黑臭底泥土著微生物促生对磷的影响
Effect of indigenous microbial promoting on phosphorus in black-odor sediment and overlying water
-
摘要: 土著微生物促生是一项低成本高效率的河湖黑臭底泥原位修复技术,然而向底泥中投加药剂可能会影响上覆水水质。为探讨该技术对水环境的不利影响,实验研究了城市湖泊黑臭底泥修复过程中上覆水中磷浓度和底泥中磷含量及形态的变化。结果表明,在投药深度为泥面以下15 cm,微生物营养剂(BE)和生物解毒剂(MT)的投加量分别低于60 mL/m3和70 mL/m3的条件下,上覆水总磷(TP)浓度低于地表水环境质量Ⅲ类(湖库类)标准值。投加微生物促生剂(BE和MT)导致上覆水磷含量升高,并促进了上覆水中藻类的增长。复配投加硝酸钙能减少上覆水中磷含量及藻类生物量,从而抑制微生物促生剂对上覆水磷浓度的影响。另外,投加微生物促生剂及硝酸钙到底泥中后,底泥磷含量以及磷形态组成的变化均不明显。Abstract: The indigenous microbial promotion is an in situ black-odor sediment remediation technology with low cost and high efficiency which is applied to river or lake. However, the adding of agent to the sediment may affects the quality of overlying water. In order to analyze the adverse effects of this technology, we determined the changes of phosphorus (P) contents and its fractions in the overlying water and black-odor sediment from an urban lake. Results showed that when the adding dose of Bio Energizer (BE) and Micatrol (MT) to sediment was 60 mL/m3 and 70 mL/m3, respectively, the total phosphorus content (TP) in the overlying water was lower than 0.05 mg/L (Grade Ⅲ value of National Environment Quality Standard for Surface Water in China). However, the adding of microbial nutrient (BE and MT) to sediment still led to the increase of TP as well as the proliferation of algae in the overlying water. Adding of Ca(NO3)2 significantly reduced the TP and algae biomass in the overlying water, which controlled the effects of adding microbial nutrient to sediment on the TP in overlying water. In addition, the adding of both Ca(NO3)2 and microbial nutrient had no obvious effect on the TP and P fractions in the sediment.
-
Key words:
- black-odor /
- sediment /
- Ca(NO3)2 /
- indigenous microbial promotion /
- phosphorus
-
贻贝是一种常见的海洋生物,它们可以强力附着在水体环境中有机或无机基底材料的表面[1]。研究发现,贻贝黏液中的黏附蛋白(mussel adhesive proteins,MAPs)是贻贝能够迅速在潮湿环境中附着在各种材料表面的主要成分[2]。而黏附蛋白中起到黏附作用的关键物质是3,4-二羟基苯丙氨酸(3,4-dihydroxylphenylalanine,L-多巴或L-DOPA)和含赖氨酸蛋白质[3]。2007年,Lee等的研究团队在表面化学的研究中发现,多巴胺(dopamine,DA)在含氧碱性水溶液中会发生自聚反应,并利用共价和非共价键作用在材料表面生成具有极强黏附性的聚多巴胺包覆层,该涂层拓宽了材料表面功能化的新途径[4]。聚多巴胺包覆层拥有大量的邻苯二酚和胺基等功能基团,为吸附结合目标物提供了大量活性位点。目前,聚多巴胺功能材料已广泛运用在生产生活的多个领域[5]。在环境护方面,聚多巴胺功能材料凭借着优异的吸附催化性能,成为净化去除水体中重金属离子和有机污染物的研究热点[6-7]。
1. 聚多巴胺的形成-附着机理(Formation-adhesion mechanism of polydopamine)
1.1 多巴胺的结构性质
多巴胺是一种生物神经递质,它的化学名称为4-(2-乙氨基)-苯-1,2-二酚(4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-diol),属于儿茶酚胺类物质[8]。在脱羧酶的作用下,L-多巴可转化形成多巴胺[9]。作为L-多巴的衍生物,多巴胺的化学结构中的邻苯二酚和氨基官能团为后续实现材料的修饰奠定了基础[10]。
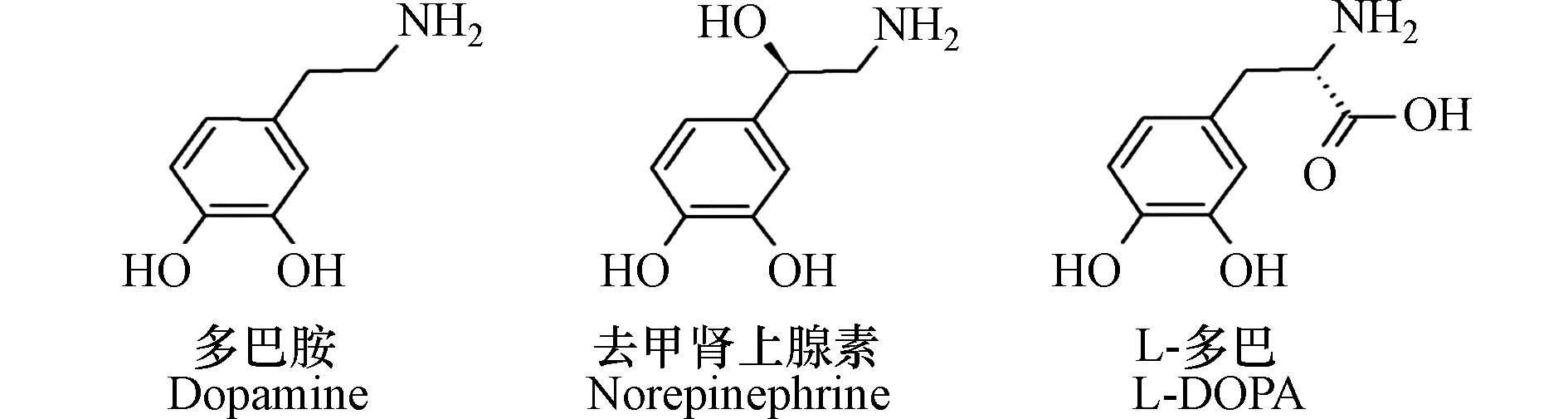
儿茶酚胺类的不同结构(引自Barclay等[10])如下:
1.2 聚多巴胺的形成-附着机理
多巴胺在氧气的参与作用下,能够在弱碱性水溶液中自发反应生成聚合物—聚多巴胺(polydopamine,PDA)[11]。目前,关于聚多巴胺形成机理的研究众说纷纭,尚没有定论。主流的聚多巴胺形成理论包括 “氧化-聚合”机理、“真黑色素”形成理论和“共价-非共价”共同作用机理等[12-18]。
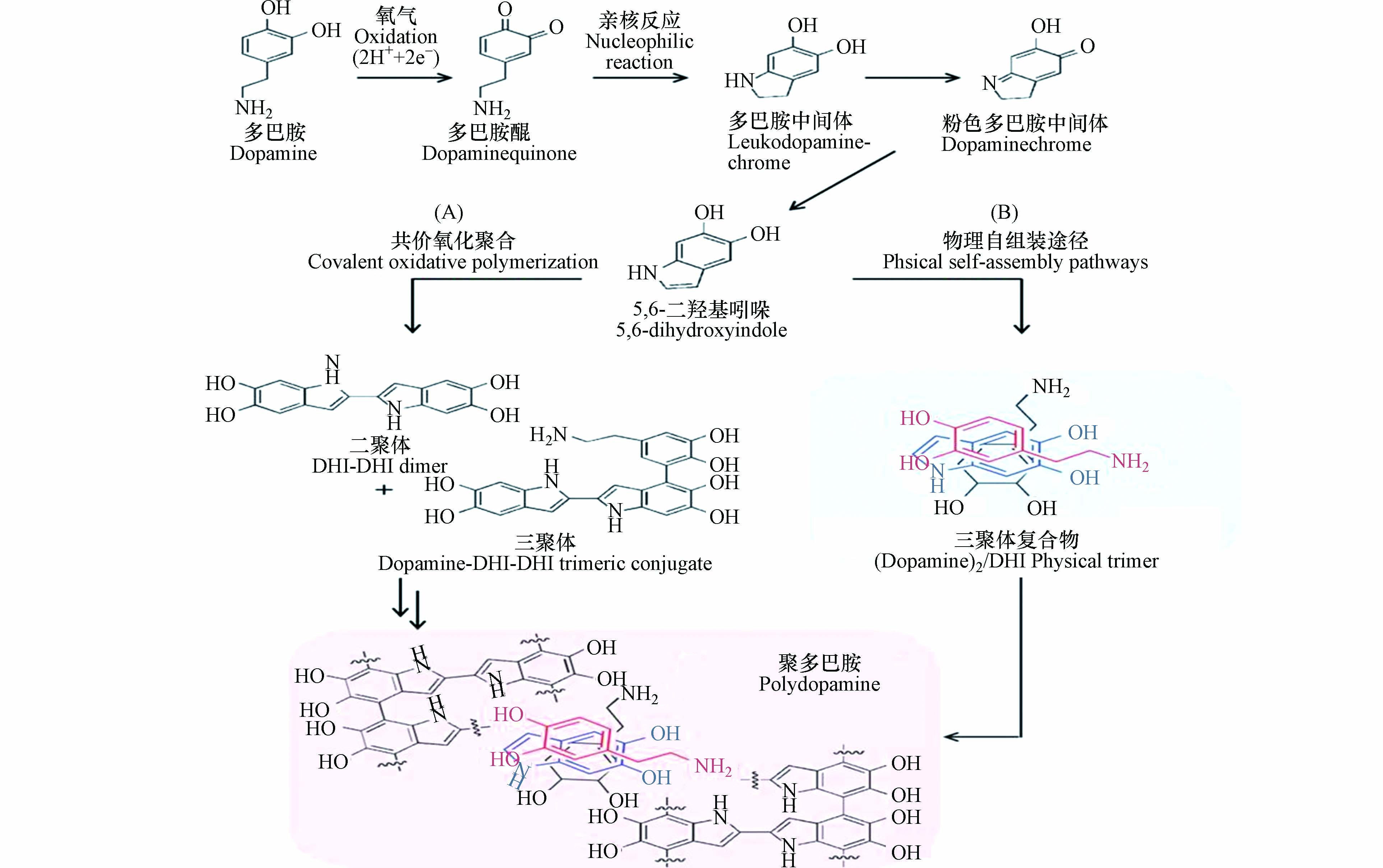
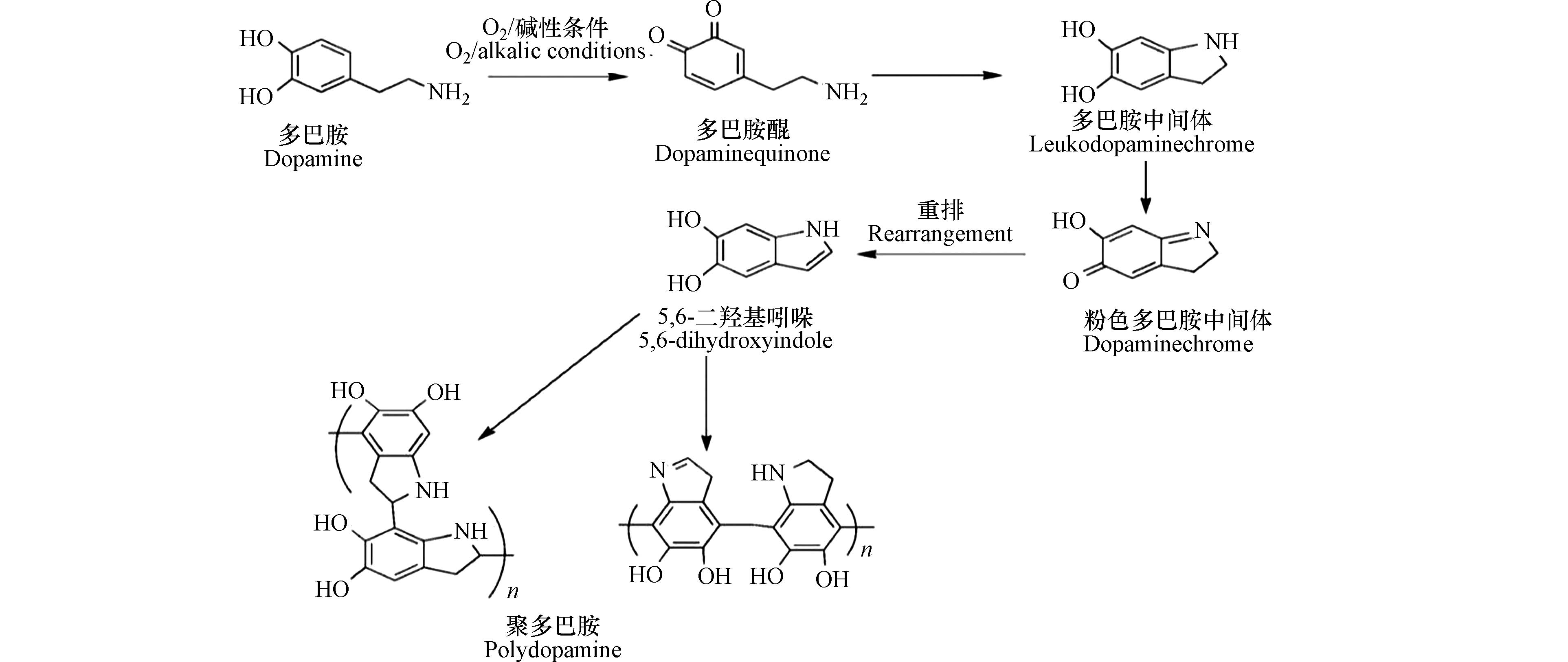
如图1所示,学者们提出了“氧化-聚合”机理:在反应过程中,多巴胺单体的邻苯二酚基团首先被氧化,生成结构性质不稳定的多巴胺醌(dopaminequinone)。多巴胺醌会发生内环化反应生成无色的多巴胺中间体(leukodopaminechrome)。该中间体发生氧化形成粉红色的多巴胺中间体(dopaminechrome),粉色中间体继续发生氧化重排生成5,6-二羟基吲哚(5,6-dihydroxyindole,DHI);5,6-二羟基吲哚与其产物5,6-醌再发生支化反应形成二聚体或其他低聚体,这些低聚体最后通过交联形成聚多巴胺包覆层[12-13]。多巴胺在溶液中的自聚反应伴随着颜色的变化,溶液颜色随着时间的延长由无色变为棕色,最终变为黑色[14]。针对该现象,科研人员通过模拟分析大量的分子数据,提出聚多巴胺的形成主要是依赖反应前期生成的低聚物,且这些受共价键束缚的低聚物以 π-π 键的相互作用堆积在一起,形成类似石墨结构的层状聚集体[15]。
Dreyer等也证明了聚多巴胺的形成与非共价键力(π-π 键、氢键和电荷转移)的作用密切相关,并且赋予了聚多巴胺在水溶液中较强的稳定性[16]。因此,大部分学者认为聚多巴胺的形成是非共价键和共价键共同作用的产物。如图2所示,Hong等[17]提出了“共价-非共价”共同作用机理:聚多巴胺是由共价聚合和非共价自组装共同作用形成的;反应前期生成的5,6-二羟基吲哚之间发生氧化聚合形成二聚体,二聚体再和一个多巴胺单体分子结合生成三聚体(DA-DHI-DHI);同时,两个多巴胺分子与5,6-二羟基吲哚通过自组装形成三聚体复合物(DA2/DHI)。DA2/DHI具有一定的生物毒性,但因其大部分被固定在聚多巴胺中,使得聚多巴胺具有较好的生物相容性。同时DA2/DHI也是聚多巴胺的形成过程中黑色沉淀产生的原因[18]。
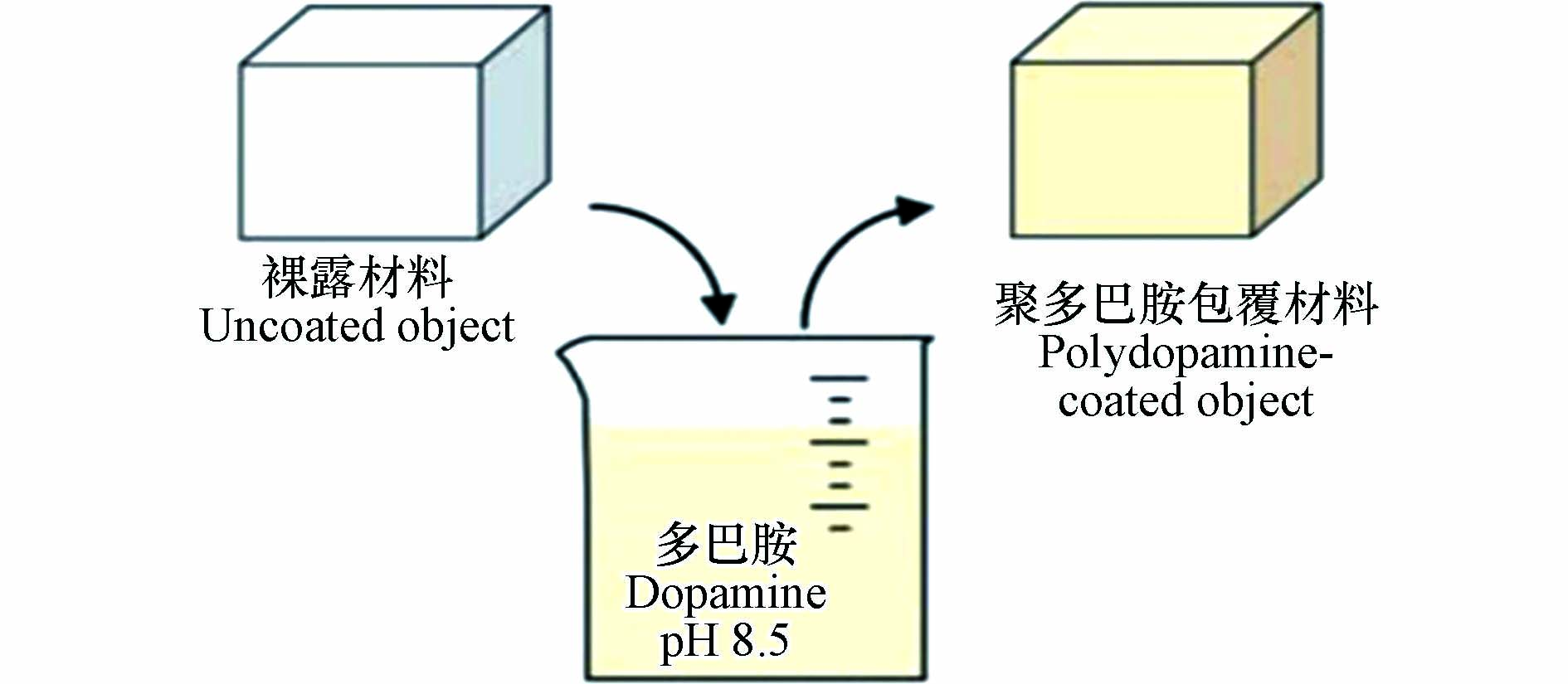
如图3所示,在避光有氧的环境条件下,基体材料置于三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)的缓冲溶液(pH=8.5)中,多巴胺可以在其表面通过自聚反应生成聚多巴胺包覆层[4]。包覆层的厚度随反应时间的推移而增加。当反应时间为24 h时,厚度达到最大,为50 nm。因此在合适的反应条件下,多巴胺能够通过非共价和共价键力的相互作用,与不同的基底材料表面进行聚合附着来实现对材料的包覆[19-20]。在非共价作用方面,聚多巴胺利用非共价键力(π-π 堆积、氢键、金属离子螯合或配位等)在基底材料表面进行聚合包覆;而在共价作用方面,聚多巴胺不仅可以利用共价键的结合作用与一些表面含有硫醇基和胺基等官能团的材料发生迈克尔加成反应或碱性条件下的希夫反应,而且通过这些反应也可在聚多巴胺包覆层上接枝功能分子,实现复合材料进一步的功能化[21-22]。
1.3 影响聚多巴胺形成-附着的因素
影响聚多巴胺形成-附着过程的因素主要包括多巴胺单体浓度、溶液pH及沉积时间/温度等。多巴胺单体浓度会影响到聚多巴胺包覆层的厚度和表面粗糙度。一般包覆层的厚度和表面粗糙度会随着多巴胺浓度的提高而增加,但超出一定范围后,浓度基本不影响包覆层的沉积[23]。通常聚多巴胺的沉积发生在弱碱性溶液中,这是因为弱碱性环境有助于多巴胺自聚反应前驱体的形成,但Wei等研究发现,在反应溶液中加入一些氧化剂(Cu2+、过硫酸铵等)后也能实现酸性条件下的自聚反应[24]。此外,沉积时间/温度也是影响反应速率的重要因素,当沉积时间或温度适当增加,包覆层沉积的速率同样会提高[25]。
2. 聚多巴胺功能材料在去除水中重金属和有机物污染物方面的应用(Applications ofpolydopamine-functional materials in the removal of heavy metals and organic pollutants in water)
随着当代社会的高速发展,人类的生产生活已严重影响到水体生态环境的稳定,水污染问题日益突出。水体污染物主要来源于工业废水、生活污水及农业污水,而污染物的种类一般分为有机物、无机物和微生物三大类[26]。目前,应用于水污染控制领域的处理技术有物理法、化学法、物理化学法及生物法。在水污染处理方面,聚多巴胺功能材料结合了基底材料的优良特性和聚多巴胺包覆层丰富的功能基团,通过吸附或催化等方法对水中重金属离子和有机污染物进行有效的去除[27]。
2.1 聚多巴胺功能材料在水中重金属去除方面的应用
作为一种利用吸附材料的高比表面积和特殊吸附位点等优势来去除水中重金属的方法,吸附法因材料廉价易得和操作简单的优势而被广泛使用[28]。聚多巴胺功能材料凭借着聚多巴胺层丰富的功能基团(邻苯二酚、胺基和亚胺基等),为与水中重金属离子结合提供了大量的吸附位点[29]。
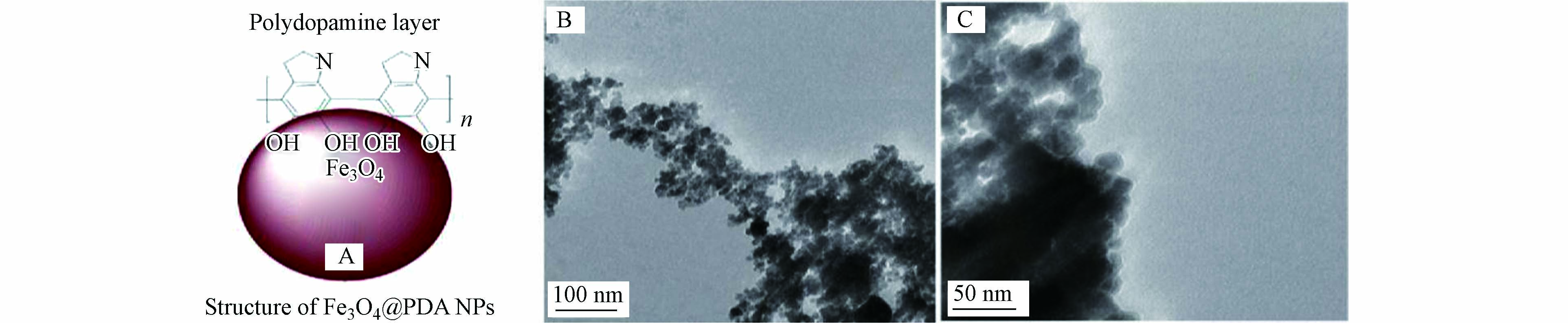
目前,研究人员在努力开发新型的基底材料和聚多巴胺表面改性手段以提高复合材料吸附去除重金属离子的效率。马玉荣等利用共沉淀法合成的聚多巴胺包覆的Fe3O4(Fe3O4@PDA NPs),通过利用聚多巴胺具有丰富吸附位点和磁性材料易于分离回收的特点,用来吸附去除模拟废水中的Pb2+[30]。由电镜表征可以看出,聚多巴胺通过羟基-铁化学作用包覆在在Fe3O4 NPs表面,形成了具有核壳结构的Fe3O4@PDA NPs(图4C)。实验表明,在最佳条件下,Fe3O4@PDA NPs对Pb2+的最大吸附量约为20.68 mg∙g−1。作为石墨烯的衍生物,氧化石墨烯(GO)具有高比表面积、丰富功能基团和优秀力学性能等特点,因此可对GO进行表面改性来调控表面性质,以提升其吸附性能[31-32]。Dong等通过控制聚多巴胺的质量分数,合成了一系列亚纳米级厚的聚多巴胺包覆的GO复合材料(PDA/GO)[33]。PDA/GO对Pb2+、Cu2+、Cd2+及Hg2+等重金属离子的最大吸附量分别为53.6、24.4、33.3、15.2 mg∙g−1,吸附性能均优于单纯的GO和PDA,体现了复合材料中PDA和GO的协同作用。Ali等同样利用共沉淀法合成了磁性氧化石墨烯(GO/Fe3O4),然后通过聚多巴胺包覆GO/Fe3O4制备出 rGO/Fe3O4@PDA,作为吸附水中Pb2+的新型磁性吸附剂[34]。由于吸附材料存在丰富的胺基和羟基等官能团,rGO/Fe3O4@PDA对Pb2+的吸附能力可达35.2 mg∙g−1,吸附性能明显优于未修饰的GO/Fe3O4。碳纳米管也是一类具有较高比表面积的碳基材料,但因表面带有的官能团较少、水分散性较差等缺点导致其在实际运用过程中存在短板[35]。刘杏红等通过将多巴胺氧化自聚到磁性碳纳米管(mMWNTs)上,合成了聚多巴胺包覆的磁性碳纳米管材料(mMWNTs@PDA)[36]。实验结果证明,mMWNTs@PDA对水中Ni2+的吸附过程符合Freundlich等温吸附和准二级动力学模型,且在最优条件下,mMWNTs@PDA对Ni2+最大吸附量可达27.9788 mg∙g−1。针对一些特殊重金属离子污染水体的治理,Yang等通过采用多巴胺聚合沉积工艺和温和水热法合成了层状双氢氧化物(LDH)原位生长修饰的Fe3O4@PDA(Fe3O4@PDA@LDH)微球,对核工业产生的含U(Ⅵ)的废水进行吸附净化[37]。在实验过程中,通过控制PDA和LDH的用量制备了不同PDA厚度和LDH含量的复合材料微球(MP2L1、MP2L2、MP2L3、ML2及MP2等)。在pH=5.0和T=298.15 K的条件下,材料对U(Ⅵ)的最大吸附容量分别为MP2L2(344 mg∙g−1)> MP2L3(291 mg∙g−1)> MP3L2(245 mg∙g−1)> MP2L1(211 mg∙g−1)> ML2(142 mg∙g−1)> MP1L2(141 mg∙g−1)> MP2(71 mg∙g−1)> Fe3O4(34 mg∙g−1),其中MP2L2具有较高的吸附容量,处理效果在含铀废水的净化方面是较为可观的。
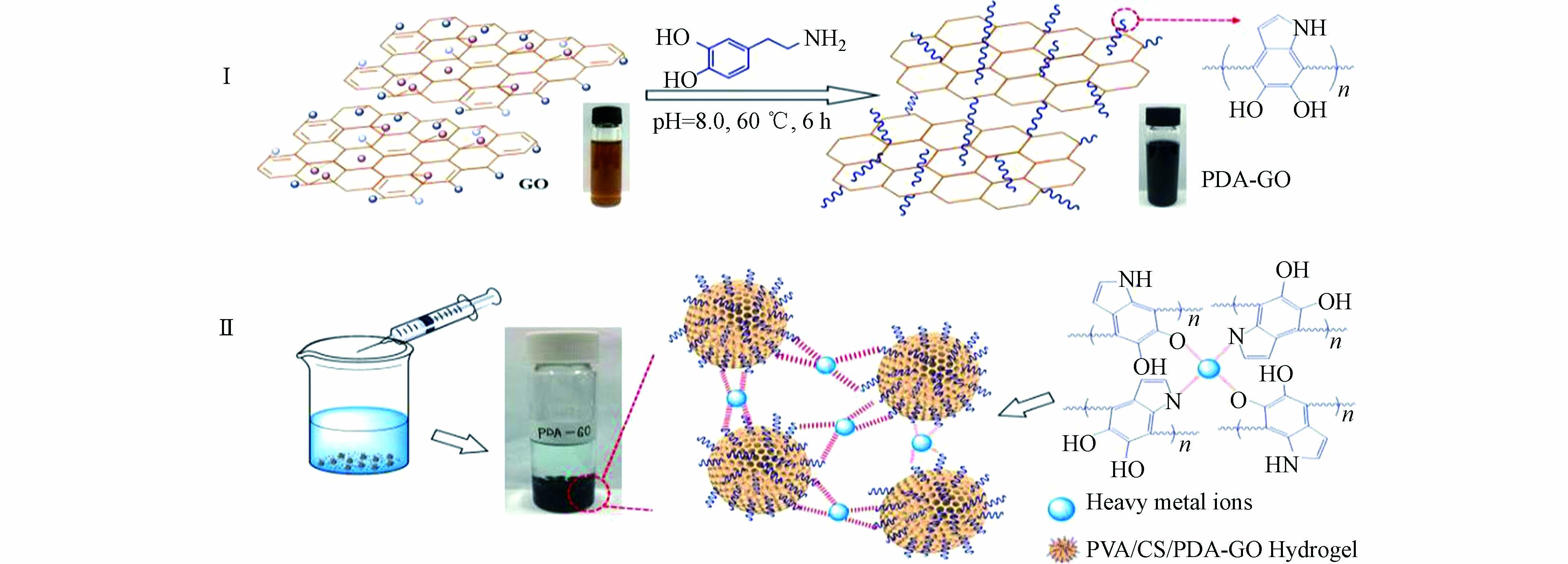
Zeng等通过将聚多巴胺掺入到支链淀粉水凝胶基质中,合成了具有高机械强度和可生物降解特性的支链淀粉/聚多巴胺(Pu/PDA)生物水凝胶吸附剂[38]。实验表明,通过调节预凝胶溶液中的聚多巴胺的浓度,可很好地控制该吸附剂的吸水率、机械强度及孔径。Pu/PDA对重金属离子具有较高的吸附能力,对Cu2+的吸附容量最高可达到100 mg∙g−1 。而Li等首先将聚多巴胺引入氧化石墨烯中合成了PDA-GO(图5-Ⅰ),然后通过瞬时凝胶法制备出聚乙烯醇/壳聚糖功能化的PDA-GO(PVA/CS/PDA-GO)水凝胶珠,用于吸附水中的Pb2+、Cu2+及Cd2+[39]。PDA-GO的存在不仅增强了水凝胶珠体系的稳定性,而且大量的活性基团的引入提高了吸附性能(图5-Ⅱ)。在最优条件下,通过Langmuir等温线对实验数据的拟合可知,PVA/CS/PDA-GO对Pb2+、Cu2+及Cd2+的最大吸附量分别为236.20、210.94、214.98 mg∙g−1。为解决实际水体环境中重金属离子共存污染的问题,Wang等采用水溶法快速制备了氨基水杨酸/聚多巴胺改性的PP无纺布吸附剂(PP/PDA/ASA)[40]。交联在聚合物末端的水杨酸分子增加了官能团的类型,有效地解决了因多组分体系中重金属离子的竞争吸附效应引起去除效率低的问题。在含有5 mg∙L−1的Cu(Ⅱ)/Cd(Ⅱ)/Pb(Ⅱ) 混合体系溶液中,由于表面氨基、羟基及羧基等官能团参与了重金属离子的吸附,PP/PDA/ASA可去除90%的Cu2+和Pb2+及80%的Cd2+。
2.2 聚多巴胺功能材料在水中有机污染物去除方面的应用
有机污染是造成水污染的重要原因之一。水中有机污染物的来源主要有生活污水、工业废水及大气污染,污染水体一旦不进行净化处理,便会对自然环境造成严重破坏并威胁到人体生命健康[41]。聚多巴胺功能材料因聚多巴胺包覆层上邻苯二酚、胺基及芳香族基团的存在,为有机污染物的去除提供了大量的活性位点。聚多巴胺功能材料可通过静电相互作用、配位或螯合作用、氢键或 π-π 键堆积相互作用对有机染料和硝基苯酚等进行吸附或催化降解,因此在水中有机污染物的净化方面具有广阔前景[42-43]。
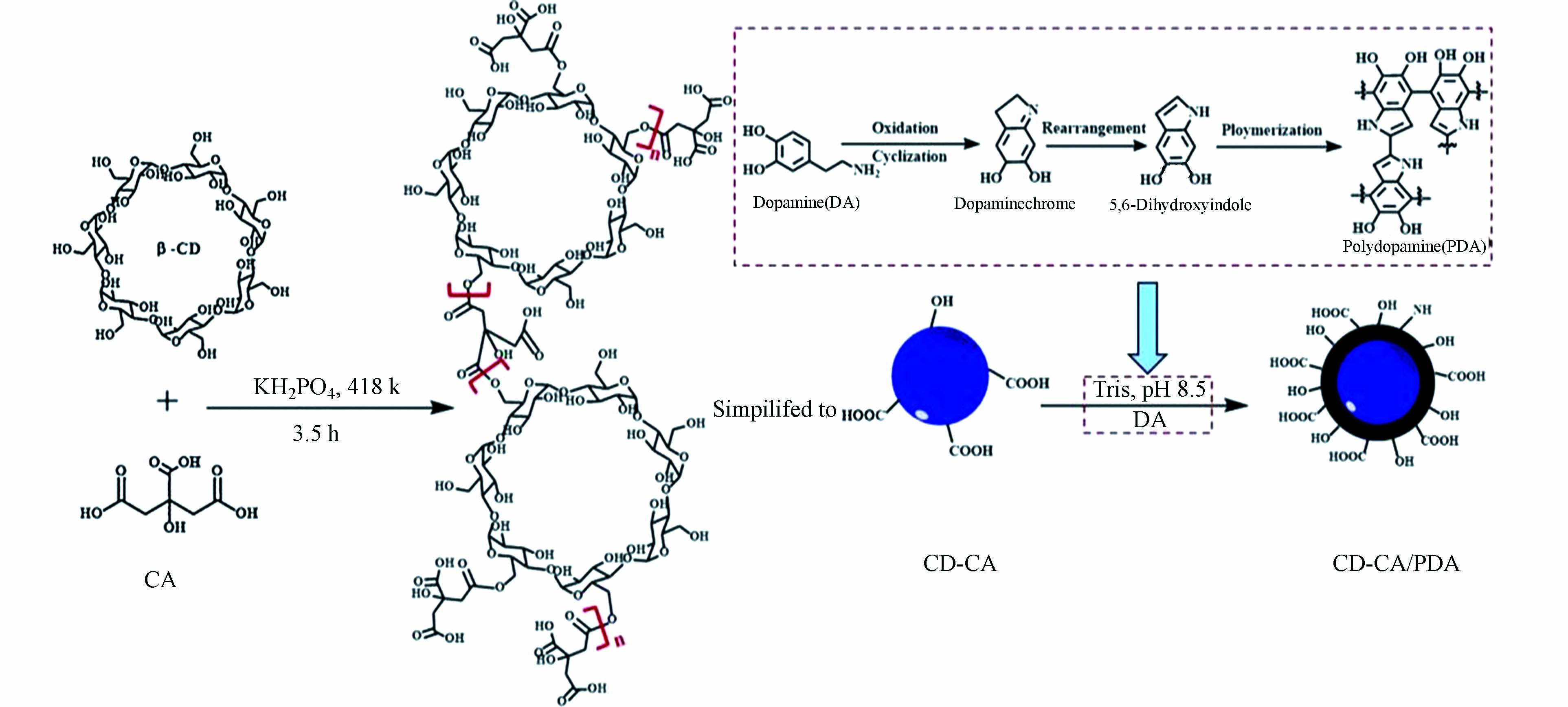
在污水中有机染料的吸附去除方面,Li等利用聚多巴胺为原料,通过将聚多巴胺包覆的CoFe2O4亚微球包裹在海藻酸钠微球中,合成了具有多孔结构和大量官能团的复合微球材料(SA@CoFe2O4-PDA),用来吸附去除亚甲基蓝(MB)、孔雀石绿(MG)及晶体紫(CV)等有机染料[44]。实验表明,SA@CoFe2O4-PDA对MB、CV及MG的最大吸附容量分别为466.60、456.52、248.78 mg∙g−1。Chen等首先将β-环糊精(β-CD)和柠檬酸(CA)酯化交联生成CD-CA,然后CD-CA与聚多巴胺结合,制备出聚多巴胺改性的环糊精聚合物(CD-CA/PDA)(如图6所示),用于MB、MG及CV等染料的吸附去除[45]。CD-CA/PDA对染料的吸附呈现出从单层吸附向多层吸附过渡的趋势,且对MB、MG及CV的吸附容量分别为582.95、1174.67、473.01 mg∙g−1。刘怡虹等将多巴胺和氧化石墨烯(GO)混合,通过聚多巴胺提供的强大粘合力,辅助GO自组装形成具有三维多孔网状结构的GO水凝胶,经水合肼对其进行还原后,生成了聚多巴胺交联的还原性石墨烯气凝胶(DA-rGA),以对MG、藏红T(ST)和罗丹明B(RhB)等阳离子染料进行吸附研究[46]。实验结果表明,DA-rGA的三维孔隙利于吸附分子在内部的快速扩散,因此对有机染料具有优异的吸附性能。Fu等通过合成的聚多巴胺微球对亚甲基蓝的吸附研究进一步证实,聚多巴胺在反应体系中会释放质子而带有负电荷,因此聚多巴胺功能材料可通过静电作用对水中阳离子染料进行吸附结合,而对阴离子染料的吸附效果就不如人意[47]。而何雪梅等利用双醛壳聚糖作为交联剂,通过在聚多巴胺修饰的羊毛织物表面上接枝季铵盐阳离子进行二次功能化,巧妙地得到了PDA/季铵盐阳离子改性的羊毛织物,用于吸附去除阴离子染料酸性大红G[48]。相较于未经处理的羊毛,羊毛织物的表面经改性后拥有更多的活性基团,大大提高了染料扩散进入纤维内部的速率。在pH值为2、染色时间为60 min等最佳实验条件下,PDA/季铵盐阳离子改性的羊毛织物对酸性大红G具有较高的吸附率。Zhan等通过将多巴胺聚合到多孔柚皮表面,成功制备了一种环保的生物吸附剂(PP-PDA)[49]。PP-PDA对水中阳离子染料表现出较高吸附能力,MB、MG和中性红(NR)的最大吸附容量分别为434.78、143.88、208.33 mg∙g−1。且PP-PDA的再生能力较强,经过20次循环后也可保持较高的吸附能力。
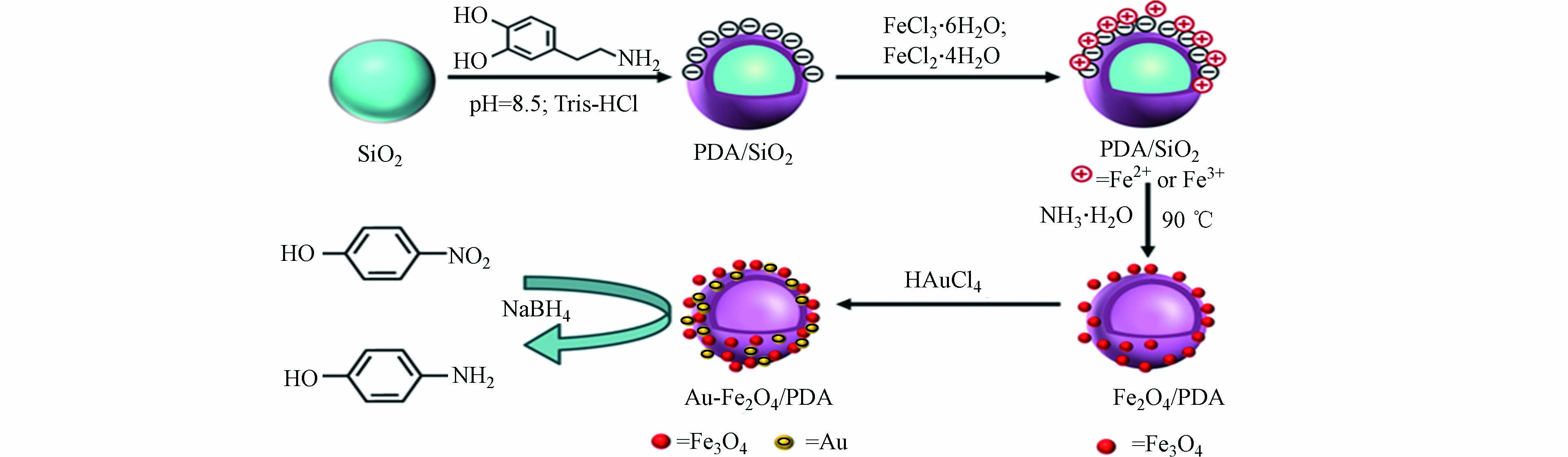
聚多巴胺功能材料也可利用催化法对水中有机染料和芳香族化合物进行去除。Ma等首次通过原位自聚反应合成了具有核壳结构的聚多巴胺包覆的CuFe2O4磁性纳米粒子(CuFe2O4@PDA MNPs),且该产品的PDA涂层厚度可通过调节制备过程中多巴胺的浓度来控制[7]。在H2O2的存在下,CuFe2O4@PDA MNPs表面吸附MB,H2O2分子被CuFe2O4@PDA激活产生的·OH可有效降解MB,最优条件下的催化降解效率可达97%以上。如图7所示,Niu等首先制备出PDA包覆的SiO2颗粒,接着利用PDA涂层作为交联剂和还原剂,在其表面接枝Fe3O4 NPs和Au NPs,合成了具有中空结构的Au-Fe3O4/PDA纳米颗粒[50]。在优化实验材料用量后,Au-Fe3O4/PDA利用金属纳米颗粒的催化性能,能够将溶液体系中的4-硝基苯酚完全还原为4-氨基苯酚,且复合材料具有较优异的可回收性。MASSARO等通过将铜离子螯合在PDA包覆的沙子表面,制备出低成本的砂载铜催化剂(Cu-PDA@Sand),对MB、CR及4-硝基苯酚进行催化还原[51]。实验表明,由于负载铜离子的存在,复合材料有效地对有机染料进行了催化降解。Cu-PDA@Sand不仅能够通过自沉淀法进行简单地回收,而且可重复使用来实现长期稳定的催化性能。而在聚多巴胺对膜材料表面的改性方面,张娇娇等利用DA作为涂层材料,聚丙烯腈(PAN)静电纺纳米纤维膜为基底材料,制备出PDA/PAN纳米纤维复合膜材料[52]。在保证较高纯水通量的前提下,经聚多巴胺涂覆后的PAN纤维膜对乳化油的截留率高达96.1%,大幅提升了处理含油废水的效果。
3. 结论与展望(Conclusions and prospects)
多巴胺在弱碱条件下可通过自聚反应生成聚多巴胺,涂覆在各种基底材料表面形成聚多巴胺功能材料。目前,社会的高速发展已经对环境造成严重破坏,尤其在水体环境方面,水污染问题日益严峻。不同于一般的水污染修复材料,聚多巴胺功能材料不仅可利用邻苯二酚和胺基等丰富的功能基团,与水中重金属离子和有机污染物通过氢键、静电相互作用、π-π 键堆积及配位螯合作用进行结合,而且可利用共价和非共价键力在聚多巴胺包覆层接枝功能分子来提升复合材料的功能特性。聚多巴胺功能材料凭借着优异的吸附和催化还原性能、简单环保的制备方法、良好的生物相容性及可二次修饰等优势,对水中的重金属离子和有机污染物具有较高的去除效率且处理后不易对水体环境造成二次污染。本篇文章首先从多巴胺的结构性质入手,介绍了目前表面化学研究中主流的聚多巴胺形成和附着机理,然后从去除水中重金属离子和有机污染物这两个方面,总结了多种聚多巴胺功能材料在水污染处理方面的具体应用。
通过上述聚多巴胺功能材料在水体污染物去除方面的应用可以看出,基底材料经聚多巴胺修饰或在聚多巴胺涂层表面进行二次修饰后,吸附和催化还原性能均有大幅度的提升。但将这些复合材料从实验室的研究运用到实际生产生活中时,却存在一些关键问题需要解决。一方面,多巴胺的自聚过程、中间产物的组成及聚多巴胺的精确分子结构尚无定论,在缩短多巴胺聚合时间和调控聚多巴胺涂层的厚度等问题上仍需要摸索实验条件。另一方面,在实际污染水样的处理中,由于较难控制的水体含氧量和流速、复杂的污染物质及过酸或过碱的水体环境等多种因素的制约,导致聚多巴胺功能材料的使用场景受到严重限制且处理效率大幅降低。因此,需要针对聚多巴胺的形成机理做进一步的研究,探究限制多巴胺自聚反应的形成过程的限制因素(例如单次反应涂层的最大厚度不会超过50 nm、酸性条件下需要特定氧化剂的帮助等)[42]。此外,还需要通过优化聚多巴胺功能材料的制备过程来提高其在各种污染水体中的稳定性和高效性,并减少复合材料对水体的二次污染。目前,研究人员正努力开发制备简单、成本较低及环境友好的新型聚多巴胺功能材料,挖掘其在医学、光学及电化学等新领域的应用潜力。未来,相信聚多巴胺功能材料凭借其优异的性能会在水污染领域中具有更广阔的前景,也定会在更广泛的领域做出更大的贡献。
-
[1] 陈振楼,许世远,徐启新,等. 长江三角洲地表水环境污染规律及调控对策. 长江流域资源与环境. 2001, 10(4):353-359 Chen Z., Xu S., Xu Q., et al. Pollution patterns and modulating countermeasures of surface water environments in the Yangtze delta. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2001, 10(4):353-359 (in Chinese) [2] 陈正勇,王国祥,杨飞,等. Fenton 试剂对富营养化湖水黑臭的氧化降解作用. 环境工程学报, 2012, 6(5): 1591-1594 Chen Z., Wang G., Yang F., et al. Effect of Fenton reagents on degradation of black odor water in eutrophic water. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012, 6(5): 1591-1594 (in Chinese) [3] Renholds J. In situ Treatment of Contaminated Sediments. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Technology Innovation Office, 1998 [4] 宗栋良,张光明. 硝酸钙在底泥修复中的作用机理及应用现状. 中国农村水利水电, 2006,(4): 52-54 Zong D., Zhang G. Mechanisms and Application of calcium nitrate in the remediation of polluted sediment. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2006,(4): 52-54 (in Chinese) [5] Na Y. M., Wang S., Park S. S. A mathematical model to estimate nitrate release from ocher pellets applied to anaerobic benthic sediment. Ecological Modelling, 2006, 199(3): 324-335 [6] Murphy T., Moller A., Brouwer H. In situ treatment of hamilton harbour sediment. Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress and Recovery (Formerly Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Health). 1995, 4(3): 195-203 [7] Murphy T. P., Lawson A., Kumagai M., et al. Review of emerging issues in sediment treatment. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 1999, 2(4): 419-434 [8] 李开明,刘军,江栋,等. 古廖涌黑臭水体生物修复及维护试验. 应用与环境生物学报, 2005, 11(6): 742-746 Li K., Liu J., Jiang D., et al. Bioremediation and management of the Guliao River. Chin J. Appl. Environ. Biol., 2005, 11(6): 742-746 (in Chinese) [9] 谢丹平,李开明,江栋,等. 底泥修复对城市污染河道水体污染修复的影响研究. 环境工程学报. 2009, 3(8): 1447-1453 Xie D., Li K., Jiang D., et al. Study on effect of polluted sediment bioremediation on water body remediation of polluted urban rivers. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009, 3(8): 1447-1453(in Chinese) [10] 卢丽君,孙远军,李小平. 用生物促生剂修复受污染底泥. 中南民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(4): 27-31 Lu L.J., Sun Y.J., Li X.P., et al. Application of Bio-stimulant to the remediation of pollutant sediment. Journal of South-Central University for Nationalities (Nat. Sci.), 2007, 26(4): 27-31(in Chinese) [11] 孙远军. 城市河流底泥污染与原位稳定化研究. 西安:西安建筑科技大学博士学位论文, 2009 Sun Y.J. A study on sediments contamination and in-situ stabilization of urban river. Xi'an:Doctor Dissertation of Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2009(in Chinese) [12] Feibicke M. Impact of nitrate addition on phosphorus availability in sediment and water column and on plankton biomass—Experimental field study in the shallow brackish schlei Fjord (Western Baltic, Germany). Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 1997, 99(1): 445-456 [13] Sommers L. E., Dorich R. A., Nelson D. W. Estimating algal available phosphorus in suspended sediments by chemical extraction. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1985, 14(3): 400-405 [14] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法(第4版).北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002 [15] Ruban V., Brigault S., Demare D., et al. An investigation of the origin and mobility of phosphorus in freshwater sediments from Bort-Les-Orgues Reservoir, France. J. Environ. Monit., 1999, 1(4): 403-407 [16] 郭建宁, 卢少勇, 金相灿, 等. 滇池福保湾沉积物不同形态磷的垂向分布. 环境科学研究, 2007, 20(2):78-83 Guo J.N., Lu S.Q., Jin X.C., et al. Vertical distribution of various forms of phosphorus in the sediments of fubao fulf,Dianchi Lake. Research of Environmental Science, 2007, 20(2):78-83 (in Chinese) [17] 许磊,李华,陈英旭,等. 南太湖地区小型浅水湖泊自净能力季节变化研究. 环境科学. 2010, 31(4): 924-930 Xu L., Li H., Chen Y.X., et al. Research on seasonal variation of self-purification ability for small shallow lakes in South Lake Taihu. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(7): 1952-1959(in Chinese) [18] 赵海超,王圣瑞,赵明,等. 洱海水体溶解氧及其与环境因子的关系. 环境科学. 2011, 32(7): 1952-1959 Zhao H.C., Wang S.R., Zhao M., et al. Relationship between the DO and the environmental factors of the water body in Lake Erhai. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(7): 1952-1959 (in Chinese) [19] Wang S., Jin X., Bu Q., et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen supply level on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2008, 316(1): 245-252 [20] Chen J., Lu S., Zhao Y., et al. Effects of overlying water aeration on phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphatase activity in surface sediment. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(2): 206-211 [21] 姜霞,王琦,金相灿,等. 光照与通气方式对蓝, 绿藻竞争生长和磷的水-沉积物界面过程的影响. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(1): 31-36 Jiang X., Wang Q., Jin X.C., et al. Effects of light and aeration on competition between Microcystis aeruginosa and Scenedesmus quadricauda and phosphorus release at the water-sediment interface. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(1): 31-36(in Chinese) -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 1990
- HTML全文浏览数: 1151
- PDF下载数: 1020
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: