了水平潜流湿地单元,但两系统的主要处理单元的功能相近,对水中氮、磷等污染物都进行了深度去除;且宜兴人工湿地面积增加了生态人工湖,湿地系统的景观性较强于江心洲人工湿地。其次两系统的填料及植物的配比方式不同,其中宜兴人工湿地因其面积较大,搭配的植物种类较多,但两系统的植物都具有较强的湿地适应性。两系统的填料区别较大,宜兴人工湿地以建筑废弃块为主要填料,江心洲人工湿地以砾石、火山石为主要填料,不同的填料对氮、磷的吸附能力有差异,可能会对湿地的处理效果产生影响。
-
2种人工湿地处理系统的效果对比,见表3。
表3可知,南京江心洲污水处理厂构建的复合式人工湿地系统实际进水水质与宜兴的尾水净化湿地系统有较大差异,主要表现在江心洲人工湿地系统中的进水COD浓度较低,处理效果却优于宜兴人工湿地系统,这可能是由于南京江心洲湿地系统为高负荷处理系统,且两者中搭建的植物、填料不同造成的;并且两系统中的TN含量相差不大,但宜兴复合式人工湿地系统去除率高于南京江心洲人工湿地系统,主要是由于江心洲湿地系统中进水COD浓度仅为(19.11±6.59 )mg/L,使得C/N不足,对湿地系统的反硝化过程产生影响,降低了TN的处理效果;宜兴人工湿地系统中对TP的去除效果最好,去除率高达72.2%,远高于江心洲人工湿地系统,这可能是由于宜兴人工湿地系统中基质选用建筑废弃块,研究表明[14-15],建筑废弃块(主要由砖块组成) 能够有效吸附水体中的磷,因而可有效去除尾水中各种形态的磷元素。总体来看,宜兴人工湿地系统与江心洲人工湿地系统虽然工艺流程、填料搭配有差异,但均对污水处理厂尾水具有良好的处理效果,说明了复合式人工湿地系统可因地制宜地选择湿地类型,实现各工艺之间的优势互补,提供一种适用于不同场景、不同标准下的城市污水处理厂尾水提标新范式。
-
(1)采用了“浅池单元+双向横流生态过滤单元+折流式潜流湿地单元+水平潜流湿地单元+表流湿地单元”组合工艺,系统调试稳定后对COD、NH4+-N、TN和TP平均去除率依次为32.2%、51.3%、25.4%和35.2%,说明该工艺有一定的工程示范作用。
(2)气温较低时湿地系统应定期收割植物,否则会降低污染物的去除效果,且该系统C/N较低,造成TN去除效果不佳,说明人工湿地稳定运行需要适宜的营养条件与配套的管理维护。
(3)复合式人工湿地系统可因地制宜地选择湿地类型,实现各工艺之间的优势互补,提供一种适用于不同场景、不同标准下的城市污水处理厂尾水提标新范式。
复合式人工湿地尾水净化工程调试与运行
Commissioning and operation of compound constructed wetland project for tail water purification
-
摘要: 采用“浅池单元+双向横流生态过滤单元+折流式潜流湿地单元+水平潜流湿地单元+表流湿地单元”构建了复合式人工湿地系统,介绍了湿地系统的设计流程,讨论和比较了启动期、过渡期与稳定期的270 d处理效果。实际运行结果显示:COD、NH4+-N、TN、TP的平均去除率分别为32.2%、51.3%、25.4%、35.2%;该系统出水水质满足《地表水环境质量标准GB3838—2002》近 Ⅳ类水标准。通过与宜兴城市污水处理厂尾水净化复合式人工湿地相比较,说明复合式人工湿地系统可根据治理目标因地制宜地进行工艺组合。Abstract: A composite constructed wetland system was established with a shallow pool unit, a bidirectional cross-flow ecological filtration unit, a baffled subsurface flow wetland unit, a horizontal subsurface flow wetland unit and a surface flow wetland unit. The design process of the wetland system was introduced. And the 270d operation results among the start-up period and the transitional period as well as the steady period were discussed and compared. The actual operation results showed that the average removal rates of COD, NH4+-N, TN, TP were 32.2%, 51.3%, 25.4% and 35.2%, respectively. The effluent water quality of the system could meet the class Ⅳ of Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (GB3838—2002). Compared with the composite constructed wetland system in Yixing municipal wastewater treatment plant, the composite constructed wetland system could be combined according to the local conditions with a significant ecological advantage and application value.
-
随着城市化水平的逐渐提高,大量生活污水和工业废水持续排入地表水体,但普通污水处理厂对污染物的处理效果有限,因此,亟需一种更为生态有效的氮、磷去除技术,来进一步提升污水处理厂尾水水质。
以“绿色生态系统”建设的人工湿地处理技术,与臭氧/活性炭[1-2]、生物滤池[3-4]和反渗透[5]等其他深度处理技术相对比,具有维护操作便捷、工程运转费用低和抗水力冲击能力强等显著优势[6-9],逐渐在尾水提标中得到更普遍的推广运用。现阶段我国大部分污水处理厂尾水已达到一级A的出水标准,但其作为生态补给水直接排入受纳水体,会导致地表水体水质恶化,甚至产生富营养化等问题,进而影响周边水环境质量。选取江心洲污水处理厂闲置用地,建设尾水人工湿地示范工程,研究湿地系统对污水处理厂尾水净化能力和效果。以该系统为研究目标,分析各处理单元的水质情况,进而确定湿地系统的适宜组合形式及运行工况,可为污水处理厂尾水水质提升和人工湿地的运用普及提供技术参数和工程示范。
1. 工艺设计
1.1 污水处理量及进出水水质
本工程为南京江心洲污水处理厂,项目建于2020年6月,项目区面积为1 800 m2,设计规模为1 200 m3/d,水力负荷约为0.67 m3/(m2·d),湿地系统进水为江心洲污水厂的一级A标准出水,实际进水负荷与设计进水负荷相比偏高,设计出水水质符合《地表水环境质量标准GB3838—2002》近Ⅳ类水标准,见表1。
表 1 复合式人工湿地系统设计进出水质指标 mg·L−1污染物 设计进水 设计出水 COD ≤50.00 ≤30.00 NH4+-N ≤5.00 ≤1.50 TN ≤15.00 消减50.0% TP ≤0.50 ≤0.30 1.2 设计流程
该人工湿地示范工程的设计流程,见图1。
待处理污水通过水泵一次提升后,进入高位水池即浅池单元A,完成水质与水量的调节与控制,同时可对悬浮物、颗粒物或泥沙等进行去除;预处理后的污水正向或反向地进入7 座并联的双向横流生态过滤单元B,实现污水中有机物氧化和反硝化脱氮;出水自流入折流式潜流单元C,污水均匀折流使湿地中的污染物质与内部基质进行充分接触,同时折流式潜流湿地单元中的缺氧环境,可促进反硝化脱氮;出水向下流入水平潜流单元D,污水在非饱和条件下,强化有机物去除、磷的吸附以及深度硝化,使水质得到稳定提升;出水流入表流湿地单元E,实现有机物和氮的去除,进一步保障水质和营造生态景观,最终出水依据相应水质标准进行再生水回用。
1.3 设计参数
复合式人工湿地处理系统的主要构筑物设计参数,见表2。
表 2 主要构筑物设计参数项目 面积/m2 基质 植物 A浅池单元 80 — 睡莲覆盖度(50%~55%) B双向横流生态单元 362 500 mm的卵石(粒径80~120 mm)2 000 mm的火山石(粒径50~80 mm)500 mm的砾石(粒径为35~55 mm)60 mm的水生植物种植床 美人蕉(3~4株/m2)再力花(3~4丛/m2)花叶芦竹(10~12丛/m2) C折流式潜流湿地单元 302 400 mm的卵石(粒径为50~80 mm)400 mm的沸石(粒径为30~50 mm)400 mm的砾石(粒径为25~35 mm) 美人蕉(3~4株/m2)再力花(3~4丛/m2) D水平潜流湿地单元 196 300 mm的卵石(粒径为50~80 mm)350 mm的火山石(粒径30~50 mm)350 mm的砾石(粒径为25~35 mm) 旱伞草(5~8株/m2) E表流湿地单元 127 300 mm厚中粗砂200 mm厚素土 芦苇(3~4株/m2)再力花(3~4丛/m2)睡莲覆盖度(50%~55%) 2. 运行效果分析
研究阶段分为:1)启动期为2020年7月1日~2020年8月31日(61 d),采样频率为1周1次;2)过渡期为2020年9月1日~2020年11月30日(91 d),采样频率为1周1次;3)稳定期为2020年12月1日~2020年3月28日(121 d),采样频率为1周1次,分析了系统从启动到稳定运行9个月(270 d)内各单元进出水TN、NH4+-N、COD和TP的变化情况。相关水质指标的测定参照《水和废水监测分析方法(第4版)》 。
2.1 人工湿地系统的启动
2020年7月湿地系统初步建设完成,随即开展湿地系统的启动调控。湿地启动过程中需保持工程基建设施与配水管路系统等稳定运转,待复合式人工湿地系统各个单元运行情况良好后(连续7~10 d对各污染物具有较为稳定的处理效果),即视为湿地启动调试工作完成。
2.2 运行效果分析
2.2.1 COD的去除效果
复合式人工湿地系统对COD的去除效果,见图2。
COD实际进水浓度为(19.11±6.59) mg/L,尾水经湿地系统处理后COD含量逐渐降低,在启动期,尾水中COD浓度在进水端有1个高速降低的阶段,这主要是因为尾水中COD含量相对不高,尾水流动的过程中大部分有机物借助填料吸附、湿地植物根系吸收和多种微生物的降解作用被有效去除。当污水从浅池单元流至其他单元时,有机物浓度已经较低且大部分为难降解有机物,因此系统其他单元对COD的去除效果减弱。启动期时系统对COD的去除能力具有较高的波动性,平均去除率为31.1%,最高去除率接近40.0%。随着系统的运行,过渡期和稳定期时对COD的去除效果逐渐趋于稳定,系统处于稳定期时对COD的平均去除率为32.2%,最高去除率接近50.0%,优于启动期与过渡期。整体来看,系统对COD的去除能力略弱,原因可能是由于实际进水中COD含量较低,并且冬季过渡期时,温度较低,造成微生物活性衰退;又由于对生态景观效果的提升,该系统在浅池单元处养殖锦鲤,其排泄物溶于水体使后续单元有机物浓度产生波动,导致系统对COD的总体去除效果不佳。虽然进水中COD水质变化较大,但COD出水水质较为平稳,出水COD均小于《地表水环境质量标准》中的Ⅳ类水标准。
2.2.2 NH4+-N去除效果
复合式人工湿地系统对NH4+-N的去除效果,见图3。
NH4+-N实际进水浓度为(0.87±0.51)mg/L,NH4+-N的处理单元主要为双向横流生态过滤单元,此单元水体横向流动,在填料上产生生物膜,前端将NH4+-N转化为NO3--N,末端DO浓度下降,形成缺氧环境,可进行初步反硝化,随着对该单元进水流向的调换,能够实现微生物的内源反硝化,有效增强NH4+-N处理效果。但在水平潜流湿地单元中偶尔出现NH4+-N含量增加的情况,王博等[10]研究表明,人工湿地中微生物的硝化过程对NH4+-N的去除起到显著作用,但氧含量的缺乏是导致潜流湿地不能进行硝化反应的重要原因。潜流湿地系统底部缺氧,抑制NH4+-N的硝化作用,使得潜流单元中NH4+-N的去除趋势相对平缓甚至出现反复。该系统初运行时对NH4+-N的处理效果不佳,但在过渡期时平均去除率上升至49.2%,稳定期NH4+-N的平均去除率为51.3%,最高去除率可达71.7%,且NH4+-N是所有水质指标中波动性最强的,显示出冬季时温度较低对NH4+-N处理效果的影响最大。出现该情况的原因可能是NH4+-N的去除以湿地填料的吸附作用和硝化-反硝化作用为主,而这2种途径受温度影响较大,在启动期时,系统刚刚运行,湿地基质的生物膜尚未形成且湿地内植物未进行种植,导致基质微生物的硝化与反硝化作用不佳,因此启动期处理效果差,随着时间的推移及植物生长,湿地基质生物膜逐渐产生,稳定期时NH4+-N的去除率明显上升。
2.2.3 TN的去除效果
复合式人工湿地系统对TN的去除效果,见图4。
TN实际进水浓度为(8.63±2.71) mg/L,尾水经处理后TN浓度逐渐降低,湿地系统中折流式潜流湿地单元对TN的去除效果较强,这是由于折流式潜流湿地单元内部设有穿水挡墙,以控制水流路径并延长水体与基质的接触时间,实现尾水的高效脱氮,因此该单元对TN的处理效果较强。启动期的平均处理率仅为12.2%,系统运转40 d左右,出现出水TN高于进水的情况,这可能是由于进水TN浓度较低,且湿地系统生物膜尚未形成,系统停留时间较长,基质中的部分污染物溶于水体,使得出水TN浓度有所升高。随着系统逐渐运行,过渡期时系统去除率起伏较大,最高去除率可达33.9%,最低为14.2%,可能是运行前期湿地植物还处于环境适应阶段,且过渡期处于冬季,气温相对较低,微生物活性偏弱。当系统处于稳定期时TN的平均去除率为25.4%,最高接近40.0%.。此外,实际进水负荷偏高,且进水中COD较低,C /N不足,对人工湿地的反硝化过程产生影响,可能是造成系统对TN去除效果较差的重要原因。
2.2.4 TP的去除效果
TP浓度的沿程变化,见图5。
TP实际进水浓度为(0.07±0.02) mg/L,尾水经系统后TP浓度逐渐降低,总体来看,双向横流生态过滤单元对TP的处理效果最佳,双向横流生态过滤单元的中层填料介质采用了火山石、碎石,有研究表明[11-12],该填料介质对湿地单元中的磷具有高效的吸附性,且湿地种植了再立花、花叶芦竹等植物,根系有较强的泌氧能力,因此好氧条件产生更有益于基质的吸附。该系统对总磷的去除效果较稳定,过渡期时TP平均去除率为35.3%,与启动期相比,稳定期时TP去除效果约提高1/4,平均去除率为35.2%,最高去除率接近50.0%。这是由于在启动期时期并未种植植物,而进入稳定期后,植物的生长以及微生物代谢作用使得去除率增高,而总体平均去除率不高是由于进水TP过低导致的,但出水TP仍满足地表水近Ⅳ类标准。
3. 与宜兴城市污水处理厂尾水净化复合式人工湿地系统对比
3.1 宜兴复合式人工湿地工艺设计
尾水首先进入生态强化单元A,再进入4座并联双向横流过滤单元B,出水自流进入多层介质潜流湿地单元C,然后通过生态配水渠同时进入折流式潜流湿地单元D和底部导流潜流单元E,出水流入表流湿地单元F,最后进入生态人工湖G。
3.2 不同尾水净化湿地处理系统对比
3.2.1 工艺对比
与研究团队前期在宜兴城市污水处理厂设计建设的尾水净化复合式人工湿地处理系统的工艺流程相比较,两系统工艺流程的区别首先在于湿地处理单元的搭载方式不同,其中宜兴人工湿地面积较大,系统处理单元较多,相较于江心洲人工湿地,两系统都设置了双向横流生态过滤湿地单元、折流式潜流湿地单元、表流湿地单元,不同之处在于宜兴人工湿地设置了多层介质潜流湿地单元、底部导流潜流湿地单元,江心洲人工湿地设置了水平潜流湿地单元,但两系统的主要处理单元的功能相近,对水中氮、磷等污染物都进行了深度去除;且宜兴人工湿地面积增加了生态人工湖,湿地系统的景观性较强于江心洲人工湿地。其次两系统的填料及植物的配比方式不同,其中宜兴人工湿地因其面积较大,搭配的植物种类较多,但两系统的植物都具有较强的湿地适应性。两系统的填料区别较大,宜兴人工湿地以建筑废弃块为主要填料,江心洲人工湿地以砾石、火山石为主要填料,不同的填料对氮、磷的吸附能力有差异,可能会对湿地的处理效果产生影响。
3.2.2 处理效果对比
2种人工湿地处理系统的效果对比,见表3。
表 3 尾水净化复合式人工湿地系统处理效果对比污染物 宜兴城市污水处理厂 江心洲污水处理厂 实际进水/mg·L−1 去除率/% 实际进水/mg·L−1 去除率/% COD 48.12±4.91 12.5 19.11±6.59 32.2 TN 8.42±0.65 40.0 8.63±2.71 25.4 NH4+-N 0.53±0.08 31.1 0.87±0.51 51.3 TP 0.11±0.05 72.2 0.07±0.02 35.2 表3可知,南京江心洲污水处理厂构建的复合式人工湿地系统实际进水水质与宜兴的尾水净化湿地系统有较大差异,主要表现在江心洲人工湿地系统中的进水COD浓度较低,处理效果却优于宜兴人工湿地系统,这可能是由于南京江心洲湿地系统为高负荷处理系统,且两者中搭建的植物、填料不同造成的;并且两系统中的TN含量相差不大,但宜兴复合式人工湿地系统去除率高于南京江心洲人工湿地系统,主要是由于江心洲湿地系统中进水COD浓度仅为(19.11±6.59 )mg/L,使得C/N不足,对湿地系统的反硝化过程产生影响,降低了TN的处理效果;宜兴人工湿地系统中对TP的去除效果最好,去除率高达72.2%,远高于江心洲人工湿地系统,这可能是由于宜兴人工湿地系统中基质选用建筑废弃块,研究表明[14-15],建筑废弃块(主要由砖块组成) 能够有效吸附水体中的磷,因而可有效去除尾水中各种形态的磷元素。总体来看,宜兴人工湿地系统与江心洲人工湿地系统虽然工艺流程、填料搭配有差异,但均对污水处理厂尾水具有良好的处理效果,说明了复合式人工湿地系统可因地制宜地选择湿地类型,实现各工艺之间的优势互补,提供一种适用于不同场景、不同标准下的城市污水处理厂尾水提标新范式。
4. 结论
(1)采用了“浅池单元+双向横流生态过滤单元+折流式潜流湿地单元+水平潜流湿地单元+表流湿地单元”组合工艺,系统调试稳定后对COD、NH4+-N、TN和TP平均去除率依次为32.2%、51.3%、25.4%和35.2%,说明该工艺有一定的工程示范作用。
(2)气温较低时湿地系统应定期收割植物,否则会降低污染物的去除效果,且该系统C/N较低,造成TN去除效果不佳,说明人工湿地稳定运行需要适宜的营养条件与配套的管理维护。
(3)复合式人工湿地系统可因地制宜地选择湿地类型,实现各工艺之间的优势互补,提供一种适用于不同场景、不同标准下的城市污水处理厂尾水提标新范式。
-
表 1 复合式人工湿地系统设计进出水质指标 mg·L−1
污染物 设计进水 设计出水 COD ≤50.00 ≤30.00 NH4+-N ≤5.00 ≤1.50 TN ≤15.00 消减50.0% TP ≤0.50 ≤0.30 表 2 主要构筑物设计参数
项目 面积/m2 基质 植物 A浅池单元 80 — 睡莲覆盖度(50%~55%) B双向横流生态单元 362 500 mm的卵石(粒径80~120 mm)2 000 mm的火山石(粒径50~80 mm)500 mm的砾石(粒径为35~55 mm)60 mm的水生植物种植床 美人蕉(3~4株/m2)再力花(3~4丛/m2)花叶芦竹(10~12丛/m2) C折流式潜流湿地单元 302 400 mm的卵石(粒径为50~80 mm)400 mm的沸石(粒径为30~50 mm)400 mm的砾石(粒径为25~35 mm) 美人蕉(3~4株/m2)再力花(3~4丛/m2) D水平潜流湿地单元 196 300 mm的卵石(粒径为50~80 mm)350 mm的火山石(粒径30~50 mm)350 mm的砾石(粒径为25~35 mm) 旱伞草(5~8株/m2) E表流湿地单元 127 300 mm厚中粗砂200 mm厚素土 芦苇(3~4株/m2)再力花(3~4丛/m2)睡莲覆盖度(50%~55%) 表 3 尾水净化复合式人工湿地系统处理效果对比
污染物 宜兴城市污水处理厂 江心洲污水处理厂 实际进水/mg·L−1 去除率/% 实际进水/mg·L−1 去除率/% COD 48.12±4.91 12.5 19.11±6.59 32.2 TN 8.42±0.65 40.0 8.63±2.71 25.4 NH4+-N 0.53±0.08 31.1 0.87±0.51 51.3 TP 0.11±0.05 72.2 0.07±0.02 35.2 -
[1] 吴春旭, 武哲如, 王鸿英, 等. 协同催化氧化用于焦化厂生化尾水深度处理[J]. 环境保护科学, 2020, 46(2): 35 − 38. [2] CHUANG Y H, SZCZUKA A, SHABANI F, et al. Pilot-scale comparison of microfiltration / reverse osmosis and ozone / biological activated carbon with UV/hydrogen peroxide or UV/free chlorine AOP treatment for controlling disinfection byproducts during wastewater reuse[J]. Water Research, 2019, 152: 215 − 225. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.12.062 [3] MALEKIAN F, FARHADIAN M, SOHRABI M, et al. Application of nanofiltration as a tertiary treatment in a polyester production industry for wastewater reus[J]. Desalination & Water Treatment, 2016, 57(16): 7175 − 7181. [4] 江荻, 陆少鸣, 端艳, 等. 微絮凝/膨胀床反硝化滤池处理污水厂尾水试验研究[J]. 环境保护科学, 2018, 44(5): 42 − 46. [5] 魏永, 姚维昊, 桂波, 等. 超低压反渗透处理太湖水的中试分析[J]. 给水排水, 2018, 54(12): 11 − 16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8471.2018.12.003 [6] 蔡然, 王征戍, 张功良, 等. 生态湿地技术在内江太子湖项目尾水处理中的应用[J]. 给水排水, 2021, 57(1): 54 − 57. [7] YU D, WILIŃSKI P R, DZAKPASU M, et al. Impact of hydraulic loading rate and season on water contaminant reductions integrated constructed wetlands[J]. Wetlands, 2011, 31(3): 499 − 509. doi: 10.1007/s13157-011-0176-5 [8] 程铭. 多级垂直流人工湿地对北方农村生活污水的处理分析[J]. 环境保护科学, 2019, 45(6): 64 − 70. [9] 王天蓓, 赵宇豪, 张怀宇, 等. 人工湿地技术对饮用水源水质保持和净化提升效果评估[J]. 给水排水, 2020, 56(6): 58 − 64. [10] 王博, 祁佩时, 刘云芝, 等. 潜流人工湿地氮素去除机理与影响因素[J]. 应用化工, 2017, 46(2): 350 − 355. [11] 翟俊, 翟豪冲, 马宏璞, 等. 多级人工湿地对生活污水中磷素的去除规律[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(21): 75 − 79. [12] 李紫霞, 唐晓丹, 崔理华. 3种负荷对模拟垂直流人工湿地去除氮、磷效果的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(2): 637 − 642. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20160220 [13] 杜曼曼, 张琼华, 连斌, 等. 城市污水处理厂尾水人工湿地净化工程调试与运行[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(9): 94 − 100. [14] 王振, 刘超翔, 李鹏宇, 等. 废砖块作为人工湿地填料的除磷能力研究[J]. 环境科学, 2012, 33(12): 4373 − 4379. [15] 张国珍, 尚兴宝, 武福平, 等. 废砖基质折流式垂直流人工湿地处理二级生化尾水[J]. 中国给水排水, 2019, 35(9): 100 − 105. -




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: