浸没式膜-生物反应器污泥组分对膜污染的影响
Study on the impact of sludge components on membrane fouling in a sub-merged membrane bioreactor
-
摘要: 研究基于中试规模的浸没式膜生物反应器长期运行的基础上,通过改变操作条件和工艺参数系统考察污泥组分对膜污染的影响。试验结果表明,泥龄10 d时,混合液悬浮固体、胶体物质和溶解性物质对膜污染阻力的贡献分别为24.1%、36.1%和39.8%;泥龄20 d时, 混合液悬浮固体、胶体物质和溶解性物质对膜污染阻力的贡献分别为43.9%、32%和24.1%;泥龄40 d时, 混合液悬浮固体、胶体物质和溶解性物质对膜污染阻力的贡献分别为50.6%、27.3%和22.1%。随着泥龄的增加,胶体物质和溶解性物质所形成的阻力之和在总阻力中所占的比例逐渐下降,但仍为膜污染的重要因素。
-
关键词:
- 浸没式膜-生物反应器 /
- 污泥组分 /
- 膜污染
Abstract: The impacts of sludge components on membrane fouling were studied by changing the operational conditions and parameters of a pilot-scale submerged membranebioreactor, which had been successfully operated for more than one year. The results showed that the contributions of suspended solid, colloids and solutes to the membrane fouling were 24.1%, 36.1%, 39.8% at SRT of 10 days, and 43.9%, 32%, 24.1% at SRT of 20 days, 50.6%, 27.3% and 22.1% at SRT of 40 days, respectively. It was also found that the proportion of fouling resistance formed by colloids and solutes, which played an important role in membrane fouling, decreased with the increase in SRT.-
Key words:
- sub-merged membrane bioreactor /
- sludge components /
- membrane fouling
-
污泥未经处理随意排放堆置,会造成严重的环境污染问题。国际上污泥主要有土地利用、卫生填埋、焚烧和投海等4种处置方式[1]。其中,填埋处置对技术指标要求相对宽松、运行成本低,是现阶段我国污泥处置的主要方式,且为简易的单独填埋,即污泥经过脱水消化后,直接倾倒于事先设置好的填埋坑中,并采用膜或土覆盖进行封场。由于我国污水处理厂对污泥处理的重视度不高,技术资金投入力度也不够,导致污泥的含水率高、物理力学性质差,不仅达不到市政污泥的填埋标准,而且造成填埋场库容的日益紧张,更严重的是会埋下安全隐患[2],如深圳下坪垃圾填埋场和山西太原垃圾填埋场均发生过填埋体的滑坡事故。为此,在《城镇污水处理厂污泥处理处置技术指南》[3]的国家规范中对填埋污泥的各项指标做出了明确规定。与此同时,我国的污泥产量也在逐年增加,目前,国内上海老港、成都长安、深圳下坪、杭州天子岭等填埋库区库容已经出现严重不足。因此,污泥填埋场内坑体加固与库内污泥深度脱水减量成为目前多数填埋场所面临的问题。
现阶段常用机械压滤方式对污泥进行深度脱水。从机械脱水原理来看,机械压滤的过程实质上就是污泥的排水固结过程,即在总应力作用下孔隙水不断被排出的过程。孙政等[4]对污水处理厂脱水污泥的固结特性进行了研究,发现污泥的固结规律与一般黏土差别较大,超孔隙水压力的消散较慢。朱婧等[5]对污泥、淤泥、粘土的压缩特性进行了对比研究,认为污泥与淤泥的固结不同,在外力荷载下其固结过程可以分多个阶段。王鹏等[6]采用纤维加筋技术,研究了不同掺量下加筋污泥的固结压缩特性。范惜辉等[7]选用普通硅酸盐水泥和硫铝酸盐水泥作为固化材料,研究了固化污泥在不同应力下的压缩、渗透规律。机械压滤技术一般是先采用化学药剂预调质,使污泥颗粒的结合水释放出来之后,再其进行深度脱水,将湿基含水率降至60%以下。采用药剂真空预压法处理污泥也是如此,调质改性后的污泥与工程废浆类似,在真空预压过程中存在流固的两相转变,并在大部分时间里处于弹塑性状态,此时需要采用土力学中的固结理论进行分析[8]。武亚军课题组[9][10]对于无机药剂调质过的新鲜污泥的真空固结特性进行了研究,由于暂存库区污泥与新鲜污泥性质不同,固结特性也必然有差异,而目前关于这方面的研究并未见有所报道。此外,FeCl3是比较常用的一种调质药剂,而芬顿试剂在污水处理中应用较多,但不常用于污泥调质,因此,一方面为了对新鲜污泥与暂存库污泥进行对比,另一方面为了对FeCl3和芬顿试剂的调质效果进行对比,本研究采用土力学中的固结实验对分别采用2种不同药剂调质过的填埋污泥的压缩固结特性进行了研究,研究结果可为机械压滤和真空预压处理填埋污泥的工程实践提供参考。
1. 实验材料与方法
1.1 试剂和仪器
实验选用的药剂分别为FeCl3·6H2O、FeSO4、浓硫酸,以上药剂均为分析纯(AR)。实验所需H2O2通过40%的双氧水颗粒(昌乐鑫富强商贸有限公司)按浓度比例添加。实验仪器主要包括中压固结仪和电子天平等。
1.2 污泥基本物理性质
对暂存库区填埋污泥与新鲜污泥的各项物理指标进行了测试,其中比重采用比重瓶法测试;密度采用环刀法测试;含水率采用低温烘干法测试;有机物采用灼失量法测试。结果表明,填埋污泥与新鲜污泥的含水率分别为74.1%和82.17%,有机质含量分别为40.9%和64.9%,比重分别为1.87和1.57,密度分别为1.2 g·cm−3和1.02 g·cm−3。由此可见,填埋污泥具有比新鲜污泥含水率低、有机物含量低、比重和密度大等特点。
1.3 实验方法
固结实验的药剂调质方案中氯化铁的添加量分别为0%、10%、20%、30%和40%;芬顿试剂的添加方案如表1所示。装入烧杯中置于常温下放置24 h,待污泥与药剂充分反应后,再均匀装填入固结仪,每个实验组别设置2组平行实验。由于污泥含水率较高,初级固结应力较大时容易发生冒浆,选取初级固结应力为3.125 kPa,加荷比为1,将最大固结应力增加至400 kPa。根据《土工试验方法标准》(GB/T50123-1999),加载过程中按规定时间记录百分表读数,由于污泥稳定达到稳定标准时间较长,每级加载48 h。第1级固结应力p设置为3.125 kPa,之后按6.25、12.5、25、50、100 kPa依次加载,以沉降量小于0.005 mm·h−1为沉降稳定的标准。
表 1 污泥固结实验芬顿试剂调质方案Table 1. Consolidation test plan of sludge conditioned by Fenton reagent编号 Fe2+/% H2O2/% H2O2/Fe2+ 1 4 4 1 2 4 6 1.5 3 4 8 2 4 8 8 1.5 5 8 12 2 6 8 16 3 注:添加量表示占污泥干基的质量比。 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 孔隙比
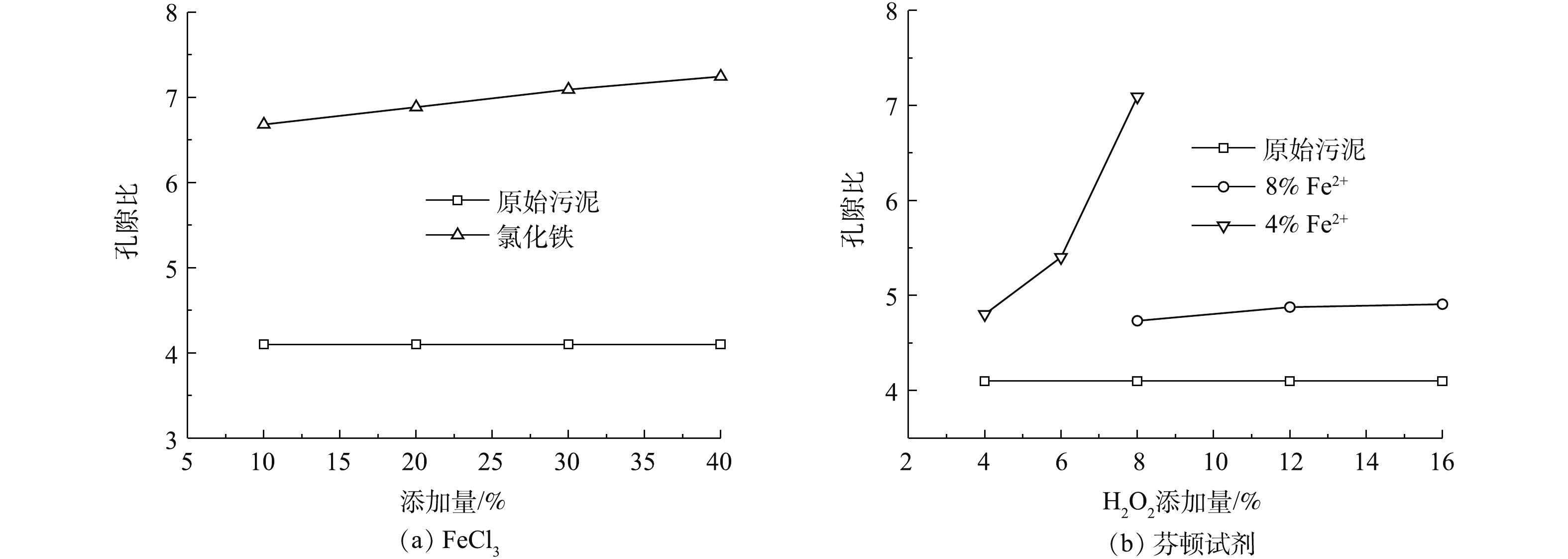
添加药剂之后污泥的孔隙比e (指污泥中孔隙体积与固体体积的比值,初始孔隙比e0采用含水率和比重进行换算,压缩过程中的孔隙比根据压缩量测试)会发生较大的变化,不同种类的药剂添加量与初始孔隙比的关系如图1所示。由图1可知,经过药剂调质改性后,e均有不同程度的增大。采用FeCl3调质后(图1(a)),污泥的初始孔隙比e0变化明显,从原始污泥的4.098上升至6.681,但随着药剂掺量的增加,污泥的孔隙变化较为平缓,最终达到7.244。采用芬顿改性后(图1(b)),当Fe2+的掺量为4%时,污泥孔隙比随着H2O2掺量的增加变化明显,由4.802上升至7.092;当Fe2+的掺量为8%时,污泥孔隙比随着H2O2掺量的增加变化较为缓慢,最终达到4.908。这是由于在药剂调质过程中产生了大量气体,这些气体不能完全从污泥中排出,而是积存分布在污泥内部,导致污泥的空隙变多,从而使得孔隙比增大。
2.2 压缩特性
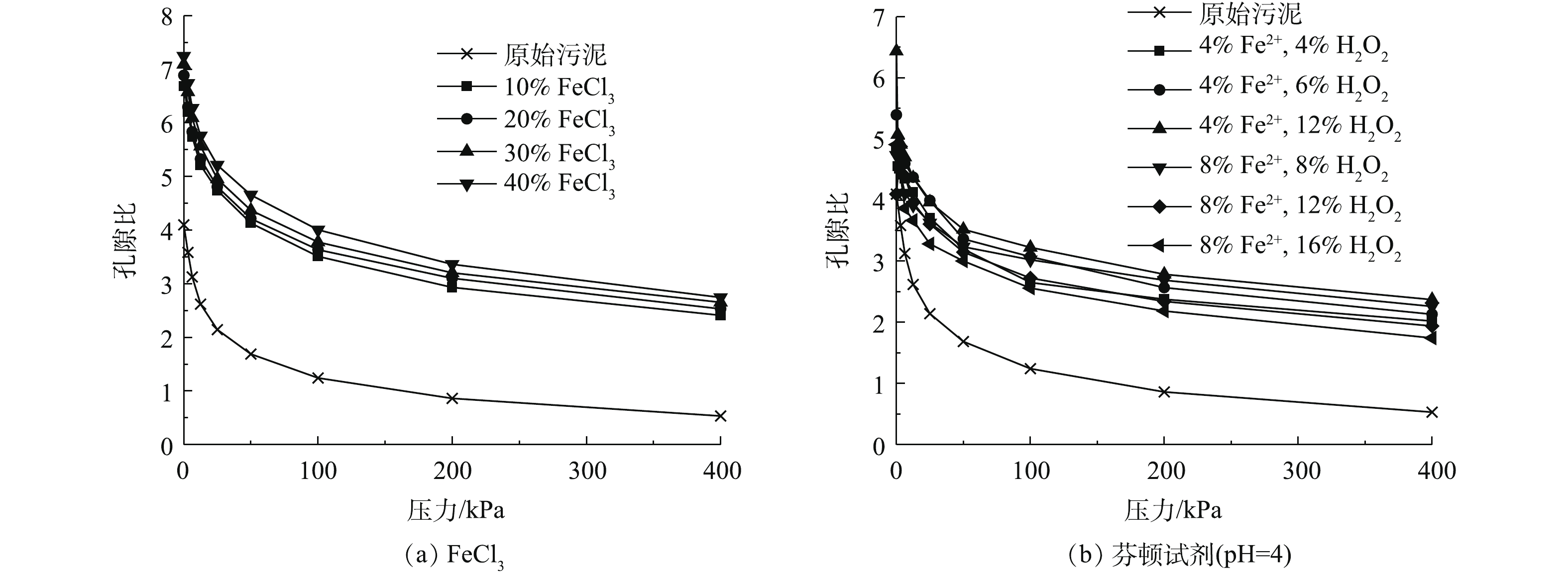
压缩实验每级荷载的加载周期为48 h,不同FeCl3添加量下改性污泥的孔隙比e与荷载p的关系如图2(a)所示。污泥初始孔隙比为4.098,略大于常规的软黏土,经过药剂调质后,污泥的初始孔隙比随着药剂添加量的增加逐渐变大,当药剂添加量为40%时,孔隙比达到7.244。不同芬顿配比掺量下改性污泥的e-p关系如图2(b)所示。由图2(b)可知,对比2种药剂调质后的污泥发现,在初级荷载作用下,样品的孔隙比迅速减小。通过对固结应力为100 kPa时的孔隙比变化量进行了分析,发现调质污泥的压缩量基本均达到总压缩量的70%以上。这是因为在前期压缩过程中,调质污泥较原始污泥颗粒间的空隙总量更多,颗粒间没有形成骨架,强度较低,在较低应力作用下,孔隙水排出顺畅,压缩量大,孔隙比减小幅度大。经过3.125、6.25、12.5、25、50 kPa荷载作用下,芬顿改性污泥的沉降量较大,孔隙被大幅压缩;当荷载大于50 kPa时,污泥沉降速率逐渐减慢,沉降幅度逐渐减小,污泥孔隙比被压缩幅度也逐渐减小。由于原始污泥中有机质含量较高,存在大量具有一定承载力的微生物残体和胶结絮状有机物,通过添加FeCl3与芬顿试剂可以一定程度上破坏微生物残体和胞外聚合物,减少了有机物的含量,样品更容易发生固结压缩。
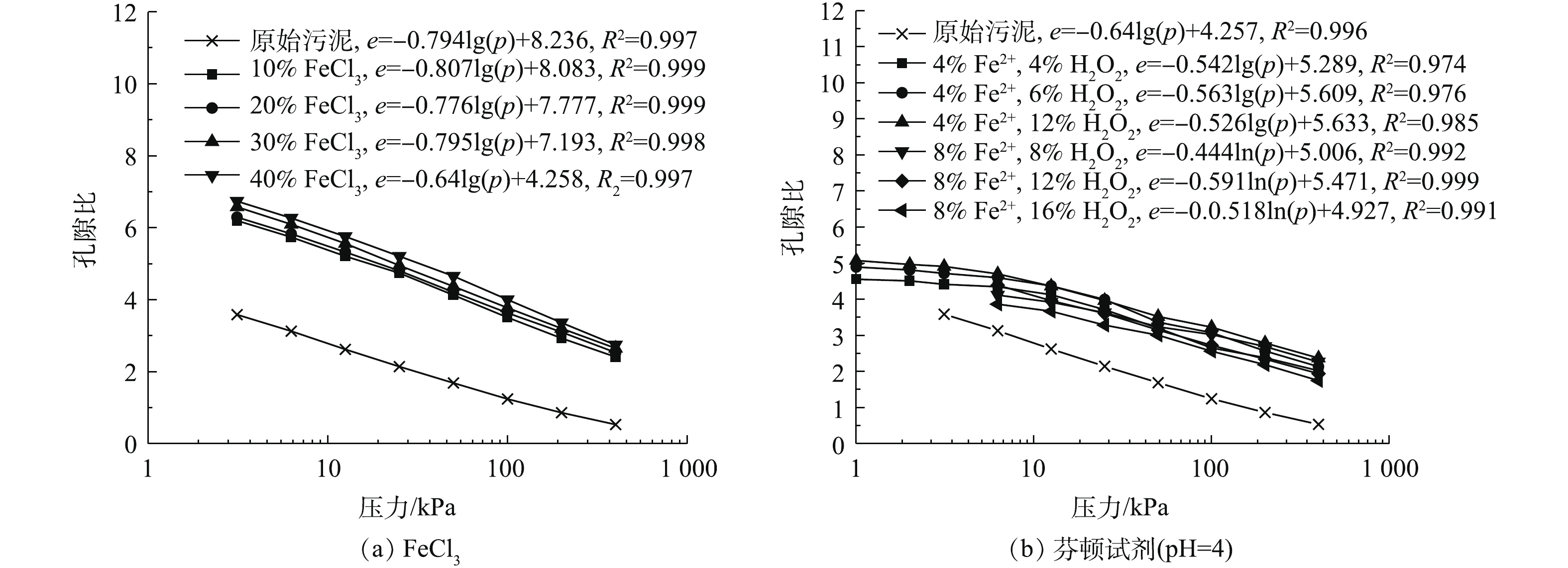
将调质污泥的孔隙比e与固结应力p之间的关系可以绘制成半对数坐标曲线 (e-lgp),如图3所示。由图3(a)可知,孔隙比e与固结压力lgp之间呈明显的线性关系,这一结果与常规淤泥类似。填埋污泥的压缩指数为0.64,调质污泥的压缩指数在0.776~0.795,跟新鲜脱水污泥差别较大,且与常规淤泥在数值上也较为接近[1, 5]。由图3(a)可知,污泥初始孔隙比的拟合值要略大于实验实测值。这是由于污泥的机械脱水和长期填埋类似于加卸载过程,压缩之后产生不仅存在塑形变形,而且也会发生一定程度的回弹。污泥的实际孔隙比和理论孔隙比的差值在一定程度上反映了不可恢复的塑形变形。同时,重塑制样及拟合精度也会对该结果产生一定影响。由于污泥中含有凝胶状结构,颗粒接触点处有一定的胶结力,能承受一定的压力而变形较小,使得在初期加荷阶段曲线平缓。此外,一般的原状土由于前期固结应力的存在会发生自重应力下的固结。其压缩曲线会出现屈服应力的折点,污泥的e-lgp曲线近似为一条直线,由此可知,调质污泥不存在应力屈服点,属于欠固结土。不同芬顿配比掺量下改性污泥的e-lgp曲线如图3(b)所示。污泥孔隙比随固结应力增大基本呈线性减小,压缩指数Cc为0.444~0.591,整体上小于原始污泥和经FeCl3调质后的污泥,和常规淤泥土较为接近,但仍属于高压缩性土。
2.3 固结特性
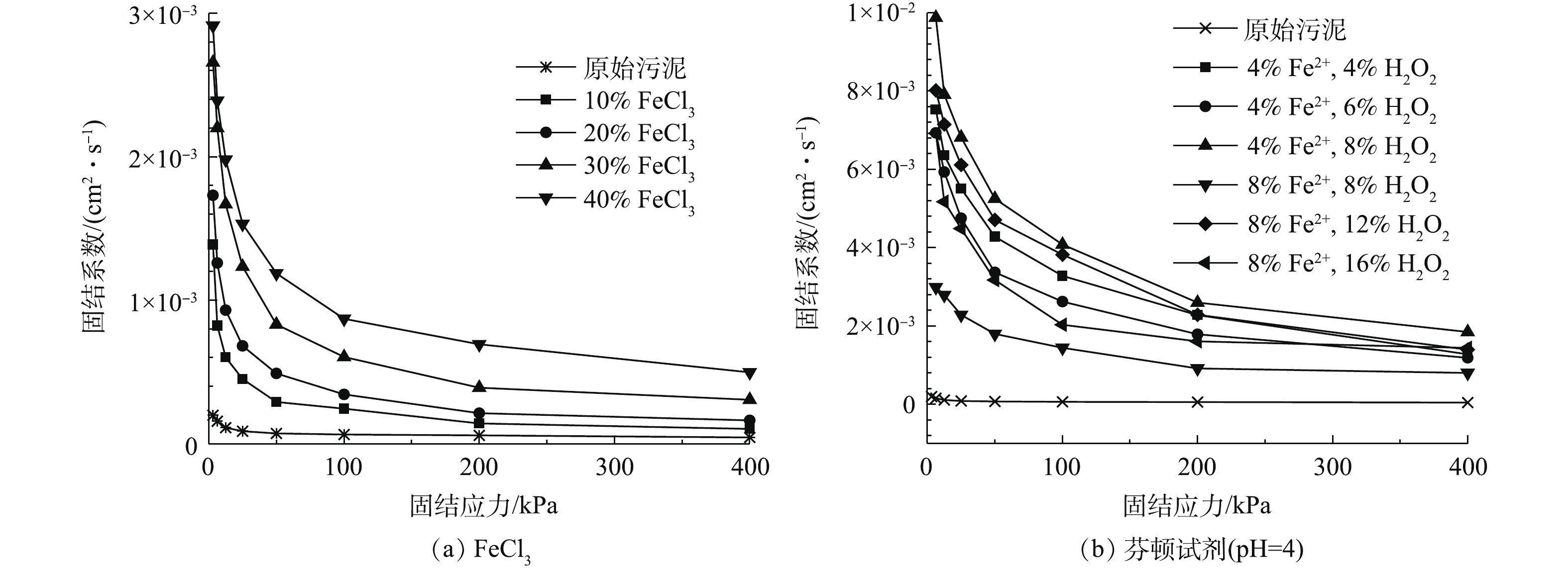
固结系数Cv是表示孔隙水压力消散快慢的物理量,固结系数越大,固结速度越快,反之越慢。采用时间平方根法可得到调质污泥固结系数Cv与固结应力p之间的关系。图4(a)为采用FeCl3在各级压力下的固结系数变化结果。由图4(a)可知,在初级压力下,调质污泥的固结系数在10−3 cm2·s−1数量级变化,随着固结应力的增大,污泥的固结系数逐渐减小。此外,随着FeCl3掺量的增大,固结系数也越大,且在前几级固结应力下固结系数的减小幅度也越来越明显。由各条固结系数曲线关系可以说明在每一级固结应力下,随着FeCl3添加量的增加,污泥的固结系数增大,即FeCl3掺量越多,固结过程中孔隙水压力消散越快,这一点与新鲜脱水污泥固结系数的变化规律一致[9]。
对比芬顿调质的实验结果(图4(b))可知:当Fe2+的添加量为4%时,样品的固结系数随着H2O2添加量的增加而增大,当H2O2的掺量为8%时达到最大;当Fe2+的添加量为8%时,样品的固结系数随着H2O2掺量的增大呈现先增大后减小的趋势。这是由于当H2O2添加量过多时,不仅不能分解产生更多的羟基自由基,反而会使最初产生的羟基自由基发生泯灭[11]。就初级固结应力下的固结系数而言,芬顿试剂改性后初级固结应力下Cvmax=9.88×10−3 cm2·s−1,当固结应力增大到400 kPa时,Cv=1.85×10−3 cm2·s−1;经过40%的FeCl3调质后Cvmax=2.91×10−3 cm2·s−1,随着固结应力的增大,Cv减小至4.98×10−4 cm2·s−1。因此,当Fe2+添加量为4%、H2O2掺量为8%时,在固结应力作用下污泥的孔压消散最快。
污泥与淤泥、黏土最大的区别是污泥的固体物质中存在40%~60%的有机物,这些有机物大多数是生物处理过程中的微生物残体[12]。因此,污泥中的水分赋存状态非常特殊,除了具有孔隙水、表面结合水以外,存在絮凝体内部的结合水和细胞颗粒内部的细胞水(或称为生物水)[13]。这些水赋存于可以承载一定压力的有机物絮体中,这使污泥中水分难以快速排出,因此,孔隙水压力消散时间非常漫长[14]。添加药剂在一定程度上使得微生物残体胞内水以及有机絮体中的结合水释放,从而大大缩短了固结时间。
2.4 渗透特性
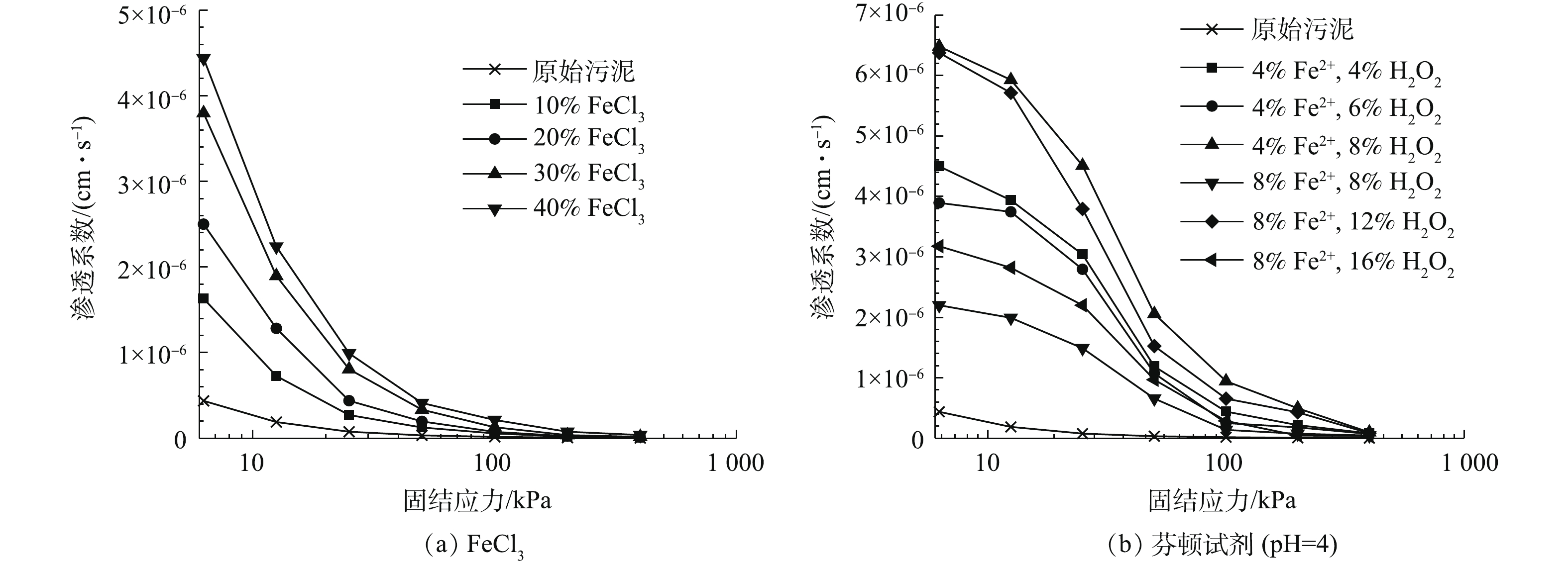
如图5所示,通过固结系数可以推演出污泥在各级固结压力下的渗透系数k。由图5(a)可知:k和固结应力的规律与固结系数Cv和固结应力的规律相似,受固结应力影响较大;在0~25 kPa阶段,污泥的渗透系数下降明显,渗透性变差,这是因为大孔隙被压缩成小孔隙或密闭孔隙,孔隙比迅速减小导致排水困难。经过试剂调质后,长期填埋污泥的渗透系数增大,初级固结应力下的k从10−7 cm·s−1数量级增大到10−6 cm·s−1数量级,随着压力的增大,k减小为10−8 cm·s−1数量级;当FeCl3的掺量为40%时,样品在初级固结应力下的k=4.439×10−6 cm·s−1,随着固结应力的增加,k减小至3.796×10−8 cm·s−1;采用芬顿试剂调质的污泥在初级固结应力下的k=6.48×10−6 cm·s−1 (图5(b)),随着固结应力的增大k则下降至9.94×10−8 cm·s−1。若以固结系数和渗透系数作为污泥固结效果好坏的指标,芬顿试剂的效果更佳。
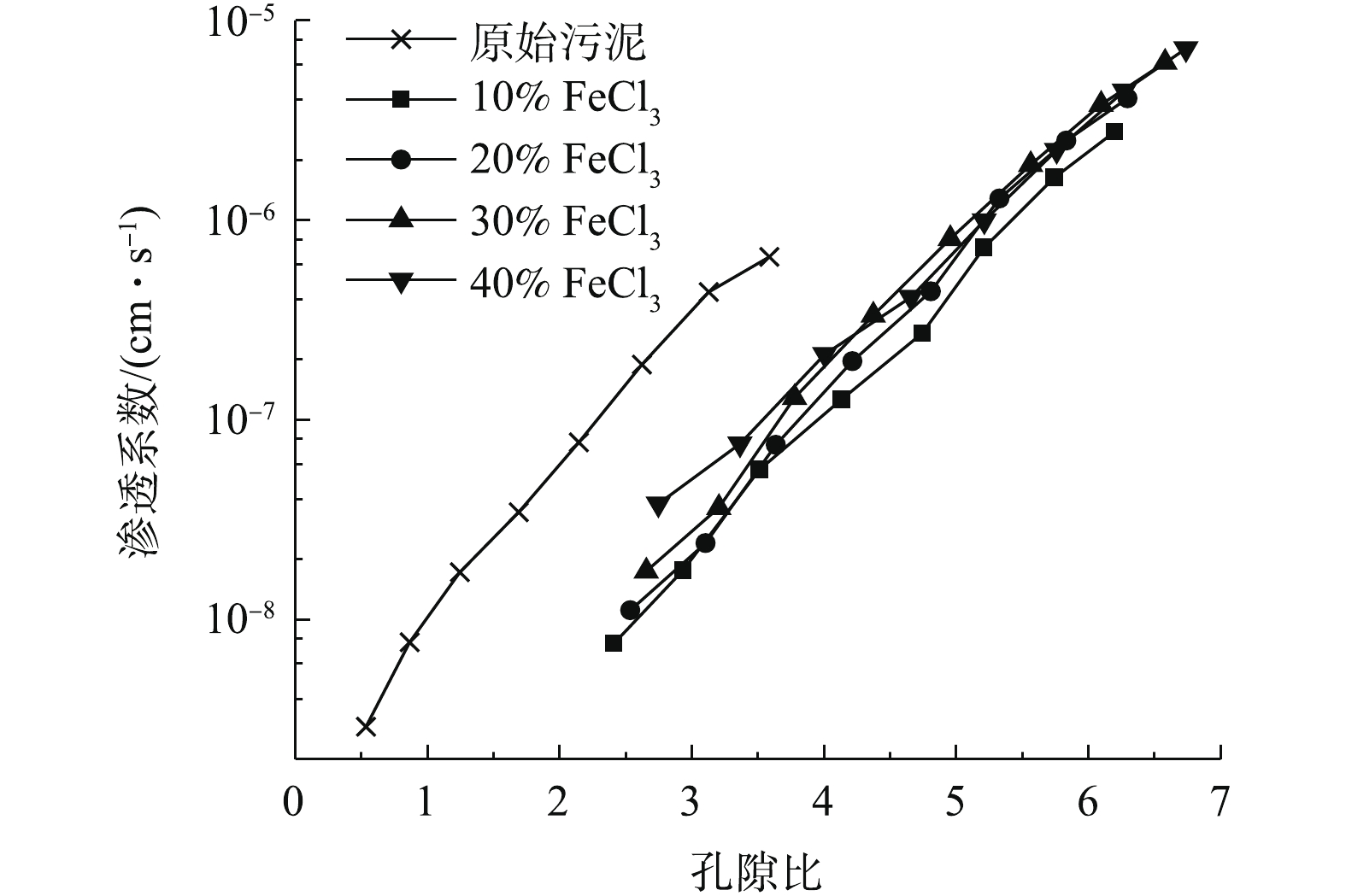
此外,土体渗透性与其孔隙比密切相关。有研究[5]表明,土体孔隙比e与lgk存在一定的关系。图6为在不同FeCl3掺量下调质污泥渗透系数与孔隙比关系曲线。由图6可知,随着孔隙比的减小,渗透系数也逐渐减小,反之,渗透性增大,e与lgk之间的线性关系近似成立。在一定孔隙比范围内,相同孔隙比下10%添加量的污泥渗透系数一直小于同样孔隙比的其他掺量污泥,20%、30%和40%添加量下的污泥在孔隙比为5~7时渗透系数较为接近,但是随着孔隙比减小,实验组污泥的渗透系数出现差异,且随着药剂掺量减小而递减,添加量为20%的实验组渗透系数接近于10%添加量的实验组。
对比调质污泥和原始污泥可以发现,在重合的孔隙比区间内,相同孔隙比下对照组的渗透系数要大于添加药剂的实验组。这是因为与天然细粒土一样,污泥由于初期的加药絮凝和板框压滤,其初始状态的结构也很复杂,一旦扰动,原有的过水通道的形状、大小及其分布都会改变,故渗透系数也不同。这一点与普通的性质相近,相同孔隙比时扰动土样的渗透系数通常小于原状土样[15]。实际加药时由于搅拌分散以及药剂的作用导致污泥颗粒分散变小,絮状结构一定程度上被破坏,使得调质后的污泥在相同孔隙比下的k小于原始污泥。
3. 结论
1)污泥经试剂调质后能在较短时间内排水固结稳定;调质污泥在低荷载水平下沉降量较大,在高荷载水平下沉降逐渐平稳,孔隙变化不大;经过FeCl3调质后的污泥压缩性增大,压缩指数由0.64增大至0.776~0.795。
2)在初级固结应力下,调质污泥的固结系数在10−3 cm2·s−1数量级内变化。添加FeCl3的实验组Cv,max=2.91×10−3 cm2·s−1;芬顿调质实验组Cv,max=9.88×10−3 cm2·s−1。比阻和固结系数并不是简单呈负相关性,两者之间的定量关系还需要进一步研究。
3)渗透系数受固结应力影响较大。当FeCl3的掺量为40%时,样品在初级固结应力下的渗透系数为4.439×10−6 cm·s−1,在400 kPa下,渗透系数减小为3.796×10−8 cm·s−1;采用芬顿试剂调质的污泥在初级固结应力下,k=6.48×10−6 cm·s−1,在400 kPa下,k=9.94×10−8 cm·s−1。
4)在芬顿试剂最小添加量时(4% Fe2++4% H2O2)的调质效果均比FeCl3最大添加量40%时的调质效果要好,因此,建议在工程实践中采用芬顿试剂进行调质污泥。
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 王上海,杨保俊,金耀宗,王琦,王百年. CeFeMn@ZSM-5催化臭氧氧化苯酚废水. 当代化工. 2024(01): 98-102+106 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 于华芹,石伟,徐会君,蒋延梅,李强,宋伟,杜庆洋. Co-Mn/γ-Al_2O_3催化剂的制备及其催化性能. 中国给水排水. 2023(17): 113-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 周龙涛,李慧敏,安静,徐阳,张栌丹. Ag_3PO_4-Fe_3O_4/g-C_3N_4非均相臭氧催化剂的制备及表征. 安全与环境学报. 2022(03): 1602-1611 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 田云福,冯晓琴,宋江锋,安富强. 高级氧化技术在高COD废水处理过程中的应用进展. 山西化工. 2022(07): 44-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘向阳,李慧敏,贾悦,卞卫国,张芳袁. 高级氧化技术处理钻井废水的应用进展. 应用化工. 2021(08): 2275-2279 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李欣欣,解立平,王蒙,张璐. 回流固定床臭氧催化氧化煤化工反渗透浓水. 化工进展. 2020(02): 760-766 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张耀辉,李军,周军,白永刚,涂勇. 厌氧消化—A/O—臭氧催化氧化—BAF工艺处理农药废水生化出水的中试研究. 化工环保. 2020(02): 137-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 曹丽华,韩雪. 臭氧/活性炭催化氧化处理港口化学品废水研究. 水道港口. 2020(04): 483-488 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 卞成萍,王晓峰,陈远. Ce-Mn/SiO_2臭氧催化剂的制备与表征. 油气田环境保护. 2020(05): 36-39+77 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 奉明. O_3/H_2O_2高级氧化技术对实验室有机废水处理研究. 广州化工. 2019(16): 65-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 孔燕燕,姜富川,邓宇. 标准加入法对页岩气压裂返排液中COD的测试研究. 中国测试. 2019(09): 65-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)
-

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2284
- HTML全文浏览数: 1009
- PDF下载数: 1214
- 施引文献: 19





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: