曝气深度对河道底泥特性及水质的影响
Effect of different aeration depth on river sediment characteristics and water quality
-
摘要: 采用室内模拟实验方法对受污河道底泥和上覆水进行研究,对比分析静置状态X0和不同曝气深度条件下(分别为水体曝气泥水界面上方10 cm,底泥曝气下方5和15 cm处,依次记为X+10、X-5和X-15)河道底泥特性及水质的影响情况。结果表明:底泥曝气较水体曝气而言,能促进水体DO更快恢复;停止曝气,DO浓度也会维持在较高的状态,有利于有机物和氨氮的进一步去除。在相同曝气量下,底泥曝气比水体曝气能更好地去除底泥中污染物,并减少再次释放,且底泥曝气深度越深,处理效果越好,至实验结束时,X-15组上覆水中COD、NH4+-N、TN及TP浓度分别为16.25、3.03、13.39及0.09 mg/L,去除率分别为69.73%、78.36%、45.98%及84.21%;停止曝气后,经曝气处理的底泥对磷的吸附容量显著增加,并且不会再向上覆水中释放污染物,避免引起水体的二次污染。Abstract: Indoor simulation tests were used to study aeration treatments for polluted river sediments and overlying water. The river sediment characteristics and water quality were evaluated under static state conditions (X0) and at different aeration depth, where the heights relative to the water-sediment interface in the aeration treatments were set to 10 cm (X+10), -5 cm (X-5), and -15 cm (X-15). The results showed that sediment aeration can achieve greater restoration levels of dissolved oxygen (DO) in water bodies and maintain higher DO levels after stopping aeration than techniques that rely solely on water aeration, which will be beneficial for the further removal of organic matter and ammonia nitrogen. Sediment aeration may also suppress the release of pollutants from the sediments to the overlying water. In this study, greater sediment aeration depth were associated with better treatment efficiencies. At the end of the tests, the chemical oxygen demand (COD) (where refers to the dichromate method), NH4+-N, total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorous (TP) concentrations of the X-15 group were 16.25, 3.03, 13.39 and 0.09 mg/L, and the corresponding removal rates were 69.73%, 78.36%, 45.98%, and 84.21%, respectively. After stopping aeration, the accumulative adsorption capacity for phosphorus in sediment subjected to aeration treatments increased significantly, and pollutant release was restrained effectively. Therefore, these water bodies were protected from the effects of secondary pollution.
-
Key words:
- polluted river /
- sediment aeration /
- aeration depth /
- overlying water
-
随着大量重金属铬污染事件的发生[1-2],水体铬污染治理成为国内外的重点关注的领域之一。由于重金属铬具有稳定性和难降解性[3-4],会给环境质量和人体健康带来威胁[5-7]。在水环境中,铬主要以Cr(Ⅵ)和Cr(Ⅲ) 2种氧化态存在。其中Cr(Ⅵ)剧毒且致癌、易迁移、在生物体内发生蓄积作用;而Cr(Ⅲ)低毒或无毒,主要以沉淀形式存在,且少量的Cr(Ⅲ)是人体所必需的微量元素[8]。因此,将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ)可有效降低水体铬污染风险。还原方法主要包括化学还原稳定技术、微生物还原修复技术、电化学还原技术。其中,化学还原稳定法具有高效、快速、经济性等优势,应用最为广泛[9]。常用的化学还原剂包括硫系还原剂和铁系还原剂[10]。多硫化钙、硫代硫酸钠、硫化氢等硫化物具有优异的Cr(Ⅵ)还原能力和较高的还原效率,但硫化物还原Cr(Ⅵ)所生成的Cr(Ⅲ)易被再氧化成Cr(Ⅵ),造成二次污染[11]。与硫化物相比,零价铁、亚铁盐、含铁矿物等铁系还原剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的还原效率要低得多,但其还原产物较稳定,主要以难溶性铬铁氢氧化物共沉淀物(CrxFe1-x(OH)3)存在,可有效避免二次氧化过程的发生[12]。由此可见,将硫化物与铁系材料进行联用有望实现高效且稳定的修复效果。
JACOBS等[13]发现多硫化钙(CaSx)可成功将Cr(Ⅵ)还原成Cr(Ⅲ),其中
S2−x 1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
实验材料:重铬酸钾,高锰酸钾,硫酸(优级纯),磷酸(色谱纯),氢氧化钠,二苯碳酰二肼,丙酮,尿素,亚硝酸钠,氨水,铜铁试剂,氯仿,氯化钠,硫酸铁,碳酸氢钠,多硫化钙质量分数45%,FeSO4·7H2O纯度98%。以上材料除特殊说明外,均为分析纯。
实验仪器:YTH-2.10型马弗炉(上海精密科学仪器有限公司)、F2-Standard便携式酸度计(上海恒勤仪器设备有限公司)、BSA-224S型电子天平(北京塞多利思科学仪器有限公司)、TU-1900紫外可见分光光度计(北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司)、DF101S型恒温磁力搅拌器及HZQ-Q型恒温振荡器(太仓市实验设备公司)、SHZ-D(Ⅲ)循环水多用真空泵(河南予华仪器有限公司)、Smart Lab 9KW型X射线多晶体衍射仪(日本理学Rigaku公司)、ESCALAB 250Xi型X射线光电子能谱仪(日本日立公司)。
1.2 实验方法
以不同初始pH(3.02、5.04、7.05、8.98、10.98) 、Cr(Ⅵ)含量为10 mg·L−1的重铬酸钾溶液为修复对象,分别模拟强酸性、弱酸性、中性、弱碱性、强碱性铬污染水体,取200 mL上述pH梯度下铬液若干份置于250 mL锥形瓶备用。通过调整多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁的投加比例,以Cr(Ⅵ)去除率为指标确定最佳药剂投加比例,综合总Cr、pH、Eh指标评价修复效果,采用单一变量原则探究不同因素对Cr(Ⅵ)去除的影响,通过反应产物材料表征分析联用药剂去除Cr(Ⅵ)的机制,设置微梯度优化联用药剂投加量。具体分为以下5个步骤。
1)投加比例确定。由化学反应方程式(1)~式(3)[22-23]可知,还原等摩尔Cr(Ⅵ)所需CaSx的用量要少于FeSO4,因此,选择固定CaSx投加量且逐渐提高FeSO4投加比例进行批实验。为使实验具有可比性,CaSx和FeSO4剂量分别以单独施加剂量的50%进行联用,实验设置了4个投加比例(表1),通过比较各组药剂单用/联用对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果,确定联用药剂最佳投加比例。
表 1 药剂联用投加比例实验设计Table 1. Experimental design of dosage ratio for reagents combination实验组 n(药剂)∶n(Cr(VI)) 修复条件 多硫化钙 硫酸亚铁 药剂联用 1 1∶1 1∶1 0.5:0.5:1 25 ℃150 r·min−11 h 2 1∶1 1.5∶1 0.5∶0.75∶1 3 1∶1 2∶1 0.5∶1∶1 4 1∶1 2.5∶1 0.5∶1.25∶1 stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (1) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (2) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (3) 2)修复效果评价。选择上述最佳投加比例的实验组,测定水样中总Cr含量,分析药剂单用/联用对总铬的去除效果,并监测反应前后水体pH和Eh的变化,综合评价修复效果。
3)影响因素探究。配制不同温度铬液向其中加入联用药剂参与反应,测定不同时间间隔铬液Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度,分析温度对反应进程的影响;将不同浓度常规离子加入到反应体系,经充分反应后测定溶液中Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度,探究不同离子对反应过程的影响。
4)修复机理分析。对反应产物进行材料表征,分析产物类型并结合实验结果,分析药剂联用对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除机制。
5)投加量优化。以确定的药剂投加比例为基准,设置微梯度逐渐增加药剂投加量,测定水样Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度并观察水体pH的变化,优化联用药剂投加量。
1.3 分析方法
待各体系充分反应,静置2 h后,采用SHZ-D(Ⅲ)循环水多用真空泵经0.45 μm滤膜进行抽滤,所得滤液进行指标测试,固体物质风干后研细进行物相分析。溶液pH和Eh采用F2-Standard便携式酸度计进行测试;Cr(Ⅵ)及总Cr含量采用TU-1900紫外可见分光光度计按照中国国家标准《二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法》(GB 7467-1987)和《高锰酸钾氧化‐二苯碳酰二肼分光光度法》(GB 7466-1987)进行测定;固体物质采用ESCALAB 250Xi型X射线光电子能谱仪和Smart Lab 9KW型X射线多晶体衍射仪进行扫描,物相组成使用MDI Jade 6进行检索。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 还原剂单用/联用对铬的去除效果
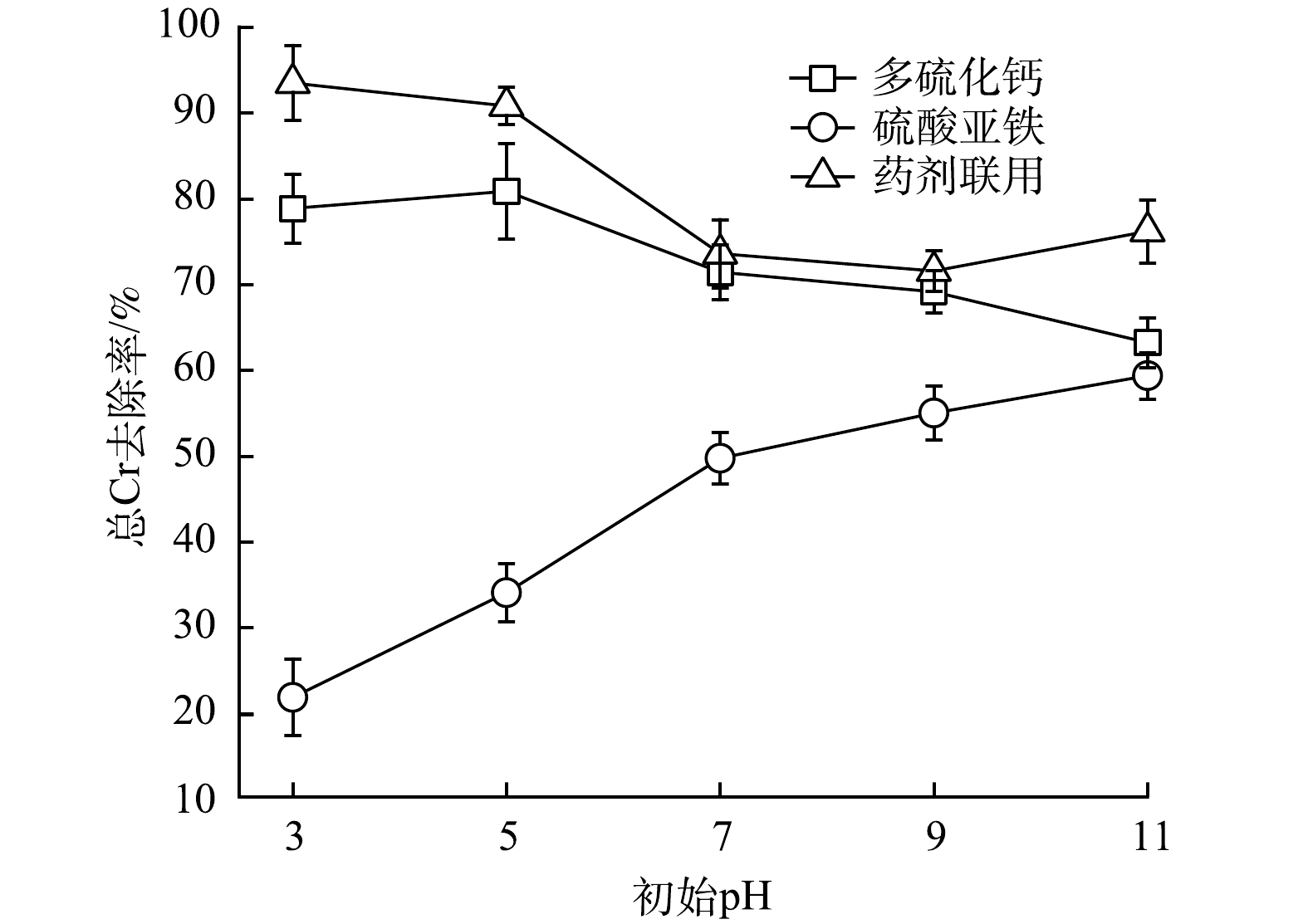
1) Cr(Ⅵ)去除效果。通过消除溶液中还原性物质对显色过程的影响后,经分光光度法对体系中六价铬含量进行测定,发现不同还原剂对体系Cr(Ⅵ)去除效果差异较大(图1)。其中,多硫化钙对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果随着体系初始pH的升高而迅速降低。这主要是由于随着体系碱性的不断增强,溶液中H+浓度持续降低,对多硫化钙还原Cr(Ⅵ)过程产生抑制[8](式(1))。与之相反,硫酸亚铁对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果随着体系pH的升高而逐渐增强。这是由于经硫酸亚铁修复后体系中Fe3+水解产生的氢氧化铁含量不断增加(式(4)),其可通过吸附作用强化对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除。药剂联用的修复效果受多硫化钙和硫酸亚铁的共同影响,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率随pH的升高表现为先快速降低后趋于平缓的变化趋势。当多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁摩尔比为1∶2时,在实验设置pH条件下药剂联用对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除效果均优于药剂单用(图1(c))。这可能是由于多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁反应生成了具有催化效果的FeS[24-25],进一步高效还原Cr(Ⅵ)(式(5)和式(6)),提高了修复效果。因此,多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁以1∶2的比例联用进行后续研究。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (4) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (5) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (6) 2)总Cr去除效果。不同还原剂对水体总Cr去除效果(图2)与Cr(Ⅵ)类似。药剂联用体系和多硫化钙体系对总Cr的去除效果总体表现为随着体系pH升高而下降的趋势,说明体系中Cr主要以Cr(Ⅵ)形式存在。硫酸亚铁体系总Cr的去除效果则随体系pH升高而增加,但始终保持在较低的水平。这是由于施加硫酸亚铁的体系始终呈强酸性,不利于Cr(Ⅲ)形成沉淀,表明该体系中Cr的主要形式为Cr(Ⅲ)。就总Cr去除率而言,药剂联用始终优于多硫化钙和硫酸亚铁单用。这是因溶液中Cr(Ⅲ)与Fe(Ⅲ)在水环境下易结合生成难溶性铬铁氢氧化物(CrxFe1-x(OH)3)造成的[18](式(7))。修复过程中所产生的铬铁氢氧化物共沉淀物,因其溶解度低且性质稳定的特点,不仅能高效固定Cr(Ⅲ),还可有效避免还原产物Cr(Ⅲ)被再次氧化为有毒态(Cr(Ⅵ))[26-28],这对总Cr去除效果的提高与维持均具有促进作用。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (7) 2.2 还原剂单用/联用对水体pH和Eh的扰动
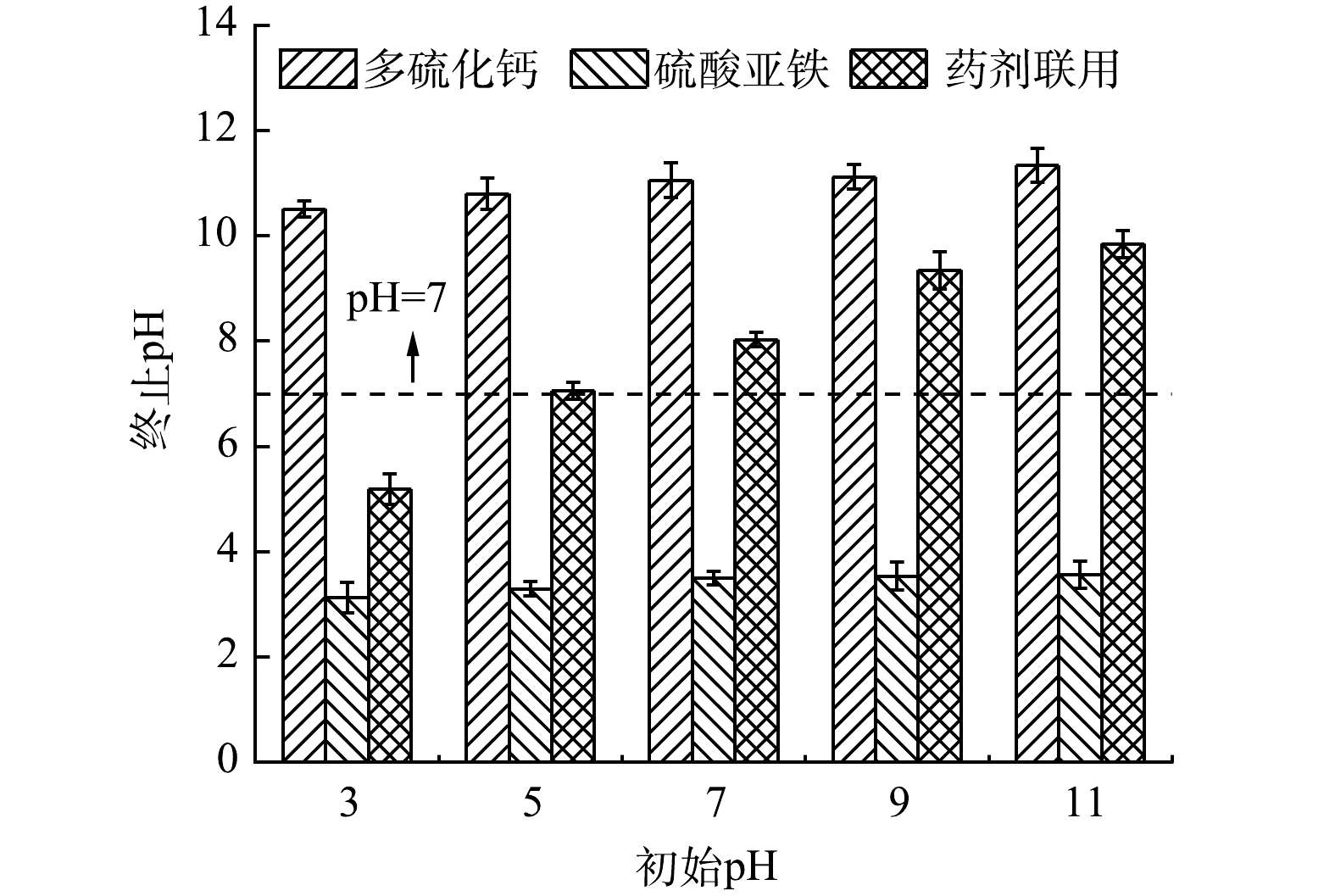
1)药剂投加对体系pH的扰动。从不同反应体系修复前后pH变化情况来看(图3),不同还原剂作用后体系pH均随着体系初始pH的增加而上升,其中多硫化钙修复后体系表现为强碱性(pH>10)。这是由于多硫化钙还原Cr(Ⅵ)时消耗大量H+ (式(1)),溶液中OH−含量显著增加造成的。相反,硫酸亚铁修复后体系表现为强酸性(pH<5)。这主要是由Fe2+氧化及Fe2+和Fe3+水解释放大量H+导致[21, 29-30](式(4)、式(8)、式(9))。多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁联用修复后体系依次呈弱酸性、中性、弱碱性。这可能是多硫化物的还原反应和Fe2+的水解过程相互抵消的结果[31]。值得注意的是,初始pH为5的Cr(Ⅵ)污染水体,经药剂联用修复后体系呈中性(pH为7.06),这表明还原剂的联用起到了中和反应体系pH的效果。
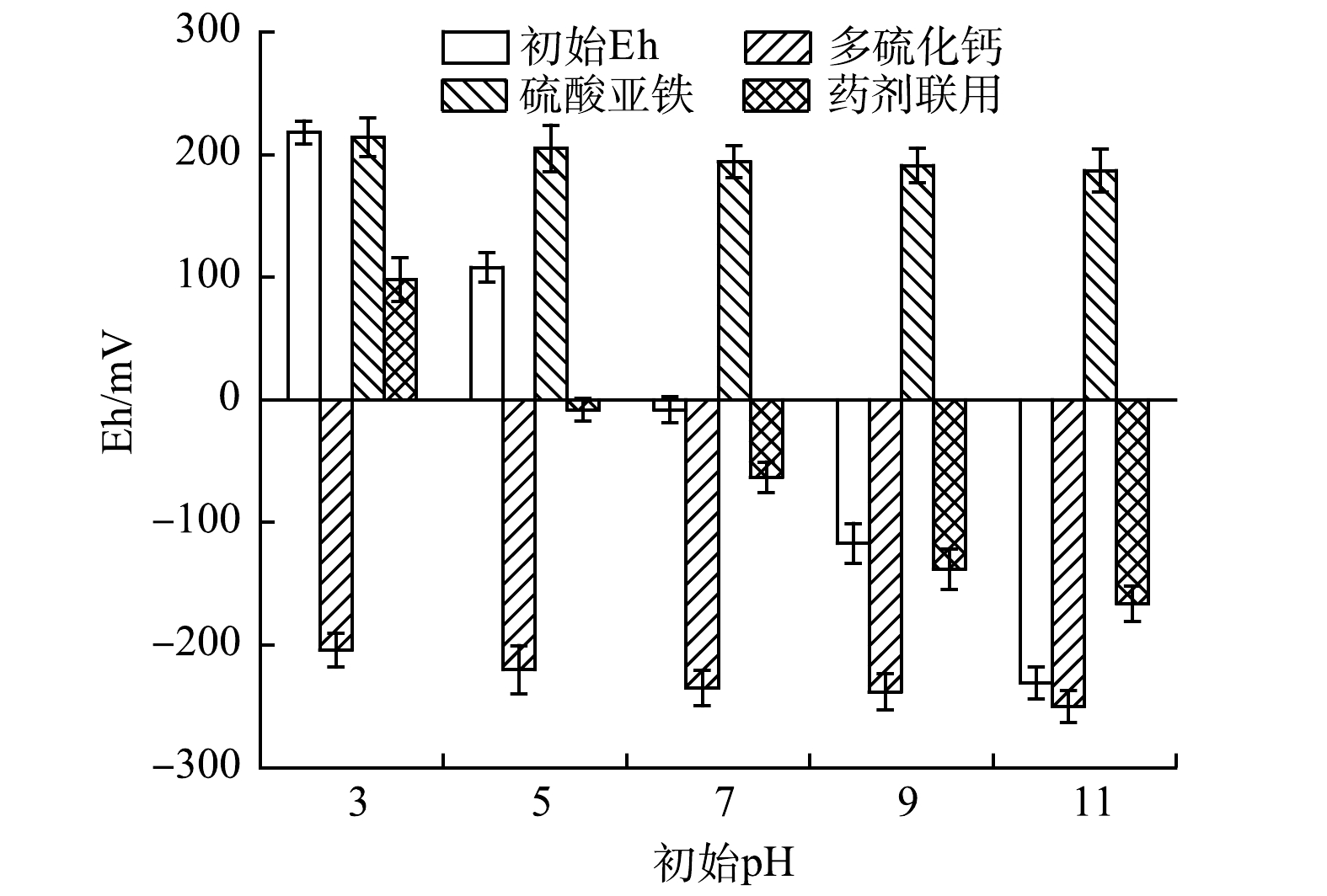
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (8) stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (9) 2)药剂投加对体系Eh的扰动。在还原剂修复过程中,各体系Eh均随溶液碱性的增强而明显降低(图4)。其中,加入多硫化钙的体系Eh均低于−200 mV,表明该体系具有较强的还原性和稳定性。CHRYSOCHOOU等[32]在使用2倍理论值的多硫化钙修复某镀铬设施Cr(Ⅵ)污染土壤时也发现,多硫化钙的加入使体系Eh快速下降到−500 mV左右,并保持较长时间,这非常有利于Cr(Ⅵ)快速转化为Cr(Ⅲ),并形成稳定的沉积物。相反,加入硫酸亚铁的体系Eh保持在200 mV左右,仍表现为较强的氧化性。这主要是由亚铁还原Cr(Ⅵ)过程中自身被氧化成三价铁(式(2)、式(3))造成的。药剂联用修复后的体系Eh与初始Eh变化趋势一致,这是多硫化钙体系的还原性与硫酸亚铁体系的氧化性相互“中和”的结果,说明还原剂的联用对体系扰动作用相对较小。
2.3 环境因素对联用药剂去除水中Cr(Ⅵ)的影响
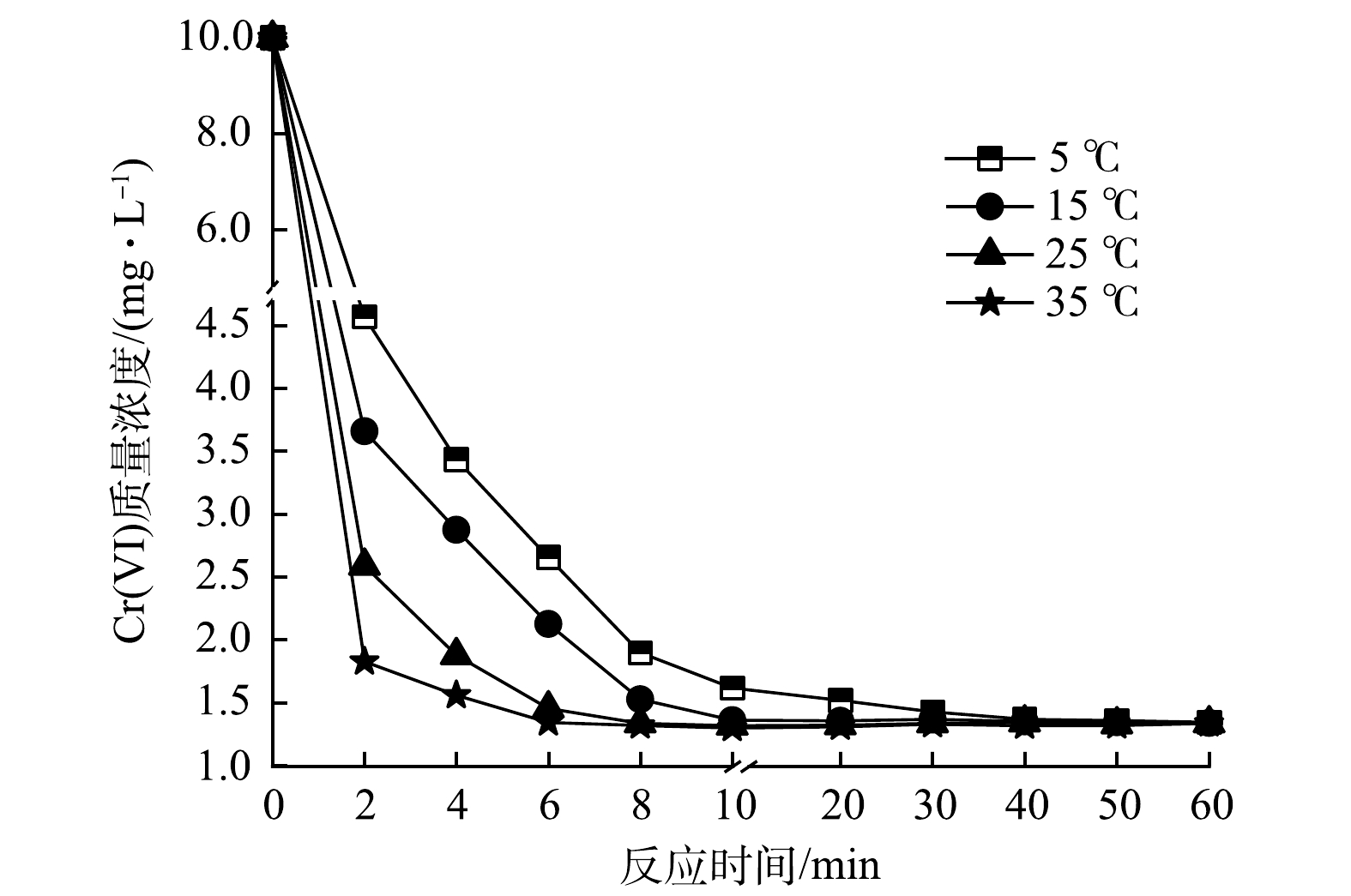
1)温度对Cr(Ⅵ)去除效果的影响。为考察温度对水中Cr(Ⅵ)去除效果的影响,分别设置体系温度为5、15、25、35 ℃,投加联用药剂进行反应,结果如图5所示。在反应初期(0~2 min),各体系Cr(Ⅵ)含量快速降低,温度(35 ℃)较高的体系在2 min时Cr(Ⅵ)去除率达到81.75%,随后去除率缓慢上升;当反应6 min时,去除率达到86.60%,直至60 min去除率未发生明显变化,故可认为6 min即达到反应平衡。在温度为25、15、5 ℃的体系中,反应2 min时Cr(Ⅵ)去除率依次为74.13%、63.41%、54.31%,随后去除率仍保持较快增长并最终趋于平缓,最大Cr(Ⅵ)去除率与35 ℃时基本一致。但达到最大去除率的时间有所延长,依次为10、20、40 min,相比温度较高的体系,分别增加了4、14、34 min。由此可见,较高温度有利于加快反应的进程,但最终Cr(Ⅵ)去除率并无明显差异,考虑到成本和环境干扰等因素,在原环境温度(25 ℃)进行反应即可。
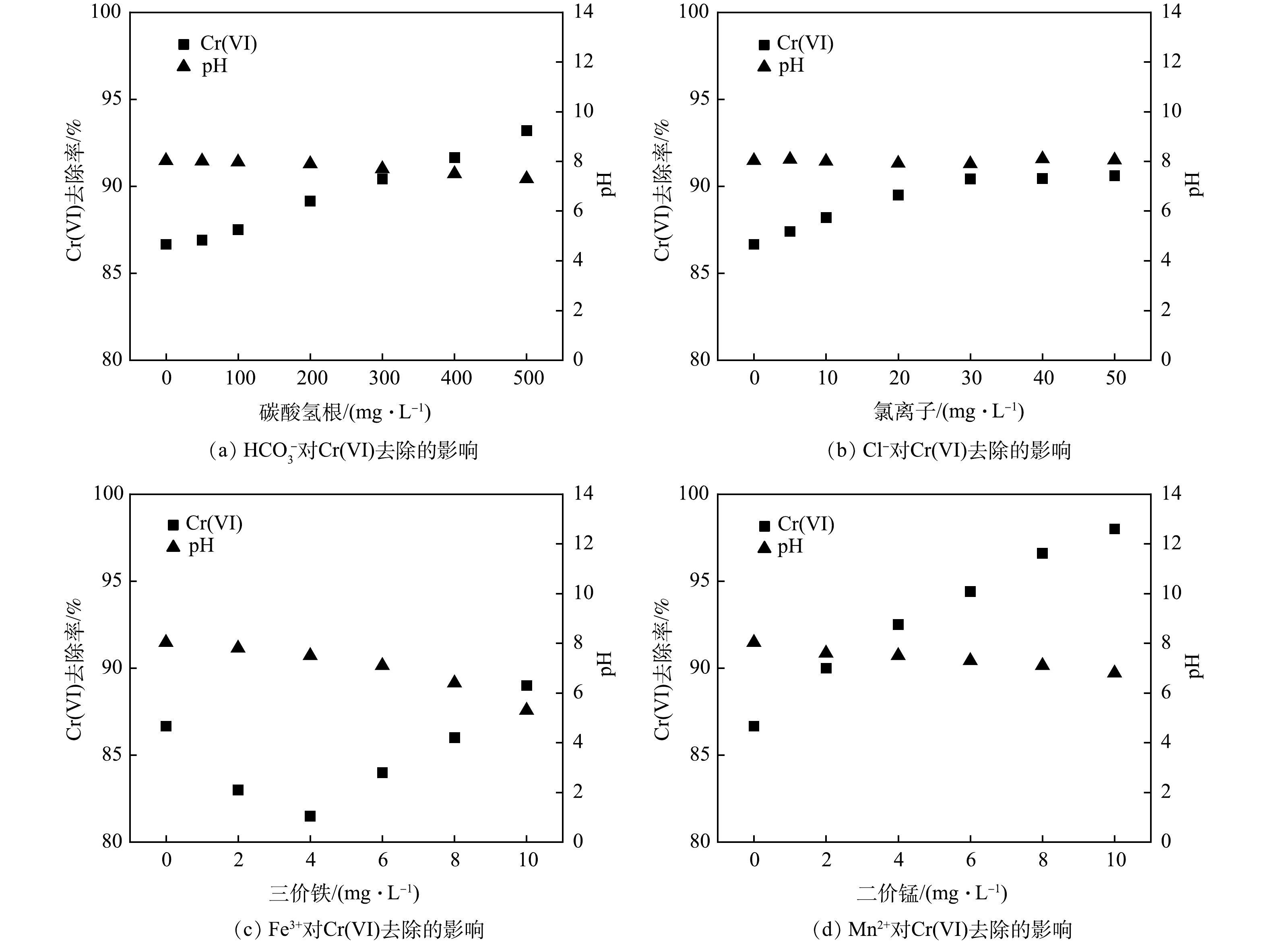
2)常规阴阳离子对联用药剂去除Cr(Ⅵ)的影响。一是碳酸氢根的影响。为探究
HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 HCO−3 二是氯离子的影响。为考察Cl−对联用药剂去除Cr(Ⅵ)的影响,向铬液中加入不同质量浓度 (0、5、10、20、30、40、50 mg·L−1) 的氯化钠,以探究Cl−对Cr(Ⅵ)去除效果的影响,结果如图6(b)所示。在添加氯化钠后,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率即开始上升,溶液中Cl−由0 mg·L−1升至30 mg·L−1,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率由86.60%上升至90.42%;继续增加Cl−浓度,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率变化不大。测定反应完全后溶液的pH可知,与原溶液相比,添加Cl−后溶液pH未发生明显变化。这是由于Cl−的存在可有效提高整个还原反应动力学:一方面,Cl−可促进铁系材料的腐蚀且可抑制钝化层的生成,使铁离子更易发生水合作用,促进铁离子进入溶液参与反应;另一方面,Cl−的离子半径较小,具有较强的穿透能力,可透过固体悬浮物或沉积物,增加颗粒孔隙率、抑制颗粒团聚,提高吸附去除效果[34]。
三是Fe3+的影响。以硫酸铁作为Fe3+供体溶于铬液,使溶液中Fe3+质量浓度分别为0、2、4、6、8、10 mg·L−1,后加入联用药剂。不同浓度的Fe3+对Cr(Ⅵ)去除影响结果如图6(c)所示。Fe3+的加入对Cr(Ⅵ)去除产生了抑制。其原因主要是,由于Fe3+与多硫化钙发生氧化还原反应消耗了部分还原剂,降低其去除效果。随Fe3+浓度的上升,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率逐渐增加,这主要是由于Fe3+与溶液中的OH−结合生成大量的Fe(OH)3沉淀,而Fe(OH)3对Cr(Ⅵ)表现出较好的吸附效果,可与Cr(Ⅵ)形成铬铁共沉淀将其除去[8]。此外,随着Fe3+浓度的增加,溶液pH不断降低,可见较高浓度的Fe3+有利于Cr(Ⅵ)的去除。
四是Mn2+的影响。Mn2+分别为0、2、4、6、8、10 mg·L−1的铬液加入联用药剂后溶液Cr(Ⅵ)去除率变化情况如图6(d)所示。溶液Cr(Ⅵ)去除率随Mn2+浓度的增加而明显上升,当Mn2+质量浓度由0 mg·L−1增至10 mg·L−1,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率由86.60%升至98.03%。由此可见,Mn2+有利于联用药剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除,且Mn2+含量越高,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率越大。这是由于低价态Mn2+属锰的还原态,可将Cr(Ⅵ)还原为Cr(Ⅲ),自身被氧化为MnO2 (式(10)),同时反应过程中Mn2+发生弱水解作用降低溶液pH[35],可进一步促进Cr(Ⅵ)的去除。
stringUtils.convertMath(!{formula.content}) (10) 2.4 多硫化钙与亚铁盐联用对Cr(Ⅵ)的修复机理
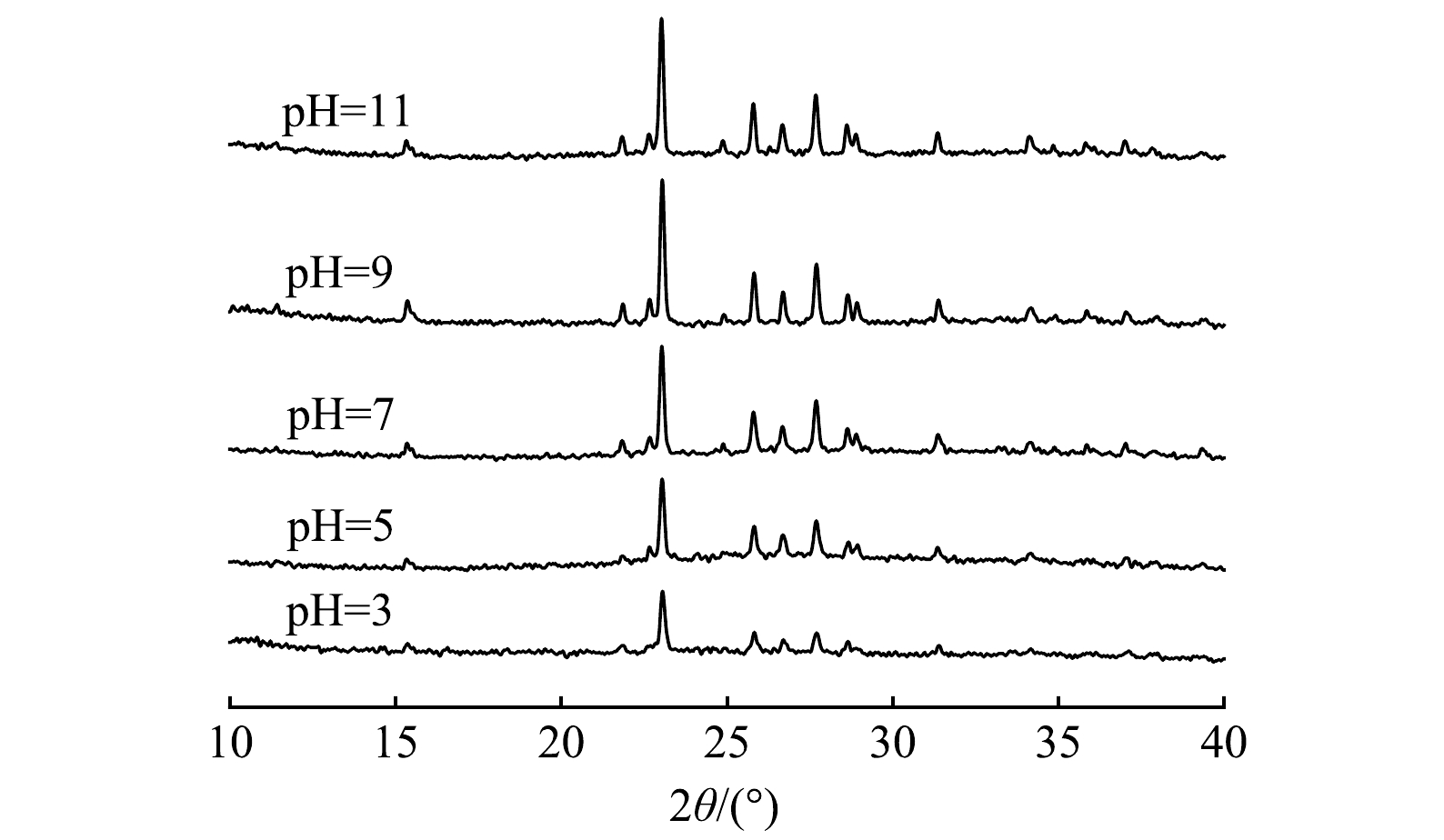
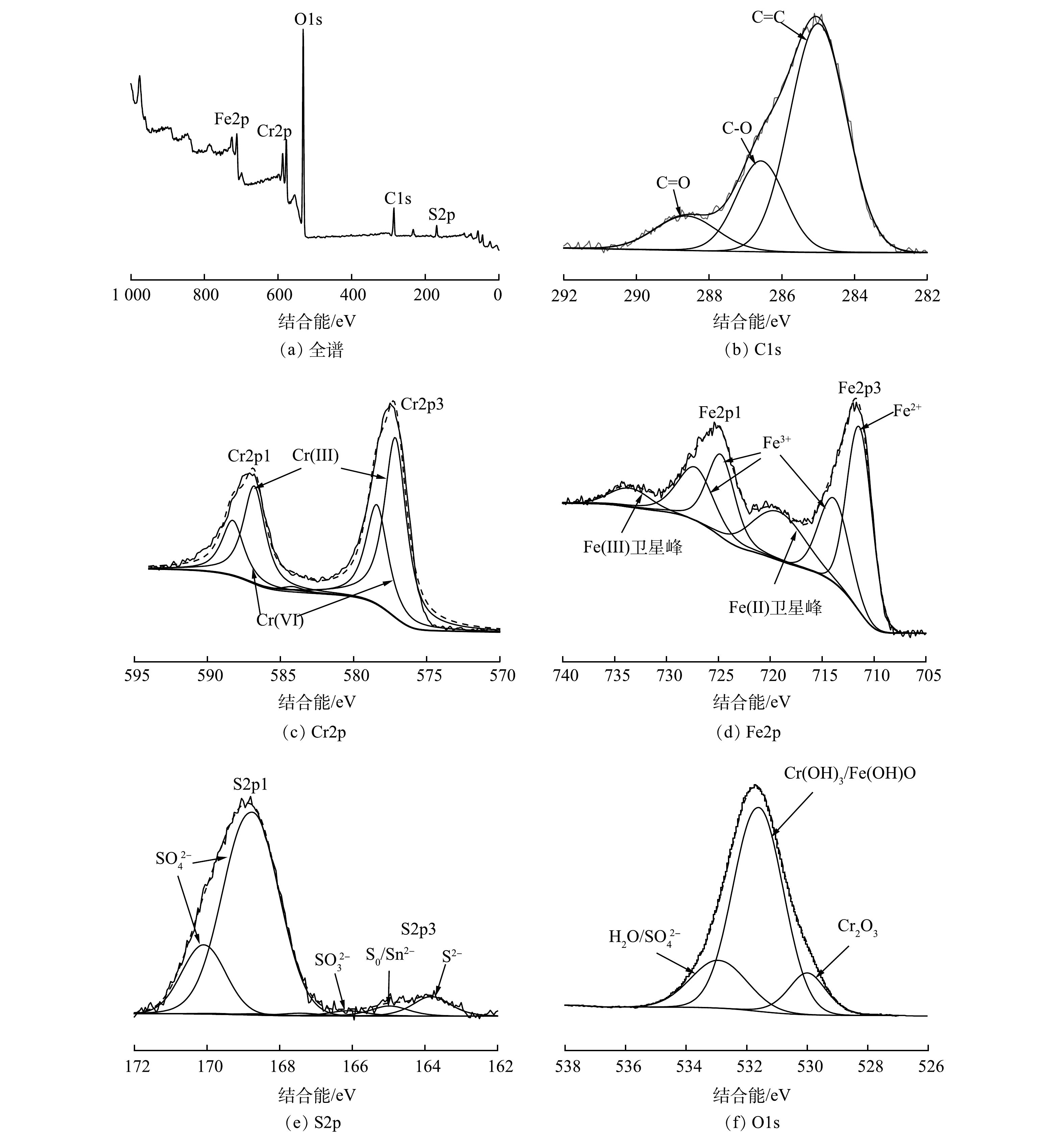
1)材料表征。图7显示了多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁在不同pH条件下联用修复铬污染水体反应产物的物相组成。由XRD图谱可以看出,不同pH条件下药剂联用修复Cr(Ⅵ)产物类型基本一致。通过峰值强度对各组产物进行半定量分析可以看出,产物含量总体呈现随体系碱性增强而增加的趋势,这意味着固定的Cr(Ⅲ)含量逐渐增多,表明碱性条件下有利于Cr(Ⅲ)的去除。经X射线光电子能谱(XPS)研究产物表面元素组成及化学态,使用外来污染碳的C1s作为基准峰进行荷电校正校准,以测量值和参考值(284.8 eV)之差作为荷电校正值来矫正谱中其他元素的结合能。图8显示了药剂联用在水体初始pH=5.0条件下与Cr(Ⅵ)反应产物的C1s、O1s、S2p、Fe2p、Cr2p的XPS谱图。Cr2p谱(图8(c))在577.16 eV处存在一个较强的峰,这与Cr3+化合物的结合能位置相符[36],表明水中Cr(Ⅵ)被成功还原成Cr(Ⅲ),在578.5 eV处的峰与Cr6+一致,证实了吸附Cr(Ⅵ)过程的直接发生。比较材料表面Cr(Ⅲ)、Cr(Ⅵ)的峰面积,得出还原沉淀为去除水中Cr(Ⅵ)的主要机制。710.30~713.60 eV对应的Fe(Ⅱ)峰主要为FeS,观察到拟合出的Fe(Ⅲ)峰化学位移较大(图8(d)),表明Fe3+化合态较为复杂,以铁的氧化态和氢氧化态为主[37]。对S2p谱的S2p1/2和S2p3/2自旋分裂轨道进行拟合分析(图8(e)),发现S元素的化学组成主要是
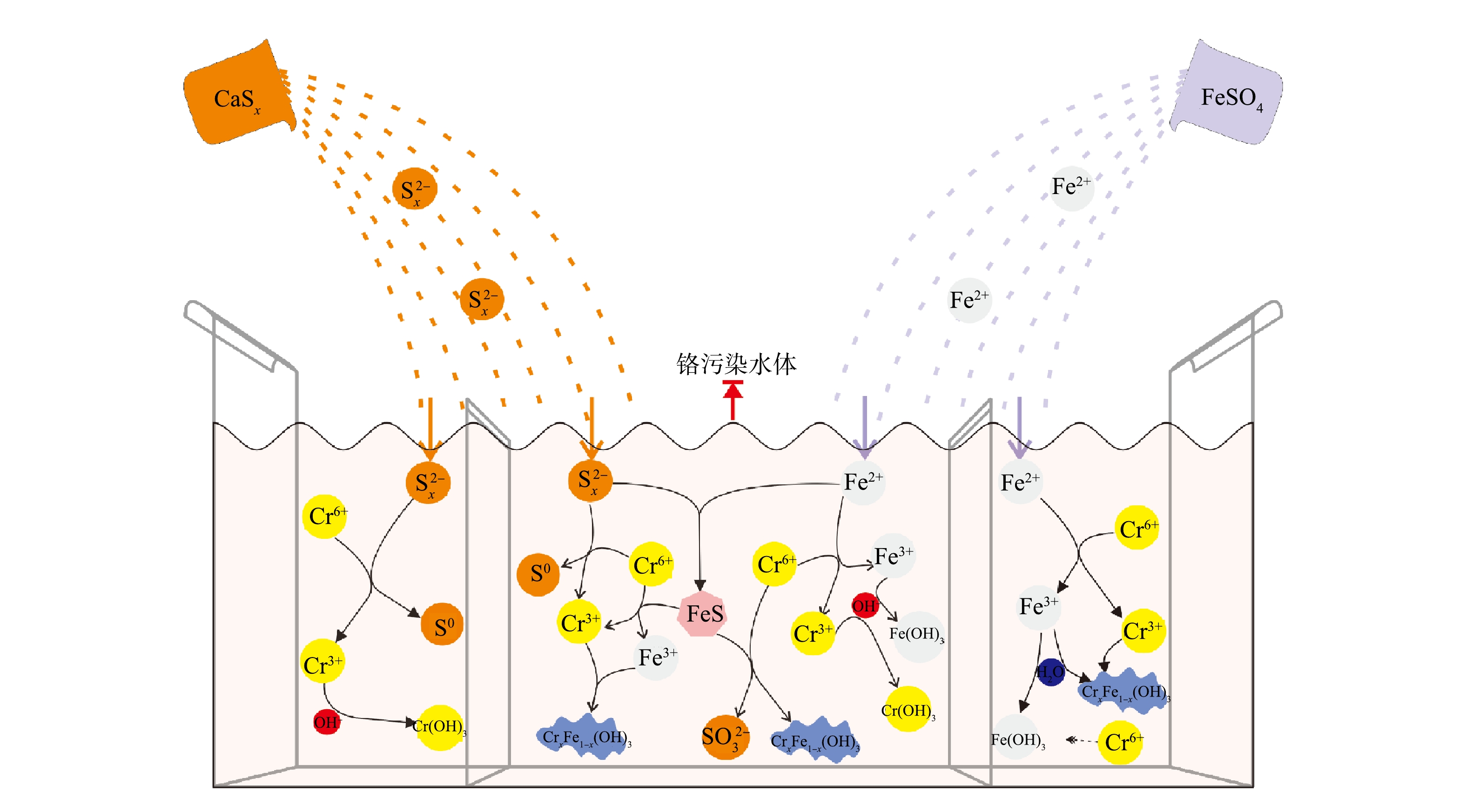
SO2−4 S2−x SO2−3 2)修复机理。基于上述实验结果,提出了多硫化钙和硫酸亚铁去除Cr(Ⅵ)的可能机理,不同种类还原剂对Cr(Ⅵ)的修复过程如图9所示。多硫化钙对铬污染水体的修复主要包括Cr(Ⅵ)还原和Cr(Ⅲ)固定2个过程[39-41]:多硫化钙中的
S2−x 多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁联用对铬污染水体的修复过程较药剂单用复杂得多,不仅包括药剂单用的全部过程,还生成了具有催化作用的中间产物FeS[24-25, 42-43]:
S2−x SO2−3 2.5 多硫化钙与亚铁盐联用去除工业废水中Cr(Ⅵ)
实验所用Cr(Ⅵ)污染废水,由适量重铬酸钾溶于水配制而成,Cr(Ⅵ)含量为10 mg·L−1,用稀硫酸将pH调节至5.0。以n(CaSx)∶n(FeSO4)∶n(Cr(Ⅵ))=0.5∶1∶1为基准(计为1)进行药剂投加量优化实验,测得各投加量下水中Cr(Ⅵ)剩余含量及水体pH,结果如表2所示。可以看出,随着联用药剂投加量的增加,水体pH呈缓慢下降趋势,但始终保持在中性,当联用药剂投加比由1增加到1.5时,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率由92.92%升至100%,且当药剂投加比达到1.4后,Cr(Ⅵ)去除率不再变化,水中Cr(Ⅵ)质量浓度低于检出限(0.05 mg·L−1),满足污水综合排放标准(GB 8978-1996)。同时达到我国地表水环境质量标准II类标准(GB 3838-2002)及地下水质量标准III类标准(GB/T 14848-2017),这为后续应用于实际污染场地的修复提供了理论支持,因此,本实验确定的联用药剂与Cr(Ⅵ)反应的最佳摩尔比为n(CaSx)∶n(FeSO4)∶n(Cr(Ⅵ))=0.7∶1.4∶1。
表 2 联用药剂投加量对Cr(VI)去除效果Table 2. Removal effect of Cr(VI) at different combined chemical dosages投加比 投加量/(mg·L−1) n(CaSx)∶n(FeSO4)∶n(Cr(VI)) Cr(VI)/ (mg·L−1) Cr(VI)去除率/% 终止pH CaSx FeSO4 1.0 42.75 54.47 0.50∶1.0∶1 0.708 4 92.92 7.06 1.1 47.03 59.91 0.55∶1.1∶1 0.483 3 95.17 7.03 1.2 51.30 65.36 0.60∶1.2∶1 0.224 5 97.75 6.98 1.3 55.58 70.81 0.65∶1.3∶1 0.057 6 99.42 6.97 1.4 59.85 76.26 0.70∶1.4∶1 0 100 6.95 1.5 64.13 81.71 0.75∶1.5∶1 0 100 6.93 3. 结论
1)当多硫化钙和硫酸亚铁以1∶2投加比例联用时,水中总Cr和Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率均高于药剂单独使用下的去除率;随着pH的升高,药剂联用和多硫化钙单用时Cr(Ⅵ)去除率逐渐降低,硫酸亚铁可提高Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率;碱性条件下更利于总Cr和Cr(Ⅲ)的去除;药剂联用对体系扰动作用相对较小。
2)较高的温度有利于加快Cr(Ⅵ)的去除,但不影响对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率;碳酸氢根、氯离子、锰离子的加入有利于Cr(Ⅵ)的去除,其中碳酸氢根通过改变pH、氯离子影响电子传递,二价锰通过还原和弱水解作用影响Cr(Ⅵ)的去除;三价铁的存在会消耗部分多硫化钙,在其含量较低时对Cr(Ⅵ)的去除产生抑制,而含量较高时可通过吸附和水解作用提高Cr(Ⅵ)的去除率。
3)多硫化钙与硫酸亚铁反应生成了FeS,产生的FeS可高效还原Cr(Ⅵ),同时与Cr(Ⅲ)形成稳定的铬铁氢氧化物沉淀,对铬污染水体的还原和稳定过程均比较重要。
4)联用药剂与Cr(Ⅵ)以摩尔比为n(CaSx)∶n(FeSO4)∶n(Cr(Ⅵ))=0.7∶1.4∶1时,对弱酸性铬污染废水进行修复后,水中Cr(Ⅵ)含量可满足各类水环境质量标准且水体pH为中性。
-
[1] 刘波, 王国祥, 王风贺, 等. 不同曝气方式对城市重污染河道水体氮素迁移与转化的影响. 环境科学, 2011, 32(10): 2971-2978 Liu Bo, Wang Guoxiang, Wang Fenghe, et al. Effect of different aeration ways on migration and transformation of nitrogen in heavily polluted urban river. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(10): 2971-2978(in Chinese) [2] Kim M., Jeong S. Y., Yoon S. J., et al. Aerobic denitrification of Pseudomonas putida AD-21 at different C/N ratios. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 2008, 106(5): 498-502 [3] 孙从军,张明旭.河道曝气技术在河流污染治理中的应用.工程与技术, 2001(4): 12-15 Sun C.J.,Zhang M.X..Application of Aeration Technique in River Pollution Control. Engineering and Technology, 2001(4): 12-15(in chinese) [4] Wang Shengrui, Jin Xiangcan, Bu Qinyun, et al. Effects of dissolved oxygen supply level on phosphorus release from lake sediments. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2008, 316(1-3): 245-252 [5] Jin Xiangcan, Wang Shengrui, Pang Yan, et al. Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution, 2006, 139(2): 288-295 [6] Eggleton J., Thomas K. V. A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environment International, 2004, 30(7): 973-980 [7] 余光伟, 雷恒毅, 刘广立, 等. 重污染感潮河道底泥释放特征及其控制技术研究. 环境科学学报, 2007, 27(9): 1476-1484 Yu Guangwei, Lei Hengyi, Liu Guangli, et al. Research on the characteristics of sediment release in a heavily polluted tidal river and control technologies. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2007, 27(9): 1476-1484(in Chinese) [8] 史云峰, 赵牧秋, 张丽莉. 双氰胺(DCD)在砖红壤中硝化抑制效果的影响因素研究. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(33): 20437-20440 Shi Yunfeng, Zhao Muqiu, Zhang Lili. Research on the factors affecting nitrification inhibition of dicyandiamide (DCD) in latosol. Journal of Auhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(33): 20437-20440(in Chinese) [9] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法(第4版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002 [10] 金相灿, 屠清瑛. 湖泊富营养化调查规范(第2版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990 [11] 古小治, 王强, 张雷, 等. 物理改良对湖泊沉积物和间隙水特征的影响. 中国环境科学, 2010, 30(2): 256-262 Gu Xiaozhi, Wang Qiang, Zhang Lei, et al. Influence of physical amelioration on the characteristic of sediments and pore waters in lake Nansi wetland. China Environmental Science, 2010, 30(2): 256-262(in Chinese) [12] Maksymowska-Brossard D., Piekarek-Jankowska H. Seasonal variability of benthic ammonium release in the surface sediments of the Gulf of Gdańsk (southern Baltic Sea). Oceanologia, 2001, 43(1): 113-136 [13] Liu Shu, Wang Qunhui, Ma Hongzhi, et al. Effect of micro-bubbles on coagulation flotation process of dyeing wastewater. Separation and Purification Technology, 2010, 71(3): 337-346 [14] Peng Jianfeng, Wang Baozhen, Song Yonghui, et al. Adsorption and release of phosphorus in the surface sediment of a wastewater stabilization pond. Ecological Engineering, 2007, 31(2): 92-97 [15] Liu Jing, Xia Wenshui. Purification and characterization of a bifunctional enzyme with chitosanase and cellulase activity from commercial cellulase. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2006, 30(1): 82-87 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 2752
- HTML全文浏览数: 2223
- PDF下载数: 910
- 施引文献: 0





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: