矿化污泥生物反应器处理生活垃圾填埋场老龄渗滤液
Aged landfill leachate treatment by aged sludge-based bioreactor
-
摘要: 经长时间稳定化形成的矿化污泥中,含有种类丰富和数量繁多的降解性微生物,具有处理渗滤液的潜力。建立3个矿化污泥生物反应器, 即C1(粉煤灰0%),C2(粉煤灰9.1%),C3(粉煤灰16.7%),以处理垃圾填埋场老龄渗滤液。在单级矿化污泥反应器中,当进水COD和 NH3-N分别约为1350和900 mg/L时,水力负荷为17.7~70.8 L/(m3·d),COD去除率可超过65%,氨氮的去除率可超过94%。粉煤灰的加入一定程度上降低了COD去除率,但有助于氨氮的去除。在二级矿化污泥生物反应器中(即C3~C1串联),水力负荷为35.4 L/(m3·d)的工况下,当COD、TOC、IC和NH3-N分别为1 500~2 500,500~900,1 200~1 600和1 200~1 450 mg/L时,出水可达到COD3-N<5 mg/L。但是,矿化污泥生物反应器对渗滤液总氮的去除率较低,仅为20%左右。Abstract: Aged sludge formed during its long-term stabilization process contains a wide spectrum and large quantity of microorganisms, and has a potential for aged landfill leachate treatment. In this work, three bioreactors, i.e. C1(coal fly ash=0%), C2(coal fly ash=9.1%) and C3 (coal fly ash 16.7%) were established to treat aged landfill leachate. In single aged sludge-based bioreactor, when the COD and NH3-N of influent were 1 350 and 1 000 mg/L approximately and hydraulic load was at 17.7~70.8 L/(m3·d), its corresponding removal can reach to 65% and 94%, respectively. The addition of coal fly ash reduced the COD removal, however, favored the removal of NH3-N. In the combined process of C1 and C3, when the COD, TOC, IC and NH3-N of influent were 1 500~2 500, 500~900, 1 200~1 600 and 1 200~1 450 mg/L, respectively, and the hydraulic load was at 35.4 L/(m3·d), its corresponding concentration of effluent can be less than 300, 180, 100 and 5 mg/L. However, the removal efficiencies of total nitrogen were quite low, only about 20%.
-
Key words:
- leachate /
- aged sludge /
- municipal solid waste /
- landfill /
- bioreactor
-
人工湿地微生物燃料电池(constructed wetland - microbial fuel cell, CW-MFC)是一种结合人工湿地(CW)和微生物燃料电池(MFC)的新兴技术,该技术能在对污水净化的同时高效产电,具有广阔的应用前景和实际价值,在近些年得到广泛关注 [1]。目前,大量的研究集中在上流式CW-MFC方面,但最大输出功率密度通常仅为10~30 mW·m−2 [2-3]。上流式CW-MFC可能由于长时间的运行,从而形成污泥堵塞效应,导致系统的内阻变大,影响电子量转移,进而引起产电性能下降 [4-5]。DOHERTY通过下流式与上流式协同作用将系统的最大输出功率密度由单一上流式的16.8 mW·m−2提高至27.6 mW·m−2 [6],由此可知,下流式作用是不可忽视的。然而,关于一体化下流式CW-MFC产电性能的研究鲜有报道。
CW-MFC运行时通常采用葡萄糖或乙酸钠作为基质碳源 [7-8],然而不同基质碳源(乙酸钠、葡萄糖和丙酸)会影响阳极生物的形成和系统内阻 [9],同时会影响系统的产电性能。当以葡萄糖和乙酸钠为下流式CW-MFC的基质碳源时,对系统启动时间及电化学性能的影响如何,目前尚未见报道。为了降低植物对实验的影响及复杂性,在设计构建的下流式CW-MFC系统中通常不种植植物。为了解基质碳源对下流式CW-MFC的电化学行为影响,本研究分析了其产电性能和电化学行为,并通过微生物群落结构分析及FAPROTAX功能预测从微生物学角度探究葡萄糖和乙酸钠作为基质碳源下的功能菌群,以期为一体化下流式CW-MFC在实现同时高效产电与治理污染水体的研究中提供参考。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 集电体及电极的制作
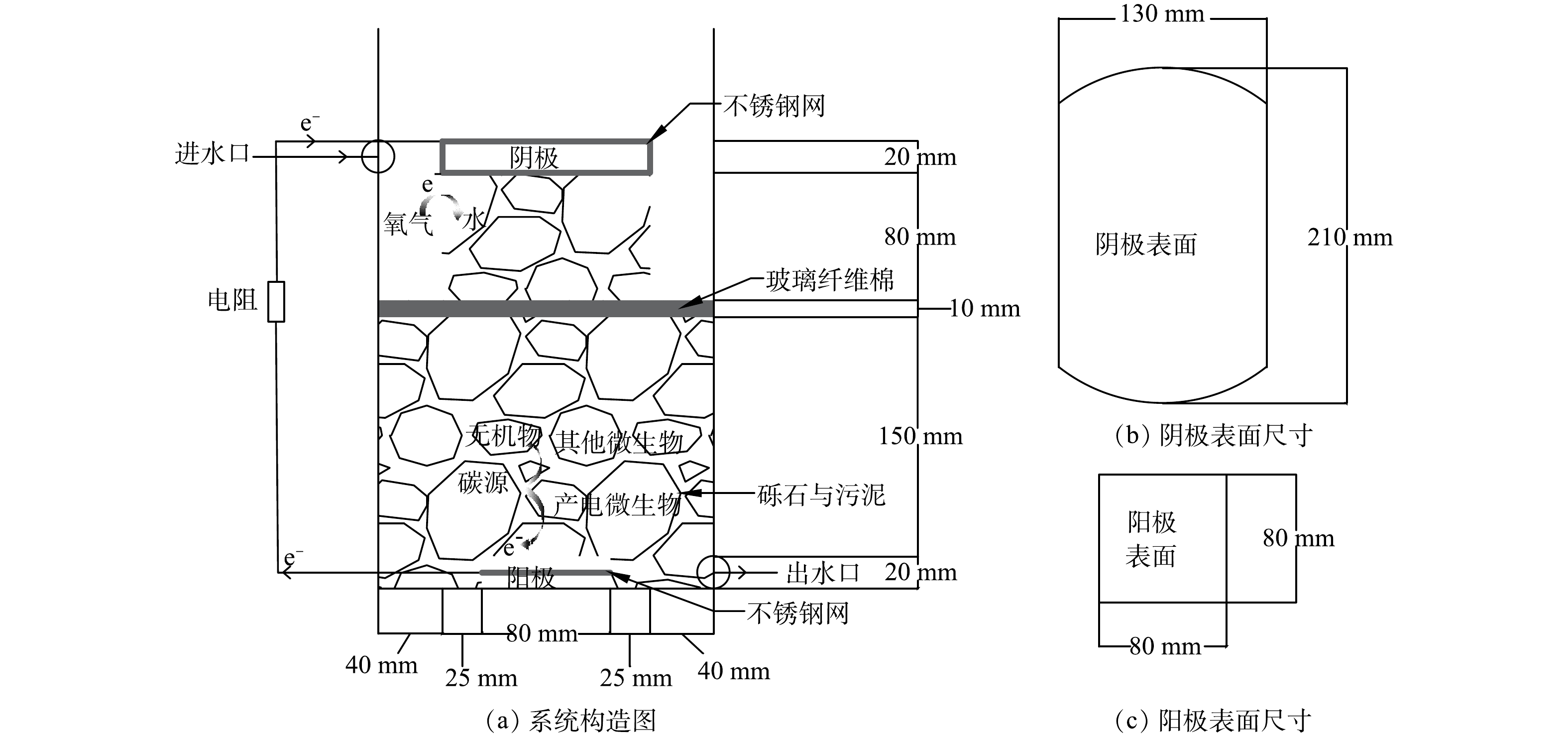
本研究所用的电极材料采用石墨毡(北京晶龙特碳石墨厂),制成厚度为2 cm表面为256 cm2的阴极以及表面为64 cm2的阳极(图1),并浸泡在0.1 mol·L−1 HCl中24 h进行预处理,以去除其表面的油渍和金属离子污染物,再用蒸馏水洗涤干净后备用 [6]。采用具有价格低廉的不锈钢丝网(5目304不锈钢丝网,钢丝丝粗直径为0.6 mm)作为集电体,有助于增强电子的传递,提高导电性,避免出现集电死区 [10]。将不锈钢丝网在1 mol·L−1 H2SO4溶液中浸泡4 h以去除表面的钝化层增加表面粗糙度,这有助于微生物富集和降低电荷转移内阻 [11]。将其制成边长为8 cm正方形埋入阳极中,以及制成能够包裹阴极的尺寸包裹阴极形成一个整体,至此电极构建完成。
1.2 系统的设计与构建
本研究构建了下流式未种植植物CW-MFC实验装置,其构造见图1。反应器使用的是直径21 cm高42 cm的圆柱桶,有效高度为28 cm。填充直径为0.3~0.6 cm的砾石共(12.15±0.1) kg作为支撑层,以改善废水在湿地中的分布并起到承托的作用 [12]。整个反应器的总有效液体体积为(2.92±0.08) L,反应器中距底部18~28 cm的区域作为阴极区,中间隔层采用厚度为15 mm压缩至10 mm且直径为21 cm的玻璃纤维棉,这样可以防止阴极区的氧气向阳极扩散,有助于降低氧气传质系数,对电子的逆向流动起缓解作用,有助于提高产电性能 [13-15]。在阴极区左右两侧空出的区域用于测定时放置参比电极。由直径为1 mm的铜导线连接阳极、阴极和外接可变电阻箱电阻(2 000 Ω)形成闭合回路 [16],并使液面处于阴极下表面在构成闭合回路的同时形成空气阴极,加入适量蒸馏水至原水位以防止水分的正常蒸发造成液面下降,从而影响反应器的运行[17]。
1.3 CW-MFC的接种和启动
污泥取自中国广西桂林市七星区七里店污水处理厂(公共自行车污水净化厂站旁)的厌氧池。污泥在投入反应器之前先进行厌氧培养(每天采用浓缩溶液更换厌氧培养液体0.6 L,1 L浓缩溶液的基本成分包括9.38 g葡萄糖、0.75 g NH4Cl、0.65 g KCl、6.8 g Na2HPO4·12H2O、0.95 g NaH2PO4·2H2O以及5 mL微量营养液),共培养60 d。厌氧培养后的混合液悬浮固体质量浓度(MLSS)为6.89 g·L−1,为确保污泥来源一致,将培养后的污泥稀释1倍并同步从各反应器的底部通入直到充满至阴极下表面以进行接种,静置1 d后形成生物膜。静置完成后,人工配置溶液以1.5 d的水力停留时间并在(30±2) °C下通过蠕动泵(雷弗BT101L DG10-2,保定,中国)从顶部连续进水,底部出水(图1)。1 L人工配置溶液的基本成分包括5 mmol·L−1磷酸盐缓冲液(0.5 g NaH2PO4·2H2O和0.64 g Na2HPO4·12H2O)、0.281 5 g葡萄糖(S.G.)或者0.384 5 g乙酸钠(S.S.)(理论COD值均为300 mg·L−1)、0.15 g NH4Cl、0.13 g KCl以及1 mL微量营养液。微量营养液的配制参考LIU等[2]的方法。并通过NaH2PO4·2H2O或Na2HPO4·12H2O调节进水溶液pH为6.5 [18]。系统运行至电压稳定时,则视为驯化成功 [19]。
1.4 电化学性能分析
1)电压、电势和功率密度曲线。采用联想扬天V110-15电脑连通LabQuest mini主机并连接电压传感器DVP-BTA(威尼尔软件与技术公司,美国),每隔30 min采集1次外接电阻的两端电压 [18]。当系统输出稳定后,开路电压达到最大值时,接入电阻箱,并采用恒阻放电法测定极化曲线。通过调节外接电阻箱的不同电阻值,稳定30 min后,读取电压并绘制极化曲线 [2,20]。用万用表(福禄克F18B,淘宝,中国)测量阴极和阳极电势。通过功率(P=V2·R−1)除以阳极表面(64 cm2)计算出功率密度,绘制功率密度曲线 [15,21]。
2)电化学测定。循环伏安法(CV)曲线、线性扫描伏安法(LSV)曲线、塔菲尔(TAFEL)曲线和电化学阻抗(EIS)测量使用CHI604E电化学工作站(上海辰华仪器有限公司,中国),并采用三电极系统即工作电极、对电极和参比电极(Ag/AgCl)电极 [22-23]。CV扫描范围为−2.0~1.8 V,扫描速度为30 mV·s−1。LSV扫描范围为0~1.0 V,扫描速度为30 mV·s−1 [24]。电容C根据CV曲线和式(1)进行计算。Tafel测试的扫描电压为−2.0~2.0 V并以10 mV·s−1的扫描速度进行扫描,记录工作电极的Tafel图 [25-26]。EIS测量在0.01~1 mHz,使用5 mV的交流电信号。通过测量EIS来拟合等效电路R(Q(RW)),可以得到电化学欧姆电阻、电荷传递电阻和传质电阻等重要参数。用Nova 2.1.4软件分析阻抗谱(Nyquist plot) [25,27]。
C=SvΔV (1) 式中:S为循环伏安环的积分面积,V·A;ν为扫描速率,V·s−1;ΔV为扫描电位区间,V。
1.5 出水COD的测定
在完成各系统电化学性能指标测定后,对各反应器的出水口取约10 mL水样,取3次。耗氧有机污染物浓度(以COD计)的测定采用哈希COD消解仪(DRB200,HACH,美国)进行快速消解,并利用COD测定仪(DR1010,HACH,美国)进行测定。采用SPSS 24.0软件进行差异显著性分析。
1.6 阳极微生物群落样品
实验结束后(第15天),取出阳极置于pH=7.0的20 mmol·L−1磷酸盐缓冲液中,用UC-6超声波振荡器(上海泰坦科技有限公司35 kHz)处理10 min,并摇匀溶液 [27]。最后,用0.45 μm滤膜过滤溶液。将过滤膜上附着的微生物样品送至苏州帕诺米克生物医药科技有限公司(BioNovoGene)进行高通量焦磷酸测序分析,以研究微生物群落结构。采用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)/十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)法提取样品DNA[28]。引物515F/806R用于PCR扩增细菌V3~V4区16S rRNA基因。配对末端rRNA测序在Illumina NovaSeq6000平台(Illumina,圣迭戈,美国)上进行。通过SILVA138的SSUrRNA数据库(http://www.arb-silva.de/),进行物种注释分析(阈值为0.8~1),获得分类学信息,并分别在门和属水平上统计每个样本的群落组成。所有样本归一化后,使用R软件(Version 4.0.4)绘制维恩图,分析不同样本之间的共同和独特的OTU。使用Qiime软件(Version 1.9.1)计算有效OTUs、Chao1、Shannon、Simpson和ace指数。根据扩增子物种注释结果,进行FAPROTAX [29]环境功能预测分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 产电性能与水体COD
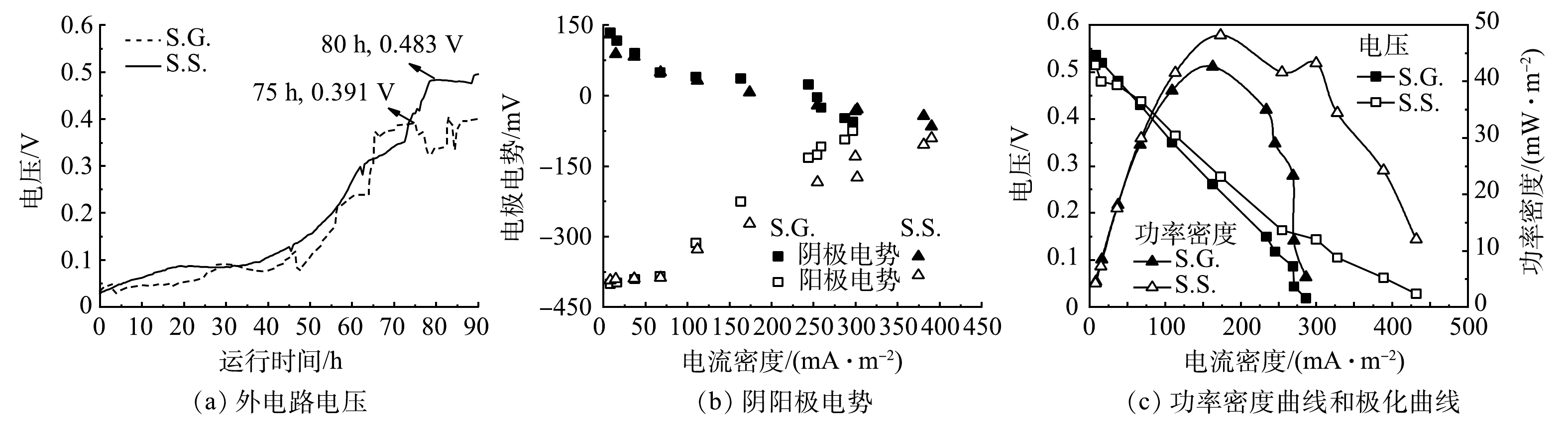
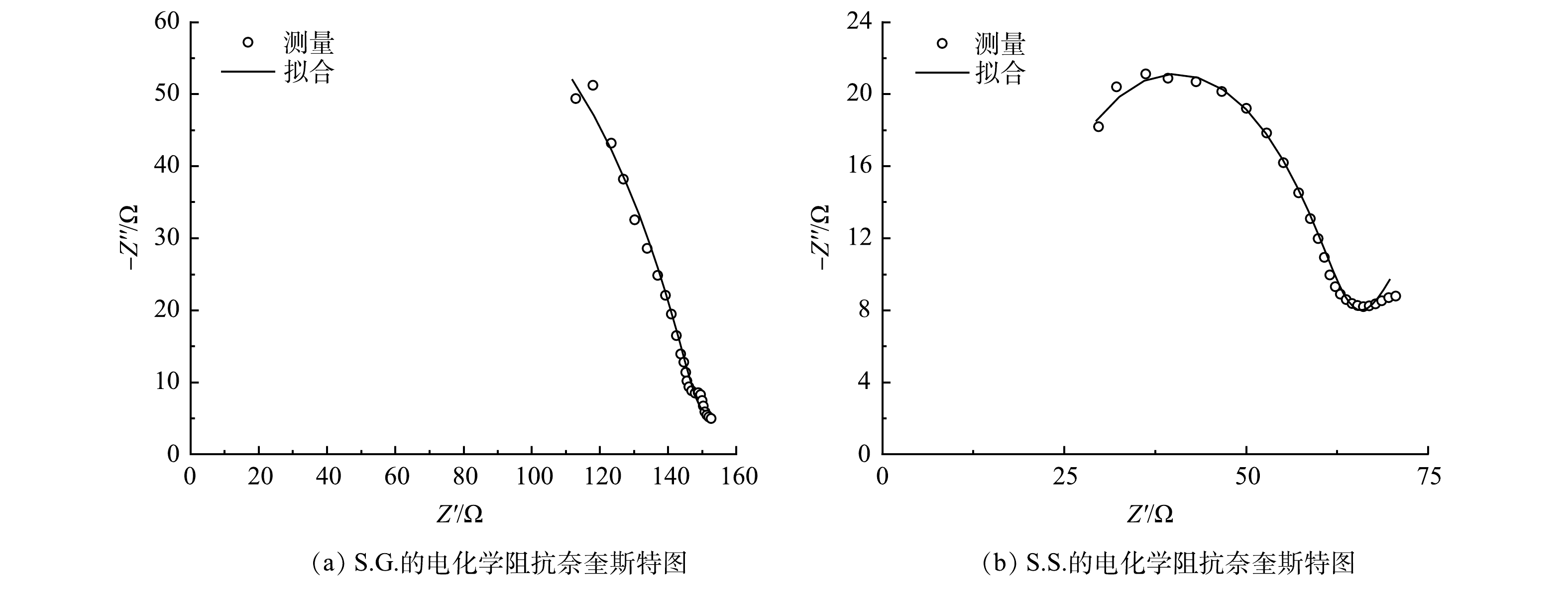
图2表明,S.S.的产电性能优于S.G.,S.G.和S.S.从开始启动至稳定所需时间分别为75 h和80 h(图2(a)),电压可分别达到0.391 V和0.483 V。以乙酸钠和葡萄糖为基质碳源的阳极反应分别见式(2)和式(3)[30]。由阴阳极电势(图2(b))可知,S.S.和S.G.的阳极电势差异均比阴极大,表明阴极发生更多的还原反应,但由于电阻的减少造成电子流出阳极的速度较大,从而正电荷的累积使得阳极电势向正方向移动。当电流密度由0 mA·m−2增加到300 mA·m−2时,S.S.和S.G.的阳极电势分别提高了55.5%和81.3%,S.S.的阳极电势随着电流密度增加的变化幅度较小,说明S.S.的阳极性能更好,生物膜稳定性更高[31]。在390 mA·m−2的电流密度下,S.S.可以维持−66 mV的阴极电势以及−91 mV的阳极电势,从而在高电流密度下S.S.依然可以保持更高的外电压进而增加功率的输出。S.S.和S.G.的最大输出功率密度分别为48.14 mW·m−2和42.61 mW·m−2(图2(c))。S.G.的电压降比S.S.更为明显,这主要由于欧姆极化和传质损耗,更高的欧姆损耗是由膜的电阻引起的,而传质损耗是由于还原化合物的有限放电能力或向电极供应氧化化合物有限所导致的[24]。S.G.具有更大内阻在EIS结果中被证实。
CH3COO−+4H2O→2HCO−3+9H++8e− (2) C6H12O6+12H2O→6HCO−3+30H++24e− (3) 本研究所采用的下流式未种植植物CW-MFC与其他已报道CW-MFC发电性能的比较见表1。可以看出,本研究构建的下流式CW-MFC在发电性能上优于其他CW-MFC系统,所产生的输出功率密度提高了74.4%~187%。因此,尽管上流式是目前主流形式,但下流式CW-MFC应得到更多关注。
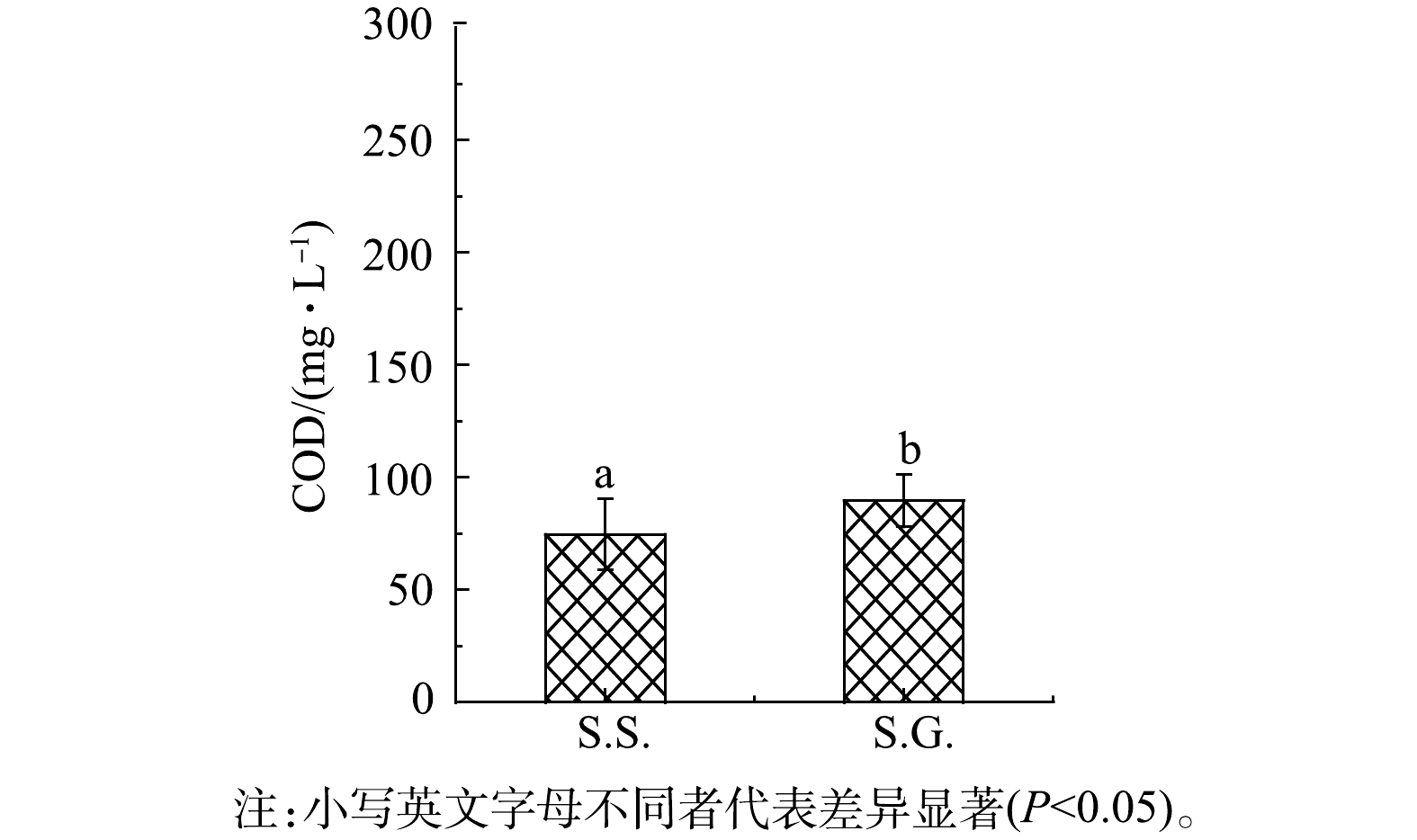
表 1 与其他已报道CW-MFC在发电性能上的比较Table 1. Compared with other reported CW-MFC on the power generation performanceS.S.出水口COD为74.7 mg·L−1,去除率达到75.1%,而S.G.的COD去除率仅为70.1%(图3)。S.S.表现出更高的水体COD去除效果,可能是由于S.S.基质碳源更容易被微生物所利用。
2.2 电化学行为
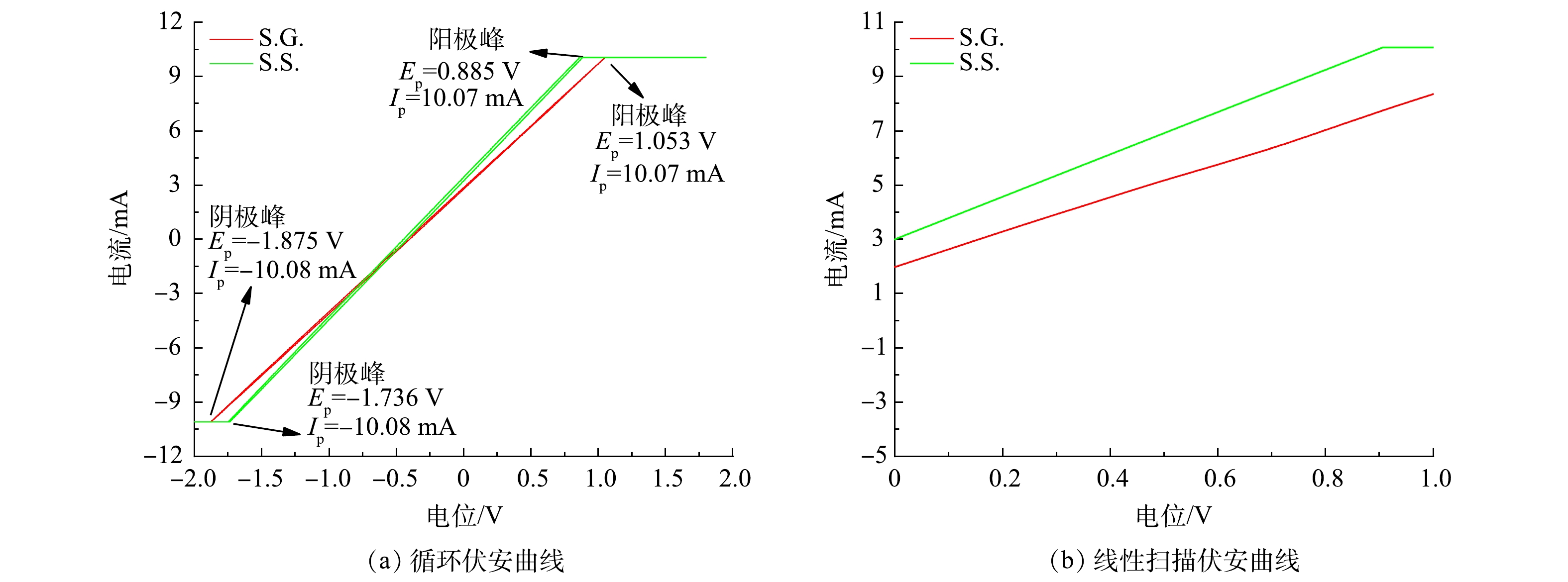
通过电化学实验考察了S.G.和S.S.阳极的生物电化学活性。CV通常用于分析基于生物膜的胞外电子传递机制 [35]。S.S.与S.G.的氧化电流同为10.07 mA(图4(a)),其还原电流/氧化电流为1.001,基本接近1,代表S.S.与S.G.均具有高可逆程度。S.G.的氧化与还原峰的峰电位差ΔE大于S.S.的ΔE,由于ΔE与转移的电子数n呈反比例关系[36],可见S.S.有着更强的产电能力。这清楚地表明S.S.具有更高的微生物活性和更快的电子转移,这可能与阳极中富集的氧化还原介质或大量参与电子传递的胞外膜蛋白覆盖在阳极有关。在JADHAV、PAREEK等的研究中 [37-38]也出现类似的原位CV扫描图。由图4(a)中可以看出,S.S.比S.G.更接近超级电容器。这是因为超级电容器的理想形状是矩形的[39]。S.S.与S.G.的电容分别为440 F和412 F,鉴于两者采用的阳极材料一致,因此S.S.的比电容比S.G.高6.7%。这是由于醋酸盐溶液的介电常数大于葡萄糖导致溶液电容的增大,并受限于位于电极及砾石上附着的生物膜自身膜电容会小于溶液电容[40]。S.S.的阳极比S.G.表现出更高的电流响应(图4(b)),表明微生物对乙酸钠的利用优于葡萄糖,并表明S.S.具有更强的氧化能力进而有助于电子转移。
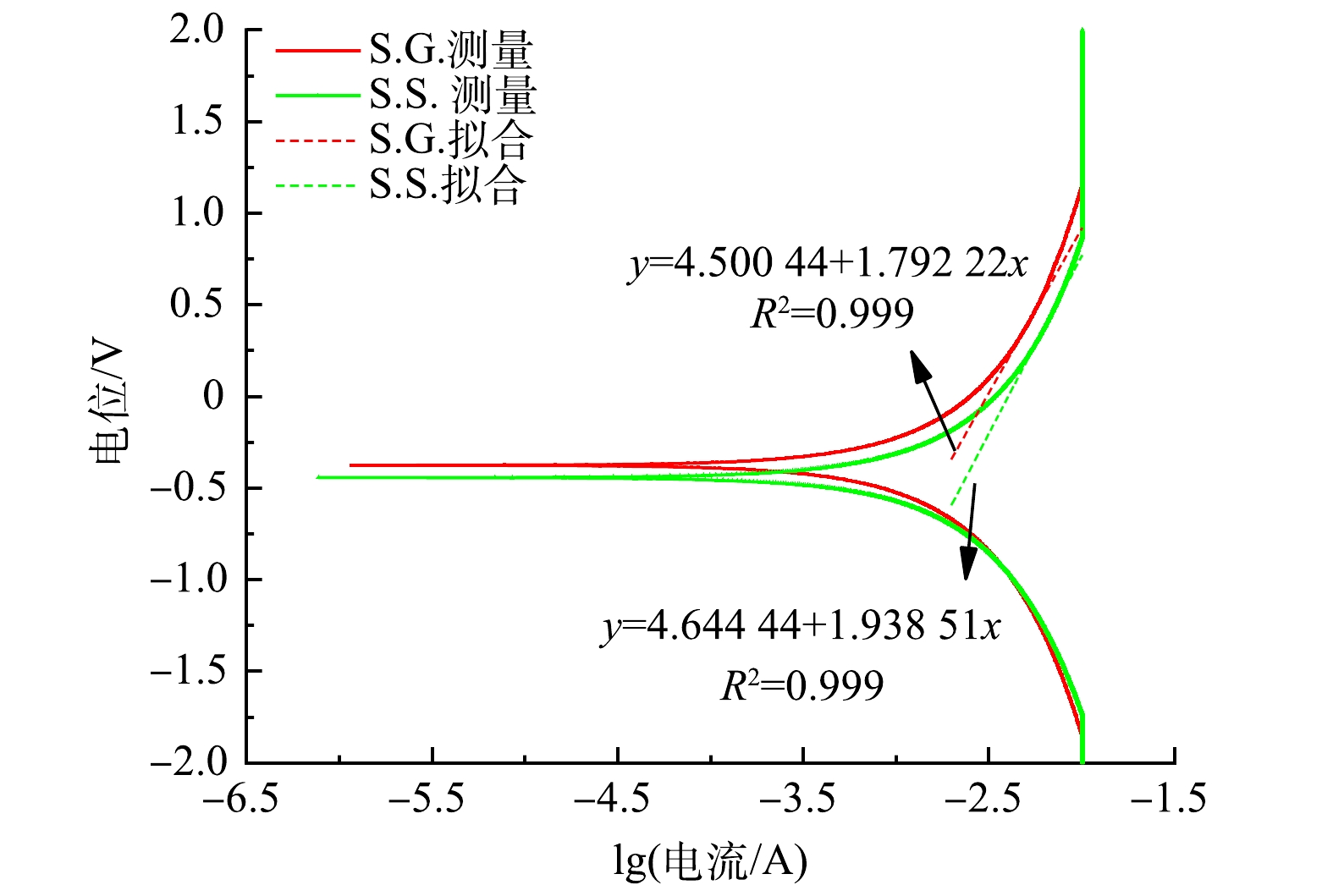
图5显示了S.G.和S.S.的阳极Tafel曲线和在0.3~0.5 V过电位区间的线性拟合曲线。将Tafel曲线外推至0 V过电位,计算出S.G.和S.S.交换电流(i0)分别为3.083×10−3 A和4.019×10−3 A。S.S.阳极的i0比S.G.高30.38%,表明S.S.阳极具有更高的动力学活性,更快的氧化还原速率,更小的活化损失。这与CV测量的电子传递速度较快的结果一致。结合LSV(图4(b))曲线结果可知,S.S.的阳极反应更容易发生,并具有更强的去极化作用。这进一步说明S.S.具有更高的功率密度输出。
在EIS分析中,奈奎斯特图表明系统的内阻决定了不同基质碳源下系统的性能。其中,高频区域的半圆与阳极生物膜的电性能有关。测量阻抗谱通常是由极化电阻(电荷转移电阻,Rp) [41]、溶液电阻(欧姆电阻,Rs)、韦伯阻抗扩散元件(W)与常相角元件(CPE)组合而成。S.S.和S.G.的Rp分别为45.2 Ω和197 Ω (图6),由于Rp与i0成反比,故此结果进一步表明S.S.阳极生物膜促进了电子从乙酸钠分子向阳极进行转移,提高了乙酸钠的氧化速率 [37],亦说明S.S.有更强的阳极电荷转移能力。之所以没有观察到完整的半圆电弧,是因为仪器的最大频率限制。同时,S.G.拟合的Rs为负值的原因可能是由于在电子学中某些电路和器件的特性,例如在BOINOVICH等的研究中也未显示出Rs的结果 [42]。EIS分析结果还显示,S.S.的韦伯阻抗电阻为3.36×10−4 Ω,小于S.G.(6.35×10−4 Ω),从而使S.S.形成的离子向电极界面的扩散能力更强,并有助于提高电荷传递能力 [43]。葡萄糖分子较乙酸钠分子大,会导致形成的离子半径大,进而在运动时存在的空间位阻就越大,而且其黏度大 [44-45]易造成局部运动能力下降,使得离子扩散受阻,这可能是S.G.内阻较大的原因。S.S.的界面电容达到1.5×10−8 F,远大于S.G.的6.18×10−9 F,这意味着S.S.能够传递更多的电流。S.S.的N值为0.939,比S.G.的0.807更接近于1,说明S.S.离理想电容的偏离度更小。这些结果均与本节所述CV、LSV和TAFEL结果一致。本研究所构建的一体化下流式CW-MFC,无论是以乙酸钠还是葡萄糖作为基质碳源所产生的内阻均远低于YE等[46]的研究结果。同时考虑到S.G.和S.S.两者的设计和运行条件都是相同的,唯独基质碳源不一样,故氧化还原活性的变化还可能与微生物代谢基质碳源有关。综上所述,乙酸钠作为基质碳源有助于在阳极上形成有效地电活性生物膜并促进电子的转移,能够实现高电压及功率密度输出,并有助于水体COD的去除。
2.3 微生物群落结构及功能预测
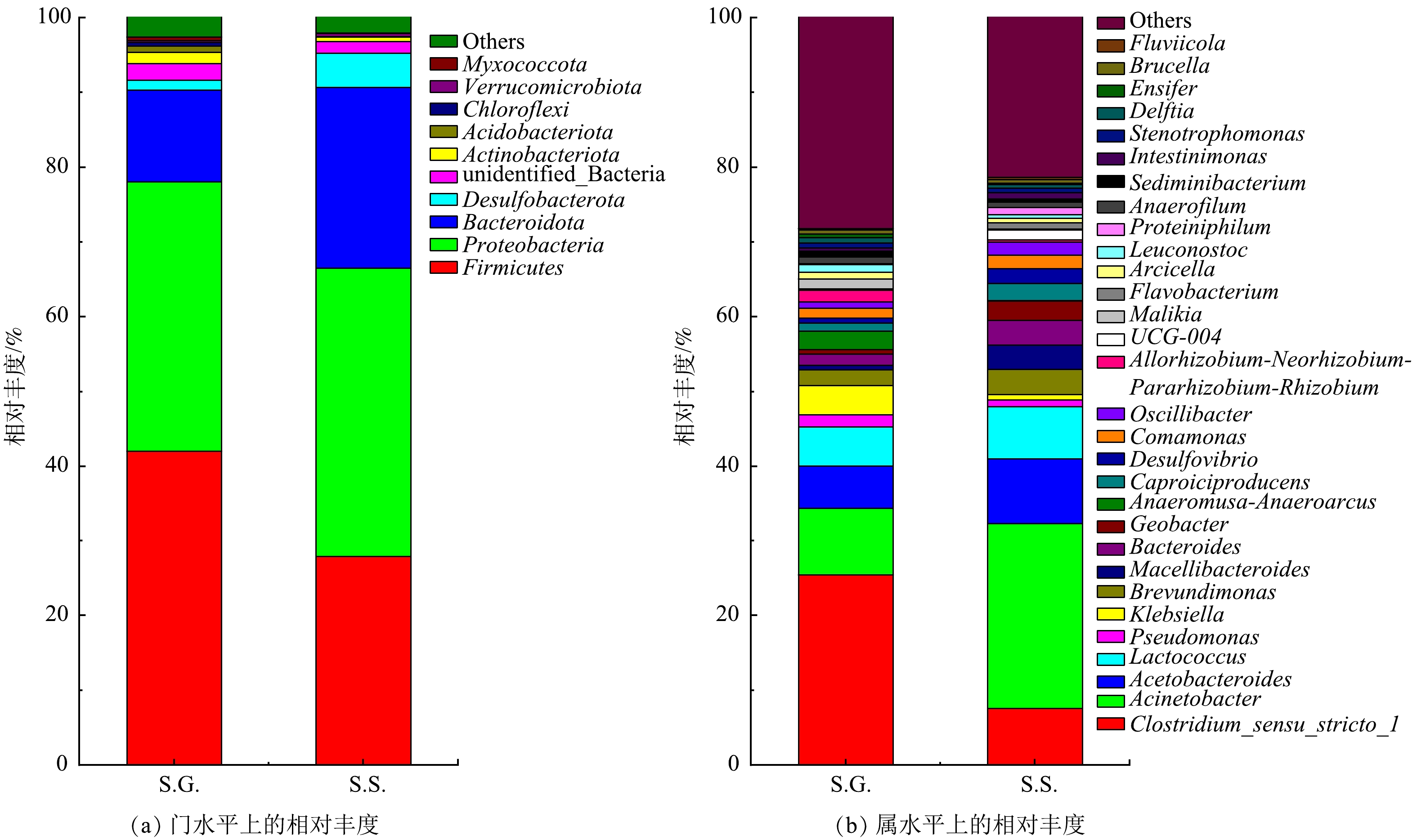
为了证明S.S.系统的发电性能优于S.G.,对S.G.和S.S.阳极中的微生物群落进行了结构分析及FAPROTAX功能预测。S.G.和S.S.的前4种优势门均被定义为MFC系统中主要的活性细菌,属于传统厌氧消化器中的关键门[47-49]。S.G.的前4种门的相对丰度之和为91.6%,其由 Firmicutes (42.0%)、Proteobacteria (36.0%)、Bacteroidota (12.3%)和 Desulfobacterota (1.3%)组成;S.S.的前4种优势门的相对丰度之和为 95.3%,其由 Firmicutes (27.9%)、Proteobacteria (38.6%)、Bacteroidota (24.2%)和 Desulfobacterota (4.6%)组成(图7(a))。
基于ACE和Chao指数的alpha多样性分析结果见表2。由于S.S.具有较高的选择性,故其微生物物种多样性更低。在属水平上(图7(b)),与S.G.相比,在S.S.中观察到 Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1(梭状芽胞杆菌)相对丰度的降低,以及 Acinetobacter(不动杆菌属)、Acetobacteroides(类醋酸杆菌属)和 Lactococcus(乳球菌属)相对丰度的升高。Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 和 Proteiniphilum 主要是沼液中的细菌,其能将有机质分解成小分子糖和小分子酸,可为产电微生物提供直接的分解基质碳源[50]。Acetobacteroides 由S.G.的5.707%增加至S.S.中的8.671%,该菌是一种产生H2和乙酸的细菌,可以降解细菌代谢的分泌物(细胞外聚合物)和死亡细菌,并能增加和丰富电子供体的数量和种类,有利于其他细菌的生长 [51-52]。众所周知,电活性微生物 Geobacter(地杆菌属)的首选电子供体是醋酸盐 [53],其相对丰度由S.G.的0.621%增加至S.S.的2.584%。Pseudomonas(假单胞菌属)可以通过电子穿梭传递电子。与其他研究 [48]结果相同, Pseudomonas 的相对丰度与 Geobacter相反,该菌由S.G.的1.533% 降低至S.S.的0.884%。Acinetobacter 由S.G.的8.879%大幅增至S.S.的24.718%,这进一步说明 Acinetobacter在发电过程中起着重要作用。SCIARRIA等[54]也得出了类似的结果。Lactococcus 从S.G.的5.259%增至S.S.的6.972%,其可以介导电子向细胞外电子受体的转移,并进行细胞外电子向阳极的转移,同时与其他微生物一起负责更高的功率密度输出[55]。本研究发现了一个有趣的现象,Brevundimonas(短波单胞菌属)由S.G.的2.052%增至S.S.的3.366%,能将硝酸盐还原为亚硝酸盐[56]。这进一步说明电子除供给给阴极以形成高电压外,还可以供给于反硝化作用。总之,S.S.系统中存在着更多的电活性微生物,但这些微生物共存对发电性能的影响还有待进一步的研究。
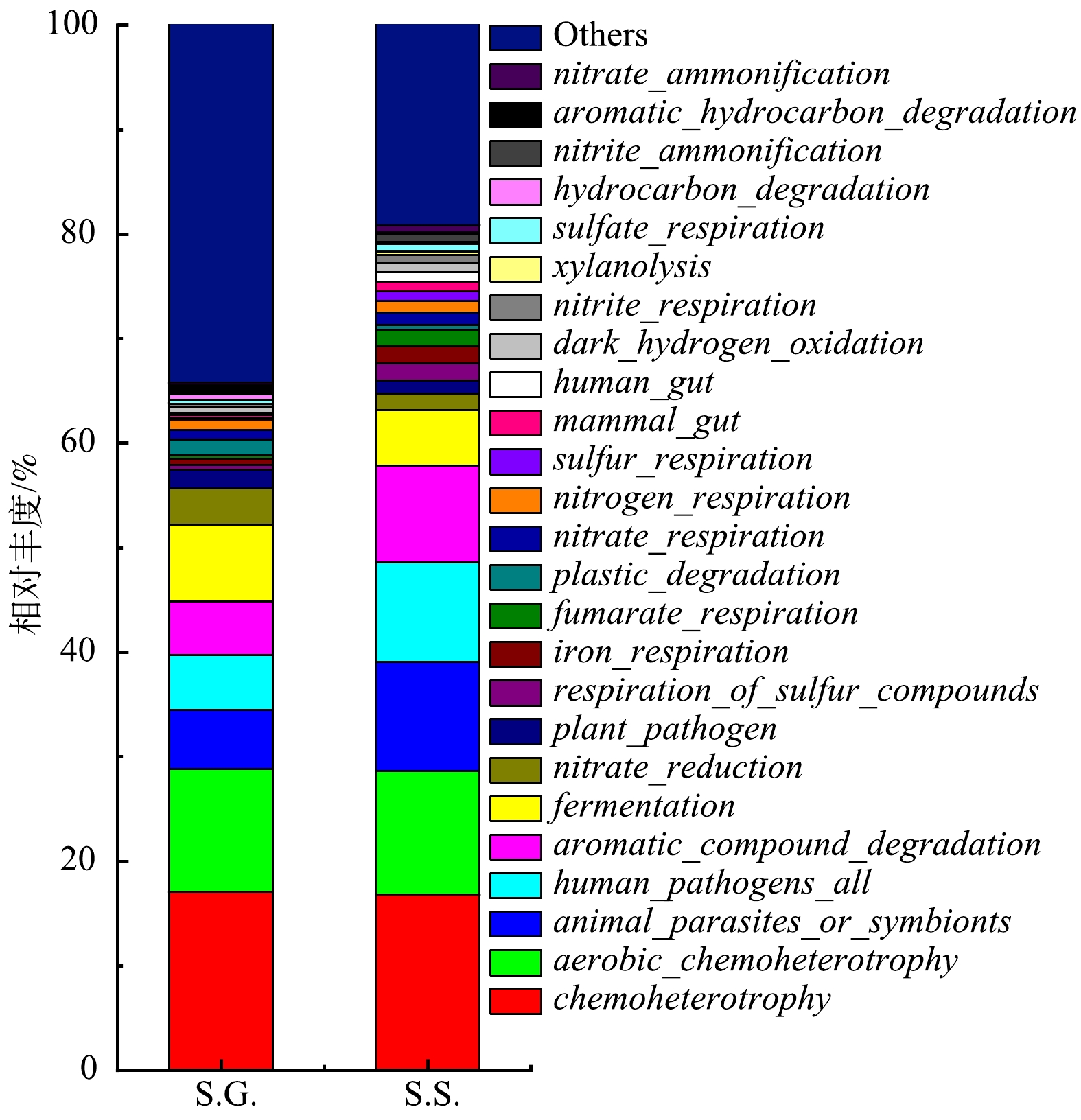
表 2 Alpha指数统计表Table 2. Alpha index statistical table基质碳源 有效OTUs Chao1 Shannon Simpson Ace S.G. 1 136 1 140.042 6.017 0.922 1 150.820 S.S. 729 777.030 5.676 0.943 783.491 根据FAPROTAX功能预测结果(图8)可知,S.G.的 fermentation 的相对丰度比S.S.高2.047%,表明S.G.系统有着更多的细菌(Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1)代谢葡萄糖。乙酸钠有助于细菌生长和繁殖,因此S.S.的呼吸细菌(iron_respiration、nitrogen_respiration、sulfur_respiration 和sulfate_respiration)相对丰度比S.G.高。由于呼吸细菌在电子传递过程中起着重要的作用,故可以氧化电子供体并伴随其他物质的还原,同时为生命活动储存能量。呼吸细菌自身还可以作为电极催化剂,促进电子从基质碳源向电极转移 [57],S.S.的呼吸细菌相对丰度更高进一步表明S.S.能够具有更强的产电性能和电化学性能。S.S.比S.G.有更高的产电性能还可能是由于 aromatic_compound_degradation 和 xylanolysis 细菌能够降解有机物,S.S.中的 aromatic_compound_degradation 和 xylanolysis 分别比在S.G.高出4.1%和0.34%。此外,以牺牲另一有机体(宿主)为代价生长的 animal_parasites_or_symbionts 从S.G.的5.6426%增至S.S.的10.4624%,其变化趋势与 Acetobacteroides 相似。在S.S.中, dark_hydrogen_oxidation 比在S.G.高0.3262%,其属于无机自养细菌可以利用H2作为电子供体并同化CO2,因此,在S.S.中可以进一步产生更多的电子。同时还观察到, nitrite_ammonification 在S.G.和S.S.的相对丰度分别为0.272%和0.709%,nitrate_ammonification 在S.G.和S.S.的相对丰度分别为0.262%和0.698%。这种氨化菌可以以氨化合物为基质进行除氨并产电 [58]。因此,与产电有关的一些细菌的相对丰度在S.S.中高于在S.G.中。
3. 结论
1)乙酸钠相比葡萄糖更适合作为CW-MFC的基质碳源,所设计的下流式未种植植物CW-MFC可产生483 mV输出电压并具有高功率密度输出(48.14 mW·m−2)。
2) S.S.具有更强的去极化能力和电荷转移能力,以及更低的Rp(45.2 Ω),并具有更大的界面电容(1.5×10−8 F)。
3)基于相同的体系在不同的基质碳源下观察到微生物群落结构及FAPROTAX功能预测结果,证实了与发电相关的细菌的相对丰度在S.S.中高于S.G.。
-
[1] 楼紫阳.填埋场渗滤液性质演化过程研究. 上海:同济大学博士学位论文, 2006 Lou Z.Y. Natural attenuation process of leachate at a closed landfill. Shanghai: Doctoral Dissertation of Tongji University, 2008(in Chinese) [2] Baun A., Reitzel L.A., Ledin A., et al. Natural attenuation of xenobiotic organic compounds in a landfill leachate plume (Vejen, Denmark). Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2003,65(3-4):269-291 [3] 欧远洋. 渗滤液化学性质研究.上海:同济大学硕士学位论文,2004 Ou Y. Y. Study on chemical characteristics of landfill leachate. Shanghai: Master's Degree Thesis of Tongji University, 2008(in Chinese) [4] 王艳捷, 邱忠平, 吴敏, 等. "中老龄"垃圾渗滤液重金属和氨氮的厌氧毒性. 环境工程学报,2008,2(10):1353-1356 Wang Y. J., Qiu Z. P., Wu M., et al. Research of anaerobic toxicity of heavy metal and ammonia nitrogen in "mature" landfill leachate. China Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2008,2(10):1353-1356(in Chinese) [5] 简放陵, 刘洁萍, 叶新方, 等. 垃圾渗滤液物化处理研究. 环境工程学报, 2007,1(3):116-118 Jian F. L., Liu J. P., Yue X. F., et al. Research on physical and chemical treatment of municipal solid waste landfill leachate. China Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007,1(3):116-118(in Chinese) [6] Kheradmand S., Karimi-Jashni A., Sartaj M. Treatment of municipal landfill leachate using a combined anaerobic digester and activated sludge system. Waste Management, 2010,30(6):1025-1031 [7] De Morais J. L., Zamora P. P. Use of advanced oxidation processes to improve the biodegradability of mature landfill leachates. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2005,123(1-3),181-186 [8] Foo K. Y., Hameed B. H. An overview of landfill leachate treatment via activated carbon adsorption process. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009,171(1-3):54-60 [9] 楼紫阳, 赵由才, 张全. 渗滤液处理处置技术及工程实例. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2006 [10] Renou S., Givaudan J. G., Poulain S., et al. Landfill leachate treatment: Review and opportunity. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008,150(3),468-93 [11] 位菁, 张彩香, 马腾. 混凝去除垃圾渗滤液中DOM的实验研究. 环境科学与技术, 2007,30(8):1-2 Wei J., Zhang C. X., Ma T. Removal of DOM in leachate by coagulation. Environmental Science and Technology, 2007,30(8):1-2(in Chinese) [12] 王宝贞, 王承武, 杨铨大, 等. A(缺氧活性污泥)/B(A/O淹没式生物膜)复合系统处理垃圾填埋场渗沥液.给水排水,1996,22(5):15-18 Wang B. Z., Wang C.W., Yang S. D., et al. Composite system of anoxic activated sludge submerged A/O biofilm to treat urban domestic refuse infiltration liquid. Water & Wastewater Engineering, 1996,22(5):15-18(in Chinese) [13] 郭广寨,苏良湖,孙旭, 等.不同粒径零价铁(ZVI)对污水污泥H2S和CH4释放速率的影响. 环境工程学报,2012,6(5):1693-1698 Guo G. Z., Su L. H., Sun X., et al. Effect of different particle sizes of zero-valent iron (ZVI) on H2S and CH4 emission in sewage sludge. China Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2012,6(5):1693-1698(in Chinese) [14] Zhen G. Y., Yan X. F., Zhou H. Y., et al. Effects of calcined aluminum salts on the advanced dewatering and solidification/stabilization of sewage sludge. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011,23(7):1225-1232 [15] 张云霞, 王瑞, 王立彤, 等. 填埋方式对污泥填埋稳定性的影响. 中国给水排水, 2011,27(11):75-77 Zhang Y. X., Wang R., Wang L. T., et al. Influence of landfill modes on stabilization of sludge landfill. China Water & Wastewater, 2011,27(11):75-77(in Chinese) [16] 朱英. 卫生填埋场中污泥降解与稳定化过程研究. 上海:同济大学博士学位论文, 2008 Zhu Y. Sludge biodegradation and stabilization process in the sanitary landfill. Shanghai: Doctoral Dissertation of Tongji University, 2008(in Chinese) [17] 张华. 污泥改性及其在填埋场中的稳定化过程研究. 上海:同济大学博士学位论文, 2007 Zhang H. Geotechnical properties transformation and stabilization process of sewage sludge in lysimeters. Shanghai: Doctoral Dissertation of Tongji University, 2007(in Chinese) [18] 马建立, 魏云梅, 赵由才. 矿化污泥基质分析及作为生物填料可行性研究. 新农村建设与环境保护:华北五省市区环境科学学会第十六届学术年会, 秦皇岛,2009.495-500 Ma J.L., Wei Y.M., Zhao Y.C. Characterization of aged sludge and its feasibility as bio-filler. Sixteenth Annual Conference of the Society of Environmental Science of the Five Provinces and Municipalities in North China:New Rural Construction and Environmental Protection, Qinhuangdao,2009.495-500(in Chinese) [19] 姜应和, 柳君侠. 粉煤灰碎砖颗粒除磷实验研究. 环境工程学报,2011,5(7):1532-1537 Jiang Y. H., Liu J. X. Experimental study on phosphorus removal by fly ash brickbat particle. China Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2011,5(7):1532-1537(in Chinese) [20] 刘转年, 刘源, 王贵荣. 超细粉煤灰基成型吸附剂的动态吸附实验. 环境工程学报, 2009,3(11):2109-2112 Liu Z. N., Liu Y., Wang G. R. Dynamic adsorption experiments of forming ultrafine coal fly ash-based adsorbent. China Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009,3(11):2109-2112(in Chinese) [21] 耿朋飞, 高帅, 楚风格.粉煤灰的综合利用. 洁净煤技术, 2012,18(2):102-104 Di P. F., Gao S., Chu F. G. Comprehensive utilization of fly ash. Clean Coal Technology, 2012,18(2):102-104(in Chinese) [22] 石磊, 张全, 牛冬杰, 等. 矿化垃圾反应床处理渗滤液的微生物学特性. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2007,35(8):1085-1089 Shi L., Zhang Q., Niu D. J., et al. Microbiological characteristics of aged-refuse-based bioreactor for landfill leachate treatment. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2007,35(8):1085-1089(in Chinese) -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2269
- HTML全文浏览数: 1146
- PDF下载数: 1038
- 施引文献: 0





 下载:
下载: