-
水体富营养化导致水体异味(off-flavor)是一个严重且普遍存在的环境问题. 异味将直接对饮用水和水产品的质量造成影响,并最终危害到饮用水和水产品的品质,造成消费者不安全感和渔业经济损失,因此水体中的异味物质研究受到越来越多的关注. 水体中最常见的两种异味物质是土臭素(geosmin)和 2-甲基异莰醇(2-methylisoborneol,2-MIB),这两种物质已经得到了较多的研究,在生活饮用水卫生标准[1]当中也规定了限量值. 但随着工业的发展和各种环境问题的爆发,仅仅关注这两种异味物质是不够的. 其他的水体异味,如土霉味、氯味、草木味、沼气味、芳香味、鱼腥味、药水味及化学品味等也需要引起我们的关注. 了解水体中异味物质的种类、分布和浓度水平是判断异味物质来源、采取针对性控制措施的基础,因此建立准确可靠并且可同时分析多种异味物质的方法十分必要.
由于异味物质的嗅觉阈值极低,例如,土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇的嗅觉阈值分别为5—10 ng·L−1和1—10 ng·L−1,因此需要高效的样品前处理和高灵敏度的检测方法. 样品富集方法目前用的比较多的有吹扫捕集法[2-3]、分散固相萃取法[4]、闭环捕集[5-6]、液液萃取[7-8]、固相萃取[9-10]、搅拌棒吸附萃取[11-12]等. 这些方法大多费时费力,需要用到有机溶剂,前处理设备如果管路多,容易存在样品残留,引起交叉污染的状况. 而20世纪80年代发展起来的固相微萃取技术由于其富集能力强,无需使用有机溶剂而深受广大科研工作者的青睐,越来越多的应用于水中异味物质的分析检测[13-17]. 2016 年,我国颁布了国家标准检测方法《GB/T 32470—2016 生活饮用水臭味物质 土臭素和 2-甲基异莰醇检验方法》[18]. 该方法采用固相微萃取技术吸附样品中的土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇,顶空富集后用气质联用仪进行分离、测定. 但是手动固相微萃取,耗时长,每天能够检测的样品数量非常少,特别不利于大批量样品的检测,并且萃取头寿命较短.
本研究中采用新的箭型固相微萃取(SPME Arrow)技术对水中的异味物质进行在线富集,涂层体积更大,加大了吸附容量,从而大大提高了富集倍数,进而提高了方法的灵敏度. 异味物质的检测技术方面,目前大多采用气相色谱-单四极杆质谱进行检测,检测的目标物种类比较少,不能满足当前水中异味物质多样化的检测需求,并且对复杂基质中的目标物检测存在基质干扰的情况. 本方法采用气相色谱-三重四极杆质谱对异味物质进行检测,提高了方法对复杂基质的抗干扰能力. 选取了57种常见的异味物质作为目标物,优化了萃取过程中对萃取效率有显著影响的关键参数,建立水体中多种异味物质的高效、稳定、全自动的SPME Arrow -气相色谱/三重四极杆质谱联用分析方法.
-
PAL3自动样品前处理平台,包含孵化炉、SPME Arrow 老化模块、加热磁力搅拌模块(瑞士CTC Analytics公司);Agilent 7890B/7000D 三重四极杆气质联用系统,配备 EI 源(美国Agilent公司).
-
异味物质标准品(固体标准品或溶液,上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司,标准品物质名称详见表1);氯化钠,乙酸,碳酸钠,均为优级纯(国药集团);甲醇,色谱纯(美国Merck公司);所用实验用水为现制备的超纯水.
-
取 5.0 mL 水样,加入 1.0 g 氯化钠,置于 20 mL 螺口顶空瓶中. 旋紧瓶盖,置于顶空样品盘中,待测定.
萃取前,将样品置于40 ℃ 下孵化3.0 min,然后将样品转移到加热磁力搅拌模块中,将 SPME Arrow 伸入样品上方顶空气相中,在40 ℃ 下顶空萃取30.0 min,最后在进样口解吸5.0 min.
-
色谱柱:Agilent DB-WAX UI 气相色谱柱,30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 µm. 多模式(MMI)进样口:不分流进样,250 ℃. 载气类型及流速:He,恒流模式,流速1 mL·min−1. 炉温升温程序:在40 ℃ 下保持3.0 min,然后以10.0 ℃·min−1的速率升至250 ℃ 并保持10.0 min. 传输线温度280 ℃. 质谱离子源温度250 ℃. 检测模式:MRM模式,57种化合物保留时间及定量离子对详见表1.
-
固相微萃取技术中吸附效率的影响因素主要包括萃取头涂层(固定相)、萃取时间、萃取温度、样品pH值和离子强度等. 本方案中着重考察了萃取时间、萃取温度、样品pH的影响. 另外在实验过程中发现了萃取头在进样口进入的深度对解析效率有显著影响,因此也对萃取头在进样口的深度进行了优化.
萃取涂层的选择上考虑到水中的异味物质既有极性化合物,也有弱极性和非极性化合物,分子量比较小,沸点较低,所以一般选用三相复合涂层DVB/CAR/PDMS来满足多种异味物质的萃取要求[16]. Arrow萃取头的长度为2 cm,直径为1.1 mm和1.5 mm两种型号,比表面积大,吸附速度快,涂层体积大,灵敏度高. 本实验中,选择了1.1 mm直径的DVB/CAR/PDMS作为萃取涂层,能够得到非常优异的结果.
-
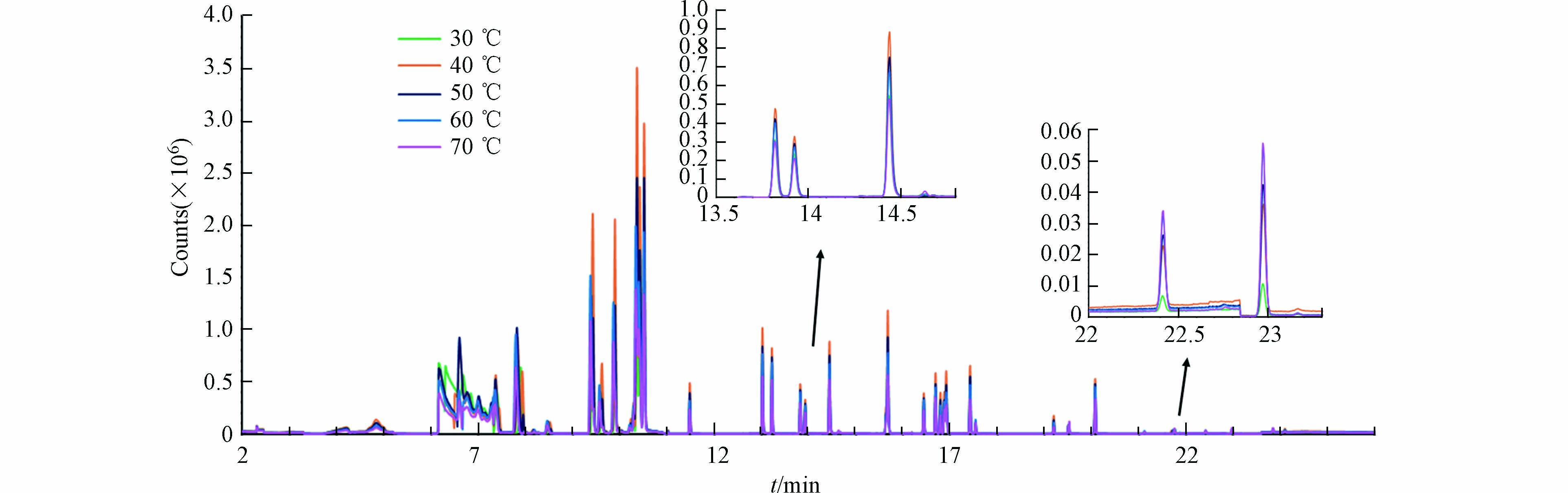
萃取温度对固相微萃取有双重作用:温度升高,可以加快目标物的分子扩散速度,有利于尽快达到平衡,但是温度的升高,又使得涂层对待测物的吸附减弱,降低了灵敏度. 在本实验中,考察了萃取温度对57种分析物的影响,考察的温度范围从30 ℃到70 ℃. 结果表明,对于保留时间在21.0 min之前的化合物,萃取温度40 ℃能够达到最优的萃取效果. 当萃取温度高于40 ℃后,随着萃取温度的升高,这些化合物的响应值逐渐降低,这是由于温度的升高减弱了目标物在涂层上的吸附而导致的结果(图1). 而对于保留时间在21.0 min之后的化合物,随着萃取温度的升高,萃取效率一直是升高的趋势. 对于这些化合物而言,温度增加,分子扩散速度的增加更为明显. 考虑到保留时间21.0 min之前的化合物占了大多数,并且温度过高,水汽的量会增加,对Arrow也会有不利的影响,因此选择40 ℃为本实验的萃取温度.
-
萃取时间即萃取达到平衡所需的时间,由待分析物的分配系数、物质的扩散速率、样品基质、样品体积、萃取头膜厚等因素决定. 本实验中,考察了萃取时间对萃取效率的影响,考察的时间范围从10 min到50 min. 结果表明,对于出峰时间较短的化合物,萃取时间10 min能够达到最优的萃取效果. 而对于出峰时间较长的化合物,随着萃取时间的加长,萃取效率一直是升高的趋势(图2). 在实际的实验中,通常选择具有较大萃取量且萃取时间不太长作为实际的萃取时间,考虑到本实验中仪器的运行时间为34 min,因此最终选择30 min为本实验的萃取时间.
-
两者在实质上是一样的,都是影响了基质的离子强度,从而影响了待分析物在样品和顶空气相之间的分配系数. 盐析是向待测样品中加入氯化钠或其他盐,使得溶液中的离子强度增加,从而减少了待测物在基质中的溶解,提高了待测物在顶空气相中的含量,从而提高了萃取效率. 本实验中向待测溶液中加入20%的氯化钠,增强离子强度,从而提高萃取效率[16] .
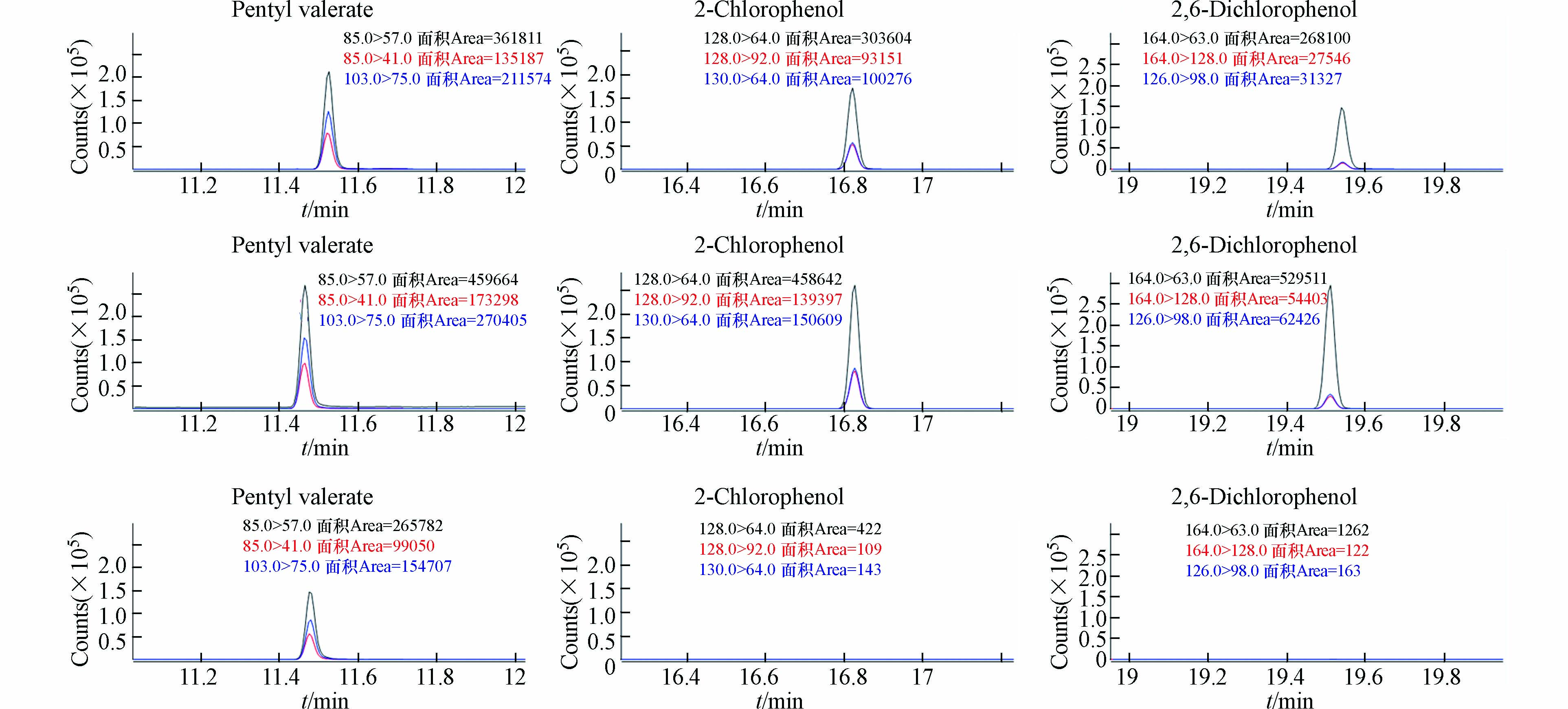
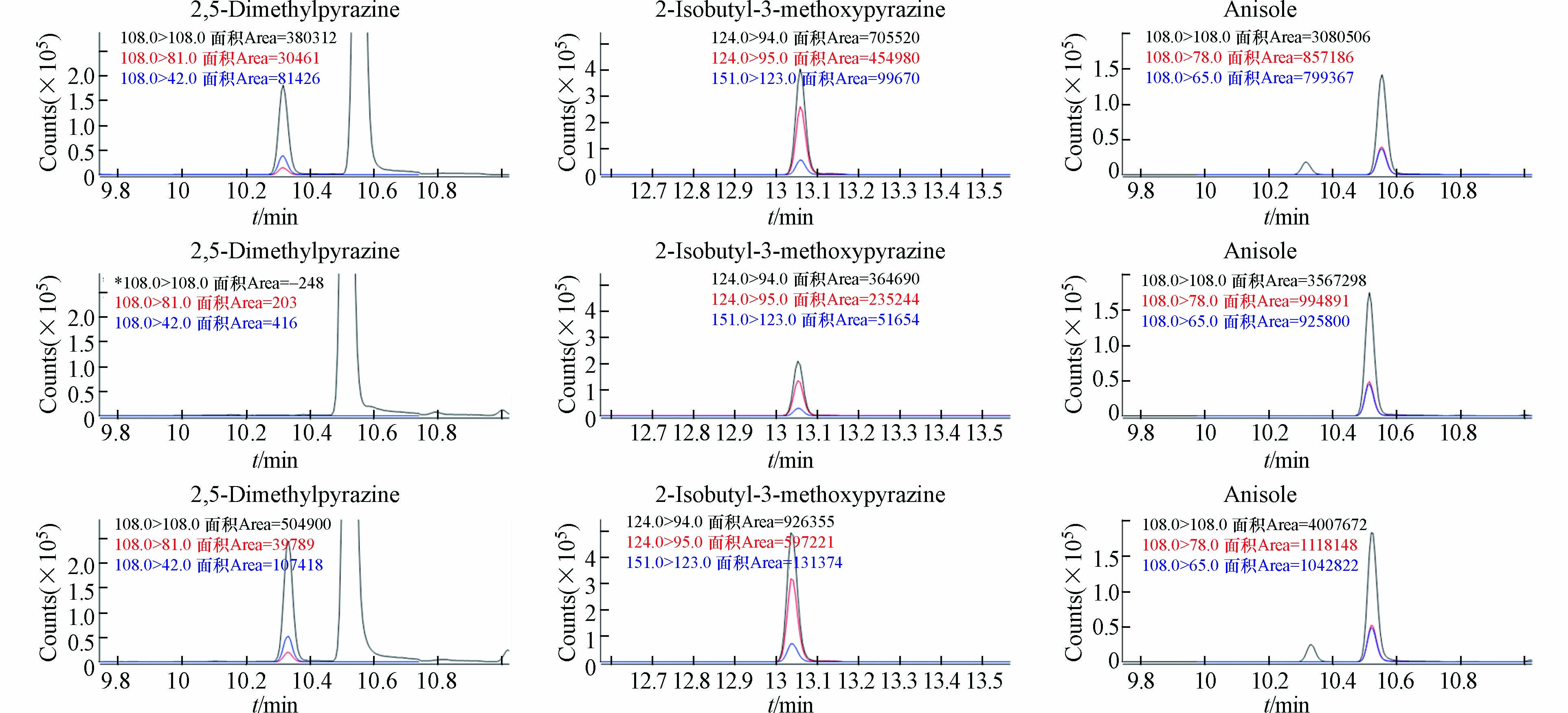
pH的影响是通过调节酸碱度而影响了溶液中的离子强度从而改变了待测物在基质中的溶解性。在 本实验中,考察了样品的pH值对萃取效率的影响:向样品溶液中加入0.1 mL乙酸,使样品在酸性条 件下萃取,可以看到,对酚类等具有羟基的化合物的萃取有明显的促进作用,对酯类化合物的萃取也 有促进作用(图3);而 向样品中添加0.1 g碳酸钠,使样品在碱性条件下萃取,对吡嗪类化合物和醚类化合物的萃取有明显的促进作用(图4)。 从图中可以观察到,酸性条件下萃取对吡嗪类化合物 的负面影响非常显著,而碱性条件下萃取对酚类化合物的负面影响非常显著。因此,最终的实验为了兼顾所有化合物的萃取,实现一次萃取进样完成所有化合物的分析,选择的是中性的萃取条件(样品只添加20%的氯化钠)。
-
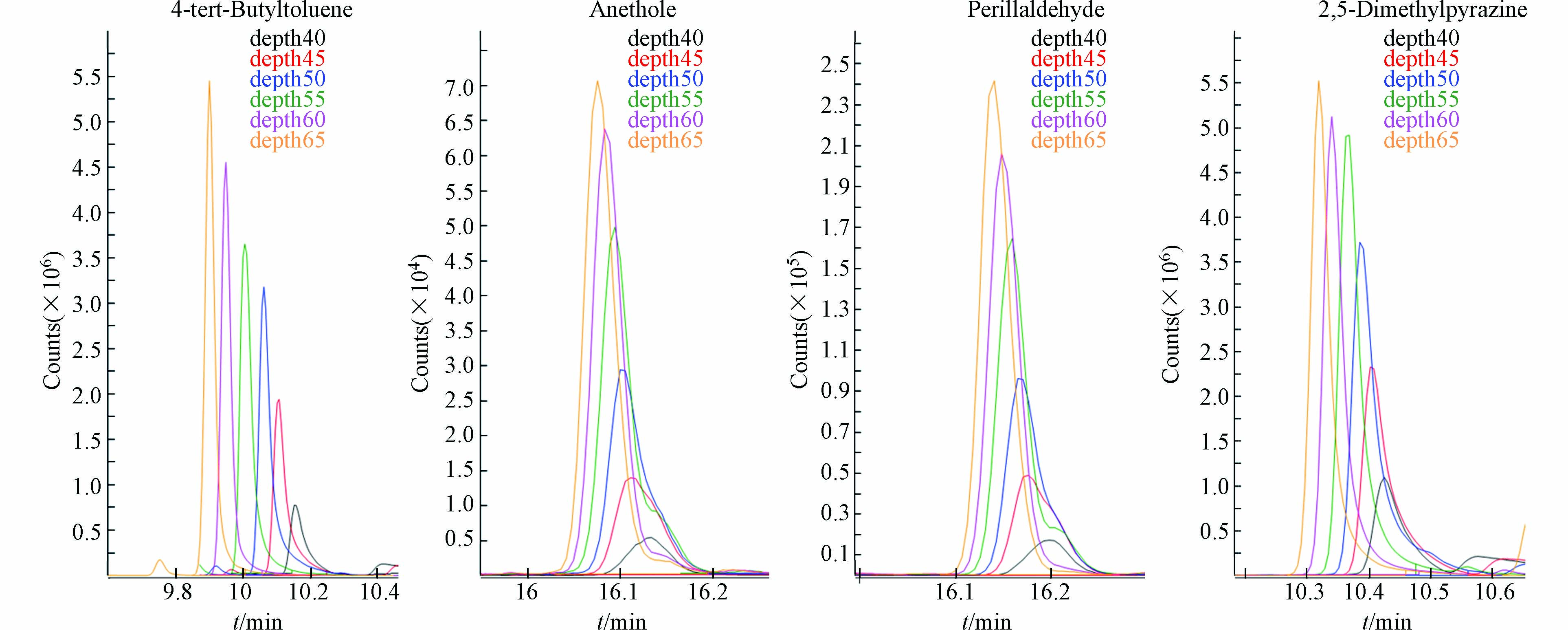
萃取头在气相进样口插入的深度对解析的效率有比较大的影响. 本实验优化了进样口插入深度对解析的影响,考察的进样口深度范围从40 mm到65 mm. 结果如图5所示,对于多模式进样口而言,萃取头在进样口插入的位置越深,峰型越尖锐,说明位置越深,解析的速度越快,解析效率也越高. 分析原因,应该是由于进样口中衬管的中下部位置温度是比较高的区域,因此,Arrow在进样口中的插入深度越深,解析速度越快,解析效率也越高.
-
配制浓度梯度为1.0、5.0、10.0、50.0、100.0、500.0 ng·L−1的标准溶液,按照上述优化后的条件,分别进行萃取:加入氯化钠(20%,M/M)以增强离子强度,提高萃取效率;然后在40 ℃下萃取30.0 min,最后在进样口插入深度65 mm的条件下解吸5.0 min. 用外标法建立校准曲线. 所有57个目标物中其线性相关系数均大于0.99.
-
实际水样加标水平10 ng·L−1,化合物出峰状况良好,峰型尖锐,基本无干扰. 重复萃取测定10次,其中52种化合物RSD小于10%;两种酚类物质(2,6-二氯酚、2,4,6-三氯酚)和嘧啶的RSD值均大于10%,但小于20%(表2).
-
方法最低检出限(MDL)是根据同一浓度的10次测定的精密度来确定的. 配置1 ng·L−1的加标样品,平行测定10次,以3倍的标准偏差为方法检出限. 计算结果显示,52个化合物检测限小于5 ng·L−1,仅有4个化合物的方法检测限大于10 ng·L−1(详见表2). 在国家标准检测方法《GB/T 32470—2016 生活饮用水臭味物质 土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇检验方法》中采用传统的固相微萃取纤维的方式,土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇的检出限分别为3.8 ng·L−1和2.2 ng·L−1,而本方法中土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇的检出限分别达到0.22 ng·L−1和0.89 ng·L−1,相比传统的方法,灵敏度分别提高17倍和2.5倍. 因此,本研究建立的方法具有非常高的检测灵敏度.
-
采用新型的箭型固相微萃取技术顶空富集水中的异味物质,然后转移至气相色谱进样口进行热解析,三重四极杆串联质谱进行异味物质的高通量筛查,方法优化过程中主要对萃取时间、萃取温度和样品pH值进行了优化,同时在优化过程中发现,对于多模式进样口来说,萃取头解析时进入进样口的深度对解析的速度和效率有显著的影响. 本方法采用了新型的箭型固相微萃取头萃取水中的异味物质,具有更高的灵敏度;整个方法前处理过程无需使用有机溶剂,减少环境污染,保护操作人员安全;萃取头小巧,方便携带,易于实现原位检测;萃取头采用金属材质,增强了机械性能,延长了使用寿命,箭型末端还能减小对隔垫的损伤. 2022年3月15日,国家卫生健康委员会发布《生活饮用水卫生标准》(GB 5749—2022),对饮用水中土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇的限量作出了明确的规定为10 ng·L−1,本方法完全能够满足该标准对饮用水和水源水的卫生检测要求.
箭型固相微萃取技术与GCMSMS联用方法用于水中异味化合物的检测
SPME Arrow combined with GCMSMS for determination of odor compounds in water
-
摘要: 箭型固相微萃取技术是近几年发展起来的一项新型样品前处理技术,灵敏度高,机械性能好,无需使用有机溶剂,利用该技术对生活饮用水中的异味物质进行富集,然后通过三重四极杆气质联用系统进行高通量筛查和定量分析. 对萃取过程中的萃取温度、萃取时间、进样口解吸的深度等影响因素进行了优化. 发现萃取头在进样口进行解吸时插入的深度对解吸速度和效率有显著的影响. 采用优化的参数建立了57种异味物质的定量测定方法. 方法验证结果显示,该方法灵敏度高,相比于传统的固相微萃取方法,检测限下降1个数量级;方法准确度高,所有化合物的线性良好,线性相关系数能达到0.99以上;方法重复性很好,实际水样加标水平10 ng·L−1,重复测定10次,所有化合物的RSD值均小于20%,90%以上的化合物RSD小于10%. 该方法各项性能均满足生活饮用水异味物质的检测要求,并且用于实际水样加标检测,无基质干扰的情况.Abstract: A novel solid-phase microextraction (SPME Arrow) system has been recently employed for sample pretreatment. It is a solvent-free microextraction technique with high sensitivity and reliable mechanical properties. In this study, the odor substances in drinking water were enriched by SPME-Arrow, followed by high-throughput screening and quantitative analysis through gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GCMSMS). Parameters influencing the extraction process, such as desorption depth of injection port, extraction time and temperature were carefully optimized. It was found that the insertion depth of SPME-Arrow at the injection port had a significant impact on the desorption speed and efficiency. A quantitative method for the determination of 57 odor substances was established based on the optimized parameters. Results showed that, compared to the conventional SPME method, this method had better sensitivity and improved the detection limit by one order of magnitude. This method also showed high accuracy and good linearity for each analyte with the values of linear correlation coefficient higher than 0.99. Ten replicate analyses of actual drinking water samples with a final internal standard concentration of 10 ng·L−1 provided reproducible results on the basis of average relative standard deviation (RSD) values. The RSD values for 90% of the analytes were lower than 10%, meanwhile those of the rest were all lower than 20%. There exhibited no matrix interference in the detection of spiked actual water samples. In general, the novel method meets the requirements for the enrichment and detection of odor substances in drinking water.
-
羰基化合物, 即醛类和酮类化合物, 广泛存在于日常生活环境中, 对人体健康有重要影响. 研究发现, 空气中的羰基化合物不仅对人体的嗅觉产生影响, 还会刺激人体免疫系统, 长时间接触羰基化合物可能会出现不良健康影响. 另外羰基化合物还会引起染色体分裂而造成遗传物质损害或断裂, 如姐妹染色体交换及染色体变异等, 使羰基化合物具有致癌性和致突变性[1-4]. 人们在室内生活工作的时间超过80%, 室内成为越来越多的人最直接和最经常接触的环境[5]. 室内空气中大多数装饰和装修材料包括建筑材料[6]、新家具(尤其是由胶合板制成的家具[7]、木地板[8])、家居用品(如胶水、油漆和涂料[9])、香烟烟雾[10]、室内烹饪[3]以及一些生活用品(如消毒剂、化妆品和空气清新剂)等都会向室内空气环境直接释放羰基化合物[11-13]. 越来越密闭的建筑结构往往又会使室内产生的化学污染物不断积累[14]. 还有些羰基化合物作为一些污染物与臭氧反应的次级产物出现在室内空气环境中[15]. 比如, 臭氧与头发和衣服上残留的人体皮肤油反应也可作为室内空气中羰基化合物的来源[16-17]. 此外, 城区的车辆尾气和工业厂房的燃料燃烧也会产生羰基化合物, 然后通过空气渗透和自然通风进入室内环境中[18-19].
许多国内学者对室内羰基化合物的污染特征、来源情况以及健康影响开展相关研究工作. 黄晓影[20]研究发现, 包头市城区住宅羰基化合物采暖季污染更严重, 其中甲醛和乙醛浓度均与换气次数呈负相关, 较高的相对湿度是甲醛、乙醛和丙醛暴露的危险因素. Pu 等[21]研究发现, 北京城区住宅12种羰基化合物中甲醛污染最严重, 乙醛、丙酮和己醛次之, 其中甲醛受沙发材料、吸烟情况、家庭位置影响, 乙醛受吸烟情况和厨房结构影响, 丙酮受厨房结构和盆栽植物影响, 己醛受盆栽植物影响. Huang 等[22]研究发现, 室内甲醛暴露可能会增加儿童患普通感冒的风险. 由于环境中气态羰基化合物的分析方法比较繁琐以及相对较高的分析费用, 多数文献针对少数几种羰基化合物展开研究, 很少关注气味污染严重的高分子量醛(己醛、庚醛、辛醛、壬醛和癸醛)以及能够诱导细胞损伤和产生晚期糖基化终产物的乙二醛和甲基乙二醛等其它羰基化合物的污染情况及其对人体健康的影响, 这不足以充分了解我国城市住宅室内外空气中羰基化合物的污染特征及健康效应. 本研究旨在通过供暖季与非供暖季在城市居民住宅开展室内外同步观测, 分析季节变化对不同羰基污染物的影响,并评估室内羰基污染物对人群的健康风险及其对嗅觉的污染情况, 以期为进一步研究住宅室内痕量羰基污染物特征及其影响提供一定的科学依据.
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 样品采集
本研究于2016 年供暖季(1月28日—30日)和非供暖季(9月23日—26日)在西安市雁塔区某住宅区5户住宅开展室内羰基化合物的同步观测, 为便于比较, 另选一住宅的露天阳台同步采集了室外样品. 采样点周围无明显工业污染源, 属于城市住宅区, 各住户家庭信息如表1所示. 采样期间, 所有仪器均放置在客厅中心位置(离地面1.0—1.5 m), 避开通风口. 采样头选用Sep-Pak DNPH(2,4-二硝基苯肼)-silica Gel cartridge + Ozone scrubber (Waters Corporation, USA), 流量为0.6—0.8 L·min−1的真空泵(Thomas)进行主动采样, 采集时间为 8 h(9:30—17:30), 采集后的DNPH样品用铝箔包裹后, 置于4 ℃以下冰箱保存, 防止样品被污染. 供暖季共采集DNPH样品18个(室内每户3个+室外3个), 均为工作日2个+周末1个; 非供暖季共采集24个(室内每户4个+室外4个), 均为工作日2个+周末2个. 此外, 采用 CO2分析仪(LI-820, LI-COR, USA)监测室内通风换气次数.
表 1 各采样住户家庭信息Table 1. Household information of each sampled household采样点Site 房屋年龄/aAge of house 面积/m2Area 装修后放置时间/monthStorage time after decoration 地板材质Floor material 壁纸Wall-paper 取暖燃料Fuel for heating 烹饪燃料Fuel for cooking 每天烹饪次数Cooking frequency 通风方式Ventilation 吸烟Smoking QJ-1 5 100 6—12 客厅+卧室复合木地板 是 天然气 天然气 > 3 半开 否 > 1 h QJ-2 5 100 6—12 客厅+卧室瓷砖 否 天然气 液化石油气 > 3 半开 否 > 1 h QJ-3 5 102 6—12 客厅+卧室复合木地板 否 天然气 天然气 1 半开 否 电 < 1 h QJ-4 5 100 3—6 客厅+卧室复合竹地板 是 天然气 天然气 3 半开 否 < 1 h QJ-5 5 148 3—6 客厅瓷砖卧室复合木地板 否 天然气 天然气 3 全开 否 < 1 h 1.2 样品分析及质控
DNPH样品经乙腈洗提, 利用高效液相色谱仪(HPLC, Aglient 1200 LC)分析. 在25 ℃柱温、流速2.0 mL·min−1、检测波长为360 nm、390 nm和420 nm、进样量为20 μL的条件下, 利用梯度洗脱程序进行分析, 可定量检测20种羰基化合物, 分别为甲醛(C1)、乙醛(C2)、丙酮(A3K)、丙醛(n-C3)、2-丁酮(MEK)、丁醛(i,n-C4)、苯甲醛(Benz)、异戊醛(i-C5)、正戊醛(n-C5)、邻甲苯甲醛(o-tol)、间甲苯甲醛(m-tol)、对甲苯甲醛(p-tol)、2,5-二甲基苯甲醛(2,5-DB)、己醛(C6)、庚醛(C7)、辛醛(C8)、壬醛(C9)、癸醛(C10)、乙二醛(Gly)和甲基乙二醛(mGly), 其中己醛、庚醛、辛醛、壬醛和癸醛, 统称为高分子量羰基化合物(C6—C10), 各物质的方法检出限如表2所示. 本方法其他的详细介绍及质量控制参见文献[23].
表 2 供暖季室内外环境中羰基化合物浓度Table 2. Concentrations of carbonyl compounds in indoor and outdoor environments in heating season羰基化合物Carbonyl compounds 方法检测限/(µg·mL−1)Method detection limit 平均值±标准偏差 (AVG±SD)/( μg·m−3) QJ-1 QJ-2 QJ-3 QJ-4 QJ-5 QJ-O 甲醛(C1) 0.002 86.7 ± 10.8 23.2 ± 5.1 40.7 ± 2.8 30.9 ± 6.4 46.3 ± 6.9 9.7 ± 1.3 乙醛(C2) 0.004 38.4 ± 6.1 24.1 ± 5.7 48.5 ± 8.9 25.1 ± 5.0 31.9 ± 7.9 12.2 ± 2.6 丙酮(A3K) 0.006 46.5 ± 11.9 35.5 ± 13.9 47.8 ± 5.9 32.2 ± 10.3 31.2 ± 4.5 14.9 ± 4.4 丙醛(C3) 0.004 4.9 ± 0.7 3.5 ± 1.0 4.6 ± 0.5 3.1 ± 0.8 4.3 ± 0.2 2.3 ± 0.4 2-丁酮(MEK) 0.005 3.5 ± 0.6 3.2 ± 0.9 5.3 ± 1.0 3.3 ± 1.1 4.5 ± 0.3 3.1 ± 0.6 丁醛(i,n-C4) 0.003 2.9 ± 0.4 2.4 ± 0.7 3.0 ± 0.3 2.4 ± 0.6 2.5 ± 0.1 1.4 ± 0.3 苯甲醛(Benz) 0.007 1.9 ± 0.2 1.8 ± 0.4 2.9 ± 0.3 2.2 ± 0.7 1.9 ± 0.2 1.0 ± 0.2 异戊醛(i-C5) 0.004 3.4 ± 0.6 2.7 ± 0.7 3.0 ± 0.3 2.6 ± 0.6 3.6 ± 0.3 1.7 ± 0.4 正戊醛(n-C5) 0.005 2.4 ± 0.4 4.5 ± 1.4 3.0 ± 0.3 2.2 ± 0.7 2.1 ± 0.3 0.6 ± 0.2 邻甲苯甲醛(o-tol) 0.006 0.5 ± 0.1 0.6 ± 0.3 0.4 ± 0.1 0.5 ± 0.4 0.7 ± 0.2 0.1 ± 0.1 间甲苯甲醛(m-tol) 0.004 0.5 ± 0.1 0.5 ± 0.1 0.5 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.1 对甲苯甲醛(p-tol) 0.003 0.3 ± 0.1 0.6 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.2 0.3 ± 0.2 0.4 ± 0.2 0.2 ± 0.0 2,5-二甲基苯甲醛(2,5-DB) 0.003 0.6 ± 0.1 0.7 ± 0.2 0.6 ± 0.2 0.6 ± 0.1 0.5 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.2 己醛(C6) 0.007 11.8 ± 2.5 30.0 ± 7.7 14.9 ± 1.6 10.8 ± 4.6 12.6 ± 2.5 0.9 ± 0.2 庚醛(C7) 0.011 4.7 ± 1.0 4.5 ± 1.2 4.6 ± 0.1 3.6 ± 0.7 3.9 ± 0.8 0.8 ± 0.3 辛醛(C8) 0.016 5.6 ± 1.0 5.9 ± 1.5 5.5 ± 0.5 5.8 ± 1.7 5.8 ± 1.5 0.9 ± 0.3 壬醛(C9) 0.017 16.4 ± 2.8 18.6 ± 5.1 15.0 ± 1.1 14.7 ± 3.2 18.9 ± 5.9 2.1 ± 0.5 癸醛(C10) 0.001 2.9 ± 0.5 3.5 ± 2.2 2.8 ± 0.8 5.4 ± 0.8 3.3 ± 0.9 0.6 ± 0.2 乙二醛(Gly) 0.001 0.4 ± 0.1 0.7 ± 0.1 0.4 ± 0.1 0.4 ± 0.1 0.4 ± 0.1 0.8 ± 0.4 甲基乙二醛(mGly) 0.001 0.6 ± 0.2 0.9 ± 0.2 0.7 ± 0.2 0.8 ± 0.2 1.1 ± 0.2 1.0 ± 0.2 总和(SUM) 235.1±33.9 167.3 ± 38.7 204.7 ± 11.6 147.2 ± 33.1 176.3 ± 25.7 55.3 ± 9.4 1.3 数据分析
绘图使用Origin 9.0软件, 统计分析用SPSS 26和 Excel 2021 软件. 样本正态性检验采用 Kolmogorov-Smirnov 检验. 若研究变量为非正态分布, 则进行非参数双样本Mann-Whitney U检验和多样本Kruskal-Wallis H检验, 比较不同住户的羰基化合物浓度差异. 所有统计分析结果在 P <0.05 时,被认为具有统计学意义.
1.4 健康风险评价方法
与成人相比, 儿童因更高的呼吸频率、更多的脆弱性和更长的暴露时间[24-25], 更易受到环境污染物的影响, 因此有必要了解室内空气中羰基化合物污染对儿童健康的影响. 本研究采用美国环境保护署(U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, EPA)提出的个人吸入暴露的计算方法评估0—6岁儿童健康风险[26], 计算公式如下:
Eij=Cij×IRj×tj (1) 式中, Eij 为微环境 (j) 中污染物(i) 的日吸入剂量, μg·d−1; Cij为微环境 (j) 中污染物 (i) 的浓度, 即室内羰基化合物的实测浓度, μg·m−3; IRj 是微环境中的吸入率 (j) , m3·h−1, 2岁以下儿童IRj为0.22 m3·h−1, 2—6岁儿童为0.33 m3·h−1; tj 是在微环境 (j) 中的暴露时间, 即儿童每天在室内度过的时间, h·d−1, 2岁以下儿童tj为21.37 h·d−1 , 2—6岁儿童为20.15 h·d−1. IRj和tj 数据均来源于中国人群暴露参数手册(儿童卷)概要[27].
根据最近的研究中采用的方法[26, 28], 对儿童而言, 需要调整无显著风险水平(no significant risk levels, NSRLs) [26] , 调整后的儿童特定NSRLs: 2 岁以下儿童, 甲醛、乙醛分别为 0.52 μg·d−1、1.16 μg·d−1; 2—6岁儿童, 甲醛、乙醛分别为 3.15 μg·d−1、7.08 μg·d−1. 此外, 用风险商(risk quotients, RQ)来表示健康风险, RQ 的计算方法是将儿童每日吸入剂量除以儿童特定的 NSRLs. RQ >1 表明儿童吸入剂量超过了 10−5 终生致癌风险阈值, 即儿童面临潜在的癌症风险.
1.5 气味污染评价方法
除了对人体健康造成影响外, 羰基化合物还会产生气味污染. 羰基化合物的质量浓度高并不意味着其气味强度也大, 而是与气味阈值共同呈比例地影响人体对气味的感知. 为了将污染物的浓度和气味强度联系起来, 需要对其气味进行污染评价. 气味污染评价中羰基化合物的气味强度用气味活性值(odor activity value, OAV)表示[13, 29]:
OAVi=CmiCti (2) 式中, OAVi 为污染物 i 的气味活性值, 无量纲; Cmi为污染物 i 的质量浓度, μg·m−3; Cti为污染物 i 的气味阈值, μg·m−3, 其取自日本环境卫生中心对有害气体污染物气味阈值的研究结果[30].
污染物的气味活性值以大多数正常人的感官为准, OAVi ≤1 表示一般人无法感知到污染物 i 的气味; OAVi >1可感知到污染物 i 所散发的气味, 且 OAVi 越大, 能感知到的气味越大, 即其气味强度越大.
2. 结果与讨论 (Results and discussion)
2.1 羰基化合物的浓度水平
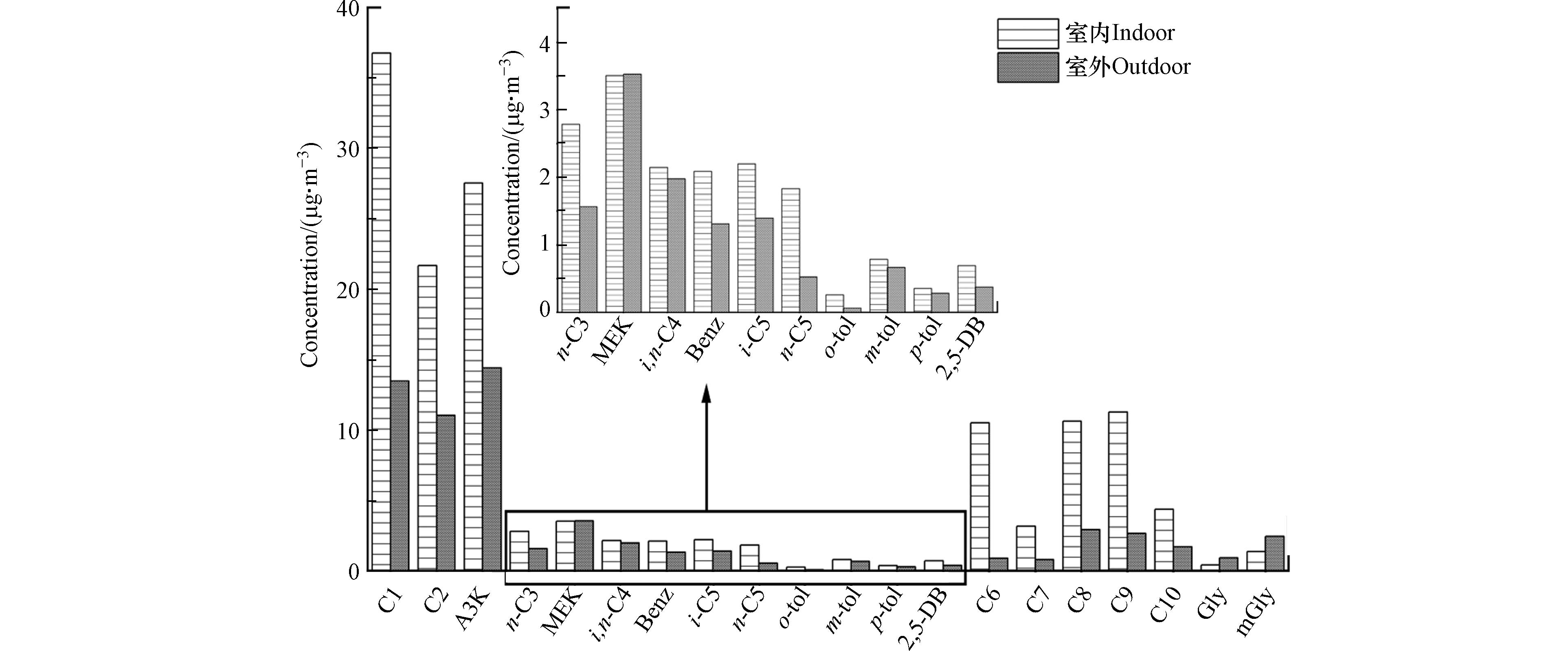
室内环境中羰基化合物的质量浓度为(144.3±56.2) μg·m−3, 其中甲醛(25.5%)、丙酮(19.1%)和乙醛(15.0%)是含量最高的3种物质, 其平均浓度分别为(36.8±21.0) μg·m−3、(27.5±14.3) μg·m−3、(21.7±14.4) μg·m−3, 均明显高于室外浓度(图1). 这3类羰基化合物的来源与居住者的生活息息相关, 可从建筑材料、环境烟草烟雾、烹饪油烟、香味消费品、个人护理产品、清洁等人为活动或通过室内VOCs(尤其是萜烯)的氧化排放[31-33]. 室内高分子量羰基化合物(C6—C10)占比也比较大, 约27.7%(15.9%—45.9%), C6—C10平均浓度(39.9 μg·m−3)是室外(9.0 μg·m−3)的4.4倍. 研究表明, 己醛不仅包含在香料和香精中, 还存在于含有植物化学物质的食物和办公家具[34]. 辛醛有很强的水果香味, 可用作食用香料, 也可作肥皂洗涤剂的香料使用. 壬醛具有玫瑰、柑橘等香气, 存在于红茶、绿茶中. 室外大气环境中羰基化合物的质量浓度为(63.0±21.8) μg·m−3, 其中丙酮浓度最高((14.4±4.8) μg·m−3), 其次是甲醛((13.5±6.8) μg·m−3)和乙醛((11.0±4.3) μg·m−3), 这3类化合物约占室外总羰基化合物浓度的61.8%. I/O 比值(室内/室外)能更好地推断室内羰基化合物的可能影响因素(室内源或室外渗透). 由图1可知, 乙二醛(Gly)和甲基乙二醛(mGly)的I/O 比值均低于1.0, 表明这两类典型的α-二羰基物质可能更多的来自室外环境的渗透. 研究发现, 室外大气环境中乙二醛和甲基乙二醛主要来源于生物质燃烧和挥发性有机化合物(如异戊二烯、芳烃和烯烃)的氧化[35-36]. 值得注意的是,低分子量的羰基化合物甲醛、乙醛、丙酮和高分子量羰基化合物(C6—C10)的 I/O 比值明显较高(1.9—11.8),说明室内排放源对这些羰基化合物有显著贡献.
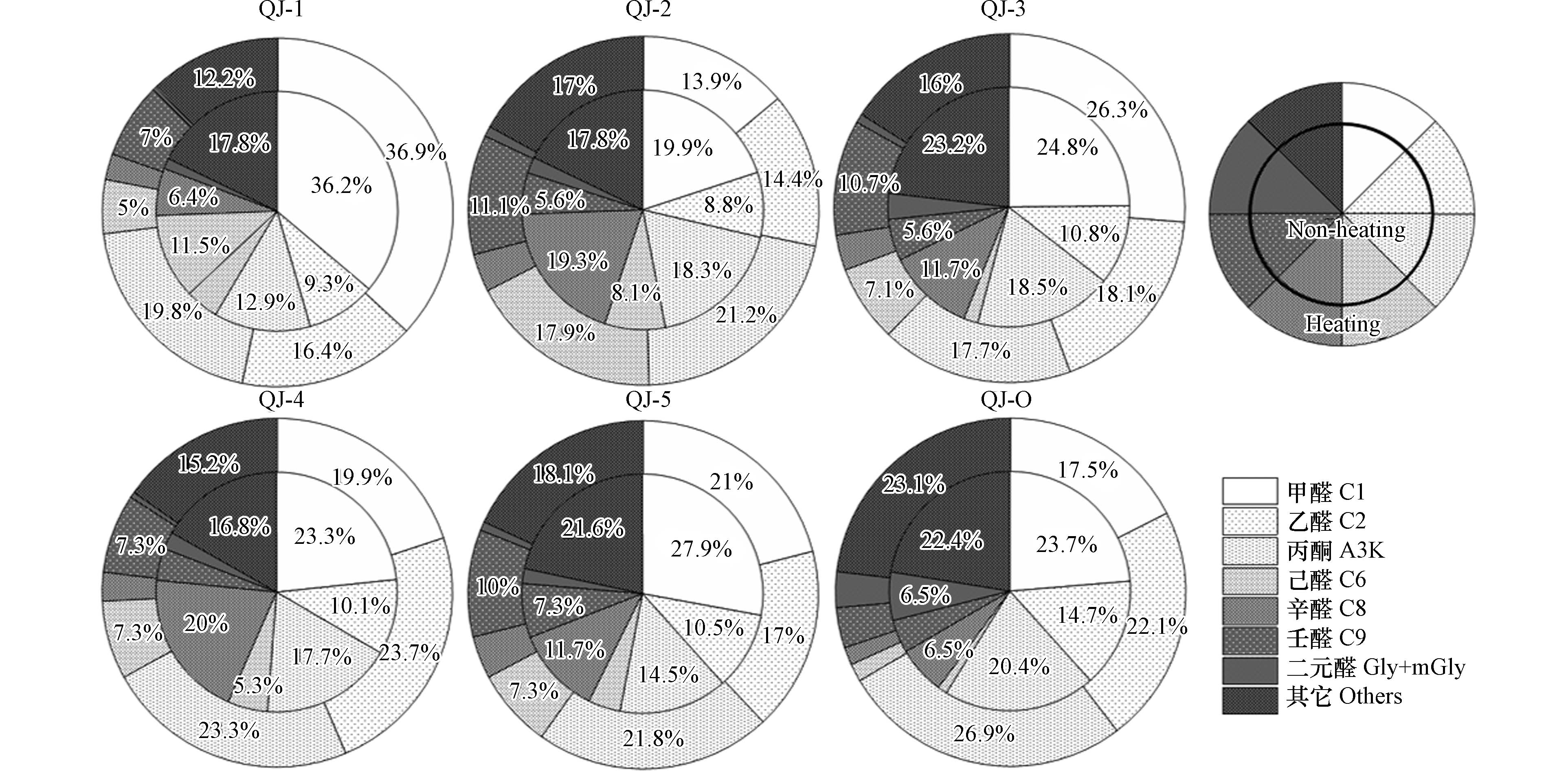
从表2和表3中可以看出, 室内环境中非供暖季浓度最高的5种羰基化合物为甲醛、丙酮、辛醛、乙醛和壬醛, 其浓度范围分别为(17.6—49.9) μg·m−3、(13.1—18.3) μg·m−3、(8.3—19.3) μg·m−3、(7.6—12.9) μg·m−3和(4.0—8.8) μg·m−3. 而供暖季则为甲醛、丙酮、乙醛、壬醛和己醛, 其浓度范围分别为(23.2—86.7) μg·m−3、(31.2—47.8) μg·m−3、(24.1—48.5) μg·m−3、(14.9—18.9) μg·m−3和(10.8—30.0) μg·m−3, 均明显高于非供暖季. 该结果与有关包头市城区住宅羰基化合物污染水平的研究结果一致, 可能与供暖季住宅内温湿度、通风换气次数以及室外环境状况等因素有关[20]. 整体来看,无论供暖季还是非供暖季, 住宅室内环境中最丰富的3类羰基化合物均为甲醛、乙醛和丙酮, 这与国内其它城市(北京、大连、上海、武汉和长沙等)的研究结果一致[26]. 另外, 本文所关注的3类高分子量羰基化合物(己醛、辛醛和壬醛)占比也较高(14.4%—33.0%)(图2). Feng 等[37]研究发现,餐饮油烟可能是造成空气中高分子量羰基化合物浓度偏高的原因之一. 由此可见, 室内高分子量的羰基化合物可能来源于住户的烹饪活动. 室外大气环境中羰基化合物浓度表现为非供暖季(68.9±28.2) μg·m−3明显高于供暖季(55.3±9.4) μg·m−3, 其中甲醛浓度增量最大(6.6 μg·m−3), 其次是辛醛(3.5 μg·m−3)和甲基乙二醛(2.5 μg·m−3), 这归因于非供暖季温度偏高, 太阳辐射较强, 有利于大气有机物发生光化学反应, 同时非供暖季植物排放对羰基化合物有重要的贡献.
表 3 非供暖季室内外环境中羰基化合物浓度Table 3. Concentrations of carbonyl compounds in indoor and outdoor environments in non-heating season羰基化合物Carbonyl compounds 平均值±标准偏差 (AVG±SD)/(μg·m−3) QJ-1 QJ-2 QJ-3 QJ-4 QJ-5 QJ-O 甲醛(C1) 49.9 ± 11.1 19.9 ± 2.3 22.4 ± 3.1 32.2 ± 7.9 17.6 ± 2.1 16.3 ± 8.2 乙醛(C2) 12.9 ± 2.8 8.7 ± 1.5 9.7 ± 2.9 12.1 ± 4.1 7.6 ± 1.9 10.1 ± 5.4 丙酮(A3K) 17.8 ± 4.1 18.3 ± 3.9 17.0 ± 6.7 16.8 ± 6.2 13.1 ± 3.6 14.1 ± 5.7 丙醛(C3) 2.1 ± 0.7 1.3 ± 0.0 1.4 ± 0.4 2.1 ± 0.6 0.9 ± 0.2 1.0 ± 0.2 2-丁酮(MEK) 2.8 ± 0.7 2.4 ± 0.4 2.5 ± 0.5 3.7 ± 2.1 4.0 ± 2.7 3.9 ± 1.4 丁醛(i,n-C4) 1.3 ± 0.2 1.1 ± 0.1 1.4 ± 0.1 1.5 ± 0.5 3.1 ± 4.1 2.5 ± 2.3 苯甲醛(Benz) 2.3 ± 0.6 2.1 ± 0.8 1.9 ± 0.8 2.7 ± 1.1 1.2 ± 0.2 1.5 ± 1.0 异戊醛(i-C5) 1.7 ± 0.4 1.2 ± 0.3 0.9 ± 0.1 2.3 ± 1.8 1.0 ± 0.2 1.2 ± 0.3 正戊醛(n-C5) 0.9 ± 0.3 1.1 ± 0.3 0.8 ± 0.3 1.0 ± 0.5 0.4 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.1 邻甲苯甲醛(o-tol) bda bd bd bd bd bd 间甲苯甲醛(m-tol) 1.1 ± 0.4 1.1 ± 0.5 1.1 ± 0.6 0.9 ± 0.2 1.0 ± 0.5 0.8 ± 0.5 对甲苯甲醛(p-tol) 0.4 ± 0.0 0.2 ± 0.0 0.3 ± 0.1 0.2 ± 0.0 0.3 ± 0.2 0.4 ± 0.2 2,5-二甲基苯甲醛(2,5-DB) 1.2 ± 0.7 0.7 ± 0.2 0.8 ± 0.4 0.9 ± 0.2 0.4 ± 0.1 0.3 ± 0.1 己醛(C6) 6.1 ± 1.9 8.1 ± 2.4 5.1 ± 2.4 5.0 ± 1.7 1.4 ± 0.2 0.9 ± 0.2 庚醛(C7) 3.5 ± 1.6 1.9 ± 0.5 1.6 ± 0.7 2.7 ± 1.1 0.9 ± 0.2 0.8 ± 0.3 辛醛(C8) 15.8 ± 5.0 19.3 ± 5.6 19.2 ± 10.4 13.6 ± 4.5 8.3 ± 2.1 4.4 ± 1.2 壬醛(C9) 8.8 ± 3.4 5.6 ± 1.1 4.2 ± 1.9 8.4 ± 3.0 4.0 ± 0.9 3.1 ± 1.5 癸醛(C10) 7.2 ± 2.8 4.6 ± 0.9 3.4 ± 1.6 7.0 ± 2.5 3.3 ± 0.7 2.5 ± 1.3 乙二醛(Gly) 0.3 ± 0.1 0.3 ± 0.2 0.4 ± 0.4 0.3 ± 0.2 0.5 ± 0.5 1.0 ± 0.9 甲基乙二醛(mGly) 1.7 ± 0.5 1.9 ± 0.7 1.9 ± 1.0 2.0 ± 0.6 2.0 ± 0.9 3.5 ± 2.2 总和 137.7 ± 35.0 100.0 ± 17.2 95.8 ± 29.5 115.4 ± 37.6 70.9 ± 10.8 68.9 ± 28.2 注: a bd 低于检测下限。represents below limit of detection. 室内环境中甲醛、乙醛、丙酮的浓度范围分别为(17.6—86.7) μg·m−3、(7.6—48.5) μg·m−3、(13.1—47.8) μg·m−3, 不同住户室内羰基化合物浓度差异明显, 这可能与不同的生活习惯以及装修样式等因素有关[20-21]. 具体来看, 供暖季QJ-1室内甲醛平均浓度((86.7±10.8) μg·m−3)明显超过2022年7月11日国家市场监督管理总局(国家标准化管理委员会)批准发布的新版标准(GB/T 18883—2022) [38]中提到的室内甲醛1小时平均浓度(80 μg·m−3), 可能与该住宅在采样前期新增家具(床和衣柜)有关. QJ-3供暖季室内乙醛浓度((48.5±8.9) μg·m−3)比日本厚生劳动省出台的室内乙醛浓度限值(48 μg·m−3)略高[39]; 整体来看, QJ-1—QJ-5室内丙醛浓度均未超过加拿大卫生部报道的暴露限值(8 μg·m−3), 丙醛达到该限值的临界效应表现为嗅觉上皮萎缩[40].
图2为供暖季与非供暖季住宅室内外空气中羰基化合物的浓度占比. 从图2可以看出, 低分子量的甲醛、乙醛和丙酮对室内外空气中羰基化合物的贡献较大, 占总羰基化合物浓度的47.0%—73.0%, 且供暖季的占比显著高于非供暖季, 其中乙醛占比全部表现为供暖季 > 非供暖季; 结合表2和表3浓度数据发现, 室内外环境中的乙醛浓度也均表现为供暖季 > 非供暖季. 值得注意的是, QJ-2无论是供暖季还是非供暖季, 己醛、辛醛和壬醛这3类羰基化合物的占比之和都超过 30%, 而甲醛、乙醛和丙酮占比之和较其它住宅偏低,推测是因为该住宅内选择瓷砖铺设且家具量较少. 此外, 与其它住户相比, QJ-2选用液化石油气作为烹饪燃料可能对室内羰基化合物的污染情况也有影响,需进一步研究.
2.2 羰基化合物的影响因素
2.2.1 通风换气次数
诸多研究表明, 通风换气次数越大, 室内污染物浓度越小[20,29]. 为了解室内的通风状况, 本研究采用CO2示踪气体衰减法[29,41]计算得到各住宅供暖季和非供暖季的通风换气次数(表4). 该方法以CO2为示踪气体, 当室内CO2浓度比室外高时, 由于室内外的空气交换,室内CO2浓度会呈指数衰减, 式(3)为该过程中的质量守恒方程, 经推导可将CO2浓度与换气次数的关系写成式(4), 再通过线性回归计算, 即可求得室内的换气次数[29].
表 4 供暖季与非供暖季住户通风换气次数Table 4. The air exchange rate of households in heating season and non-heating season采样点Site 供暖季Heating season 非供暖季Non-Heating season 范围/h−1Range 平均值±标准偏差/h−1Mean±SD 范围/h−1Range 平均值±标准偏差/h−1Mean±SD QJ-1 0.1—0.7 0.3 ± 0.2 2.6—23.5 8.5 ± 8.6 QJ-2 0.4—0.8 0.6 ± 0.2 4.2—13.4 7.0 ± 3.8 QJ-3 0.2—0.6 0.4 ± 0.2 3.2—34.5 12.1 ± 15.0 QJ-4 0.2—0.5 0.4 ± 0.1 3.0—21.6 10.3 ± 8.8 QJ-5 0.1—0.6 0.3 ± 0.2 5.8—48.6 16.7 ± 18.0 VdCindτ=G(Cout−Cin) (3) ln(Cin−Cout)=ln(Cin,0−Cout)−ACHτ (4) 式中, Cin为室内CO2实时浓度, mg·m−3; Cout为室外CO2浓度, mg·m−3; G为通风量, m3·h−1; ACH为每小时换气次数, h−1; τ为时间, h; Cin,0表示室内CO2初始浓度, mg·m−3.
如表4所示, 供暖季室内通风换气次数为(0.1—0.8) h−1, 非供暖季为(2.6—48.6) h−1, 非供暖季换气次数比供暖季高1—2个数量级. 显然, 高频率的通风换气次数是非供暖季室内环境中羰基化合物浓度显著低于供暖季的原因. 但是, 室内羰基化合物的浓度还受室内温湿度、烹饪活动、人员情况(人员数量、人员类型等)、生活习性(个人护理产品、卫浴产品使用等)以及室外污染状况等其它诸多因素影响[31-33,37]. 此外, 室内外环境中二元醛(Gly+mGly)浓度则表现为非供暖季高于供暖季, 而且室内二元醛浓度随着室外浓度的增加而增加, 进一步表明室外源对室内贡献明显.
2.2.2 周末效应
“周末效应”的概念在 1974 年被Cleveland 等[42]首次提出. 研究表明, 大气污染物质量浓度变化在工作日和周末存在明显差异, 这种变化被称为“周末效应”[43-44]. 周末效应源于工作和休息模式的节律性, 与人类活动密切相关. 本文采用如下方式量化周末效应(ΔWE)[44-46]:
ΔWE=[(C周末−C工作日)/C工作日] (5) 式中, C工作日 表示工作日的浓度均值, C周末 表示周末的浓度均值. 为保持数据一致性, 本研究中C工作日 采用周五的污染物浓度, C周末 采用周六的污染物浓度.
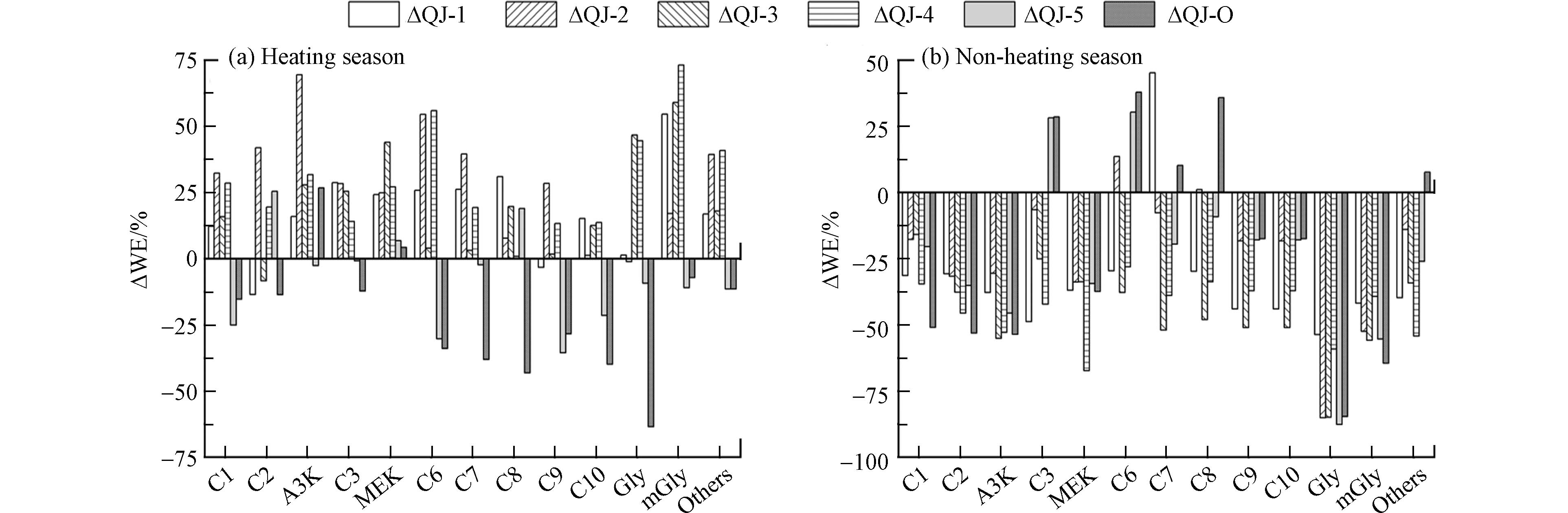
图3绘制了供暖季(a)和非供暖季(b)住宅室内外空气中羰基化合物浓度的相对偏差. 从图3可以看出, 供暖季, 不同住宅室内环境中羰基化合物的周末效应并不一致, 除QJ-5外, 其余4户住宅室内甲醛和丙酮浓度周末相比工作日增加, 分别增加了12.3%—32.3%、15.9%—69.4%; 高分子量羰基化合物(C6—C10)也表现出周末浓度高于工作日的“周末效应”. 室外大气环境中甲醛和乙醛浓度周末相比工作日减少, 分别减少了15.3% 和13.7%, 而丙酮则增加了26.7%; 高分子量的羰基化合物(C6—C10)浓度降幅超过30%. 非供暖季, “周末效应”更明显, 无论室内环境还是室外大气, 甲醛、乙醛、丙酮、壬醛、癸醛、乙二醛和甲基乙二醛均表现出工作日浓度高于周末的“周末效应”. 室内环境中甲醛、乙醛和丙酮周末浓度相较于工作日分别减少了15.9%—34.6%、30.7%—45.6%、30.6%—55.1%; 室外大气中这三类污染物浓度同样是周末低于工作日, 分别减少了51.0%、53.1%和53.6%.
综上所述, 住宅室内环境中, 供暖季多数羰基化合物呈周末高于工作日的“周末效应”, 非供暖季则呈工作日高于周末的“周末效应”; 这归因于供暖季室外较低的温度, 居民周末更多选择室内活动以及低频的通风换气次数导致室内环境中多数羰基化合浓度周末高于工作日; 而非供暖季相对较好的通风条件使室内外羰基化合物浓度的“周末效应”变化一致, 均表现为周末低于工作日. 室外环境中羰基化合物浓度不受季节变化影响, 均呈现工作日高于周末的“周末效应”. 研究发现, 在典型的城市地区PM2.5具有明显的工作日偏高, 周末偏低的“周末效应”[46]. 由此可见, 室外羰基化合物受到人类活动、污染排放和气象等各种因素的综合影响.
2.3 健康风险评估
表5总结了各住户室内儿童每日吸入甲醛和乙醛的剂量. 2岁以下儿童的甲醛和乙醛日吸入量最高值分别为313.9 μg·d−1和121.1 μg·d−1, 2—6岁的儿童甲醛和乙醛日最高吸入量分别为457.5 μg·d−1和176.5 μg·d−1. 可发现随着年龄的增长, 身体不断发育, 儿童羰基污染物吸入剂量增加. 供暖季室内甲醛、乙醛浓度高于非供暖季, 因此供暖季节室内羰基化合物污染情况更值得关注.
表 5 各住户室内儿童每日吸入的甲醛和乙醛剂量及风险商Table 5. Daily inhalation doses and risk quotients of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde by children in each household甲醛Formaldehyde 乙醛Acetaldehyde 采样点Site 2岁以下Birth to < 2 years 2—6 岁2 years to < 6 years 2岁以下Birth to < 2 years 2—6 岁2 years to < 6 years 吸入剂量/(μg·d−1) Daily inhalation dose 风险商Risk Quotients 吸入剂量/(μg·d−1) Daily inhalation dose 风险商Risk Quotients 吸入剂量/(μg·d−1) Daily inhalation dose 风险商Risk Quotients 吸入剂量/(μg·d−1) Daily inhalation dose 风险商Risk Quotients QJ-1 313.9 609.0 457.5 145.4 117.9 101.6 171.9 24.3 QJ-2 99.2 192.4 144.5 45.9 75.4 65.1 109.9 15.5 QJ-3 140.2 272.1 204.4 64.9 121.1 104.4 176.5 24.9 QJ-4 145.0 281.3 211.3 67.1 85.5 73.7 124.6 17.6 QJ-5 137.4 266.6 200.3 63.6 82.9 71.5 120.9 17.1 儿童特定的无显著风险水平用于表征儿童在家中接触甲醛和乙醛的健康风险[26]. 如表5所示,每户儿童接触甲醛和乙醛的风险商均远大于1, 表明各住户儿童皆面临潜在的癌症风险. 2岁以下儿童甲醛暴露RQ值为192.4—609.0, 2—6岁儿童甲醛暴露RQ值为45.9—145.4, 即儿童的甲醛暴露量是“安全限”水平的数十至数百倍. 2岁以下儿童乙醛暴露RQ值为65.1—104.4, 2—6岁儿童乙醛暴露RQ值为15.5—24.9. 与乙醛相比, 儿童在家接触甲醛对其健康的影响相对更大. 这与Bradman 等[28]研究中甲醛暴露的 RQ 值(12.0—51.7)高于乙醛暴露的 RQ 值(2.3—9.8)的结果一致.
需指出, 在计算儿童吸入甲醛和乙醛的剂量时, 只考虑了儿童在住宅中接触羰基化合物的情况, 如果还考虑到儿童在学校等其它室内环境接触羰基化合物, 患癌风险会更大. 因此, 室内羰基化合物污染对儿童健康的影响, 需要居民和标准制定者高度重视. 此外, 由于缺乏指南和风险指数, 其它含量较高的羰基化合物(例如己醛和壬醛)的化学危害潜力或癌症风险无法系统地评估.
2.4 气味污染评价
各住户室内环境中不同污染物对应的气味活性值如表6所示. 在分析各住宅所散发的羰基化合物成分时, 检测到较高浓度的甲醛、乙醛和丙酮, 但由于甲醛和丙酮的气味阈值相对较高, 因此这两种高浓度污染物的气味活性要低得多, 只有乙醛的气味活性更明显, 其气味活性值均大于5. 各住宅室内环境中高分子量的己醛、庚醛、辛醛、壬醛和癸醛的气味活性值均大于1, 尤其是辛醛最大, 均大于100, 其次是己醛. 对于广泛用作装修和家居的木质材料释放的气味物质——辛醛具有肥皂和柑橘味, 己醛具有香草味. 吴可[29]研究发现, 装修完工后室内环境中的气味污染主要来自于庚醛、辛醛、壬醛和己醛等醛类污染物. 而且这些高分子量的醛类污染物释放量在臭氧的影响下还会随时间而增加[47]. 因此, 室内环境中羰基化合物的气味污染更多应关注高分子量羰基化合物. 已有研究表明, 室内不良的气味感知是病态建筑综合征(sick building syndrome, SBS)的危险因素, 高分子量的羰基化合物对SBS的影响相当明显, 己醛对SBS的一般症状的危险性达到了显著性水平, 癸醛和辛醛对SBS的皮肤症状的危险性也达到了显著性水平[48]. 所以, 考虑针对室内环境中高分子量羰基化合物规定限值亦十分必要.
表 6 各住宅室内污染物的气味活性值Table 6. Odor activity values of indoor pollutants in various residences羰基化合物Carbonyl compounds 气味阈值/(μg·m−3)Odor threshold 气味活性值Odor activity value QJ-1 QJ-2 QJ-3 QJ-4 QJ-5 甲醛 670.3 0.10 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.04 乙醛 3.0 8.7 5.6 8.9 6.3 6.1 丙酮 108900.0 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 丙醛 2.6 1.4 0.9 1.1 1.0 0.9 2-丁酮 1416.4 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 丁醛 1.6 1.3 1.1 1.3 1.2 1.7 异戊醛 0.4 6.7 5.1 4.7 6.3 5.4 正戊醛 1.6 1.1 1.8 1.1 1.0 0.7 己醛 1.3 7.1 15.2 7.4 6.3 4.9 庚醛 0.8 5.1 4.0 3.5 3.9 2.7 辛醛 0.06 187.8 220.4 232.1 169.1 126.3 壬醛 2.2 5.8 5.6 4.0 5.4 4.8 癸醛 2.8 1.8 1.5 1.1 2.2 1.2 3. 结论(Conclusion)
本研究选择5户城市住宅进行同步观测, 对室内外空气环境中痕量羰基化合物的浓度水平、影响因素、健康风险及气味污染展开研究. 通过分析, 得出以下结论:
(1)居民住宅室内外环境中总羰基化合物浓度变化表现为: 室内 > 室外; 室内供暖季 > 室内非供暖季; 室外供暖季 < 室外非供暖季; 室内外空气中甲醛、乙醛和丙酮3类羰基化合物比重高(47.0%—73.0%), 室内高分子量的羰基化合物(C6—C10)总浓度(39.9 μg·m−3)是室外(9.0 μg·m−3)的4倍多. 季节变化表明, 通风换气次数对室内环境中羰基化合物污染影响显著.
(2)供暖季室内多数羰基化合物呈周末高于工作日的“周末效应”, 非供暖季则呈工作日高于周末的“周末效应”. 室外环境中羰基化合物浓度不受季节影响均呈现工作日高于周末的“周末效应”.
(3)健康风险评估显示各住户儿童甲醛和乙醛的吸入剂量均远超过OEHHA 给出的暴露剂量安全限值, 表明各家庭的儿童都面临潜在的癌症风险. 住宅室内环境中主要气味污染来自于气味阈值较低的高分子量羰基化合物, 包括己醛、庚醛、辛醛、壬醛和癸醛.
需指出, 本研究中样本量并不是很充足, 但室内外同步观测结果也能反映城市住宅室内外空气中痕量羰基化合物不同季节的污染情况; 此外, 不同住户家庭成员的数量以及不同的生活习惯等因素对室内羰基污染物的影响各不相同, 关于这部分讨论还有待于进一步的研究. 尽管如此, 这些痕量羰基化合物的测定对我国室内空气质量监管的来源分配和数据保存仍具有价值.
-
表 1 57种化合物保留时间、名称、CAS、定量离子对
Table 1. Retention time, name, CAS, quantitative ion pair of 57 compounds
序号No. 保留时间/minRT 英文名称Name 中文名称Name CAS 定量离子对Quantitative ion pair 1 2.94 1-Propanethiol 1-丙硫醇 107-03-9 76.0 -> 42.0 2 3.16 1-Bromopropane 1-溴丙烷 106-94-5 122.0 -> 43.0 3 4.87 n-Valeric aldehyde 正戊醛 110-62-3 44.0 -> 43.0 4 4.47 2,3-Butandione 2,3-丁二酮 431-03-8 86.0 -> 43.0 5 6.20 Dimethyl disulfide 二甲基二硫 624-92-0 94.0 -> 79.0 6 6.63 β-Pinene β-蒎烯 127-91-3 93.0 -> 93.0 7 6.79 Diethyl carbonate 碳酸二乙酯 105-58-8 91.0 -> 63.0 8 6.81 n-Amylformate 甲酸正戊酯 638-49-3 70.0 -> 42.0 9 7.20 Isoamyl methyl ketone 甲基异戊酮 110-12-3 43.0 -> 43.0 10 7.91 Cumene 异丙苯 98-82-8 105.0 -> 77.0 11 8.52 Cineole 桉叶素 470-82-6 139.0 -> 43.0 12 8.25 Pyridine 吡啶 110-86-1 79.0 -> 52.0 13 8.63 Pyrazine 吡嗪 290-37-9 80.0 -> 53.0 14 9.43 p-Cymene 对伞花烃 99-87-6 119.0 -> 119.0 15 9.62 Terpinolene 萜烯 586-62-9 136.0 -> 121.0 16 9.59 pyrimidine 嘧啶 289-95-2 80.0 -> 53.0 17 9.82 Cyclohexanone 环己酮 108-94-1 98.0 -> 55.0 18 9.90 1,3-Diethylbenzene 1,3-二乙苯 141-93-5 105.0 -> 77.0 19 10.29 2,5-Dimethylpyrazine 2,5-二甲基吡嗪 123-32-0 108.0 -> 108.0 20 10.37 4-tert-Butyltoluene 4-叔丁基甲苯 98-51-1 133.0 -> 105.0 21 10.42 1,2,3-Trimethyl benzene 1,2,3-三甲基苯 526-73-8 105.0 -> 105.0 22 10.42 tert-Amylbenzene 叔戊苯 2049-95-8 91.0 -> 91.0 23 10.51 Anisole 苯甲醚 100-66-3 108.0 -> 108.0 24 10.53 n-Butyl glycidyl ether 正丁基缩水甘油醚 2426-08-6 57.0 -> 57.0 25 11.48 Pentyl valerate 戊酸戊酯 2173-56-0 85.0 -> 57.0 26 12.61 Acetonylacetone 丙酮基丙酮 110-13-4 99.0 -> 99.0 27 13.02 2-Isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine 2-异丁基-3-甲氧基吡嗪 24683-00-9 124.0 -> 94.0 28 13.04 N,N-Dimethylacrylamide N,N-二甲基丙烯酰胺 2680-03-7 98.0 -> 42.0 29 13.23 Linalool 芳樟醇 78-70-6 93.0 -> 93.0 30 13.83 Isoborneol acetate 乙酸异冰片 125-12-2 136.0 -> 121.0 31 13.93 2-Methylisoborneol 2-甲基异莰醇 2371-42-8 108.0 -> 93.0 32 14.44 L-Menthol L-薄荷醇 2216-51-5 81.0 -> 81.0 33 14.44 Dicyclohexylamine 二环己基胺 101-83-7 138.0 -> 55.0 34 14.45 trans-2-Decenal 反-2-癸烯醛 3913-81-3 55.0 -> 55.0 35 15.64 4-Ethylbenzaldehyde 4-乙基苯甲醛 4748-78-1 134.0 -> 105.0 36 15.67 Naphthalene 萘 91-20-3 128.0 -> 128.0 37 16.31 Perillaldehyde 紫苏醛 18031-40-8 122.0 -> 79.0 38 16.44 Ethyl salicylate 水杨酸乙酯 118-61-6 120.0 -> 92.0 39 16.65 Anethole 茴香脑 104-46-1 148.0 -> 105.0 40 16.69 Geosmin 土臭素 16423-19-1 112.0 -> 97.0 41 16.79 2-Chlorophenol 2-氯酚 95-57-8 128.0 -> 64.0 42 16.87 α-Ionone 2-紫罗兰酮 127-41-3 121.0 -> 77.0 43 16.91 2-Methylnaphthalene 2-甲基萘 91-57-6 142.0 -> 142.0 44 16.93 Guaiacol 愈创木酚 90-05-1 109.0 -> 81.0 45 17.42 2,6-Dimethylphenol 2,6-二甲基苯酚 576-26-1 107.0 -> 77.0 46 17.53 p-Ethylaniline 对乙基苯胺 589-16-2 106.0 -> 106.0 47 19.19 Methyl cinnamate 肉桂酸甲酯 103-26-4 131.0 -> 103.0 48 19.51 2,6-Dichlorophenol 2,6-二氯苯酚 87-65-0 164.0 -> 63.0 49 20.07 2,4-Dichlorophenol 2,4-二氯苯酚 120-83-2 162.0 -> 162.0 50 21.12 Dihydrojasmonic acid methyl ester 二氢茉莉酸甲酯 24851-98-7 153.0 -> 97.0 51 21.81 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol 2,4,6-三氯酚 88-06-2 196.0 -> 97.0 52 22.41 4-Chlorophenol 4-氯酚 106-48-9 128.0 -> 65.0 53 22.97 4-Chloro-m-cresol 4-氯-3-甲酚 59-50-7 142.0 -> 107.0 54 23.16 Ethyl vanillin 乙基香兰素 121-32-4 166.0 -> 137.0 55 23.53 Vanillin 香兰素 121-33-5 152.0 -> 151.0 56 23.83 p-Bromophenol 对溴苯酚 106-41-2 172.0 -> 65.0 57 24.09 Benzyl benzoate 苯甲酸苄酯 120-51-4 212.0 -> 105.0 表 2 57种化合物线性范围、相关系数、重复性、检出限
Table 2. Linear range, correlation coefficient, repeatability, MDL of 57 compounds
序号No. 保留时间/minRT 中文名称Name 线性范围/(ng·L−1) 线性相关系数R2 相对标准偏差RSD 方法检出限/(ng·L−1)MDL 1 2.94 1-丙硫醇 10—500 0.9936 7.21 1.20 2 3.16 1-溴丙烷 10—500 0.9956 7.26 1.24 3 4.87 正戊醛 10—500 0.9991 3.15 2.90 4 4.47 2,3-丁二酮 10—500 0.9973 8.72 2.96 5 6.20 二甲基二硫 1—500 0.9888 1.18 0.49 6 6.63 β-蒎烯 1—500 0.9993 2.72 0.35 7 6.79 碳酸二乙酯 10—500 0.9958 8.12 1.02 8 6.81 甲酸正戊酯 10—500 0.9973 6.99 1.43 9 7.20 甲基异戊酮 10—500 0.9975 5.56 0.81 10 7.91 异丙苯 10—500 0.9997 6.02 0.46 11 8.52 桉叶素 10—500 0.9999 7.00 1.47 12 8.25 吡啶 10—500 0.9933 7.25 5.75 13 8.63 吡嗪 10—500 0.9920 6.79 2.90 14 9.43 对伞花烃 10—500 0.9903 2.13 0.73 15 9.62 萜烯 10—500 0.9006 3.10 1.02 16 9.59 嘧啶 50—500 0.9986 17.35 18.03 17 9.82 环己酮 10—500 0.9902 9.50 3.34 18 9.90 1,3-二乙苯 10—500 0.9993 8.19 1.07 19 10.29 2,5-二甲基吡嗪 10—500 0.9993 7.15 1.10 20 10.37 4-叔丁基甲苯 10—500 0.9994 6.05 1.96 21 10.42 1,2,3-三甲基苯 10—500 0.9989 6.63 1.30 22 10.42 叔戊苯 10—500 0.9990 3.61 1.48 23 10.51 苯甲醚 10—500 0.9978 6.75 0.77 24 10.53 正丁基缩水甘油醚 10—500 0.9960 8.28 1.29 25 11.48 戊酸戊酯 10—500 0.9967 2.15 0.82 26 12.61 丙酮基丙酮 10—500 0.9930 1.21 1.69 27 13.02 2-异丁基-3-甲氧基吡嗪 10—500 0.9975 4.42 1.18 28 13.04 N,N-二甲基丙烯酰胺 200—1000 0.9998 — 204.80 29 13.23 芳樟醇 1—500 1.0000 4.78 0.92 30 13.83 乙酸异冰片 1—500 0.9983 7.65 0.65 31 13.93 2-甲基异莰醇 1—500 1.0000 2.92 0.89 32 14.44 L-薄荷醇 10—500 0.9980 8.71 3.22 33 14.44 二环己基胺 10—500 0.9986 9.37 3.26 34 14.45 反-2-癸烯醛 10—500 0.9989 8.66 1.57 35 15.64 4-乙基苯甲醛 10—500 0.9989 5.74 2.02 36 15.67 萘 10—500 0.9998 9.85 2.98 37 16.31 紫苏醛 1—500 0.9998 4.60 0.65 38 16.44 水杨酸乙酯 1—500 0.9955 1.45 0.93 39 16.65 茴香脑 1—500 0.9991 2.91 0.91 40 16.69 土臭素 1—500 1.0000 1.09 0.22 41 16.79 2-氯酚 1—500 0.9984 5.14 0.77 42 16.87 2-紫罗兰酮 1—500 0.9958 1.97 0.81 43 16.91 2-甲基萘 10—500 0.9990 9.18 2.46 44 16.93 愈创木酚 10—500 0.9996 5.99 1.41 45 17.42 2,6-二甲基苯酚 10—500 0.9998 7.38 1.88 46 17.53 对乙基苯胺 10—500 0.9951 3.13 9.54 47 19.19 肉桂酸甲酯 10—500 0.9971 3.16 1.41 48 19.51 2,6-二氯苯酚 10—500 0.9864 13.83 3.44 49 20.07 2,4-二氯苯酚 10—500 0.9991 4.24 1.43 50 21.12 二氢茉莉酸甲酯 10—500 0.9952 7.96 3.53 51 21.81 2,4,6-三氯酚 10—500 0.9864 12.40 2.87 52 22.41 4-氯酚 10—500 0.9990 6.77 2.40 53 22.97 4-氯-3-甲酚 10—500 0.9992 3.15 1.09 54 23.16 乙基香兰素 100—500 0.9983 — 76.41 55 23.53 香兰素 50—500 0.9972 7.67 15.70 56 23.83 对溴苯酚 10—500 0.9992 5.86 1.85 57 24.09 苯甲酸苄酯 1—500 0.9988 1.77 0.48 -
[1] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. 生活饮用水卫生标准: GB 5749—2022[S]. 2022. State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Standards for drinking water quality: GB 5749—2022[S]. 2022(in Chinese).
[2] 朱帅, 贾静, 饶竹, 等. 吹扫捕集-气相色谱-质谱法联用测定水中典型的嗅味物质 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(10): 2127-2133. ZHU S, JIA J, RAO Z, et al. Determination of typical taste and odor compounds in water by purge and trap-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(10): 2127-2133(in Chinese).
[3] 吕建霞, 梁立娜. 吹扫捕集-气相色谱/质谱联用法测定水中臭味物质 [J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(11): 2223-2224. LYU J X, LIANG L N. Determination of odorous compounds in water using pruge and trap coupled with GCMS [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(11): 2223-2224(in Chinese).
[4] 闫晖敏, 顾海东, 许文雅, 等. 分散固相萃取-气相色谱-质谱法测定地表水中的异味物质 [J]. 理化检验-化学分册, 2015, 51(1): 82-85. YAN H M, GU H D, XU W Y, et al. GC-MS determination of smelly substances in surface water with dispersive solid-phase extraction [J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2015, 51(1): 82-85(in Chinese).
[5] EATON A D, CLESERI L S, GREENBERG A E. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater [M]. 19th ed. Washington DC: APHA, 1995. [6] KRASNER S W, WANG C J H, MCGUIRE M J. Development of a closed-loop stripping technique for the analysis of taste- and odor-causing substances in drinking water [M]. AnnArbor, MI: Ann Arbor Science Publishers, 1981. [7] SHIN H, AHN H S. Simple, rapid, and sensitive determination of odorous compounds in water by GC-MS [J]. Chromatographia, 2004, 59: 107-113. [8] ZHANG L F, HU R K, YANG Z G. Routine analysis of off-flavor compounds in water at sub-part-per-trillion level by large-volume injection GC/MS with programmable temperature vaporizing inlet [J]. Water Research, 2006, 40(4): 699-709. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2005.11.048 [9] PALMENTIER J P F P, TAGUCHI V Y, JENKINS S W D, et al. The determination of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water using isotope dilution high resolution mass spectrometry [J]. Water Research, 1998, 32(2): 287-294. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00280-7 [10] 李学艳, 陈忠林, 沈吉敏, 等. 固相萃取-气质联机测定水中嗅味物质2-甲基异茨醇和土霉素 [J]. 中国环境监测, 2006, 22(2): 18-21. LI X Y, CHEN Z L, SHEN J M, et al. Determination of MIB and geosmin in water by SPE-GC/MS [J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2006, 22(2): 18-21(in Chinese).
[11] NAKAMURA S, NAKAMURA N, ITO S. Determination of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin in water by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry using stir bar sorptive extraction [J]. Journal of Separation Science, 2001, 24(8): 674-677. doi: 10.1002/1615-9314(20010801)24:8<674::AID-JSSC674>3.0.CO;2-E [12] BENANOU D, ACOBAS F, de ROUBIN M R, et al. Analysis of off-flavors in the aquatic environment by stir bar sorptive extraction-thermal desorption-capillary GC/MS/olfactometry [J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2003, 376(1): 69-77. doi: 10.1007/s00216-003-1868-3 [13] 徐振秋, 张晓赟, 徐恒省. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱法测定饮用水中9种嗅味物质 [J]. 化学分析计量, 2017, 26(2): 48-51. XU Z Q, ZHANG X Y, XU H S. Detection of nine odor compounds in drinking water by headspace solid phase micro-extraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry [J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2017, 26(2): 48-51(in Chinese).
[14] 夏雪, 陈倩茹, 王川, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用测定黑臭水体中的4种主要异味物质 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(12): 2789-2796. XIA X, CHEN Q R, WANG C, et al. Determination of four major odor compounds in black and odorous water by headspace solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(12): 2789-2796(in Chinese).
[15] 陈丽君, 吴宇伉, 孔令灿, 等. 水中异味物质的顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-三重四级杆质谱联用测定法 [J]. 环境与健康杂志, 2019, 36(2): 153-155. CHEN L J, WU Y K, KONG L C, et al. Determination of musty odorants in water by headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Environment and Health, 2019, 36(2): 153-155(in Chinese).
[16] 宋荣娜, 杨晓芳, 吕明晗, 等. HS-SPME-GC/MS同时测定污废水中多种VOCs异味物质 [J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1047-1056. SONG R N, YANG X F, LYU M H, et al. Simultaneous determination of various odorous VOC substances in sewage wastewater by HS-SPME-GC/MS [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1047-1056(in Chinese).
[17] 彭鹭, 杨创涛, 黄慧星, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱串联质谱法检测水中30种异味物质 [J]. 城镇供水, 2021(4): 56-61. PENG L, YANG C T, HUANG H X, et al. Determination of thirty odor compounds in water by headspace solid phase microextraction Arrow coupled with gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry [J]. City and Town Water Supply, 2021(4): 56-61(in Chinese).
[18] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 生活饮用水臭味物质 土臭素和2-甲基异莰醇检验方法: GB/T 32470—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Organic compounds in drinking water-Test methods of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol: GB/T 32470—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016(in Chinese).
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 崔敏,刘劲毅,侯筱筱,韩缘欣,张帆,李嘉. 生物柴油机械羰基化合物排放特征及环境效应研究. 实验技术与管理. 2024(11): 52-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: