-
农村黑臭水体治理是改善农村人居环境、解决农村突出水环境问题的重要工作[1-2]。近年来,随着农村社会经济的发展和农民生活水平的提高,加快治理农村地区房前屋后河塘沟渠以及群众反映强烈的黑臭水体势在必行[3-6]。2018年1月,中共中央办公厅、国务院办公厅印发《农村人居环境整治三年行动方案》(中办发[2018]5号),要求各地采取综合措施恢复水生态,逐步消除农村黑臭水体[7]。沈阳市作为辽宁省省会城市,位于辽宁省中部地区,是东北地区重要的中心城市。沈阳市农村黑臭水体类型丰富、完成治理比例高,2020年有2个区纳入第一批国家级农村黑臭水体治理试点。因此,文章总结分析了沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理工作措施以及治理效果,为辽宁省农村黑臭水体后续治理工作提供参考。
-
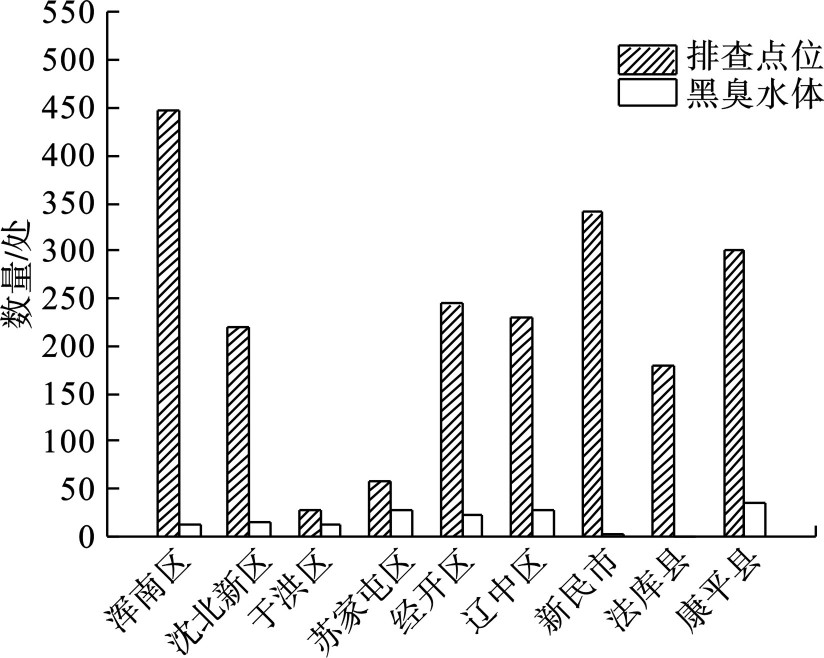
2019—2020年,沈阳市启动农村黑臭水体排查及治理工作,2年共排查2 047个点位,累积确认农村黑臭水体154处,见图1。
依据行政划分,各区(县、市)行政区域内,除法库县和新民市确认黑臭水体低于5处,其余区(县、市)在12~35处之间,合计确认农村黑臭水体流域面积359 837 m2,合计长度103 892 m,见表1。依据农村黑臭水体类型划分,全市共有河流型农村黑臭水体32处、塘型农村黑臭水体32处、沟渠型农村黑臭水体83处、排干型农村黑臭水体7处。全市以沟渠型农村黑臭水体占比最多,超过50%。(1)由于农村黑臭水体排查范围主要集中于“房前屋后”的河塘沟渠,而房前屋后主要以沟渠和塘居多;(2)由于当地农民生活习惯,将农业废弃物、垃圾、养殖废弃物等丢弃在“房前屋后”的沟渠和塘中,造成沟渠污染;(3)即使有少量河流在排查范围内,由于本身流动性大,自净能力好,加之无较明显的污染源进入,整体水质达不到黑臭程度。
-
沈阳市农村黑臭水体,最终汇入其他水体(河、湖)的67处,占全市农村黑臭水体的43.5%。其中,河流型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为100%,最终汇入辽河、浑河、蒲河、北沙河等河流;塘型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为3.1%,仅1条水体汇入卧龙湖;沟渠型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为33.7%,最终汇入八家子河、黑柳河、白塔河、小沙河等小型河流;排干型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为85.7%,最终汇入上一级排干以及蒲河、北沙河等,见表2。
-
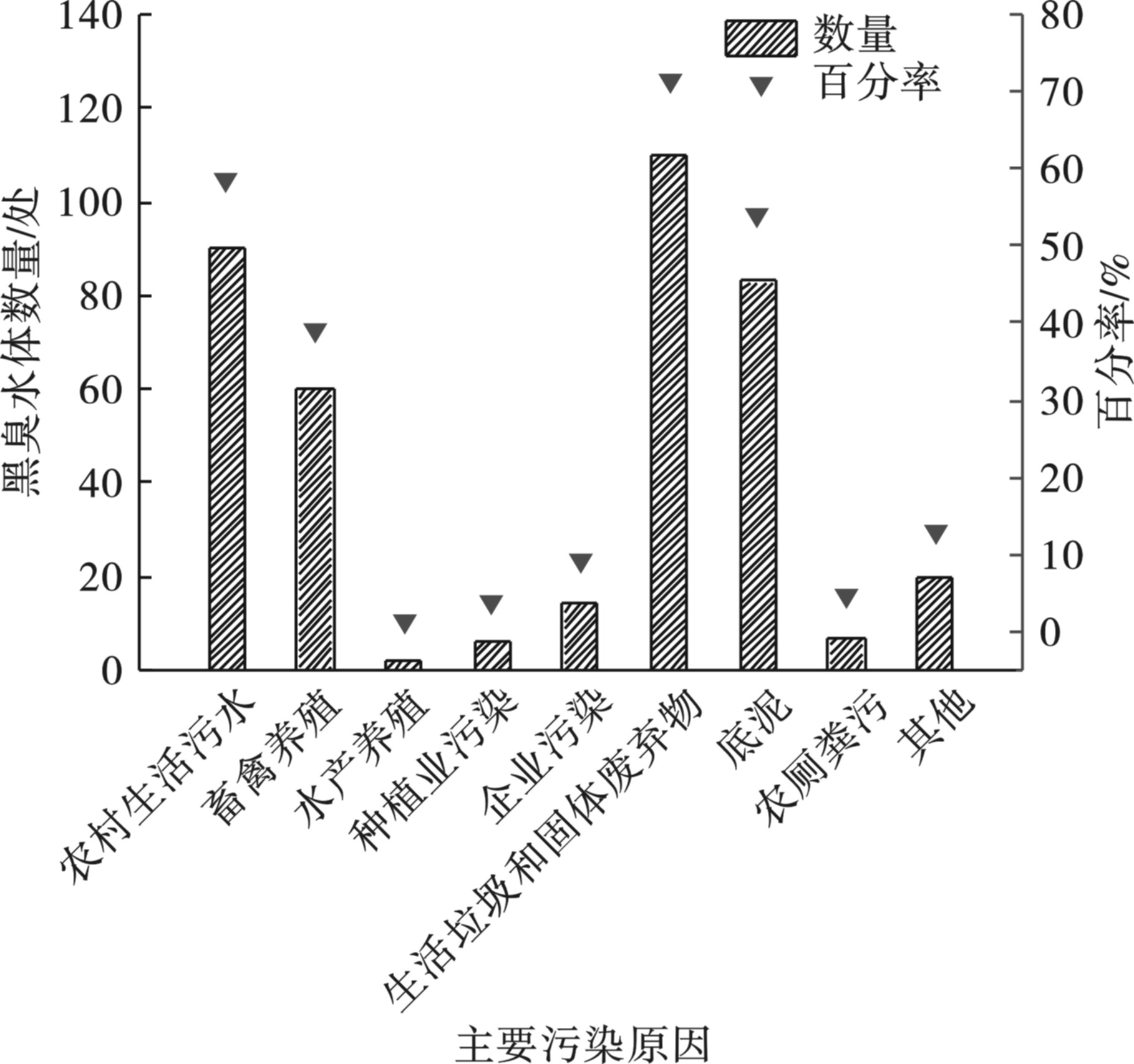
为方便后续管理和研究,根据实地调研及跟踪评估,将沈阳市农村黑臭水体污染来源分为农村生活污水、畜禽养殖、水产养殖、种植业污染、企业污染、生活垃圾和固体废弃物、底泥、农厕粪污、其他等9类[8-9]。沈阳市农村黑臭水体因单一污染源导致黑臭的为38处,两类污染源导致黑臭的为42处、三类以上污染源导致黑臭的为74处。154条农村黑臭水体中,受农村生活污水污染的水体有90处,受畜禽养殖污染的有60处,受水产养殖污染的有2处,受种植业污染的有6处,受企业污染的有14处,受生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染的有110处,受底泥污染的有83处,受农厕粪污污染的有7处,受其他污染的有20处,见图2。基于现有数据分析,沈阳市农村黑臭水体污染源主要集中在生活垃圾和固体废弃物、农村生活污水、底泥和畜禽养殖污染。
-
对沈阳市农村黑臭水体污染源污染形式进行了总结:(1)农村生活污水污染可分为城郊地区和农村地区生活污水。城郊和乡镇等人口集中地区存在居住用楼房,部分楼房无污水处理设施,生活污水在楼内汇集后直排形成污染;少数因已建设施规模不足或出现破损导致收集后的生活污水直排形成污染;农村地区生活污水由于受地区经济及生活习惯影响,多以20~30 L的桶收集后倾倒,厨余垃圾与生活污水混合形式为主。(2)畜禽养殖可分为养殖户和散养,养殖户养殖规模相对较大但达不到规模化程度,既无畜禽粪污处理设施也无粪污利用途径,导致畜禽粪污直排或者倾倒在村内边沟和塘内;散养畜禽污染则主要以倾倒边沟和塘内为主。(3)水产养殖则以养殖废水排放到邻近的水沟为主。(4)种植业污染主要以农业固体废弃物为主要污染形式,农业废弃物丢弃沟、塘内长期无人清理,经浸泡后逐渐腐烂成为底泥一部分[10-11]。(5)企业污染可分为企业生活污水和企业生产废水,企业生活污水是由于企业员工生活形成的生活污水,直接排放形成污染;企业生产废水因企业类型不同而不同,形成排放主要是为了节约生产成本或已建污水处理设施运行不到位,导致排放污水不达标形成污染。(6)生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染则主要是农村生产生活产生的垃圾和废弃物。(7)底泥污染则是受污染水体长期接收外来污染物,在水体内不断淤积最终形成较厚底泥,底泥的污染来源包括畜禽粪污倾倒、垃圾及渗滤液入河、农业废弃物入河、企业污染等[12-13]。(8)农厕粪污则主要为水体岸边修建的旱厕。
-
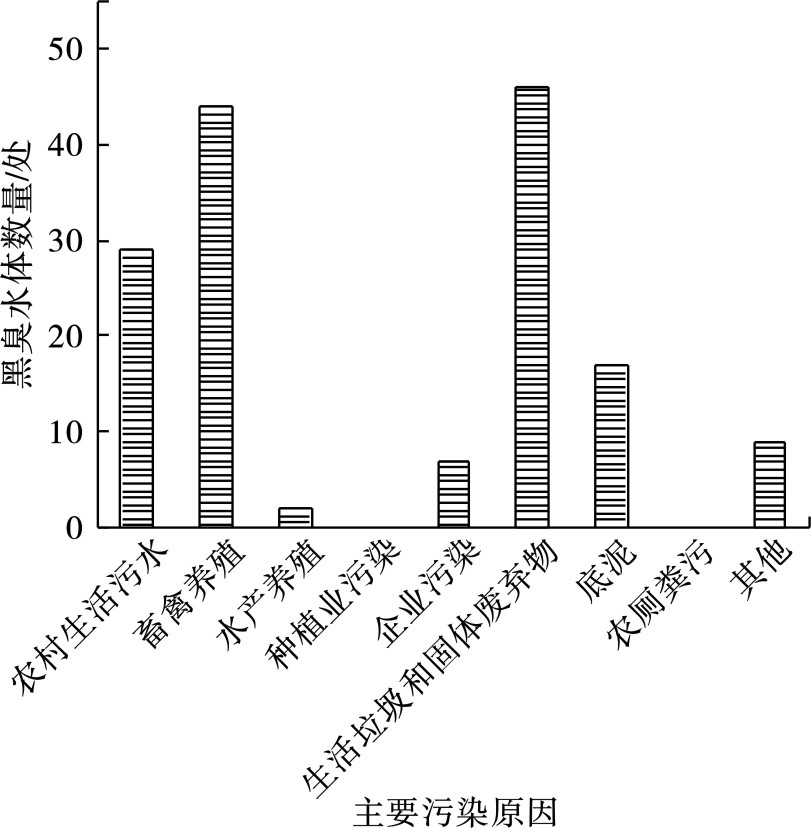
对154条农村黑臭水体主要污染原因进行了分析:农村生活污水29处;畜禽养殖44处;水产养殖2处;企业污染7处;生活垃圾和固体废弃物46处;底泥农厕粪污17处;其他9处,见图3。
-
沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理工作从2019年延续至今尚有1条水体未完成治理。对已完成治理的农村黑臭水体治理措施及管控措施如下总结。
-
90处受农村生活污水污染的水体,分为城郊地区、农村地区以及企业生活污水。其中,城郊地区楼房生活污水距离已有管网距离较近的,采用纳管进行收集占比13.3%;距离已有管网较远的地区,采用新建农村生活污水处理设施收集并处理占比6.7%;维修已建设施破损管网占比1.1%。农村地区生活污水,采用宣传教育、修建告示牌禁等占比57.8%;修建隔离网防止河内倾倒生活污水占比4.4%;修建农村污水处理设施和氧化塘收集处理生活污水占比3.3%;改变村内雨水汇集形成的塘为鱼塘,避免村民倾倒生活污水、垃圾和粪污占比2.2%;将村内雨水汇集形成的塘填埋占比2.2%;村庄搬迁致使污染源间接消失占比1.1.%,见表3。
-
60处受畜禽养殖污染的水体,可分为直接排放和粪污倾倒。其中,采用关停或搬迁养殖户解决粪污直排污染占比5.0%;采用修建粪污收储设施解决粪污直排占比28.3%;采用宣传教育、立牌、罚款等禁止排放的监管措施解决粪污直排占比10.0%。对于受倾倒粪污影响的水体,采用设置隔离网解决倾倒占比1.7%;采用宣传教育、立牌等禁止倾倒的监管措施占比45.0%;采用村内雨水汇集形成的塘填埋占比5.0%;采用将水塘改变为鱼塘方式防止倾倒占比5.0%,见表4。
-
2处受水产养殖污染水体治理则全部弃养后清理岸边及水体内垃圾后等待自然修复。
-
6处受种植业污染的水体,清理丢弃在水体附近的农业废弃物,并立警示牌。已经进入水体并腐烂的部分,伴随底泥清理而一并清理。
-
14处受企业污染的水体,可分为企业生活用水污染和企业生产废水污染。针对企业生活污水采用封堵排污口后企业自建设污水处理设施或处理达到标准后进入市政管网的占比35.7%;采用封堵排污口占比14.3%。针对企业生产废水,采用监督企业污水处理设施达标排放措施占比14.3%;采用封堵排污口占比28.6%,采用关停小作坊治理措施占比7.1%,见表5。
-
110处生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染的水体,均对河面和岸边垃圾及固体废弃物进行了清理。其中,新建隔离网避免废弃物入河占比3.6%;其他污染水体则均有垃圾收集装置。
-
83处受底泥污染的水体,均进行了底泥清理。小型沟、渠、塘等主要采用挖掘机、钩机、人工等方式直接进行清理,较大型水体则采用修建临时性拦截坝后进行清淤。清理后的底泥,部分运送至垃圾填埋场填埋,部分经晾晒风干后作为水体护坡进行原位利用。
-
7处受旱厕粪污影响的水体,3处影响较大、沿河旱厕较多的水体进行了沿河旱厕拆除,并修建生态厕所。其他4处未进行处理。
-
基于以上8类污染因素采取治理措施的基础数据分析,沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理包括工程措施与管控措施。其中,城郊地区生活污水治理主要采用纳管和建设施等工程措施,城郊地区环境敏感、人口相对集中,此方式可从源头控制污染,能取得较好治理效果。农村生活污水治理主要采用修建隔离网等管控措施,农村地区人口稀薄,污水产生量低,修建设施易出现“设施晒太阳”现象,采用纳管措施性价比不高,在做好管理确保生活污水不进入水体前提下,农村地区广袤的土地即为天然的土地渗滤系统,靠当地土壤自净能力,就能较好地去除生活污水中的污染物。畜禽粪污污染则采用管控措施较多,采用修建设施等其他工程措施较少,由于畜禽养殖粪污治理设施投资较多,而国家及省、市相关方面的资金支持不多,农村地区粪污污染主要是养殖户和散养引起的,畜禽养殖污染防治工作在法律层面具有一定的空白性,因此粪污处理设施建设需要政府投资,而当地政府受经济制约,多采取管控措施。水产养殖污染采用弃养为主要治理措施,分析原因是两处鱼塘为村民自行挖掘的养殖鱼塘,经济收益不高,未能形成区域性养殖,采用弃养从源头治理污染既能取得较好治理效果又不会带来较大的经济损失。种植业污染、生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染以及底泥均主要采用清理方式进行治理,能直接解决此类污染问题,经济适用性较高。企业污染则主要以管控措施和封堵排污口为主,分析原因是企业已建设设施的,加强监管提高设施运行效率,即可取得良好的治理效果。同时,企业污染采用修建设施比例也相对较高,分析原因是企业生活污水和企业生产废水排水量高,需采用源头治理工程措施控制污染。农厕粪污只有影响较大的进行了拆除并修建生态厕所,分析原因是这3处水体沿河旱厕数量多,对水体影响大,不进行拆除将持续影响水体水质;其他未治理水体,水体自净能力可以承载少量旱厕,从经济适用性和优先农户生活习惯考虑,并未进行拆除。
-
依据国家对农村黑臭水体的排查和评估要求,选取了透明度(SD)、溶解氧(DO)、氨氮(NH3-N)作为水质分析的3个指标[14],指标阈值,见表6。透明度采用十字铅盘法、DO采用快速溶氧仪测定法、氨氮则采用快速测定试纸和纳氏试剂分光光度法进行检测。第1年,现场检测氨氮主要采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,第2—3年,氨氮检测则主要以快速测定试纸为主,存有疑问的再次采用纳氏试剂分光光度法进行检测。
-
去除治理后完全无水和评估期间季节性无水水体,以及未完成治理水体,加上部分水体距离较长,采样点较多,合计共获得有效数据298组。其中,2020年有效数据86组,2021年有效数据93组,2022年有效数据119组。总体上,DO指标合格率为67.33%,NH3-N指标合格率为92.33%,SD指标合格率为96.31%。3年内DO指标合格率在43.01%~92.05%之间,NH3-N指标合格率在89.25%~96.59%之间,SD指标合格率在94.12%~100%之间,见表7。
298个DO数据范围在0.02~14.9 mg/L,高值与低值各去除5%数据后,90% DO数值分布于0.6~8.2 mg/L之间,见图4(a~c)。NH3-N数据范围在0~410 mg/L,高值与低值各去除5%数据后,90% NH3-N分布于0~24 mg/L之间,见图4(d~f)。SD在2~90 cm之间,高值与低值各去除5%数据后,90%SD分布于5~50 cm之间,见图4(g~i)。
-
对于农村黑臭水体治理效果评价,依据生态环境部出台的《农村黑臭水体治理工作指南(试行)》,首先要以感官判断为主,无法判断的采用问卷调查和水体检测方法进行判断[14]。沈阳市判断农村黑臭水体是否黑臭则主要以水质检测为依据,3项指标全部合格的则认定为消除黑臭;NH3-N超标的则直接判定为黑臭;部分水体出现感官十分清澈,但氨氮合格,DO和SD有1项或2项不达标的,则结合感官与水质数据进行综合判断,感官上颜色无异常、气味无异常则认定为消除黑臭。依据上述原则,对2020—2022年沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理效果进行了评估,见表8。
-
经统计,3年中出现返黑返臭的水体合计21条,1年出现返黑返臭水体有14条,2年出现返黑返臭水体有7条。1年出现返黑返臭现象的水体中,受畜禽粪污直排影响的2条;受畜禽粪污倾倒影响的7条;受企业生产废水偷排影响的1条;治理完成后逐渐自行修复中1条,目前已经合格;受生活污水影响的3条。2年出现返黑返臭现象的水体中,受畜禽粪污直排影响的5条,受畜禽粪污倾倒影响的2条,见表9。
-
受城郊生活污水污染影响的水体,采用纳管、建设施、维修已有破损设施治理方式的水体均起到了较好的治理效果;采用水体自净、监管工艺不合理或规模不足设施稳定运行方式的水体,则不同程度出现返黑返臭。农村生活污水采用管控、隔离网、填埋、建设施等取得了较好的治理效果。受畜禽粪污污染影响的水体,采用关停、搬迁治理措施的取得了较好效果;采用修建粪污贮存设施起到了一定作用,但部分因设施修建规模不足,无法满足后期贮存需求而出现了粪污直排和倾倒现象,引起水体返黑返臭;采用宣传、立牌、禁止倾倒等管理措施的,则出现了较明显的返黑返臭现象;另有新出现的畜禽粪污污染源导致水体返黑返臭。水产养殖污染水体弃养后清理并等待自然修复取得了较好效果。清理丢弃的农业废弃物,对改善水体质量有效。受企业污染的水体,建设施、纳管、关停等措施均取得了较好效果,但采用监管手段的尚有部分出现返黑返臭。生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染、底泥污染采取清理、建设隔离网等措施,取得了较好效果。旱厕粪污拆除后并修建生态厕所,取得了较好效果;其他4处未进行处理的旱厕,也并未出现超过水体自净能力导致水体黑臭的现象。
-
农村黑臭水体治理工作是一项长期而繁重的工作,其发生具有随机性,治理过程具有反复性,应循序渐进开展治理工作。应确保资金支持,避免因治理时间过急或资金不足,出现采取临时性措施应付检查的现象。同时,农村黑臭水体治理工作应确保从源头上根治污染并做好后续监管。(1)对于规模较大的农村生活污水污染源应修建设施或纳管;小规模农村生活污水污染源,应结合辽宁省农村生活污水资源化管控模式,做好污水资源化和地下水监测工作。(2)畜禽养殖粪污治理,修建的设施应具有“防渗、防雨、防外溢”功能,拓展畜禽粪污资源化利用途径,畅通粪污资源化利用渠道,方能有效解决畜禽粪污直排和倾倒问题。(3)对企业污水处理设施和农村生活污水处理设施的运行情况进行监管,落实企业和运营单位主体责任,避免出现偷排、溢流等现象;现有设施规模、工艺等不足以应对处理需求的,应及时进行维护和升级改造。(4)完善农村生活垃圾、农业固体废弃物等收集、运输、处理体系,垃圾和农业废弃物是放错位置的资源,做好垃圾分类和农业废弃物利用,既能有效地改善农村人居环境,又能带来一定的经济效益。(5)应结合当地实际情况,从环境、经济、人文等多角度出发,探索出适合本地区的治理和管理方式,如部分地区将废弃水塘修整为鱼塘并承包给当地居民,既解决了污染问题,又为当地农民带来了一定的经济收益。(6)治理措施应科学合理,如部分地区采用将无水体功能的塘填埋,许多村内水塘均为当地低洼地,填埋后应处理好村内的雨水排水问题。(7)加大宣传力度,农村黑臭水体很大程度上与当地人民的生活习惯息息相关,良好的生活习惯能有效地减少不必要的污染源形成;提升农民、养殖户保护环境的自觉性和能动性,在农村黑臭水体治理过程中具有很重要的意义。(8)建立长期排查、监督、考核制度,及时发现新出现农村黑臭水体,返黑返臭水体及时重新开展治理,做好已完成治理农村黑臭水体效果保持。
沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理效果及对策研究
Treatment effect and countermeasures of rural black-odorous water in Shenyang
-
摘要: 沈阳市农村黑臭水体排查、治理等工作处于辽宁省前列,全市共排查出农村黑臭水体154处,类型可分为河、塘、沟渠、排干等;污染源类型丰富,涉及生活污水、畜禽养殖、企业、底泥、生活垃圾等多种污染因素。文章重点对沈阳市农村黑臭水体黑臭成因、治理措施进行了分析,以连续3年的水质检测为基础对沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理效果进行了评估,并对农村黑臭水体返黑返臭原因以及措施有效性等进行了分析,可为辽宁省农村黑臭水体治理提供参考。Abstract: There is a good implementation for the investigation and treatment of rural black-odorous water in Shenyang with the top position in Liaoning Province. 154 rural black-odorous waters are identified, which can be divided into rivers, ponds, ditches, drainage, and so on. There are many types of pollution sources, including domestic sewage, livestock and poultry breeding, enterprises, sediment, domestic garbage and other pollution factors. This paper analyzed the causes and treatment measures of rural black-odorous water in Shenyang, evaluated the treatment effect of rural black-odorous water based on the water quality testing for three years, and analyzed the reasons and effectiveness of measures for rural black-odorous water, thus aimming to provide a reference for the treatment of the rural black-odorous water in Liaoning Province.
-
农村黑臭水体治理是改善农村人居环境、解决农村突出水环境问题的重要工作[1-2]。近年来,随着农村社会经济的发展和农民生活水平的提高,加快治理农村地区房前屋后河塘沟渠以及群众反映强烈的黑臭水体势在必行[3-6]。2018年1月,中共中央办公厅、国务院办公厅印发《农村人居环境整治三年行动方案》(中办发[2018]5号),要求各地采取综合措施恢复水生态,逐步消除农村黑臭水体[7]。沈阳市作为辽宁省省会城市,位于辽宁省中部地区,是东北地区重要的中心城市。沈阳市农村黑臭水体类型丰富、完成治理比例高,2020年有2个区纳入第一批国家级农村黑臭水体治理试点。因此,文章总结分析了沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理工作措施以及治理效果,为辽宁省农村黑臭水体后续治理工作提供参考。
1. 农村黑臭水体现状
1.1 农村黑臭水体排查及分类
2019—2020年,沈阳市启动农村黑臭水体排查及治理工作,2年共排查2 047个点位,累积确认农村黑臭水体154处,见图1。
依据行政划分,各区(县、市)行政区域内,除法库县和新民市确认黑臭水体低于5处,其余区(县、市)在12~35处之间,合计确认农村黑臭水体流域面积359 837 m2,合计长度103 892 m,见表1。依据农村黑臭水体类型划分,全市共有河流型农村黑臭水体32处、塘型农村黑臭水体32处、沟渠型农村黑臭水体83处、排干型农村黑臭水体7处。全市以沟渠型农村黑臭水体占比最多,超过50%。(1)由于农村黑臭水体排查范围主要集中于“房前屋后”的河塘沟渠,而房前屋后主要以沟渠和塘居多;(2)由于当地农民生活习惯,将农业废弃物、垃圾、养殖废弃物等丢弃在“房前屋后”的沟渠和塘中,造成沟渠污染;(3)即使有少量河流在排查范围内,由于本身流动性大,自净能力好,加之无较明显的污染源进入,整体水质达不到黑臭程度。
表 1 沈阳市农村黑臭水体信息汇总Table 1. Summary of information on rural black-odorous water in Shenyang区(县、市) 排查点位/处 农村黑臭水体类型/处 合计/处 合计流域面积/m2 合计长度/m 河 塘 沟渠 排干 浑南区 447 8 0 4 0 12 52 242 19 416 沈北新区 220 10 1 3 0 14 37 480 13 460 于洪区 29 0 1 11 0 12 24 579 5 180 苏家屯区 58 8 3 13 3 27 88 606 21 632 经开区 244 0 11 9 2 22 61 602 18 469 辽中区 230 0 7 19 1 27 25 296 9 073 新民市 340 0 0 4 0 4 1 432 955 法库县 179 1 0 0 0 1 20 5 康平县 300 5 9 20 1 35 68 580 15 702 总计 2 047 32 32 83 7 154 359 837 103 892 1.2 汇入水体情况
沈阳市农村黑臭水体,最终汇入其他水体(河、湖)的67处,占全市农村黑臭水体的43.5%。其中,河流型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为100%,最终汇入辽河、浑河、蒲河、北沙河等河流;塘型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为3.1%,仅1条水体汇入卧龙湖;沟渠型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为33.7%,最终汇入八家子河、黑柳河、白塔河、小沙河等小型河流;排干型农村黑臭水体汇入其他水体比例为85.7%,最终汇入上一级排干以及蒲河、北沙河等,见表2。
表 2 沈阳市农村黑臭水体汇入河流情况统计Table 2. Statistics on the situation of rural black-odorous water flowing into rivers in Shenyang区(县、市) 河/处 塘/处 沟渠/处 排干/处 占全区黑臭水体比例/% 浑南区 8 0 4 0 100.0 沈北新区 10 0 2 0 85.7 于洪区 0 0 5 0 41.7 苏家屯区 8 0 7 3 66.7 经开区 0 0 3 2 22.7 辽中区 0 0 0 1 3.7 新民市 0 0 0 0 0.0 法库县 1 0 0 0 100.0 康平县 5 1 7 0 37.1 合计 32 1 28 6 43.5 2. 农村黑臭水体成因
2.1 农村黑臭水体污染情况
为方便后续管理和研究,根据实地调研及跟踪评估,将沈阳市农村黑臭水体污染来源分为农村生活污水、畜禽养殖、水产养殖、种植业污染、企业污染、生活垃圾和固体废弃物、底泥、农厕粪污、其他等9类[8-9]。沈阳市农村黑臭水体因单一污染源导致黑臭的为38处,两类污染源导致黑臭的为42处、三类以上污染源导致黑臭的为74处。154条农村黑臭水体中,受农村生活污水污染的水体有90处,受畜禽养殖污染的有60处,受水产养殖污染的有2处,受种植业污染的有6处,受企业污染的有14处,受生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染的有110处,受底泥污染的有83处,受农厕粪污污染的有7处,受其他污染的有20处,见图2。基于现有数据分析,沈阳市农村黑臭水体污染源主要集中在生活垃圾和固体废弃物、农村生活污水、底泥和畜禽养殖污染。
2.2 污染源解析
2.2.1 污染源污染形式
对沈阳市农村黑臭水体污染源污染形式进行了总结:(1)农村生活污水污染可分为城郊地区和农村地区生活污水。城郊和乡镇等人口集中地区存在居住用楼房,部分楼房无污水处理设施,生活污水在楼内汇集后直排形成污染;少数因已建设施规模不足或出现破损导致收集后的生活污水直排形成污染;农村地区生活污水由于受地区经济及生活习惯影响,多以20~30 L的桶收集后倾倒,厨余垃圾与生活污水混合形式为主。(2)畜禽养殖可分为养殖户和散养,养殖户养殖规模相对较大但达不到规模化程度,既无畜禽粪污处理设施也无粪污利用途径,导致畜禽粪污直排或者倾倒在村内边沟和塘内;散养畜禽污染则主要以倾倒边沟和塘内为主。(3)水产养殖则以养殖废水排放到邻近的水沟为主。(4)种植业污染主要以农业固体废弃物为主要污染形式,农业废弃物丢弃沟、塘内长期无人清理,经浸泡后逐渐腐烂成为底泥一部分[10-11]。(5)企业污染可分为企业生活污水和企业生产废水,企业生活污水是由于企业员工生活形成的生活污水,直接排放形成污染;企业生产废水因企业类型不同而不同,形成排放主要是为了节约生产成本或已建污水处理设施运行不到位,导致排放污水不达标形成污染。(6)生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染则主要是农村生产生活产生的垃圾和废弃物。(7)底泥污染则是受污染水体长期接收外来污染物,在水体内不断淤积最终形成较厚底泥,底泥的污染来源包括畜禽粪污倾倒、垃圾及渗滤液入河、农业废弃物入河、企业污染等[12-13]。(8)农厕粪污则主要为水体岸边修建的旱厕。
2.2.2 主要污染源解析
对154条农村黑臭水体主要污染原因进行了分析:农村生活污水29处;畜禽养殖44处;水产养殖2处;企业污染7处;生活垃圾和固体废弃物46处;底泥农厕粪污17处;其他9处,见图3。
3. 农村黑臭水体治理
3.1 治理措施
沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理工作从2019年延续至今尚有1条水体未完成治理。对已完成治理的农村黑臭水体治理措施及管控措施如下总结。
3.1.1 生活污水治理措施
90处受农村生活污水污染的水体,分为城郊地区、农村地区以及企业生活污水。其中,城郊地区楼房生活污水距离已有管网距离较近的,采用纳管进行收集占比13.3%;距离已有管网较远的地区,采用新建农村生活污水处理设施收集并处理占比6.7%;维修已建设施破损管网占比1.1%。农村地区生活污水,采用宣传教育、修建告示牌禁等占比57.8%;修建隔离网防止河内倾倒生活污水占比4.4%;修建农村污水处理设施和氧化塘收集处理生活污水占比3.3%;改变村内雨水汇集形成的塘为鱼塘,避免村民倾倒生活污水、垃圾和粪污占比2.2%;将村内雨水汇集形成的塘填埋占比2.2%;村庄搬迁致使污染源间接消失占比1.1.%,见表3。
表 3 生活污水污染治理措施统计Table 3. The statistical table of rural domestic sewage pollution control measures分类 数量/处 治理措施占比/% 纳管 建设施 设施修复与维护 隔离网 管控 搬迁 填埋 其他 城郊 20 13.3 6.7 1.1 - - - - - 农村 65 - 3.3 1.1 4.4 57.8 1.1 2.2 2.2 企业 5 - 1.1 3.3 - 1.1 - - 1.1 3.1.2 畜禽养殖污染治理措施
60处受畜禽养殖污染的水体,可分为直接排放和粪污倾倒。其中,采用关停或搬迁养殖户解决粪污直排污染占比5.0%;采用修建粪污收储设施解决粪污直排占比28.3%;采用宣传教育、立牌、罚款等禁止排放的监管措施解决粪污直排占比10.0%。对于受倾倒粪污影响的水体,采用设置隔离网解决倾倒占比1.7%;采用宣传教育、立牌等禁止倾倒的监管措施占比45.0%;采用村内雨水汇集形成的塘填埋占比5.0%;采用将水塘改变为鱼塘方式防止倾倒占比5.0%,见表4。
表 4 畜禽养殖污染治理措施统计Table 4. The Statistical table of pollution control measures for livestock and poultry breeding分类 数量/处 治理措施占比/% 关停搬迁 建设施 隔离网 管控 填埋 其他 粪污直排 26 5.0 28.3 - 10.0 - - 粪污倾倒 32 - - 1.7 45.0 5.0 5.0 3.1.3 水产养殖污染治理措施
2处受水产养殖污染水体治理则全部弃养后清理岸边及水体内垃圾后等待自然修复。
3.1.4 种植业污染治理措施
6处受种植业污染的水体,清理丢弃在水体附近的农业废弃物,并立警示牌。已经进入水体并腐烂的部分,伴随底泥清理而一并清理。
3.1.5 企业污染治理措施
14处受企业污染的水体,可分为企业生活用水污染和企业生产废水污染。针对企业生活污水采用封堵排污口后企业自建设污水处理设施或处理达到标准后进入市政管网的占比35.7%;采用封堵排污口占比14.3%。针对企业生产废水,采用监督企业污水处理设施达标排放措施占比14.3%;采用封堵排污口占比28.6%,采用关停小作坊治理措施占比7.1%,见表5。
表 5 企业污染治理措施统计表Table 5. The Statistical table of enterprise pollution control measures分类 数量 治理措施占比/% 自建设施 管控措施 封堵排污口 关停 其他 生活废水 7 35.7 14.3 - - - 生产废水 7 - 14.3 28.6 7.1 - 3.1.6 生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染治理措施
110处生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染的水体,均对河面和岸边垃圾及固体废弃物进行了清理。其中,新建隔离网避免废弃物入河占比3.6%;其他污染水体则均有垃圾收集装置。
3.1.7 底泥污染治理措施
83处受底泥污染的水体,均进行了底泥清理。小型沟、渠、塘等主要采用挖掘机、钩机、人工等方式直接进行清理,较大型水体则采用修建临时性拦截坝后进行清淤。清理后的底泥,部分运送至垃圾填埋场填埋,部分经晾晒风干后作为水体护坡进行原位利用。
3.1.8 农厕粪污治理措施
7处受旱厕粪污影响的水体,3处影响较大、沿河旱厕较多的水体进行了沿河旱厕拆除,并修建生态厕所。其他4处未进行处理。
3.1.9 主要治理措施与原因分析
基于以上8类污染因素采取治理措施的基础数据分析,沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理包括工程措施与管控措施。其中,城郊地区生活污水治理主要采用纳管和建设施等工程措施,城郊地区环境敏感、人口相对集中,此方式可从源头控制污染,能取得较好治理效果。农村生活污水治理主要采用修建隔离网等管控措施,农村地区人口稀薄,污水产生量低,修建设施易出现“设施晒太阳”现象,采用纳管措施性价比不高,在做好管理确保生活污水不进入水体前提下,农村地区广袤的土地即为天然的土地渗滤系统,靠当地土壤自净能力,就能较好地去除生活污水中的污染物。畜禽粪污污染则采用管控措施较多,采用修建设施等其他工程措施较少,由于畜禽养殖粪污治理设施投资较多,而国家及省、市相关方面的资金支持不多,农村地区粪污污染主要是养殖户和散养引起的,畜禽养殖污染防治工作在法律层面具有一定的空白性,因此粪污处理设施建设需要政府投资,而当地政府受经济制约,多采取管控措施。水产养殖污染采用弃养为主要治理措施,分析原因是两处鱼塘为村民自行挖掘的养殖鱼塘,经济收益不高,未能形成区域性养殖,采用弃养从源头治理污染既能取得较好治理效果又不会带来较大的经济损失。种植业污染、生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染以及底泥均主要采用清理方式进行治理,能直接解决此类污染问题,经济适用性较高。企业污染则主要以管控措施和封堵排污口为主,分析原因是企业已建设设施的,加强监管提高设施运行效率,即可取得良好的治理效果。同时,企业污染采用修建设施比例也相对较高,分析原因是企业生活污水和企业生产废水排水量高,需采用源头治理工程措施控制污染。农厕粪污只有影响较大的进行了拆除并修建生态厕所,分析原因是这3处水体沿河旱厕数量多,对水体影响大,不进行拆除将持续影响水体水质;其他未治理水体,水体自净能力可以承载少量旱厕,从经济适用性和优先农户生活习惯考虑,并未进行拆除。
3.2 治理效果
3.2.1 水质分析方法
依据国家对农村黑臭水体的排查和评估要求,选取了透明度(SD)、溶解氧(DO)、氨氮(NH3-N)作为水质分析的3个指标[14],指标阈值,见表6。透明度采用十字铅盘法、DO采用快速溶氧仪测定法、氨氮则采用快速测定试纸和纳氏试剂分光光度法进行检测。第1年,现场检测氨氮主要采用纳氏试剂分光光度法,第2—3年,氨氮检测则主要以快速测定试纸为主,存有疑问的再次采用纳氏试剂分光光度法进行检测。
表 6 检测指标Table 6. Detection index监测指标 指标阈值 SD/cm >25* DO/mg·L−1 NH3-N/mg·L−1 >2 <15 注:*,透明度水深不足25 cm时,按水深40%取值。 3.2.2 水质分析结果
去除治理后完全无水和评估期间季节性无水水体,以及未完成治理水体,加上部分水体距离较长,采样点较多,合计共获得有效数据298组。其中,2020年有效数据86组,2021年有效数据93组,2022年有效数据119组。总体上,DO指标合格率为67.33%,NH3-N指标合格率为92.33%,SD指标合格率为96.31%。3年内DO指标合格率在43.01%~92.05%之间,NH3-N指标合格率在89.25%~96.59%之间,SD指标合格率在94.12%~100%之间,见表7。
表 7 沈阳市农村黑臭水体水质范围统计Table 7. The statistics of water quality range of rural black-odorous water in Shenyangt/a DO NH3-N SD 水深/cm 范围/mg·L−1 合格率/% 范围/mg·L−1 合格率/% 范围/cm 合格率/% 2020 0.90~14.90 92.05 0~38.30 96.59 5~90 100 5~90 2021 0.30~14.10 43.01 0~31.00 89.25 2~50 95.70 2~80 2022 0.02~10.95 68.07 0~410.00 91.60 3~70 94.12 3~150 合计 0.02~14.90 67.33 0~410.00 92.33 2~90 96.31 2~150 298个DO数据范围在0.02~14.9 mg/L,高值与低值各去除5%数据后,90% DO数值分布于0.6~8.2 mg/L之间,见图4(a~c)。NH3-N数据范围在0~410 mg/L,高值与低值各去除5%数据后,90% NH3-N分布于0~24 mg/L之间,见图4(d~f)。SD在2~90 cm之间,高值与低值各去除5%数据后,90%SD分布于5~50 cm之间,见图4(g~i)。
3.2.3 治理效果分析
对于农村黑臭水体治理效果评价,依据生态环境部出台的《农村黑臭水体治理工作指南(试行)》,首先要以感官判断为主,无法判断的采用问卷调查和水体检测方法进行判断[14]。沈阳市判断农村黑臭水体是否黑臭则主要以水质检测为依据,3项指标全部合格的则认定为消除黑臭;NH3-N超标的则直接判定为黑臭;部分水体出现感官十分清澈,但氨氮合格,DO和SD有1项或2项不达标的,则结合感官与水质数据进行综合判断,感官上颜色无异常、气味无异常则认定为消除黑臭。依据上述原则,对2020—2022年沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理效果进行了评估,见表8。
表 8 沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理效果分析Table 8. Analysis on the treatment effect of rural black-odorous water in Shenyangt/a 完成治理/处 返黑返臭/处 综合评估无黑臭(感官正常)/处 3项指标均合格 DO低 SD低 DO、SD低 2020 146 3 137 5 0 1 2021 148 15 91 37 2 3 2022 153 10 112 24 4 3 3.2.4 返黑返臭原因分析
经统计,3年中出现返黑返臭的水体合计21条,1年出现返黑返臭水体有14条,2年出现返黑返臭水体有7条。1年出现返黑返臭现象的水体中,受畜禽粪污直排影响的2条;受畜禽粪污倾倒影响的7条;受企业生产废水偷排影响的1条;治理完成后逐渐自行修复中1条,目前已经合格;受生活污水影响的3条。2年出现返黑返臭现象的水体中,受畜禽粪污直排影响的5条,受畜禽粪污倾倒影响的2条,见表9。
表 9 农村黑臭水体返黑返臭原因情况Table 9. The causes of rural black-odorous water returning to black and odorous分类 返黑返臭原因 返黑返臭水体/条 采取措施 备注 1年出现返黑返臭 粪污倾倒 7 禁止倾倒 - 粪污直排 1 修建设施 设施储存量不足 1 - 新增直排 企业偷排 1 监管 - 生活污水处理设施 1 生态修复 工艺不合理 1 - 规模不足溢流 生活污水 1 未建设施 - 垃圾倾倒 1 清理垃圾 经自行修复,已消除黑臭 2年出现返黑返臭 粪污倾倒 1 建立岸边清理机制 - 1 - 新增倾倒 粪污直排 1 修建设施 设施储存量不足 1 - 新增直排 3 禁止直排 - 3.2.5 治理措施有效性分析
受城郊生活污水污染影响的水体,采用纳管、建设施、维修已有破损设施治理方式的水体均起到了较好的治理效果;采用水体自净、监管工艺不合理或规模不足设施稳定运行方式的水体,则不同程度出现返黑返臭。农村生活污水采用管控、隔离网、填埋、建设施等取得了较好的治理效果。受畜禽粪污污染影响的水体,采用关停、搬迁治理措施的取得了较好效果;采用修建粪污贮存设施起到了一定作用,但部分因设施修建规模不足,无法满足后期贮存需求而出现了粪污直排和倾倒现象,引起水体返黑返臭;采用宣传、立牌、禁止倾倒等管理措施的,则出现了较明显的返黑返臭现象;另有新出现的畜禽粪污污染源导致水体返黑返臭。水产养殖污染水体弃养后清理并等待自然修复取得了较好效果。清理丢弃的农业废弃物,对改善水体质量有效。受企业污染的水体,建设施、纳管、关停等措施均取得了较好效果,但采用监管手段的尚有部分出现返黑返臭。生活垃圾和固体废弃物污染、底泥污染采取清理、建设隔离网等措施,取得了较好效果。旱厕粪污拆除后并修建生态厕所,取得了较好效果;其他4处未进行处理的旱厕,也并未出现超过水体自净能力导致水体黑臭的现象。
4. 建议
农村黑臭水体治理工作是一项长期而繁重的工作,其发生具有随机性,治理过程具有反复性,应循序渐进开展治理工作。应确保资金支持,避免因治理时间过急或资金不足,出现采取临时性措施应付检查的现象。同时,农村黑臭水体治理工作应确保从源头上根治污染并做好后续监管。(1)对于规模较大的农村生活污水污染源应修建设施或纳管;小规模农村生活污水污染源,应结合辽宁省农村生活污水资源化管控模式,做好污水资源化和地下水监测工作。(2)畜禽养殖粪污治理,修建的设施应具有“防渗、防雨、防外溢”功能,拓展畜禽粪污资源化利用途径,畅通粪污资源化利用渠道,方能有效解决畜禽粪污直排和倾倒问题。(3)对企业污水处理设施和农村生活污水处理设施的运行情况进行监管,落实企业和运营单位主体责任,避免出现偷排、溢流等现象;现有设施规模、工艺等不足以应对处理需求的,应及时进行维护和升级改造。(4)完善农村生活垃圾、农业固体废弃物等收集、运输、处理体系,垃圾和农业废弃物是放错位置的资源,做好垃圾分类和农业废弃物利用,既能有效地改善农村人居环境,又能带来一定的经济效益。(5)应结合当地实际情况,从环境、经济、人文等多角度出发,探索出适合本地区的治理和管理方式,如部分地区将废弃水塘修整为鱼塘并承包给当地居民,既解决了污染问题,又为当地农民带来了一定的经济收益。(6)治理措施应科学合理,如部分地区采用将无水体功能的塘填埋,许多村内水塘均为当地低洼地,填埋后应处理好村内的雨水排水问题。(7)加大宣传力度,农村黑臭水体很大程度上与当地人民的生活习惯息息相关,良好的生活习惯能有效地减少不必要的污染源形成;提升农民、养殖户保护环境的自觉性和能动性,在农村黑臭水体治理过程中具有很重要的意义。(8)建立长期排查、监督、考核制度,及时发现新出现农村黑臭水体,返黑返臭水体及时重新开展治理,做好已完成治理农村黑臭水体效果保持。
-
表 1 沈阳市农村黑臭水体信息汇总
Table 1. Summary of information on rural black-odorous water in Shenyang
区(县、市) 排查点位/处 农村黑臭水体类型/处 合计/处 合计流域面积/m2 合计长度/m 河 塘 沟渠 排干 浑南区 447 8 0 4 0 12 52 242 19 416 沈北新区 220 10 1 3 0 14 37 480 13 460 于洪区 29 0 1 11 0 12 24 579 5 180 苏家屯区 58 8 3 13 3 27 88 606 21 632 经开区 244 0 11 9 2 22 61 602 18 469 辽中区 230 0 7 19 1 27 25 296 9 073 新民市 340 0 0 4 0 4 1 432 955 法库县 179 1 0 0 0 1 20 5 康平县 300 5 9 20 1 35 68 580 15 702 总计 2 047 32 32 83 7 154 359 837 103 892 表 2 沈阳市农村黑臭水体汇入河流情况统计
Table 2. Statistics on the situation of rural black-odorous water flowing into rivers in Shenyang
区(县、市) 河/处 塘/处 沟渠/处 排干/处 占全区黑臭水体比例/% 浑南区 8 0 4 0 100.0 沈北新区 10 0 2 0 85.7 于洪区 0 0 5 0 41.7 苏家屯区 8 0 7 3 66.7 经开区 0 0 3 2 22.7 辽中区 0 0 0 1 3.7 新民市 0 0 0 0 0.0 法库县 1 0 0 0 100.0 康平县 5 1 7 0 37.1 合计 32 1 28 6 43.5 表 3 生活污水污染治理措施统计
Table 3. The statistical table of rural domestic sewage pollution control measures
分类 数量/处 治理措施占比/% 纳管 建设施 设施修复与维护 隔离网 管控 搬迁 填埋 其他 城郊 20 13.3 6.7 1.1 - - - - - 农村 65 - 3.3 1.1 4.4 57.8 1.1 2.2 2.2 企业 5 - 1.1 3.3 - 1.1 - - 1.1 表 4 畜禽养殖污染治理措施统计
Table 4. The Statistical table of pollution control measures for livestock and poultry breeding
分类 数量/处 治理措施占比/% 关停搬迁 建设施 隔离网 管控 填埋 其他 粪污直排 26 5.0 28.3 - 10.0 - - 粪污倾倒 32 - - 1.7 45.0 5.0 5.0 表 5 企业污染治理措施统计表
Table 5. The Statistical table of enterprise pollution control measures
分类 数量 治理措施占比/% 自建设施 管控措施 封堵排污口 关停 其他 生活废水 7 35.7 14.3 - - - 生产废水 7 - 14.3 28.6 7.1 - 表 6 检测指标
Table 6. Detection index
监测指标 指标阈值 SD/cm >25* DO/mg·L−1 NH3-N/mg·L−1 >2 <15 注:*,透明度水深不足25 cm时,按水深40%取值。 表 7 沈阳市农村黑臭水体水质范围统计
Table 7. The statistics of water quality range of rural black-odorous water in Shenyang
t/a DO NH3-N SD 水深/cm 范围/mg·L−1 合格率/% 范围/mg·L−1 合格率/% 范围/cm 合格率/% 2020 0.90~14.90 92.05 0~38.30 96.59 5~90 100 5~90 2021 0.30~14.10 43.01 0~31.00 89.25 2~50 95.70 2~80 2022 0.02~10.95 68.07 0~410.00 91.60 3~70 94.12 3~150 合计 0.02~14.90 67.33 0~410.00 92.33 2~90 96.31 2~150 表 8 沈阳市农村黑臭水体治理效果分析
Table 8. Analysis on the treatment effect of rural black-odorous water in Shenyang
t/a 完成治理/处 返黑返臭/处 综合评估无黑臭(感官正常)/处 3项指标均合格 DO低 SD低 DO、SD低 2020 146 3 137 5 0 1 2021 148 15 91 37 2 3 2022 153 10 112 24 4 3 表 9 农村黑臭水体返黑返臭原因情况
Table 9. The causes of rural black-odorous water returning to black and odorous
分类 返黑返臭原因 返黑返臭水体/条 采取措施 备注 1年出现返黑返臭 粪污倾倒 7 禁止倾倒 - 粪污直排 1 修建设施 设施储存量不足 1 - 新增直排 企业偷排 1 监管 - 生活污水处理设施 1 生态修复 工艺不合理 1 - 规模不足溢流 生活污水 1 未建设施 - 垃圾倾倒 1 清理垃圾 经自行修复,已消除黑臭 2年出现返黑返臭 粪污倾倒 1 建立岸边清理机制 - 1 - 新增倾倒 粪污直排 1 修建设施 设施储存量不足 1 - 新增直排 3 禁止直排 - -
[1] 刘海东, 崔艳智, 贾小梅, 等. 农村黑臭水体治理现状、问题及对策建议[J]. 中国环境管理, 2022, 14(3): 54 − 59. [2] 任甜. 典型农村黑臭水体污染成因及治理对策[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2021(10): 100 − 102. [3] 李为实, 赵寅成. 安徽省农村黑臭水体成因及治理研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2020, 45(2): 154 − 157. [4] 王梅, 刘红茹, 王阵阵, 等. 北方地区农村黑臭水体成因及治理对策研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2022, 47(6): 15 − 18. [5] 刘驰, 王莉, 姜惠源, 等. 河南农村黑臭水体及影响因素调查与分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2021(3): 1 − 5. [6] 中共中央办公厅, 国务院办公厅. 农村人居环境整治三年行动方案[S/OL]. [2022-08-05]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2018-02/05/content_5264056.htm. [7] 王彩彩, 刘恩丽, 马建源. 浅谈农村黑臭水体的治理进展与建议[J]. 广东化工, 2021, 48(12): 136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2021.12.056 [8] 郝晓娟, 胡昌旭, 李敏. 农村黑臭水体治理技术研究[J]. 广东化工, 2021, 48(4): 88 − 89. [9] 张美玲. 林彰文.广东省农村黑臭水体现状及治理对策研究[J]. 四川农业科技, 2022(11): 102 − 105. [10] 王世恒, 袁卫东, 陆娜宋, 等. 农作物废弃物焚烧和水体腐化过程对环境的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2018, 30(6): 1022 − 1028. [11] 张依章, 乔丽丽, 范博渊. 河道污染底泥成分及其形成机理研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2022, 47(3): 88 − 92. [12] LIU M S, LI T T, WANG Z C, et al. Effect of aeration on water quality and sediment humus in rural black-odorous water[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 320: 115867. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115867 [13] LU K T, GAO H, YU H B, et al. Insight into variations of DOM fractions in different latitudinal rural black-odor water bodies of eastern China using fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with structure equation model[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 816: 151531. [14] 生态环境部.农村黑臭水体治理工作指南(试行).[S/OL].[2022-11-07]. http://sxxxgk.huaibei.gov.cn/group1/M00/04/BB/rBIoG1-Fg2OAM14PABC5FJHnaMI863.pdf. -






 下载:
下载: