-
交替式生物反应池(UNITANK)作为一种结构紧凑、运行灵活的活性污泥工艺,在我国城市污水处理中得到了较广泛的应用[1-2]。然而,由于结构上的不足,UNITANK在运行过程中普遍存在污泥分布不均、低负荷释磷不充分、池体容积布局不合理等问题[3-4]。为了解决这些问题,张发根等[4]提出了双流态UNITANK,即将UNITANK工艺中的1个边池改成2个以上,且交替向中间池提供污泥,他们同时利用ASM2D模型和实验验证了双流态UNITANK工艺的可行性,但这种工艺的运行周期调控相对更为复杂。因此,改良型UNITANK工艺应运而生。改良型UNITANK是在UNITANK的基础上增设了单独的厌氧池和缺氧池,同时增加了内回流点,以强化工艺的脱氮除磷效果。目前国内对改良型UNITANK工艺的研究报道较少。朱海敏等[5]、夏海波等[6]比较了改良型UNITANK工艺与UNITANK工艺的实际运行效果,结果均表明,改良型UNITANK工艺可以获得更高、更稳定的脱氮除磷能力。朱海敏等[5]提出,在处理水量持续超设计负荷15%的情况下,改良型UNITANK出水水质仍可以稳定达到一级A排放标准,且产泥量远低于UNITANK工艺。但是,目前有关改良型UNITANK工艺的报道均未对工艺特性进行探讨。
目前,工艺特性研究普遍基于实验方法开展。然而,受进水、环境条件变化、采样代表性等多因素影响,实验研究面临着局限性,无法全面表征污水处理厂复杂工艺面临的实际问题。污水生物处理系统的数学模拟是利用数学模型类比复杂的生化反应,以寻求其中的过程规律。大量研究[7-8]表明,数学模型可以成功应用于污水处理系统的优化,并指导污水处理系统的运行调控。宋纯金等[9]、董姗燕等[10]、张发根等[4]分别采用数学模拟方法对UNITANK工艺特性进行了模拟分析,证明采用模型研究复杂的交替式工艺的可行性和可靠性,为工艺特性研究提供了新工具。此外,我国城市污水处理厂普遍采用季节性调控策略,大部分污水厂的运行实践表明[11-13],夏季出水水质稳定达标;而冬季,由于水温降低影响微生物的活性,导致系统的生物脱氮除磷能力下降,容易出现出水水质浓度波动大、超标等问题。因此,冬季的运行调控一直是城市污水处理厂运行过程中的难点。本研究以苏州某城市污水处理厂改良型UNITANK工艺为研究对象,针对污水厂冬季普遍存在的运行稳定性差等问题,采用模型分析了改良型UNITANK工艺的周期性运行特征,同时利用高通量测序技术分析了微生物群落组成,旨在为实际污水厂改良型UNITANK工艺冬季运行提供参考。
全文HTML
-
苏州某城市污水处理厂主要接纳生活污水,设计规模1.2×105 t·d−1,采用4组改良型UNITANK工艺。改良型UNITANK出水依次进入高效沉淀池、气水反冲洗滤池、紫外线消毒池,出水执行《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准》(GB 18918-2002)一级A标准。改良型UNITANK工艺冬季进、出水水质如表1所示,冬季出水水质波动较大,运行稳定性仍有待进一步提高。
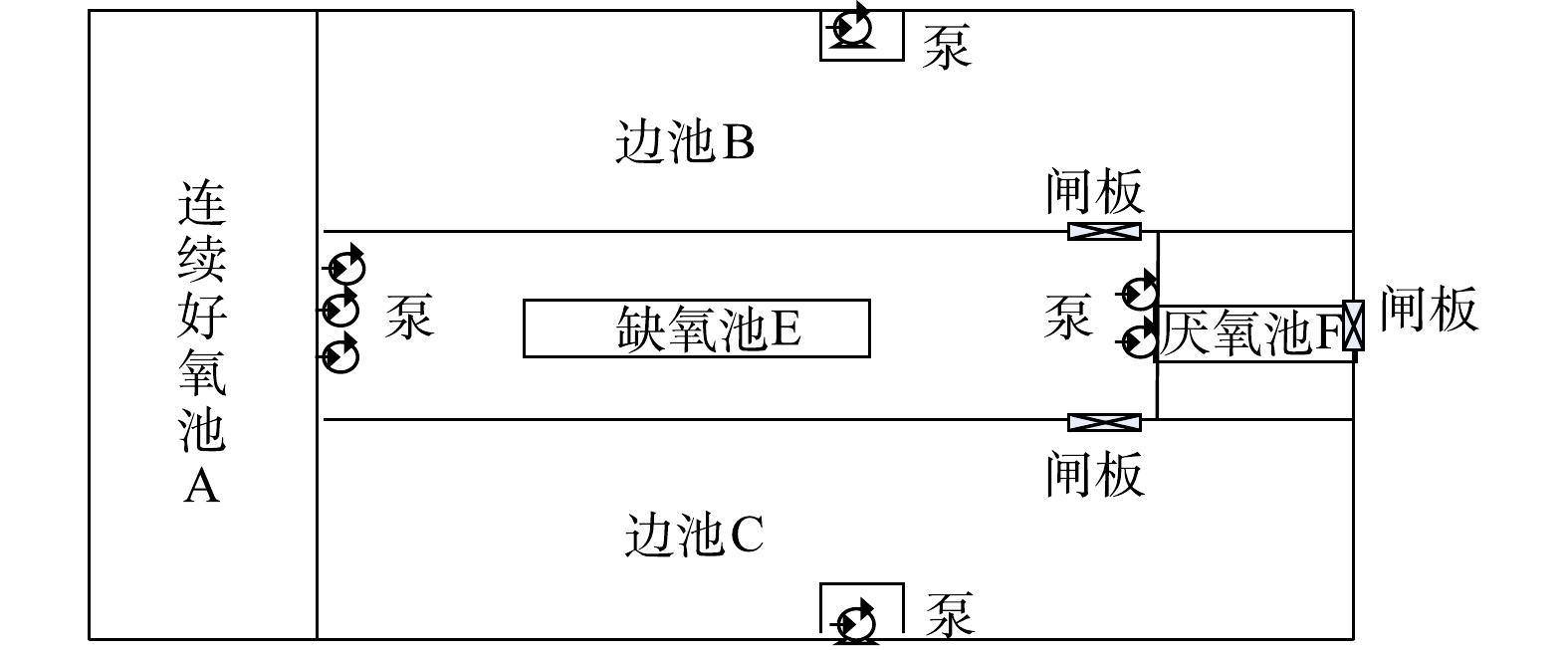
每组改良型UNITANK工艺分隔成5格顺序连通的矩形反应池,分别为1个厌氧池F,1个缺氧池E、1个连续好氧池A、2个边池B和C(图1)。每组平面尺寸为89.85 m×44.85 m,有效水深7.50 m。平均水力停留时间23.72 h,厌氧、缺氧、好氧、边池停留时间分别为1.32、5.63、3.36、13.41 h。厌氧池F与缺氧池E、连续好氧池A与边池之间通过隔墙底部开孔水力连通;缺氧池E至连续好氧池A、缺氧池E到厌氧池F通过泵强制实现混合液流动;边池到缺氧池E通过边池末端底部闸阀控制;剩余污泥由边池两侧的剩余污泥泵定期排放。
改良型UNITANK工艺运行周期为 8 h。上半周期(0~3 h):污水依次进入厌氧池F、缺氧池E、连续好氧池A和边池B(边池B作为曝气池),边池C作为沉淀池(不曝气),出水从边池C通过空气堰排出,剩余污泥从边池C通过泵排放。过渡周期(3~4 h):边池B停止曝气,转换为沉淀模式。污水仍依次进入F、E、A、B,出水从边池C流出。下半周期与上半周期的运行完全一致,通过过渡周期进行衔接。下半周期(4~7 h): B池和C池功能互相转换,边池B作为沉淀池,出水从边池B通过空气堰排出,边池C作为曝气池。过渡周期(7~8 h):边池C停止曝气,转换为沉淀模式。
-
2020年2月中旬取自改良型UNITANK工艺曝气池末端活性污泥,取3个平行样(标记为M1、M2、M3),以代表系统经过冬季低温后微生物群落的分布特征。样品经过30 min静置并离心(4 ℃、8 000 r·min−1、5 min)后保存于−20 ℃冰箱内,用于后续的分子生物学测定。
-
DNA提取采用PowerSoil® DNA Isolation Kit试剂盒,提取后经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测条带完整性。PCR扩增所用引物为338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′)和806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′)。反应体系为20 μL,PCR扩增管中添加DNA模板10 ng,正反向引物各0.8 μL,灭菌水20 μL,d NTP 2 μL,缓冲液4 μL,FastPfu聚合酶0.4 μL。PCR反应程序:首先95 ℃预变性3 min,然后进行27个循环(95 ℃变性30 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸45 s),最后72 ℃延伸10 min。扩增结束后,采用2%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测PCR产物,结果表明,PCR产物条带大小正确,浓度合适,可进行后续实验,委托美吉生物进行Illumina MiSeq高通量测序。
高通量测序获得的原始序列数据经过质控过滤后得到高质量数据,采用USEARCH进行OTU聚类分析,通过贝叶斯算法在97%相似水平对OTU进行物种分类学注释。基于OTU数据,对反映微生物群落丰富度(Sobs, Chao, ACE指数)和多样性(Simpson, Shannon指数)的参数进行统计。
-
氨氮采用纳氏试剂分光光度法测定;
NO−3 -N采用麝香草酚分光光度法测定;TN采用TOC-VCPN总氮测定仪测定;PO3−4 -P采用钼锑抗分光光度计法测定;TP采用钼酸铵分光光度法测定;SS采用重量法测定;COD采用重铬酸钾法测定;DO和温度由德国WTW multi3420测定仪在线监测。 -
以BioWIN软件为平台,选择ASM2D模型为核心机理描述生物碳、氮、磷的去除过程。采用1个非曝气完全混合反应池(CSTR)模拟厌氧池F,4个非曝气CSTR(缺氧池E-1、E-2、E-3、E-4)串联模拟缺氧池E,3个曝气CSTR的串、并联模拟连续好氧池A,5个等体积SBR(边池B-1、B-2、B-3、B-4、B-5/边池C-1、C-2、C-3、C-4、C-5)串联模拟边池B/C的运行,通过分离器的控制实现2组边池的交替运行。
采用该厂改良型UNITANK工艺中2组冬季历史数据进行模型校准和验证,通过调整进水有机物组分(表2)和氨氧化菌最大比生长速率(由默认值0.9 d−1校准为0.7 d−1),改良型UNITANK出水中COD、氨氮、TN、TP、SS模拟值和实测值的绝对误差分别为4.7、1.1、1.6、0.3、2.1 mg·L−1;同时,改良型UNITANK工艺沿程氨氮、
NO−3 -N、溶解性磷酸盐(SPO3−4 -P)模拟值与实测值的变化趋势拟合基本一致(图2(b)),因此,经校准后的模型可以反映该厂改良型UNITANK工艺生物碳、氮、磷的去除过程。
1.1. 改良型UNITANK工艺及处理效果
1.2. 样品采集
1.3. DNA提取,PCR扩增及Illumina MiSeq高通量测序分析
1.4. 水质指标与分析方法
1.5. 模型构建
-
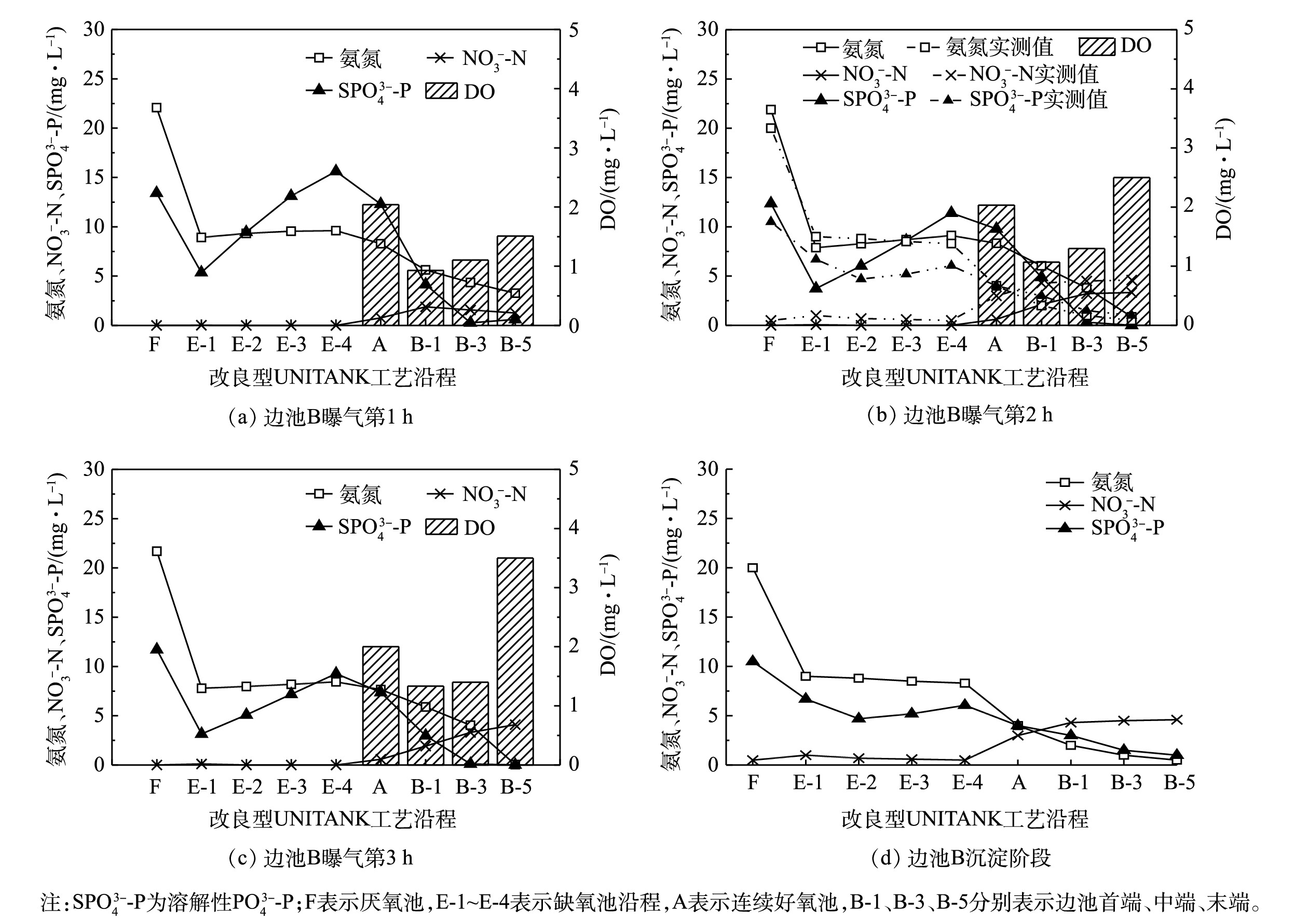
采用经校准和验证后的模型为工具,模拟冬季低温(12 ℃)条件下,在1个运行周期内,改良型UNITANK沿程氨氮、
NO−3 -N、SPO3−4 -P的变化如图2所示。当边池B处于曝气第2 h时,分别采集改良型UNITANK工艺中厌氧池F、缺氧池E沿程、连续好氧池、边池B首端、中端和末端的水样,以确定工艺沿程氨氮、NO−3 -N、SPO3−4 -P实测值的变化。由图2(a)可知,在上半周期边池B曝气第1 h,污水首先流入厌氧池F,并与从缺氧池E首端回流的混合液混合,在厌氧池F内利用搅拌形成局部污泥负荷较高的区域,促进磷的释放,因此,厌氧池F内
SPO3−4 -P升高至13.4 mg·L−1。受边池B到缺氧池E混合液回流的稀释作用影响,氨氮和SPO3−4 -P在缺氧池首端(缺氧池E-1)迅速下降到8.9 mg·L−1和5.4 mg·L−1。整个缺氧池E内的水流呈推流状态,在水流的推动作用下,缺氧池沿程氨氮和SPO3−4 -P逐渐升高至9.6 mg·L−1和15.6 mg·L−1,而沿程NO−3 -N基本维持在0.2 mg·L−1以下。模拟结果表明,改良型UNITANK工艺冬季反硝化彻底。该工艺沿程实测结果(图2(b)) 验证了这一结论。由于反硝化充分,聚磷菌在缺氧池内进行了有效释磷,同时部分有机氮发生了水解,导致SPO3−4 -P、氨氮在缺氧池E沿程升高。在上半运行周期,连续好氧池A和边池B均为曝气池,因此,A、B曝气池沿程氨氮逐渐降低至3.3 mg·L−1,相应NO−3 -N升高至1.9 mg·L−1,SPO3−4 -P降低到0.3 mg·L−1,曝气池内发生了硝化和吸磷过程。当边池B处于曝气第2、3 h及沉淀阶段,沿程氨氮、
NO−3 -N和SPO3−4 -P变化趋势(图2(b)~(d))与曝气第1 h相同,但随着曝气时间的延长,沿程氨氮、SPO3−4 -P逐渐下降。在曝气第3 h,边池B末端(B-5)氨氮接近0 mg·L−1,表明此区域氨氮已彻底转化为NO−3 -N;但此时,边池B前端(B-1)和中段(B-3)氨氮仍高于5 mg·L−1。改良型UNITANK工艺边池沿程均匀曝气,沿程DO分布是曝气量、污染物浓度共同作用的结果。在边池的推流作用下,边池B首端和中段污染物浓度较高,在整个曝气过程中,边池B首端和中段的DO始终保持在0.9~1.5 mg·L−1,末端DO达到1.5~3.5 mg·L−1,因此,均匀曝气导致了边池前端及中段DO偏低,边池末端DO偏高,从而导致上半周期内边池首端和中段的硝化不充分。当工艺进入下半周期,边池B切换为沉淀池,边池B末端通过空气堰出水,改良型UNITANK出水氨氮、
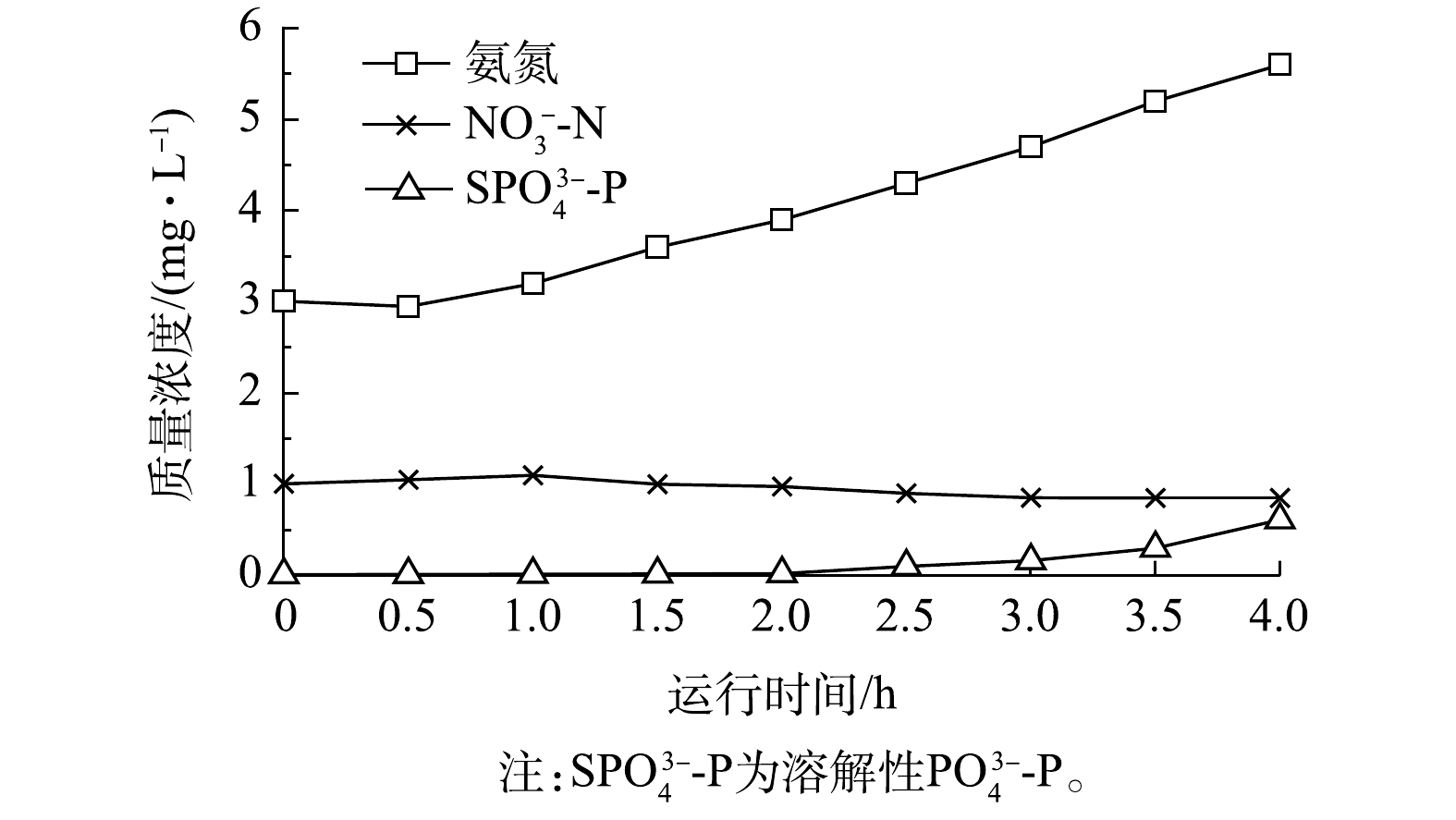
NO−3 -N、SPO3−4 -P变化规律如图3所示。在4 h的出水周期内,出水氨氮、SPO3−4 -P逐时升高,出水NO−3 -N逐渐降低。出水水质的波动特征主要受上半周期边池B沿程污染物分布影响,在边池水流推动作用下,在接下来的出水周期(4 h)内,出水氨氮由3.0 mg·L−1逐渐升高到5.6 mg·L−1,出水SPO3−4 -P升高到0.6 mg·L−1。因此,边池均匀曝气是导致改良型UNITANK工艺冬季出水水质波动大的主要原因。针对推流式边池,加大边池前端的曝气量,同时适当削弱后端曝气量可作为改进措施以解决这一问题。 -
1)多样性分析。污水厂改良型UNITANK工艺冬季活性污泥微生物群落的多样性指数见表3所示。3组污泥样品的有效序列为43 774~43 967,经抽平处理后,3组样品的有效序列标准化至43 774。在97%的相似水平上,覆盖率均高于98%,表明本次测序相对于整体样本的覆盖程度极高,测序结果能够较准确地反映改良型UNITANK内冬季的生物特性。3组污泥样品中的Sobs指数为2 017~2 106,略高于张晓红等[14]和韩文杰等[15]的研究结果。张晓红等[14]针对京津冀地区市政污水厂活性污泥种群结构研究发现,5个污水厂AO或AAO工艺中的Sobs指数在1 006~1 965。韩文杰等[15]在长三角地区污水厂低温季节微生物多样性分析中指出,5个污水厂AAO及其变形工艺中Sobs指数为1 014~1 782。因此,该污水厂改良型UNITANK的微生物多样性较高。与张晓红等[14]和韩文杰等[15]对国内其他污水厂的研究结果相比,该厂3组样品的Shannon指数、ACE指数和Chao指数属于较高水平,Simpson指数显著低于文献报道[14-15]的平均水平,证实了生物多样性在改良型UNITANK工艺中较高。ZHANG等[16]提出,进水水质差异是导致系统内微生物多样性的关键因素。而SEIB等[17]发现,除了进水水质,反应器结构也会对污泥群落结构产生影响。本研究中的污水厂进水水质为典型的城市污水,与张晓红等、韩文杰等[14-15]研究的污水厂进水水质处于类似水平。因此,导致该系统生物多样性较高的原因可能与改良型UNITANK独特的工艺运行方式有关,边池交替式的运行控制模式导致微生物多样性较高。郑向阳等[18]发现,微生物多样性与运行条件有关,同一进水条件下,缺氧段多样性明显高于好氧段。彭永臻等[19]在对城市污水处理厂生物脱氮污泥菌群结构分析中发现,更为复杂的运行方式会导致污水处理系统中生物多样性更高。
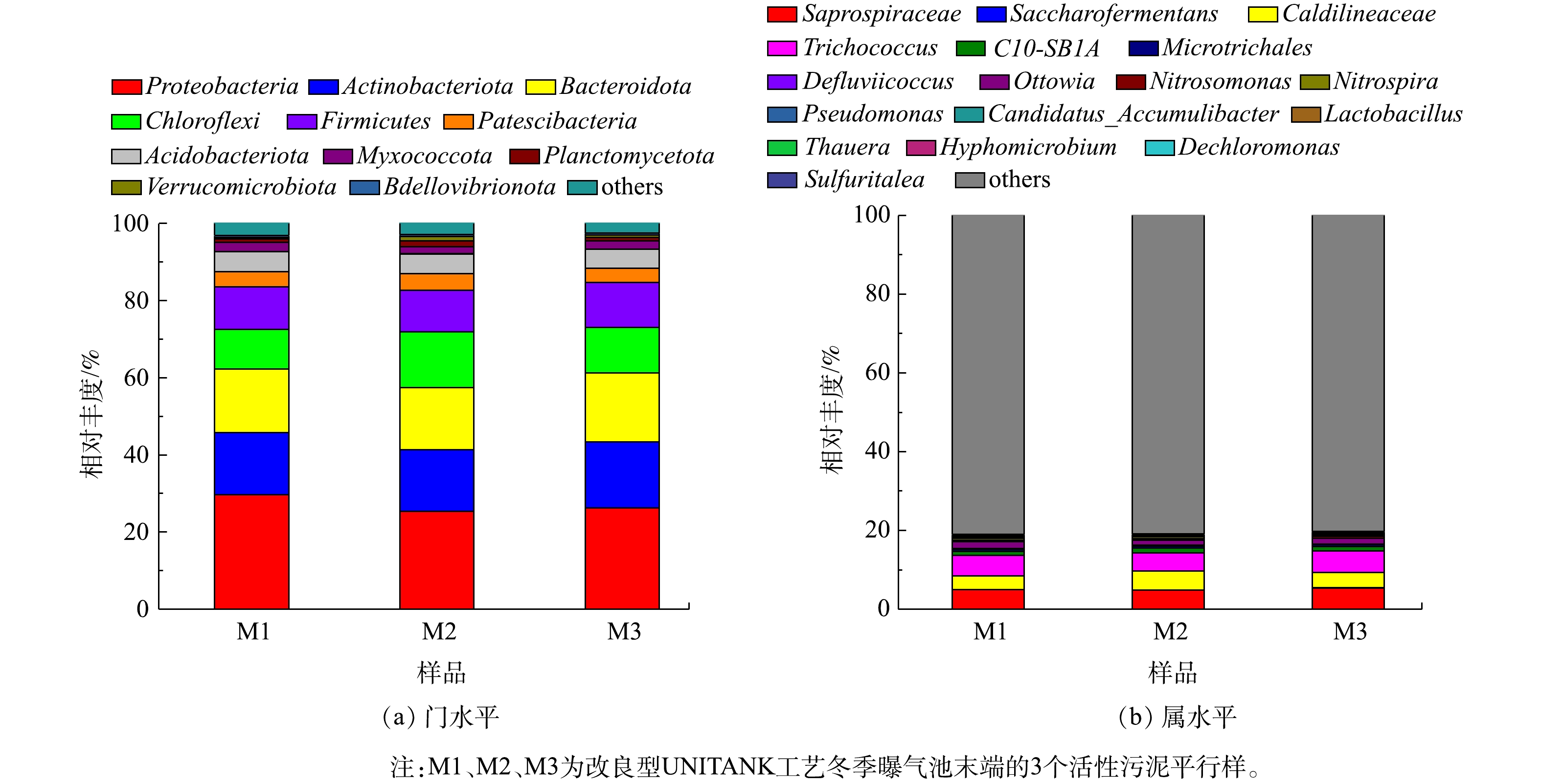
2)物种组成分析。在门水平上,3组污泥样品共检测到48个门,其中,有9种物种的丰度高于1%。由图4可以看出,Proteobacteria、Actinobacteria、Chloroflexi、Bacteroidetes、Firmicutes是3组污泥样品中的主要优势菌群,其总相对丰度达到82.73%~84.76%,与文献报道[14-15]的城市污水厂活性污泥系统中门水平上的微生物组成结论一致。其中,Proteobacteria是样品中丰度最高的菌门,其相对丰度达到25.40%~29.65%;Actinobacteria、Chloroflexi相对丰度分别为15.89%~17.04%、10.31%~14.50%。Proteobacteria和Actinobacteria是生物脱氮除磷和异养生物降解的主要微生物,而Chloroflexi在功能上多与生物除磷有关。王思佳等[20]的研究表明,以乙酸钠为碳源时,会促进Bacteroidetes含量上升。因此,3组污泥样品中门水平上的优势菌群均与生物脱氮除磷功能有关。
在属水平上丰度高于2%的微生物的分析表明,Caldilineaceae、Saprospiraceae、Trichococcus是优势菌属,其相对丰度分别可达3.41%~4.87%、4.83%~5.40%、4.55%~5.52%。 张朝升等[21]的研究表明,Saprospiraceae是以亚硝酸盐为电子受体的反硝化除磷系统中的优势菌种。徐伟峰等[22]的研究表明,延长泥龄,反硝化除磷对系统除磷所起的作用增强。该厂改良型UNITANK工艺冬季的泥龄控制在20 d左右,为Saprospiraceae的生长提供了良好的条件。因此,改良型UNITANK可能存在反硝化除磷现象。有研究[14-15]表明,除了Saprospiraceae,Pseudomonas和Candidatus_Accumulibacter也是污水处理系统中常见的聚磷菌。本研究中,Pseudomonas和Candidatus_Accumulibacter在3组污泥样品中的丰度分别为0.03%~0.05%和0.03%~0.04%,显著低于Saprospiraceae的丰度。Defluviicoccus、Micropruina属于常见的聚糖菌属,在厌氧段会与聚磷菌竞争碳源,从而导致生物除磷效果恶化,这2种菌属在改良型UNITANK工艺冬季污泥样品中的相对丰度仅为0.16%~0.21%、0.51%~0.56%,表明聚糖菌所占比例较低,这与目前的普遍研究结论[13]一致,即在低温条件下,聚磷菌更具竞争优势,而当温度高于20 ℃,聚糖菌的生长占优势。
Nitrosomonas为氨氧化菌(AOB)优势菌属,其功能是将氨氮转化为亚硝酸盐,该菌属在改良型UNITANK工艺内所占比例为 0.31%~0.45%。Nitrospira为亚硝酸盐氧化菌(NOB)优势菌属,其作用是将亚硝酸盐转化为硝酸盐,该菌属所占比例为0.41%~0.60%。在污水处理系统中,常见的NOB菌属包括Nitrospira和Nitrobacter[23]。然而,在改良型UNITANK工艺冬季3组污泥样品中均未检测出Nitrobacter。已有研究[24]表明,Nitrobacter生长速率高,但与底物之间的亲和能力弱,适合生长于基质充足的环境;Nitrospira的生长速率仅为Nitrobacter的1/3,但Nitrospira对基质亲和力更大。因此,在氨氮浓度较低的城市污水处理系统中Nitrospira更具优势。韩文杰等[15]针对长三角地区5座污水厂低温季节微生物检测结果中也指出,在活性污泥系统中Nitrospira为NOB优势菌,相对丰度达0.25%~3.06%,未检测到Nitrobacter。张晓红等[14]在京津冀区域5座城市污水厂的微生物检测中虽发现了Nitrobacter的存在,但其丰度远低于Nitrospira。
2.1. 改良型UNITANK工艺运行特性
2.2. 活性污泥群落结构分析
-
1)改良型UNITANK工艺冬季反硝化充分,均匀曝气导致边池前端和中段硝化不充分,在边池的推流作用下,出水氨氮、
SPO3−4 -P逐时升高。边池均匀曝气是导致改良型UNITANK工艺冬季出水水质波动的主要原因,加大边池前端的曝气量,同时适当削弱后端曝气量可作为解决这一问题的措施。2)改良型UNITANK工艺冬季微生物多样性较高,可能与独特的工艺运行方式有关。Saprospiraceae是优势菌属,其相对丰度可达4.83%~5.40%,工艺内可能存在反硝化除磷现象。Defluviicoccus和Micropruina 2种聚糖菌属的相对丰度仅为0.16%~0.21%和0.51%~0.56%。
3) Nitrosomonas、Nitrospira分别为AOB、NOB的优势菌属,其在改良型UNITANK工艺中的相对丰度分别为0.31%~0.45%、0.41%~0.60%,这2类菌属主要完成了冬季改良型UNITANK工艺脱氮功能。



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: