水解/AMBBR/好氧工艺和传统A/O工艺处理低碳源污水的对比研究
Comparative study of low carbon source wastewater treatment by hydrolysis acidification/anoxic moving biological biofilm reactor/aerobic process and conventional anoxic/aerobic process
-
摘要: 为提高低碳氮比污水中易生物降解有机物的含量,实验设计了水解(H)/移动床生物膜反应器(AMBBR)/好氧(O)工艺,并与传统A/O工艺对比,考察其作为低碳源污水脱氮工艺的可行性。通过小试对比低温下(10.9~13℃)两工艺中污泥的反硝化性能,并进行了实验室规模的中试运行。小试结果显示,AMBBR两相污泥对硝酸盐的去除率比单纯反硝化污泥高出19.4%。中试结果表明,相同的运行条件下,两工艺对COD和NH3-N的去除效率相当,但H/AMBBR/O工艺对总氮的去除效率均优于传统A/O工艺;在各自最优工况下,前者平均总氮去除率较后者高出22.39%,且前者通过剩余污泥的回流水解实现了部分污泥减量化,尤其是对于温暖地区,该工艺能够有效改善低碳源污水脱氮性能。Abstract: The hydrolysis acidification (H)/anoxic moving biological biofilm reactor (AMBBR)/aerobic (O) process was employed to improve the content of easily biodegradable organisms in low carbon source wastewater, and it was compared with the conventional anoxic (A)/aerobic (O) process, to see its feasibility in nitrogen removal of low carbon source wastewater. Denitrification performance of both sludge from the two processes were investigated at low temperatures(10.9~13℃), and the laboratory pilot scale operation of the two processes were also studied. Results from bench scale test show that the nitrate removal efficiency of two-phase sludge from AMBBR was 19.4% higher than that of single anoxic sludge. Also, results from pilot scale test showed that under the same conditions, the removal efficiencies of COD and ammonia were almost the same in both process, while total nitrogen removal efficiency in H/AMBBR/O process was always higher than that of A/O process, and the D-value attains 22.39% under their best conditions. Besides, in the process of H/AMBBR/O, sludge reduction was realized through backflow hydrolysis. It was believed that the H/AMBBR/O process could improve carbon source effectively, especially in warm areas.
-
Key words:
- low C/N ratio /
- sewage wastewater /
- nitrogen removal /
- H/AMBBR/O
-
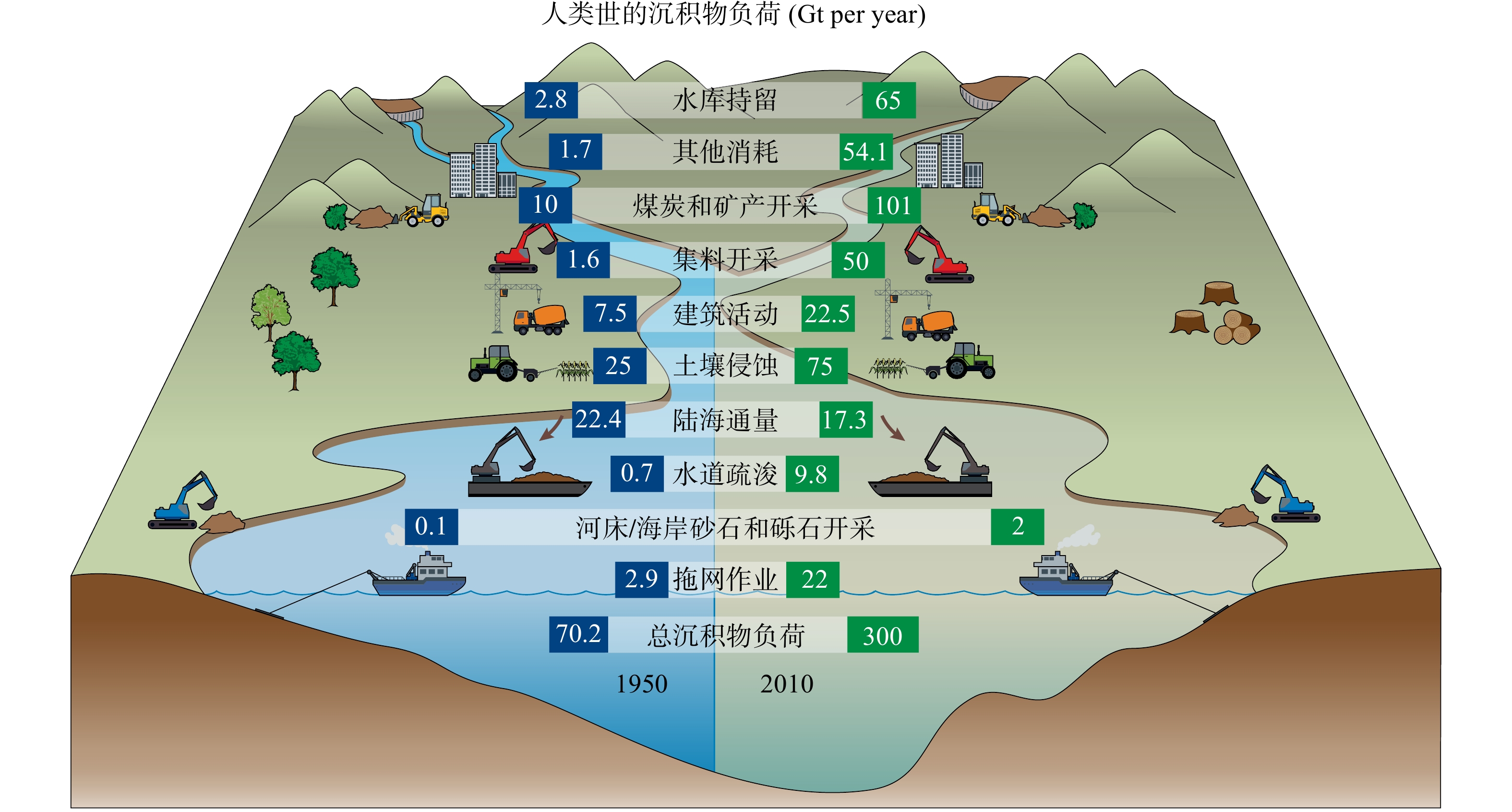
河流是连接陆海的物质循环通道,其对颗粒物的输移过程是全球沉积循环的重要环节。人类活动改变了沉积物的迁移、输运和封存,如今人类活动已在全球尺度上主导了上述通量过程[1]。我国长江流域的沉积物也呈现出类似的演变特征[2-3]。2006—2017年长江上游和全流域的泥沙输出量相较于1950—1985年平均水平,分别减少了96%和74%。上游大坝建设已成为泥沙减少的主要原因。随着上游梯级大坝体系的建成并运行,导致流域沉积物传输的连通性相应下降,河流水文节律随之改变,河流-湖泊相互作用减弱。不仅如此,沉积物来源正在从上游流域的地表土壤侵蚀向中下游流域河道侵蚀转变,沉积物成分和相关养分负荷均在发生变化[2]。中下游河流河道和河岸侵蚀严重,威胁着长江堤岸的稳定性。以三峡水利枢纽为代表的中上游水库群建设运行后,长江沉积物通量变化引起的中游崩岸、长江口侵蚀等问题需要高度关注。
沉积物通量的变化还将引起碳、磷、硅等生源要素海陆循环的深刻变化(图1)。河流生源要素输送对海洋及流域本身的水生生态系统均具有极为重要的意义。亚马逊河、长江等大河输送的营养物质为河口海区海洋生物以及河流内部的水生生物的繁殖提供了重要营养物质保证[2, 4]。然而,全球闸坝建设会导致河流沉积物通量减少,从而对生源物质循环造成深刻影响[5]。同样以长江为例,2003年,以三峡水利枢纽为核心的上游干支流水库群运行以后,长江中下游的总磷和颗粒态磷通量分别减少了77%和75%[6]。上游水库拦截了大约50×103~100×103 t·a−1的潜在生物有效磷[6],其潜在环境效应超过了当前人类活动注入磷的数量。上游水库磷累积增加了水域富营养化潜势,成为潜在的污染源,而这本应该成为长江河口及近岸海域的生物营养资源。由此可以看出,由于河流闸坝建设及河运等人类活动所带来的全球沉积循环的变化,将对生源要素的陆海生物地球化学产生深刻影响,其中,大河流域沉积物通量减少,以及伴随的生源要素的减少,其长期环境效应必须引起学者们的重视。
长江经济带横跨中国东中西三大地理区域,是具有全球影响力的内河经济带、东中西互动合作的协调发展带、沿海沿江沿边全面推进的对内对外开放带,也是生态文明建设的先行示范带。2016年1月5日,习近平总书记在推动长江经济带发展座谈会上强调,共抓大保护、不搞大开发,努力把长江经济带建设成为生态更优美、交通更顺畅、经济更协调、市场更统一、机制更科学的黄金经济带,探索出一条生态优先、绿色发展新路子。经过各方共同努力,目前,长江经济带生态环境总体改善、经济发展向好。但同时也应该看到,由于长江流域水沙新态势的形成,长江流域物质基础边界发生了新的变化,这种变化必须在长江生态环境修复和保护工作中予以足够的考虑。正如SYVITSKI Jaia 在论文中所提议,在学界发起地球沉积循环重大挑战性问题(“Earth Sediment Cycle Grand Challenge”)研究计划,开展生物地球物理-工程-社会耦合的多维度分析,以期为与之相关人类活动的规划和工程提供参考与指导。为此,希望我国学术界针对长江流域人类世沉积循环新的特征,结合长江流域详实的监测数据进行分析和研判,全面认识和把握长江水资源及其高度关联的水环境、水生态重大问题,形成长江水资源保护与开发的系统观点看法和对策建议,从而为长江经济带战略提供科技支撑。

原文作者
SYVITSKI Jaia, 国际著名沉积学家、美国科罗拉多大学教授。研究领域为沉积物输送、海陆相互作用和地球表面动力学。她曾担任地表动力学模拟系统研究群体(Community Surface Dynamics Modeling System,CSDMS)执行主任,领导68个国家科学家开发、支持和应用综合计算机模型;主持了国际科学协会理事会(International Council for Science,ICSU)的国际地圈生物圈计划(2011—2016年)。2009年获得加拿大皇家学会亨斯迈奖章,2016年获得SEPM Francis Shepard奖章。E-mail:jai.syvitski@colorado.edu。
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 1513
- HTML全文浏览数: 730
- PDF下载数: 923
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载:
