-
污泥作为城市污水处理厂的主要废物,因其含有大量病原微生物、寄生虫卵、重金属以及大量难降解的有机物[1],所以,污泥最终的处理处置技术广受关注。截至2017年12月,我国建成污水处理厂5 072座,年产生含水率80%的污泥超过5×107 t,如果这些污泥得不到妥善处置,将对环境和生态造成严重危害。目前,对于污泥的处置多采用填埋和堆肥,填埋处理要求污泥的含水率达到60%以下[2],而我国大多数污水处理厂不能达标,所以,须在污泥脱水之前对污泥进行调理,改变污泥的组织结构,减小污泥的黏性,实现污泥高效脱水[3]。有研究[4]发现,污泥难以脱水的主要原因是由于胞外聚合物(EPS)的存在,将EPS絮体破解,释放内部水分,才能实现污泥高效脱水。EPS是细菌分泌于体外的一些高分子聚合物,主要成分是多糖、蛋白质和核酸等高分子物质。
此外,随着我国造纸行业的发展,造纸污泥的量也在逐年增加。造纸污泥是制浆造纸过程中产生的固体废物,富含碳酸钙、高岭土等无机物和纤维素、半纤维素、木素等有机物,并且还存在部分成分复杂的污染物,如果处理不当,将对环境造成严重危害[5]。
目前,Fenton法和酸处理法用于污泥调理,但对pH的要求较为苛刻[6]。高级氧化法中的过硫酸盐经过渡金属、紫外以及热活化产生的硫酸根自由基(
SO2−4 ·),其氧化还原电位E0=2.50~3.10 eV[7],具有很强的氧化性和非选择性,可以氧化绝大部分有机物,使EPS絮体破解。宋秀兰等[8]和ZHEN等[9]采用亚铁离子活化过硫酸盐对污泥进行调理,可以有效降低污泥的含水率,提高污泥的脱水效果。基于上述研究基础,本研究采用Fe2+活化过硫酸盐联合造纸初沉污泥对市政污泥进行调理,探究不同调理方式对市政污泥的各项指标的影响,以期解决市政污泥高含水率、难以脱水的难题。
-
实验污泥取自某污水处理厂的浓缩池污泥(原泥),污泥性质如表1所示。骨架构建所用的造纸污泥取自某造纸废水处理厂初沉污泥,有机质(VSS/TSS)为44.25%。
-
实验药品:过硫酸钾(K2S2O8)、硫酸亚铁(FeSO4·7H2O)、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、氯化钠(NaCl)、苯酚(C6H5OH)、考马斯亮蓝(C47H48N3NaO7S3),抗坏血酸(C6H8O6),钼酸铵((NH4)6Mo7O24·4H2O),所用药品均为分析纯,浓硫酸(98%)。
实验仪器设备:毛细吸水时间测定装置(HDFC-10A型,北京恒奥德仪器仪表有限公司)、污泥比阻测定装置(KL-WBC-1型,武汉科林高教学设备有限公司)、黏度计(NDJ-8SN型,上海平轩科学仪器有限公司)、恒温干燥箱(WGL-125B型,天津泰斯特仪器有限公司)、紫外分光光度计(SP-UV1100型,上海奥析科学仪器有限公司)、搅拌器(JJ-4型,国华电器有限公司)、雷磁pH计(PHS-3C型,上海仪电科学仪器有限公司)、马弗炉(KSL-1200X型,上海虔钧科学仪器有限公司),手提式压力蒸汽灭菌锅(DSX-280B型,济南欧迪医疗器械有限公司),化学需氧量(COD)快速测定仪(5B-6C型,上海沛升仪器设备有限公司)等。
-
将取回的污泥放置在4 °C冰箱中保存。实验取200 mL待测污泥于500 mL烧杯中,置于机械搅拌器上搅拌5 min,加入过硫酸钾继续搅拌10 min,继续加入硫酸亚铁继续搅拌5 min,最后加入100 mL造纸初沉污泥继续搅拌10 min,量取100 mL污泥进行污泥比阻的测定,量取10 mL调理后的污泥进行毛细吸水时间测定。污泥脱水实验在各个条件下进行3次,以保证实验的可靠性。
-
1)污泥泥饼含水率:泥饼含水率是作为表征污泥调理效果好坏最为直观的参数,泥饼含水率越低,污泥调理效果越好。
2)污泥比阻SRF:SRF是表征污泥过滤特性的综合指标,SRF越大,表示污泥脱水效果越差[10],SRF按式(1)进行计算。
式中:RSRF为污泥比阻,1012 m·kg−1;P为过滤压力,Pa;A为过滤面积,m2;b为布氏抽滤实验的t/V对V作线性图的斜率,s·m−6;μ为滤液黏度,Pa·s;C为单位体积滤液产生的滤饼质量,kg。
3)毛细吸水时间CST:CST也是污泥脱水效果的表征指标,CST越大,污泥脱水效果越差[11]。
4)污泥EPS:污泥中EPS分为溶解型EPS(S-EPS)、松散结合型EPS(LB-EPS)、紧密结合型EPS(TB-EPS),参照文献中的方法[12]提取EPS,测定蛋白质和多糖含量,蛋白质采用考马斯亮蓝法[13],多糖采用苯酚硫酸法[14],探究胞外聚合物的破解程度。
5)滤饼和滤液中总氮、总磷:由于脱氮除磷工艺过程中,氮和磷被微生物吸收合成细胞,通过排泥得到去除[15],EPS破解后,氮、磷释放进入滤液中,造成滤液中总氮和总磷的含量增加。
-
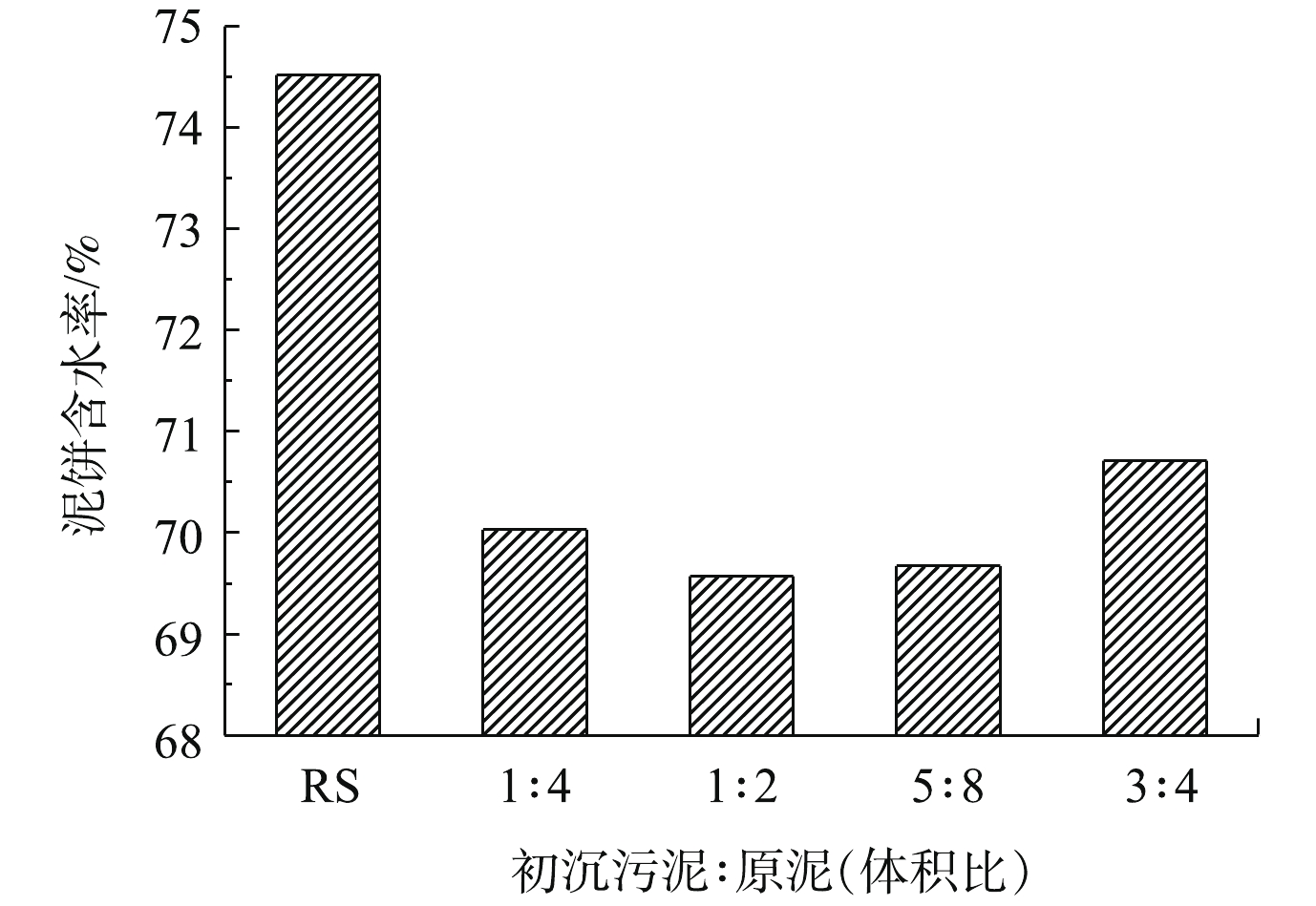
造纸污泥投加量对污泥泥饼含水率的影响如图1所示。由图1可以看出,未经调理的污泥泥饼含水率为74.52%,采用过硫酸盐联合造纸初沉污泥调理后,泥饼的含水量显著降低。随着初沉污泥与原泥混合比例的增加,泥饼的含水率先迅速降低,后又出现上升的趋势;当初沉污泥与原泥以1∶2的体积比混合时,泥饼的脱水效果达到最好,泥饼含水率降至69.57%。这是因为造纸初沉污泥中含有细小纤维、碳酸钙等物质[5],一定量的细小纤维可以在污泥中起到骨架支撑的作用,使污泥在抽滤过程中保持多孔性,形成水通道,使污泥内部的水分高效脱出[16]。随着初沉污泥投加量的增加,细小纤维的含量增加,会在污泥脱水过程中阻塞水通道,不利于水分的脱出,所以初沉污泥与原泥最优的混合比例为1∶2。
-
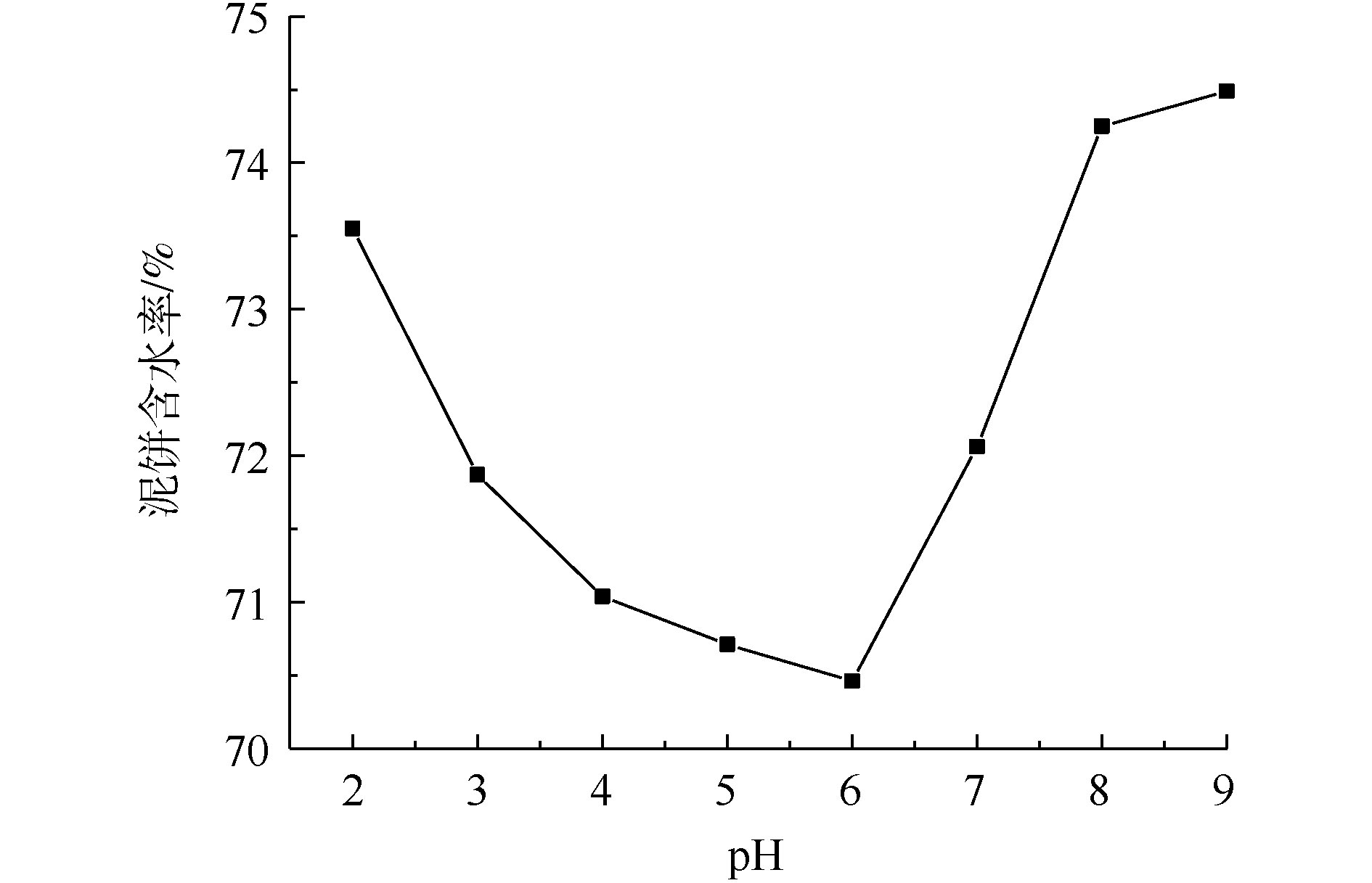
污泥初始pH对泥饼含水率的影响如图2所示。由图2可以看出,随着污泥初始pH的增加,泥饼含水率出现先降低后增加的趋势;当污泥初始pH=6时,泥饼的含水率由74.52%降至70.46%。在酸性条件下,随着pH的增大,泥饼的含水率下降。这是因为当pH<3时,硫酸根自由基的氧化性能受到抑制,使得泥饼含水率没有明显的降低。当3<pH<6时,EPS会在酸性条件下破解,形成细小的絮体,使内部的水分释放,在抽滤过程中过小的絮体可能会导致污泥系统崩溃,堵塞水通道,使内部的水分不能顺利脱出。当pH=6时,由于体系接近于中性环境,一方面由于硫酸根自由基的氧化性能,另一方面由于酸环境,污泥含水率可以显著降低。当污泥初始pH>7时,污泥系统处于碱性环境,体系中的Fe2+和Fe3+会形成低活性的氢氧化物沉淀[17],导致能活化过硫酸盐的Fe2+量减少,限制了过硫酸盐的氧化效率。
-
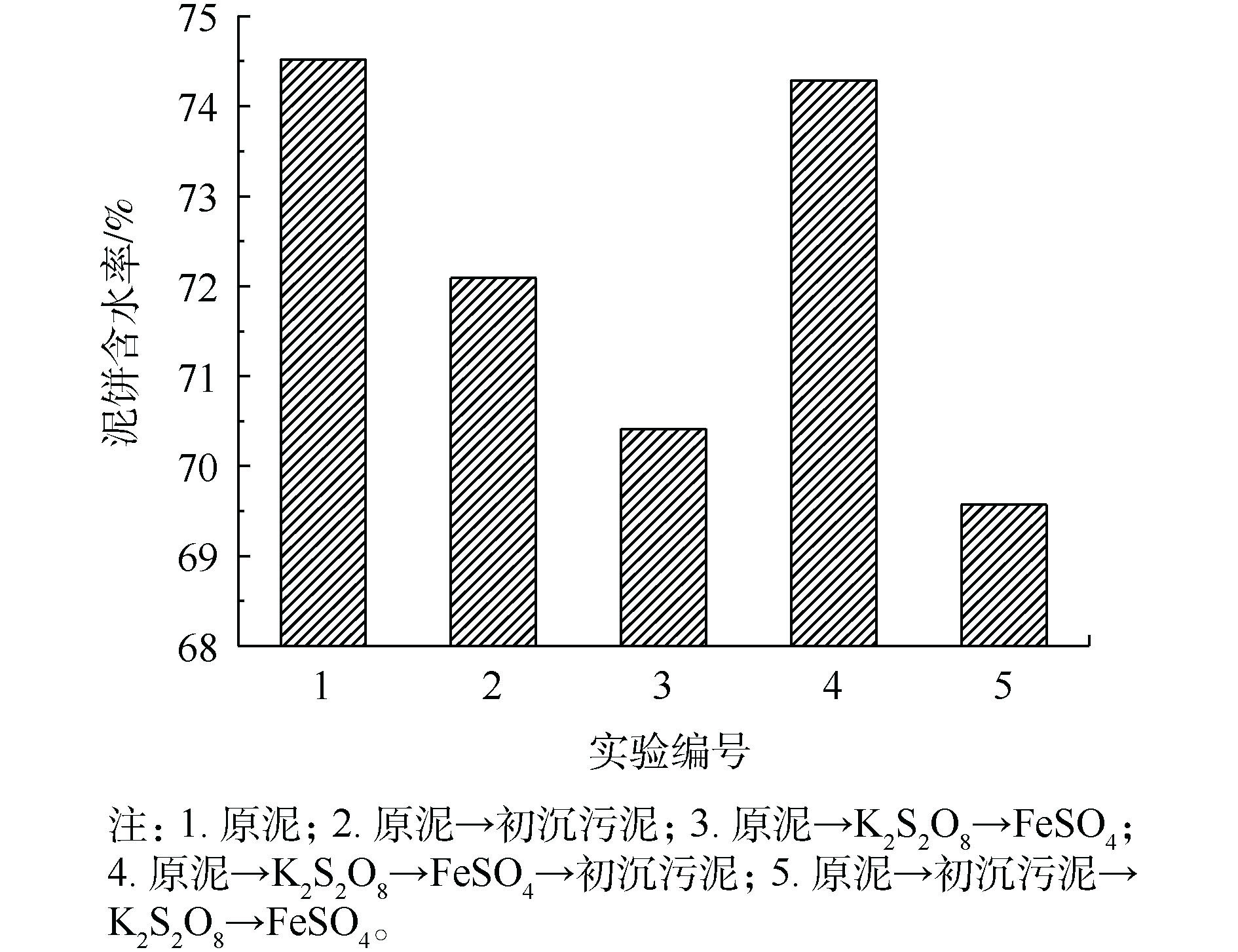
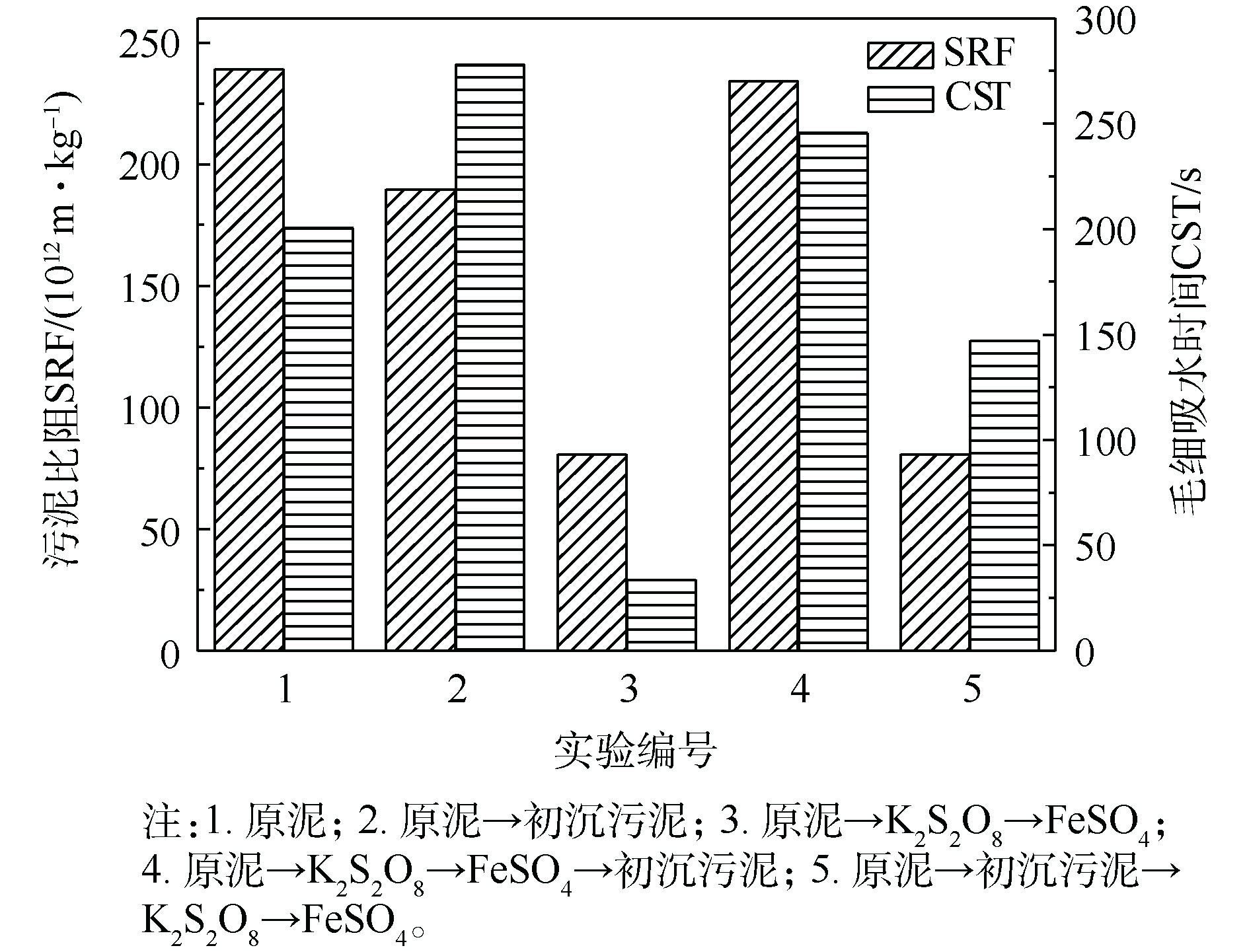
不同调理方式对污泥泥饼含水率、SRF以及CST的影响如图3和图4所示。由图3和图4可以看出,未经调理的原泥经抽滤脱水后泥饼的含水率为74.52%,SRF为238.97×1012 m·kg−1,CST为199.8 s;采用亚铁活化过硫酸盐调理后,原泥泥饼的含水率降至70.41%,SRF下降至80.75×1012 m·kg−1;单独使用初沉污泥调理后,泥饼含水率降至72.09%,SRF降至189.70×1012 m·kg−1;经初沉污泥复合调理后污泥泥饼的含水率69.57%,污泥SRF下降至80.71×1012 m·kg−1,较原泥含水率降低6.64%,污泥比阻降低了66.23%。
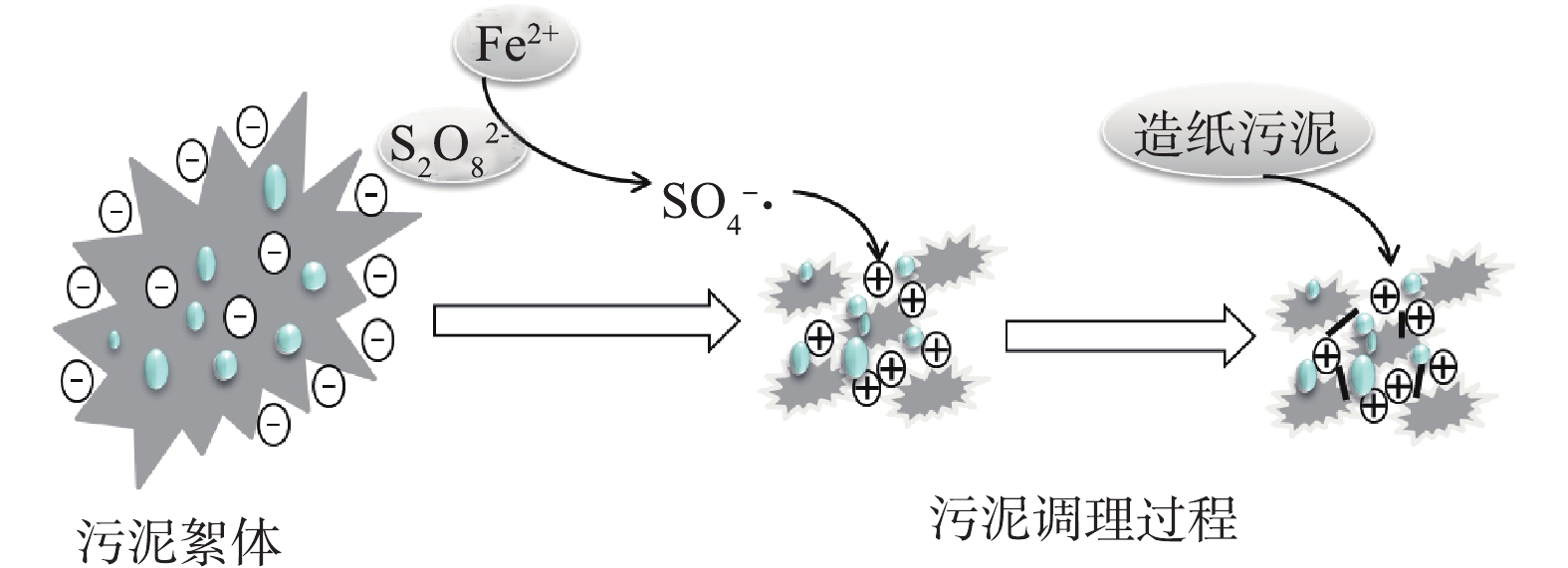
第2组较第1组的含水率、SRF和CST有所降低。这是因为初沉污泥中含有的细小纤维在污泥抽滤过程中形成了水通道,使水分有效脱出。污泥调理示意图如图5所示。第3组的含水率较第1、2组有所降低。这是因为亚铁活化过硫酸盐产生强氧化性的SO4−·将胞外聚合物氧化破解,细胞内部水分释放,降低泥饼含水率。第4组与第5组相比,泥饼的含水率以及SRF、CST指标较高。这可能是因为造纸污泥中的纤维粒径过大,不能起到骨架支撑的作用,不利于内部水分脱除。第5组将原泥与初沉污泥进行混合后再用过硫酸盐进行调理,SO4−·的强氧化性可以将纤维分解为小粒径,使其在污泥内部成功搭建骨架,胞外聚合物破解后将内部的水分释放,可以通过水通道将水分抽滤脱除,使泥饼的含水率进一步降低,这一现象与吴彦[16]的研究结果一致,当稻壳粉的粒径为109~150 μm时,泥饼的含水率降至最低。
-
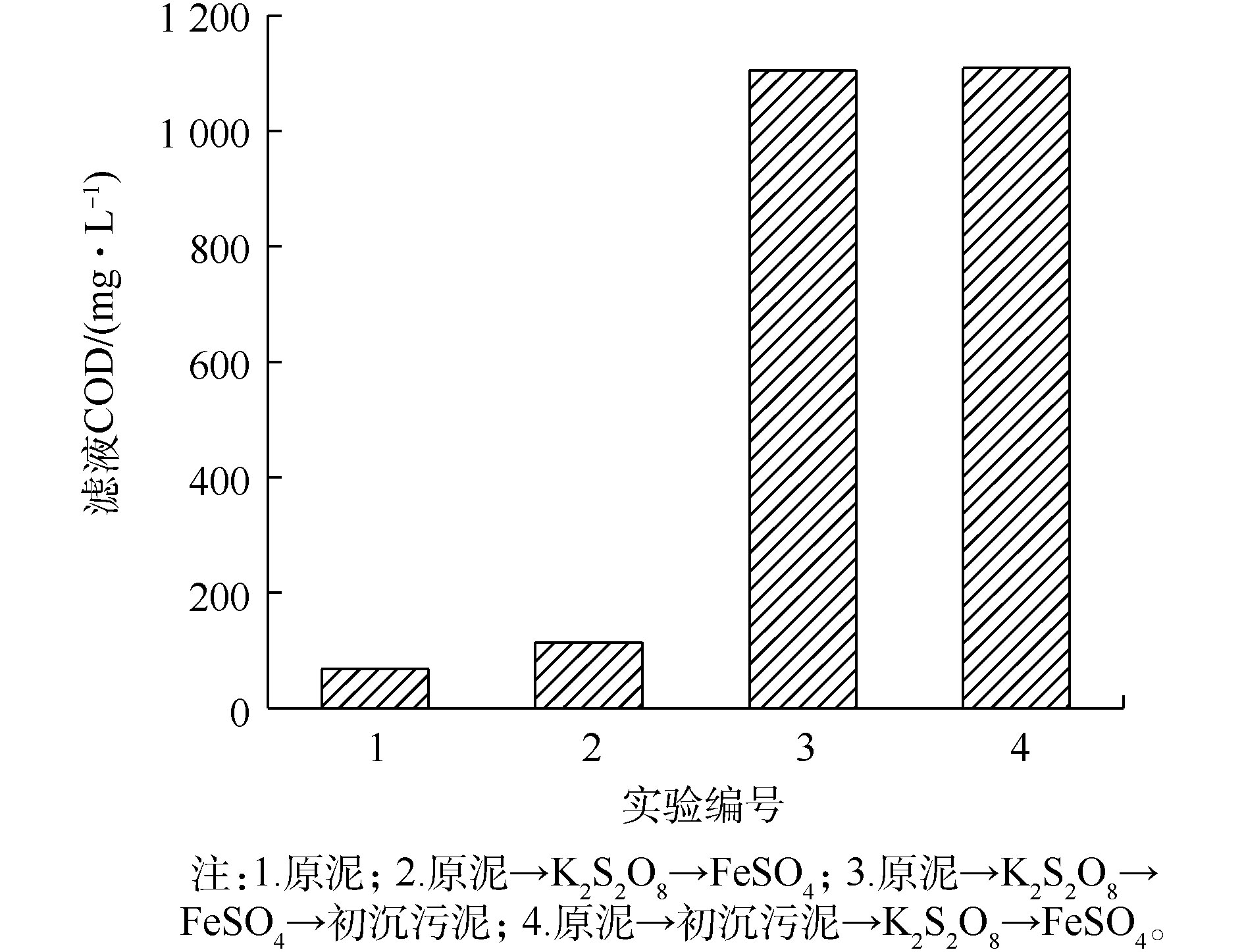
不同调理方式对污泥滤液COD的影响如图6所示。由图6可以看出,原泥滤液COD为67.22 mg·L−1,经过硫酸盐调理之后滤液COD上升至114.4 mg·L−1。这是因为
SO2−4 ·将EPS破解使细胞内部的蛋白质、多糖、核酸等有机物释放进入污泥中,经过滤后有机物进入滤液中,导致滤液COD含量升高。而经造纸污泥联合调理之后滤液COD上升至1 104.67 mg·L−1,较原泥滤液COD增加了16.5倍。这是因为初沉污泥中含有EPS和大量有机物,在构建骨架的同时,部分有机物进入滤液中,造成滤液COD值急剧增加。 -
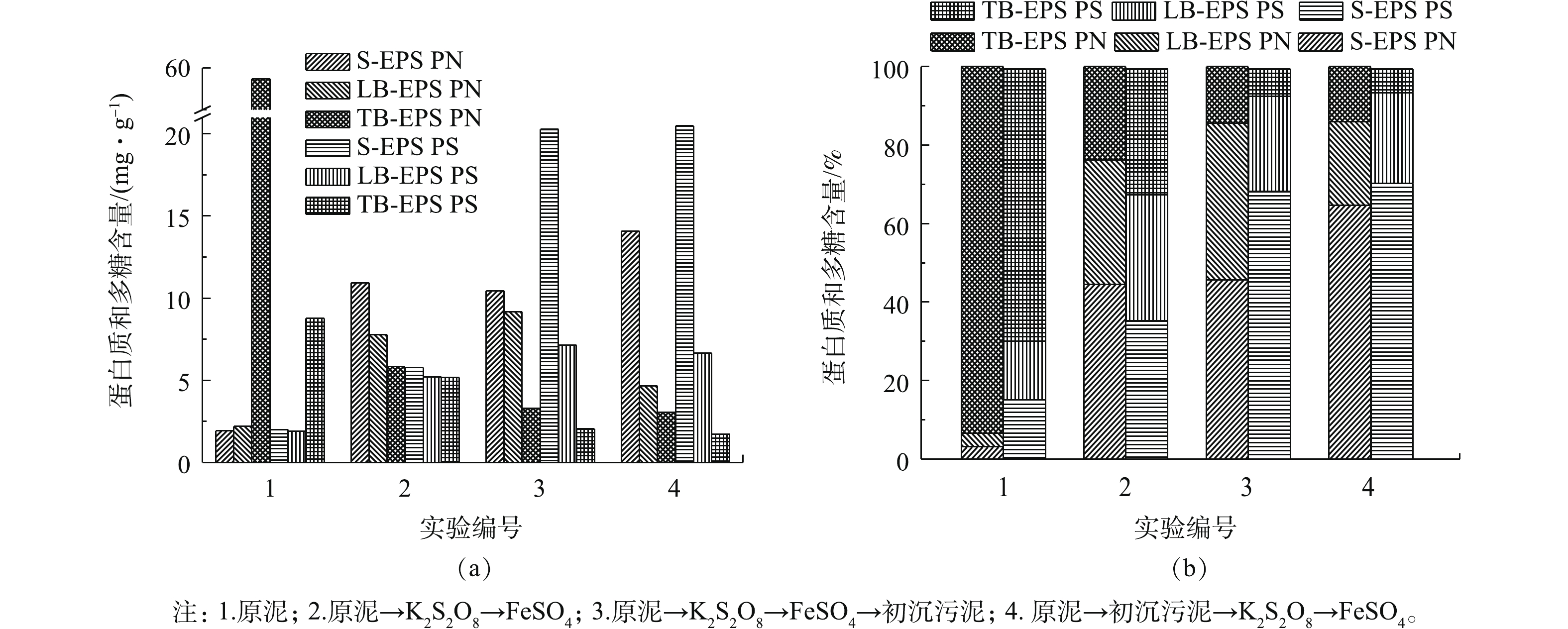
不同调理方式对污泥EPS中蛋白质(PN)和多糖(PS)的影响如图7所示。由图7可以看出,原泥中PN和PS的分布关系为TB-EPS>LB-EPS>S-EPS,经调理后PN和PS的分布关系为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS,其中变化最为显著的是第4组。由图7(a)可以看出,S-EPS中的PN由1.92 mg·g−1上升至14.074 mg·g−1,较原泥增加61.56%;PS由1.99 mg·g−1上升至20.48 mg·g−1,较原泥增加55.25%。同时,由图7(b)可以看出,经调理后污泥的S-EPS中的PN和PS明显增多,而TB-EPS和LB-EPS中的PN和PS也显著增多,这一结果与张昊[18]的研究相一致。
因为污泥中的EPS被SO4−·氧化破解,使细胞内部的PN和PS等物质释放,转化为溶解态,使得S-EPS中PN和PS含量增大。调理后PN和PS的含量较原泥有大幅降低,因为
SO2−4 ·具有强氧化性,可以将PN和PS氧化分解为小分子的有机物。骨架复合调理较单独使用过硫酸盐调理的S-EPS中PN和PS要多,是因为造纸污泥中也存在EPS,SO2−4 ·会将其氧化释放,使得PN和PS的含量增多。 -
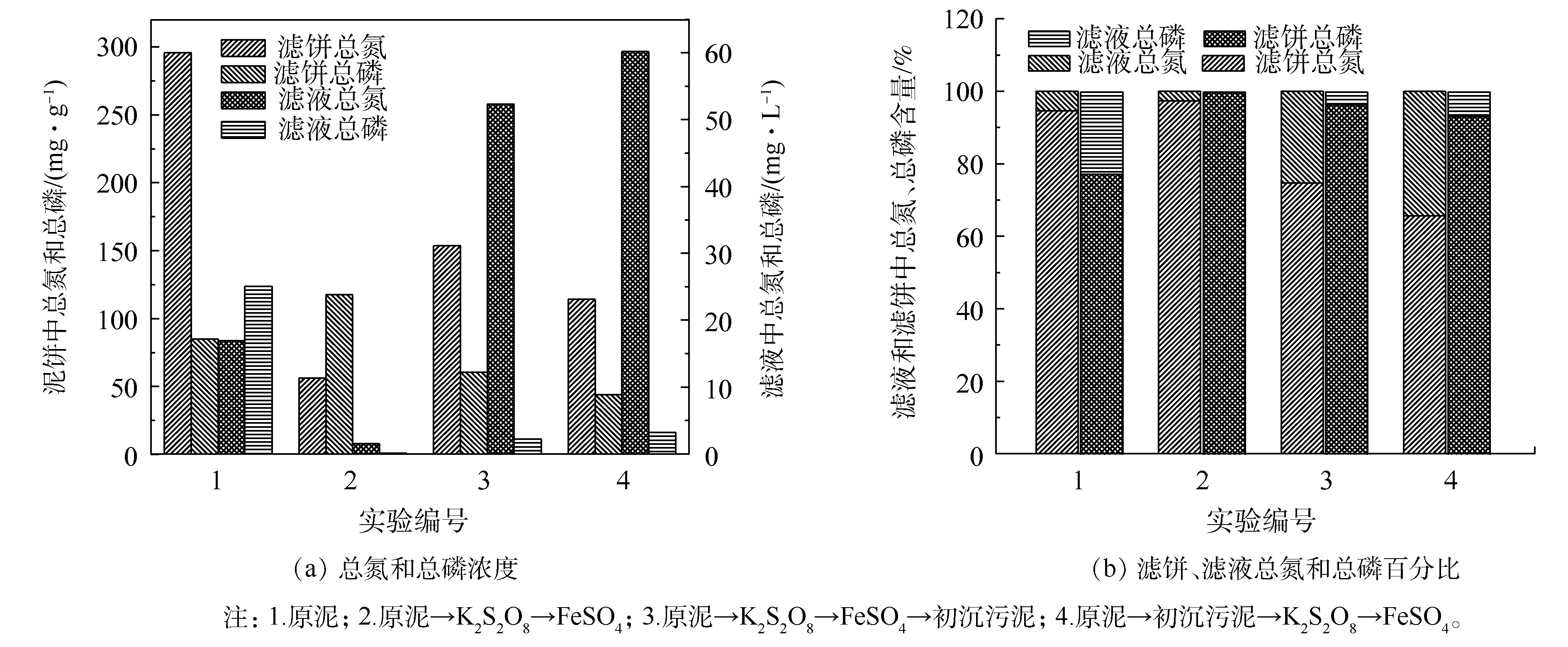
不同调理方式对滤饼和滤液中总氮、总磷的影响如图8所示。由图8(a)可以看出,原泥泥饼中总氮的含量为295.75 mg·g−1,总磷的含量为85.00 mg·g−1。这是因为经脱氮除磷工艺后,将大部分的氮和磷固定在污泥当中,最终随污泥排出污水处理系统。由图8(b)可以看出,经过硫酸盐单独调理的污泥,泥饼中总磷的含量较原泥所占比例更大。这是因为污泥中存在Fe3+和Fe2+,会吸附泥饼中的磷,产生沉淀,截留在泥饼中造成泥饼中总磷所占比例增加,这一结果与阚丹等[19]的研究中混价铁氢氧化物对无机磷的吸附/沉淀相一致。
经初沉污泥复合调理后,泥饼中总氮所占比例下降,由原泥的94.60%下降至65.62%。这是因为2种污泥中的EPS被破解,将含有N元素的物质(蛋白质、核酸等)释放到滤液中,造成滤液中总氮的增加,而总磷由于Fe3+和Fe2+的存在并无显著变化。总氮和总磷分布关系的变化验证了
SO2−4 ·的强氧化性能可破解EPS,从而提高污泥脱水性能。 -
1)经初沉污泥复合调理后污泥的脱水效果显著增强,SRF由121.18×1012 m·kg−1下降至32.67×1012 m·kg−1,降低了73.04%;泥饼含水率由75.51%下降至71.75%,降低了4.98%。
2)经过硫酸盐调理之后滤液COD由67.22 mg·L−1上升至114.4 mg·L−1,而经造纸污泥联合调理之后滤液COD上升至1,104.67 mg·L−1,较原泥滤液COD增加了16.5倍。
3)过硫酸盐可以有效破解EPS,使细胞内部水分释放,并通过初沉污泥骨架形成的水通道排出,从而有效降低泥饼的含水率,调理后泥饼中PN和PS的分布关系为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS。
4)经调理后的污泥由于EPS的破解,使泥饼中总氮所占比例由原泥的94.60%下降至65.62%,而总磷由于Fe3+和Fe2+所产生的吸附/沉淀作用并无显著变化。
Fe2+活化过硫酸盐对市政污泥EPS性能的影响
Effect of Fe2+ activated persulfate on EPS properties of sewage sludge
-
摘要: 针对污泥难以脱水、处理难度大的问题,通过过硫酸盐高级氧化技术联合造纸污泥作为骨架对市政污泥进行调理,以泥饼含水率、污泥比阻(SRF)、毛细吸水时间(CST)、胞外聚合物(EPS)中蛋白质和多糖的分布关系,以及滤饼和滤液中总氮、总磷含量为指标,研究Fe2+活化过硫酸盐联合造纸污泥骨架构建体对EPS的影响。结果表明:将造纸污泥与市政污泥1∶2混合,再添加过硫酸盐和Fe2+,对污泥的调理效果最好,泥饼的含水率由74.52%降至69.57%,SRF降低了66.23%;蛋白质和多糖的分布关系为S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS,滤饼中总氮所占比例由94.60%下降至65.62%,EPS被有效破解,污泥脱水效果显著改善。
-
关键词:
- 市政污泥 /
- 造纸污泥 /
- 骨架 /
- 胞外聚合物(EPS)
Abstract: In response to the difficulty in sewage sludge dewatering and treatment, the combination of Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation and skeleton builders of paper sludge was used to condition the sewage sludge. In this study, moisture content of sludge cake, specific resistance to filtration (SRF), capillary sunction time (CST), the distribution of protein and polysaccharide in the EPS, and the total nitrogen and total phosphorus content in the filter cake and filtrate were used to evaluate the effect of above combination on the EPS. The result showed that when the sewage sludge was mixed with the paper sludge with a ratio of 1:2, the addition of Fe2+ and persulfate could result in the best dewaterability effect. The moisture content of sludge cake decreased from 74.52% to 69.57%, and the SRF was reduced by 66.23%. The distribution of protein and polysaccharide was S-EPS>LB-EPS>TB-EPS, and the proportion of total nitrogen in cake decreased from 94.60% to 65.62%. The EPS was effectively disrupted, and the sludge dewaterability was significantly improved.-
Key words:
- sewage sludge /
- paper sludge /
- skeleton /
- extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
-
活性染料具有颜色鲜艳、均染性好、应用简便、染色牢度高、价格低廉等特点,是我国染料工业中第2大类染料品种[1]。对位脂(对氨基苯基-ß-羟乙基砜硫酸)含有重氮化组分的氨基和能发生化学反应生成染料-纤维共价键的反应性基团,能大大提高染料的利用率,所以成为活性染料最重要的中间体,市场需求更为庞大[1-2]。目前国内对位酯产量约为1.6×105~1.8×105 t·a−1。但是生产1 t对位脂要产生30 t的废水,同时这些废水COD浓度高,可生化性差[3],因此,高效处理对位酯生产废水具有很重要的实际意义。已有研究[3-4]表明,采用Fenton-水解酸化-好氧组合工艺和铁碳微电解-Fenton-光催化联合工艺,能去除大部分的COD;但是Fenton反应作为预处理,过氧化氢和酸碱试剂消耗成本太高。在工程实践中,处理高浓度难降解有机废水时,使用厌氧工艺作为前端处理工艺,具有沼气可回收利用、可提高废水的生化性及可降低运行成本等特点。由于对位脂生产废水含有大量的硫酸盐(COD/
SO2−4 为3.58),同时对位酯属于有机硫化合物,其含有磺酰基和硫酸盐基团,容易水解(结构式见图1),因此,也间接地增加了进水硫酸盐的负荷,使COD/TSO2−4 (总硫酸盐)降至2.4。有研究[5]表明,在进水COD/SO2−4 >3.3(碳硫比>10)时,产甲烷菌不会受硫酸盐被还原时所产生硫化物的抑制,这也是厌氧工艺在工程应用的基本条件。已有研究[6]采用单一的厌氧复合床处理该废水,只能运行到COD至15 000 mg·L−1,对应COD容积负荷为5.0 g·(L·d)−1,如进一步提高COD至20 000 mg·L−1,产甲烷和反硝化能力完全丧失。本研究利用微电场-零价铁,来提高UBF处理高硫酸盐和高有机硫废水中的运行负荷及同步产甲烷和反硝化的能力。结果表明,同步产甲烷反硝化过程具有一定的经济可行性,能为后续的硝态氮去除工艺减轻负担。1. 实验部分
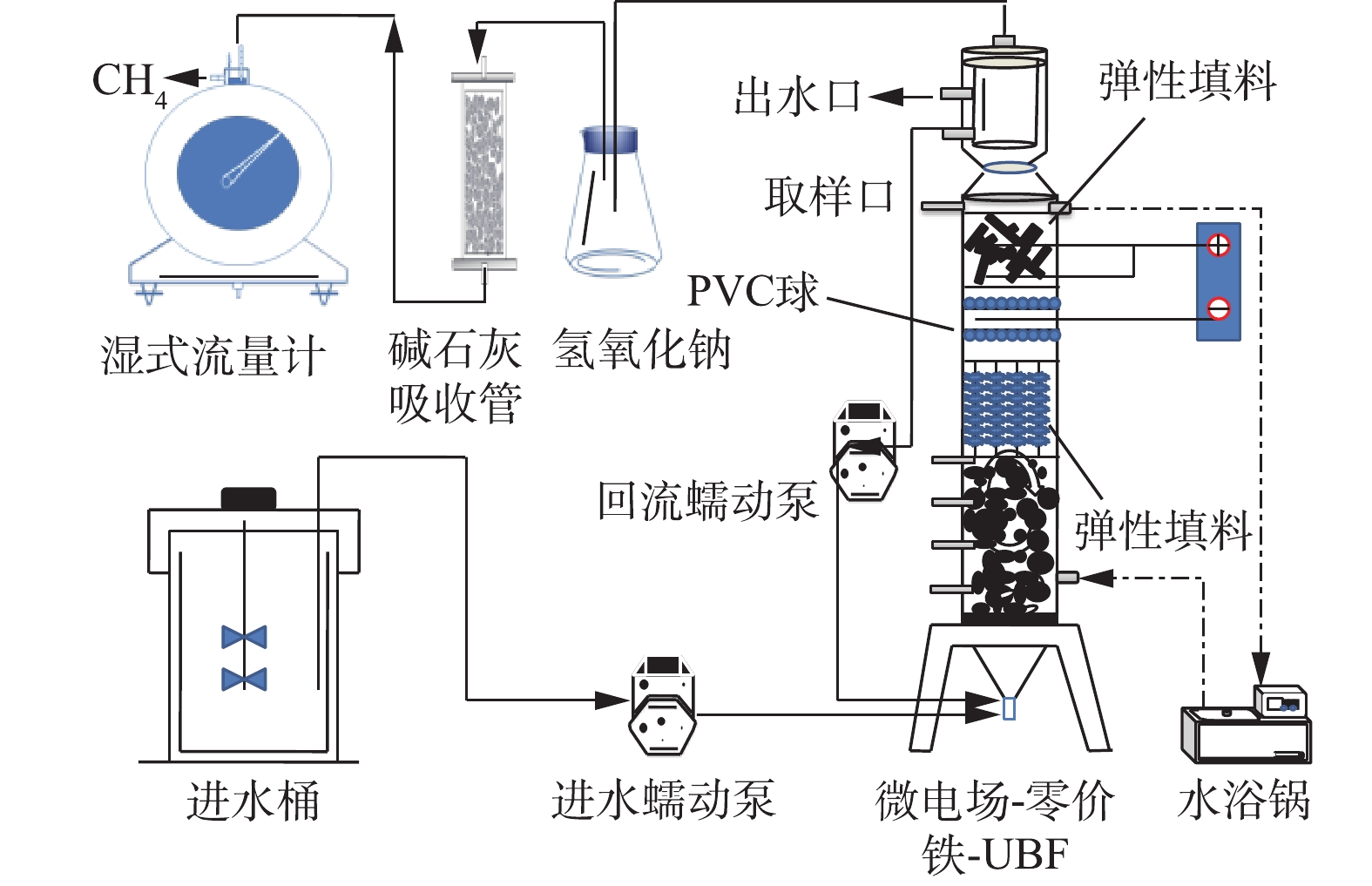
1.1 实验装置
微电场-零价铁-UBF实验装置及工艺流程如图2所示。其中,复合床有效容积为6 L,材料为聚氯乙烯,内径和外径分别为100 mm和140 mm,高为80 mm。复合床下部是厌氧污泥区,污泥区上部安装有弹性填料。中部是铁区,填充的是铁刨花,电源阳极通过多个铜线和中部铁区相连,以多孔不锈钢盘作为阴极放在铁区和弹性填料中间。在工程上,补充铁粉的途径有2种:第1种方式是将铁粉和污泥混合,由潜污泵从厌氧罐底粉和罐内污泥充分混合;第2种方式是通过顶部的三相分离器投加,同时打开内循环泵,使铁粉和罐内污泥充分混合。为防止铁区与阴极直接接触引起的短路,不锈钢盘上部安装有塑料托盘和PVC球,起绝缘作用。本研究采用的是复合床的设计,弹性填料起截流污泥的作用,因此,厌氧污泥不会黏附在钢盘上。产生的沼气经过反应器上部的三相分离器,通过洗气瓶里面的3 mol·L−1氢氧化钠吸收H2S和CO2,然后再经过装有碱石灰的干燥管以吸收水蒸气,最后使用湿式流量计进行测量。废水经蠕动泵依次进入反应区、铁区、复合床底部,从而实现微电场-零价铁-UBF耦合过程。在整个反应期,利用恒温循环水浴箱控制复合床水温在35 ℃左右。回流蠕动泵回流比控制在400%左右。
1.2 污水及其来源
实验进水为山东某化工厂2018年1月对位脂生产车间的出水。原水pH在7.0左右,COD约为35 000 mg·L−1。原水硫酸盐约为9 770 mg·L−1,COD/
SO2−4 约为3.58,有机硫约为4 788 mg·L−1(按硫酸盐计),所以加上有机硫水解产生的硫酸盐,原水COD/TSO2−4 可降低至2.4。同时,检测到原水中硝态氮的含量约为77 mg·L−1。在实验中,进水硫酸盐浓度的变化是通过人工投加Na2SO4(分析纯)的方式来调节的。进水碱度按1.0 g COD投加0.3 g NaHCO3(工业级)的比例调节。厌氧反应器种泥的接种体积为3 L,种泥来自厂区附近工业园区污水处理厂的絮状干泥(含水率为80%), VSS约为20.2 g·L−1。不同阶段废水水质学参数及COD容积负荷见表1。表 1 微电场-零价铁-UFB各个运行阶段的废水成分及COD容积负荷Table 1. Water quality parameters and COD volume load of wastewater inmicro-electric field-ZVI-UBF at different stages阶段 时间/d COD/(mg·L−1) 对位酯/(mg·L−1) 硫酸盐/(mg·L−1) 有机硫(以 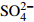 计)/(mg·L−1)
计)/(mg·L−1)硝态氮/(mg·L−1) OLR/(g·(L·d)−1) I 1~30 500 100 223 68.4 1.1 0.167 I 31~45 2 000 400 558 273.6 4.4 0.668 I 46~60 5 000 1 000 1 395 684 11 1.67 I 61~75 10 000 2 000 2 790 1 368 22 3.34 I 76~90 15 000 3 000 4 185 2 052 33 5.01 I 91~105 20 000 4 000 5 580 2 736 44 6.68 II 106~125 20 000 4 000 10 000 2 736 44 5.01 III 126~140 20 000 4 000 20 000 2 736 44 5.01 IV 141~160 20 000 4 000 10 000 2 736 44 5.01 1.3 实验步骤
为期160 d的实验分4个阶段运行,阶段划分见表1。在运行过程中,微电场的电压设为0.5 V。前30 d,污泥驯化完成后,向复合床投加铁刨花100 g。因为运行过程中铁刨花不断被消耗,故每隔30 d补充50 g。进水COD用去离子水来稀释成要求的COD(见表1)。在整个实验过程中,每天进水为2 L,HRT为3 d。在第I阶段,通过逐步提高进水COD来提高容积负荷,考察复合床的运行情况。第II阶段,加入4 420 mg·L−1硫酸盐,使COD/
SO2−4 降低至2(COD/TSO2−4 =1.57),继续考察降低碳硫比对复合床产甲烷量的影响。第III阶段,继续加入10 000 mg·L−1硫酸盐,使COD/SO2−4 降低至1(COD/TSO2−4 =0.88)。第IV阶段,COD/SO2−4 恢复至第II阶段,考察复合床系统恢复能力。1.4 分析方法
COD、pH、VFA(以乙酸计)、硫化物、总硫和有机硫含量的测定均参考文献中的方法[6]。产生的甲烷体积由湿式流量计(LML-1型,青岛科迅电子有限公司)来计量。硫酸盐和硝态氮含量的测定均采用离子色谱法(戴安离子色谱仪DIONEX, ICS-2100)。对位酯含量的测定采用反向离子抑制色谱法。具体色谱分析条件如下:色谱柱为Agilent公司的Zorbax Extend-C18 (150 mm× 4.6 mm, 5 µm);柱温设为室温;流动相水与甲醇的体积比为38∶62;pH调整为3.5;进样量为20 µL;流速为1.0 mL·min−1;检测波长为254 nm[7]。在对位脂浓度为1~20 mg·L−1时建立标准曲线(R2 =0.999)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 提高容积负荷对复合床同步产甲烷反硝化能力的影响(阶段I)
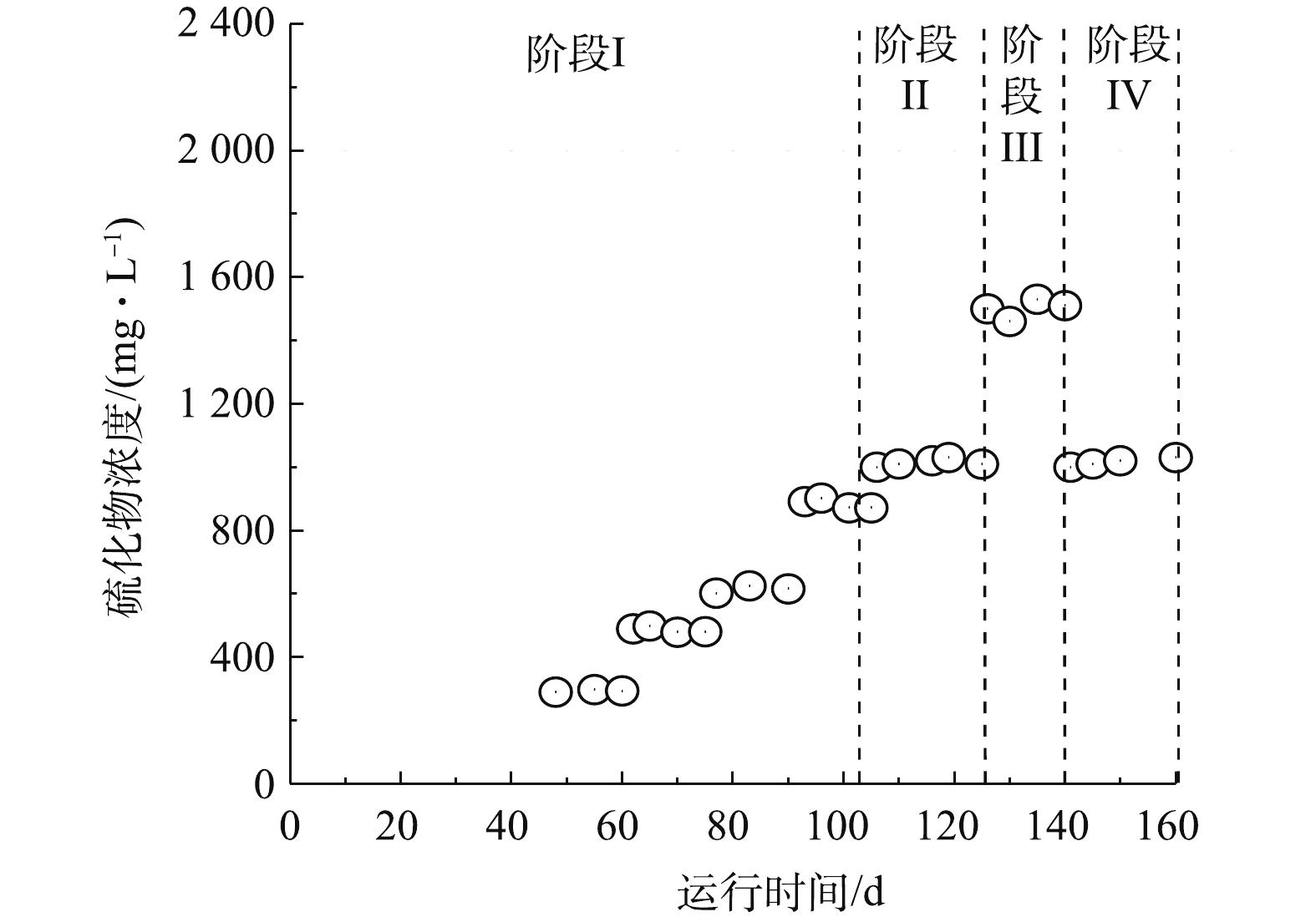
在第I阶段(1~105 d),运行参数见表1。这个阶段COD/
SO2−4 为3.58(COD/TSO2−4 为2.4)左右,通过提高进水COD的方式来逐步提高OLR(图3)。前30 d是污泥驯化阶段,所以进水COD为500 mg·L−1(OLR为0.167 g·(L·d)−1)。可以看出,在初始COD为2 000 mg·L−1,OLR为0.67 g·(L·d)−1的条件下,COD的去除率高达82%,产甲烷率为0.18 L·(L·d)−1。逐步提高进水COD至15 000 mg·L−1(OLR为5.0 g·(L·d)−1),COD的去除率亦达74%,产甲烷率为1.23 L·(L·d)−1,对位脂的去除率为83% (图3和图4)。此时进水硝态氮约为33 mg·L−1,出水硝态氮为3.2 mg·L−1,反硝化率为90.3%(图5)。进水COD提高至20 000 mg·L−1(OLR为6.67 g·(L·d)−1)时,虽然COD/TSO2−4 只有2.4左右(远低于3.3),但COD的去除率仍能高达70%,产甲烷率依然能达到1.41 L·(L·d)−1,对位脂的去除率为74%(图4),反硝化率为87%(图5)。在采用单一的UBF来处理对位脂生产废水的研究[6]中,系统中进水COD最高为15 000 mg·L−1,即OLR为5.0 g·(L·d)−1。当进水COD升高至20 000 mg·L−1时,硫酸根的浓度为5 583 mg·L−1,有机硫为2 286 mg·L−1,复合床系统很快受到严重抑制,甲烷产气很快停止,反硝化能力丧失,出水pH降至6.0。零价铁的加入明显提高了厌氧复合床在高COD运行负荷下产甲烷和反硝化的能力。零价铁能大幅提高厌氧反应器的处理效果是由多方面原因的协同作用造成的。零价铁能显著降低厌氧反应器内的氧化还原电位,中和有机酸,促进厌氧还原氛围,从而有助于厌氧微生物的生长[8]。最近的一组对比研究表明,零价铁不仅使厌氧古菌的丰度大幅提高,也增加了厌氧反应器中微生物的多样性[9]。此外,阴极产生的H2能作为产甲烷菌、硫酸盐还原菌和硝酸盐还原菌的电子供体[10]。这些都为提高产甲烷和反硝化的能力提供了基础。加入的零价铁在厌氧消化环境中还能缓慢产生Fe2+,而Fe2+能有效压缩胶体污泥的双电层,降低Zeta电位,进而促进污泥颗粒化[11]。同时,铁作为还原剂也能直接作用于某些污染物,所产生的Fe(OH)2、Fe(OH)3胶体也能沉淀污染物[12]。有研究[13]表明,采用零价铁强化厌氧工艺处理垃圾渗透液,COD的去除率达65.1%,而未加铁体系的COD去除率只有48.2%。微电场的作用一方面是能刺激微生物的代谢,另一方面是能强化零价铁的表面反应,有效解决零价铁床的板结和钝化[14]。最近的研究[15]表明,微电场-零价铁强化UASB能显著提高处理3, 4, 5-三甲氧基苯甲醛生产废水能力。本研究采用复合床设计,安装的弹性填料能拦截大部分的污泥,可避免零价铁床层被覆盖而导致的零价铁失活。2.2 COD/
TSO2−4 浓度对复合床同步产甲烷反硝化能力的影响(阶段II~阶段IV)在第II阶段(106~125 d),保持进水COD 20 000 mg·L−1不变(即COD容积负荷不变),加入4 420 mg·L−1硫酸盐,使COD/
SO2−4 降低至2(图6),此时COD/TSO2−4 降低至1.57,产生的硫化物(以S-SO2−4 计)为1 000 mg·L−1(图7)。但这个体系中COD的去除率依然能稳定在60%,产甲烷率为1.21 L·(L·d)−1,反硝化率为79%(图4)。所投加的零价铁能起到去除部分硫化物的作用,从而降低硫化物对产甲烷菌的抑制[16]。本实验中COD/TSO2−4 为1.57,这远远低于COD/SO2−4 >3.3(碳硫比>10)的厌氧工艺要求的极限。最近的研究[17]表明,在COD/SO2−4 为0.5时,单一的UASB依然取得了满意的COD去除率和甲烷产率。但是,UASB所处理的是很容易生物降解的乙酸和乙醇混合废水,不能代表典型工业废水。在第III阶段(126~140 d),继续加入10 000 mg·L−1硫酸盐,使COD/SO2−4 降低至1.0(COD/TSO2−4 =0.88),硫化物(以S-SO2−4 计)达到1 580 mg·L−1,产生的硫化物对产甲烷菌和硝酸盐还原菌产生了中等程度的抑制,出水pH和产甲烷率持续下滑,VFA大幅提高至3 600 mg·L−1(见图3),而反硝化率只有25%(图4)。在第IV阶段,COD/SO2−4 恢复至第2阶段,在7 d内,系统产甲烷率和反硝化能力基本恢复,说明微电场-零价铁-UASB反应器系统在产生高硫化物条件下也有很强的恢复能力。值得关注的是,虽然一直有硫化物的产生(见图6),但出水中的硫酸盐浓度却一直高于进水(见图5),这是由于对位脂中的有机硫容易水解而产生额外的硫酸盐。另外,在整个运行过程中,出水pH一直比进水pH高(见图2),这是因为硫酸盐还原菌在还原硫酸盐的过程中以及硝态氮在反硝化过程中会产生一定的碱度[18-19]导致的。3. 结论
实验结果表明,在原水COD/
SO2−4 约为3.58(COD/TSO2−4 低至2.4)时,即使进水COD高达20 000 mg·L−1(OLR为6.67 g·(L·d)−1),耦合复合床体系的COD去除率也能达到70%,相应的产甲烷率达1.41 L·(L·d)−1,反硝化率达87%,对位脂降解率达74%。2)第II阶段实验结果表明,联合系统能忍受更低的碳硫比,在COD/
TSO2−4 低至1.57时,系统依然能够稳定运行。3)第III和第IV阶段实验表明,在COD/
TSO2−4 降低至0.88时,产甲烷菌受到中等程度的抑制;COD/TSO2−4 恢复至1.57后,耦合复合床系统展示了很强的恢复能力,在5 d后即恢复正常。 -
表 1 污泥的特性
Table 1. Characteristics of sludge
含水率/% 污泥比阻/(1012 m·kg−1) 毛细吸水时间/s pH 有机质(VSS/TSS)/% 98.68 238.97 199.8 6.71 49.85 -
[1] KRACH K R, BURNS B R, LI B, et al. Odor control for land application of lime stabilized biosolids[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2008, 8(3/4): 369-378. [2] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 城镇污水处理厂污泥处置混合填埋用泥质: GB/T 23485-2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012. [3] 高廷耀, 顾国维, 周琪. 水污染控制[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015. [4] MARIE C, ZHANG Y R, YANG J K. Extracellular polymeric substances and sludge solid/liquid separation under Moringa oleifera and chitosan conditioning: A review[J]. Environmental Technology Reviews, 2017, 6(1): 59-73. doi: 10.1080/21622515.2017.1282544 [5] 毛杰, 林珩, 郑柏存, 等. 造纸污泥表面改性的研究[J]. 中国造纸, 2017, 36(1): 31-35. [6] SUN W Q, TANG M D, SUN Y J, et al. Effective sludge dewatering technique using the combination of Fenton’s reagent and CPAM[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 96(6): 1256-1263. doi: 10.1002/cjce.v96.6 [7] 邵永, 肖蕾, 吴云霞, 等. 过硫酸钠降解印染有机废水的研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2017, 46(1): 180-183. [8] 宋秀兰, 石杰, 吴丽雅. 过硫酸盐氧化法对污泥脱水性能的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(11): 5585-5590. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.20151172 [9] ZHEN G Y, LU X Q, ZHAO Y C, et al. Enhanced dewaterability of sewage sludge in the presence of Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 116: 259-265. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.01.170 [10] MA W C, ZHAO L, LIU H L, et al. Improvement of sludge dewaterability with modified cinder via affecting EPS[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science and Engineering, 2017, 11(6): 19-32. doi: 10.1007/s11783-017-0967-x [11] 徐文迪, 常沙, 明铁山, 等. 基于硫酸根自由基(SO4−·)的污泥预处理技术[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(5): 1528-1535. [12] LI X Y, YANG S F. Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge[J]. Water Research, 2007, 41(5): 1022-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2006.06.037 [13] 赵璐, 何婷, 丁文欢, 等. 考马斯亮兰法(Bradford法)测定驼乳中蛋白质的含量[J]. 应用化工, 2016, 45(12): 2366-2368. [14] GHOLIKANDI G B, ZAKIZADEH N, MASIHI H. Application of peroxymonosulfate-ozone advanced oxidation process for simultaneous waste-activated sludge stabilization and dewatering purposes: A comparative study[J]. Journal of Environmental Mangement, 2018, 206: 523-531. [15] 孟维, 汪苹, 唐文涛. 反硝化聚磷菌在低碳源城市污水脱氮除磷处理中的应用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(7): 91-95. [16] 吴彦. 稻壳基骨架颗粒制备及调理城市污泥脱水作用和机理分析[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2016. [17] LU M C, LIN C J, LIAO C H, et al. Dewatering of activated sludge by Fenton’s reagent[J]. Advances in Environmental Research, 2003, 7(3): 667-670. doi: 10.1016/S1093-0191(02)00039-4 [18] 张昊. 基于新型骨架构建体与高级氧化剂的污泥复合调理及脱水研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014. [19] 阚丹, 孙静娴, 张雯, 等. 混价铁氢氧化物对无机磷的吸附/沉淀[J]. 土壤, 2012, 44(3): 520-524. -







 下载:
下载: