-
水库大多作为城市生活饮用水水源地,受人类活动影响较大[1],其污染来源广、途径多、种类复杂,累积在水库沉积物中营养盐和重金属等污染物在适宜条件下可从沉积物中重新释放到上覆水体[2],将会威胁水库水质安全进而影响人体健康[3]。磷是湖库富营养化的限制因子,水库沉积物中磷的沉积总量及赋存形态[4],湖泊物理化学过程等[5],都对沉积物磷生物地球化学过程,对上覆水磷含量有着深远的影响[6]。因此,研究水库沉积物中磷的累积特征和赋存形态,评估其释放强度和影响,对于藻华发生风险防控和区域供水安全保障至关重要。
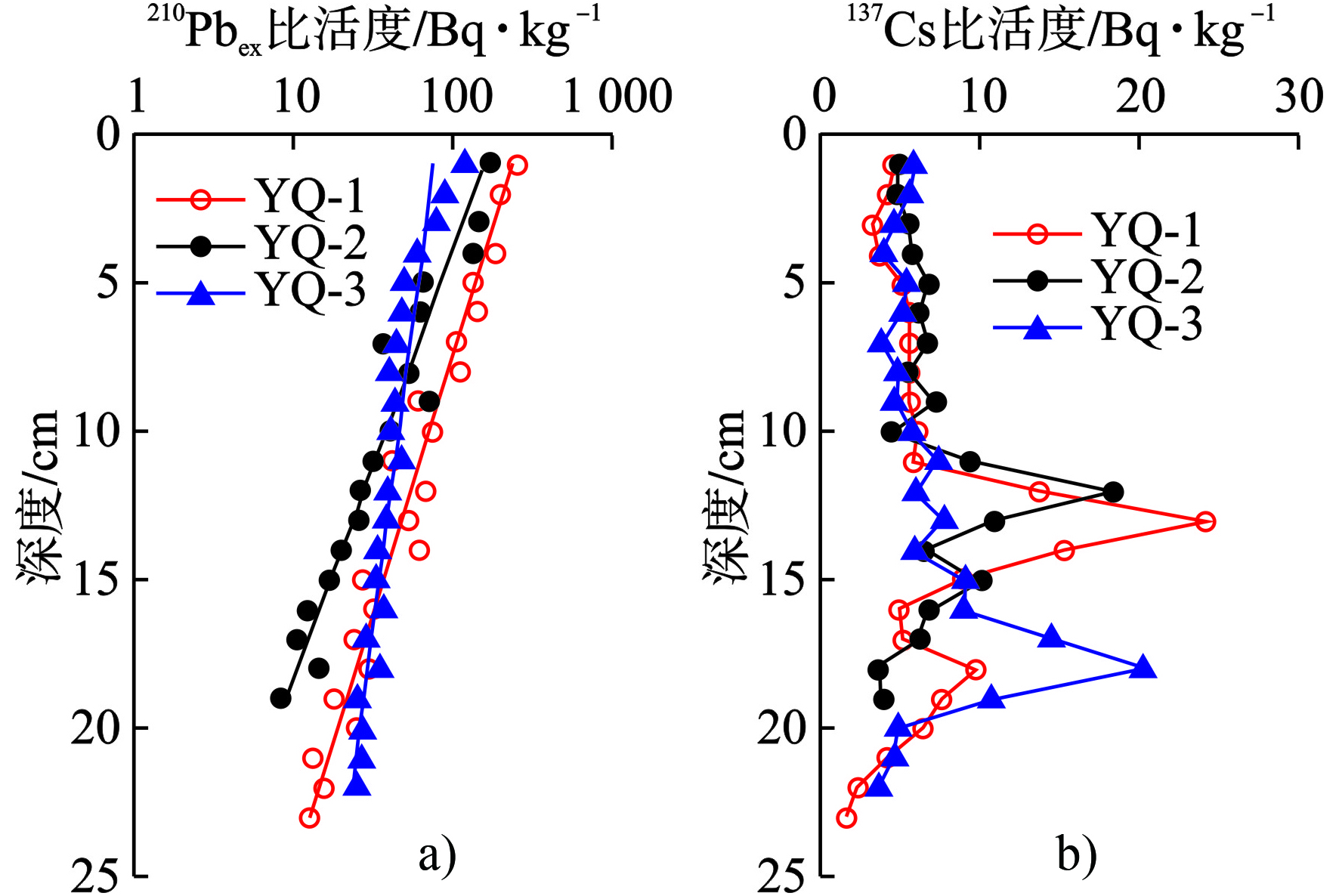
于桥水库是引滦入津最重要调蓄湖泊[7],也是天津市唯一的集中式饮用水水源[8],承担着天津千万人口的饮用水供给功能。于桥水库磷污染及富营养化问题对于供水安全的影响[9],受到广泛关注。自1997年于桥水库发生首次藻华事件以来[10],水库一直处于富营养化向重度营养化过渡、接近重度营养化边缘[11]。磷是于桥水库富营养化的限制性因子,水库TP浓度自2008~2016年呈现逐步上升的趋势[8],推测上游流域和沉积物内源是磷的主要来源。迄今为止,对于桥水库的研究报道主要集中在水质、水量和环境治理方面,而对其沉积物磷赋存形态历史分布特点,以及其释放潜势和贡献的研究较少,仅有部分学者对其表层沉积物中磷赋存形态分布进行了调查[12-13]。作为水环境组成的重要部分,对沉积物的研究尤其是磷累积历史、赋存形态和释放通量的评估是对于桥水库水环境质量评价研究不可或缺的组成部分。
随着于桥水库上游流域治理力度加大,上游磷输入负荷逐渐削减,但藻华现象仍时有发生[10],推测可能与水库沉积物内源磷释放有关。于桥水库建于1959年[8],经过50多年累积,水体中磷以颗粒态形式赋存及颗粒吸附的磷在库底聚集,沉积物中磷含量已趋于饱和[14]。鉴于此,采集于桥水库柱状沉积物,利用210Pb和137Cs放射性同位素方法,构建其沉积年代学,分析磷及其赋存形态的历史分布特征,计算其累计通量及演变过程,评估水库内源磷释放通量和对上覆水的贡献,探讨于桥水库藻华爆发的驱动因素,以期为藻华发生风险防控和水质管理提供支撑。
全文HTML
-
于桥水库位于天津市蓟县城东,是天津市生活及工农业用水的重要水源地之一。于桥水库正常蓄水位21.16 m,蓄水水面86.8 km2,总库容15.59 亿m3;水库流域面积2 035 km2,其中天津境内共涉及10个乡镇、200多个自然村,约16万人,流域土地利用类型主要为果园、旱地、村庄建设用地等,产业结构以旅游业、农业为主。于桥水库流域属温带大陆性季风性半湿润气候,年平均气温为10.4~11.5 ℃,多年平均降水量为748.5 mm,主要集中在6~9月。水库汇水主要包括流域内地表径流汇水、引滦输水和地下水汇入,流域内主要入库河流为果河和淋河,分别位于水库东南岸和东北岸,果河由沙河和黎河汇入而成,黎河为引滦输水通道。于桥水库地理位置和柱状沉积物采样布点见图1。
-
沉积物于2017年6月采集,利用奥地利Uwitec公司的柱状采泥器采集,每个采样点采集样柱3根,共采集9根沉积样柱,确保采集样柱未扰动、管内上覆水澄清。选取一根样柱在现场按1 cm分层,然后分别放入自封袋中密封,运回实验室冷冻保存,主要用于沉积物中磷和重金属的分析。另两根保持原始采样状态(包含上覆水)静置运回实验室,分别用于沉积物孔隙水中磷分析和沉积物年代学序列构建。
-
1)沉积物孔隙水中TP测定。沉积物柱芯采集后运回实验室,静置24 h,然后用虹吸管缓慢移除上覆水。再按照每0.5 cm分层(0~5 cm内)和1 cm分层(>5 cm之后),分别抽滤采集各层沉积物孔隙水。然后用全自动化学分析仪(Smart Chem 200, AMS, USA)对孔隙水中的活性磷酸盐(SRP)进行定量分析。
2)沉积物中总磷和有机磷测定。分层后的沉积物样品利用冷冻干燥机(FD-1,北京德天佑科技有限公司)冷冻干燥,然后压散,剔除砾石、贝壳等杂质,研磨后过150 μm筛后备用。沉积物总磷测定采用HNO3-HF-HClO4消煮法[15],利用微波消解仪(MARS X,CEM,USA)进行消解,然后用等离子体发射光谱仪ICP-OES(Prodigy,Leeman,USA)进行定量。每批次分析均采用6个空白样品和3个标准样品(水系沉积物成分分析标准物质GSD-12,GBW07312,国土资源部物化探研究所)进行质量控制。磷分级提取方法参考文献[16],用不同化学浸提液提取,将总磷分为可交换态磷(Ex-P),铁铝结合态磷(Fe/Al-P),有机磷(Org-P),钙结合态磷(Ca-P)和残渣磷(Res-P)测定过程中所用试剂均为优级纯,所用的水均为超纯水(Milli-Q Advantage A10, Millipore, USA)。
3)210Pb和137Cs放射性同位素比活度测定和年代学构建。沉积柱的年代序列通常采用高纯锗γ能谱仪(GSW1522,CANBERRA,法国)进行测定。称取大约5 g左右沉积物干燥样品置于7 mL离心管中,用薄膜密闭封口,静置一个月左右。每个样品上机测定24 h,利用标准样品定量,计算得到各核素的比活度值。沉积物样品的226Ra(以子同位素214Pb指示,沉积物本底210Pb)和210Pb的比活度,两者的差即为过剩210Pb(210Pbex)的比活度值。然后采用恒定补给速率模型计算于桥水库沉积柱每层对应的年代和沉积速率。同理可获得137Cs的比活度剖面,由于137Cs是核爆炸产生的一种人工放射性元素,从20世纪50年代开始北半球的137Cs开始明显增加,1964年达到最大值,利用该时标峰可以构建137Cs年代学。将210Pb和137Cs年代学结果相互比较引证,可以保证沉积物年代学的准确性。
-
沉积物-上覆水界面磷转移过程主要包含了分子扩散,湍流,生物扰动等多个过程,其中,分子浓度梯度扩散是唯一可以采用数学模型定量的过程。通常采用Fick第一定律估算磷酸盐的扩散通量,见公式(1)。
式(1)中,F为沉积物-水界面磷酸盐扩散通量,mg/(m2·d);
∂C∂x|x=0 为孔隙水磷酸盐浓度梯度,mg/(L·cm);Ds为校正的沉积物磷酸盐扩散系数,m2/s;其与孔隙度之间的经验关系式:Ds=φD0(φ<0.7);Ds=φ2D0(φ>0.7),其中D0为理论扩散系数;φ为沉积物孔隙度,见公式(2)。
1.1. 研究区概况
1.2. 沉积物样品采集
1.3. 样品分析测试方法
1.4. 沉积物磷扩散通量估算方法
-
于桥水库沉积物柱芯中210Pbex比活度垂直分布剖面见图2a。210Pbex比活度随着深度的增加呈现下降趋势,但在不同深度依然有波动。分别拟合3根沉积物柱芯210Pbex比活度随沉积深度变化的指数衰减关系,柱芯YQ-1、YQ-2和YQ-3的线性拟合的相关系数R2分别为0.949,0.930和0.834。根据上述拟合关系,采用恒定210Pbex量和恒定沉积速率模式(Constant Flux and Constant Sedimentation Model,CFS),得到3个区域的平均线性沉积物速率(Linear sedimentation rare, LSR)为0.348 cm/yr。上述3个沉积物柱芯137Cs比活度的最大峰值分别出现在16 cm层处(图2b)。分别以此3处作为1964年计年时标,计算得到3个柱芯的平均沉积速率为0.333 cm/yr。上述210Pb和137Cs计算得到的平均沉积速率误差为,表明本研究中利用沉积物反演构建的年代学系列是合理的。此外,一般的湖库沉积物的沉积速率的范围为0.1 ~ 1.0 cm/yr[17],于桥水库的沉积速率也处于该合理范围之内。
-
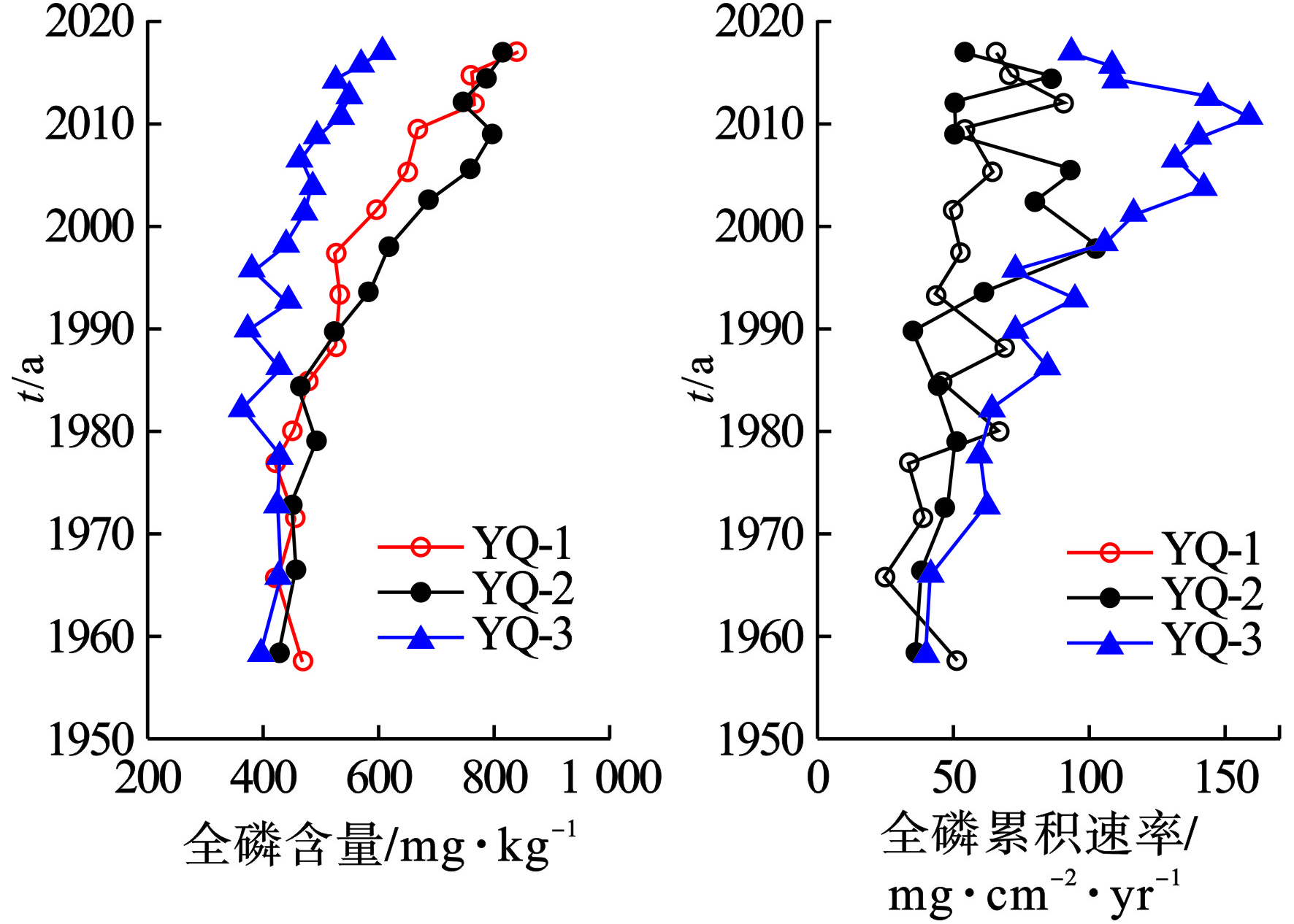
于桥水库3个沉积柱中全磷含量和累积量历史分布见图3。
图3可见,于桥水库沉积物中总磷(TP)含量范围为364~837 mg/kg(图3a)。在时间尺度上,1980年之前,水库沉积物中TP含量较为恒定,平均为(440±24.8) mg/kg,3个沉积物柱芯间的差异也较小。但1980年以来,TP呈现明显的累积特征(图2),均值为(579±136) mg/kg,3根柱芯最高值分别为837、814和605 mg/kg。研究表明[18],在改革开放(1978年)之后,全国工农业经济迅速发展,城镇废污水量稳步增加,加之污水收集和处理设施相对落后,大部分污染物,如氮磷等,排入湖库并在沉积物中累积。不仅如此,为提高粮食产量,化肥使用量和强度也逐年增加[4],由于磷肥利用率较低,过量的磷肥以地表径流或者壤中流的形式,最终排入湖库等末端水体。于桥水库上游流域以农业生产为主[19],肥料的使用强度,这可能是导致于桥水库沉积物中磷含量剧增的重要原因。
综合磷含量和沉积速率,可以得到于桥水库沉积物磷的质量累积速率(Mass accumulation rate of phosphorus, P-MAR),结果见图3b。和磷含量分布特点类似,在1980年之前,全磷的累积速率虽有波动,但维持在50 mg/(cm2·yr)。之后累积速率逐渐上升,尤其是靠近大坝的YQ-3区域,在2010年左右超过了150 mg/(cm2·yr)。对于YQ-1和YQ-2两个柱芯,其全磷累积速率小幅上升,这可能与沉积速率的变化有关[20]。上述研究结果表明,改革开放之后于桥水库受到流域人类活动强烈影响,流域人口的增加、工业的发展、闸坝的修建等增加了水库营养盐的输入。
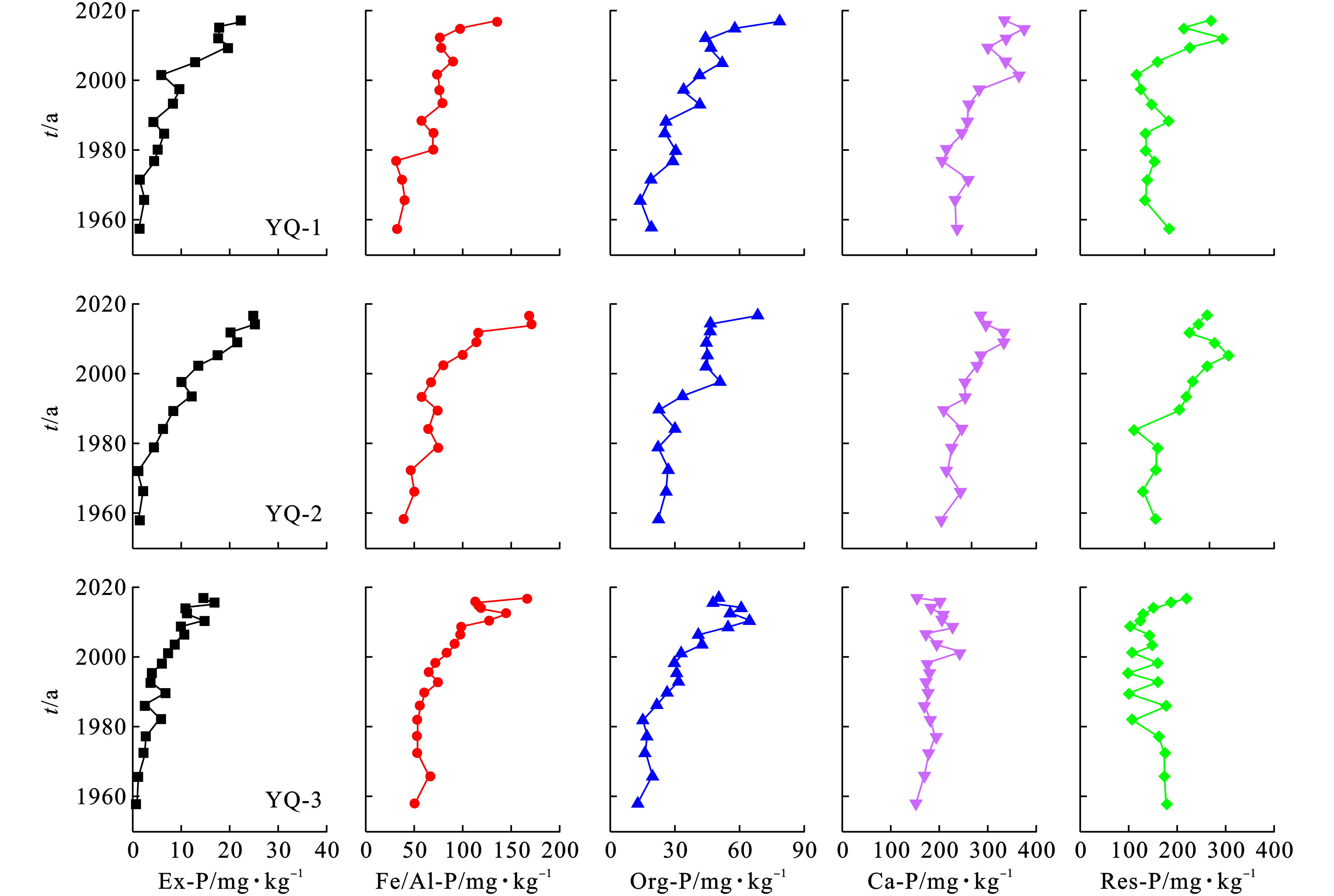
3个沉积物柱芯中磷的赋存形态见图4。
沉积物中Ex-P一般代表了沉积物无机磷的易解析组分。这部分磷活性较强,具有直接的生物可利用性,对于植物生长以及控制上覆水体磷浓度具有重要影响[21]。Ex-P含量在0.94~25.4 mg/kg,占全磷比例的0.24%~3.23%。在时间序列上,与全磷的分布类似,Ee-P在时呈现明显的累积特征。尤其是2000年以后,其累积趋势进一步加强,研究表明[21],湿地沉积物中KCl-P一般为全磷含量2%左右,于桥水库中Ex-P含量说明吸附于水库沉积物上的磷的易解析组分较高,其直接的生物可利用性较强。沉积物中Fe/Al-P组分一般视为无定形态或弱晶型Fe/Al水合氧化物和氢氧化物结合的磷形态,是潜在的生物可利用性磷库[21]。Fe/Al-P占全磷的6.9%~27.3%,此类赋存形态的磷磷影响着沉积物孔隙水中的磷酸盐浓度,对磷释放过程有着重要影响。与全磷和Ex-P分布特征类似,从时间尺度上看,也呈现增长趋势,且在2000年后进一步增强。活性有机磷(Org-P)代表了沉积物中具有生物活性的有机磷组分,既包括可以被快速生物利用的有机磷,也包括了可以被缓慢利用的有机磷组分[21],是潜在的生物可利用性磷源之一。Org-P在于桥沉积物中的含量较低,在80 mg/kg以下。钙镁结合的无机磷组分(Ca-P)代表了水塘沉积物中与Ca和Mg矿物结合形成稳定化合物的磷形态,一般很难被生物体利用[21]。Ca-P含量在153~372 mg/kg,占全磷比例的25.5%~60.6%,是于桥水库磷的主要赋存形态,这与我国南方沉积物完全不同[16],与南北土壤中的钙镁含量差异有关。经过连续浸提后残渣中剩余的磷组分(Res-P)一般代表了沉积物中高度惰性的有机磷和不能被酸碱提取的矿物结合态磷[21]。通常认为Res-P不具有生物可利用性。于桥水库沉积物中Res-P平均含量在174 mg/kg左右。除近年来稳步增加外,总体而言,Res-P含量在沉积物中保持相对稳定水平。
-
基于上述磷赋存形态分析,于桥水库沉积物磷Ex-P和Fe/Al-P可能具有较高的释放潜势。对于水库等水体的沉积物-水界面,上覆水的流速一般都非常低,浓度梯度扩散是磷酸盐迁移的最重要形式[22]。因此,采用沉积物孔隙水一维扩散模型,估算了正磷酸盐的扩散通量,结果见表1。
表1可知,三个沉积物采集位置(YQ-1,YQ-2和YQ-3)的磷酸盐扩散通量分别为2.791、3.665和1.130 mg/(m2·d),均表现为由沉积物向上覆水释放,且在库中(YQ-2)和库尾(YQ-1)的释放通量要明显高于坝前位置(YQ-3),这可能与支流输入,以及水库藻华发生的特征有关。已有研究表明,上游支流是于桥水库氮磷等物质的主要来源[14]。在支流汇入区,随着水流速度降低,支流来水中的颗粒物携带氮磷沉积,形成了富含磷的沉积物,因此也产生了较高的磷扩散通量。不仅如此,由于于桥水库藻华主要发生在水库西北岸,严重时会发展到库心区[8],藻华发生也会在沉积物表层形成富含有机质的沉积层,有机质矿化过程可能导致磷释放[23],进而表现出较高的磷释放通量。而在坝前位置,随着有机质矿化过程的完成,沉积物中的磷活性降低,因此表现出相对较低的磷扩散通量。
2.1. 于桥水库沉积速率变化
2.2. 于桥水库磷沉积过程
2.3. 于桥水库沉积物磷释放通量估算
-
本研究基于210Pb和137Cs年代学方法,建立了于桥水库建库(1959年)以来沉积物总磷的历史累积特征。水库总磷含量范围为364~837 mg/kg;1980年之前,水库沉积物中TP含量较为恒定,平均为(440±24.8) mg/kg,之后呈现明显的累积特征,均值上升为(579±136) mg/kg,最高达837 mg/kg。沉积物中可交换态磷(Ex-P)、铁铝结合态磷(Fe/Al-P)和有机磷(Org-P)在时间上均呈现与总磷类似的逐渐累积的变化特征,钙结合态磷和残渣磷是主要的成分。于桥水库沉积物-水释放通量分为1.130~3.665 mg/(m2·d),水库内源磷是藻华发生的重要物质来源,内源磷控制可能是减少于桥水库藻华发生概率的有效途径。



 DownLoad:
DownLoad: