-
近海河流是陆地与海洋联系的重要纽带,是城市发展和生物多样性的基础,河流水质是体现城市发展水平和生态环境的重要指标[1-2]. 近年来,随着城市的快速发展,各种点源污染(工业污染、生活污染等)、面源污染(农业污染)及城市本身遗留的污染已经对河流水环境稳定及生物健康构成了威胁[3-4],大量N、P等污染物随着污水输入到河流中,超出河流的自净能力,引起水体富营养化,造成水体溶解氧降低、水体酸化、生物栖息地退化、有毒有害藻类大量繁殖[5-7]、生物多样性减少、水生生态系统的结构和功能发生异常等问题[8-9]. 水体富营养化是国际上共同关注的水环境问题[10],针对城市地表水开展调查研究,了解地表水污染现状,对城市水治理、修复等工作有着十分重要的意义.
三亚河由北向南贯穿三亚市,注入三亚港入海,对城市居民生活及旅游业的发展具有十分重要的意义. 2015年三亚市自然资源和规划局出台《三亚市中心城区水系综合规划》,提出改善三亚河水环境状况,然而三亚人口众多,城市废水的排放、土地利用的改变给三亚河水环境治理带来严峻的挑战. 2018—2019年,三亚河的水质为仍为Ⅲ、Ⅳ类,主要污染指标为氨氮[11].
本文通过对三亚河进行调查,旨在系统地探究三亚河营养盐的时空分布特征,评价水体富营养化现状,为相关部门围绕海南“三区一中心”的战略定位,稳步有效推进三亚河流域水环境综合治理提供基础数据,丰富对三亚河营养盐分布的认识.
-
三亚河(18°19′—18°37′N、108°36′—109°46′E)发源于三亚市和保亭黎族苗族自治县交界的中间岭右侧高山南麓,由六罗水、水蛟溪和半岭水3条河流组成. 流域面积337.02 km2,年平均流量为6.7 m3·s-1[12]. 三亚地属热带海洋性季风气候,年平均气温25.5 ℃,年平均降水量1537.04 mm[13],全年90%的降水量集中在雨季(5—10月份),旱季(11月—次年4月)仅占10%[14]. 三亚河属潮汐河流,日纳潮量为253 m3[15],不规则的全日潮汐可影响至辽家坡路河段. 依据河流地形、河道及水文特征将三亚河分为上游(DGB—LJPL)、中游(YLXL—YCQ)和下游(RGQ—SYDQ). 上游河道狭窄,属低山丘陵区,植被覆盖好,水土流失弱,沿河两岸有大片的农田,上游水库拦蓄河道河流,河流流量小,水深较浅[16]. 中游河道为河网的过度带,有支流汤他水汇入,属城市河段,潮汐作用影响较弱. 下游河道为感潮、城市河段,有支流半岭水汇入,河流分为东西河,平均潮差约为1.0 m,靠近入海口处纳潮量大. 中下游河道两侧生长着大量红树林,沿河两岸有大量居民区、酒店及餐饮等,此外周围污水管网有破损等情况,沿河部分地区未纳入城市污水管网系统,污水直接排入到河流中[17]. 三亚河水深受降雨和潮汐影响较大,采样期间旱季上游河段水深均小于0.5 m,中游河段约为0.5—1 m,下游河段约为1—2 m,入海口的SYG站位较深,约为9 m. 雨季上游河段水深约为0.5—1 m,中游河段约为1—2 m,下游河段约为2—3 m,入海口的SYG站位约为11 m.
-
于2018年6月—2019年5月对三亚河干、支流进行逐月采样,根据河流特征从下游到上游分别在三亚港(SYG)、三亚大桥(SYDQ)、新风桥(XFQ)、月川桥(YCQ)、水城路桥(SCLQ)、辽家坡路(LJPL)、槟榔桥(BLQ)以及打狗坝(DGB),支流的溶根桥(RGQ)、潮见桥(CJQ)及育林新路(YLXL)共11个站位采集表层水样(见图1). 另根据采样时站位的实际水深情况分别于1、3、9月份采集SYG站位,10月份采集下游YCQ、RGQ、XFQ、CJQ、SYG站位的底层水样.
水样用2.5 L有机玻璃采水器采集,分装于1 L聚乙烯瓶中,带回实验室用0.45 μm醋酸纤维滤膜过滤后装于聚乙烯瓶中(经30%的盐酸浸泡24 h后,用超纯水清洗至中性),冷冻保存(−20 ℃),1周内测完,水样均为双样. 水温(T)、盐度(S)、溶解氧(DO)等参数用多参数水质分析仪现场测定(WTW Multi36308),其中DO用温克勒滴定法校正. 营养盐浓度使用紫外可见分光光度计测定,测定方法见表1,其中溶解的无机氮(DIN)为铵盐(
NH+4 –N)、硝酸盐(NO−3 –N)、亚硝酸盐(NO−2 –N)三者浓度之和,测量过程中采用国家海洋局标准物质中心生产的营养盐标准系列作为外标质控样.NH+4 –N、NO−3 –N、NO−2 –N、DIP(活性磷酸盐)的检测限分别为0.002、0.005、0.0005、0.0008 mg·L−1,平行样相对偏差分别为0.5%—4.8%、0.2%—3.4%、0.3%—4.2%. DO检测限为0.2 mg·L−1,平行样相对偏差为0—2.3%.本研究采用适用于河流水体的对数型幂函数普适指数公式法计算三亚河水体富营养化的评价综合指数(EI),水体中常规指标依据《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002)进行,选取了DO、DIP、
NH+4 –N、NO−2 –N、NO−3 –N为评价标准,计算公式[19]如下:式中,EI为富营养化评价综合指数;Wj为指标j的归一化权重值;本研究将各指标视为等权重;EIj为指表j的富营养化评价普适指数;Xj为指标j的规范值;上述四者都是无量纲参数(表2).
-
相关实验数据分析运用Origin 2017,营养盐与理化参数的相关性分析运用SPSS 26.0,站位图使用Sufer 15软件进行绘制.
-
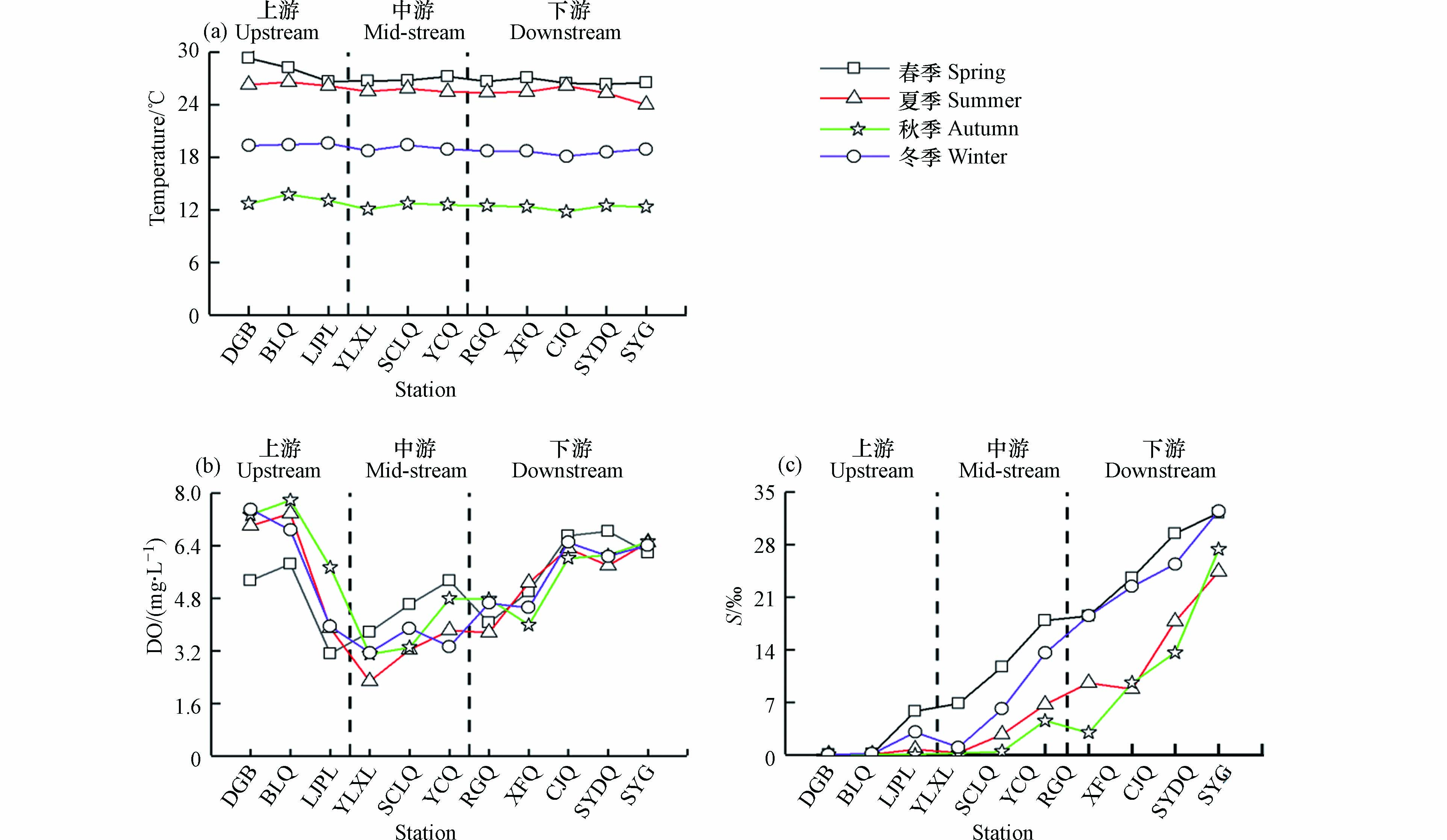
三亚河不同季节各站位T、S及DO变化特征如图2所示. 表层水体温度变化范围为4.1—32.0 ℃,年平均水温为(21.1±5.8)℃. 采样调查期间三亚河春、夏、秋、冬季节的平均水温分别为(27.1±0.9)、(25.7±0.7)、(12.6±0.5)、(19.0±0.4)℃,季节变化显著,表现为春季>夏季>冬季>秋季,这与该时间段内气温的季节变化趋势一至. 空间分布上,同一月份各站位水温相差不大,主要是受采样时间和水深的影响(图2a).
表层水体盐度变化范围为0.05‰—32.81‰,平均值为(10.0‰±10.4‰),整体表现为春季>冬季>夏季>秋季,主要受降雨及潮汐作用的影响. 春、冬季(旱季)河流径流量小,潮汐可影响至LJPL站位,夏、秋季(雨季)降雨较多,潮汐作用仅能影响到SCLQ河段,部分月份暴雨后表层水体在入海口附近盐度接近0. 在空间分布上,各季节受潮汐作用影响显著,从上游至下游盐度逐渐增大(图2b).
三亚河表层水体DO含量变化范围为0.12—8.75 mg·L−1,平均含量为(5.19±1.45)mg·L−1. 整体表现为秋季>冬季>春季>夏季. 上游,DO在春季最低,主要是由于春季净流量小,水体流动性差,水体温度相对较高,中下游各站位不同季节溶解氧含量相差不大. 空间分布上,上游(DGB、BLQ)及入海口(CJQ、SYDQ及SYG)河段部分站位DO含量相对较高. 中游溶解氧含量普遍较低(图2c),主要是由于上游河段连接水库,沉积环境多为砾石,水体清澈,中游及下游部分河段为居民区,河流较浅,落潮时部分河段裸露,两岸有大量的树木,河床分布有大面积水草,且较为曲折,沉积环境为泥质沉积,有机质含量高,消耗大量氧气[20]. 下游入海口河段受潮汐混合影响,DO逐渐增大.
-
不同季节三亚河水体中营养盐的时空分布见图3,各季节营养盐含量见表3. 在空间分布上,N、P营养盐均表现为上游及入海口处浓度低、中下游区域浓度高的特点(图3). 主要是因为上游河段沉积环境多为砾石,沿河植被覆盖好,地表径流输入到河流的营养盐相对较低[16]. 中下游区域位于中心城区地段,河流两岸分布大量居民区、酒店、饭店等,人口密集,河流受人为污染严重,同时河道两测分布不同面积的红树林,沉积物中携带大量的有机物,退潮时红树林沉积物中部分有机物被带入到河流中,使得中游河段整体营养盐较高[21]. 下游潮汐作用强烈,涨潮时海水上溯带走并稀释部分营养盐,使得下游营养盐随盐度的增加逐渐降低. 支流站位(YLXL、RGQ和CJQ)营养盐含量与其附近站位相比较高或相当,说明支流输入是三亚河营养盐的重要来源之一. 另外,10月份下游各站位由于水深较浅(约1—2 m),表、底层水体营养盐含量相差不大.
在入海口SYG站位,旱季(1、3月份)表、底层(约9 m)水体DIN(DIP)平均含量分别为0.087(0.070)mg·L−1和0.065(0.055)mg·L−1,相差不大,但在雨季(9、10月份)表、底(约11 m)层水体DIN(DIP)的平均含量分别为0.680(0.204)mg·L−1和0.042(0.064)mg·L−1,表层远高于底层,体现了三亚河冲淡水向近岸输送营养盐.
全年尺度上DIN的浓度范围为0.028—2.096 mg·L−1,平均浓度为(0.700±0.279)mg·L−1,冬季>秋季>夏季>春季,
NH+4 –N、NO−3 –N、NO−2 –N的占比分别为32.0%、58.8%和9.2%,NO−3 –N和NH+4 –N是水体中DIN的主要存在形式.NH+4 –N各季节浓度相差不大,冬季最高,特别是在SCLQ站位,其浓度是附近站位的2倍以上. 微生物分解有机含氮化合物是河流中NH+4 –N的重要来源之一[22],而冬季是三亚的旅游旺季,侯鸟人数为三亚户籍人口总数的70%[23],在人为活动的影响下,生活污水以及流域周边农业、畜牧业养殖废水大量排入河流中,导致水体中NH+4 –N浓度相对较高. 河流中NO−3 –N浓度季节变化显著,秋季NO−3 –N整体平均浓度最高,主要是因为上游河段两岸多为农田,土壤为电负性,不易吸附带负电荷的NO−3 –N,秋季降雨较多,雨水冲刷土壤使NO−3 –N易被淋溶到河流中. 同时,秋季溶解氧含量高,促进了硝化作用的进行,使水体中NO−3 –N浓度升高. 中下游河段,水体中NO−3 –N浓度与冬季相当,其污染来源可能与NH+4 –N相似. 在RGQ站位冬季含量最高,主要是冬季人为影响较大,支流半岭水携带大量NO−3 –N汇入的影响. 春季NO−3 –N浓度低,主要是由于春季属旱季,降雨较少,另外,春季水温较高,浮游植物生长代谢快,加快NO−3 –N的消耗,这与中下游河段水体中DO含量较高相一致.NO−2 –N季节变化为冬>春>秋>夏,冬、春季均明显高于夏、秋季,即旱季高于雨季.NO−2 –N是NO−3 –N和NH+4 –N之间的过度形态,在热力学上很不稳定,易被微生物及氧化剂转化NH+4 –N和NO−3 –N,其循环转化与生物活动、废水排放、水温、溶解氧等因素有关,浓度变化较复杂[24]. DIP浓度范围为0.007—0.442 mg·L−1,平均浓度为(0.140±0.066)mg·L−1,夏季>春季>冬季>秋季. 夏秋季均为雨季,降雨量较大,地表径流冲刷陆地,携带含P废水进入河流,但由于三亚地处热带,秋季台风较多,农业种植活动普遍减少,含磷化肥的使用远低于其他季节,秋季水体中无机磷的含量最低. 研究表明,在pH为6—8的范围内,沉积物对磷解吸作用随pH增大而增强,沉积物对磷解吸作用随着盐度增加逐渐增强[25],春、冬季,降雨较少,潮汐作用影响范围更大,河流盐度较高,内源磷释放可能是水体中无机磷含量较高的重要原因. 各个季节中游YLXL站位DIP浓度异常增高,是由于三亚育林新路河段存在小区生活污水特别是洗涤用水通过雨水管道排入到三亚河中,输入大量DIP.国内外其他河流不同形态N、P营养盐的平均浓度见表4. 三亚河NO3−-N平均浓度与国内外大小型河流相比均较低. NO2−-N浓度远低于珠江(广州段)[26],与黄河相差不大[27],但均高于长江、万泉河、图尔河及石狩河[28-31]. NH4+-N浓度远低于国内外受人为影响剧烈的河流,如海河(市区段)[32]、珠江(广州段)[26]、渭河(咸阳段)[33]及图尔河[30]. 远高于大型河流长江、黄河以及污染影响较小的小型河流万泉河、香溪河[27-29,34]. 但与受农业污染为主的石狩河、斯兹雷尼亚瓦河相差不大[31,35]. DIP含量在人为污染以及农业污染为主的河流中处于中等水平,但远高于大型河流长江、黄河以及受污染影响较小的小型河流万泉河、香溪河[27-29,34].
-
三亚河中下游区域人口密集,水体污染较严重,潮汐作用可影响至LJPL河段,因此,在分析营养盐与环境因子关系时扣除了上游DGB和BLQ站位. 三亚河流域营养盐与环境因子的相关性系数见表5. S与DO在春、夏、冬季呈显著正相关(P<0.01),一方面富氧海水随潮汐作用与河水混合,另一方面潮汐作用导致的水体扰动有利于水-气界面DO的交换.
NH+4 –N与S在春季、夏季呈显著负相关(P<0.05),与DIP在春、夏、冬季呈显著负相关(P<0.01),主要是由于潮汐作用的稀释造成的.DO与NH4+–N在春、夏季以及与DIP在各季均表现为显著负相关(P<0.05),这是由于水体中浮游植物在吸收NH4+–N及DIP进行光合作用同时释放大量氧气[36] ,各季节水体中不同形态的氮之间存在不同程度的相关性,氮的循环转化较为活跃. 另外,在春季和秋季,无机氮、磷之间呈较好的正相关,说明他们来源相一致.
-
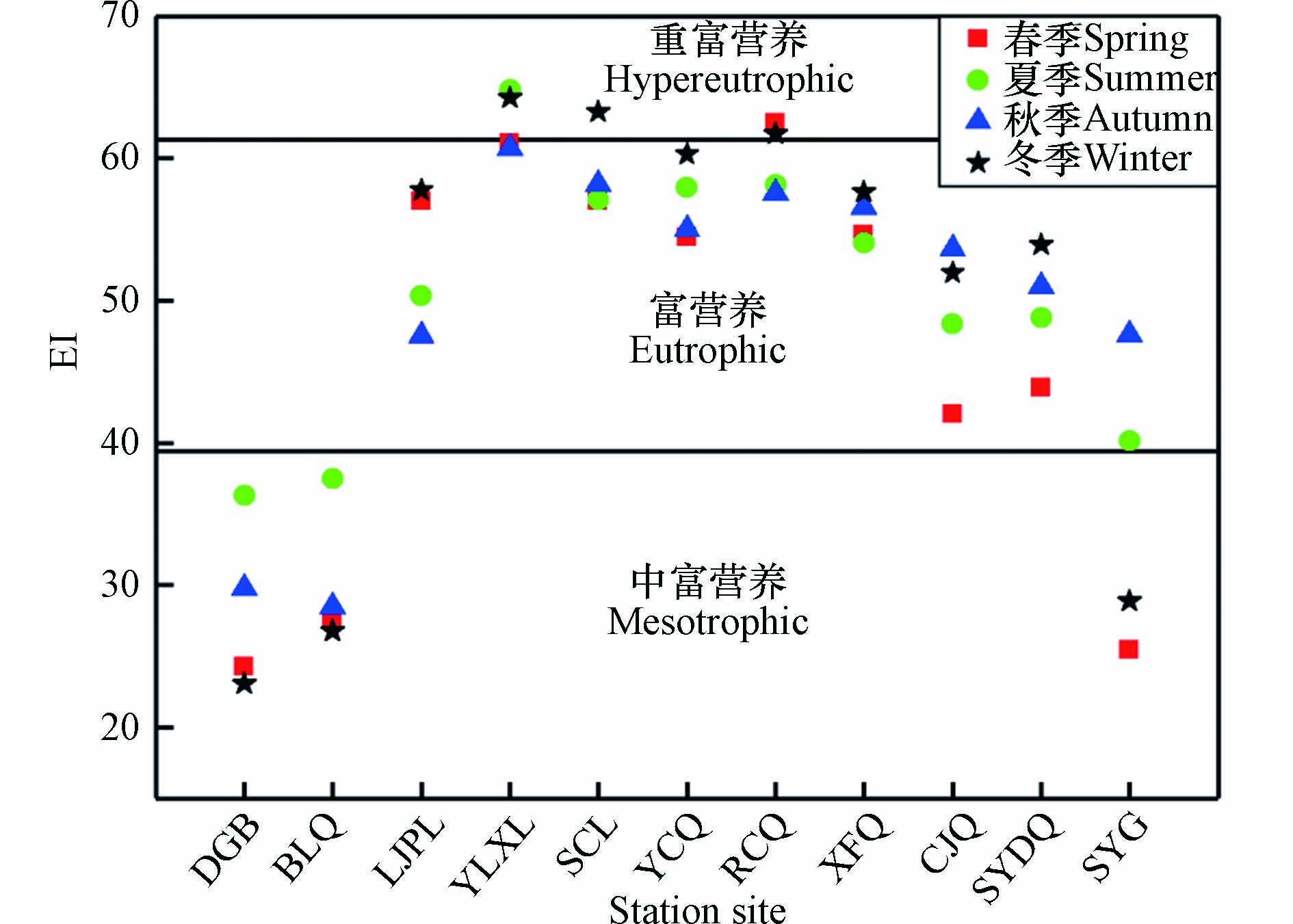
依据的营养化等级划分(表2)可以看出,各季节三亚河流域均处于富营养化状态(图4),其中春、夏、秋、冬季三亚河水处于重富营养化的站位数量占比分别为9.1%、9.1%、0%、27.3%,富营养化占比分别为63.6%、72.7%、81.8%、45.5%. 重富营养化多出现在冬季中游河段(图4),主要是由于中游河段位于三亚市中心,同时冬季正值旅游旺季,河流受人为活动影响剧烈,污染较严重. 空间分布上中富营养化主要分布在上游及下游入海口站位,严重的富营养化水域多集中在中游及中下游河段.
N/P是营养盐结构的主要指标,河流水体中可被生物利用的N、P多为溶解的无机氮(DIN)和无机磷(DIP)[37]. Guildford等[38]提出了水体中营养物质的限制性标准,当N/P≤9体时(质量比),N为限制性因子,当9<N/P<22.6时,适合藻类的生存的,N/P≥22.6时,为磷限制性因子. 三亚河各站位水样N/P(质量比)空间分布见图5,总体而言,三亚河流域多处于N限制状态,其中春、夏季整体水域都处于氮限制状态,秋季54.5%的站位处于氮限制状态,36.4%的站位适合藻类生存,仅有1个站位(BLQ)站位在秋季处于磷限制状态,可能是由于该河段藻类大量生长,消耗水体中N、P有机物,P营养盐被优先消耗到低于阈值,使得出现磷限制[37]. 冬季45.5%的站位处于氮限制状态,54.5%的站位适合藻类生存. 河流水质均与三亚湾早期研究得出附近海域其生产力主要受氮素限制情况相一致[39]. 近年来随着三亚市旅游业的不断发展,人口密集程度不断上升,据统计2013—2019年三亚旅游人数增长近千万,磷酸盐在沿岸人口密集的区域一般浓度较高[13,40].
-
由于缺乏调查期间三亚河实时径流量数据,所以本文采用的是三亚河历年平均径流量5.86 m3·s–1 [41]来估算三亚河营养盐年入海通量. DIN、
NO−3 -N、NO−2 -N、NH+4 -N、DIP年入海通量分别为118.37、70.93、11.18、38.67、23.75 t,其中NH+4 -N入海通量与以往调查数据显示每年向三亚湾输入的氨氮污染物37 t相差不大[15]. 与国外内已报道小型河流,如灌河下游[2]、北部湾入海河流[42]、石狩河[31]营养盐年入海通量相比均明显较低,尽管输入不大,但是对三亚湾水质生态环境有着重要的影响[43]. -
(1)三亚河水体中DIN的浓度范围为0.028—2.096 mg·L−1,平均浓度为(0.700±0.279)mg·L−1. 空间分布上,N、P营养盐均呈现出上游及入海口河段浓度低,中下游河段浓度高的特点. 水体中营养盐季节变化明显,DIN冬季>秋季>夏季>春季,
NO−3 -N和NH+4 -N是水体中DIN的主要存在形式. DIP浓度范围为0.007—0.442 mg·L−1,平均浓度为(0.140±0.066)mg·L−1,夏季>春季>冬季>秋季. 河段环境特征、人为活动、降雨、潮汐作用是影响三亚河营养盐分布的主要因素. 与国内外人为及农业污染为主的河流相比,三亚河水体中NH+4 -N、NO−2 -N、DIP均处于中等水平,NO−3 -N处于低等水平.(2)依据富营养状态综合指数(EI),三亚河上游的DGB和BLQ站位及入海口的SYG站位的春、冬季水体处于中富营养化状态,其他站位各季节水体呈现富营养化或重富营养化状态. N/P值结果表明,春、夏、秋季河流多处于N限制状态,冬季大部分河段适合藻类生存,水华风险较高. 根据三亚河年平均径流量和营养盐浓度估算,DIN、
NO−3 -N、NO−2 -N、NH+4 -N、DIP年入海通量分别为118.37、70.93、11.18 、38.67、23.75 t,河流径流量是影响三亚湾海域营养盐入海通量的主要因素.
三亚河营养盐时空分布及富营养化研究
Study on temporal and spatial distribution and eutrophication of nutrients in Sanya River
-
摘要: 为了解三亚河营养盐污染状况,于2018年6月—2019年5月对三亚河流域进行逐季调查,分析水体中氮磷营养盐的时空分布特征及影响因素,评估河流富营养化状况,并进一步估算三亚河营养盐入海通量. 结果表明,三亚河水体中营养盐浓度季节变化显著,三亚河水体中DIN的浓度范围为0.028—2.096 mg·L−1,平均浓度为(0.700±0.279)mg·L−1,冬季>秋季>夏季>春季,
NO−3 –N和NH+4 –N是水体中DIN的主要存在形式. DIP浓度范围为0.007—0.442 mg·L−1,平均浓度为(0.140±0.066)mg·L−1,夏季>春季>冬季>秋季. 空间分布上,N、P营养盐均呈现出上游及入海口河段浓度低,中下游河段浓度高的特点. 河段环境特征、人为活动、降雨、潮汐作用是影响三亚河营养盐分布的主要因素. 综合富营养盐指数(EI)结果显示,各季节三亚河上游及入海口河段均处于中富营养化状态,中下游河段均处于富营养化和重富营养化状态. 春、夏、秋季N/P值表明河流多处于N限制状态,冬季大部分河段适合藻类生存,有发生藻华的风险. 根据营养盐浓度和三亚河年平均径流量估算出,DIN、NO−3 –N、NO−2 –N、NH+4 –N、DIP年入海通量分别为118.37、70.93、11.18、38.67、23.75 t.Abstract: To understand the nutrient pollution status of Sanya River, a seasonal survey was conducted in the Sanya River basin from June 2018 to May 2019 to analyze the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics and influencing factors of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient salts in the water column. The state of eutrophication was evaluated, and further the flux of nutrients into the sea through Sanya River was estimated. The results show that the seasonal variation of nutrient concentration in Sanya River is significant. The concentrations of DIN ranged from 0.028 mg·L−1 to 2.096 mg·L−1, with an average concentration of(0.700±0.279) mg·L−1, with a sequential increase in spring, summer, autumn and winterNO−3 -N and NH4+-N are the main forms of DIN present in the water column. The concentrations of DIP ranged from 0.007 mg·L−1 to 0.442 mg·L−1, with an average concentration of(0.140±0.066)mg·L−1, with a sequential increase in autumn, winter, spring, and summer. The spatial distribution of N and P nutrients was similar, with low concentration in the upstream and estuaries and high concentrations in the middle and downstream. The environmental characteristics of river sections, anthropogenic activities, rainfall and tide are the main factors affecting the nutrient distribution in the Sanya River. The results of eutrophication index(EI)evaluation showed that the upper reaches and estuaries of Sanya River are moderately eutrophic in all seasons, while the middle and lower reaches are eutrophic and heavily eutrophic. The N/P in spring, summer and autumn indicate that most rivers are in nitrogen limitation, and most of the river were suitable for algal survival in winter, with the risk of algal blooms. Based on nutrient concentrations and the average annual runoff of Sanya River, it was estimated that the annual flux of DIN,NO−3 –N,NO−2 –N,NH+4 –N and DIP into the sea are 118.37, 70.93, 11.18, 38.67 and 23.75 t, respectively.-
Key words:
- sanya river /
- nutrients /
- spatio-temporal distribution /
- eutrophication.
-
钴(Cobalt, Co)是海洋中一种关键的无机痕量金属,在海洋生物地球化学过程中扮演着重要角色。Co是海洋浮游生物的必需元素。浮游生物可利用Co作为金属因子构成体内一些有机结构,如作为维生素B12的中心原子在海洋生物中广泛存在[1-3];或利用Co作为辅基参与形成生物体内的金属酶,如替代锌参与碳酸酐酶的辅酶或利用Co胺素在体内合成蛋氨酸等[4-9]。生物吸收实验表明,在海洋环境中浮游生物对Co的需求可能介于锰和营养型金属元素(如锌等)之间[10],且与浮游生物的需求相比,海水中的生物可利用Co处于匮乏状态[11-12]。溶解态Co在海水中主要以自由离子或络合物的形态存在,且活性Co相对稳定络合态有着更高的生物活性[13]。
开阔大洋Co分布大多为营养盐型分布模式,表层的溶解态Co被生物消耗而浓度较低,随着再矿化作用浓度从表层到中深度呈上升趋势,中深度到深海呈稳定或下降的趋势。海盆尺度上的Co分布状况为:北冰洋表层Co的浓度极高,可达0.80 nmol·L−1,10倍于北大西洋和南太平洋的表层浓度;北冰洋深层水Co含量约为0.05—0.06 nmol·L−1,略高于太平洋深层水(0.03—0.04 nmol·L−1),而略低于大西洋深层水(0.01—0.09 nmol·L−1)[14-20]。大洋中Co的主要来源是陆地径流、沉积物再悬浮、热液活动及大气沉降[13,15,17-18]。Co从大洋的移除过程主要包括清除作用、生物吸收作用以及随铁锰氧化物等的共沉降[10,18,21-23]。全球大洋Co的通量模型估算结果表明:每年海底沉积物向海输送量达4.0×1010 g,大气沉降为3.8×109 g,河流输送为3.4×108 g。Co在大洋的平均停留时间约为70 a,其中上层海洋受到强烈的生物消耗、颗粒物沉降及再生等共同作用停留时间仅7 a,而深层海洋可长达250 a[24]。
河流是大洋Co的一个重要来源,并显著影响河口及近海Co的分布。例如,北冰洋在极点处受到穿极流携带的河流输入的补充,Co浓度高达0.21 nmol·L−1 [22];地中海和墨西哥湾表层水Co与盐度的显著负相关关系也表明河流输入对河口或和边缘海Co分布的重要影响 [15,25-27]。人类活动会导致河流中Co含量的增加,例如伊比利亚半岛南部工业区附近的河流体系中Co含量可达背景值的17700倍。这也意味着随着人类活动程度的加剧,河流向大洋输送Co的通量可能会增加[28]。
河口是河流向海物质输送的通道和关键界面,是生物地球化学循环中一种重要的环境体系[29-31]。河流中携带的Co在河口区域受移除作用、颗粒物解吸及悬浮颗粒物再生等作用的影响,并非完全参与全球海洋的生物地球化学循环。因此,Co在河口的行为决定了河流向海洋Co输送的最终通量。例如对圣劳伦斯河的研究指出,由于河口的移除效应,河流中携带的Co最终只有约8%能进入开阔大洋[23,32]。目前,河口区域Co的生物地球化学的行为及其影响因素尚未得出明确的结论,例如:韩国Geum河口Co表现为移除型[33];日本Sagami湾和Wakasa湾的河口区域在低/中盐度区域呈现出溶解态Co的最大值,且保守性随季节变化[34];加拿大Mackenzie河口区域Co则表现出非保守的添加行为[35]。河口Co的行为的不确定性限制了对河流向海洋Co输送通量的估算。
长江是我国第一大河,世界第三长河,河流总长度达6300 km,流域覆盖面积达180万km2,多年径流量平均值达9000亿 m3[36-37]。长江贡献了东海90%以上的淡水输入量,也是我国近海痕量金属的重要来源[37-38]。长江中的Co主要来自于流域岩石矿物的风化与侵蚀[39-40],已有报道长江上、中、下游水体中Co的平均浓度分别为1.53、0.85、0.85 nmol·L−1,若忽略河口的过滤器效应,长江每年向东海Co的输送通量可达40 吨[41]。而Co在长江口行为研究的缺失,限制了对长江向大洋Co输送通量及其生物地球化学规律的认识。为此,本文通过对长江口盐度梯度变化下Co浓度的观测,结合水文和化学辅助参数探讨长江口及其附近海域海水中痕量金属Co的生物地球化学行为及其季节变化。
1. 材料与方法(Materials and methods)
1.1 采样区域
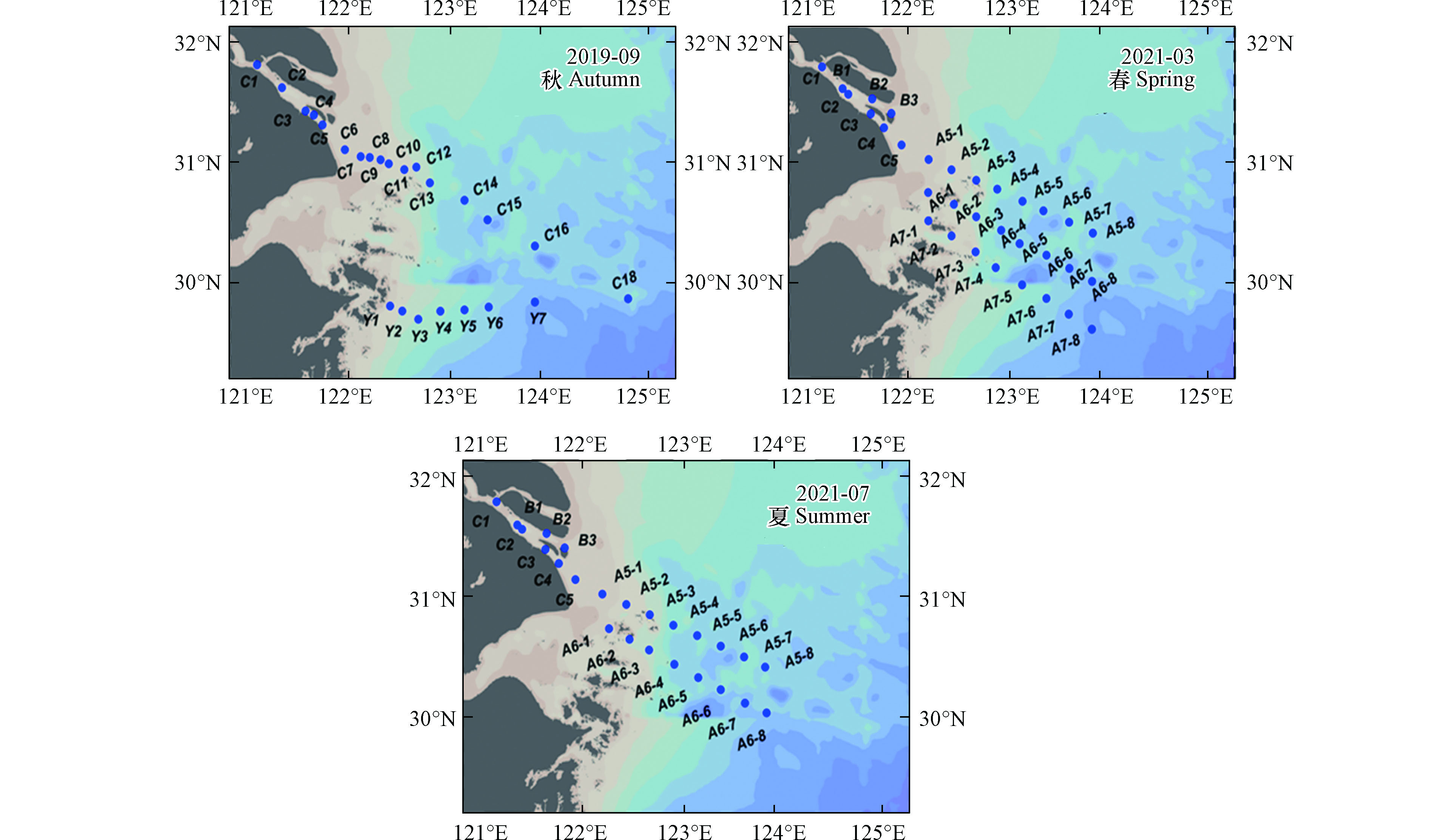
本研究通过搭载同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室共享航次(KECES-2019)和国家自然科学基金委员会共享航次,分别于2019年9月(秋季),2021年3月(春季)和2021年7月(夏季),在121.05°E—124.00°E,29.60°N—31.77°N的长江口区域,搭载“浙渔科2号 ”和“润江1号”科考船开展长江口及其附近海域痕量金属Co的季节性分布的研究。分别获取了24个秋季、32个春季和24个夏季长江口的表层水样品(图1)。
1.2 样品采集
表层水样品采用实验室自制的痕量采水器,在船头位于水流的上游区域采集表层水样品。所取水样立即在船舱内搭建的洁净环境中使用蠕动泵经Pall® 0.8/0.2 μm的囊式滤器过滤后装入60 mL 低密度聚乙烯(Nalgene)样品瓶,并装入3层自封袋后封入样品箱,常温保存带回。
1.3 材料与方法
1.3.1 试剂与材料
样品带回后的所有实验操作均在上海交通大学1000级微量金属洁净实验室的100级高效微粒空气(high efficiency particulate air,HEPA)过滤通风橱中进行。实验所用试剂及材料见表1。
表 1 试剂与材料Table 1. Reagents and materials类别 Category 名称 Name 纯度 Purity 公司 Company 用途 Application 试剂 硝酸 Optima级别 Thermo Fisher 配置洗脱液及润洗液等 盐酸1 Optima级别 Thermo Fisher 样品及超纯水酸化等 醋酸 Optima级别 Thermo Fisher 配制缓冲液等 氨水 Optima级别 Thermo Fisher 配制缓冲液等 盐酸2 Trace Metal级别 Thermo Fisher 实验用具清洗 钴标准溶液 ICP-MS级别 Inorganic Ventures 配置外标 Citranox酸性清洁剂 — Alconox 清洁实验所需用具 材料 低密度聚乙烯瓶 — Nalgene 样品采集及酸化 聚乙烯离心管 — VWR Scientific 样品预处理 低密度聚乙烯背板 — ESI 洗脱液收集 seaFAST使用的缓冲液由氨水和醋酸按比例混合制备(pH=6.0±0.2),使用的洗脱液为0.5 mol.L−1的硝酸。ICP-MS自动进样器和seaFAST的润洗液均为0.5%的硝酸。小瓶、离心管和背板均在洁净实验室中按照以下步骤进行清洗[42-43]:在2%Citranox清洁剂中浸泡24 h,用超纯水冲洗7次,然后在10%盐酸中浸泡7 d,用超纯水冲洗7次,使用三层塑料自封袋密封。用于ICP-MS的氩气和氦气为超纯级(>99.999%)。
1.3.2 仪器设备
Milli-Q纯水机:Merck公司。seaFAST S2:Elemental Scientific公司。ESI-2DX自动进样器:Elemental Scientific公司。ICP-MS/MS:Thermo Fisher iCAP TQ电感耦合等离子质谱仪。ICP-MS/MS的工作条件见表2。
表 2 ICP-MS/MS的运行条件Table 2. Operating conditions of ICP-MS/MS运行参数Operating parameters 取值Value 聚焦透镜Focus Lens/V 1.25 透镜1 Lens/V −350 透镜2 Lens/V −148 碰撞/反应气体流速/ (mL·min−1) 4.5 偏转透镜 Deflection lens/V −30 雾化室温度 Spray Chamber temperature/℃ 2.7 蠕动泵转速/ (r·min−1) 40 冷却气流速 Cool flow /(L·min−1) 14 采样深度 Sampling depth/mm 5 功率 Plasma power/W 1550 辅助气流速 Auxilliary flow/ (L·min−1) 0.8 提取透镜电压 Extraction lens /V −120 载气流速 Nebulizer flow/ (L·min−1) 1.08 1.3.3 样品分析流程
样品带回实验室后使用盐酸l按照1:1000的比例进行酸化并摇匀,静置保存3个月及以上,使未络合的各种形态的Co在酸介质中充分分解[44]。静置后的样品先使用以盐酸l酸化至pH=2的Milli-Q水进行适当稀释,以盐度(Salinity, S)为划分标准进行稀释,0≤S<1‰稀释100倍,1‰≤S<15‰时稀释20倍,S≥15‰时稀释10倍,以避免金属浓度过高而污染seaFAST系统。稀释后的样品使用seaFAST进行分离和富集[45-46],主要经过如下步骤。1. 上样:10 mL样品进入定量环,样品和缓冲液在线混合进入预浓缩柱。在这个过程中,元素被螯合树脂选择性吸附;2. 基质淋洗:超纯水和缓冲液在线混合后通过预富集柱后弃去,从而去除干扰离子和未被螯合的离子;3. 柱洗脱:0.5 mL的0.5 mol·L−1硝酸通过预富集柱,将被分析物从螯合树脂上洗脱至低密度聚乙烯背板,供ICP-MS/MS分析。
本研究用西太平洋表层标准海水(LEMON)为基体配制浓度梯度为0、0.001、0.005、0.01、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.5 μg.L−1的标准曲线进行定量。本方法经过严格的验证,Co的方法检出限为0.003 nmol·L−1,流程空白低于检测限。对加拿大国家研究委员会(National Research Council, Canada)认证的标准样品SLEW-3,SLR-6,CASS-6和NASS-7的分析结果见表3。
表 3 标准参考物质Co分析结果( nmol·L−1)Table 3. Reported analytical results of certified reference seawater( nmol·L−1)国际标准物质Certified reference seawater NASS-7(n=10) CASS-6(n=10) SLEW-3(n=10) SLRs-6(n=10) 测试值 0.0007±0.0001 0.0036±0.0004 0.002±0.000 0.003±0.000 标准值 0.0009±0.0001 0.0040±0.0003 0.002±0.001 0.003±0.001 注:n为测试样本数,标准值由加拿大国家研究委员会发布. Note: n is the number of test samples, and the standard value is published by the National Research Council of Canada. 1.4 辅助参数与数据处理
本文用于认识长江口Co生物地球化学规律的辅助参数,例如温度、盐度、营养盐、溶解氧及叶绿素等环境参数,通过同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室共享航次和国家自然科学基金委共享航次的数据共享获取。所得数据以Ocean Data View进行平面图绘制,使用IBM SPSS statistics数据编辑器对样品各参数之间进行双变量相关性检验,相关性采用Pearson相关系数,显著性检验采用双尾检验。
2. 结果与讨论(Results and discussion)
2.1 不同季节长江口表层水的水文特征
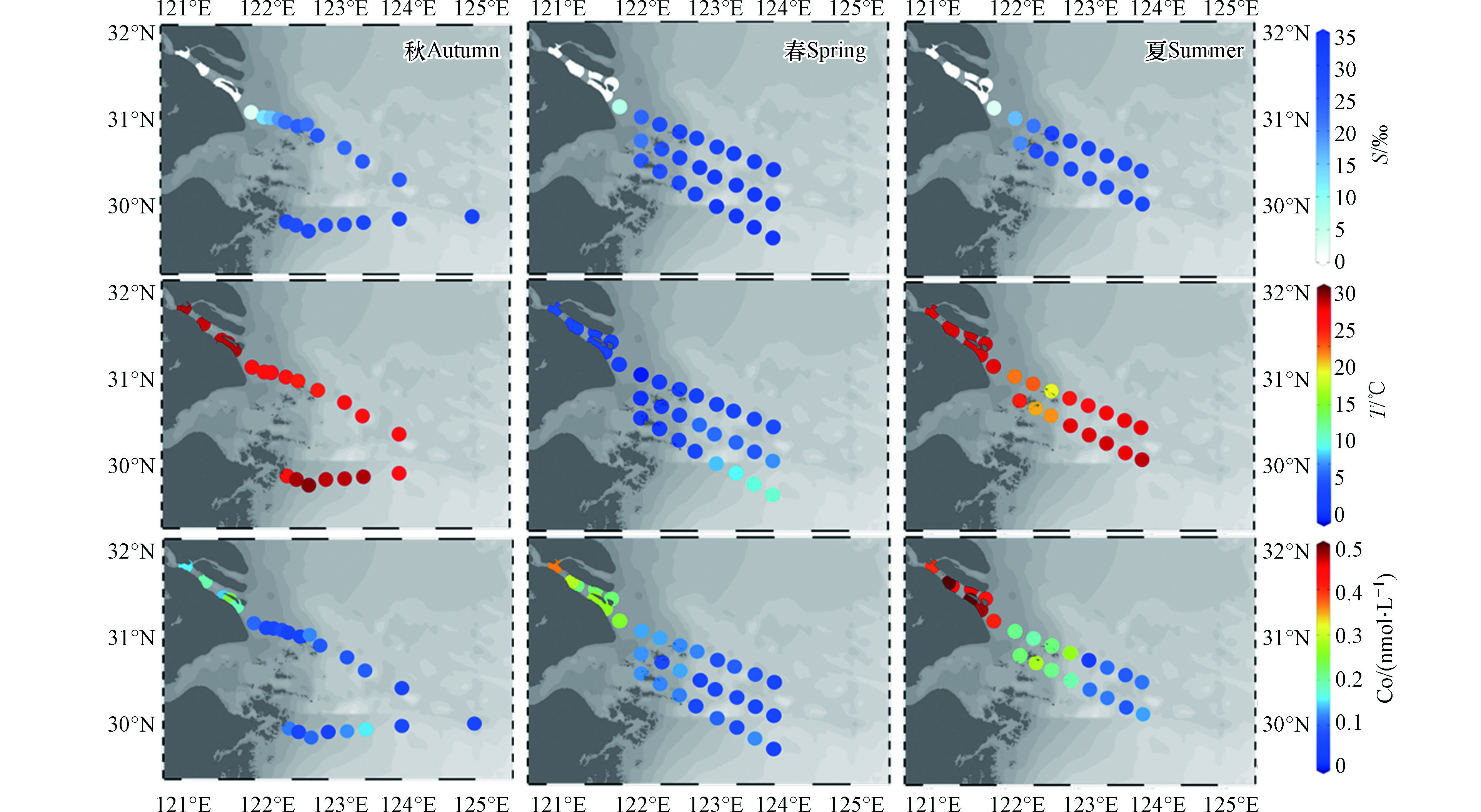
本研究3个季节长江口及其邻近水域各站位表层水的盐度(S)、温度(T)及Co浓度详细数据见表4。2019年9月秋季航次的水温范围为26.39—29.46 ℃,盐度范围为0.00—32.10‰;2021年3月春季航次水温范围为10.10—17.00 ℃,盐度范围为0.19‰—34.82‰;2021年7月夏季航次水温范围为22.89—28.77 ℃,盐度范围为0.11‰—31.39‰。春季航次中长江口的水温偏低,而研究范围表层水整体盐度较高。在2021年7月和9月的夏秋两季,观测到的温盐范围接近。
表 4 本研究三个航次表层水温度(T)、盐度(S)和钴浓度(Co)Table 4. Temperature (T), salinity (S) and cobalt concentration(Co) in surface water of the three cruises in this study2019年9月(秋季)Autumn 2021年3月(春季)Spring 2021年7月(夏季)Summer 站位Site 盐度/‰Salinity 温度/℃Temperature Co/(nmol·L−1) 站位Site 盐度/‰Salinity 温度/℃Temperature Co/(nmol·L−1) 站位Site 盐度/‰Salinity 温度/℃Temperature Co/(nmol·L−1) C1 0.00 28.92 0.15 B1 0.20 12.41 0.22 B1 0.13 28.41 0.45 C2 0.00 28.67 0.19 B2 0.25 12.08 0.23 B2 0.14 28.62 0.46 C3 0.10 28.79 0.15 B3 1.17 11.88 0.22 B3 0.14 28.49 0.42 C4 0.10 28.87 0.24 C1 0.19 12.73 0.37 C1 0.14 28.39 0.40 C5 0.00 28.92 0.19 C2 0.20 12.45 0.28 C2 0.14 28.46 0.54 C6 2.80 27.77 0.10 C3 0.24 12.24 0.27 C3 0.15 28.48 0.52 C7 12.50 27.25 0.06 C4 1.00 11.97 0.26 C4 0.11 28.43 0.48 C8 15.10 27.47 0.06 C5 6.37 11.24 0.25 C5 2.84 28.30 0.41 C9 18.80 — 0.08 A5-1 23.69 10.10 0.13 A5-1 15.98 24.62 0.21 C10 22.10 26.88 0.05 A5-2 28.93 11.04 0.13 A5-2 21.45 25.06 0.19 C11 24.60 26.39 0.05 A5-3 30.64 11.90 0.12 A5-3 31.39 22.89 0.22 C12 22.10 — 0.12 A5-4 30.36 11.37 0.12 A5-4 29.77 26.69 0.27 C13 25.80 26.40 0.09 A5-5 31.63 12.08 0.08 A5-5 30.92 27.61 0.03 C14 23.10 27.42 0.09 A5-6 32.49 12.36 0.09 A5-6 30.06 28.03 0.10 C15 25.60 27.13 0.09 A5-7 32.71 12.52 0.08 A5-7 29.61 28.20 0.09 C16 25.60 27.43 0.06 A5-8 34.07 12.74 0.06 A5-8 29.08 28.24 0.11 C18 32.10 — 0.06 A6-1 21.09 10.66 0.12 A6-1 19.78 26.44 0.22 Y1 28.80 27.14 0.11 A6-2 26.89 11.09 0.07 A6-2 27.49 23.92 0.28 Y2 27.80 29.07 0.06 A6-3 31.37 12.12 0.13 A6-3 27.66 24.22 0.21 Y3 29.50 29.46 0.10 A6-4 33.20 14.14 0.05 A6-4 29.56 28.29 0.19 Y4 28.40 28.82 0.05 A6-5 33.51 14.17 0.06 A6-5 28.19 28.37 0.11 Y5 28.40 28.84 0.12 A6-6 33.94 14.01 0.07 A6-6 28.46 28.53 0.11 Y6 30.40 29.00 0.15 A6-7 34.01 13.49 0.06 A6-7 29.91 28.22 0.09 Y7 30.60 27.63 0.07 A6-8 34.28 14.89 0.05 A6-8 29.97 28.77 0.13 A7-1 25.89 11.08 0.12 A7-2 27.44 11.24 0.12 A7-3 29.62 12.28 0.12 A7-4 31.53 12.41 0.06 A7-5 34.29 15.62 0.10 A7-6 34.50 16.26 0.07 A7-7 34.82 16.74 0.12 A7-8 34.52 17.00 0.05 注:“—”表示数据缺失. Note: “—” means data missing. 本研究采取咸淡水划分模式,将研究区域划分为淡水区、冲淡水区及海水区。具体以盐度(S)1和30为界限[47-48],将S<1‰划分为淡水区域,1‰≤S≤30‰为冲淡水区域,S>30‰为海水区域,对各站位所属海域进行详细区分可知,2019年9月航次C1—C5位于淡水区,C18、Y6和Y7位于海水区,其余在冲淡水区;2021年3月航次B1—B2、C1—C3位于淡水区,A5的3—8号站、A6的3—8号站及A7的4—8号站位于海水区,其余站位在冲淡水区;2021年7月B1—B3、C1—C4位于淡水区,A5—3/5/6位于海水区,其余在冲淡水区。
2.2 Co的浓度范围和季节变化
长江口金属Co的浓度在不同季节有所差异:秋季Co浓度分布范围0.05—0.24 nmol·L−1,均值0.10 nmol·L−1;春季Co浓度分布范围为0.05—0.37 nmol·L−1,均值为0.13 nmol·L−1;夏季Co浓度较高,其分布范围在0.03—0.54 nmol·L−1,均值高达0.26 nmol·L−1,几乎达到春秋季节的最高值;以Co含量的均值来看,Co在长江口浓度的季节变化表现为夏季>春季>秋季。
从季节变化的角度对本研究中各水域的盐度、温度及Co浓度进行统计(表5)。对于全水域,秋季Co的平均浓度淡水>海水>冲淡水;春夏两季趋势一致Co浓度表现为淡水>冲淡水>海水的规律。区分咸淡水域后观察其在不同季节的浓度数据可知,淡水Co浓度随季节变化幅度最大,表现为秋季<春季<夏季;海水Co浓度随季节变化幅度较小,其含量春季<秋季<夏季;冲淡水中Co含量受到淡水及海水的共同作用,其浓度介于二者之间,表现为秋季<春季<夏季。
表 5 长江口及其临近水域的钴浓度、盐度及温度Table 5. Co, salinity and temperature of the Changjiang Estuary and its adjacent waters季节Season 水域Area 盐度/‰Salinity 温度/℃Temperature Co/(nmol·L−1) 样本数Number 最小值Min 最大值Max 均值Mean 样本数Number 最小值Min 最大值Max 均值Mean 样本数Number 最小值Min 最大值Max 均值Mean 秋 全水域 24 0.00 32.10 18.93±11.82 21 26.39 29.46 28.01±0.97 24 0.05 0.24 0.10±0.05 淡水 5 0.00 0.10 0.04±0.05 5 28.67 28.92 28.83±0.10 5 0.14 0.24 0.18±0.04 冲淡水 16 2.80 29.50 22.56±7.20 14 26.39 29.46 27.68±0.99 16 0.05 0.12 0.08±0.02 海水 3 30.40 32.10 31.03±0.93 2 27.63 29.00 28.31±0.97 3 0.06 0.15 0.09±0.05 春 全水域 32 0.19 34.82 23.60±13.56 32 10.10 17.00 12.76±1.76 32 0.05 0.37 0.13±0.08 淡水 5 0.19 0.25 0.22±0.03 5 12.08 12.73 12.38±0.24 5 0.22 0.37 0.27±0.06 冲淡水 10 1.00 29.62 19.21±11.64 10 10.10 12.28 11.26±0.64 10 0.07 0.26 0.16±0.06 海水 17 30.36 34.82 33.05±1.46 17 11.37 17.00 13.75±1.80 17 0.05 0.13 0.08±0.03 夏 全水域 24 0.11 31.39 18.46±13.48 24 22.89 28.77 27.3±1.8 24 0.03 0.54 0.26±0.16 淡水 7 0.11 0.14 0.13±0.01 7 28.39 28.62 28.47±0.08 7 0.40 0.54 0.47±0.05 冲淡水 14 2.84 29.97 24.98±7.73 14 23.92 28.77 26.99±1.80 14 0.09 0.41 0.19±0.09 海水 3 30.06 31.39 30.79±0.68 3 22.89 28.03 26.18±2.8 3 0.03 0.22 0.12±0.10 2.3 驱动长江口Co分布变化的因素解析
海水中Co的生物地球化学循环受到水团输运混合、盐度变化、吸附与解吸、生命活动等过程的影响。为解析驱动长江口Co生物地球化学行为的主要因素,在不考虑季节变化的前提下,将长江口所采样品按水域分析Co浓度与盐度(salinity, S)、温度(temperature, T)、溶解无机氮(dissolved inorganic nitrogen , DIN)、溶解无机磷酸盐(dissolved inorganic phosphates , DIP)、溶解态无机硅酸盐(dissolved inorganic silicate , DSi)、溶解氧(dissolved oxygen, DO)及叶绿素(chlorophyll, Chl)等环境因子的皮尔逊相关性(表6)。结果表明,在统计学上Co的浓度与环境参数之间存在一定程度上的相关,且不同水域和不同季节的相关性存在差异。
表 6 各水域Co浓度与其它环境因子的皮尔逊相关性Table 6. Pearson correlation between Co and other environmental factors in different areas水域Area 盐度Salinity 温度Temperature 氮盐DIN 磷盐DIP 硅盐DSi 叶绿素Chlorophyll 溶解氧Dissolved oxygen 全水域 −0.73** 0.2 0.76** 0.33** 0.51** −0.22* −0.36** 淡水 0.27 0.25 0.70* −0.13 −0.72* −0.71** −0.75** 冲淡水 −0.44** −0.17 0.63** 0.22 0.39* −0.38* −0.57** 海水 −0.39 0.18 0.40 0.74** −0.06 0.36 0.02 注:**指相关性在0.01 级别上显著(双尾检验);*指相关性在0.05级别上显著(双尾检验). Note: ** indicates a very significant correlation at the 0.01 level (two-sided), and * indicates a significant correlation at the 0.05 level (two-sided). 较好的相关性可以证明来源上的相关或生物地球化学行为上的相似[49],长江口及其邻近海域Co与盐度、3种营养盐及溶解氧表现出极显著相关,与叶绿素显著相关;相较于其他因子,盐度和氮营养盐与Co相关性较强。着眼于不同水域,淡水区域Co与水体中Chl和DO含量极显著正相关,与DIN、DSi显著相关;冲淡水区域Co与环境因子的相关性则较为复杂,与S、DIN及DO极显著相关,与DSi和Chl含量呈现显著相关;海水区域 Co的生物地球化学行为与环境因子的关系较为单一,仅与DIP表现出极显著的正相关关系。
DSi与Co的相关性或为来源上的相关。有研究表明,上游岩石矿物的强烈风化剥蚀或为长江中Co的主要来源[50-53],且Co与铝硅酸盐和其他风化条件等有着较好的相关性[54-55],因此越靠近淡水区二者相关性越强。DIP与Co则主要为生物地球化学行为上的相似,溶解态Co和可溶性活性磷酸盐(Co: DIP)在海洋透光带内表现为正相关,可以解释为该区域主要浮游生物群落对Co的利用程度及其随后从生物颗粒相再矿化在时间尺度上的综合积累信号[56-57];同时在海洋环境中浮游植物对 Co的比吸收率高于锰,这可能使得Co成为具有介于锰和更多营养类型元素(如锌)之间的生物地球化学效应的中间体,从而被更多浮游生物利用[10],因此Co与DIP的相关性在海水区域明显高于淡水区和冲淡水区。
当忽略地理位置,仅对Co随季节变化加以讨论,对长江口及其邻近海域Co浓度与环境因子做皮尔逊相关性分析(表7),以分析不同季节、水域条件下Co的生物地球化学循环可能的驱动因素。
表 7 Co浓度在不同季节与其他环境参数的皮尔逊相关性Table 7. Pearson correlation between Co and other environmental factors in different seasons季节Season 盐度Salinity 温度Temperature 氮盐DIN 磷盐DIP 硅盐DSi 叶绿素Chlorophyll 溶解氧Dissolved oxygen 秋季 −0.65** 0.55** 0.61** 0.10 0.62** −0.40 −0.15 春季 −0.93** −0.34 0.92** 0.56** 0.92** 0.83** −0.30 夏季 −0.92** 0.18 0.78** 0.67* 0.58* 0.15 −0.76** 注:**指相关性在0.01 级别上显著(双尾检验);*指相关性在0.05级别上显著(双尾检验). Note: ** indicates a very significant correlation at the 0.01 level (two-sided), and * indicates a significant correlation at the 0.05 level (two-sided). 盐度与Co在每个季节都表现出极显著的负相关,可以认为盐度是主导河口Co的重要影响因子,对墨西哥湾的研究也指出Co浓度与水体盐度有很强的线性关系[15, 25],且盐度升高时颗粒态Co更容易被移除[34],因此盐度升高时通常伴随着Co的浓度的降低。对于营养盐,DIN与Co始终表现出较好的相关性,且春季>夏季>秋季;DSi次之,春季>秋季>夏季;DIP与Co的相关性在3种营养盐中相对较低,仅在春夏季节表现出相关性,秋季相关性不显著。春秋两季Co与DSi的相关性大于夏季,或为 Co随铝硅酸盐的风化侵蚀作用较强所致。
对于各季节的特殊影响因子,秋季Co与温度存在较好的相关性,或为温度影响水体中的氧化细菌的活性所致[24];结合盐度及营养盐数据,温度也可以通过咸淡水混合程度或浮游生物消耗程度产生影响。春季时Co与营养盐相关性更强,同时与Chl也有着极显著的相关性,表现出生物吸收作用的主导地位。夏季与DO的极显著的负相关关系,可能是因为溶解氧会影响水体中Co的存留状态[18],由于夏季水温较高使得水体中溶氧较低,伴随氧化颗粒物的移除的Co减少,此外当沉积物中氧化颗粒物被还原时Co也将随之释放到水体中[26];夏季Co与DSi的强相关性或也指示来源上的增多。
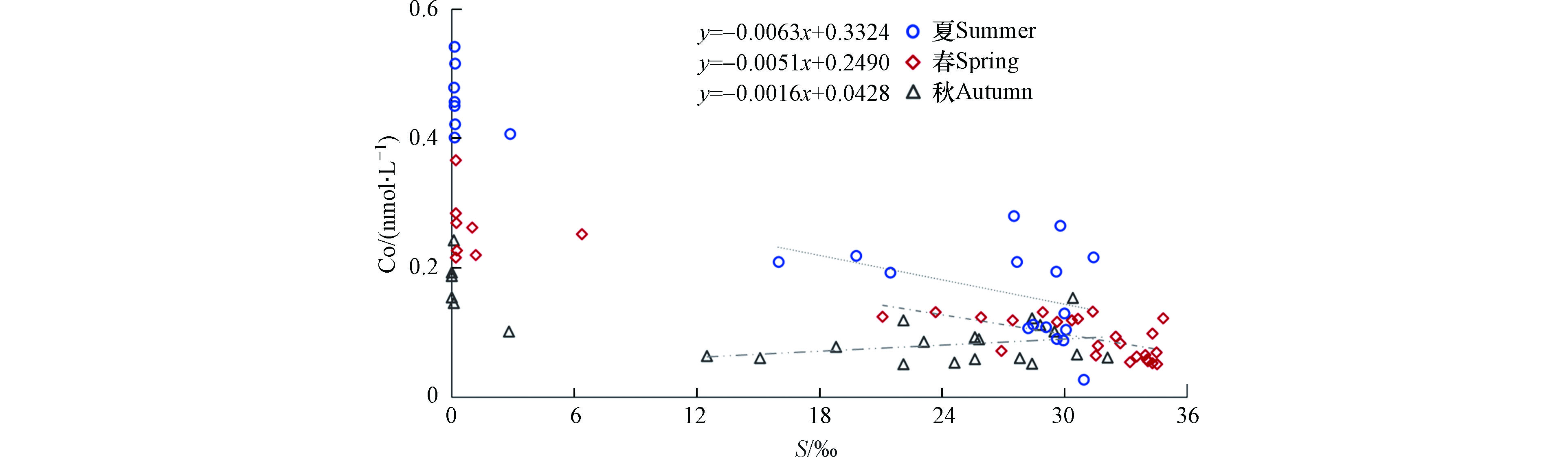
2.4 Co跨越长江口盐度梯度的行为分析
Co在长江口及其邻近海域的浓度随盐度梯度的上升呈现降低趋势(图2)。西班牙Vigoria河口的研究指出河流输送是该区域Co的主要来源[26],本研究表明长江携带的Co也是影响河口Co分布的重要因素。其中,长江口的春季淡水端元Co浓度明显高于秋季,夏季的Co分布类似春季,但其浓度显著高于秋季与春季,河口处浓度可达0.5 nmol·L−1。
对不同季节Co浓度随盐度梯度的变化进行分析(图3),可见Co在长江口的生物地球化学行为除物理意义上的咸淡水混合导致的稀释作用外还存在其它因素的干扰,总体表现为移除型分布。相较而言,锦江(韩国)河口及麦肯齐河河口处Co在盐度为9‰—12‰范围内存在一个Co的峰值[33,35],加尔沃斯顿湾Co在河口中盐度区域表现出非保守的补充行为[58],但本研究在中盐度范围的样品量有限,导致对长江口中盐度Co行为的认识尚不清晰。
采用Vieira的方法[59]计算3个季节的Co移除率:对各航次中高盐度站位数据点进行线性拟合,拟合线见图3中3条虚线,拟合回归方程如图所示;取其截距(y0)与本研究在河口处0盐度区域的Co浓度平均值(C0)进行比对,最终对其移除率(removal rate, RR)进行量化(式1,表8)。
表 8 各季节长江口Co移除率及有效输送通量Table 8. Removal rate and effective flux of cobalt in the Changjiang Estuary in different seasons时间Time 季节Season C0 / (nmol·L−1) y0 / (nmol·L−1) 移除率/%RR 径流量/亿m3Runoff 有效通量/geffective flux 19年9月 秋 0.17 0.04 74.82 632.4 1.60×105 21年3月 春 0.26 0.25 4.23 530.3 7.78×105 21年7月 夏 0.46 0.33 27.74 1 178 2.31×106 stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) 基于本研究3个季节的河口端Co浓度及移除率,采用长江水利网发布的《长江流域重要控制断面水资源监测通报》 (数据来源:www.cjw.gov.cn)所报道的大通站各季节长江向海输水量(Q),对3个季节长江向海输送的有效Co通量(flux)进行计算(式2),结果见表8。如表8所示,Co在长江口的移除效果秋季最为明显,夏季次之,春季较微。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) 表8展示了由3个航次长江口Co分布推算出的移除率,表现为秋季>夏季>春季。夏季移除率较高,但由于夏季淡水端元Co浓度最高且径流量极高,夏季向海输送Co通量最高;秋季移除率最高且淡水端元浓度最低,因此向海洋输送Co最少;春季虽径流量较低,但淡水端元Co浓度高于秋季,且移除率最低,因此Co的向海输送通量高于秋季,但受径流量及淡水端浓度限制,输送通量仍然低于夏季。综上所述,长江口Co的有效入海通量表现为夏季>春季>秋季。
2.5 世界河流Co的入海通量初步估算
目前对河流中Co的研究主要集中在重工业区域,人为因素造成的影响愈发显著,在工业区或点源污染的河流区域所采样品浓度显著高于本研究报道数据,如汉江[60]污染区Co浓度达38.01 nmol·L−1,印度Mahanadi河[61]污染区达57.35 nmol·L−1、Manjira河[62]达47.51 nmol·L−1,意大利的Po河[63]甚至可达103 nmol·L−1。全球河流向海输送Co通量估算见表9。Co浓度采用河流或河口处溶解态Co浓度的平均值,同时以河流径流量对各区域Co浓度进行归一化得Cn,计算其在全球各河流向海输送Co浓度的平均值。归一化系数即为河流径流量在给出的全部河流径流量之和中的占比。
表 9 世界大河Co浓度、径流量及归一化浓度(Cn)Table 9. Cobalt concentration, runoff and normalized concentration(Cn) in several worldwide rivers河流River 注入海洋Sea areas Co/(nmol·L−1) 径流量/亿m3Runoff 归一化系数Normalization coefficient Cn/(nmol·L−1) 参考文献References 亚马逊河(Amazon River) 大西洋 2.01 47462 0.47 0.94 [64-65] 密西西比河(Mississippi River) 墨西哥湾 0.16 6307 0.06 0.01 [66-67] 长江(Changjiang River) 东海 0.16 9282 0.09 0.01 本研究,[68] 黄河(Yellow River) 渤海 0.43 443 0.00 0.00 [42,68] 珠江(Pearl River) 南海 4.85 4821 0.05 0.23 [68-69] 锦江(韩国)(Geum River) 黄海 1.2 64 0.00 0.00 [33,70] 加尔沃斯顿湾(Galveston Bay) 大西洋 1.6 13600 0.13 0.22 [58] 万泉河(Wanquan River) 南海 1.16 52 0.00 0.00 [71] 文昌/文教河(Wenchang/Wenjiao River) 南海 3.07 6 0.00 0.00 [71] 麦肯齐河(Mackenzie River) 北冰洋 1.1 3160 0.03 0.03 [35] 淡水河(Tanshui River) 台湾海峡 0.3 70 0.00 0.00 [72] 刚果河(Congo River) 大西洋 1 12331 0.12 0.12 [73-74] 圣劳伦斯河(Saint Lawrence River) 大西洋 1.1 3374 0.03 0.04 [74-75] 对上述河流基于流量归一化估算出全球河流向海输送平均Co浓度为1.61 nmol·L−1。河流向海年输水量以3.80×1019 g计[76-77],在不考虑移除效果时,全球河流年向海输送Co通量可达3.60×109 g。当考虑移除效果时,假设移除率采用本研究长江口3个季度移除率的平均值(36%),计算可得河流有效年向海输送通量仅为2.32×109 g。
Gaillardet等根据全球河流溶解Co浓度计算所得的年通量为5.5×109 g[74],而Tagliabue等基于Co/C为12 μmol·mol-1[24]估算出河流对全球大洋的Co年贡献值为3.4×108 g。两种估算方法得到的通量相差1个数量级。在不考虑移除效果时,本研究的估算通量与Gaillardet的估算结果类似,但考虑到Co在河口区域的移除,Gaillardet估算的河流向海年输送Co的通量可能被高估。本研究表明了河口界面Co行为研究的重要性。如果考虑到河流携带颗粒物可能通过输运和解吸向海洋输送,河流向海年输送Co的通量达2.48×1010 g[23,32,78]。本文目前的数据无法对长江颗粒态Co的贡献进行定量,相关结论需待进一步研究。
3. 结论(Conclusion)
本研究对Co在长江口的生物地球化学行为及其可能存在的机理做出如下阐释:(1)长江口及其临近海域的Co浓度分布呈现出明显的自河口向远海降低的趋势,整体表现出河口的移除行为;(2)从季节来看,长江口表层水Co浓度夏季>春季>秋季,春秋两季较为接近;(3)相关性分析表明Co浓度与盐度表现出强烈的相关性,表明咸淡水混合是调控长江口Co分布的主要因素;(4)长江口表层水Co在不同季节与不同营养盐种类呈现了不同的相关性,在春季显现出与叶绿素的相关性,夏季则与水体中溶解氧显著负相关;(5)长江口Co的移除率秋季>夏季>春季,向海有效输送通量夏季>春季>秋季;(6)河口的行为影响河流向海输送Co的通量,本研究表明了河口界面Co行为研究的重要性。
致谢:感谢国家自然科学基金委员会共享航次计划项目提供的共享航次(航次编号:NORC2021-03),以及同济大学海洋地质国家重点实验室共享航次(航次编号:KECES-2019)的资助。感谢“浙渔科2”号/“润江1”号科考船的船员帮助样品采集。感谢航次期间协助完成采样的同事和同学。感谢在样品分析、数据分析等方面提供帮助的同学。
-
表 1 水样中各营养盐要素的分析方法
Table 1. Analysis methods of nutrient elements in water samples
表 2 地表水富营养化状态等级划分
Table 2. The classification of surface water eutrophication status
营养化程度Eutrophication degree 贫营养Oligotrophic 中营养Mesotrophic 富营养Eutrophic 重富营养Hypereutrophic 极富营养 Extreme eutrophic 等级 ≤20 20—39.42 39.42—61.29 61.29—76.28 76.28—99.77 表 3 2018—2019年四个季度三亚河营养盐氮、磷含量及理化参数的变化范围及平均值1)
Table 3. Variation range and average value of nitrogen and phosphorus contents and physicochemical parameters in Sanya River from 2018 to 2019
季节 Season NH4+-N /(mg·L−1) NO3−-N/(mg·L−1) NO2−-N/ (mg·L−1) DIP/(mg·L−1) T/℃ S/‰ DO/(mg·L−1) 春季 Spring 范围 0.014—0.448 0.007—0.830 0.001—0.197 0.007—0.391 24.5—31.3 0.06—32.81 2.69—8.42 均值±SD 0.186±0.109 0.216±0.162 0.073±0.052 0.156±0.120 27.1±0.9 14.63±11.0 5.16±1.43 夏季 Summer 范围 0.026—0.434 0.006—1.212 0.002—0.104 0.008—0.442 15.8—32.0 0.05—31.56 0.96—8.38 均值±SD 0.209±0.093 0.364±0.133 0.043±0.024 0.180±0.072 25.7±0.7 7.13±7.91 5.02±1.62 秋季 Autumn 范围 0.003—0.445 0.134—0.868 0.001—0.122 0.008—0.215 7.9—17.8 0.05-32.37 0.12—8.05 均值±SD 0.240±0.103 0.543±0.112 0.063±0.033 0.099±0.042 12.6±0.5 5.91±8.42 5.40±1.48 冬季 Winter 范围 0.013—1.321 0.017—1.600 0.001—0.272 0.009—0.295 4.1—28.0 0.06—32.65 2.75—8.75 均值±SD 0.264±0.156 0.495±0.327 0.087±0.054 0.132±0.094 19.0±0.4 12.30±11.3 5.17±1.47 1) SD标准偏差. SD: Standard deviation. 表 4 三亚河与其他河流营养盐含量对比
Table 4. Comparison of nutrient content between Sanya River and other rivers
流域 Basin NH+4 NO−3 NO−2 DIP/(mg·L−1) 参考文献 Reference 三亚河 0.229±0.104 0.420±0.171 0.066±0.038 0.140±0.066 本研究 珠江广州段 3.380 1.510 0.340 0.130 [26] 黄河 0.074 3.770 0.069 0.003 [27] 长江 0.010 1.148 0.020 0.038 [28] 万泉河 0.076 0.640 0.016 0.022 [29] 图尔河 1.380 0.620 0.056 0.110 [30] 石狩河 0.167 0.932 0.011 0.026 [31] 海河市区段 1.480 1.995 — — [32] 渭河咸阳段 2.43 — — — [33] 香溪河 0.061 0.740 — 0.060 [34] 斯兹雷尼亚瓦河 0.230 3.440 — 0.320 [35] 表 5 营养盐与环境因子的相关性分析1)
Table 5. Correlation analysis between nutrients and environmental factors
季节 Season T S DO NH+4 NO−3 NO−2 DIN DIP 春季 T 1 S −0.226 1 DO −0.373 0.900** 1 NH+4 0.285 −0.728* −0.768* 1 NO−3 0.274 −0.144 −0.319 0.673* 1 NO−2 0.556 −0.66 −0.679* 0.864** 0.735* 1 DIN 0.348 −0.446 −0.57 0.888** 0.933** 0.897** 1 DIP 0.472 −.866** −.767* 0.855** 0.383 0.865** 0.670* 1 夏季 T 1 S −0.635 1 DO −0.388 0.899** 1 NH+4 0.488 −0.741* −.708* 1 NO−3 0.191 −0.107 −0.232 0.166 1 NO−2 0.193 −0.157 −0.355 0.599 0.65 1 DIN 0.373 −0.34 −0.439 0.579 0.887** 0.864** 1 DIP 0.39 −0.879** −0.939** 0.831** 0.296 0.438 0.544 1 秋季 T 1 S −0.437 1 DO −0.042 0.673 1 NH+4 0.088 0.008 −0.048 1 NO−3 −0.265 −0.501 −0.575 −0.468 1 NO−2 −0.656 −0.246 −0.521 −0.097 0.779* 1 DIN −0.536 −0.163 −0.365 −0.067 0.782* 0.923** 1 DIP −0.469 −0.401 −0.692* 0.073 0.753* 0.942** 0.882** 1 冬季 T 1 S −0.571 1 DO −0.549 0.858** 1 NH+4 0.424 −0.591 −0.472 1 NO−3 −0.411 −0.065 −0.161 0.221 1 NO−2 0.06 −0.512 −0.584 0.495 0.842** 1 DIN −0.144 −0.331 −0.365 0.595 0.914** 0.919** 1 DIP 0.271 −0.929** −0.792* 0.602 0.247 0.57 0.481 1 1) *表示P<0.05,**表示P<0.01 -
[1] 陈雯, 吴亚, 张宏鑫, 等. 北海冯家江流域地表水体中氮磷营养盐的时空分布特征 [J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(1): 169-175,188. CHEN W, WU Y, ZHANG H X, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in surface water of Fengjiajiang River watershed, Beihai [J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(1): 169-175,188(in Chinese).
[2] 刘静, 杨福霞, 王俊杰, 等. 灌河下游营养盐浓度的季节变化及其入海通量研究 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 51(5): 72-80. LIU J, YANG F X, WANG J J, et al. Seasonal variation and fluxes of nutrients in the lower reaches of the Guanhe River [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2021, 51(5): 72-80(in Chinese).
[3] 陈明霞, 熊贵耀, 张佳鹏, 等. 湘江流域水质综合评价及其时空演变分析 [J]. 环境工程, 2019, 37(10): 83-90,104. CHEN M X, XIONG G Y, ZHANG J P, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of water quality in Xiangjiang River Basin from multi-dimensional perspective and its spatial-temporal evolution analysis [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2019, 37(10): 83-90,104(in Chinese).
[4] 余丽燕, 杨浩, 黄昌春, 等. 夏季滇池和入滇河流氮、磷污染特征 [J]. 湖泊科学, 2016, 28(5): 961-971. doi: 10.18307/2016.0505 YU L Y, YANG H, HUANG C C, et al. Characteristic of nitrogen and phosphorous pollution in Lake Dianchi and its inflow rivers in summer [J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2016, 28(5): 961-971(in Chinese). doi: 10.18307/2016.0505
[5] ZHANG P, CHEN Y, PENG C H, et al. Spatiotemporal variation, composition of DIN and its contribution to eutrophication in coastal waters adjacent to Hainan Island, China [J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2020, 37: 101332. doi: 10.1016/j.rsma.2020.101332 [6] 李昂臻, 陈思旭, 李海燕, 等. 北方某省会城市主要水库富营养化程度、特征和防治对策 [J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(9): 2529-2539. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020040902 LI A Z, CHEN S X, LI H Y, et al. Characteristics and evaluation of eutrophication in major reservoirs of a northern city in China [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(9): 2529-2539(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020040902
[7] 周坤朋, 刘阳春, 王崇臣. 北京什刹海区域水体富营养化时空演变特征分析 [J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(4): 703-712. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015093001 ZHOU K P, LIU Y C, WANG C C. Analysis on temporal-spatial variation of eutrophication in Shichahai area, Beijing [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(4): 703-712(in Chinese). doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2016.04.2015093001
[8] WANG X L, CUI Z G, GUO Q, et al. Distribution of nutrients and eutrophication assessment in the Bohai Sea of China [J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2009, 27(1): 177-183. doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-0177-x [9] 张美, 毛硕乾, 楼巧婷, 等. 2018年梅山湾营养盐的时空变化及富营养化分析 [J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020, 39(6): 853-859. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190210 ZHANG M, MAO S Q, LOU Q T, et al. Spatial-temporal variations and eutrophication analysis of nutrients in Meishan Bay in 2018 [J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020, 39(6): 853-859(in Chinese). doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190210
[10] 卢龙, 谢芳立. 赣江水体氮磷营养盐分布特征及影响因素 [J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版), 2017, 41(6): 567-571. LU L, XIE F L. Research on the factors of Ganjiang River water nitrogen and phosphorus distribution characteristics and influence [J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science), 2017, 41(6): 567-571(in Chinese).
[11] 三亚市生态环境局. 三亚市生态环境局关于2019年三亚市环境状况的公报[EB/OL]. [2022-3-2]. http://hbj.sanya.gov.cn/sthjsite/tzgg/202006/10ff196e4e884549a564e4475e9f9963.shtml. Sanya Ecological Environment Bureau. Bulletin of Sanya Ecological Environment Bureau on the environmental condition of Sanya City in 2019 [EB/OL]. [2022-3-2]. http://hbj.sanya.gov.cn/sthjsite/tzgg/202006/10ff196e4e884549a564e4475e9f9963.shtml.
[12] 车志伟, 史云峰, 曲江勇, 等. 三亚河口叶绿素a含量及其与环境因子的关系 [J]. 琼州学院学报, 2014, 21(2): 88-92. CHE Z W, SHI Y F, QU J Y, et al. The content of chlorophyll - a and its relationship with the environmental factors in the Sanya Estuary [J]. Journal of Qiongzhou University, 2014, 21(2): 88-92(in Chinese).
[13] 三亚市统计年鉴(2020年)[EB/OL]. [2022-3-20]. http://tjj.sanya.gov.cn/tjjsite/2020nnjf/tjnj.shtml. Statistical Yearbook of Sanya City (2020)[EB/OL]. [2022-3-20]. http://tjj.sanya.gov.cn/tjjsite/2020nnjf/tjnj.shtml (in Chinese).
[14] 陈文术, 王胜男, 杨波. 三亚绿地系统中海绵城市建设的思考 [J]. 安徽农业科学, 2017, 45(17): 153-154,192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.17.055 CHEN W S, WANG S N, YANG B. The construction of sponge city in Sanya green space system [J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(17): 153-154,192(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2017.17.055
[15] 车志伟. 三亚河入海口与感潮河段悬浮物分布特征及潮汐之影响 [J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2007, 27(6): 89-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2007.06.021 CHE Z W. Suspension distributing characteristics of Sanya River Estuary and tide-induced effects [J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2007, 27(6): 89-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2007.06.021
[16] 李晨曦. 红树林的生态修复与滨海城市的景观营造: 以三亚河红树林自然保护区生态修复为例 [J]. 林业科技情报, 2017, 49(4): 88-89,93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3303.2017.04.032 LI C X. Ecological restoration of mangrove and landscape construction of coastal city—A case study of ecological restoration of mangrove nature reserve in Sanya River [J]. Forestry Science and Technology Information, 2017, 49(4): 88-89,93(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3303.2017.04.032
[17] 杨星, 邱彭华, 钟尊倩. 三亚河红树林自然保护区水环境-红树植物-沉积物重金属污染综合分析 [J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(9): 1163-1170. YANG X, QIU P H, ZHONG Z Q. Comprehensive analysis of heavy metal pollution of water-mangrove plants-sediments system in Sanya River mangrove nature reserve [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(9): 1163-1170(in Chinese).
[18] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 海洋监测规范 第4部分: 海水分析: GB 17378.4—2007[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. The specification for marine monitoring—Part 4: Seawater analysis: GB 17378.4—2007[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008(in Chinese).
[19] 李祚泳, 汪嘉杨, 郭淳. 富营养化评价的对数型幂函数普适指数公式 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2010, 30(3): 664-672. LI Z Y, WANG J Y, GUO C. A universal index formula for eutrophic evaluation using a logarithmic power function [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2010, 30(3): 664-672(in Chinese).
[20] 李洪涛, 刘阳, 于国庆, 等. 威海南部近岸海域表层海水化学要素时空变化及富营养化研究 [J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2016, 35(3): 356-363. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2016.03.006 LI H T, LIU Y, YU G Q, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of sea water chemicals and eutrophication evaluation in surface water of southern Weihai coastal area [J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2016, 35(3): 356-363(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2016.03.006
[21] 陈攀, 李晓梅, 王梅, 等. 旅游旺季三亚河水体中有机物含量的分析 [J]. 琼州学院学报, 2014, 21(5): 93-98. CHEN P, LI X M, WANG M, et al. Analysis of organic matters content in water of Sanya River in tourist season [J]. Journal of Qiongzhou University, 2014, 21(5): 93-98(in Chinese).
[22] GAO Y X, YU J H, SONG Y Z, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of different forms of inorganic nitrogen in three types of rivers around Lake Taihu, China [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2019, 26(7): 6898-6910. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04154-w [23] 任丙南, 耿静. 三亚市水体中PPCPs的污染水平、分布特征及生态风险评价 [J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(10): 4717-4726. REN B N, GENG J. Occurrence, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of pharmaceutical and personal care products in the aquatic environment of Sanya City, China [J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(10): 4717-4726(in Chinese).
[24] de SANTIS BRAGA E, BERBEL G B B, CHIOZZINI V G, et al. Dissolved organic nutrients (C, N, P) in seawater on the continental shelf in the Southwestern South Atlantic with emphasis State Marine Park of Laje de Santos (SMPLS) - São Paulo - Brazil [J]. Brazilian Journal of Oceanography, 2017, 65(4): 614-627. doi: 10.1590/s1679-87592017136506504 [25] 安敏, 文威, 孙淑娟, 等. pH和盐度对海河干流表层沉积物吸附解吸磷(P)的影响 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(12): 2616-2622. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.12.021 AN M, WEN W, SUN S J, et al. Effects of pH and salinity on phosphorus sorption and desorption in the surface sediments of the mainstream of the Haihe River [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(12): 2616-2622(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2009.12.021
[26] LIU Q, HU X J, JIANG J L, et al. Comparison of the water quality of the surface microlayer and subsurface water in the Guangzhou segment of the Pearl River, China [J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2014, 24(3): 475-491. doi: 10.1007/s11442-014-1101-7 [27] 谷文艳, 陈洪涛, 姚庆祯, 等. 黄河下游溶解态营养盐季节变化及入海通量研究 [J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(3): 74-79,86. GU W Y, CHEN H T, YAO Q Z, et al. Seasonal variation and fluxes of dissolved nutrients in the lower reaches of the Huanghe [J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(3): 74-79,86(in Chinese).
[28] 江涛, 俞志明, 宋秀贤, 等. 长江水体溶解态无机氮和磷现状及长期变化特点 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2012, 43(6): 1067-1075. JIANG T, YU Z M, SONG X X, et al. Analysis of distribution, flux and long-term variations of dissolved inorganic nitrogen and phosphate in the Changjiang River [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2012, 43(6): 1067-1075(in Chinese).
[29] LI R H, LIU S M, ZHANG G L, et al. Biogeochemistry of nutrients in an estuary affected by human activities: The Wanquan River estuary, eastern Hainan Island, China [J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2013, 57: 18-31. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2012.02.013 [30] ALTANSUKH O, WHITEHEAD P, BROMLEY J. Spatial patterns and temporal trends in the water quality of the Tuul River in Mongolia [J]. Energy and Environment Research, 2012, 2(1): 62-78. [31] JHA P K, MASAO M. Factors affecting nutrient concentration and stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratio of particulate organic matter in the Ishikari River system, Japan [J]. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2013, 224(5): 1-23. [32] 高翔, 蒙海涛, 易晓娟. 天津市主要水体的氮污染特征分析 [J]. 中国给水排水, 2011, 27(15): 51-55. GAO X, MENG H T, YI X J. Analysis of nitrogen pollution characteristics in water bodies of Tianjin [J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2011, 27(15): 51-55(in Chinese).
[33] WANG S J, LU A G, DANG S H, et al. Ammonium nitrogen concentration in the Weihe River, central China during 2005-2015 [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(6): 512. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-5224-7 [34] 谭路, 蔡庆华, 徐耀阳, 等. 三峡水库175m水位试验性蓄水后春季富营养化状态调查及比较 [J]. 湿地科学, 2010, 8(4): 331-338. TAN L, CAI Q H, XU Y Y, et al. Survey of spring eutrophication status after 175 m experimental impoundment of Three Gorges reservoir and comparison [J]. Wetland Science, 2010, 8(4): 331-338(in Chinese).
[35] KOWALCZYK A, SMOROŃ S, KOPACZ M. Influence of runoff of suspended solids on quality of surface water: Case study of the Szreniawa River [J]. Journal of Water and Land Development, 2019, 41(1): 83-90. doi: 10.2478/jwld-2019-0031 [36] 刘小涯, 潘建明, 张海生, 等. 南海海水中DO的平面、垂直分布以及海-气交换通量 [J]. 海洋学研究, 2005, 23(4): 41-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2005.04.007 LIU X Y, PAN J M, ZHANG H S, et al. Horizontal and vertical distributions of DO content and its flux of ocean-atmosphere exchange in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2005, 23(4): 41-48(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2005.04.007
[37] 曹承进, 秦延文, 郑丙辉, 等. 三峡水库主要入库河流磷营养盐特征及其来源分析 [J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(2): 2310-2315. CAO C J, QIN Y W, ZHENG B H, et al. Analysis of phosphorus distribution characters and their sources of the major input rivers of Three Gorges reservoir [J]. Environmental Science, 2008, 29(2): 2310-2315(in Chinese).
[38] GUILDFORD S J, HECKY R E. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? [J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2000, 45(6): 1213-1223. doi: 10.4319/lo.2000.45.6.1213 [39] 凌娟, 张燕英, 董俊德, 等. 三亚湾珊瑚礁海域蓝藻群落组成的空间分布特征及其与环境因子的关系 [J]. 科学通报, 2013, 58(17): 1610-1619. doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-17-1610 LING J, ZHANG Y Y, DONG J D, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of cyanobacteria community in coral reef area of Sanya Bay and its relationship with environmental factors [J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(17): 1610-1619(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2013-58-17-1610
[40] 李由明, 刘明, 王平, 等. 旅游旺季三亚湾水体中磷营养盐含量的分析研究 [J]. 海洋信息, 2013(3): 35-37. LI Y M, LIU M, WANG P, et al. Analysis and study on the content of phosphorus nutrients in Sanya Bay in peak tourist season [J]. Marine Information, 2013(3): 35-37(in Chinese).
[41] 孙文凭, 徐继荣, 殷建平, 等. 三亚河与三亚湾溶存N2O分布特征与影响因素研究 [J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(2): 266-273. SUN W P, XU J R, YIN J P, et al. N2O distribution and mediating factors in Sanya River and Sanya Bay [J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(2): 266-273(in Chinese).
[42] 劳齐斌, 刘国强, 申友利, 等. 北部湾入海河流营养盐的分布特征及入海通量研究 [J]. 海洋学报, 2020, 42(12): 93-100. LAO Q B, LIU G Q, SHEN Y L, et al. Distribution characteristics and fluxes of nutrients in the rivers of the Beibu Gulf [J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2020, 42(12): 93-100(in Chinese).
[43] 王汉奎, 董俊德, 王友绍, 等. 三亚湾近3年营养盐含量变化及其输送量的估算 [J]. 热带海洋学报, 2005, 24(5): 90-95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.05.011 WANG H K, DONG J D, WANG Y S, et al. Variations of nutrient contents and their transportation estimate at Sanya Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2005, 24(5): 90-95(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2005.05.011
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 吴喆,余春瑰,刘美璇,李翀,段高旗,彭剑峰,李艳红. 典型热带近海河流微生物群落结构特征及其碳氮磷循环特征与机制. 环境科学学报. 2025(01): 201-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-















 下载:
下载: