-
雨水作为非常规水资源,其开发和利用对缓解城市化发展过程中带来的水资源短缺问题具有重要的战略地位。2012年我国提出“海绵城市”理念,旨在提升城市生态系统功能和降低洪涝灾害风险的同时,优先将雨水资源进行就地消纳和利用[1-2]。然而,据《2021中国水资源公报》显示,统计年我国非常规水资源利用量为138.3亿m3,仅占年供水总量的2.3%,其中雨水资源的开发利用率极低[3]。如何提高雨水储用效率,规范雨水利用模式成为雨水战略实施的关键。道路作为汇入市政管网前的末端集水空间受人为活动的干扰较大,同时与城市功能的正常运转密切相关,因此道路径流的安全泄放尤为关键。屋面空间占城市硬质下垫面近2/3,且受人类活动影响较小,其在水质与水量方面具有独特的储用优势[4-6]。传统的城市灰色储水设施主要担负地表径流洪峰削减的功能。除此之外,初期冲刷携带的高浓度污染负荷在储水系统中累积,直接影响回用水质[7-8]。因此,开发面向屋面径流接续储用的新型雨水系统是城市雨水战略实施和雨水资源高质量回用的主要方向。
本研究从水质和水量两个方面对现有屋面雨水储用现状进行了分析和讨论,尝试构建雨水原位储用系统,采用Fluent软件对该系统内部流态和接续污染归趋进行实态模拟,基于模拟结果构建了一种原位新型雨水储用系统,可有效净化初期雨水污染,实现雨水资源高质量回用。
-
雨水径流中污染物浓度峰值常常出现在径流初期。车伍等[9]和王倩等[10]研究发现初期雨水中含有大量悬浮固体(如SS)、耗氧污染物(如COD、BOD)、营养物(如N、P)和重金属等,可生化性较差,将其弃流进入河道会造成受纳水体水质恶化,进入污水收集管网势必会降低污水处理效能。传统储水系统用于水质质量控制的辅助设备主要为初期雨水分流器、碎屑筛和过滤器。其中,分流器作用是将初期径流导流,大幅度降低污染物质在系统中的富集,进而提高回用水水质并延长储水周期。然而,由于初期冲刷的随机性、多变性和复杂性,针对高污染负荷初期雨水的导流量核算目前仍存在争议[11-12]。目前,人们主要通过降雨历时、降雨深度两种方法表征初期雨水阶段,但降雨强度和下垫面的差异性导致初期雨水阶段定量应以降低径流污染物负荷到一定当量为宜[13]。碎屑筛和过滤器主要用于拦截固体(沉积物、碎屑、树叶等)和颗粒态物质防止其进入储水系统[14]。传统储水系统由于单一的箱结构形式,污染物自然沉降累积在储水系统底部,不仅不利于排泥和运维管理,同时在接续降雨过程中水力扰动和卷携会使沉积污染物二次弥散在储水系统中,导致水质恶化。除此之外,类比对雨水窖水质演变过程的研究,认为长期储存过程中存在水质恶化甚至腐败的风险[15]。而目前对于储水过程中的水质恶化和净化相关研究鲜有报道,同时缺乏以具体回用用途为导向的雨水水质标准作为参考和指导。
-
储水规模是雨水资源回用过程中的关键参数,直接影响到投资成本、占地空间、储水水量以及供水规模,甚至影响储水水质[16]。同时,它也是基于多个变量平衡而确定。目前针对雨水储水系统规模主要是通过建模进行多目标优化设计。由于降雨和需水量在时间上是可变的,储水系统评估模型经常被用作一种设计工具,用于计算平衡流入和流出所需的储水量,从而充分满足特定建筑物或地点的用水需求[17]。储水系统的规模设计主要包括经验设计、随机分析和接续储用下的连续物质平衡模拟。典型的连续物质平衡模型包含4个模块[18]:(1)用水需求分析模块;(2)雨水流入模块;(3)物质平衡计算模块;(4)输出模块。研究表明,引入环境目标可能会对水箱尺寸产生重大影响,这取决于安装储水系统的建筑物类型[19]。除此之外,储水过程中系统的接续空间与多次进水规模的优化平衡是在保障储水水质的基础上提高储用效率的主要研究方向。
-
为了保障和提升雨水储水系统的水质,尝试优化传统雨水储水系统结构并分隔构建沉淀区和澄清区,通过Fluent软件模拟,进一步识别降雨过程尤其是携带大量污染的初期雨水接续储水的水质扰动,掌握污染物质接续扩散的水力学特性。
-
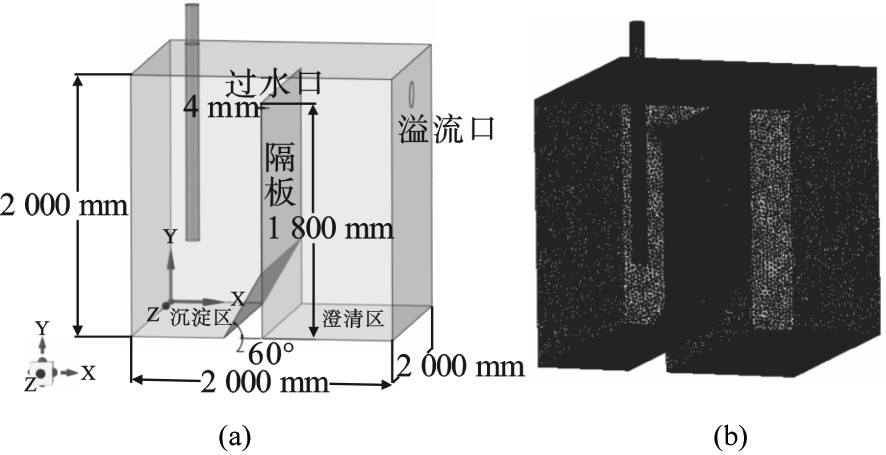
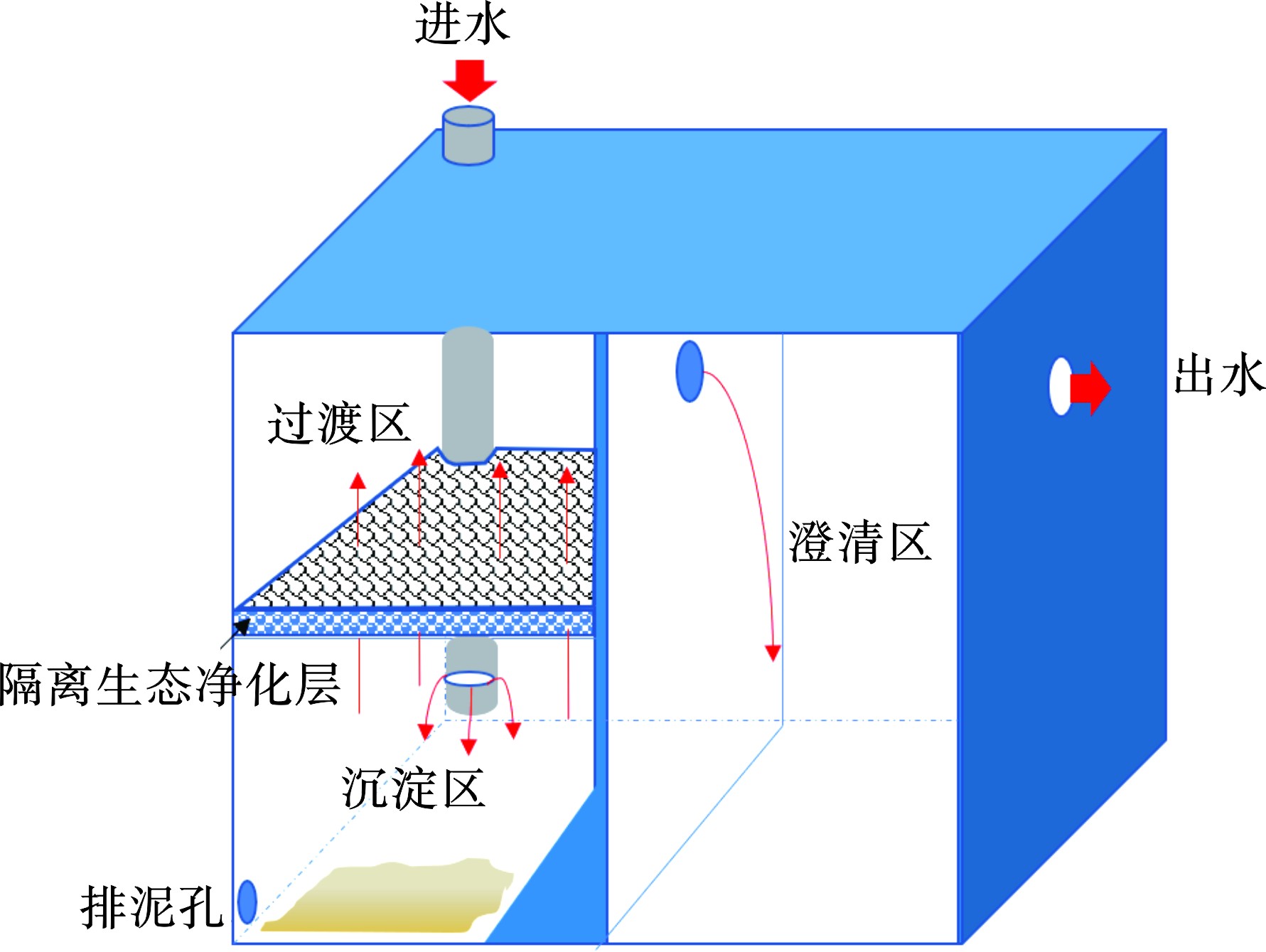
基于Space claim建立箱体物理模型,长宽高均设置为2 m,由高1.8 m、厚4 mm的隔板分成沉淀区与澄清区。沉淀区设置60°斜板,进水管直径为DN110,见图1(a)。三维计算区域采用Workbench meshing进行网格划分,见图1(b),并对进水管、进出口及挡板处进行网格加密处理,共计网格单元2 601 249个。
本研究借助稳态与瞬态Eulerian固-液两相流混合模型分别模拟单场次降雨及雨水接续扰动过程。降雨过程采用SST k-ω湍流模型求解,静置时黏性模型选用层流,且均使用Simple压力速度耦合算法,其中压力差值设置为Body Force Weighted。动量、湍流动能和比耗散速率均设置为Second Order Upwind,其亚松弛因子分别为0.3、0.5和0.5。水为第一相且各项参数采用系统默认设置,固体颗粒为第二相。以SS作为固体颗粒物模拟对象,并参考西安市屋面初期径流污染特征及Dufresne数据,设置SS浓度:440 mg/L;密度:1 100 kg/m3;平均粒径:0.1 mm;黏性系数:2.001×10−2,并换算出固体颗粒体积分数0.04%[20-21]。以SS浓度和速度为0作为初始状态,设置速度入口和压力出口(出口压力为1个标准大气压)边界条件,固体壁面边界条件设置为无滑移壁面。
采用式(1~2)对SS在沉积区与澄清区的分布特征进行计算[22]:
式中:
η1 为沉淀区对SS的沉积率,%;η2 为箱体对SS的截留率,%;ϕ1 、ϕ2 、ϕ3 分别为进口、过水口、溢流口处SS的体积分数,%。 -
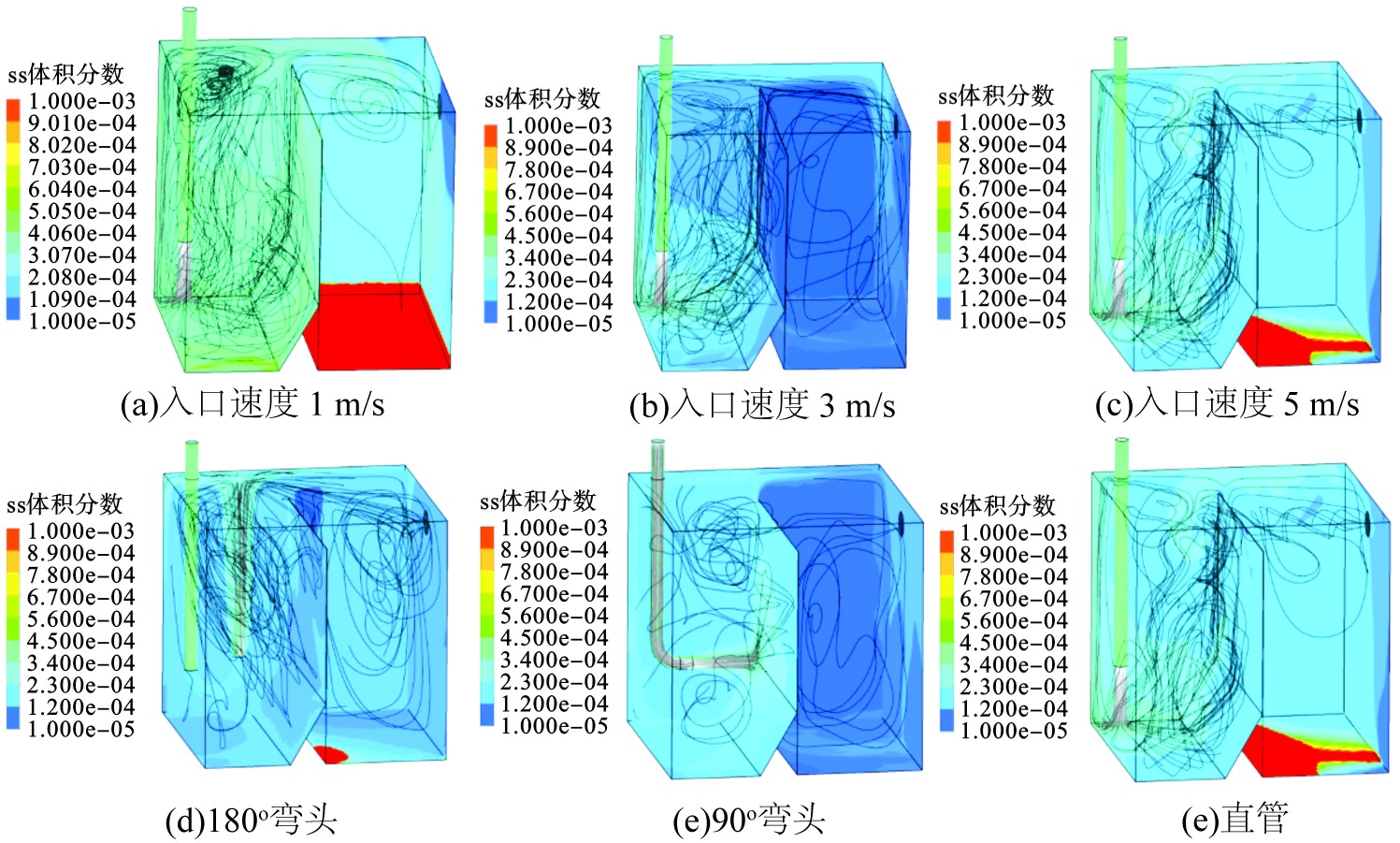
通过调控系统进水速率(1、3、5 m/s)以及进水管出口角度(0°、90°、180°)分别模拟单场次降雨条件下储水系统的水力特性以及SS归趋特性,模拟结果见图2。同时,根据模拟结果计算出调控条件下SS归趋分布与污染物截留率,见表1。
结果显示,单场次降雨过程中其他参数不变的情况下,增大进水管弯头角度或降低进水速率有利于SS在储水系统中沉积。沉淀区对SS的沉积率在入口速度3 m/s时最佳,见图2(b),而相同进水速率下,带有180°弯头进水条件下的沉淀区的沉积率最高,见图2(e)。直管条件下,入口速度5 m/s时,沉淀区靠近挡板处紊动程度较大,越过挡板后大部分SS直接被卷携带出,只有少部分沉积到底面;1 m/s时,沉淀区整体紊动程度较大而澄清区仅上端形成较小涡流,易于SS沉降;而3 m/s时,沉淀区紊动程度大小介于其他两状态之间,但在澄清区形成大涡流导致SS沉降困难。相同速度下,增加弯头易于SS沉积,见图2(f),180°弯头下紊动区域集中在后端及水管出口处,且沿澄清区溢流口附近形成的较大涡流易扰动并带出底部中后端沉积的SS,而在90°弯头澄清区扰动范围较大,但携带出的SS较少。
-
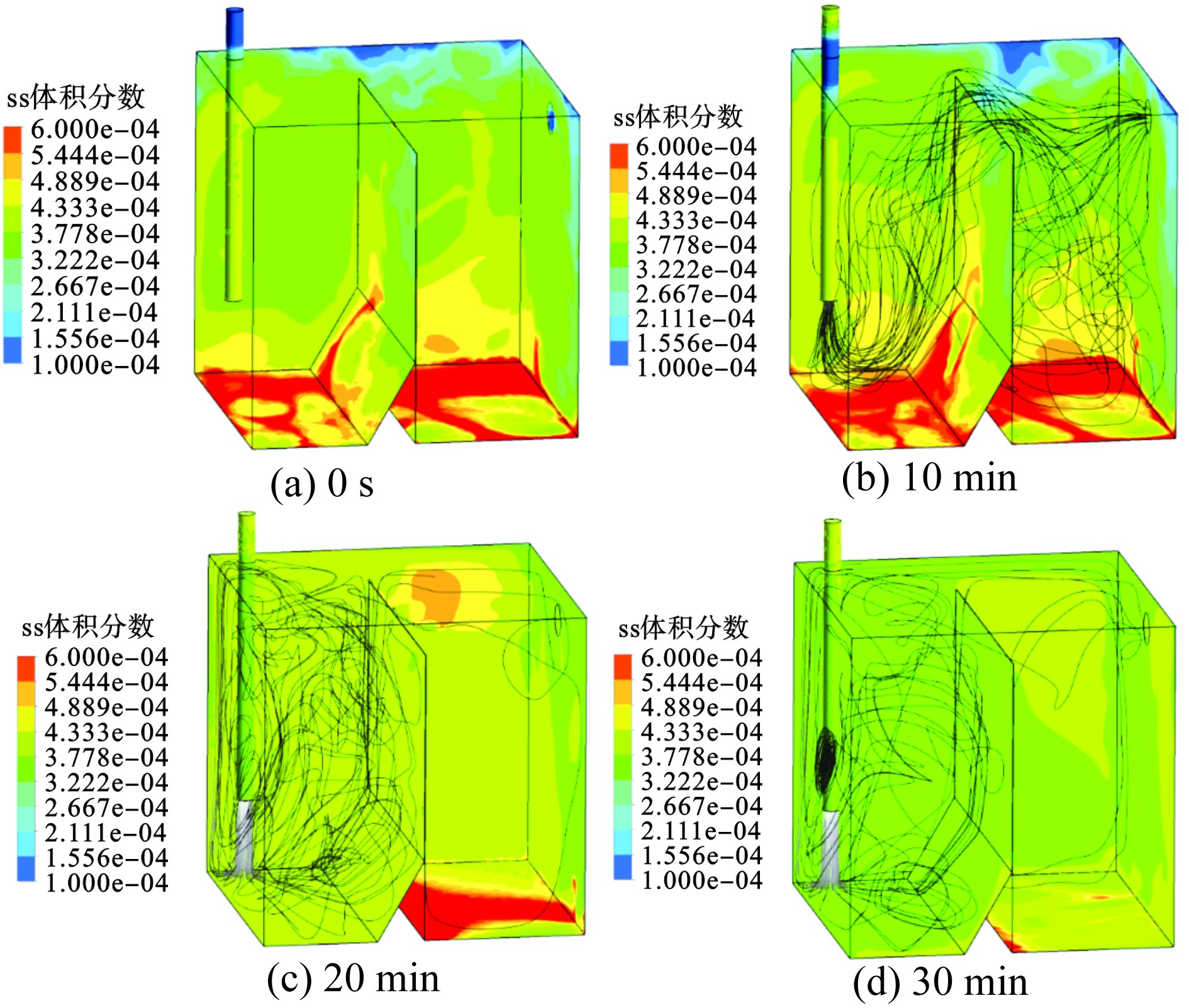
基于fluent软件模拟降雨事件对储水系统的扰动过程,设置时长30 min的降雨事件,待降雨结束,静置10 min后模拟二次降雨事件,系统接续进水30 min,见图3。同时,根据模拟结果计算出SS归趋分布与污染物截留率,见表2。
图3可知,接续进水对系统沉淀区已沉积的SS产生扰动并卷携带入澄清区,影响澄清区水质。系统在初次进水事件结束并静置10 min后的污染物分布见图3(a)所示,沉淀区与澄清区均有SS沉积。接续进水10 min后,沉淀区已沉积SS发生扰动,并有进入澄清区的趋势,见图3(b)。进水20 min后,紊动范围集中在沉淀区后部及澄清区前部,因此沉淀区前端及澄清区后端沉积大量SS。在进水30 min后,由于持续的SS溢流,系统沉淀区和澄清区的沉积态SS均有所减少。
-
基于以上模拟结果发现,储水系统内部分区有利于污染物物理沉淀和自然澄清,但接续雨水会扰动已沉淀污染物卷携并产生二次污染。研究表明,颗粒态物质(如SS)在径流过程中是其他污染物质(如溶解态物质)的良好载体[23]。因此,基于颗粒态物质的重力沉降以及物理截留效果,试图进一步强化储水系统污染物质截留、富集以及生物净化功能。尝试通过分隔并营造沉淀区、过渡区和澄清区实现净化与储水双重功效,同时可降低接续扰动对净化水质的影响。基于此,创新性提出系统加载隔离生态净化层的思路,研发了新型屋面雨水接续储用系统。
-
为了进一步研究新型屋面雨水接续储用系统的净化效果,本研究选取西安建筑科技大学雁塔校区建筑外立面落水管,其汇水面积约100 m2,匹配屋面雨水接续储用系统容积为1 m3。储水系统左右分腔容积比1∶1,左侧0.5 m处设置隔离生态净化层,净化层厚度设置8 cm,由双层过滤棉加裹5 cm砾石(8 mm)组成,采用轻质不锈钢框架固定在系统中,见图4。
-
为保证实验结果的可靠性,本研究选取2023年3月27日、4月2日、4月13日和4月21日4场降雨事件的初期雨水作为装置进水进行平行实验。采集新型储水系统装置进出水水样并放置4 ℃下保存,同时进行样品预处理和相关指标的测定,测定指标包括TN、COD、NH3-N和SS。具体的分析方法见表3。数据采用Origin软件进行处理和分析。
-
新型储水系统对屋面初期雨水的净化效果见图5。进水水质COD、SS、TN和NH3-N的浓度范围分别为80~120 mg/L、55~90 mg/L、16~21 mg/L和9~17 mg/L,出水浓度分别为30~45 mg/L、4~8.5 mg/L、6~11 mg/L和4~9 mg/L,平均去除率分别为64.4%、91.2%、52.7%和49.6%。新型储水系统对SS的净化效率高达90%以上,其在对颗粒态污染物质高效富集的过程中实现部分溶解态物质同步去除。经核算,强化隔离生态净化层耦合重力沉降作用可有效截留初期雨水中60%以上的污染负荷,大大降低回用水水质恶化风险,保障回用水其水质稳定。依据《城市污水再生利用-景观环境用水水质:GB/T 18921—2019》、《城市污水再生利用-城市杂用水水质:GB/T 18920—2020》和《城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准:GB 18918—2002》一级A标准,新型储水系统净化后水质均达到排放至地表水体或景观、杂用水回用标准(图中虚线表示)。
-
(1)在优化传统雨水储水系统结构并分隔构建为沉淀区和澄清区,并基于Fluent软件进行固-液两相流的模拟结果中发现,单场次降雨过程中,直管进水或降低进水速率有利于颗粒态物质在储水系统中沉积。沉淀区对颗粒态物质的沉积率在进水速率为3 m/s时最佳,而相同进水速率下,带有180°弯头进水条件下沉淀区的沉积率最高。
(2)接续进水对储水系统已沉积污染物扰动影响较大,易产生二次污染。同时在持续的接续进水扰动作用下,优化分区后的储水系统沉淀区污染物被卷携进入澄清区,并有持续溢流污染的趋势。
(3)通过设置隔离生态净化层的新型储水系统对SS的净化效率高达90%以上,其在对颗粒态污染物质高效富集的过程中实现部分溶解态物质同步去除。经核算,强化隔离生态净化层耦合重力沉降作用可有效截留初期雨水中60%以上的污染负荷,大大降低雨水水质恶化风险,保障回用水质稳定。
屋面雨水原位接续储用系统研发与应用
Development and application of in-situ continuous roof runoff storage system
-
摘要: 屋面雨水储用的水质保障是雨水资源高质量回用的关键。传统储水系统由于结构性缺陷和污染物质接续扩散的影响,导致储水水质不佳。该研究采用Fluent软件,通过改变进水水力条件和系统结构,模拟和识别了储水系统接续过程中的污染物质归趋;创新性提出增设隔离生态净化层,构建基于沉淀区、过渡区和澄清区的新型屋面雨水原位接续储用系统;通过4场降雨的原位净化效果研究,结果表明该新型储水系统净化效果极佳,水质稳定达到城市杂用及景观水回用标准,可作为屋面雨水储用系统装备广泛使用。Abstract: The water quality guarantee of the roof rainwater storage is crucial for ensuring the high-quality reuse of rainwater resources. Traditional water storage systems suffer from poor water quality due to structural defects and the continuous diffusion of pollutants. Fluent software was used to simulate and identify the fate of pollutants during the connection process of the water storage system by altering the hydraulic conditions and system structure of the inlet water. A novel approach was proposed by adding an isolated ecological purification layer and constructing a new type of roof rainwater in-situ continuous storage system based on a sedimentation zone, transition zone, and clarification zone. Through the in-situ purification effect study of four rainfall events, the results showed that the new water storage system had excellent purification effect, and the water quality was stable and met the standards for urban miscellaneous and landscape water reuse. It could be widely adopted as the equipment for roof rainwater storage systems.
-
Key words:
- roof runoff /
- storage system /
- fluent /
- first flush /
- ecological purification
-
电镀工业是我国经济发达地区的重要加工行业,由于其在工业中适用性高,广泛分布于各个工业部门,电镀生产在耗费大量工艺用水的同时,也产生大量的电镀废水[1]。电镀废水具有重金属含量高、毒性大、污染物杂、环境危害严重等特点[2-4],属于难处理的工业废水。目前电镀废水的处理工艺主要采用物化预处理+生化处理+深度处理的组合工艺,涉及中水回用的主要采用膜分离技术[5],淡水回用于生产漂洗工段.常规的废水深度处理工艺不能彻底将其从水中去除,出水无法稳定达到电镀污染物排放标准(GB 21900-2008)的排放标准,开发高效的深度处理工艺已成为水处理领域的关注点。
臭氧氧化作为一种绿色处理工艺具有易操作、污染物去除效率高、无二次污染等优点已被广泛运用于饮用水和废水深度处理领域[6-9] 。由于臭氧氧化具有一定的选择性[10-11],研究人员开发了多相催化臭氧化技术克服了上述缺点,通过在臭氧氧化过程中加入非均相催化剂,使水中溶解性臭氧在催化剂表面发生链式反应产生羟基自由基(·OH)[12-13],从而提高水中有机物的去除率。
常见的非均相臭氧催化剂有金属氧化物(MnO2、FeOOH、TiO2等)[14-16]、多金属负载催化剂(RuO2/Al2O3、MnO2/Al2O3、TiO2/Al2O3等)[17-19]、矿物(Cu/堇青石、Mn/蜂窝陶瓷[20]等)和活性炭(MnOx/GAC[21]、多壁碳纳米管等)。目前工程项目中应用较广的催化剂多以球形陶瓷颗粒为载体负载多金属氧化物,常装填于固定床形式的反应器[22]内进行进行臭氧催化反应,但其传质效率低,水流易产生局部短流,影响臭氧催化氧化对水中有机物的去除效率。为了开发更为高效、稳定和经济的臭氧催化剂,研究人员除了在催化剂表面负载的活性组进行改进外,对催化剂的结构也进行了研究及优化。
基于陶瓷膜具有优异的化学性能,研究人员就臭氧预氧化+陶瓷膜工艺去除有机物和陶瓷膜改性催化臭氧氧化等开展了相关研究。2003年SCHLICHTER等[23]首次将臭氧氧化和陶瓷膜过滤相结合处理地表水和微污染原水,之后臭氧与陶瓷膜结合的相关研究开始逐渐增多。BYUN等[24]对陶瓷膜进行了改性,将氧化锰或氧化铁负载于陶瓷膜制备成催化膜,发现有机物的去除取决于陶瓷膜被金属氧化物纳米粒子包覆的类型,而且氧化锰膜的性能优于其他测试膜。我国对臭氧/陶瓷膜工艺的研究起步较晚,2011年清华大学的张锡辉课题组首先在国内使用臭氧预氧化/陶瓷膜组合工艺处理水中甲硫醚[25],此后该课题组使用该技术在饮用水处理、微污染水净化等领域的研究。
本研究以陶瓷膜为载体,采用浸渍-焙烧工艺制备了多组分臭氧催化过滤膜,实现了膜分离技术与催化臭氧氧化技术的同步耦合,利用陶瓷过滤膜的微米级孔道过滤废水,可实现污染物的定向移动,有效地促进了扩散传质,同时微米级孔道内部负载的催化剂,增大了催化模块的有效催化比表面积。利用XRD、SEM、DEX等技术对催化过滤膜进行了表征,并以电镀园区物化预处理后的混合废水为研究对象,考察催化过滤膜在常温下臭氧氧化过程中的催化活性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
陶瓷膜,购自江苏久吾高科技股份有限公司;La(NO3)3、Ce(NO3)3,均为分析纯,购自济宁天亿新材料有限公司;Mn(CH3COO)2、氢氧化钠、硝酸、浓硫酸、重铬酸钾,均为分析纯,购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 催化过滤膜的制备及表征
采用浸渍-焙烧法制备催化过滤膜:选用无机陶瓷膜作为催化过滤膜基体,用8%的氢氧化钠溶液浸泡,之后用质量百分比为13%的稀硝酸溶液浸渍1~2 h,再用去离子水洗净至出水中性后烘干备用;选用La(NO3)3、Ce(NO3)3和Mn(CH3COO)2作为催化剂活性组分的前驱物,配置不同质量比(La3+、Ce3+和Mn2+)的浸渍液,将烘干后的陶瓷膜在浸渍液中浸泡24 h后,在105 ℃真空烘4 h, 反复浸渍-烘干步骤5次;置于马弗炉中,在400~950 ℃条件下焙烧2~6 h即得陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜。
通过JEOL JSM-6480LV型扫描电镜(SEM)观察催化过滤膜的表面和断面形貌;催化过滤膜活性层的组成和晶体结构由电子能量色散X射线光谱(EDS)和X射线衍射(XRD, Bruker D8)进行表征,采用Cu Ka(λ=0.154 nm)辐射,扫描范围为10°~80°;利用干湿重量法测定催化过滤膜的孔隙率[26];测定陶瓷膜对不同尺寸聚苯乙烯微球的截留率,确定陶瓷膜的孔径大小[27]。
1.3 臭氧催化氧化化工园区废水的实验
1)目标废水水质。实验所用废水为常州某电镀园区物化预处理后的混合废水,用去离子水稀释4倍后用作实验废水。目前该园区共有28个电镀车间,32条生产线,镀种涉及镀镍、镀铜、镀铬、镀锌、镀银和镀金。稀释后的废水COD为135 mg·L−1,总镍为0.04 mg·L−1,总铬为0.09 mg·L−1,浊度为6 NTU,pH为7.8,废水中有机物主要来源于镀液中添加的稳定剂、络合剂和光亮剂,包含聚乙二醇、柠檬酸、十二烷基磺酸钠和未知名称含氮杂环类物质等。
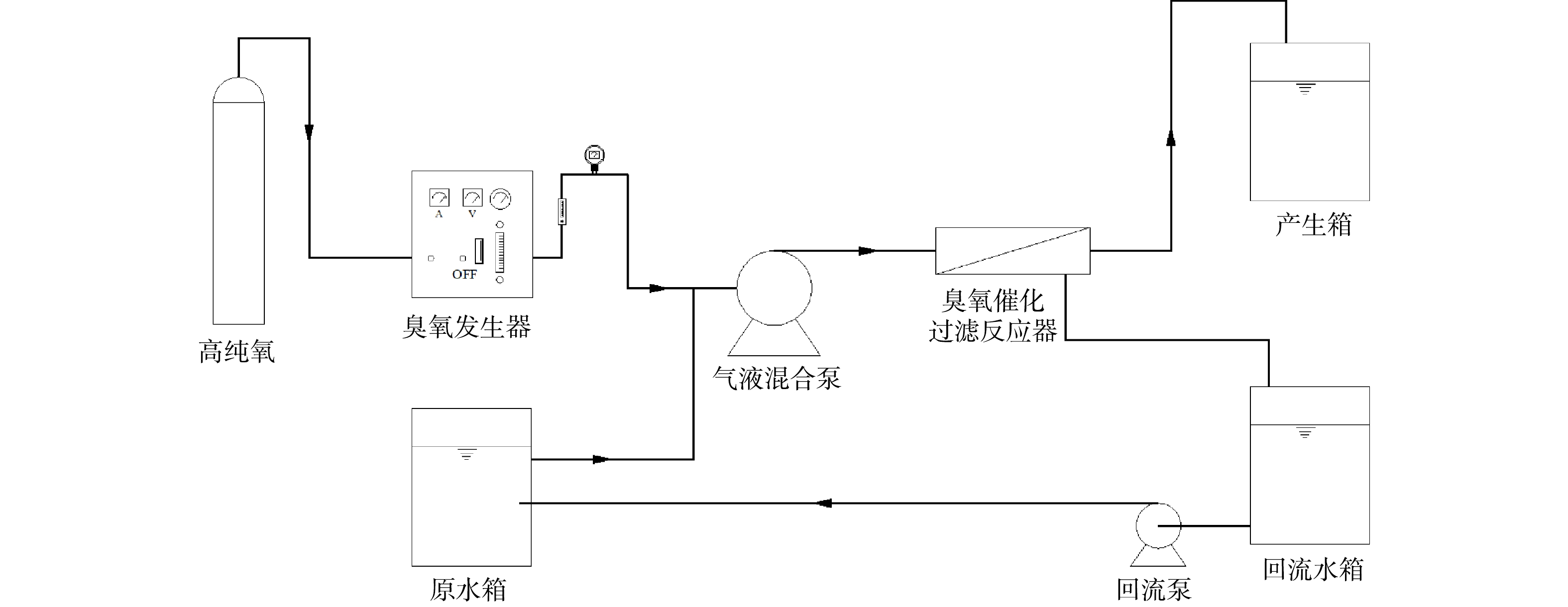
2)实验装置及运行参数。本实验所用装置如图1所示,实验在室温(25±2) °C下进行,实验装置处理规模为200 L·h−1,不锈钢材质。选用最优条件下制备得到的臭氧催化过滤膜处理废水,采用两支臭氧催化过滤膜并联的形式。通过控制臭氧投加量、回流比、跨膜压差、错流速率等反应条件,具体运行参数为:臭氧投加量1~5 mg·L−1;回流比90%;跨膜压差0.15 Mpa;错流速率1.0 m·s−1。观察废水COD降解情况考察催化剂的活性。
1.4 分析测试方法
COD采用重铬酸钾标准方法[28]测定;pH采用酸度计(pHB-2,上海雷磁仪器厂)测定;镍和铬浓度采用焰原子吸收分光光度法测定(GB/T5750.6-2006),所用仪器型号为(TAS-990MFG,北京普析通用仪器厂);浊度采用便携式浊度仪(2100P,HACH)测定。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 臭氧催化过滤膜制备工艺的优化
臭氧催化过滤膜的制备主要分为浸渍和焙烧2个主要步骤。笔者在前面的研究中发现催化剂的催化活性与浸渍液活性组分的配比、焙烧温度及焙烧时间有关[29]。本实验以电镀园区物化预处理出水进行一定比例稀释后的废水的COD去除率和臭氧催化过滤膜的膜通量为指标,对陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜的制备工艺进行了优化。
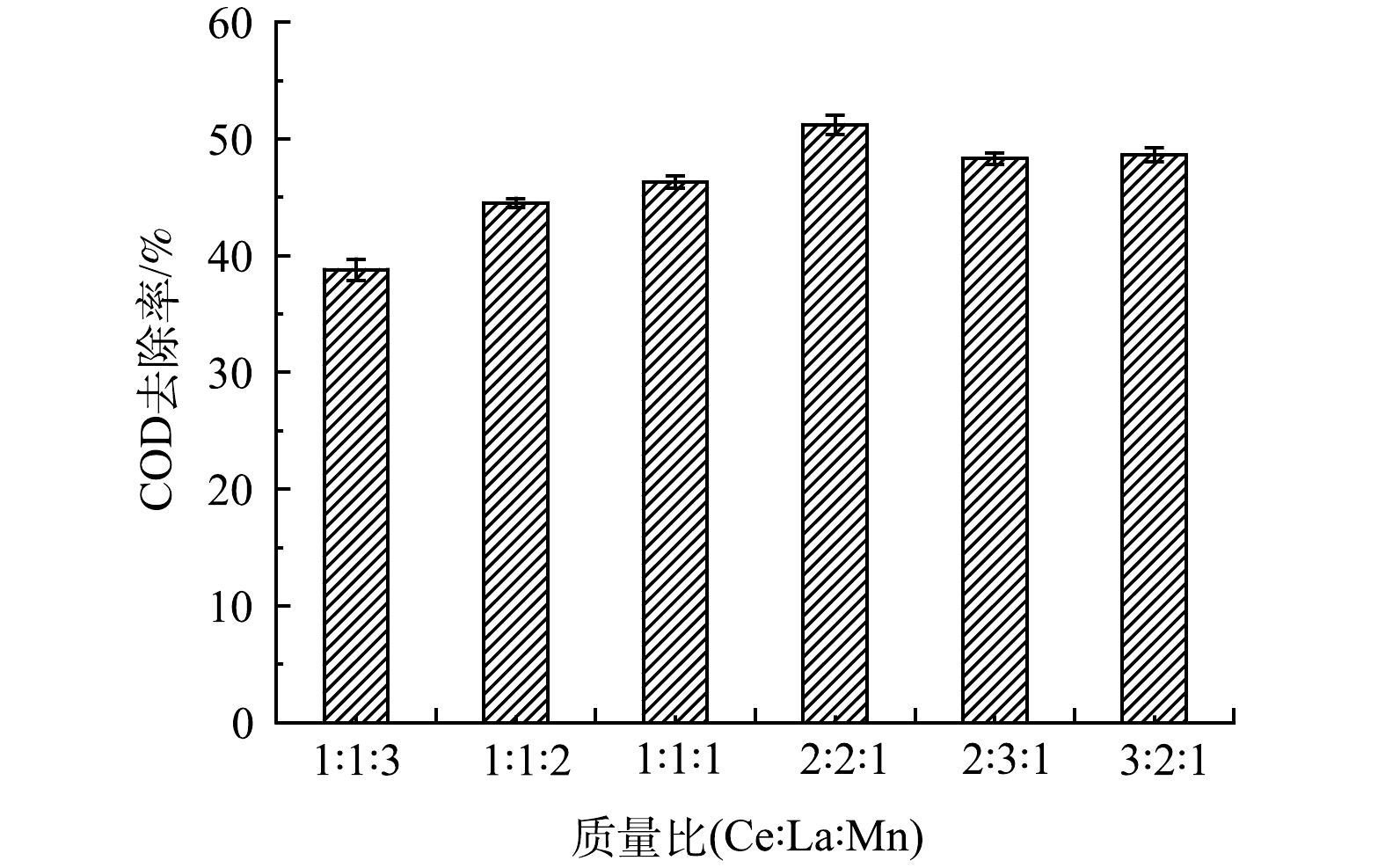
1)活性组分比例的影响。配制以活性组分La3+、Ce3+、Mn2+不同质量比的浸渍液,保持其他条件相同,煅烧温度为700 ℃,煅烧时间 3 h,制备陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜,以一定比例稀释后的电镀园区物化预处理出水为污染物,考察浸渍液中金属离子的质量比与COD去除率的关系,结果如图2所示。可见,随着La3+和Ce3+含量的增加,催化剂的催化活性随之增加,在Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比到2:2:1,COD的去除率最高。一方面由于随着浸渍液中硝酸铈浓度的增加,煅烧后CeO2的结构更加有规律,晶核更成熟,镧作为同系元素性状与铈类似。另一方面,有研究[30-31]表明,金属氧化物的催化活性由高到低依次为La2O3>CeO2>MnO2。
但当浸渍液中Ce3+和La3+的比例进一步增加时,催化效率反而有所下降,一方面随着浓度的增加,催化活性物质的晶核增大,比表面积减小,不利于增加催化反应活性;另一方面由于尾水中特征有机污染物种类较多,MnO2对部分有机污染物的催化效果明显。因此,将浸渍液中金属离子Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比确定为2:2:1。
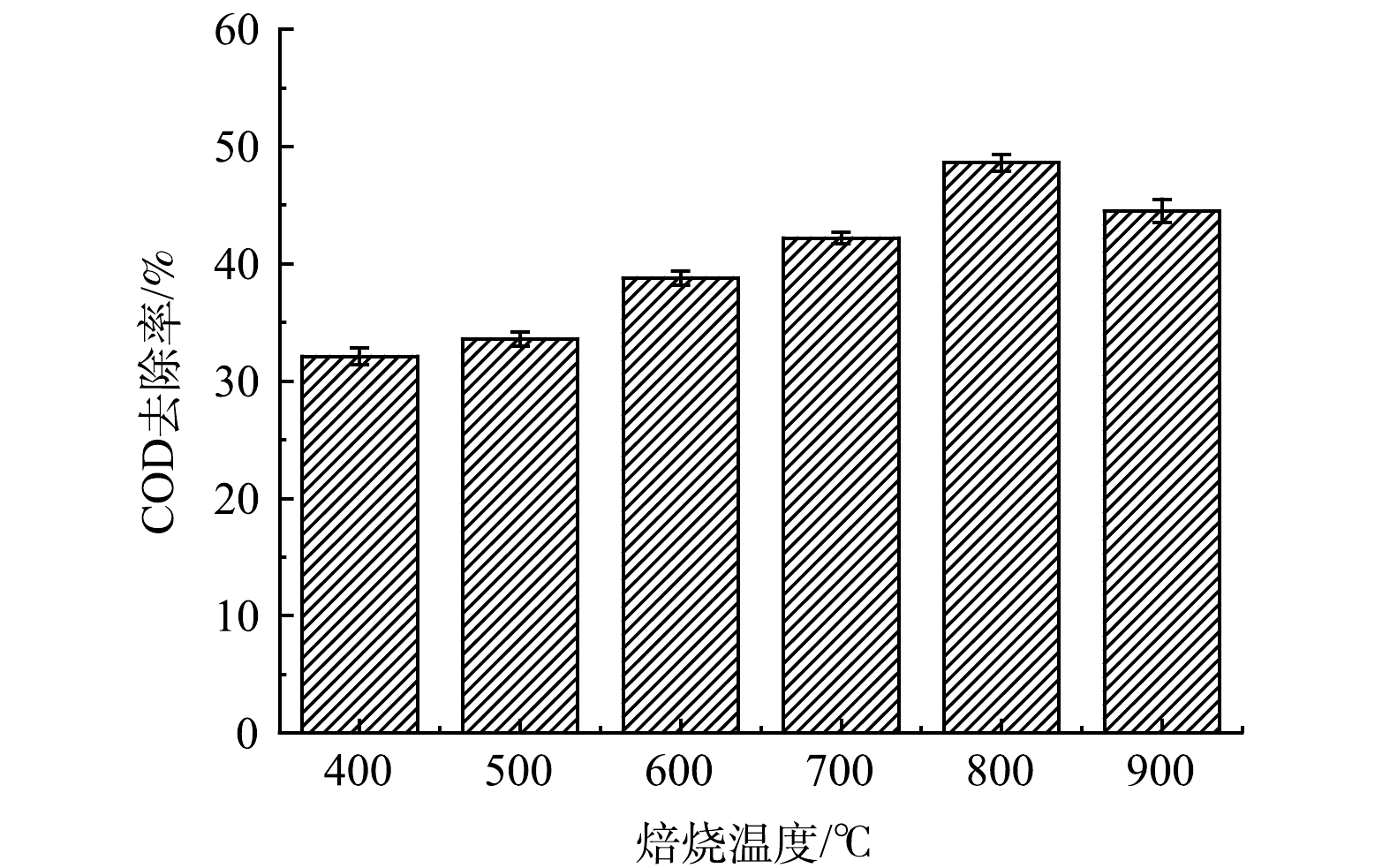
2)焙烧温度的影响。选择适宜的焙烧温度是臭氧催化过滤膜制备中的关键步骤。在浸渍液活性组分Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比为2:2:1,煅烧时间3 h的条件下,不同焙烧温度下制得的臭氧催化过滤膜在臭氧催化氧化下对废水COD的降解影响如图3所示。由图3可知,随着温度的逐渐升高,催化剂的催化活性先升高后呈现下降趋势。当焙烧温度为800 ℃时,陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜的催化活性最高。这是由于硝酸镧在500 ℃下焙烧得到的产物主要成分为La5O7NO3和La2CO5,在650 ℃下焙烧得到的产物主要是La2O3,还含有少量杂质,当温度达到780 ℃时焙烧产物均是纯度较高的La2O3。当焙烧温度低于500 ℃时,La2O3和CeO2催化剂尚未完全形成,且催化剂的结晶差,颗粒粒径小,催化剂活性低。随着焙烧温度升高,催化剂结晶逐渐变好,颗粒粒径变大,催化效果增强。900 ℃以上高温焙烧时,CeO2催化剂内部结构坍塌,活性位减少,催化剂活性降低。另一方面温度过高也容易导致催化剂烧结,使催化活性组分在载体表面团聚,降低催化剂的比表面和导致活性位点缺失,催化效率降低。因此,本实验中将催化剂的焙烧温度确定为800 ℃。
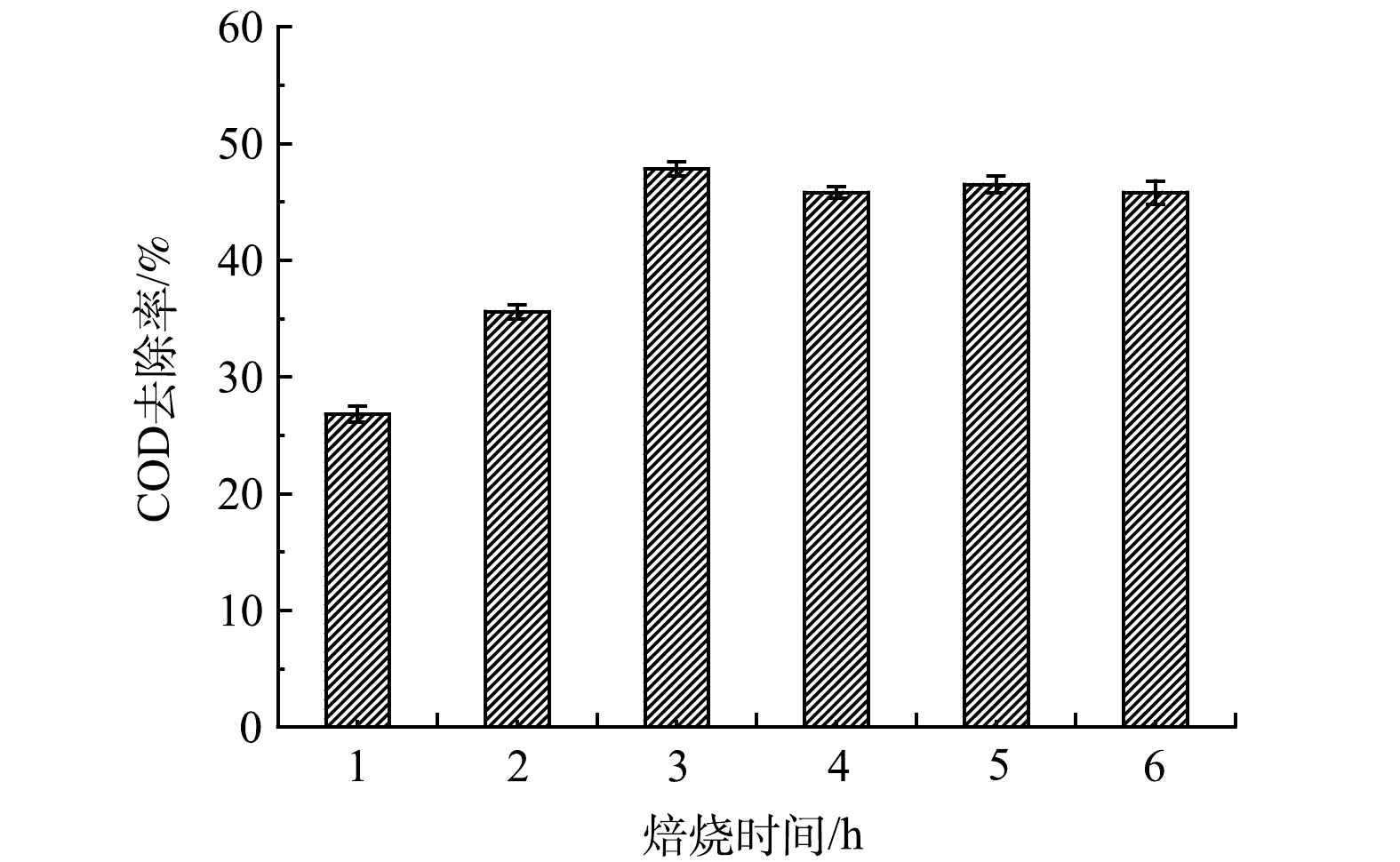
3)焙烧时间的影响。催化剂的焙烧时间对活性组分的前驱体能否转变成活性组分及最终催化剂活性有较大影响. 在浸渍液活性组分Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比为2:2:1条件下,分别在700 ℃下煅烧0.5、1、2、3、4、6 h制得的臭氧催化过滤膜在臭氧催化氧化下对废水COD的降解影响如图4所示。初始时催化剂的活性随着焙烧时间的延长而增加,当焙烧时间达到3 h时,催化剂的活性趋于稳定,当焙烧时间进一步增加至6 h后,催化效果反而出现小幅下降。因为焙烧时间较短时反应尚未全部完成,催化剂强度达不到要求,无法满足催化剂高温定型的要求,活性组分易出现粉末化;若焙烧时间过长,容易造成已形成的孔道结构塌陷,表面形貌改变,活性组分出现烧结或被掩蔽。因此,本实验中将陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜的最佳焙烧时间定为3 h。
根据以上的研究结果,将陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜的最佳制备条件确定为:将预处理后的无机陶瓷膜浸渍于含有La(NO3)3、Ce(NO3)3和Mn(CH3COO)2的溶液中,其中Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比为2:2:1。室温下浸渍24 h,然后在105 ℃真空烘4 h,反复浸渍-烘干步骤5次,在马弗炉中800 ℃条件下焙烧3 h,最后得到负载型金属氧化物臭氧催化剂。
2.2 催化过滤膜的表征
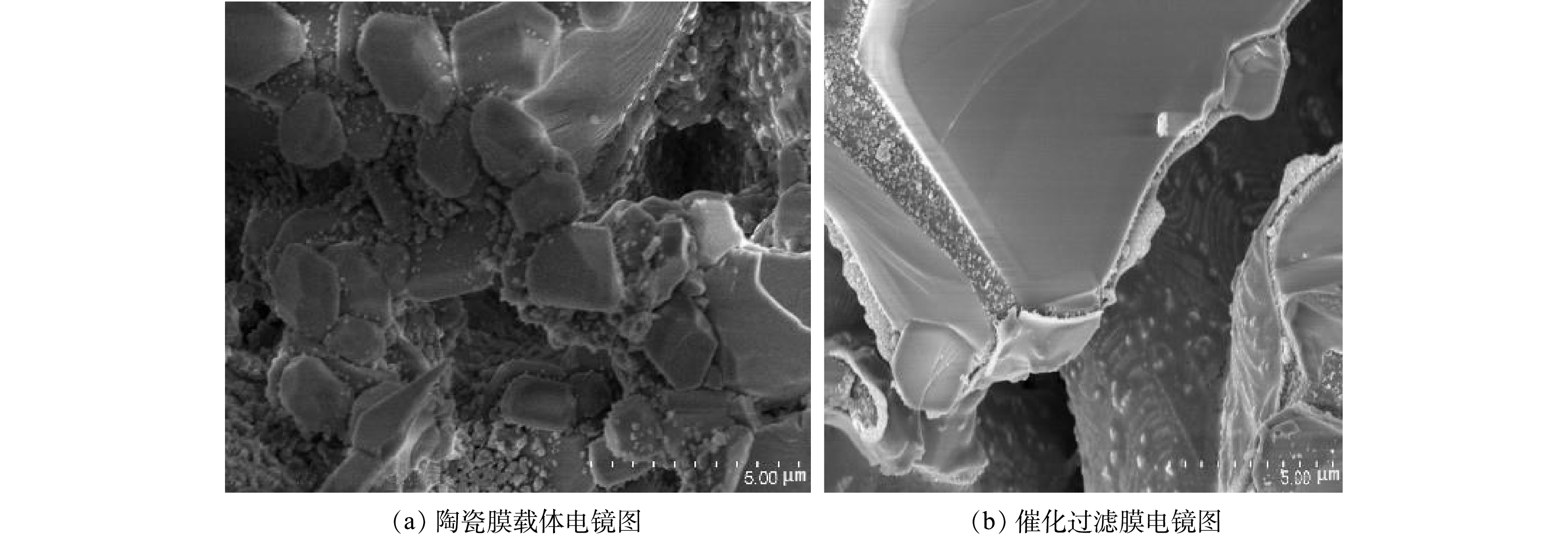
1) SEM和EDS测试结果。图5无机陶瓷膜载体及陶瓷负载型MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜的SEM图像。由图5(a)可以看出陶瓷膜表面呈疏松多孔结构,孔道彼此交错贯通,具有较大的比表面积孔体积,能提供较多的负载点位。图5(b)呈现了负载后催化过滤膜的形貌,可以明显看出在陶瓷膜表面和孔道内存在大量负载物,活性组分的晶粒大小匀称且分布均匀,未在表面发生团簇现象。
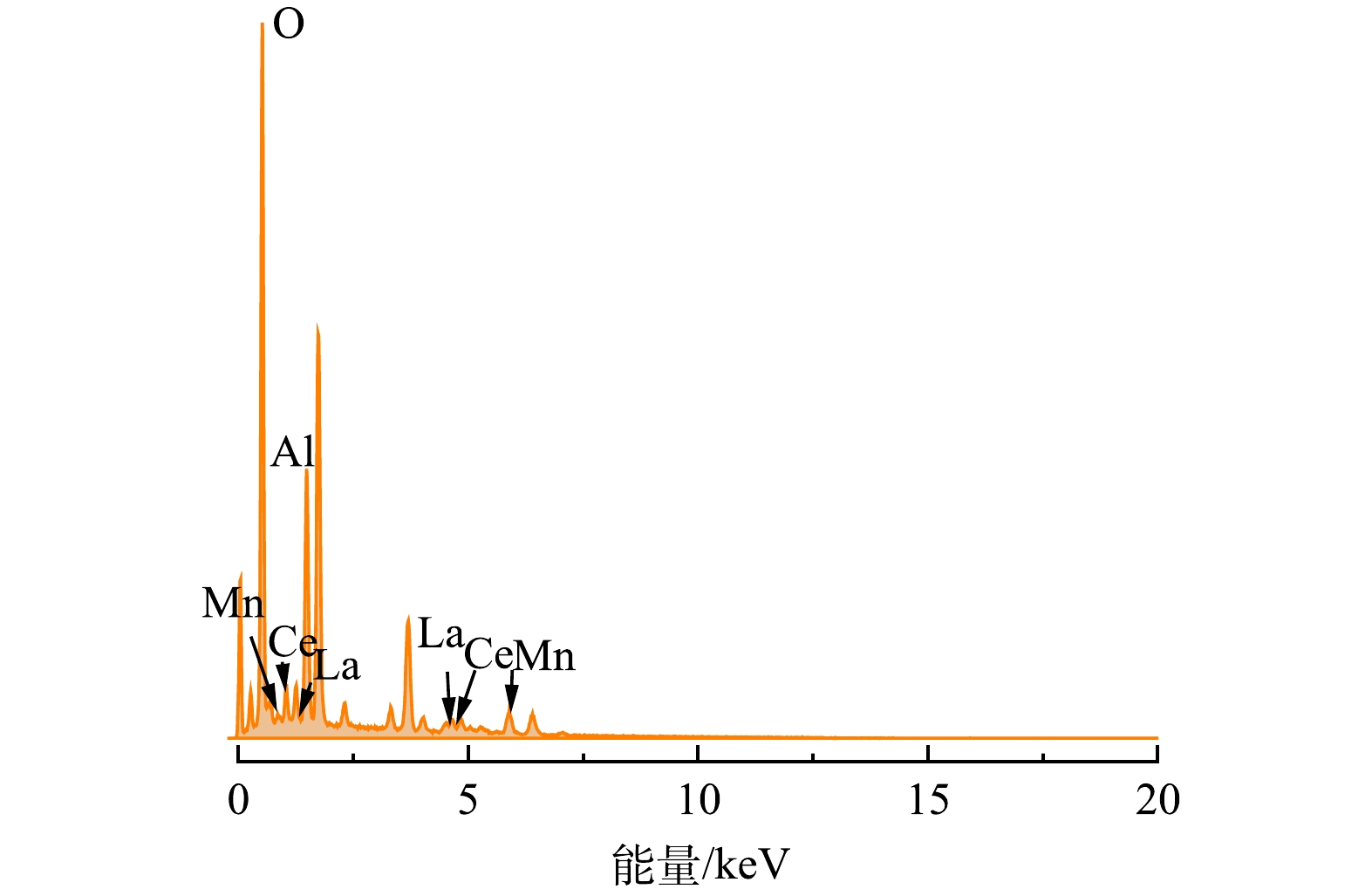
EDS通常被运用于分析物体表面涂层的元素组成。选取浸渍液的金属离子Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比为2:2:1,焙烧时间3 h,焙烧温度800 ℃的催化剂样品,进行EDS表征,结果如图6所示。由图6可知,陶瓷膜载体主要成分为Al2O3,载体经浸渍、高温煅烧后,催化剂表层的EDS谱图中增加了La、Ce和Mn的特征峰。结合表1可知,表层活性组分金属元素占总质量的11.85%,从而推测在催化剂的表层形成了Ti、Mn和Fe的金属氧化物,且活性组分负载率较高。
表 1 催化过滤膜各活性组分元素含量Table 1. Element content of active components of the catalytic ceramic filtration membranes元素 质量分数/% 原子分数/% O 48.07 65.11 Al 40.08 32.17 Mn 3.65 1.44 La 4.21 0.66 Ce 3.99 0.62 为进一步探究催化活性组分在陶瓷膜载体上孔道内的负载情况,分析了负载后的陶瓷膜截面元素分布情况。对陶瓷膜外部膜层的截面做了元素面分布图(EDS mapping)分析。由图7中可以清晰发现除了陶瓷膜基材元素Al和O外,Mn、La、Ce 3种元素在陶瓷膜孔道内呈现均匀分布。
2)催化过滤膜性能参数与分析。选用孔径为50 nm的陶瓷膜为载体,选取浸渍液的金属离子Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比为2:2:1,焙烧时间3 h,焙烧温度800 ℃的催化剂样品进行测试。负载前后膜孔径由原来的50 nm变为30 nm(表2),膜通量下降33%。这是因为经负载后,膜孔道被氧化生成的MnO2、CeO2和La2O3活性组分所占居,导致膜孔隙率和膜孔径的减少,从催化剂的SEM表征结果也可以证实这一点,膜通量的下降与孔径的下降有直接关系。负载后陶瓷膜的盐酸可溶率值为0.6%,说明了活性组分与陶瓷膜结合紧密,催化过滤膜稳定性强。
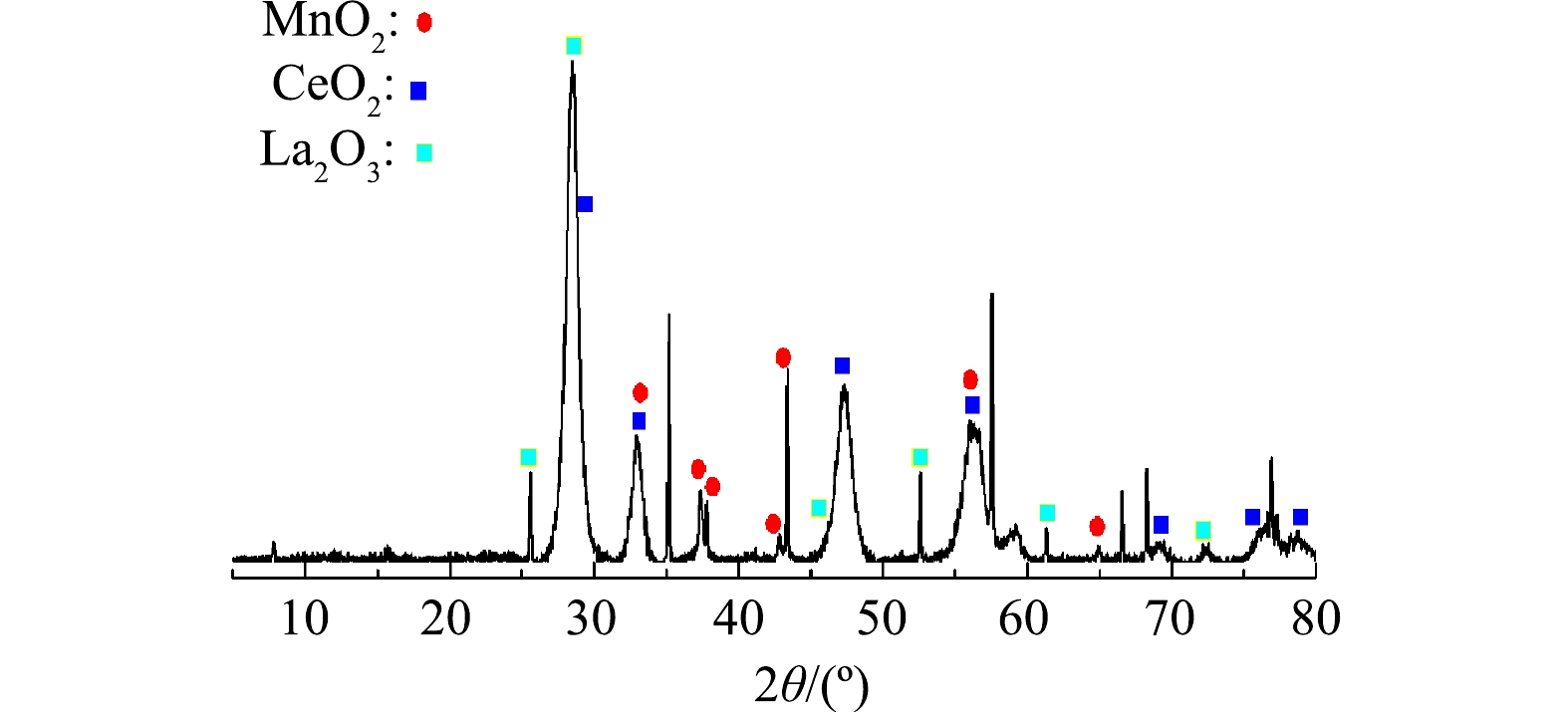
表 2 催化过滤膜的性能参数Table 2. Parameters of the catalytic ceramic filtration membranes陶瓷膜种类 孔隙率/% 孔径/nm 纯水通量/(L·(m2·h·Mpa)−1) 盐酸可溶率/% 陶瓷膜基体 33 50 2 000 — 负载后的陶瓷膜 26 30 1 260 0.6 3) XRD表征结果。将负载后的催化过滤膜表层和孔道内的活性组分刮下进行XRD分析,结果如图8所示。可见,对照JCPDS标准卡,所得物质主相为Al2O3、CeO2、La2O3、MnO2,所得产物粉体为灰色,在2θ=28.8°、33.1°、47.5°、56.8°、69.4°、76.7°、79.1°附近出现的吸收峰属于立方萤石晶相结构的CeO2。在2θ=26.1°、27.9°、46.1°、53.7°、62.2°、73.4°出现的次强峰属于六方晶型La2O3,在2θ=33.3°、36.9°、37.9°、42.8°、44.1°、56.4°、64.8°出现的次强峰属于四方晶系的α-MnO2,未发现其他晶型是由于反应时间延长可使δ-MnO2 向α-MnO2转化。在2θ=35.1°、57.9°、59.1°、66.7°等处出现的一些强峰主要为Al2O3。这是由于Al2O3基体陶瓷膜的主要成分。以上表征结果表明,通过浸渍、焙烧可有效地将CeO2、La2O3、MnO2活性组分负载于陶瓷膜表面及孔道内。
2.3 催化过滤膜的催化性能评估
1)催化过滤膜的催化活性。为了评估臭氧催化过滤膜的催化活性,将其与未负载的普通陶瓷膜进行对比实验,在臭氧投加量为5 mg·L−1,跨膜压差为0.15 MPa,回流比为90%的条件下进行实验,观察其膜通量变化和对水中COD的去除情况。
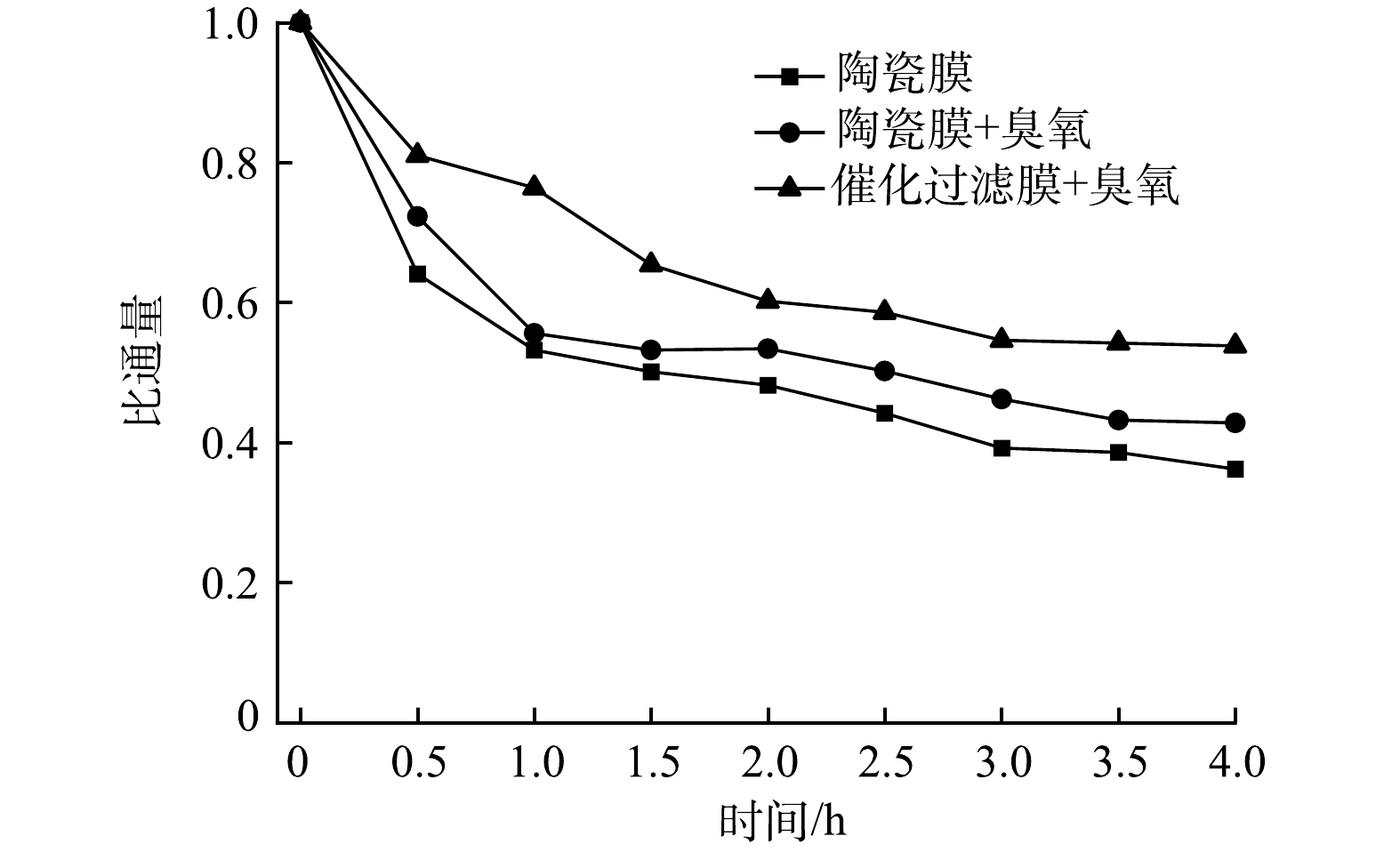
图9为膜通量的变化趋势。由图9可知,随着反应时间的增加,普通陶瓷膜和臭氧催化过滤膜的膜通量呈下降趋势,在臭氧条件下臭氧催化过滤膜的膜通量下降较为缓慢。经过4 h的分离后,在不投加臭氧的情况下,陶瓷膜的膜通量降低了63.8%;在臭氧条件下,普通陶瓷膜和臭氧催化过滤膜的膜通量分别降低了57.2%和46.2%,说明臭氧氧化可以缓解膜污染,同时在催化活性物质的作用下,膜污染的缓解作用更为明显。究其原因是上述反应为过滤和臭氧氧化反应的同步过程,在膜分离的过程中大部分有机物被截止在膜表面和孔道内,臭氧氧化可以降解膜表面的有机物,从而在一定程度上减缓膜污染。臭氧氧化具有一定的选择性[10],因而对膜污染的缓解效果不明显,而催化臭氧氧化产生的活性氧物种[32-33]能够无选择性的氧化有机物,从而更好地缓解膜污染。
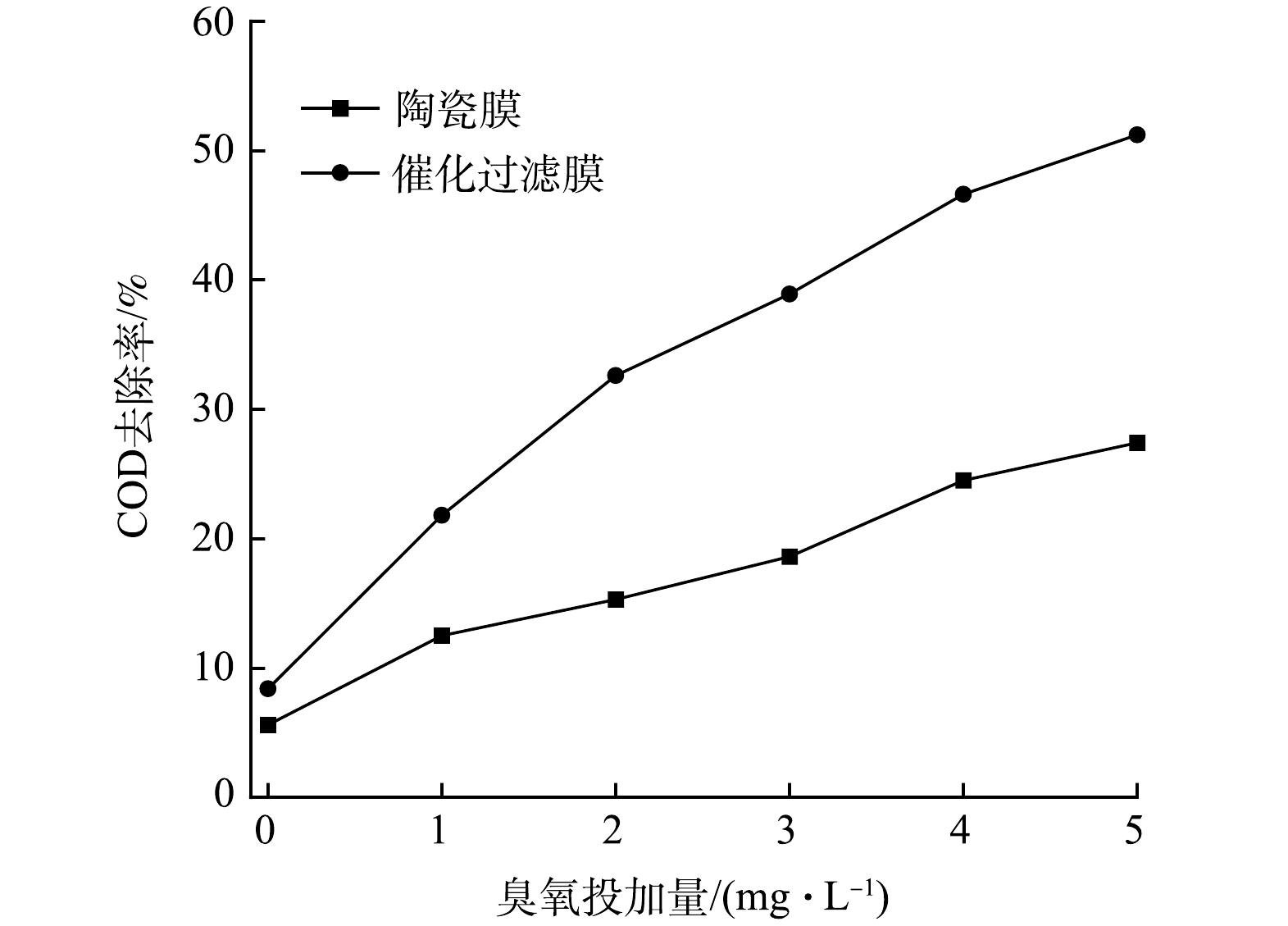
图10反映了当臭氧投加量由0 mg·L−1逐步增加至5 mg·L−1,其余实验参数不变的条件下,水中COD的变化趋势。由图10可知,随着臭氧投加量的增加,催化过滤膜对水中COD的去除率不断升高,当臭氧投加量增加到5 mg·L−1时,污水COD的去除率达到51.2%。采用普通陶瓷过滤膜和催化过滤膜进行对比实验,在不投加臭氧的情况下,2种过滤膜对污水COD的去除率分别为5.6%和8.4%。这是由于在膜表面发生了过滤的物理反应,水中部分大分子有机污染物被截留,催化过滤膜由于负载了活性氧化物导致膜孔径更小,对有机污染物截留效率更高。当臭氧投加量逐步增高,催化过滤膜对水中COD的去除率明显高于普通陶瓷过滤膜;在臭氧投加量为5 mg·L−1时,2种过滤膜对污水COD的去除率分别为27.4%和51.2%,由于催化过滤膜上负载的CeO2、La2O3和MnO2活性组分能够有效地催化臭氧反应生产羟基自由基等活性基团,进而无选择性地氧化降解污水中的有机物污染物。
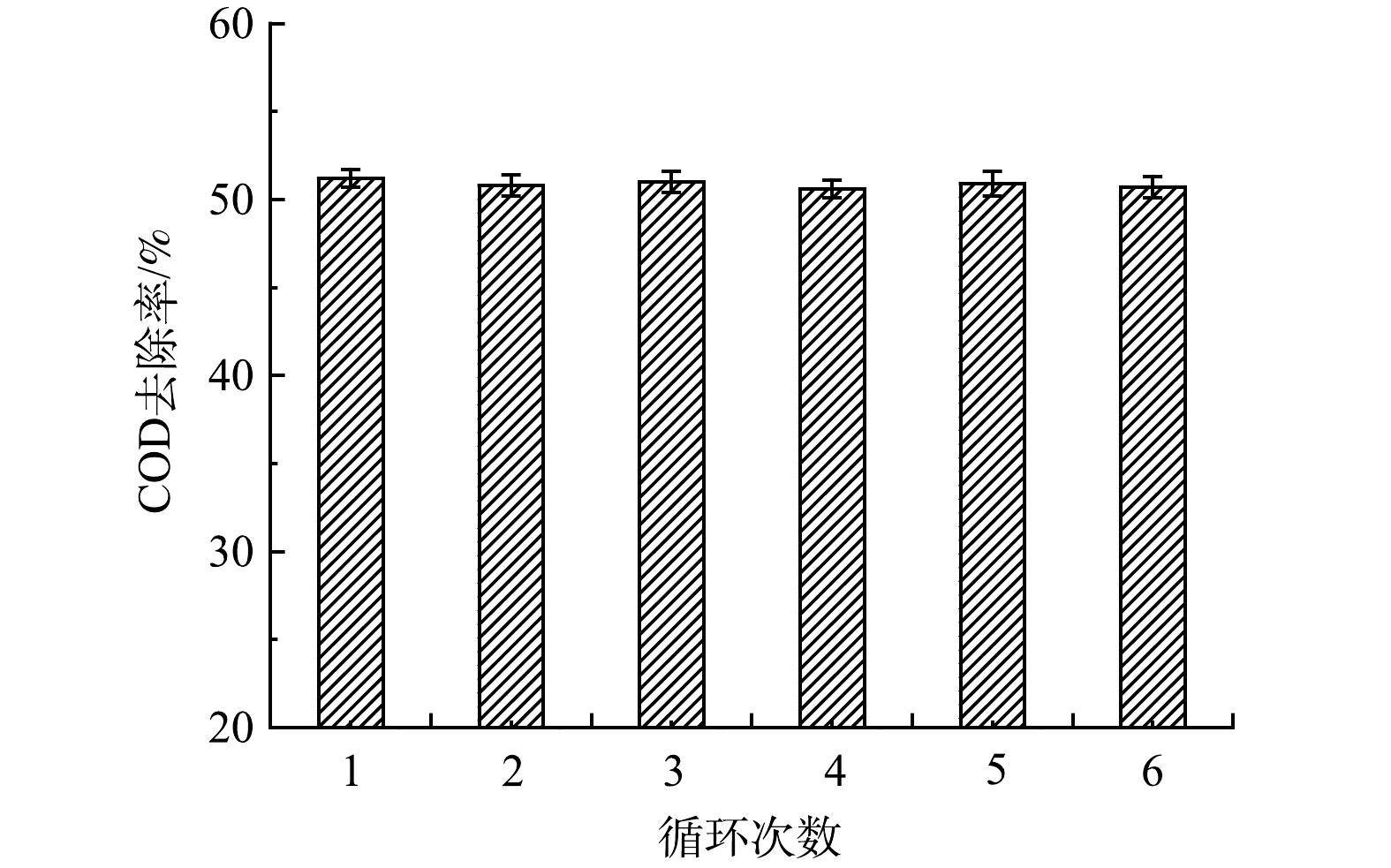
2)催化过滤膜稳定性测试。催化过滤膜的稳定性是评价其性能的一个重要指标,是决定催化剂使用寿命和产业化应用的关键因素。在臭氧投加量为5 mg·L−1,跨膜压差为0.15 MPa,回流比为90%的条件下进行实验,每次反应结束后的催化过滤膜不变,将实验废水更换为初始质量浓度的新鲜实验废水,连续使用5次为1个循环,每次使用1 h。经过6个循环后(每个循环催化剂应用5次),催化过滤膜多次使用对实验废水中COD去除率的影响如图11所示。由图11可知,随着使用次数的增加,催化过滤膜的活性并未有明显减弱,经多次循环后对水中COD的去除率稳定在50%以上,表现出较好的稳定性。对经臭氧催化过滤膜处理后的水样进行多次检测,均未检测出上述负载的金属离子,表明陶瓷膜载体上负载的金属氧化物在此实验条件下不易溶出。
3. 结论
1)以陶瓷膜为载体,La(NO3)3、Ce(NO3)3和Mn(CH3COO)2为催化活性成分的前躯体,采用浸渍-焙烧法制备了MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜,实现膜分离技术与催化臭氧氧化技术的耦合。浸渍液中Ce3+、La3+、Mn2+的质量比为2:2:1,焙烧时间为3 h,焙烧温度为800 ℃条件下制备出的催化过滤膜在臭氧催化氧化工艺中的催化活性最佳。
2)浸渍后的陶瓷膜经高温煅烧后生成的活性组分均匀地附着在表面及孔道内,陶瓷膜的孔隙率、孔径和通量均有所减小,XRD分析结果表明,催化剂表面形成了活性组分La2O3、CeO2和MnO2,表层活性组分金属元素占总质量的比例达到11.85%。
3)以MnO2-CeO2-La2O3臭氧催化过滤膜为研究对象,在常温和常压下,采用同步臭氧催化和过滤工艺处理电镀园区物化预处理后的混合废水取得了良好的处理效果。在臭氧投加量为5 mg·L−1、跨膜压差为0.15 MPa、回流比为90%的条件下,水中COD的去除率达到51.2%。催化过滤膜经过6次循环后对水中COD的去除率稳定在50%以上,表现出较好的稳定性。
-
表 1 单场次降雨中各面SS分布及对系统污染物沉积率和截留率
Table 1. Distribution of SS on each surface in a single rainfall event and the deposition and retention efficiency of pollutants in the system
模拟条件 进口SS体积分数/% 出口SS体积分数/% 进水口SS体积分数/% 沉淀区污染物沉积率/% 污染物截留率/% 直管 入口速度 1m/s 0.04 0.000 2 0.027 0 0.33 0.99 入口速度 3 m/s 0.04 0.005 5 0.010 0 0.75 0.86 入口速度 5 m/s 0.04 0.016 9 0.018 5 0.54 0.58 入口速度 5 m/s 弯管 90° 0.04 0.011 4 0.017 0 0.58 0.72 弯管 180° 0.04 0.012 8 0.014 3 0.64 0.68 表 2 接续降雨过程不同时间段SS分布及系统污染物沉积率和截留率
Table 2. Distribution of SS and deposition and retention efficiency of systemic pollutants at different time intervals of successive rainfall processes
% 进水时间/min 进口SS体积分数 出口SS体积分数 过水口SS体积分数 沉淀区污染物沉积率 污染物截留率 10 0.04 0.037 3 0.037 6 −0.06 0.07 20 0.04 0.039 6 0.041 6 0.04 0.01 30 0.04 0.040 0 0.038 9 −0.03 0.00 表 3 水质分析方法
Table 3. Methods of water quality analyses
测定指标 分析方法 参考标准 COD 快速密闭催化消解法(含光度法) 《水和废水监测分析方法》第四版 SS 重量法 《水和废水监测分析方法》第四版 TN 碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法 《水质 总氮的测定 碱性过硫酸钾消解紫外分光光度法:GB 11894—1989》 NH3-N 纳氏试剂分光光度法 《水质 氨氮的测定 纳氏试剂分光光度法:GB 11894—1989)》 -
[1] 习近平. 中央城镇化工作会议[R/OL]. (2013-12-14)[2023-04-23]. https://www.gov.cn/ldhd/2013-12/14/content_2547880.htm. [2] 李文娟. 国务院办公厅印发指导意见推进海绵城市建设[J]. 工程建设标准化, 2015(10): 39 − 39. doi: 10.13924/j.cnki.cecs.2015.10.013 [3] 中华人民共和国水利部. 2021中国水资源公报[R/OL]. [2023-04-23]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-06/16/content_5695973.htm. [4] PINFOLD J V, HORAN N J, WIROJANAGUD W, et al. The bacteriological quality of rainwater in rural northeast Thailand[J]. Water Research, 1993, 27(2): 297 − 302. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(93)90089-Z [5] SIMMONS G, HOPE V, LEWIS G, et al. Contamination of potable roof-collected rainwater in Auckland, New Zealand[J]. Water research, 2001, 35(6): 1518 − 1524. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00420-6 [6] FARRENY R, MORALES-PINZÓN T, GUISASOLA A, et al. Roof selection for rainwater harvesting: Quantity and quality assessments in Spain[J]. Water Research, 2011, 45(10): 3245 − 3254. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.03.036 [7] GRUNG M, MELAND S, RUUS A, et al. Christensen, Occurrence and trophic transport of organic compounds in sedimentation ponds for road runoff[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021(751): 141808. [8] MATTEO M D, LIANGR H, MAIER R, et al. Controlling rainwater storage as a system: An opportunity to reduce urban flood peaks for rare, long duration storms[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2019(111): 34 − 41. [9] 车伍, 刘燕, 李俊奇. 国内外城市雨水水质污染控制[J]. 给水排水, 2003, 29(10): 38 − 42. [10] 王倩, 张琼华, 王晓昌. 国内典型城市降雨径流初期累积特征分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2015, 35(6): 1719 − 1725. [11] 张琼华, 王晓昌. 初期雨水识别及量化分析研究[J]. 给水排水, 2016, 52(S1): 38 − 42. doi: 10.13789/j.cnki.wwe1964.2016.0335 [12] VIALLE C, SABLAYROLLES C, SILVESTRE J, et al. Pesticides in roof runoff: Study of a rural site and a suburban site[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2013, 120(15): 48 − 54. [13] GAO Z, ZHANG Q H, LI J, et al. First flush stormwater pollution in urban catchments: A review of its characterization and quantification towards optimization of control measures. [J]Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 340, 117976. [14] ABBASI T, ABBASI S A. Sources of pollution in rooftop rainwater harvesting systems and their control[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 41(23): 2097 − 2167. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2010.497438 [15] 杨浩. 窖水中细菌群落结构和功能的季节性变化及其与水质因子的交互响应[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学. 2018. [16] UNAMI K, MOHAWESH O, SHARIFI E, et al. Stochastic modelling and control of rainwater harvesting systems for irrigation during dry spells[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 88: 185 − 195. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.100 [17] TAFFERE G R, BEYENE A, VUAI S A H, et al. Dilemma of roof rainwater quality: applications of physical and organic treatment methods in a water scarce region of Mekelle, Ethiopia[J]. Urban Water Journal, 2017, 14(5): 460 − 466. doi: 10.1080/1573062X.2016.1176225 [18] LASH D, WARD S, KERSHAW T, et al. Robust rainwater harvesting: probabilistic tank sizing for climate change adaptation[J]. Journal of water and climate change, 2014, 5(4): 526 − 539. doi: 10.2166/wcc.2014.080 [19] MORALES-PINZÓN T, RIERADEVALL J, GASOL C M, et al. Modelling for economic cost and environmental analysis of rainwater harvesting systems[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 87: 613 − 626. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.10.021 [20] 陈望. 西安市屋面径流污染特征及控制技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019. [21] DUFRESNE M, VAZQUEZ J, TERFOUS A, et al. Experimental investigation and CFD modelling of flow, sedimentation, and solids separation in a combined sewer detention tank[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2009, 38(5): 1042 − 1049. [22] 谭志程. 基于数值模拟的新型CSO调蓄池结构优化与运行参数研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2021. [23] MIGUNTANNA N P, LIU A, EGODAWATTA P, et al. Characterising nutrients wash-off for effective urban stormwater treatment design[J]. Journal of environmental management, 2013, 120: 61 − 67. -




 下载:
下载: