河口水生态完整性评价方法研究和进展
Research and Advances in Estuarine Aquatic Ecological Integrity Assessment Methods
-
摘要: 河口是连接淡水和海洋环境的重要过渡区,在维持生物多样性和生态系统服务方面发挥着重要作用。河口的生态完整性对于生态系统的可持续管理和保护至关重要。本文对河口生态完整性评价进行了文献计量学分析,重点介绍了河口生态完整性评价的评价方法和指标选择。主要包括物理化学指标、生物指标和社会经济指标。通过案例研究系统分析了不同指标选取对河口生态完整性评价的重要性。最后,指出了在河口生态完整性评价中仍面临一些问题,并针对这些问题提出了几点建议。Abstract: The estuary is a critical transitional zone between freshwater and marine ecosystems, which plays a pivotal role in the preservation of biodiversity and the provision of ecosystem services. The ecological integrity of estuaries is vital in the sustainable ecosystem management and conservation. This study conducted a bibliometric analysis of estuarine ecological integrity assessment, focusing on the methodologies and the selection of relevant indicators. The methodology primarily included physical-chemical, biological, and socio-economic indicators. The evaluation's significance was systematically analyzed through various indicators in several case studies. Finally, the paper identifies ongoing challenges in assessing estuarine ecological integrity and offers several suggestions to address them.
-
全氟及多氟烷基化合物(per‐ and polyfluoroalkyl substances,PFASs)是一类以烷基链为骨架,氢原子被氟原子全部或部分取代的有机化合物。由于PFASs特殊的理化特性,如黏度较低、表面张力小、并具有疏水、疏油特性[1-2],自1950年以来,PFASs和借助PFASs制造的表面活性剂和聚合物已广泛用于许多工业和商业应用中。在2019年的调查中发现,全球市场中PFASs已增加至4 700种[3]。由于PFASs在各个行业的广泛应用以及较难降解的特性,其不可避免地引发了相应的环境污染问题。近几年,PFASs已在全球多个地区、多种环境介质中被广泛检出[4-9]。在对各海域特别是极地PFASs的检测表明其具有远距离迁移能力,目前已成为全球性污染物。由于PFASs的广泛生产和使用,目前已经在环境、野生动物和人类中检测到多种相关化合物,其中最有代表性的为全氟辛酸(perfluorooctanoic acid,PFOA)和全氟辛基磺酸(perfluorooctane sulfonic acid,PFOS)[10-13]。有研究指出PFASs可能引起生殖毒性、发育毒性和肝毒性等多种毒性效应[14-19]。因此,由于PFASs在环境中的广泛存在,并具有环境持久性、生物蓄积及多种毒性作用,其在环境科学领域的相关研究已引起了国内外研究者的广泛关注。
文献计量学是通过采用数学和统计学的方法来定量分析某领域科学技术现状与未来发展趋势的科学[20]。文献计量分析对某领域的科学技术发展具有一定的指导意义[21]。WOS是由美国科学情报研究所(Institute for Scientific Information)于1997年创建的大型综合型、多学科、核心期刊引文索引数据平台,是目前提供引文回溯数据最深的数据库。VOSviewer是由荷兰雷登大学Van Eck与Waltman设计开发的一款文献计量分析软件,可用于进行关键词、主题词和作者等信息的“共现”分析,其在可视化图谱展示尤其在聚类分析中有着独特的优势。本文采用文献计量学的方法,以WOS数据库为基础,运用VOSviewer对全球范围内环境科学领域PFASs相关研究文献进行可视化分析,揭示该领域的研究现状和前沿动态,同时重点分析我国在该领域的研究情况及未来发展趋势,为未来该领域的研究提供更有价值的借鉴和参考。
1. 数据来源与分析方法
1.1 数据来源
本文以Web of Science(WOS)为数据来源,采用perfluoroalkyl substances或polyfluoroalkyl substances或PFAS或PFASs作为检索主题词,时间范围为2002~2019年,共查得环境科学领域中全氟类化合物研究的相关文献1 734篇。
1.2 方法与指标
1.2.1 分析方法
通过WOS对所查相关文献进行数据计量分析,包括国家/地区的发文量、主要研究人员、主要研究机构和主要发表期刊等。运用VOSviewer对该研究领域的合作关系以及近期的研究热点进行分析,并进一步讨论未来该领域的研究热点与方向。
1.2.2 主要指标
(1)发文量:即论文的发表数量,分别从时间、国家/地区、研究机构和作者几个方面统计相关领域的发文量,其也是一个重要的评价科研能力的指标。
(2)被引频次:即论文被文引用的次数,可以反映论文在该领域的影响力。
(3)H指数:是一个混合量化指标,可以用来相对准确地反映研究者在相关领域的科研成就[22]。
(4)研究热点分析:基于VOSviewer,对关键词进行共现分析,分析该领域研究热点及未来发展趋势。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 文献产出趋势分析
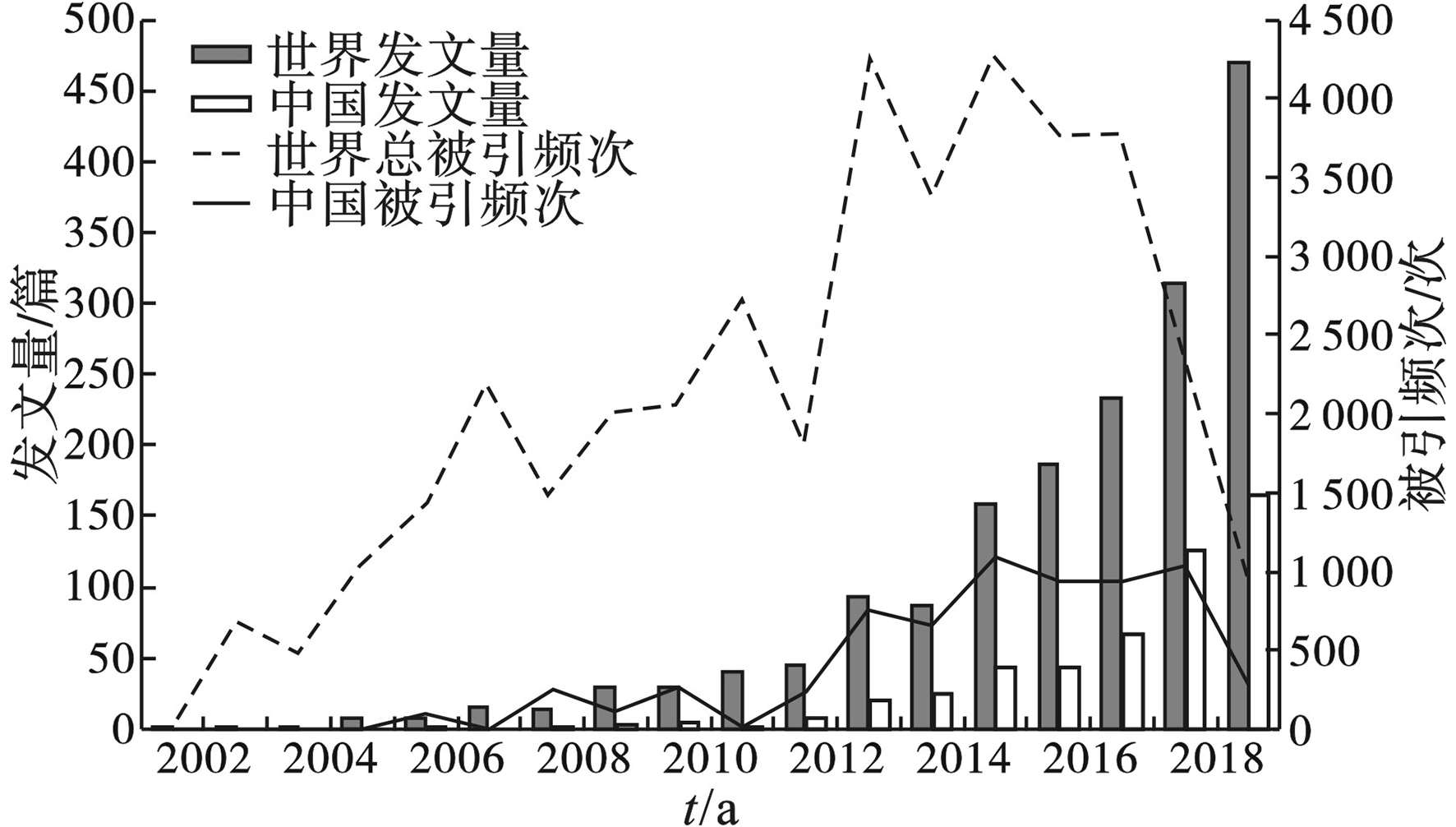
论文在时间上的分布可以反应该领域在不同时间段的研究情况及发展速度,对该领域的不同研究时期进行分类,分别对其进行深入分析[23],见图1。
图1可见,2002~2019年,WOS数据库中全球环境科学领域有关PFASs文献共1 734篇,呈逐年上升趋势。根据发文量和被引频次可以分为3个阶段:2002~2006年为研究起始阶段,该阶段文献较少,只有19篇,占总文献数量的1.10%,年均发文量不到5篇,且总被引频次波动范围较大,最高为1 419次,最低为7次,2005和2006年被引频次均超过1 000次;2007~2012年环境领域PFASs研究进入缓慢发展阶段,论文数量逐渐增高,共有文献174篇,占总量的10.03%,年均29篇,总被引频次也呈现升高趋势,最高达2 712次,但增长速度仍然较慢;2013~2019年为快速发展阶段,论文数量快速增高,发文总量为1 541篇,占总量的88.87%,年均文献220.14篇,大大高于前2个阶段的发文量,2019年发文量达到了469篇,由于文献时间较近,总被引频次暂时呈现下降趋势。
中国在该领域的研究比世界范围内的研究较晚,2006~2012年间发文18篇,平均每年发表2.57篇文献,为国内对PFASs研究的起始阶段;2013~2017年发文数量呈上升趋势,此阶段共发文199篇,年均39.8篇,总被引量稳定增高;2018~2019年文献增长速度显著加快,这两年发表文献量达到了291篇,占我国总量的57.28%,占世界同年文献数量的37.16%,表明我国对环境领域PFASs的研究关注度越来越高。
2.2 国家及机构分析
2.2.1 国家和地区
论文发表的数量和被引频次反映了一个国家/地区的整体科研实力和影响力[24]。美国发文量最多(524篇),占前20国家文献总量的20.67%,中国发文量仅次于美国,排第二位(508篇)。在被引频次方面,美国第一(13 111次),加拿大第二(9 481次),中国排名第三位(6 655次)。从篇均被引量来看,瑞士最高为45.75次,中国篇均被引量仅有13.1。通过以上结果发现,发文总量排名中等的德国、瑞士和比利时等国家篇均被引数很高。美国在文献总量、总被引及H指数方面均排名第一,因此,美国在环境科学领域中PFASs的研究在全球仍处于主导地位,我国虽然发文量较多,但总被引和篇均被引量相对较低,还需要进一步提升文章质量,以提高我国在该领域的影响力,见表1。
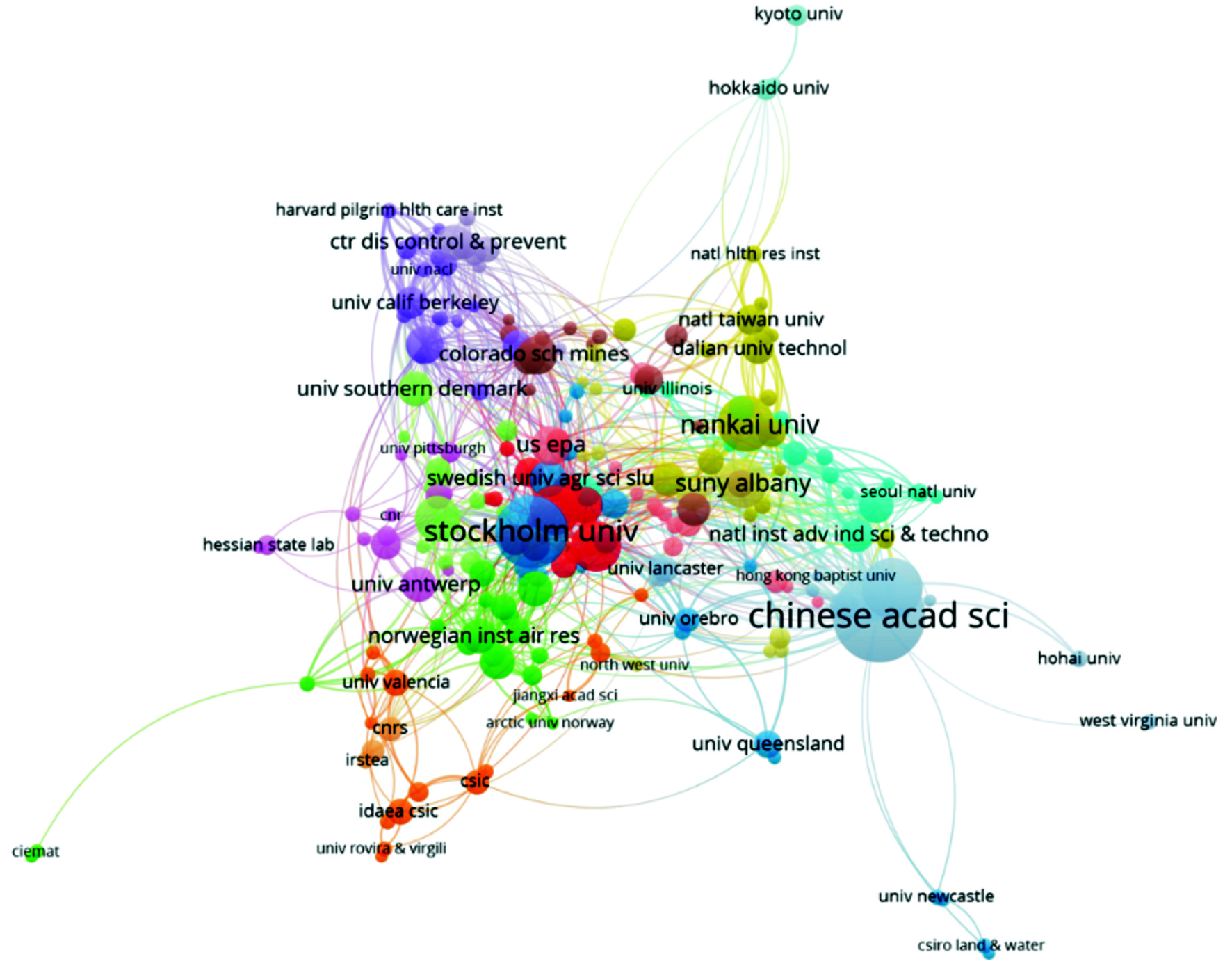
用VOSviewer可视化软件分析2002~2019年环境领域PFASs研究全球各国之间的合作关系,见图2。
图2可见,瑞士、德国、瑞典、挪威和捷克等国家的合作较为密切,与中国的合作相对密切国家主要是美国、加拿大、日本和韩国。
表 1 前20位发文国家发文量及被引频次国家 发文量/篇 总被引量/次 篇均被引量/次 H指数 美国 524 13 111 25.02 56 中国 508 6 655 13.10 40 加拿大 250 9 481 37.92 49 瑞典 206 6 540 31.75 42 德国 144 5 799 40.27 39 挪威 136 2 937 21.6 29 西班牙 95 1 577 16.60 24 丹麦 87 1 995 22.93 24 日本 75 1 754 23.39 23 荷兰 66 1 714 25.97 23 法国 63 890 14.13 19 澳大利亚 58 698 12.03 16 英国 57 1 388 24.35 21 瑞士 48 2 196 45.75 23 比利时 45 1 921 42.69 15 意大利 45 1 554 34.53 16 韩国 45 1 263 28.07 20 捷克 39 1 415 36.28 16 中国台湾 27 514 19.04 13 希腊 17 112 6.59 5 2.2.2 研究机构
在研究机构方面,中国科学院发文量最高(148篇)位居第1位,被引量2 238次,篇均被引15.12次,前20的研究机构中有2所中国机构,为中国科学院和南开大学。在被引量方面,前5名分别为加拿大环境部、斯德哥尔摩大学、多伦多大学、亥姆霍兹联合会和中国科学院。多伦多大学虽然发文量只排在第11位(56篇),但被引量排名第3位(3 114次)。中国科学院虽然发文量最高,但是篇均被引较低,仅为15.12次,见表2。
各研究机构之间的合作关系,见图3。
图3可见,发文量排在第二位的斯德哥尔摩大学同其他研究机构合作最为密切,包括多伦多大学、加拿大环境部、挪威大气研究所、瑞典农业科技大学和科罗拉多矿业学院等。中国科学院虽然发文量较大,但合作关系相对较少,目前相对合作较多的机构主要有香港浸会大学、日本先进工业科学技术研究所和首尔国立大学等。因此我国在环境领域PFASs的研究中应该进一步加强国际合作。
表 2 发文量前20研究机构统计分析研究机构 所属国家 发文量/篇 总被引量/次 篇均被引量/次 H指数 中国科学院 中国 148 2 238 15.12 27 斯德哥尔摩大学 瑞典 97 4 175 43.04 35 加拿大环境部 加拿大 89 4 791 53.83 34 亥姆霍兹联合会 德国 75 3 091 41.21 32 挪威大气研究所 挪威 70 1 860 26.57 23 纽约州立大学 美国 64 2 216 34.63 22 南开大学 中国 61 954 15.64 19 哈佛大学 美国 57 1 139 19.98 19 多伦多大学 加拿大 56 3 114 55.61 27 纽约州立大学 奥尔巴尼分校 美国 54 2 144 39.70 21 加州大学 美国 54 1 192 22.07 18 奥尔胡斯大学 丹麦 53 1 314 24.79 20 沃兹沃思中心 美国 45 1 899 42.20 21 瑞典农业科技大学 瑞典 44 740 16.82 16 皇家科学理事会 西班牙 43 958 22.28 18 美国疾病与预防控制中心 美国 42 1 212 28.86 15 美国环境保护署 美国 41 1 877 45.78 21 厄勒布鲁大学 瑞典 37 768 20.76 15 法国国家科研中心 法国 36 472 13.11 14 科罗拉多矿业学院 美国 35 1 226 35.03 15 2.3 作者及期刊分析
2.3.1 主要作者
论文发表作者分析是衡量科技工作者个人科研情况的重要指标,发文量前3位的作者是瑞典农业科技大学的AHRENS L(60篇),斯德哥尔摩大学的COUSINS I T(49篇)以及纽约州立大学奥尔巴尼分校的KANNAN K(46篇)。在被引量方面,前3位分别为MUIR D C G(2 924次)、MARTIN J W(2 571次)和MABURY S A(2 255次),他们分别来自加拿大环境部、斯德哥尔摩大学和多伦多大学。环境领域发文量进入前20的中国作者为南开大学祝凌燕、孙红文和中国科学院的吕永龙、王佩,见表3。
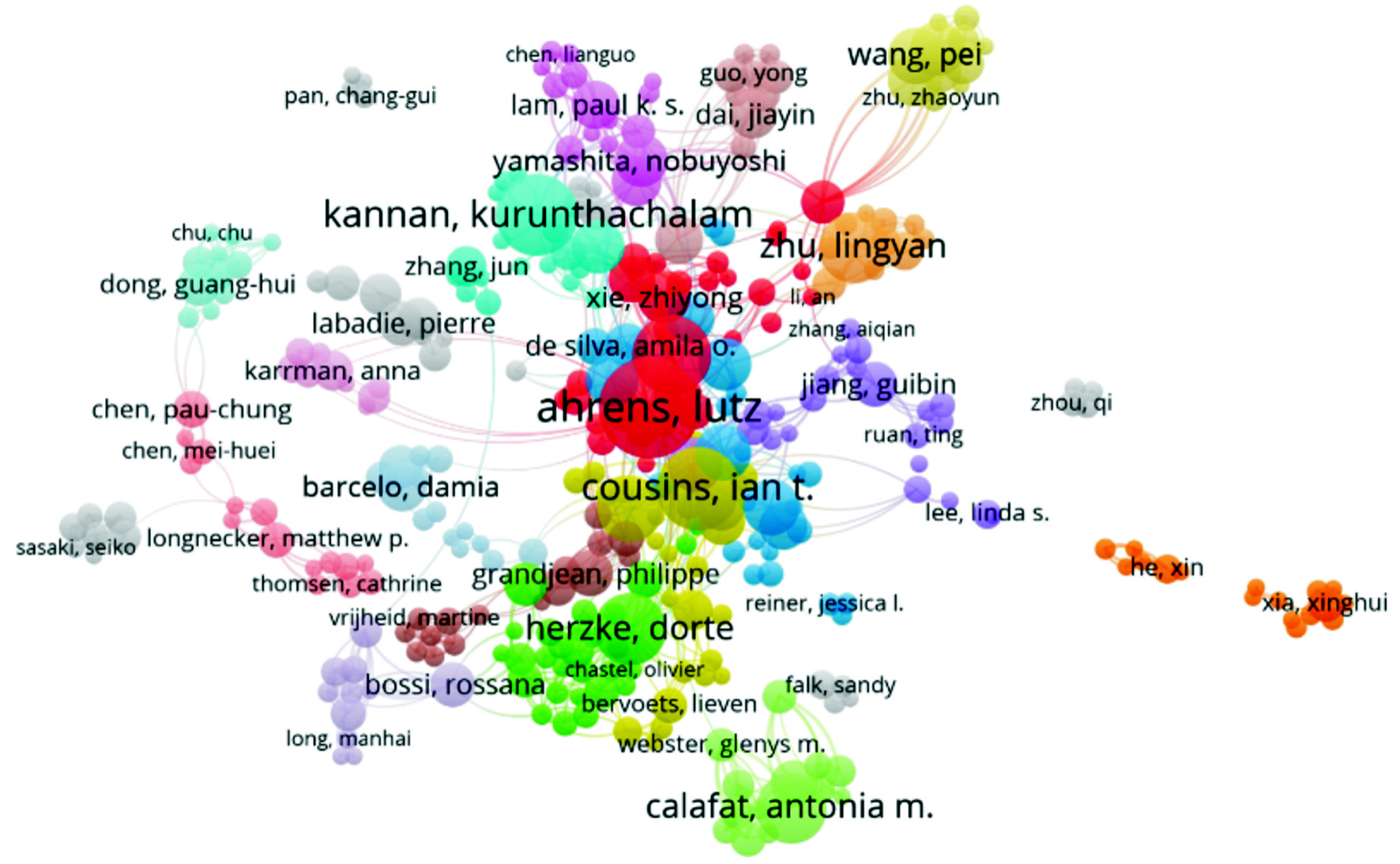
环境领域PFASs重要研究者之间的合作关系,见图4。
图4可见,瑞典农业科技大学的AHRENS L在该领域与其他学者最为密切,主要有发文量位于第二位的COUSINS I T、第四位的EBINGHAUS R及第五位的HERZKE D,但其和中国学者的合作较少。中国学者方面,南开大学的祝凌燕和孙红文合作较多,中国科学院生态环境研究中心的江桂斌、郭良宏、王亚韡、蔡亚岐及史亚利等学者合作较多。中国科学院动物研究所的戴家银也进行了相关合作研究。
表 3 发文量前20位作者统计分析作者 单位 发文量/篇 总被引量/次 篇均被引量/次 H指数 AHRENS L 瑞典农业科技大学 60 1 882 31.37 22 COUSINS I T 斯德哥尔摩大学 49 1 913 39.04 23 KANNAN K 纽约州立大学奥尔巴尼分校 46 2 130 46.30 22 EBINGHAUS R 德国亥姆霍兹联合会 41 1 742 42.49 25 HERZKE D 挪威大气研究所 41 588 14.34 15 CALAFAT A M 美国疾病与预防控制中心 35 1 176 33.60 14 BERGER U 亥姆霍兹环境研究中心 33 1 871 56.70 20 ZHU L Y 南开大学 33 544 16.48 13 MUIR D C G 加拿大环境部 30 2 924 97.47 19 MARTIN J W 斯德哥尔摩大学 27 2 517 93.22 19 YAMASHITA N 日本先进工业科学技术研究所 27 1 041 38.56 14 HIGGINS C P 科罗拉多矿业学院 26 1 474 56.69 14 WANG P 中国科学院 25 416 16.00 12 BENSKIN J P 斯德哥尔摩大学 25 748 29.92 14 MABURY S A 多伦多大学 25 2 255 90.20 20 SUN H W 南开大学 25 384 15.36 12 LYU Y L 中国科学院 24 428 17.83 12 TANIYASU S 日本先进工业科学技术研究所 24 987 41.13 13 VESTERGEREN R 瑞典环境研究所 24 677 28.21 16 FIELD J A 俄勒冈州立大学 23 1 423 61.87 16 2.3.2 主要期刊
对发文量前10的期刊进行了统计分析,见表4。
出版PFASs研究文献数量前10的期刊共出版文献1 293篇,其中数量最多的是《Environmental Science and Technology》,发文量达282篇,占前10期刊的21.81%,居第2位的是《Chemosphere》,发文量为215篇,占16.63%,第3位是《Science of the Total Environment》,发文量为211篇,占16.32%,前3位期刊的文献总量占前10位期刊文献总量的54.76%。从总被引频次及H指数来看,均是《Environmental Science and Technology》排名第1位,《Chemosphere》总被引量排名第2位,篇均被引第6位,H指数第2位,《Environment International》总被引量第3位,篇均被引第5位,《Water Research》虽然发文量排名较低,但是篇均被引排名第1。以上几种期刊在环境领域PFASs的研究中具有较高的权威性。
2.4 高被引论文分析
排名前10位的被引论文统计分析结果,见表5。
总被引量最高的为HOUDE M(MUIR D C G为通讯作者)于2006年发表的文章《Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: A review》,总被引次数为779次,该文主要综述了野生动物和人体中相关PFASs的生物监测,比较了不同物种和暴露区域之间的浓度和污染情况,评估了环境中的生物累积/生物放大并讨论了可能的来源[25]。排名第2位的论文是《Polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the US population: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003—2004 and comparisons with NHANES 1999—2000》,该文主要通过检测美国12岁以上代表性人群血液中PFASs水平进而评估PFASs在人群中的相对暴露情况[26]。该文献发表于2007年,总被引次数为595次。排名第3位的论文是《Polyfluorinated Compounds: Past, Present, and Future》,其通过对PFASs相关研究文献的综述,提出了与环境密切相关的PFASs研究的重要性与紧迫性[27]。作者LOOS R有2篇文章被引次数位于前10位,分别发表于2010和2013年,被引频次均为456次。
表 4 发文量前10的期刊统计分析期刊 发文量/篇 总被引量/次 篇均被引量/次 H指数 Environmental Science Technology 282 12 513 44.37 60 Chemosphere 215 4 186 19.47 32 Science of the Total Environment 211 3 132 14.84 29 Environmental Pollution 156 2 563 16.43 28 Environment International 137 3 229 23.57 31 Environmental Research 87 1 029 11.83 18 Environmental Science and Pollution Research 69 868 12.58 16 Environmental Health Perspectives 46 1 419 30.85 18 Water Research 46 2 378 51.70 21 Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 44 1 712 38.91 18 表 5 排名前10位的被引论文统计分析第一作者 题名 发文时间/a 总被引量/次 HOUDE M Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: A review 2006 779 CALAFAT A M Polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the US population: Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003—2004 and comparisons with NHANES 1999—2000 2007 595 LINDSTROM A B Polyfluorinated Compounds: Past, Present, and Future 2011 579 CONDER J M Are PFCAs bioaccumulative? A critical review and comparison with regulatory lipophilic compounds 2008 541 LOOS R EU-wide monitoring survey on emerging polar organic contaminants in wastewater treatment plant effluents 2013 456 LOOS R Pan-European survey on the occurrence of selected polar organic persistent pollutants in ground water 2010 456 MARTIN J W Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) 2003 411 HIGGINS C P Quantitative determination of perfluorochemicals in sediments and domestic sludge 2005 356 MARTIN J W Dietary accumulation of perfluorinated acids in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) 2003 295 WANG Z Y Fluorinated alternatives to long-chain perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs), perfluoroalkane sulfonic acids (PFSAs) and their potential precursors 2013 274 2.5 关键词及研究热点
一个关键词在不同文献中出现的频次越高,说明相关的研究越多,被关注度也越高。基于VOSviewer,对2002~2019年间关键词建立环境科学领域中PFASs的知识图谱,分析此领域研究热点:一是全氟类化合物的生物体暴露及毒性研究;二是其在水体中的生物降解消除研究;三是对中国某些地区的全氟类化合物的空间分布等研究。同时多溴联苯醚类污染物在全氟类化合物的研究中也一同被关注见图5。我国对于PFASs的研究热点和世界研究热点基本一致见图6。
近5年前20位关键词统计,见表6。
表 6 2015~2019年近5年关键词统计分析排名 关键词 频次 1 水体 279 2 暴露 146 3 全氟辛酸 127 4 饮用水 111 5 时间变化趋势 100 6 血清浓度 95 7 人体暴露 89 8 归趋 87 9 产前暴露 84 10 废水 84 11 多溴联苯醚 84 12 生物富集 75 13 吸附 70 14 空间分布 68 15 沉积物 60 16 转运 60 17 中国 57 18 毒性 55 19 组织分布 53 20 儿童 52 结果表明,PFASs在不同水体及生物体中的暴露仍然是近5年的研究热点,尤其关注饮用水及人体暴露方面。近5年研究最多的环境介质是水体,其次是沉积物。对于我国全氟类化合物的环境暴露也是近期研究的重点之一。
3. 结论
本文主要对2002~2019年WOS数据库收录的环境科学领域PFASs研究文献进行计量学分析。
(1)全球环境领域中PFASs研究文献数量呈上升趋势,并且目前仍处于加速研究阶段,中国在此领域的研究虽然较晚,但发展较快,2018~2019年中国发文量占世界同年发文量的37.16%,表明我国对环境领域PFASs的研究关注度越来越高。
(2)美国在环境科学领域PFASs的研究方面在全球仍处于主导地位,我国虽然发文量较多,但总被引和篇均被引量相对较低,还需要进一步提升文章质量,以提高我国在该领域的影响力。
(3)斯德哥尔摩大学、加拿大环境部和亥姆霍兹联合会位居研究机构H指数前3名,且斯德哥尔摩大学同其他研究机构合作最为密切。中国科学院虽然发文量最多,但篇均被引量较低,且合作关系相对较少,因此我国在环境领域PFASs的研究中应该进一步加强国际合作。
(4)在高被引论文方面,HOUDE M(MUIR D C G为通讯作者)发表的《Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: A review》居榜首,我国未有论文进入全球高被引论文前10位,这可能和我国在该领域的研究起步较晚有关,但仍需加强我国论文在国际上的影响力。
本研究系统分析了环境领域PFASs的研究动态及现状,并对未来该领域的研究热点进行了展望。由于PFASs在各个行业的广泛应用以及较难降解的特性,其对人类的环境健康效应已经引起了研究者的广泛关注,关注人体暴露与健康效应将成为PFASs未来最为重要的研究热点。通过对关键词的分析发现,PFASs在不同水体及生物体中的暴露是未来的关注热点,尤其是饮用水安全及人体暴露;同时我国PFASs的环境暴露也越来越得到研究者的关注。该研究为相关研究者进一步把握该领域的研究方向提供了较全面的数据参考。
-
刘培, 黄鹏飞, 张艳艳, 等. 我国河口管理研究进展[C]. 2022中国水利学会学术年会. 北京: 中国水利学会, 2022: 397-402 郭丽霞, 王亚松, 乔德会, 等. 夏季长江口南北支溶解有机质的比较[J]. 海洋科学, 2022, 46(11): 67-82 Guo L X, Wang Y S, Qiao D H, et al. Comparative study on dissolved organic matter in the north and south branches of the Changjiang River Estuary in summer[J]. Marine Sciences, 2022, 46(11): 67-82(in Chinese)
Halpern B S, Walbridge S, Selkoe K A, et al. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems[J]. Science, 2008, 319(5865): 948-952 Bricker S B, Longstaff B, Dennison W, et al. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation's estuaries: A decade of change[J]. Harmful Algae, 2008, 8(1): 21-32 Johnston E L, Mayer-Pinto M, Crowe T P. Chemical contaminant effects on marine ecosystem functioning[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 52(1): 140-149 Tolkkinen M J, Mykrä H, Virtanen R, et al. Land use impacts on stream community composition and concordance along a natural stress gradient[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 62: 14-21 叶敦雨. 南四湖入湖河流水环境质量状况及其对流域土地利用空间格局的响应[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学, 2022: 22-24 孙福红, 郭一丁, 王雨春, 等. 我国水生态系统完整性研究的重大意义、现状、挑战与主要任务[J]. 环境科学研究, 2022, 35(12): 2748-2757 Sun F H, Guo Y D, Wang Y C, et al. Significance, current situation, challenges and future direction and development of research on freshwater ecological integrity in China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2022, 35(12): 2748-2757(in Chinese)
Leopold A. A Sand County Almanac: And Sketches Here and There[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1949: 48-68 Karr J R, Dudley I J. Ecological perspective on water quality goals[J]. Environment Manage, 1981(5): 55-68 Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Core set of indicators for environmental performance reviews: A synthesis report by the group on the state of the environment[R]. Paris: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, 1993 Rapport D J. What constitutes ecosystem health?[J]. Perspectives in Biology and Medicine, 1989, 33(1): 120-132 Costanza R, Norton B G, Haskell B D. Ecosystem Health: New Goals for Environmental Management[M]. Washington DC: Island Press, 1992: 52-66 彭涛, 陈晓宏. 海河流域典型河口生态系统健康评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2009, 42(5): 631-634, 639 Peng T, Chen X H. Assessment of ecosystem health for typical estuary in Haihe River Basin[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2009, 42(5): 631-634, 639(in Chinese) 董君杰, 赵民, 王闯. 月河口至浉河口段河流生态系统健康评价[J]. 河南水利与南水北调, 2013(11): 30-31 徐浩田, 周林飞, 成遣. 基于PSR模型的凌河口湿地生态系统健康评价与预警研究[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(24): 8264-8274 Xu H T, Zhou L F, Cheng Q. Study on ecosystem health evaluation and risk assessment for Linghekou wetlands based on a PSR model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(24): 8264-8274(in Chinese)
王铁良, 孙一民. 双台河口湿地生态系统健康评价研究[J]. 沈阳农业大学学报, 2013, 44(6): 793-798 Wang T L, Sun Y M. Ecosystem health assessment of Shuangtaihekou wetland[J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2013, 44(6): 793-798(in Chinese)
Xu F, Yang Z F, Chen B, et al. Development of a structurally dynamic model for ecosystem health prognosis of Baiyangdian Lake, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2013, 29: 398-410 王福峰. 锦凌水库生态环境现状调查与评价[J]. 黑龙江水利科技, 2014, 42(1): 237-239 Souza G B G, Vianna M. Fish-based indices for assessing ecological quality and biotic integrity in transitional waters: A systematic review[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2020, 109: 105665 Rocha L, Hegoburu C, Torremorell A, et al. Use of ecosystem health indicators for assessing anthropogenic impacts on freshwaters in Argentina: A review[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2020, 192(9): 611 Chen Y, Xiong K N, Ren X D, et al. An overview of ecological vulnerability: A bibliometric analysis based on the Web of Science database[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2022, 29(9): 12984-12996 Qiu H H, Liu L G. A study on the evolution of carbon capture and storage technology based on knowledge mapping[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(5): 1103 Elliott M, Quintino V. The Estuarine Quality Paradox, Environmental Homeostasis and the difficulty of detecting anthropogenic stress in naturally stressed areas[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 54(6): 640-645 Borja A, Ranasinghe A, Weisberg S B. Assessing ecological integrity in marine waters, using multiple indices and ecosystem components: Challenges for the future[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 59(1-3): 1-4 Stevenson L H, Kennish M J. Ecology of estuaries: Anthropogenic effects[J]. Estuaries, 1992, 15(3): 428 Cloern J E, Abreu P C, Carstensen J, et al. Human activities and climate variability drive fast-paced change across the world's estuarine-coastal ecosystems[J]. Global Change Biology, 2016, 22(2): 513-529 牛明香, 王俊. 河口生态系统健康评价研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(7): 1977-1982 Niu M X, Wang J. Review on estuary ecosystem health assessment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(7): 1977-1982(in Chinese)
Meng W, Liu L S. On approaches of estuarine ecosystems health studies[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 86(3): 313-316 O'Brien A, Townsend K, Hale R, et al. How is ecosystem health defined and measured? A critical review of freshwater and estuarine studies[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016, 69: 722-729 Gibson R, Atkinson R, Gordon J. Loss, status and trends for coastal marine habitats of Europe[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology, 2007, 45: 345-405 Zhang F, Peng G Y, Xu P, et al. Ecological risk assessment of marine microplastics using the analytic hierarchy process: A case study in the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent marine areas[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 425: 127960 Le Guen C, Tecchio S, Dauvin J C, et al. Assessing the ecological status of an estuarine ecosystem: Linking biodiversity and food-web indicators[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2019, 228: 106339 林海荣. 闽三角地区生态系统完整性评价方法研究[D]. 福州: 福州大学, 2019: 3-6 刘雪萍, 卢双舫, 唐明明, 等. 河流-潮汐耦合控制下河口湾坝体沉积动力学数值模拟[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(8): 2944-2957 Liu X P, Lu S F, Tang M M, et al. Numerical simulation of sedimentary dynamics to estuarine bar under the coupled fluvial-tidal control[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(8): 2944-2957(in Chinese)
Galois R, Blanchard G, Seguignes M, et al. Spatial distribution of sediment particulate organic matter on two estuarine intertidal mudflats: A comparison between Marennes-Oléron Bay (France) and the Humber Estuary (UK)[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2000, 20(10/11): 1199-1217 Smith S V, Hollibaugh J T. Coastal metabolism and the oceanic organic carbon balance[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1993, 31(1): 75-89 许宇田. 长江口南汇东滩潮间带盐沼湿地鱼类物种多样性及其营养结构[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2019: 4-5 Jiang M Q, Nakano S I. The crucial influence of trophic status on the relative requirement of nitrogen to phosphorus for phytoplankton growth[J]. Water Research, 2022, 222: 118868 刘春涛, 刘秀洋, 王璐. 辽河河口生态系统健康评价初步研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2009, 26(3): 43-48 陈静. 河口区水生态健康评价技术方法及其应用[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2013: 4-7 刘焱序, 彭建, 汪安, 等. 生态系统健康研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2015, 35(18): 5920-5930 Liu Y X, Peng J, Wang A, et al. New research progress and trends in ecosystem health[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2015, 35(18): 5920-5930(in Chinese)
牛明香, 王俊, 徐宾铎. 基于PSR的黄河河口区生态系统健康评价[J]. 生态学报, 2017, 37(3): 943-952 Niu M X, Wang J, Xu B D. Assessment of the ecosystem health of the Yellow River Estuary based on the pressure-state-response model[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2017, 37(3): 943-952(in Chinese)
王锦东, 苏海磊, 李会仙, 等. 典型流域生态完整性评价和应用研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(10): 233-241 Wang J D, Su H L, Li H X, et al. Research progress of water ecological integrity assessment and application in typical watersheds[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(10): 233-241(in Chinese)
叶属峰, 刘星, 丁德文. 长江河口海域生态系统健康评价指标体系及其初步评价[J]. 海洋学报, 2007, 29(4): 128-136 Ye S F, Liu X, Ding D W. Ecosystem health assessment of the Changjiang River Estuary: Indicator system and its primarily assessment[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(4): 128-136(in Chinese)
Müller F, Lenz R. Ecological indicators: Theoretical fundamentals of consistent applications in environmental management[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2006, 6(1): 1-5 Pinto R, Patrício J, Baeta A, et al. Review and evaluation of estuarine biotic indices to assess benthic condition[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2009, 9(1): 1-25 马廷婷, 范亚民, 李宽意, 等. 基于浮游植物完整性指数的太湖主要河口生态健康评价[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2021, 37(4): 501-508 Ma T T, Fan Y M, Li K Y, et al. Ecological health assessment of main estuaries of Lake Taihu based on phytoplankton index of biotic integrity[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2021, 37(4): 501-508(in Chinese)
Hallett C S, Trayler K M, Valesini F J. The fish community index: A practical management tool for monitoring and reporting estuarine ecological condition[J]. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 2019, 15(5): 726-738 Kido M H. A native species-based index of biological integrity for Hawaiian stream environments[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(5): 4063-4075 Dauvin J C. Paradox of estuarine quality: Benthic indicators and indices, consensus or debate for the future[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2007, 55(1-6): 271-281 Elliott M, Whitfield A K. Challenging paradigms in estuarine ecology and management[J]. Estuarine, Coastal Shelf Science, 2011, 94(4): 306-314 Hess S, Alve E, Andersen T J, et al. Defining ecological reference conditions in naturally stressed environments: How difficult is it?[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 2020, 156: 104885 Rapport D J, Costanza R, McMichael A J. Assessing ecosystem health[J]. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 1998, 13(10): 397-402 Arocena R, Castro M, Chalar G. Ecological integrity assessment of streams in the light of natural ecoregions and anthropic land use[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2022, 194(10): 748 Barbier E, Hacker S, Kennedy C J, et al. The value of estuarine and coastal ecosystem services[J]. Ecological Monographs, 2011, 81: 169-193 Alongi D M. Mangrove forests: Resilience, protection from tsunamis, and responses to global climate change[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2008, 76(1): 1-13 Borja A, Bricker S B, Dauer D M, et al. Overview of integrative tools and methods in assessing ecological integrity in estuarine and coastal systems worldwide[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2008, 56(9): 1519-1537 Zhao C, Shao N, Yang S, et al. Integrated assessment of ecosystem health using multiple indicator species[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2019, 130: 157-168 Lane C R, Brown M T. Diatoms as indicators of isolated herbaceous wetland condition in Florida, USA[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2007, 7(3): 521-540 Wang Y Y, Yin K, Yang Q, et al. Research and application progress of assessment for river water ecosystem quality[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2014, 30(4): 1-9(in Chinese) Kane D D, Gordon S I, Munawar M, et al. The Planktonic Index of Biotic Integrity (P-IBI): An approach for assessing lake ecosystem health[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2009, 9(6): 1234-1247 Li Z X, Ma C, Sun Y N, et al. Ecological health evaluation of rivers based on phytoplankton biological integrity index and water quality index on the impact of anthropogenic pollution: A case of Ashi River Basin[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2022, 13: 942205 Ruaro R, Gubiani É A. A scientometric assessment of 30 years of the Index of Biotic Integrity in aquatic ecosystems: Applications and main flaws[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2013, 29: 105-110 Zogaris S, Tachos V, Economou A N, et al. A model-based fish bioassessment index for Eastern Mediterranean Rivers: Application in a biogeographically diverse area[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 622-623: 676-689 Li J, Li Y, Qian B, et al. Development and validation of a bacteria-based index of biotic integrity for assessing the ecological status of urban rivers: A case study of Qinhuai River Basin in Nanjing, China[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2017, 196: 161-167 Li T H, Huang X L, Jiang X H, et al. Assessment of ecosystem health of the Yellow River with fish index of biotic integrity[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2018, 814(1): 31-43 Guerrero E, Gili J M, Maynou F, et al. Diversity and mesoscale spatial changes in the planktonic cnidarian community under extreme warm summer conditions[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 2018, 40(2): 178-196 Diaz R J, Solan M, Valente R M. A review of approaches for classifying benthic habitats and evaluating habitat quality[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2004, 73(3): 165-181 Jiang M Z, Chen H Y, Chen Q H, et al. Wetland ecosystem integrity and its variation in an estuary using the EBLE index[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2015, 48: 252-262 Frashure K M, Bowen R E, Chen R F. An integrative management protocol for connecting human priorities with ecosystem health in the Neponset River Estuary[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2012, 69: 255-264 李燕, 马晓婷, 胡潇涵, 等. 基于熵权的新疆典型流域生态健康评价[J]. 新疆环境保护, 2015, 37(4): 39-43 , 51 Li Y, Ma X T, Hu X H, et al. Entropy weight based ecological health evaluation on typical watershed system in Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Protection of Xinjiang, 2015, 37(4): 39-43, 51(in Chinese)
刘惠君, 闫旭骞, 林大泽. 矿区生态系统健康现状模糊综合评价方法[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2009, 19(12): 154-158 Liu H J, Yan X Q, Lin D Z. A fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method for ecosystem health status in mining area[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2009, 19(12): 154-158(in Chinese)
李海霞, 韩丽花, 蔚青, 等. 基于灰色关联分析法的辽河保护区河流水生态健康评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2020, 10(4): 553-561 , 531 Li H X, Han L H, Yu Q, et al. Assessment on river water ecological health based on grey relation analysis in Liaohe Conservation Area[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2020, 10(4): 553-561, 531(in Chinese)
Dauvin J C, Ruellet T. The estuarine quality paradox: Is it possible to define an ecological quality status for specific modified and naturally stressed estuarine ecosystems?[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2009, 59(1-3): 38-47 Ferreira J G. Development of an estuarine quality index based on key physical and biogeochemical features[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2000, 43(1): 99-122 Borja A, Dauer D M. Assessing the environmental quality status in estuarine and coastal systems: Comparing methodologies and indices[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2008, 8(4): 331-337 Chiu G S, Wu M A, Lu L. Model-based assessment of estuary ecosystem health using the latent health factor index, with application to the richibucto estuary[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e65697 Shamaskin A C, Correa S B, Street G M, et al. Considering the influence of land use/land cover on estuarine biotic richness with Bayesian hierarchical models[J]. Ecological Applications: A Publication of the Ecological Society of America, 2022, 32(7): e2675 孙涛, 杨志峰. 河口生态系统恢复评价指标体系研究及其应用[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(3): 381-384 Sun T, Yang Z F. Studies on the evaluating index system for estuarine ecosystem restoration and its application[J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(3): 381-384(in Chinese)
惠秀娟, 杨涛, 李法云, 等. 辽宁省辽河水生态系统健康评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(1): 181-188 Hui X J, Yang T, Li F Y, et al. Health assessment on aquatic ecosystem in Liaohe River of Liaoning Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(1): 181-188(in Chinese)
张芮, 徐宾铎, 薛莹, 等. 黄河口及其邻近水域鱼类生物完整性评价[J]. 中国水产科学, 2017, 24(5): 946-952 Zhang R, Xu B D, Xue Y, et al. Evaluation of the biotic integrity of fish assemblages in the Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2017, 24(5): 946-952(in Chinese)
Karr J R, Larson E R, Chu E W. Ecological integrity is both real and valuable[J]. Conservation Science and Practice, 2022, 4(2): e583 Whitfield A K. Fishes and the environmental status of South African estuaries[J]. Fisheries Management and Ecology, 1996, 3(1): 45-57 Meng L S, Orphanides C D, Christopher Powell J. Use of a fish index to assess habitat quality in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island[J]. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 2002, 131(4): 731-742 Harrison T D, Whitfield A K. Application of a multimetric fish index to assess the environmental condition of South African Estuaries[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 2006, 29(6): 1108-1120 Medeiros J P, Chaves M L, Silva G, et al. Benthic condition in low salinity areas of the Mira Estuary (Portugal): Lessons learnt from freshwater and marine assessment tools[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2012, 19: 79-88 Cabral H N, Fonseca V F, Gamito R, et al. Ecological quality assessment of transitional waters based on fish assemblages in Portuguese Estuaries: The Estuarine Fish Assessment Index (EFAI)[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2012, 19: 144-153 Kido M H. A native species-based index of biological integrity for Hawaiian stream environments[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2013, 185(5): 4063-4075 Itsukushima R, Yoshikawa H, Morita K. A dataset of molluscan fauna sampled in river estuaries of medium and small size river in Kyushu Island, Japan[J]. Biodiversity Data Journal, 2018(6): e26101 Nestlerode J A, Murrell M C, Hagy J D, et al. Bioassessment of a northwest Florida estuary using benthic macroinvertebrates[J]. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 2020, 16(2): 245-256 Mulik J, Sukumaran S, Dias H Q. Is the benthic index AMBI impervious to seasonality and data transformations while evaluating the ecological status of an anthropized monsoonal estuary?[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2020, 186: 105080 周晓蔚, 王丽萍, 郑丙辉, 等. 基于底栖动物完整性指数的河口健康评价[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 30(1): 242-247 Zhou X W, Wang L P, Zheng B H, et al. Estuary health assessment using a benthic-index of biotic integrity in Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 30(1): 242-247(in Chinese)
Qiu B C, Zhong X, Liu X S. Assessment of the benthic ecological status in the adjacent waters of Yangtze River Estuary using marine biotic indices[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 137: 104-112 张嵩, 张崇良, 徐宾铎, 等. 基于大型底栖动物群落特征的黄河口及邻近水域健康度评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(5): 65-71 Zhang S, Zhang C L, Xu B D, et al. Ecological status assessment based on macrobenthic community characteristics in Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(5): 65-71(in Chinese) -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2144
- HTML全文浏览数: 2144
- PDF下载数: 175
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: