中药抗菌剂对费氏弧菌的单一及联合毒性效应
Single and Combined Toxicities of Traditional Chinese Medicine Antibacterials on Aliivibrio fischeri
-
摘要: 抗生素滥用所导致的环境问题日益受到人们的关注,寻找传统抗生素的可能替代品迫在眉睫。从中药中提取的具有抗菌活性的化合物(简称中药抗菌剂)因具有资源丰富、抗菌谱广和不良反应低等特点,有望成为未来替代抗生素的关键。因此,有必要探究中药抗菌剂的毒性效应,这可以对未来中药抗菌剂使用后的生态风险提供指导。本文以费氏弧菌作为模式生物,分别测定了大黄素(emodin,EMO)、大黄酸(rhein,RH)、芦荟大黄素(aloe-emodin,AE)和双氢青蒿素(dihydroartemisinin,DHA)4种中药抗菌剂对费氏弧菌的单一和多元联合毒性,同时进行了抑菌作用机理的初步讨论。结果表明,4种中药抗菌剂对费氏弧菌的生物荧光均能产生较为明显的抑制作用,毒性排序是EMO>RH>AE>DHA。而当EMO、RH、AE和DHA混合暴露时,混合物在高浓度区间的联合毒性作用模式均为拮抗,推测是受试中药抗菌剂之间互相竞争性地对NADH脱氢酶产生抑制作用,从而导致对发光反应的抑制作用较单一暴露时减弱。本研究对未来中药抗菌剂单一及联合毒性效应的研究具有积极的推动作用,有望为今后中药抗菌剂的生态风险评价提供参考。Abstract: More and more attention has been paid to the environmental problems caused by the overuse of antibiotics, and it is urgent to seek possible alternatives to traditional antibiotics. Due to the rich resources, wide antibacterial spectrum, and low adverse reactions, traditional Chinese medicine antibacterials (TCM antibacterials for short) are deemed to be the possible substitutes for antibiotics in the future. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the toxic effects of TCM antibacterials, which could provide a guidance for the ecological risks after the use of TCM antimicrobials. In this study, the single and joint toxicities of four TCM antibacterials (including emodin (EMO), rhein (RH), aloe-emodin (AE), and dihydroartemisinin (DHA)) on Aliivibrio fischeri were tested, and the antibacterial mechanism was preliminarily explored. The results showed that the four TCM antibacterials exhibited significant inhibition on the bioluminescence of Aliivibrio fischeri, and the order of toxicity was EMO > RH > AE > DHA. When EMO, RH, AE, and DHA were mixed, the joint toxicities of the mixtures in the high concentration range were antagonism. It was speculated that the TCM antibacterials competitively inhibited NADH dehydrogenase, leading to a weaker inhibitory effect of the mixtures on the luminescence reaction than that of single agent. This study will promote the study of single and joint toxicities of TCM antibacterials in the future, and provide a reference for the ecological risk assessment of TCM antibacterials.
-
Key words:
- TCM antibacterials /
- Aliivibrio fischeri /
- single toxicity /
- joint toxicity /
- bioluminescence /
- antagonism
-
在农业生产中有大量未被完全利用的农药、化肥等可随农田退水一起汇入地表水中。农田退水中有机氮、耗氧有机物(以COD计)、无机磷酸盐等含量丰富[1],且具有碳氮比(C/N)低、易造成面源污染等特点[2],这使水体中氮(N)、磷(P)去除难度加大[3]。乌梁素海作为黄河中上游重要的保水、蓄水和调水湖泊,其补给水源主要是河套灌区的农田退水,其次是流域内入湖工业废水和生活污水[4]。据统计,每年排入乌梁素海的总氮为2 037.23 t,总磷为55.82 t[5]。因此,缓解乌梁素海水体N、P污染显得尤为重要。
人工湿地作为一种强化的生态处理设施,具有净化效果好、易运行管理等优点,在国内外被广泛应用于污染水体的处理[6]。人工湿地是通过植物、基质和微生物间的物理、化学和生物作用完成对进水污染物的降解[7],且不会产生二次污染。因此,运用人工湿地缓解乌梁素海水体的N、P污染是一种更为生态、环保的措施。然而在采用人工湿地处理污水时,常因碳源不足而影响微生物反硝化过程,进而影响对污水的净化效果。因此,外加碳源是强化人工湿地脱氮效果的有效途径[8-12]。常见的有机碳源包括甲醇、乙醇等小分子有机物,但其易被微生物分解和利用,导致消耗量大,且成本较高[13]。而植物碳源具有来源充足、成本低廉、取材方便等优点,故日益受到广泛关注[14]。植物碳源可在浸泡过程中溶出大量的碳(C),析出少量的N、P[15],可为人工湿地提供充足碳源的同时降低系统N、P污染程度。
近年来,关于人工湿地的研究[16-20]逐年增多,对于乌梁素海富营养化的治理也受到人们普遍关注。目前,关于乌梁素海富营养化问题,一方面是从湖泊N、P等营养盐时空分布等方面进行机理上的探究[21-23];另一方面则通过植物修复[24-25]、人工浮岛技术等治理湖泊富营养化[26],或通过生态补水措施改善湖区水质[27]。而对运用人工湿地技术治理乌梁素海富营养化问题的相关研究十分匮乏。因此,本研究通过实验室模拟实验,选择乌梁素海大型优势水生植物芦苇、水葱,经过简单处理、碱泡处理、碱热处理,分析了不同预处理方式下芦苇、水葱2种植物碳源对C、N、P的析出规律,据此选出优质碳源,并进一步探究了添加优质碳源强化垂直潜流人工湿地处理农田退水的效果,以期为后续人工湿地治理乌梁素海农田退水处理提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 植物碳源预处理
芦苇、水葱为人工湿地常见植物[28],是乌梁素海大型优势水生植物[29]。本研究选择以上2种植物做为植物碳源。材料收集后,使用蒸馏水清洗干净,置于50 ℃烘箱烘干至恒重后备用。将恒重后的碳源材料剪碎至1~2 cm并等分为3份:1份不再做任何处理;1份在自然条件下用2%的NaOH溶液浸泡24 h;1份在水浴90 ℃条件下用2%的NaOH溶液浸泡1 h。3种预处理方式分别标记为简单处理、碱泡处理、碱热处理。处理后的碳源材料经过水洗、调pH至中性、50 ℃烘干至恒重后备用。
1.2 碳源静态析出实验
称取经过简单处理、碱泡处理、碱热处理的2种碳源材料各2 g,加250 mL蒸馏水浸泡。每隔2 d更换瓶中蒸馏水,对浸泡液取样,测定浸泡液中COD、TN、TP浓度,计算各组实验中的C、N析出量,以选出最优植物碳源添加至后续人工湿地实验中。每个处理做3组平行。
1.3 人工湿地实验
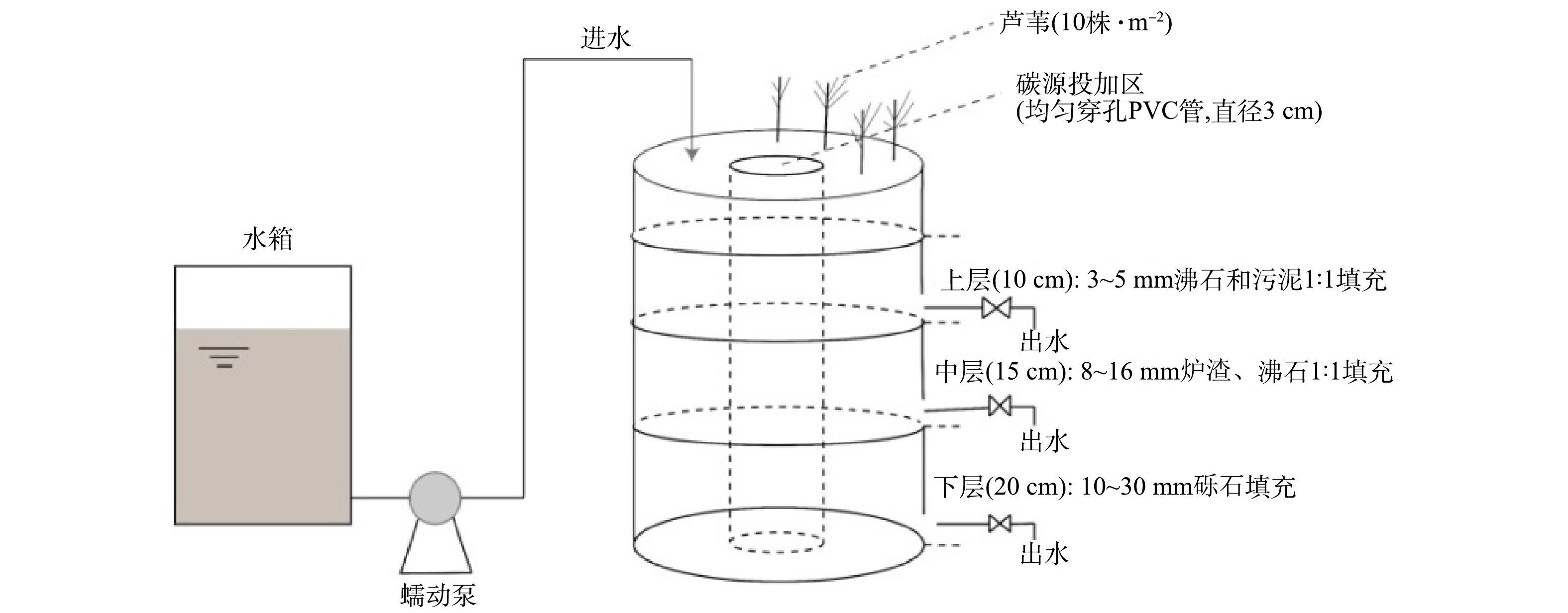
在实验室内,采用有机玻璃(PMMA)材料构建2组构造相同的垂直潜流人工湿地系统(对照组CW0和投加碳源组CW1),其直径为30 cm,高度为55 cm。人工湿地系统示意图如图1所示。湿地系统所填基质高度为45 cm,从下到上依次采用不同基质填充:下层20 cm,铺设粒径为10~30 mm的砾石;中层15 cm,铺设粒径为8~16 mm的炉渣和沸石的1∶1混合物;上层10 cm,铺设粒径为3~5 mm沸石及采自乌梁素海主排干区污泥1∶1混合物。分别在距离顶部15、30、50 cm处设置出水口。湿地系统中间插入直径为3 cm且带有均匀穿孔的聚氯乙烯塑料管,作为植物碳源投加区。种植植物为取自乌梁素海的大小均匀的芦苇,种植密度为10株·m−2。
人工湿地启动前,先用取自乌梁素海主排干区农田退水进行60 d的微生物驯化。从2020年7月中旬开始,采用蠕动泵序批式间歇进水的方式通入实验用水,水力停留时间为3 d,实验用水是通过向自来水中添加C6H12O6、KNO3、NH4Cl、KH2PO4模拟乌梁素海农田退水(C/N=2),配置后的COD为28.00 mg·L−1、TN为12.00 mg·L−1、NH4+-N为1.50 mg·L−1、NO3−-N为10.50 mg·L−1、TP为1.50 mg·L−1。
实验分为2个阶段。第1阶段为探究添加植物碳源对人工湿地净化农田退水效果的影响。CW0为对照组(不添加植物碳源),直接通入实验用水(C/N=2),通过计算在CW1组碳源投加区投加30 g(C/N=4)碱热处理芦苇,测定CW0和CW1组进出水各污染物浓度。第2阶段为探究碳源添加至不同C/N时人工湿地净化效果。经计算,在CW1组分批次投加35 g(C/N=5)、60 g(C/N=7)碱热处理芦苇,测定湿地系统内沿程(0.15、0.3、0.5 m)处进出水各污染物的浓度,探究不同C/N时净化效果,水力停留时间3 d,每3 d进行1次采样分析。
1.4 水质及数据分析
在90 d的实验周期内,每3 d对2组人工湿地的进出水进行1次取样分析。其中DO采用哈希HQ30d53LEDTM测定;pH采用PHS-3CW型号的pH计测定;COD、TN、TP等按照《水和废水监测分析方法》进行测定[30]。数据统计、分析、绘图则使用Excel 2016、Origin 2019和SPSS 26.0软件进行。
1.5 碳/氮源累积析出量计算方法
碳元素累积析出量根据式(1)进行计算[31]。氮元素累积析出量的计算方式与碳元素相同,以TN表征氮元素的析出量[31]。
mk=mk−1+ckv/m植物 (1) 式中:
mk ck m植物 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 不同物质成分的静态析出规律
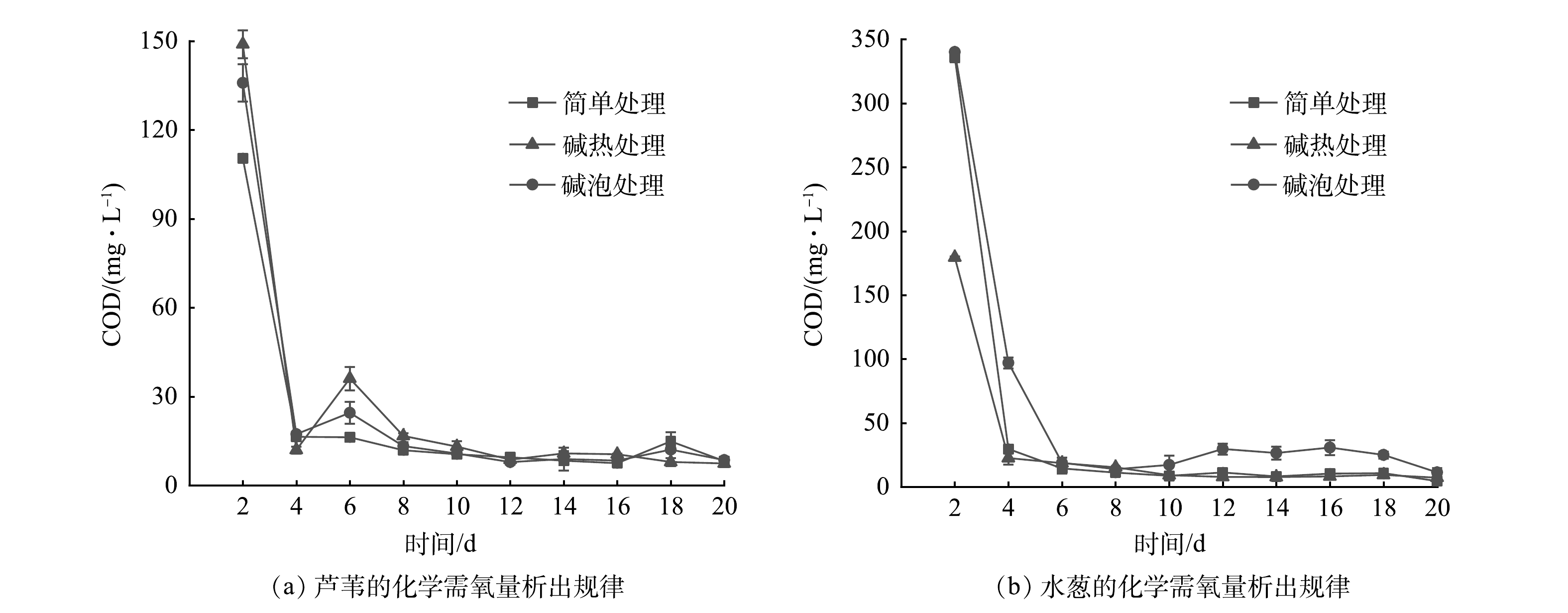
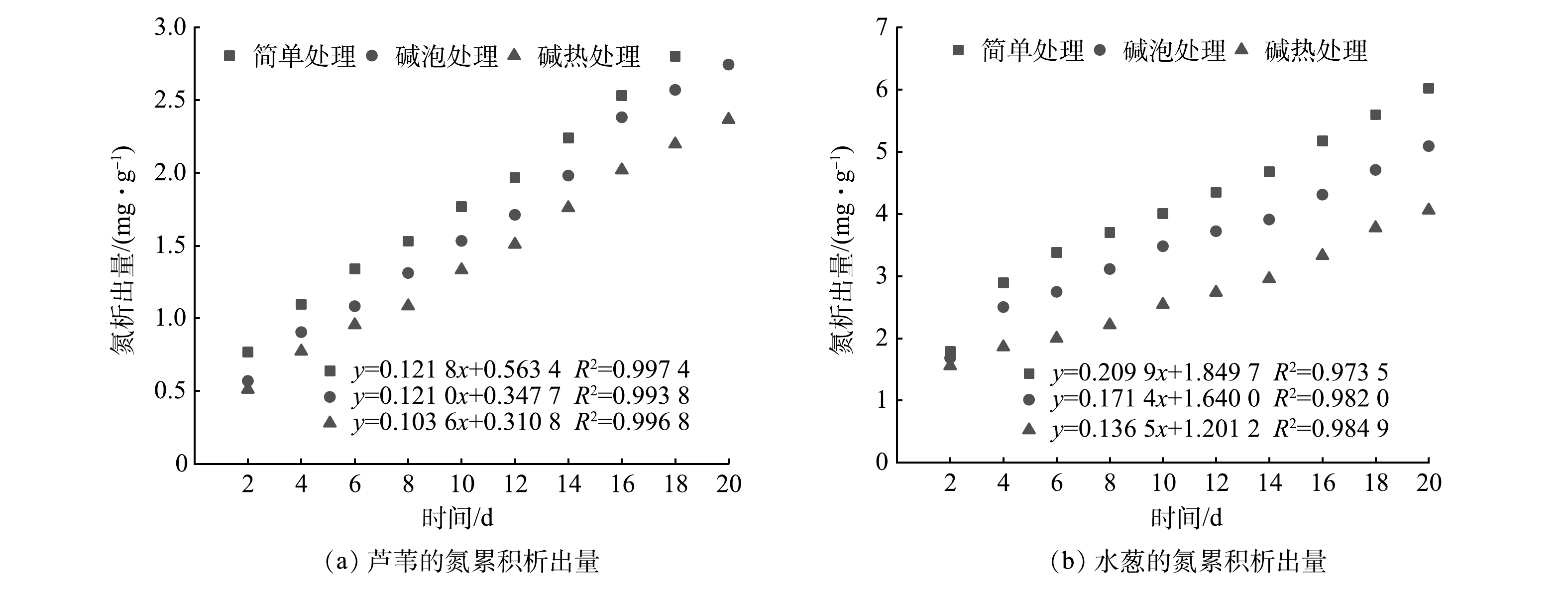
在不同预处理方式(简单处理、碱泡处理、碱热处理)下2种植物碳源(芦苇、水葱)的碳析出规律见图2。由图2可见,2种植物碳源具有相似的析出规律:均在实验开始达到碳最大析出量,在第4天时迅速下降并逐渐趋于稳定。植物析出碳(以COD计)的过程一般分为2个阶段[32]:前期植物表层的糖类、有机酸和易溶性无机盐等水溶性物质快速分解;后期在碱作用下植物体内木质素、纤维素、半纤维素等难分解物质开始分解,且分解速率缓慢。本研究中2种植物碳源的析碳过程符合上述阶段。初期水葱中的COD值显著高于芦苇,可能是水葱表面含有更多的可溶性有机碳和易脱落的有机颗粒物[33],这些物质迅速溶解于水中且析出碳源。芦苇经过简单处理、碱泡处理、碱热处理后的最大碳源析出量分别为110.42、135.89、148.93 mg·L−1;水葱的最大碳源析出量分别为336.01、340.05、179.41 mg·L−1。通过衡量计算得出不同预处理下平均碳源析出量:芦苇分别为21.44、24.81、27.27 mg·L−1,水葱分别为44.52、61.60、28.55 mg·L−1。比较3种不同预处理方式可见:对于芦苇,碱热处理>碱泡处理>简单处理;对于水葱,碱泡处理>简单处理>碱热处理。碱处理的植物有较好的碳源析出量,这是因为碱破坏了木质纤维素的内部酯键,木质纤维素空隙率增加,内部表面积增大,聚合度和结晶度下降,使半纤维素及木质素含量均有一定程度的降低,纤维素含量增加,且碱处理增强了纤维素的水解糖化,从而促进了有机质的析出[34]。对于2种植物,水葱在处理初期碳源析出量较大,可能引起人工湿地系统出水有机物二次污染,而且在浸泡过程中其分解残留物较多,呈絮状分散在浸泡液中,在人工湿地系统中会引起系统堵塞等问题。与水葱相比较,芦苇析出碳量适中且后续问题少,因此,确定碱热处理后的芦苇为最佳碳源用于后续人工湿地实验。
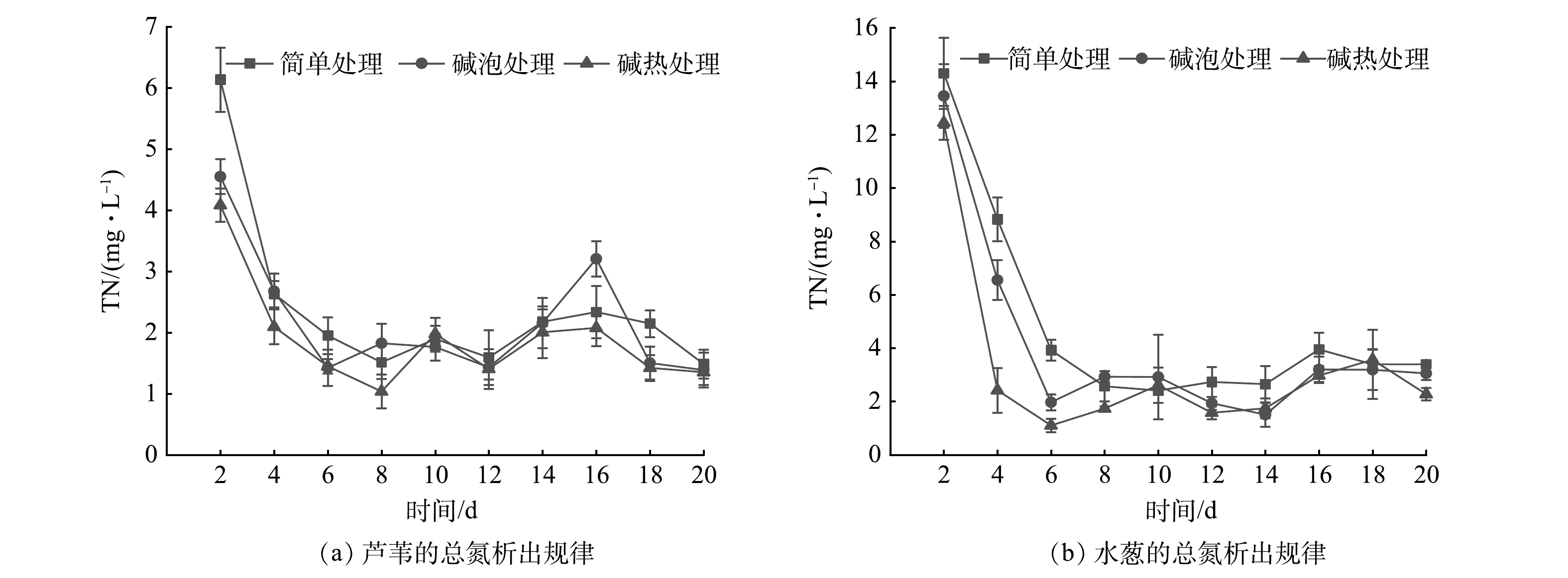
由图3可以看出,在不同预处理方式下2种植物碳源TN的析出规律与COD相似。实验开始即达到TN的最大析出量(4 mg·L−1以上),在第6天迅速下降至2 mg·L−1左右,并逐渐趋于稳定。不同处理方式下2种植物TN初期析出量存在明显差异。初期芦苇最大析出量分别为6.14、4.55、4.09 mg·L−1;水葱分别为14.30、13.45、12.45 mg·L−1。水葱TN析出量较大,N元素的大量快速析出易造成人工湿地系统水质恶化。3种预处理方式下TN平均析出量分别为:芦苇2.39、2.20、1.89 mg·L−1;水葱4.82、4.07、3.25 mg·L−1。2种植物TN平均析出量从大到小依次为简单处理>碱泡处理>碱热处理组。这说明经过碱处理后,植物的纤维素结构被破坏,在预处理过程完成氮元素的提前析出,对水质的负面影响程度降低。总体来看,2种植物经过碱泡、碱热处理后TN平均析出量均有所减少,而经过碱热处理的芦苇TN平均析出量最低为1.89 mg·L−1,故芦苇可作为人工湿地最佳外加碳源。
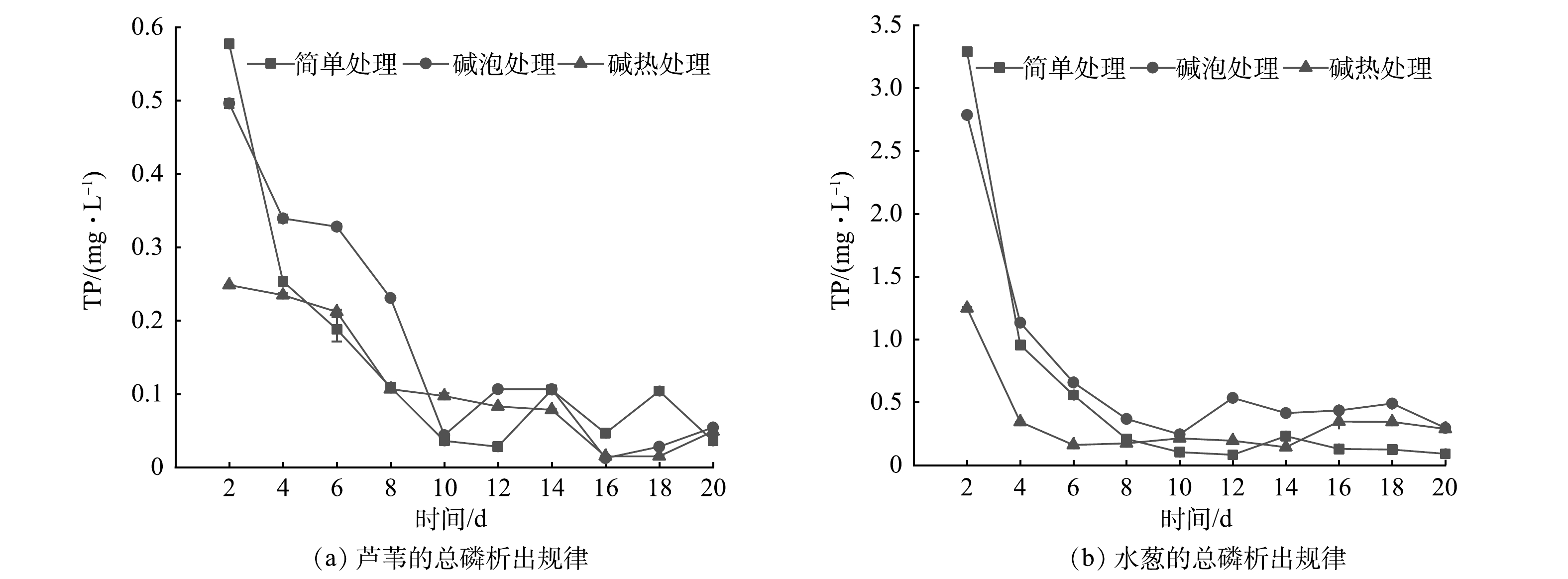
随着植物的分解,其中所含有的磷元素也会析出到水中,因此,考察植物在水中析出的TP量非常必要。不同预处理方式下2种植物碳的TP析出规律见图4。由图4可以看出,水葱TP析出量明显高于芦苇,芦苇在不同预处理方式下TP析出量始终在0.60 mg·L−1以下,并且缓慢下降并趋于稳定;水葱初期TP析出量超过1.00 mg·L−1,第4天迅速降至0.50 mg·L−1左右,并趋于稳定。在不同处理方式下,初期芦苇最大析出量分别为0.58、0.50、0.15 mg·L−1,水葱为3.29、2.79、1.25 mg·L−1;芦苇平均析出量分别为0.18、0.16、0.09 mg·L−1,水葱为0.58、0.74、0.35 mg·L−1,水葱3个处理组TP析出量均很高,而磷元素的快速大量析出易造成人工湿地系统水质富营养化。因芦苇碱热处理组TP析出量最小,可做人工湿地最佳外加碳源。
2.2 碳、氮累积析出特性及累积量的C/N分析
将2.1部分不同预处理下2种植物析出的碳、TN实测值通过1.5部分公式计算得出对应碳、氮累积析出量数值,后用MATLAB软件进行线性拟合。
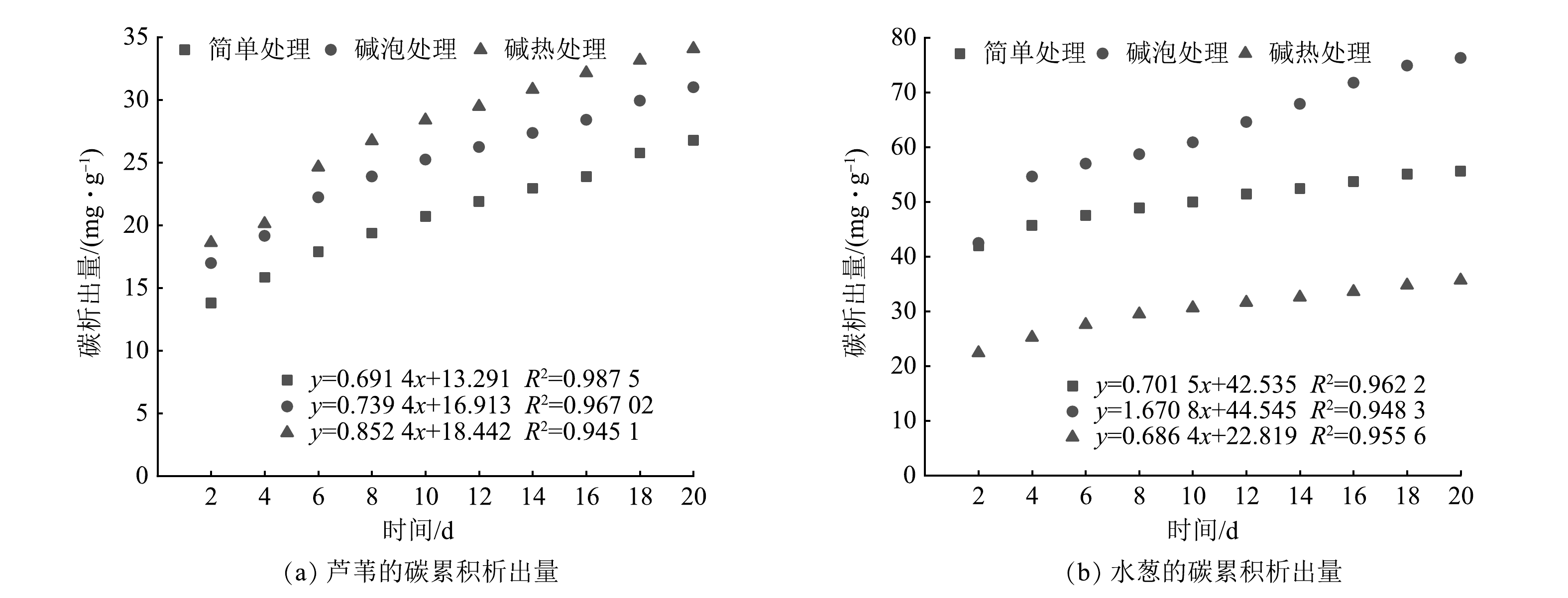
以COD计算碳的累积析出量,经 MATLAB 线性拟合后所得的拟合方程见图5。曲线R2均达0.94以上,表明碳累积析出量的拟合曲线能够反映释碳规律。由图5可知,不同预处理下芦苇碳累积析出量分别为20.90、25.05、27.82 mg·g−1;水葱分别为50.25、62.92、30.37 mg·g−1。碳累积量从大到小的顺序为:芦苇为碱热处理>碱泡处理>简单处理;水葱为碱泡处理>简单处理>碱热处理。对于芦苇,随着时间推移,碱热处理组的碳累积量拟合曲线趋于平行于X轴所需时间较长,具备持久析出碳源的特性,而简单处理和碱泡处理的碳源持久析出特性欠佳;对水葱而言,简单处理和碱热处理持久析出碳源特性欠佳,碱泡处理具备持久析出碳源特性。结合图2可以看出,2种植物碳源前期碳析出速率较快,而后逐渐达到平衡。
以TN浓度计算氮的累积析出量,后将2种植物的氮累积析出量进行线性拟合(图6),拟合度均达0.97以上,说明拟合曲线能够反映实际氮析出规律。由图6可见,经简单、碱泡、碱热处理后芦苇氮累积析出量分别为1.90、1.68、1.45 mg·g−1;水葱分别为4.16、3.53、2.70 mg·g−1。2种植物氮累积析出量由大到小的顺序依次为:简单处理组>碱泡处理组>碱热处理组。总体来看,2种植物经过碱泡处理、碱热处理后氮累积析出量均有所减少,经过碱热处理芦苇氮累积析出量最低,为1.45 mg·g−1。结合图3可知,2种植物前期氮析出速率较快,且随着时间的延长逐渐达到平缓。
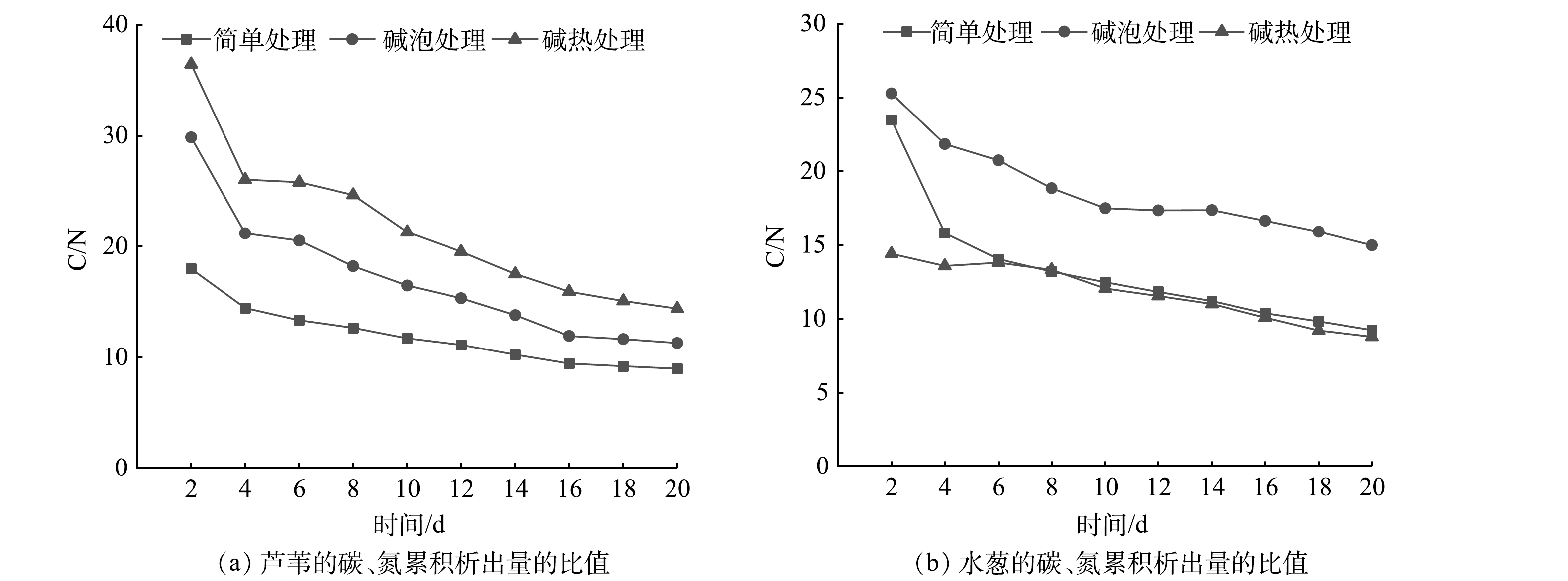
不同预处理下的2种植物在碳、氮元素析出过程中累积析出量的比值(C/N,以COD与TN比值表征)特征见图7。在不同预处理下,芦苇C/N平均值为11.92、17.03、21.67;水葱13.16、18.65、11.79。随着时间的延长,植物固体碳源中的纤维素类物质逐渐分解析出到水中,碳、氮析出量逐渐减少,导致C/N值先下降后趋于平稳。碱处理能够加速碳元素析出,去除大量氮元素,从而有较高的C/N。经过碱热处理的芦苇释所含碳元素较多、氮元素较少,C/N最大为21.67,故可优选为人工湿地外加碳源。
2.3 植物固体碳源添加对人工湿地净化效果影响
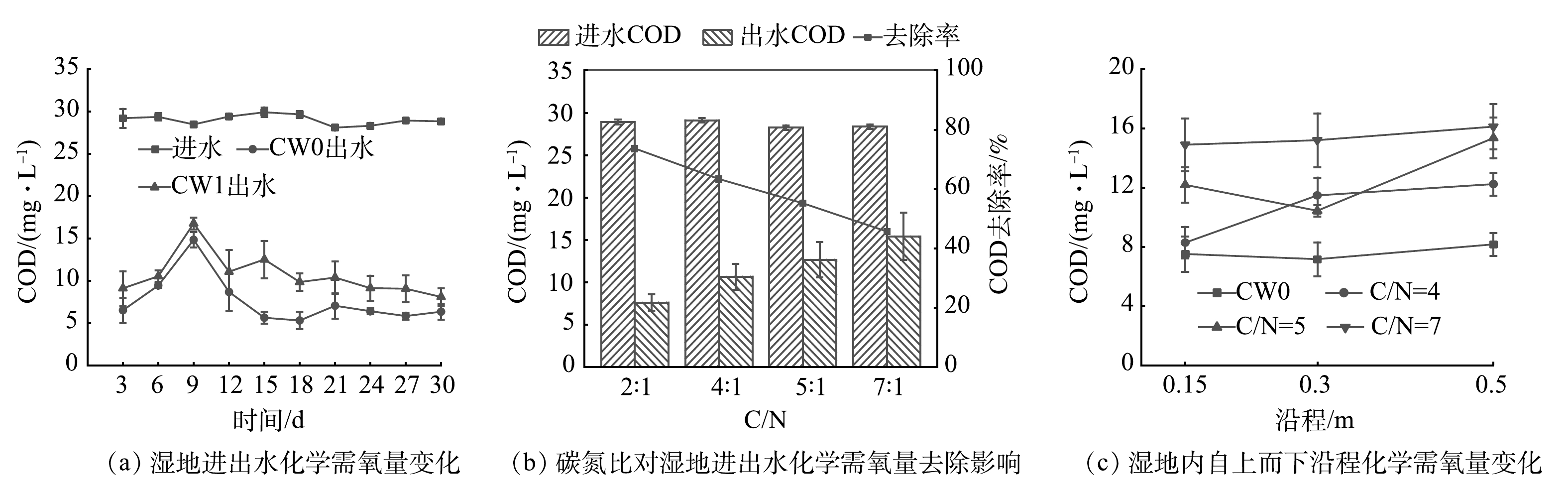
将优选出的经过碱热处理的芦苇投至CW1组中,以探究碳源添加对人工湿地处理污染物的强化效能。湿地进出水COD变化见图8(a)。可以看出,2组人工湿地系统进水COD平均值为29.02 mg·L−1,CW0和CW1出水COD平均值分别为7.62 mg·L−1和10.66 mg·L−1,去除率分别为73.67%和63.38%。2组人工湿地系统出水COD有相似的变化趋势。整个实验期间CW1出水COD始终是高于CW0。CW1出水COD较高的原因是,所添加的植物碳源的半纤维素和纤维素逐渐水解而不断析出有机物[35]。
在CW1中再次分别投加35 g和60 g经碱热处理的芦苇,以调节系统初始水质C/N为5、7,从而探究不同C/N条件下污染物的去除情况。由图8(b)可见,在不同C/N下,其出水COD均低于进水COD,但随着C/N增大,出水COD有所增加。CW0系统C/N为2,COD去除率为73.67%,当C/N为4、5、7时,COD去除率分别为63.38%、55.20%、45.68%。C/N增加会导致系统出水COD增加,去除率降低。这说明过量添加碱热处理的芦苇一定程度上会削弱湿地系统对COD的去除效果,同时也说明C/N是影响人工湿地高效处理COD的关键因素。当湿地系统COD较高时,会导致溶解氧大量减少,从而抑制微生物的硝化去污能力;而当COD过低时,由于碳源不足,反硝化又受到抑制[36],因此,应将外加碳源控制在合适的范围内。
不同C/N条件下湿地内自上而下沿程(0.15~0.5 m)COD变化见图8(c)。可以看出,CW0系统COD浓度沿程各部分基本一致,0.15 m以下COD降低至10 mg·L−1以下,此时系统内碳源严重不足,会影响系统的脱氮效果。当C/N为4、5、7时,湿地内沿程COD均高于CW0,而且系统底层(0.5 m)COD略高于中上层,微生物反硝化所需碳源更充足。
图9(a)反映了2组人工湿地进出水TN的变化规律。可以看出,2组人工湿地进水TN的平均质量浓度为12.01 mg·L−1,CW0和CW1出水TN的平均质量浓度分别为6.80 mg·L−1和3.35 mg·L−1。结合图9(a)和图9(b)可知,CW0和CW1 中的TN平均去除率分别为43.72%和72.00%,CW1显著高于CW0(P<0.05)。由此可知,植物碳源的添加增强了湿地系统对TN的去除。这与晋凯迪等[37]研究结果一致,证明了植物碳源调控提高人工湿地脱氮效果的可行性与高效性。
不同C/N条件下进出水TN浓度及去除率见图9(c)。CW0的TN去除率最低为43.72%,C/N从4提高到7,TN去除率先升高后降低,分别为72.00%、75.67%、69.94%。 C/N为7时的TN去除效果降低,是由于碳源投加量较大,随着反应进行,系统内溶解氧被逐渐消耗,使硝化反应受到抑制,并且添加量较大会导致植物析出氮素增多,从而影响TN去除效果。当C/N较低时,会造成人工湿地系统中电子供体不足,抑制微生物反硝化,从而降低了人工湿地系统脱氮效率[38]。李晓晨等[39]指出,满足完全反硝化的C/N在4~15,但C/N会随着人工湿地的运行情况、碳源类型等不同而发生变化,所以,人工湿地最适C/N比的探讨需要针对某一特定情况进行研究。本实验中根据TN去除效果可知,其最适C/N为5。
图9(d)反映了添加碳源至不同C/N时湿地自上而下沿程(0.15~0.5 m)TN浓度的变化情况。可以看出,TN平均浓度沿程逐渐降低,去除率则沿程逐渐升高,底层(0.5 m)脱氮效果好于中上层。其可能的影响因素是溶解氧,底层溶氧浓度较低,更利于微生物进行反硝化作用脱氮。CW0系统因缺乏碳源,不能为微生物反硝化作用提供充足的电子供体,导致其脱氮效果较差,沿程TN浓度降低缓慢。添加C/N为4、5、7时的CW1系统在0.15 m以下TN浓度持续降低,明显低于CW0,脱氮效率较高。C/N=5的系统TN浓度沿程降低幅度最大,其次为C/N=7系统、C/N=4系统、CW0系统。
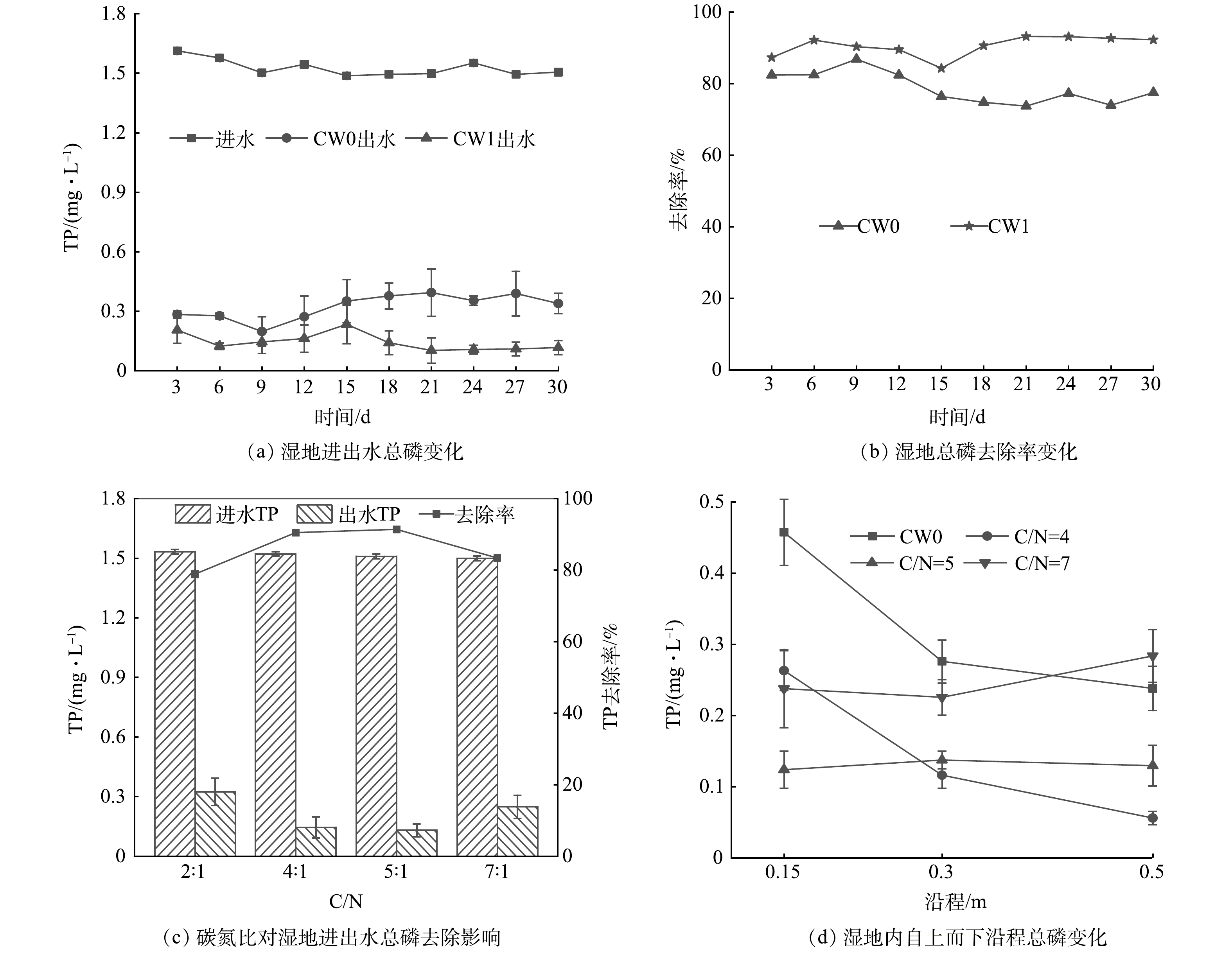
图10(a)描述了2组人工湿地进出水TP的变化规律。可以看出,进水的TP平均浓度为1.53 mg·L−1,CW0和CW1出水TP的平均浓度分别为0.32 mg·L−1和0.15 mg·L−1,结合图10(b)可知,平均去除率分别为78.86%和90.45%,CW1的TP去除率显著高于CW0(P<0.05)。人工湿地对磷的去除主要是通过基质吸附、微生物以及植物吸收等作用实现。在人工湿地运行初期,因植物生长密度较低,致使其发挥的作用较低,而在基质吸附能力较差的情况下,微生物的除磷作用则更为重要[40]。同时,在厌氧条件下,兼性反硝化细菌能够利用硝态氮作为电子受体,可产生与氧同样的摄磷作用,从而能将反硝化脱氮与生物除磷2个相互独立的过程有机地联合在一起[41]。通过在人工湿地中添加植物碳源,系统中反硝化菌和聚磷菌都可获得充足的碳源进行反硝化和吸磷,进而同步提高了人工湿地的脱氮除磷效果。
从图10(c)可以看出不同C/N条件下湿地出水TP浓度及去除率。CW0的TP去除率最低为78.86%,当C/N从4提高到7时,TP去除率先升高后降低,分别为90.45%和91.37%、83.39%。当C/N提高到7时,因为过量的碳会消耗溶解氧,从而影响聚磷菌吸磷,使TP去除率降低。湿地系统内添加的植物碳源不仅为微生物反硝化作用提供电子供体,还可以作为微生物生长的载体,故随反应时间的持续,湿地系统内微生物量逐渐增大,从而加大了对湿地系统内P元素的吸收[42]。结合图9(c)可知,外加碳源至C/N为5时,湿地系统内的TN、TP去除效果较好,达到了同步强化脱氮除磷的目的。
不同C/N下湿地内自上而下沿程(0.15~0.5 m)TP浓度的变化情况见图10(d)。可以看出,C/N为4和5的系统TP平均浓度随沿程低于CW0,碳源的添加强化了湿地系统的TP去除效果。在CW0及C/N为4的湿地系统内,二者TP去除效果随沿程增加而增强,底层(0.5 m)去磷效果最好;在C/N为5的湿地系统内,自上而下沿程TP的去除效果相差不大,且效果较好,为最适碳氮比。C/N为7的系统因碳源增加底层除磷效果变差,溶氧可能是限制因素。
3. 结论
1)2种植物碳源经简单处理、碱泡处理和碱热处理后,依据其COD、TN、TP的平均析出量可知,碱热处理的芦苇能提供大量碳源,氮、磷析出较少,可作为人工湿地的优质外加碳源,且具备持久析出碳源的特性。
2)人工湿地系统中添加碱热处理的芦苇时,在不显著增加系统出水COD的前提下,总氮、总磷平均去除率可达75.67%、91.37%,显著提高了人工湿地的脱氮除磷能力。
3)通过添加不同量植物碳源以调控初始水质C/N,发现植物碳源添加的最适C/N为5,此时可达到同步强化脱氮除磷的目的。
4)由沿程(0.15~0.5 m)变化可知,在碳源充足的情况下,TN、TP在人工湿地底层的去除效果好于中上层,底层微生物反硝化作用强,可促进系统脱氮。其中,氧气可能是脱氮的限制因素之一。
-
Deng Y, Liu J Y, Peters B M, et al. Antimicrobial resistance investigation on Staphylococcus strains in a local hospital in Guangzhou, China, 2001-2010[J]. Microbial Drug Resistance, 2015, 21(1):102-104 Peng L C, Kang S, Yin Z Q, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of berberine against Streptococcus agalactiae[J]. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 2015, 8(5):5217-5223 Chinnam N, Dadi P K, Sabri S A, et al. Dietary bioflavonoids inhibit Escherichia coli ATP synthase in a differential manner[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2010, 46(5):478-486 Ma F, Chen Y, Li J, et al. Screening test for anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of traditional Chinese herbal medicines[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2010, 16(44):5629-5634 Wu C M, Cao J L, Zheng M H, et al. Effect and mechanism of andrographolide on the recovery of Pseudomonas aeruginosa susceptibility to several antibiotics[J]. Journal of International Medical Research, 2008, 36(1):178-186 黄秀凤. 中药提取物及其化学成分抑菌作用的研究进展[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2007, 7(5):370-371 邓丽红, 谢臻, 麦蓝尹, 等. 蒽醌类化合物抗菌活性及其机制研究进展[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2016, 25(21):2450-2455 Deng L H, Xie Z, Mai L Y, et al. Advances in studies on antibacterial activity and mechanism of anthraquinone compounds[J]. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 2016, 25(21):2450-2455(in Chinese)
刘静, 王丽. 大黄素的研究进展[J]. 中国药房, 2014, 25(35):3351-3354 Azelmat J, Larente J F, Grenier D. The anthraquinone rhein exhibits synergistic antibacterial activity in association with metronidazole or natural compounds and attenuates virulence gene expression in Porphyromonas gingivalis[J]. Archives of Oral Biology, 2015, 60(2):342-346 Smolarz H D, Swatko-Ossor M, Ginalska G, et al. Antimycobacterial effect of extract and its components from Rheum rhaponticum[J]. Journal of AOAC International, 2013, 96(1):155-160 Li B, Yao Q, Pan X C, et al. Artesunate enhances the antibacterial effect of β-lactam antibiotics against Escherichia coli by increasing antibiotic accumulation via inhibition of the multidrug efflux pump system AcrAB-TolC[J]. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2011, 66(4):769-777 任皓, 王金荣, 陈行杰, 等. 应用发光细菌法检测饲用抗生素单一及联合毒性的研究[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2011, 47(21):49-53 Ren H, Wang J R, Chen X J, et al. Primary research on single and combined toxicity of antibiotics in feeds by luminescent bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2011, 47(21):49-53(in Chinese)
Wang D L, Wu X D, Lin Z F, et al. A comparative study on the binary and ternary mixture toxicity of antibiotics towards three bacteria based on QSAR investigation[J]. Environmental Research, 2018, 162:127-134 阎鹏, 孙礼. 利用发光菌快速检测环境污染物急性毒性的研究概况[J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2001, 18(4):250-252 Yan P, Sun L. Survey of study on rapid determination of acute toxicity of environmental pollutants by luminescent bacteria[J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2001, 18(4):250-252(in Chinese)
González Barrios A F, Zuo R J, Hashimoto Y, et al. Autoinducer 2 controls biofilm formation in Escherichia coli through a novel motility quorum-sensing regulator (MqsR, B3022)[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 2006, 188(1):305-316 De Zwart D, Slooff W. The Microtox as an alternative assay in the acute toxicity assessment of water pollutants[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 1983, 4(2):129-138 刘树深, 刘玲, 陈浮. 浓度加和模型在化学混合物毒性评估中的应用[J]. 化学学报, 2013, 71(10):1335-1340 Liu SS, Liu L, Chen F. Application of the concentration addition model in the assessment of chemical mixture toxicity[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71(10):1335-1340(in Chinese)
Faust M, Altenburger R, Backhaus T, et al. Joint algal toxicity of 16 dissimilarly acting chemicals is predictable by the concept of independent action[J]. Aquatic Toxicology, 2003, 63(1):43-63 Thorpe K L, Gross-Sorokin M, Johnson I, et al. An assessment of the model of concentration addition for predicting the estrogenic activity of chemical mixtures in wastewater treatment works effluents[J]. Environmental Health Perspectives, 2006, 114(Suppl 1):90-97 Wu Y W, Gao W Y, Xiao X H, et al. Calorimetric investigation of the effect of hydroxyanthraquinones in Rheum officinale Baill on Staphylococcus aureus growth[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2005, 429(2):167-170 Hastings J W, Potrikusv C J, Gupta S C, et al. Biochemistry and physiology of bioluminescent bacteria[J]. Advances in Microbial Physiology, 1985, 26:235-291 Jablonski E, DeLuca M. Studies of the control of luminescence in Beneckea harveyi:Properties of the NADH and NADPH:FMN oxidoreductases[J]. Biochemistry, 1978, 17(4):672-678 Meighen E A. Bacterial bioluminescence:Organization, regulation, and application of the lux genes[J]. FASEB Journal, 1993, 7(11):1016-1022 陈春麟, 何冰芳, 陈琼华. 中药大黄的生物化学研究——蒽醌衍生物对线粒体NADH氧化酶和琥珀酸氧化酶的抑制作用[J]. 生物化学杂志, 1988, 4(1):36-41 Chen C L, He B F, Chen Q H. Biochemical study of Chinese rhubarb inhibition of anthraquinone derivatives on NADH oxidase and succinate oxidase of mitochondrion[J]. Chinese Biochemical Journal, 1988, 4(1):36-41(in Chinese)
韩冬, 宋志英, 付正卿, 等. 三种羟基蒽醌类药物与溶菌酶的作用及其构效关系研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2014, 26(5):679-684 Han D, Song Z Y, Fu Z Q, et al. Study on interaction and structure-activity relationship between three kinds of hydroxyanthraquinone drugs and lysozyme[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2014, 26(5):679-684(in Chinese)
陈蓉蓉. 光谱法研究四种青蒿素类抗疟药与人血清白蛋白的相互作用[D]. 广州:暨南大学, 2013:52-64 Chen R R. Spectrometric studies on the interaction between four anti-malarial drugs of the artemisinins and human serum albumin[D]. Guangzhou:Jinan University, 2013:52 -64(in Chinese)
Gautam P, Upadhyay S K, Hassan W, et al. Transcriptomic and proteomic profile of Aspergillus fumigatus on exposure to artemisinin[J]. Mycopathologia, 2011, 172(5):331-346 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2614
- HTML全文浏览数: 2614
- PDF下载数: 72
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: