全文HTML
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
Table 1 Raw water quality in experiment
Table 1 Raw water quality in experiment
| K+/ (mg·L-1) |
Na+/ (mg·L-1) |
Ca2+/ (mg·L-1) |
Mg2+/ (mg·L-1) |
SO42-/ (mg·L-1) |
Cl-/ (mg·L-1) |
NO3-(以N计)/ (mg·L-1) |
Cu2+/ (mg·L-1) |
pH |
| 14.0 | 29.8 | 36.3 | 8.74 | 47.8 | 24.7 | 0.856 | 0.007 | 7.65 |
1.2 方法
1.2.1 吸附动力学、不同吸附剂投加量和吸附等温线实验
1.2.2 脱附实验
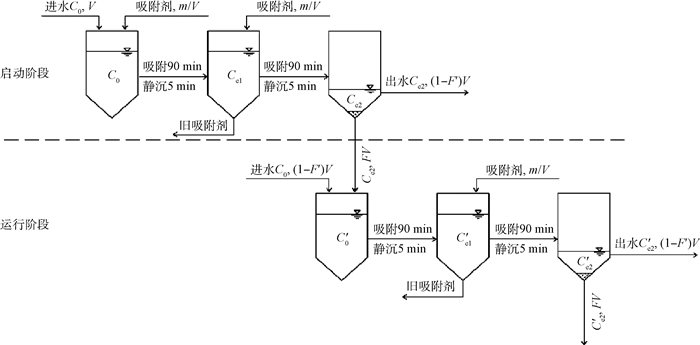
1.2.3 新型二级逆流吸附实验装置与运行
Fig. 1 Set-up diagram of new countercurrent two-stage adsorption system
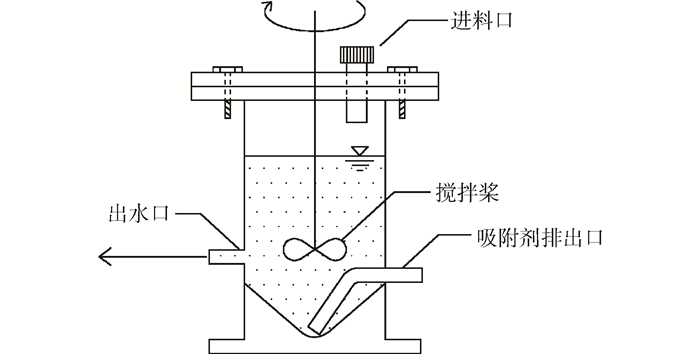
2 结果与讨论
2.1 吸附动力学
Fig. 2 Change of I- concentration and removal efficiency in effluent with adsorption time
Fig. 2 Change of I- concentration and removal efficiency in effluent with adsorption time
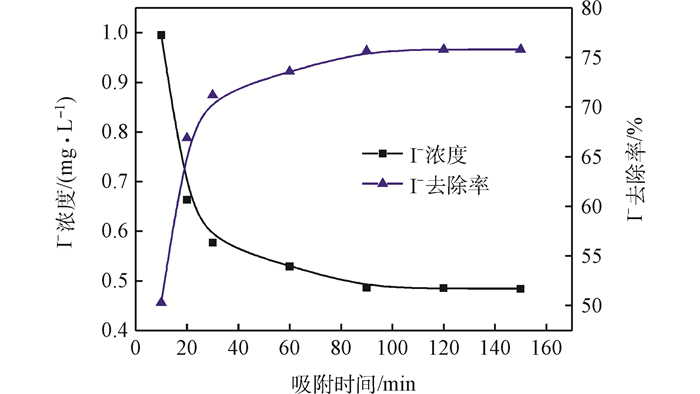
2.2 吸附剂投加量对自来水中I-吸附效果的影响
Fig. 3 Effect of adsorbent dosage on I- removal in tap water
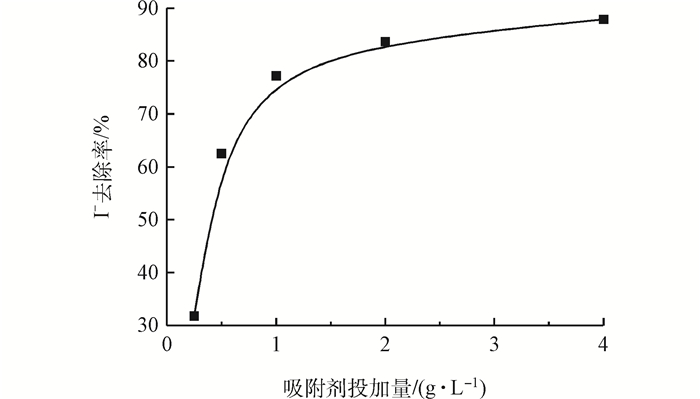
2.3 吸附等温线
| qe=C0−CemV=abCe1+aCe | (1) |
Fig. 4 Langmuir adsorption isotherm fitting curve
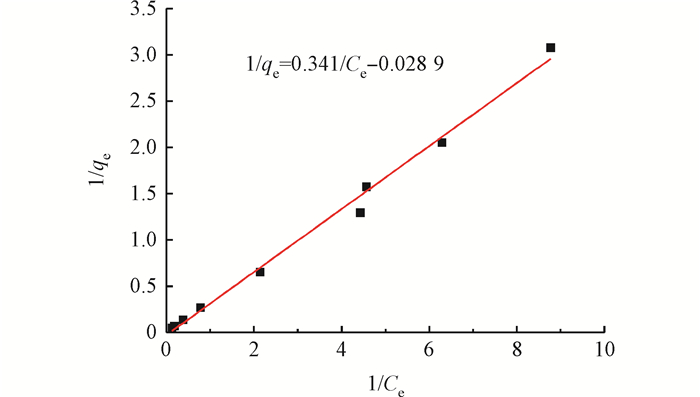
| qe=2.94Ce1−0.084 9Ce | (2) |
2.4 脱附实验
Table 2 Concentration of I- in liquid and adsorbent phase at adsorption and desorption equilibrium
Table 2 Concentration of I- in liquid and adsorbent phase at adsorption and desorption equilibrium
| 项目 | 液相平衡浓度/ (mg·L-1) |
平衡后吸附剂相浓度/ (mg·g-1) |
| 吸附 | 0.471 | 1.53 |
| 脱附 | 0.267 | 1.31 |
2.5 新型二级逆流吸附的理论计算
Fig. 5 Schematic illustration of new countercurrent two-stage adsorption system
| C0−Ce1mV=2.94Ce11−0.084 9Ce1 | (3) |
| Ce1−Ce2mV=2.94Ce21−0.084 9Ce2 | (4) |
| Ce1−Ce2mV+C′0−C′e1mV=2.94C′e11−0.084 9C′e1 | (5) |
| C′e1−C′e2mV=2.94C′e21−0.084 9C′e2 | (6) |
Table 3 Calculated values of I- concentration in each stage
Table 3 Calculated values of I- concentration in each stage
| mg·L-1 | |
| 参数 | 浓度 |
| Ce1 | 0.492 |
| Ce2 | 0.124 |
| C′0 | 1.62 |
| C′e1 | 0.490 |
| C′e2 | 0.124 |
2.6 计算方法的验证
Fig. 6 Comparison of experimental and calculated values in effluent cycles
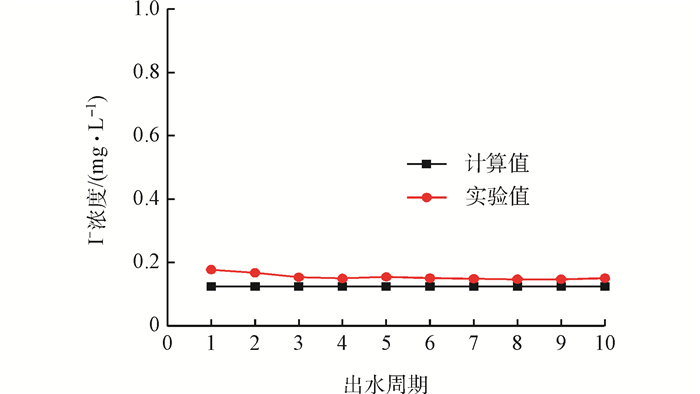
Table 4 Effluent quality from new countercurrent two-stage adsorption process
Table 4 Effluent quality from new countercurrent two-stage adsorption process
| K+/ (mg·L-1) |
Na+/ (mg·L-1) |
Ca2+/ (mg·L-1) |
Mg2+/ (mg·L-1) |
SO42-/ (mg·L-1) |
Cl-/ (mg·L-1) |
NO3-(以N计)/ (mg·L-1) |
Cu2+/ (mg·L-1) |
pH |
| 3.01 | 29.1 | 36.8 | 8.72 | 39.6 | 23.1 | 5.92 | 1.60 | 7.55 |
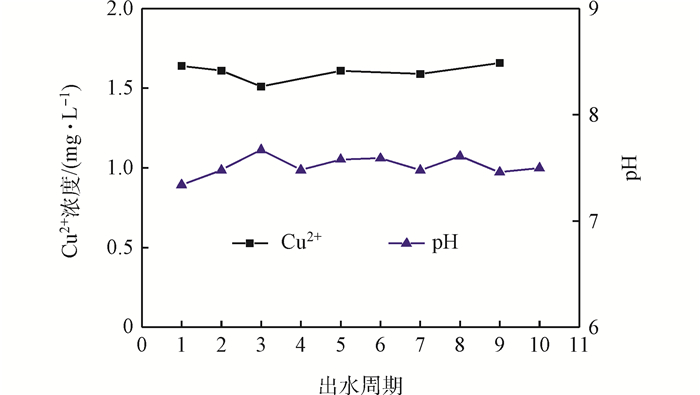
Fig. 7 Change of Cu2+ and pH in effluent with cycles





 百度学术
百度学术


 下载:
下载:
