响应曲面法优化絮凝处理木薯淀粉废水
Application of response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize coagulation treatment of cassava starch wastewater
-
摘要: 采用中心复合实验设计和响应面分析法研究复合絮凝剂聚合氯化铝锌(PAZC)和聚合氯化铝(PAC)混凝处理木薯淀粉废水,进行设计和分析,以溶液pH值和絮凝剂用量为考察因素,分别以COD、浊度去除率为考察指标,选用最佳优化数学模型描述考察指标和考察因素之间的数学关系,并以设定PAZC和PAC对COD去除率(65%),浊度去除率(90%)和SS去除率(90%)的目标值,通过等高线叠加图预测最优实验条件,得到PAZC投量为6.5 mg/L,pH为7.7时,COD去除率和浊度去除率分别达到最大为76.6%和99.9%;PAC投量为19.2 mg/L,pH为7.8时,COD去除率和浊度去除率最大值分别为64.4%和97.1%。经对最优条件进行验证,预测值与验证实验平均值接近。Abstract: The removal efficiencies for chemical oxygen demand (COD), turbidity using a new polymer flocculent polymeric aluminum zinc chloride (PAZC) were compared with those obtained using polyaluminum chloride (PAC) as a conventional coagulant. Central composite design (CCD) and response surface method (RSM) were applied to optimize the operating variables viz. pH and coagulant dosage. Quadratic models developed for the two responses (COD and turbidity) studied and the contour plot overlaying critical response contours (65% COD removal, 90% turbidity removal and 90% SS removal) indicated the optimum conditions to be PAZC dosage of 6.5 mg/L at pH 7.7 and PAC dosage of 19.2 mg/L at pH 7.8. The experimental data and model predictions agreed well.
-
为了增强镀液的分散能力和达到良好的镀层效果,电镀工艺常向镀液中投加大量络合剂,这些络合剂与重金属离子配位结合形成络合重金属[1]。电镀过程中,仅有一小部分金属被有效镀在物件上,其他的均以废水的形式排出[2]。络合重金属具有生物难降解性和高毒性,由于络合重金属具有很高的水溶性,且可在广泛的pH范围内稳定存在,故常规的化学沉淀法难于将其从水中去除[3]。
高级氧化技术广泛用于络合重金属的处理,如芬顿氧化[4]、臭氧氧化[5]和电催化氧化[6],解络后游离的重金属离子一般是通过加碱沉淀予以去除。但在电催化处理中,由于可以通过电还原的方式使重金属离子在阴极表面沉积,因此,电催化技术在络合重金属解络的同时还可以实现重金属离子的回收,使出水中的重金属离子浓度极大地降低,从而减少碱的投加和污泥的产生[7]。目前,电催化技术大多基于电催化氧化原理,利用氧化性活性物种(·OH、Cl·和
SO⋅−4 粒子电极是近些年研究比较多的电极材料,通过填充在阴阳极板间构成电极床而实现污染物质的降解去除[9]。在电场的驱动下,粒子可以形成微小的复极性电极,粒子的一端为阳极端,另一端为阴极端,因此在粒子电极的表面既可以发生氧化反应又可以发生还原反应[10]。由于粒子电极大大地增加了污染物与电极之间的有效接触面积,是传统板状电极面积的几十到几百倍,而且每2个相邻的粒子电极之间距离很小,因此,粒子电极的填充缩短了污染物迁移距离和传质距离,提高了传质速率。因而,仅需较低的电流密度即可获得较高的电流强度,并实现较高的电流利用效率[11]。粒子电极床广泛运用在印染废水[12]、焦化废水[13]和制药废水[14]等的废水处理中。粒子电极通常由催化剂和载体组成。常用于电还原的金属催化剂包括Pd、Pt、Fe、Cu、Co和Ni[15-18]。贵金属催化剂具有高催化活性,然而,他们的稀有性和高昂的价格阻碍了其大规模应用。Ni是一种过渡金属,具有高电流密度和低过电位的特点,并且资源丰富、价格低廉和稳定性高。Ni具有出色的还原性能,法拉第效率接近100%,因此,被广泛用作电还原催化剂[19-20]。粒子电极的载体材料有高岭土[21]、γ-Al2O3[22]、泡沫镍[23]、活性炭[24]和介孔碳[25]等,活性炭由于价格低廉、比表面积巨大和化学性质稳定等优点而被广泛用作粒子电极的载体,但其导电性和电子传递效率较差[26]。石墨烯是一种二维碳材料,可以为离子和电子的传输提供较短的有效长度,从而可以增强传质和电荷传输[27-28],在活性炭载体材料中掺杂石墨烯可以增强粒子电极的传质效率和导电性。因此,本文以Ni为催化剂,活性炭(PAC)和氧化石墨烯(GO)为载体制备了催化粒子电极。由于乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)是一种非常重要的络合剂,广泛应用于镀铜工艺,故本文选择Cu-EDTA作为目标污染物,考察了粒子电极焙烧温度、焙烧时间和PAC与GO比例对Cu-EDTA解络效能的影响,探讨了最佳制备条件下的粒子电极对Cu-EDTA解络和铜回收率的影响及相关机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 试剂与仪器
1)主要试剂和材料:活性炭(PAC)购于北京科诚光华公司,氧化石墨烯(GO)购于深圳图灵公司;阴极板Ti(6 cm×2.5 cm)和阳极板Ti/RuO2(6 cm×2.5 cm)购于北京恒力钛公司;五水合硫酸铜、乙二胺四乙酸二钠、六水合硝酸镍、硫酸钠、聚乙烯醇、叔丁醇、苯酚均为分析纯,磷酸铵为优级纯,购于国药公司;5,5-二甲基-1-氧化吡咯啉(DMPO)购于梯希爱化成公司;乙腈为色谱纯,购于赛默飞世尔科技公司。
2)主要仪器:高效液相色谱仪(Agilent 1260,安捷伦科技有限公司),原子吸收分光光度计(AA7000,日本岛津有限公司),扫描电子显微镜(SU8220,日立高新技术公司),X射线衍射分析仪(XRD-7000s,日本岛津有限公司),电子顺磁共振仪(EMX plus,Bruker),电化学工作站(CHI660E,上海辰华公司)。
1.2 Cu-EDTA模拟废水的配制
称取CuSO4·5H2O和Na2EDTA溶解于去离子水中,配制10 mmol·L−1 Cu-EDTA储备液,Cu2+与EDTA摩尔比为1∶1。实验前,使用去离子水稀释至1 mmol·L−1,并加入10 mmol·L−1 Na2SO4作为电解质。
1.3 粒子电极的制备及表征方法
1)粒子电极的制备。将Ni(NO3)2·6H2O 溶于去离子水中配得0.5 mol·L−1溶液,将PAC与GO充分混合并浸渍于硝酸镍溶液中,恒温振荡8 h后,离心取出并烘干。向混合粉末中加入质量分数为5%的聚乙烯醇,造粒后在马弗炉中焙烧。为了解焙烧温度和时间的影响,焙烧温度设置为200、300、450、600和800 ℃,焙烧时间4 h;焙烧时间设置2、4、6和8 h,焙烧温度为800 ℃。在最佳焙烧温度和时间下,分别制备PAC、Ni/PAC、Ni/GOx-PACy粒子电极,其中x∶y的质量比为0.5∶9.5、1∶9和2∶8。
2)粒子电极的表征。采用扫描电子显微镜观察粒子电极使用前后的表面形貌,并采用能谱仪(EDS)对样品表面元素的分布情况进行分析。使用X射线衍射分析仪对晶体结构和物相组成进行分析。
1.4 实验装置及操作方法
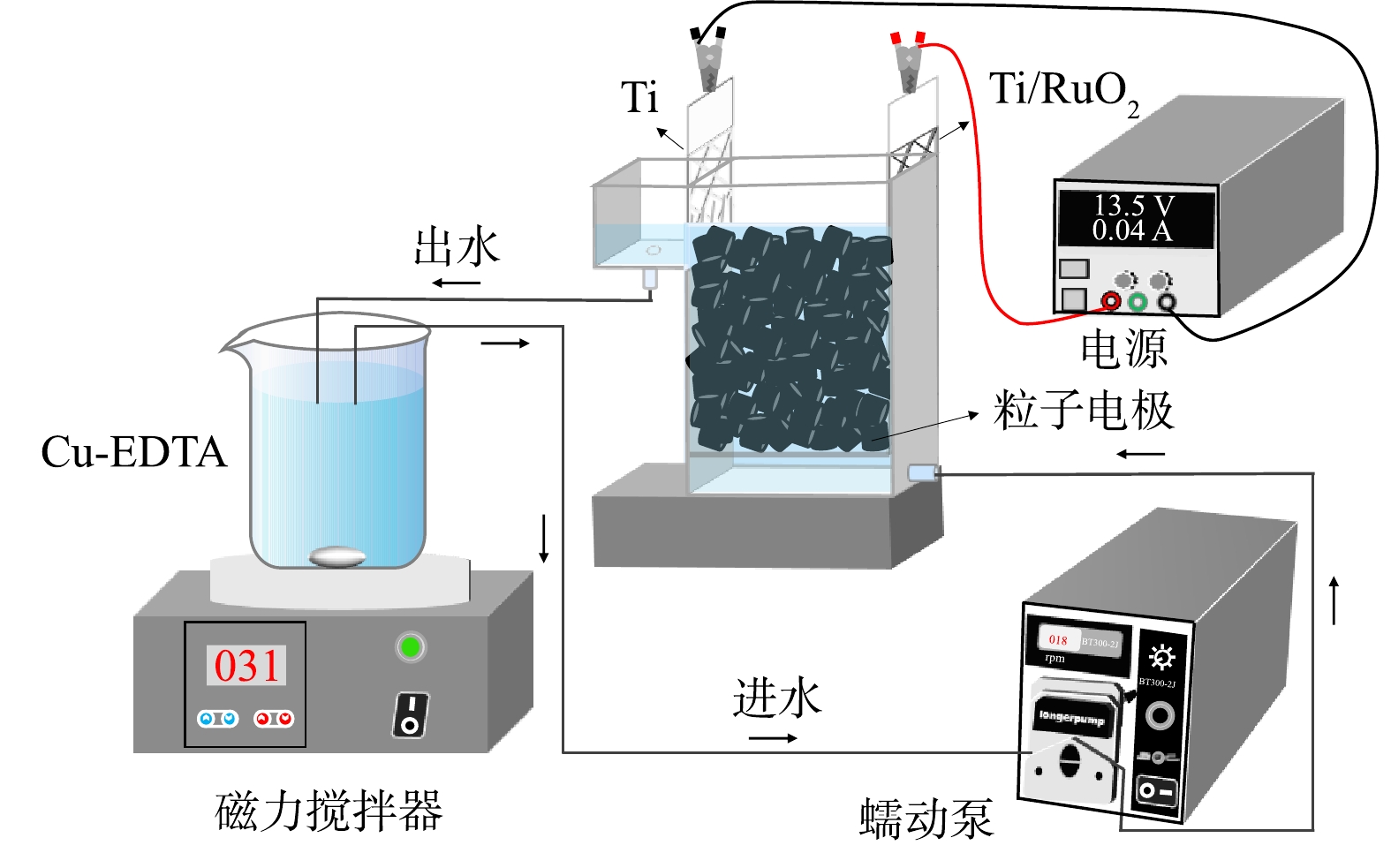
实验装置如图1所示。有机玻璃反应器的长×宽×高为3 cm×3.5 cm×2 cm,粒子电极填充量为5 g,1.00 L的Cu-EDTA模拟废水以循环方式处理,处理时间为360 min,每间隔30 min取样。一部分样品直接用于总铜(TCu)浓度的测定;另一部分样品用1 mol·L−1 NaOH调节pH至11.0,静置过夜以沉淀游离铜离子,上清液用于Cu-EDTA和总络合态铜(TCCu)的测定。TCCu指所有络合态铜物种,包括Cu-EDTA和中间态络合铜,TCu指所有铜物种,包括TCCu和游离的铜离子。
1.5 自由基的检测
使用DMPO为捕获剂,采用电子顺磁共振仪(ESR)技术测定系统中自由基的产生情况。自由基淬灭实验采用叔丁醇和苯酚作为淬灭剂,叔丁醇浓度为3.0 mol·L−1,苯酚浓度为0.7 mol·L−1。
1.6 电化学性能测试
在-0.87~2.00 V电势窗口下,采用三电极体系测试催化粒子电极在CuSO4、EDTA和Cu-EDTA中的循环伏安曲线,三者浓度均为50 mmol·L−1,扫速为50 mV·s−1。铂丝为对电极,Ag/AgCl电极为参比电极,覆有粒子电极材料的玻碳电极为工作电极。工作电极制备中,取10 mg粒子电极材料,加入质量分数为5% Nafion溶液50 μL和1 mL乙醇,混匀充分;取10 μL混合液滴于玻碳电极表面。测试前向待测溶液中充15 min氮气以除去氧气。使用能斯特方程将测试电位EAg/AgCl转换为可逆氢电极电位ERHE[29],转换关系如式(1)所示。
ERHE=EAg/AgCl+0.059pH+0.197 (1) 1.7 分析测试与计算方法
采用高效液相色谱法测定Cu-EDTA浓度,色谱柱为Agilent TC-C18柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),流动相为75%磷酸铵(20 mmol·L−1,pH为3.0)和25%乙腈,流速为1 mL·min−1,检测波长为254 nm。TCCu、TCu和镍离子的浓度采用原子吸收分光光度法测定。
电催化解络的单位电能消耗量的计算见式(2)[30]。
EEO=UjStVlog(C0C) (2) 式中:EEO为Cu-EDTA降解一个能级所需的电能,kWh·m−3;U为施加的电压,V;j为电流密度,mA·cm−2;S为电极表面积,cm2;t为反应时间,h;V为反应溶液的总体积,cm3;C0和C分别是在开始和在时间t时的Cu-EDTA浓度,mmol·L−1。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 粒子电极制备条件对Cu-EDTA解络效能的影响
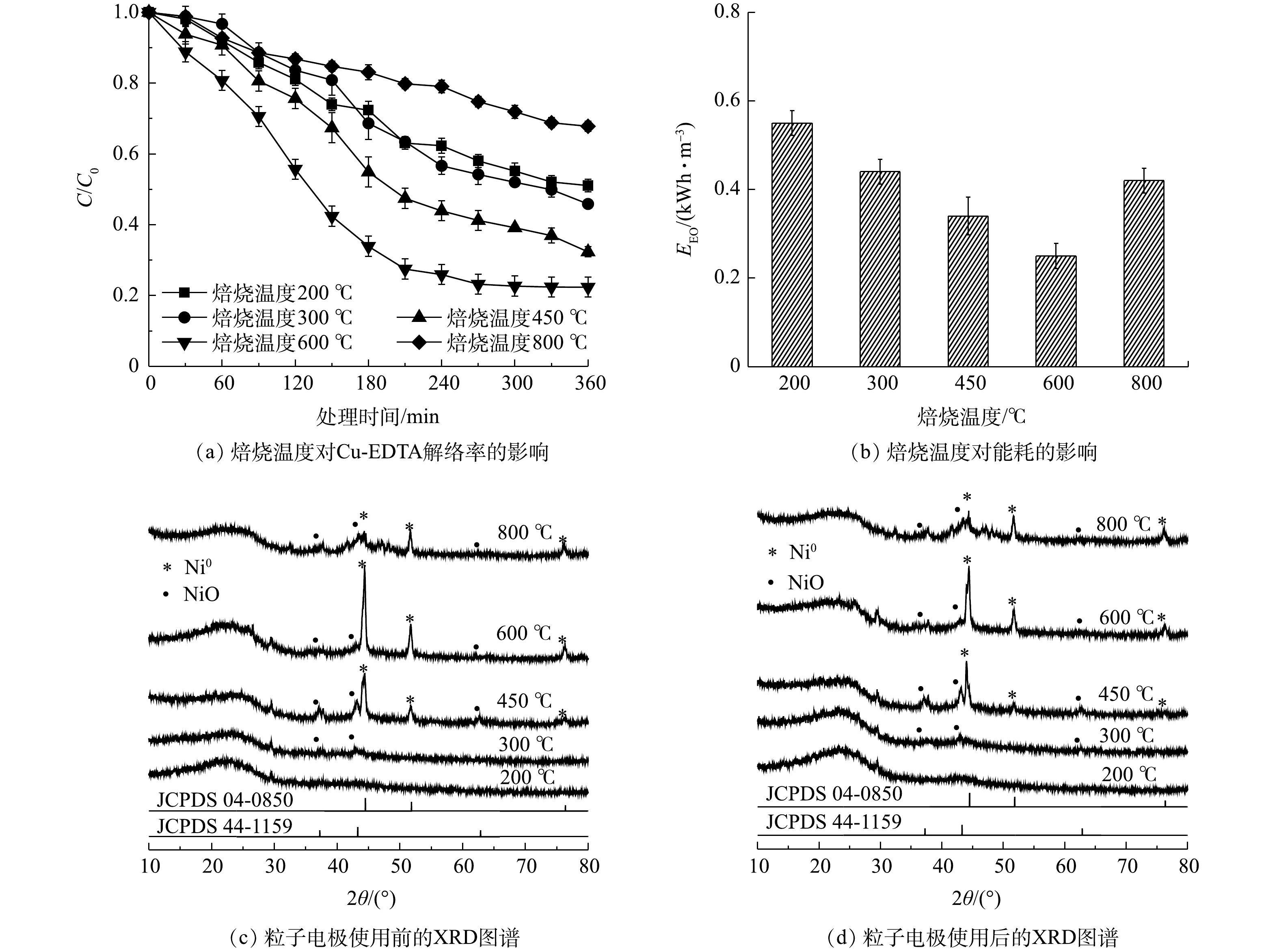
1)焙烧温度对Cu-EDTA解络效能的影响。在PAC:GO质量比为9:1和焙烧时间4 h条件下,制备了不同焙烧温度下的粒子电极。如图2(a)所示,随着温度的升高,Cu-EDTA的解络率先增加后降低,焙烧温度为600 ℃时的解络率达到最高,为77.6%;此时能耗也为最低,仅为0.25 kWh·m−3(图2(b))。由图2(c)中的XRD结果可以看出,Ni在200 ℃和300 ℃下未形成明显的催化剂晶体结构;在450~800 ℃焙烧温度下,观测到2θ为44.51°、51.85°和76.37°的3个特征峰,分别对应零价态的镍(Ni0,JCPDS 04-0850)的(111)、(200)和(220)晶面。还观测到37.25°、43.28°和62.88°处的3个微弱的特征峰,分别对应着NiO(JCPDS 44-1159)的(101)、(012)和(110)晶面。较低的焙烧温度不能使镍催化剂完全活化,因此,在催化剂上不能形成良好的晶体结构,导致粒子电极的电催化活性较低[31]。而当焙烧温度增加到800 ℃时,由于催化剂在过高的焙烧温度下容易烧结而导致粒子电极失去电催化活性[32]。正因为金属性Ni0具有一定导电性,使600 ℃下粒子电极的导电性增强,从而降低了单位电能消耗量。Ni/GO0.1-PAC0.9用于降解Cu-EDTA后,Ni的晶体结构没有发生明显变化(图2(d)),且在处理360 min后,溶液中未检测到镍离子,说明所负载的催化剂不易受到电催化过程的影响。
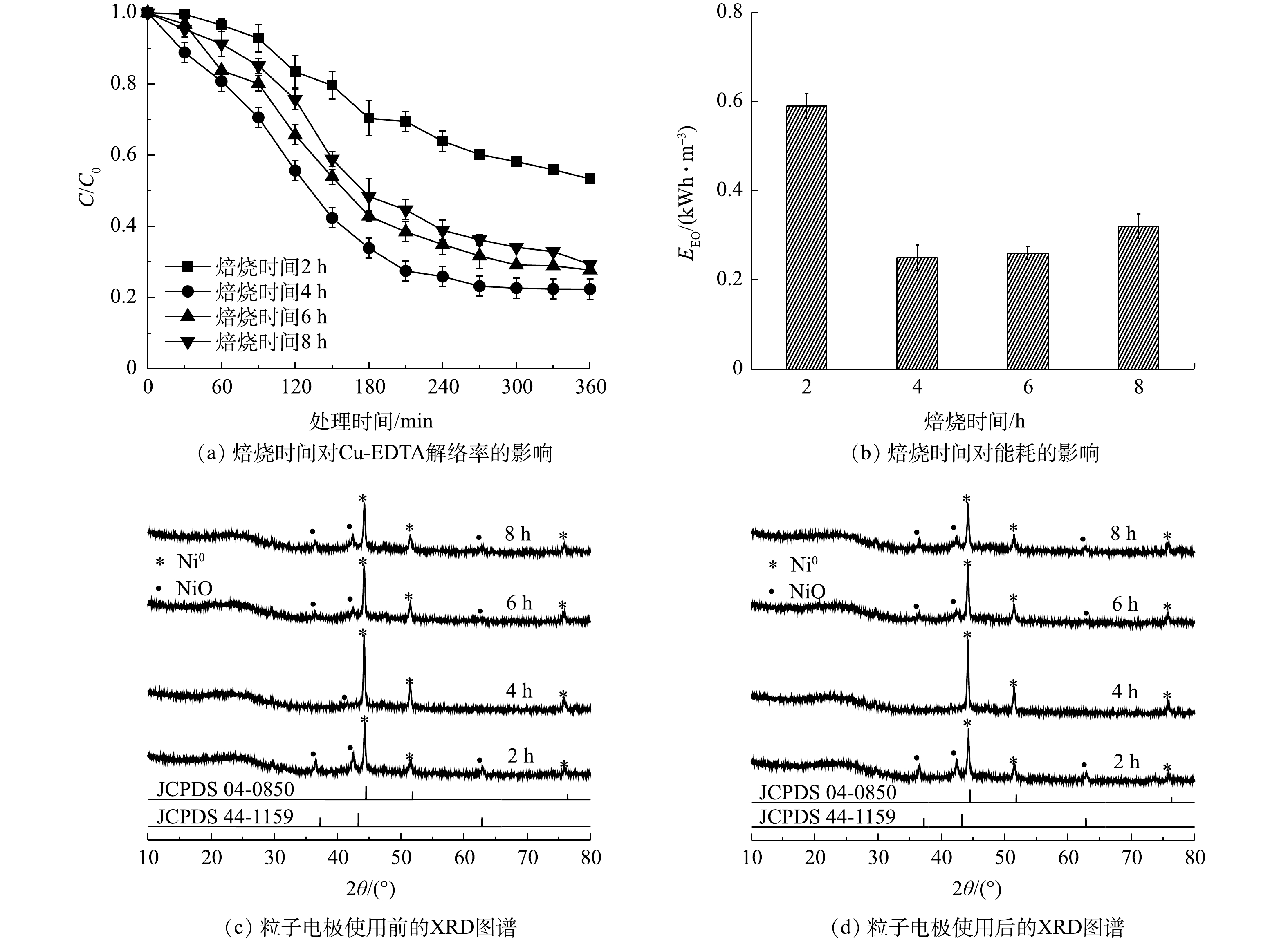
2)焙烧时间对Cu-EDTA解络效能的影响。如图3(a)所示,当PAC:GO质量为9:1、焙烧温度为600 ℃时,焙烧时间4 h的解络效果最好,Cu-EDTA的解络率为77.6%,比焙烧时间2 h的提高了30.9%,能耗也由0.59 kWh·m−3降低为0.25 kWh·m−3。随着焙烧时间继续延长,粒子电极的电催化活性略有降低,6 h和8 h下的解络率下降至72.2%和71.6%,能耗分别增加至0.26 kWh·m−3和0.32 kWh·m−3。焙烧时间的延长可以增加催化剂和载体之间结合的强度,能够充分地活化催化剂,但过长的焙烧时间会破坏催化剂原有的催化活性和粒子电极原有的空隙结构,从而影响粒子电极的电催化性能[31]。由XRD图谱(图3(c)~(d))可以看出,不同焙烧时间下所形成的催化剂仍以Ni0为主,含有少量的NiO,焙烧时间对于Ni0衍射峰的强弱有一定影响,焙烧4 h时衍射峰最强。但无论焙烧时间为多长,在处理Cu-EDTA后,粒子电极的晶体结构均没有发生明显变化。
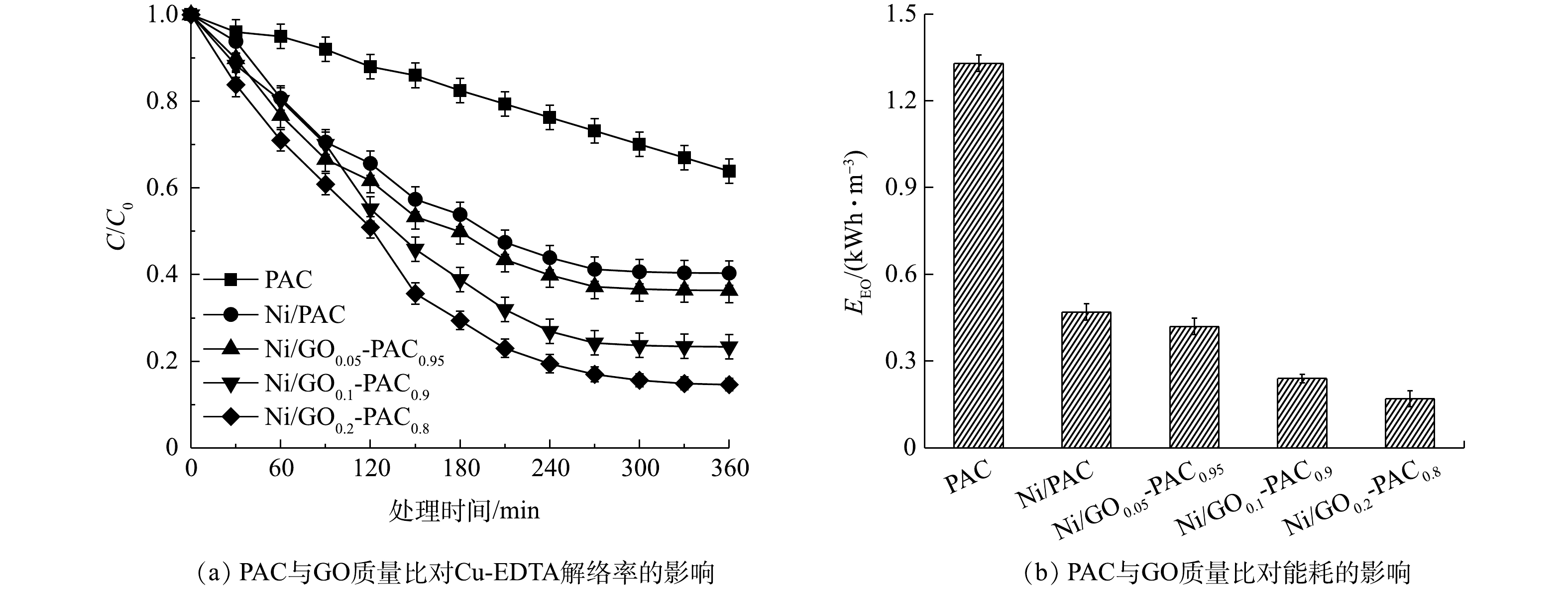
3) PAC与GO质量比对Cu-EDTA解络效能的影响。在焙烧温度为600 ℃和焙烧时间为4 h条件下,制备了PAC与GO不同质量比的粒子电极。如图4(a)所示,当PAC不负载Ni时,Cu-EDTA的解络率只有36.1%,电耗EEO值高达1.33 kWh·m−3(图4(b))。当仅使用PAC作为载体,负载Ni催化剂后,Cu-EDTA的解络率升高到了59.6%,可见Ni的负载明显提升了粒子电极的催化性能。不仅如此,负载Ni后,PAC的EEO值下降至0.47 kWh·m−3。这是因为PAC本身导电性较差,Ni0的负载可以增强粒子电极的导电性。当粒子电极材料中分别掺杂5%、10%和20%的GO后,Cu-EDTA的解络率再进一步提升到63.4%、76.6%和85.4%,可见GO的掺入进一步使粒子电极的催化性能得到提升。这是因为GO表面的含氧官能团为GO提供了丰富的缺陷位点,并且良好的电子传递性能,可以促进电极表面的电荷转移,使得GO具有一定的电催化性能[33]。当在粒子电极材料中掺杂GO后,粒子电极的催化性也得到增强。不仅如此,随着GO掺杂比例的增加,EEO值明显下降,当GO的掺杂比为20%时,EEO值仅为0.17 kWh·m−3,说明GO确实增加了粒子电极的导电性能,降低了能耗。在惰性气氛中,经高温焙烧后,GO表面的含氧官能团在高温作用下被分解,能很大程度恢复石墨烯的共轭结构,从而提高导电性[34]。结合以上解络率和耗能结果,确定焙烧温度600 ℃、焙烧时间4 h和PAC∶GO为8∶2作为后续粒子电极的最佳制备条件,制得电极为Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8。
2.2 SEM分析
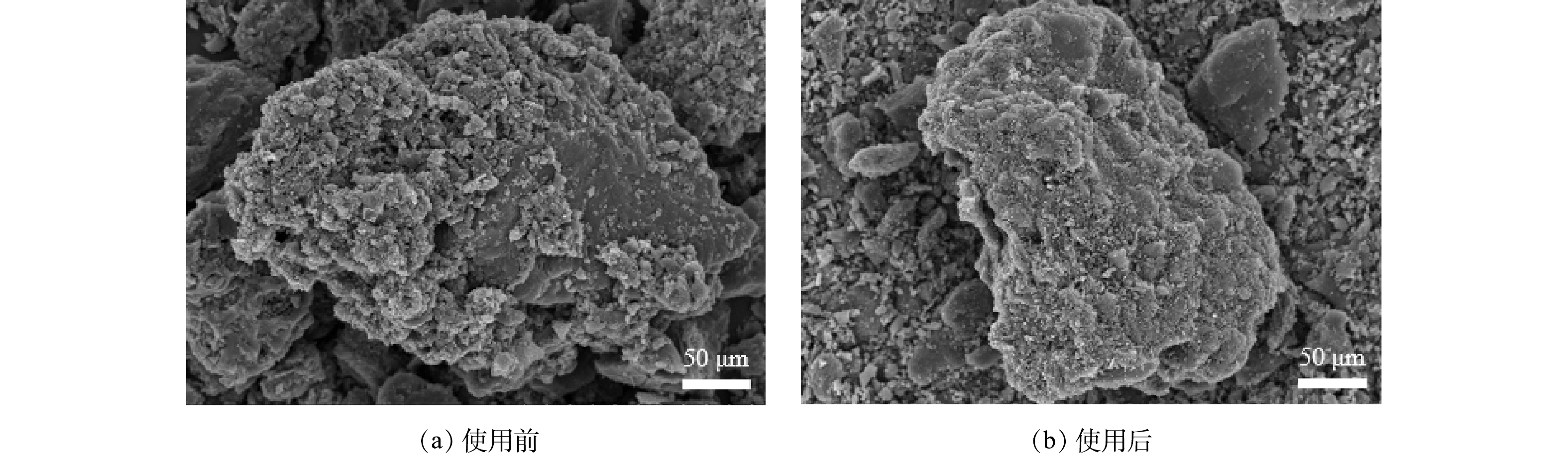
对Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极使用前后的表面形貌进行了表征,结果如图5所示。可以看出,不管是使用前还是使用后,PAC载体表面都比较粗糙,这有利于催化剂的负载。此外,还观察到有白色细小的晶体颗粒物附着在PAC表面,这是Ni元素所形成的催化晶粒。能谱分析结果显示(表1),使用前电极表面存在C、O和Ni三种元素,Ni的质量分数为10.74%。使用后电极表面Ni的质量分数为下降至9.00%。除了C、O和Ni外,还检测到Cu和S元素。Cu的质量分数为2.33%,表明电催化解络过程中粒子电极表面沉积有大量的铜元素。由于使用了Na2SO4作为电解质,因此,也观测到6.57%的S元素。
表 1 Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8使用前后的EDS分析Table 1. EDS analysis of Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8 before and after use元素 使用前 使用后 质量分数/% 原子分数/% 质量分数/% 原子分数/% C 74.05 84.46 67.00 77.59 O 15.21 13.03 17.10 17.06 Ni 10.74 2.51 9.00 1.53 Cu — — 2.33 0.54 S — — 6.57 3.28 2.3 Cu-EDTA解络和铜回收效能
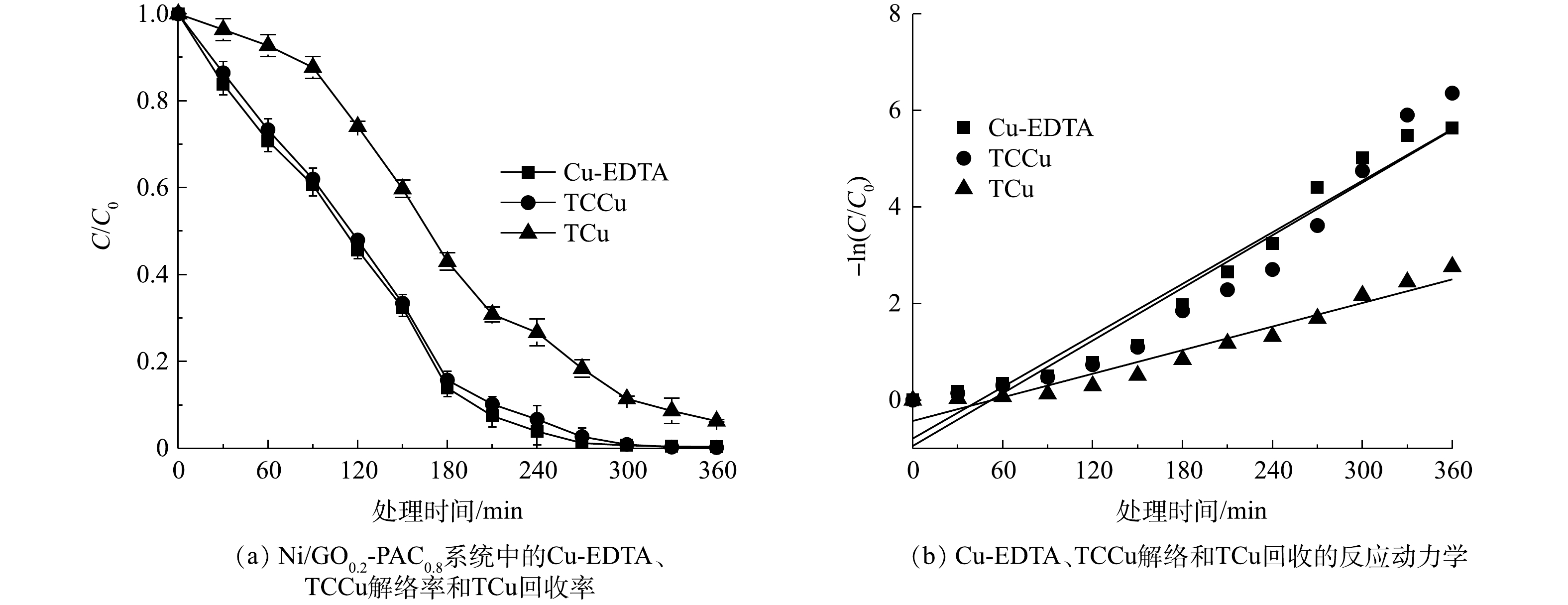
使用Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极,在电流密度为1.6 mA·cm−2下,对Cu-EDTA解络和铜回收的效能进行了研究。结果表明(图6(a)),Cu-EDTA的解络率达到99.6%,而其他电催化方法对于Cu-EDTA的解络率仅为15%~60%[35-36]。TCCu的解络率为99.4%,仅比Cu-EDTA低0.2%。通常EDTA降解过程中会形成乙二胺三乙酸、乙二胺二乙酸和乙二胺单乙酸等中间产物,这些产物也具有一定的络合性[8]。0.2%的解络率差别说明铜以其他络合形态存在的量非常低,Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极对Cu的所有络合态都具有解络效果。实验结果还显示,TCu的回收率达到93.7%,溶液中仅含有5.9%的铜未去除。在以不锈钢为阴极、TiO2/Ti为阳极的电氧化解络过程中,总铜的回收率仅为18%~40%[36-37]。可以看出,总铜的高回收率说明粒子电极具有良好的还原性能。
如图6(b)所示,Cu-EDTA、TCCu和TCu的-ln(C/C0)与处理时间之间均呈良好的线性关系,拟合系数R2均在0.9以上(表2),说明Cu-EDTA、TCCu的解络和TCu的回收符合拟一级反应动力学规律。Cu-EDTA和TCCu的反应速率常数均为0.018 min−1,而TCu的反应速率常数为0.008 min−1。与臭氧氧化过程中Cu-EDTA反应速率常数0.450 min−1相比[5],本实验中的反应速率常数偏低,这是因为施加电流密度较低,反应速率较慢,也可能是铜不断在粒子电极上沉积而导致反应速率偏慢。
表 2 Cu-EDTA、TCCu解络和TCu回收反应动力学拟合参数Table 2. Kinetics parameters of Cu-EDTA, TCCu decomplexation and TCu recovery污染物 拟合方程 kobs/(min−1) R2 Cu-EDTA −ln(C/C0)=0.018t−0.792 0.018 0.947 TCCu −ln(C/C0)=0.018t−0.946 0.018 0.916 TCu −ln(C/C0)=0.008t−0.428 0.008 0.940 2.4 粒子电极降解Cu-EDTA机制
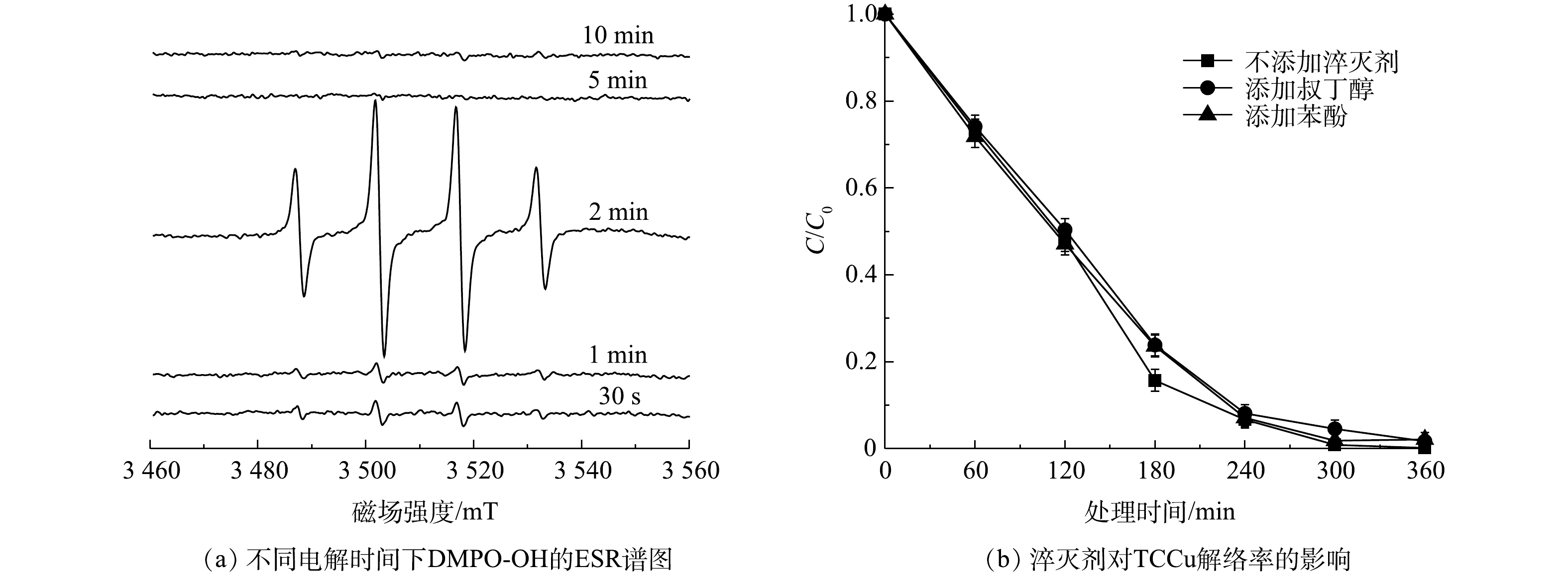
采用电子顺磁共振谱法测定了反应体系中的自由基,结果如图7(a)所示。可见,系统中出现了峰高为1∶2∶2∶1的四重峰,超精细耦合常数为a(N)=a(H)=14.9 G,这是DMPO-OH加成物的特征峰,表明Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8系统中产生了·OH自由基,在粒子电极的阳极H2O会发生电解产生·OH[25]。当使用叔丁醇和苯酚作为·OH的淬灭剂时,淬灭剂的加入没有抑制TCCu的降解(图7(b)),TCCu的解络率仍达到97%以上,·OH对Cu-EDTA的解络没有影响。在UV/氯[8]、非热等离子体[38]氧化解络体系中,是通过破坏EDTA结构来使Cu-EDTA解络,当
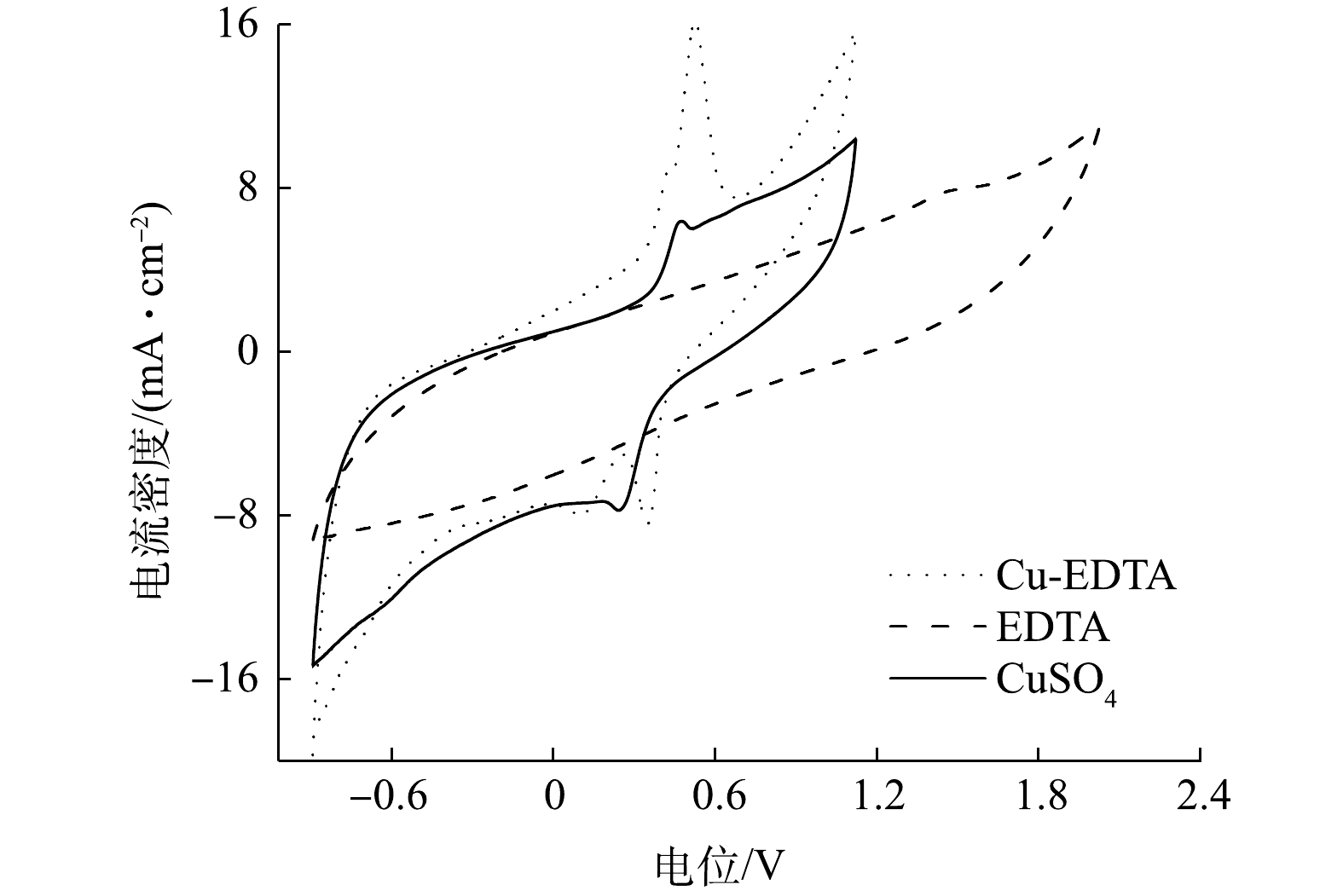
⋅O−2 为进一步了解Cu-EDTA在粒子电极上的电化学行为,对Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8在EDTA、Cu-EDTA和CuSO4溶液中的循环伏安特征进行了分析。如图8所示,在EDTA溶液中,除1.55 V处出现一个较弱的氧化峰外,在-0.87~1.2 V内都没有氧化还原峰的出现。这说明EDTA很难在Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极表面发生直接氧化或还原反应。而对于CuSO4溶液,在0.22 V和0.48 V处出现一对还原峰和氧化峰,这是由于Cu2+在电极上还原和氧化引起的。当使用Cu-EDTA溶液时,在0.09 V和0.31 V处出现2个还原峰,在0.49 V和0.55 V处出现2个氧化峰。这说明Cu-EDTA在Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极上发生了直接还原和氧化反应。0.09 V和0.31 V的2个还原峰来自Cu+还原为Cu0和Cu2+还原为Cu+;而在0.49 V和0.55 V处的2个氧化峰分别对应于Cu0氧化为Cu+和Cu+氧化为Cu2+的过程。结合自由基淬灭实验的结果,可以看出Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极电催化Cu-EDTA解络是通过Cu(Ⅱ)的逐步还原完成,Cu-EDTA中的Cu2+先还原为Cu+,再还原为Cu0。由于Cu2+的还原,从而导致Cu-EDTA的络合结构受到破坏。
3. 结论
1)通过Cu-EDTA的解络率和耗能结果确定粒子电极的最佳焙烧温度为600 ℃,焙烧时间为4 h,PAC与GO的最佳质量比为8:2。
2)粒子电极上的镍主要以Ni0存在,含有少量NiO;Ni0的负载增强了粒子电极的电催化性能和导电性,粒子电极在处理Cu-EDTA后,其形貌和催化剂结构没有受到影响。
3) Cu-EDTA、TCCu的解络率和TCu的回收率分别为99.8%、99.6%和93.7%,解络和回收均符合拟一级反应动力学。
4) Cu-EDTA在Ni/GO0.2-PAC0.8粒子电极体系中的解络是通过电还原完成,Cu-EDTA中的Cu2+先还原为Cu+,再还原为Cu0并沉积在粒子电极表面上。
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 10202
- HTML全文浏览数: 4654
- PDF下载数: 11841
- 施引文献: 0




 下载:
下载: